Atomic parity nonconservation in Ra+ Wansbeek, L. W.; Sahoo, B. K.; Timmermans, Robertus; Jungmann, Klaus-Peter; Das, B. P.; Mukherjee, D.
|
|
|
- Wendy Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University o Groningen Atomic parity nonconservation in Ra+ Wansbeek, L. W.; Sahoo, B. K.; Timmermans, Robertus; Jungmann, Klaus-Peter; Das, B. P.; Mukherjee, D. Published in: Physical Review A DOI: /physreva IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) i you wish to cite rom it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version o record Publication date: 008 Link to publication in University o Groningen/UMCG research database Citation or published version (APA): Wansbeek, L. W., Sahoo, B. K., Timmermans, R. G. E., Jungmann, K., Das, B. P., & Mukherjee, D. (008). Atomic parity nonconservation in Ra+. Physical Review A, 78(5), [050501]. DOI: /physreva Copyright Other than or strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to orward/distribute the text or part o it without the consent o the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy I you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded rom the University o Groningen/UMCG research database (Pure): For technical reasons the number o authors shown on this cover page is limited to 10 maximum. Download date:
2 Atomic parity nonconservation in Ra + L. W. Wansbeek, B. K. Sahoo, R. G. E. Timmermans, and K. Jungmann KVI, University o Groningen, NL-9747 AA Groningen, The Netherlands B. P. Das Non-accelerator Particle Physics Group, Indian Institute o Astrophysics, Bangalore , India arxiv: v3 [physics.atom-ph] 4 Aug 008 D. Mukherjee Department o Physical Chemistry, Indian Association or Cultivation o Science, IACS, Kolkata 7003, India and Raman Center or Atomic, Molecular and Optical Sciences, IACS, Kolkata 7003, India (Dated: August 4, 008) We report on a theoretical analysis o the suitability o the 7s S 1/ 6d D 3/ transition in singly ionized radium to measure parity nonconservation, in the light o an experiment planned at the KVI o the University o Groningen. Relativistic coupled-cluster theory has been employed to perorm an ab initio calculation o the parity nonconserving electric dipole amplitude o this transition, including single, double, and leading triple excitations. We discuss the prospects or a sub-1% precision test o the electroweak theory o particle physics. In atomic systems, parity is broken due to the exchange o the neutral vector boson Z 0, which mediates the weak interaction between the atomic electrons and the quarks in the nucleus. This atomic parity nonconservation (APNC) gives rise to small parity nonconserving electric dipole transition amplitudes (E1 PNC ). The APNC eect gets strongly enhanced in heavy atoms and can be measured by the intererence o E1 PNC with a suppressed electromagnetic transition amplitude (M 1, E) [1, ]. The accurate measurement o the 6s S 1/ 7s S 1/ transition in atomic 133 Cs by the Boulder group [3, 4] constitutes a precision test o the electroweak sector o the Standard Model (SM) o particle physics [5]. By combining the measurement with a many-body atomic structure calculation, the weak nuclear charge could be determined [6]. The importance o APNC to particle physics is a strong incentive to urther pursue these challenging experiments. With the experimental and theoretical accuracies at an impressive 0.35% [3, 4] and 0.5% [6] level, respectively, the 133 Cs result agrees with the SM prediction within one standard deviation. Nevertheless, it is desirable to consider other candidates or APNC studies, see e.g. Re. [7]. New experiments have been proposed or Cs [8] and Fr [9] atoms. O special interest is the proposal by Fortson to measure APNC in one single laser-cooled and trapped ion []. Such single-ion experiments oer important beneits, such as long coherence times and precise control o various systematic eects. Promising ions rom the experimental and atomic-theory point o view are heavy alkali-like ions, in particular Ba + and Ra + [10]. Proo-o-principle experiments have been carried out with 138 Ba + by the Fortson group [10, 11, 1]. 7 P 3/ 1/ 7 P " =381 nm "=468 nm 1/ n 1/ E 7 S (+! n P ) "=78 nm Ra + " = 801 nm " =1.08 µ m E E1 PNC "=88 nm FIG. 1: Relevant energy levels in Ra +. 6 D 5/ 6 D 3/ At the TRIµP acility [13, 14] at the accelerator institute KVI in Groningen an APNC experiment on Ra + is in progress [15]. An important advantage o Ra + is that all relevant transitions are in the optical regime, c. Fig. 1, and thus are accessible by commercially available solid-state laser technology. The goal is to measure the E1 PNC amplitude o the 7s S 1/ 6d D 3/ transition. We address here the question what the prospects are to push the corresponding atomic theory below 1%, such that the experiment can serve as a high-precision test o the SM. We analyze various relevant properties o Ra + and assess the remaining uncertainties. The parity-nonconserving nuclear-spin independent (NSI) interaction is due to the electron-quark neutral weak interaction, the Hamiltonian o which is given by H NSI PNC = G F Q W γ 5 ϱ nuc (r), (1) Electronic address: timmermans@kvi.nl where G F is the Fermi constant, ϱ nuc the nuclear density,
3 and γ 5 is the standard Dirac matrix; Q W is the weak nuclear charge, which is equal to (Z +N)c 1u +(N +Z)c 1d in terms o the coupling constants o the electron to the up and down quarks; Z and N are the number o protons and neutrons. The Hamiltonian in Eq. (1) mixes atomic states o opposite parity but with the same angular momentum. Its strength is weak enough to consider it as a irst-order perturbation. We thereore write the valence state (v) atomic wave unction as Ψ v = Ψ (0) v + G F Ψ (1) v, () where Ψ (0) v is the atomic wave unction o the Dirac- Coulomb (DC) Hamiltonian (H DC ) and Ψ (1) v is the irstorder correction due to the PNC NSI interaction. To a irst-order approximation, the E1 PNC transition amplitude between the 7s S 1/ (= i) and 6d D 3/ (= ) states is given by E1 PNC = G D Ψ(1) + Ψ (1) D Ψ(0) F Ψ(0) which, ater expansion, takes the orm E1 PNC = D Ψ(0) I i (E i E I ) + J (E E J ) I I HNSI PNC Ψ(0) J H NSI PNC Ψ(0) Ψ(0) Ψ(0) J D Ψ(0) Ψ(0), (3), (4) where D is the electric dipole (E1) operator, I and J represent the allowed intermediate states, and E is the energy o the state. An accurate determination o E1 PNC depends on the precision o the matrix elements o D and o HPNC NSI, and o the energy dierences between the dierent states. At the same time, it is also important to take all intermediate states into account, something which is not possible in the oten-used sum-over-states approach. We thereore employ the relativistic coupledcluster (RCC) theory, which allows us to evaluate the properties to all orders in perturbation theory. The RCC method was previously used to calculate APNC in 137 Ba + with sub-1% accuracy [16]. We obtain the irst-order wave unctions o Eq. (3) in the RCC ramework as the solution o G F (H DC E v ) Ψ (1) v = HPNC Ψ NSI (0) v, (5) where v stands or valence electron, which is either i or. The unperturbed and perturbed wave unctions are expressed as and Ψ (0) v = exp(t (0) ){1 + S (0) v } Φ v, (6) Ψ (1) v = exp(t ){1 + S v} Φ v = exp(t (0) )(T (1) {1 + S (0) v } + {S (1) v }) Φ v,(7) respectively, where Φ v is the mean-ield wave unction determined with the Dirac-Fock (DF) method. T and S v are the core and valence-core RCC correlation operators, respectively, where the superscript 0 indicates in the presence o the Coulomb interaction, the prime ( ) indicates in the presence o both the Coulomb and APNC interaction, and 1 indicates their linear approximations. Substituting the above expressions in Eq. (3), we obtain where Φ C E1 PNC = G D(0) C i Φ F (1 + N (0) )(1 + N (0) i ), (8) N v (0) = Φ v S v (0) exp(t (0) ) exp(t (0) )S v (0) Φ v, (9) C v = T (1) {1 + S v (0) } + S v (1), (10) and D (0) = exp(t (0) )D exp(t (0) ). The matrix element is evaluated using the generalized Wick s theorem [16]. Our RCC work has two salient eatures. We evaluate E1 PNC by using the direct solution o the irst-order perturbed equation as given in Eq. (5) rather than summing over a inite number o intermediate states [17]. The core correlation eects modiied by the parity nonconserving weak interaction are evaluated to all orders through T (1) in the ramework o the relativistic CCSD(T) method. These eects cancel strongly in Cs and Fr, where both the initial and inal states are S-states. However, it is essential to consider them accurately in the S-D transitions in Ba + and Ra +, where these contributions are signiicant. For our calculation, we have used numerical DF/V N 1 orbitals to describe the occupied and bound virtual orbitals. The continuum states were represented by V N 1 Gaussian-type orbitals (GTOs) [18] using the parameters α = and β =.73. The inite size o the nucleus is accounted or by assuming a Fermi charge distribution [18]. In Table I, we present our RCC results or the E1 PNC amplitude o the 7s S 1/ 6d D 3/ transition in the isotope 6 Ra +. Shown are the results o the DF method, o the RCC method with single and double excitations (CCSD), and with the leading triple excitations (CCSD(T)). The dierence between the CCSD(T) and CCSD results is small. Our best value is the CCSD(T) result E1 PNC = iea 0 ( Q W /N). Also shown are two results o Dzuba et al. [19]: in a sum-over-states TABLE I: E1 PNC or the 7s S 1/ 6d D 3/ transition in the isotope 6 Ra +, in units o iea 0( Q W /N). This work Re. [19] DF 40.4 CCSD 46.1 Mixed-states 4.9 CCSD(T) 46.4 Sum-over-states 45.9
4 3 approach they ound iea 0 ( Q W /N); in a mixed-states approach, wherein the APNC interaction explicitly mixes states o opposite parity, they obtained iea 0 ( Q W /N). Neither calculation includes structural radiation, the weak correlation potential, and normalization o states, eects which are included by us. The E1 PNC amplitude or the 6s S 1/ 7s S 1/ transition in Cs is about iea 0 ( Q W /N) [6]. Thus, the APNC eect in Ra + is larger by a actor close to 50. In heavy atoms, ANPC gets enhanced by the overall actor K r Z Q W (Z, N), where Q W N Z, and K r is a relativistic actor that depends on the nuclear charge and radius. This is the aster-than-z 3 law [1], which implies that Ra + is avored over Cs by a actor o about 0. An additional actor o around can be understood as ollows. For Cs (and Fr) the S-S transition is used, or Ra + (and Ba + ) the S-D transition. Since the Z 0 -boson is very heavy, the weak interaction between electrons and the quarks in the nucleus has (almost) zero range. The overlap o the electrons with the nucleus is largest or the S states, and thus the mixing o the P -states into the S states gives the major contribution to E1 PNC. However, in Cs and Fr the initial and inal S states contribute with opposite signs, which leads to a signiicant cancellation in E1 PNC. In act, or Cs there are three dominant terms in the sum over the states, which add up to a total value that is hal the size o the largest individual term [6]. The S-D transitions in Ba + and Ra + do not suer rom such a cancellation, since the contribution rom the D-state to APNC is small. In Table II, we analyze which intermediate states contribute most to the total sum. Clearly, in contrast to the Cs S-S case, the sum is strongly dominated by one term: the contribution rom the 7p P 1/ state. These qualitative results are robust, they are consistent with the indings o Re. [19], and they are, in act, already borne out by a simple calculation with quantum-deect theory, analogous to Re. [0]. This simple estimate gives or Cs, Fr, Ba +, and Ra + results accurate to some 10%; or Ra + we ind E1 PNC = 45(4) iea 0 ( Q W /N). In Table III, we present our results or the excitation energies, E1 transition amplitudes, and hyperine constants or the relevant transitions and states in Ra +. We also list experimental values where available. For the excitation energies, we compare to the only available spec- TABLE II: The contributions to the E1 PNC rom the dierent P -states (%). State type % State type % 6p P 1/ core 8.7 8p P 1/ bound 3.3 6p P 3/ core 15 9p P 1/ bound 0.7 7p P 1/ bound p P 1/ continuum 0.1 7p P 3/ bound.6 11p P 1/ continuum 1.1 TABLE III: Excitation energies, E1 transition amplitudes, and A I/g I or dierent low-lying states o Ra +. Transition 7s S 1/ 7s S 1/ 6d D 3/ 6d D 3/ 7p P 1/ 7p P 3/ 7p P 1/ 7p P 3/ Excitation energy [cm 1 ] This work Experiment [1] E1 transition amplitude [a.u.] This work Re. [19] GTOs [] State 7s S 1/ 7p P 1/ 7p P 3/ 6d D 3/ Hyperine interaction constant (A I/g I) [MHz] This work Experiment [3] troscopy measurement [1], which dates back to For the E1 transition amplitudes, or which there are no experimental data, we list the results o Re. [19] and o our previous work [] using GTOs. Therein, the lietimes o the metastable D-states were calculated to be 0.67(4) s or 6d D 3/ and 0.97(4) s or 6d D 5/. Since the hyperine structure is a good probe o the wave unctions at the nucleus, we have, in order to estimate the accuracy o the HPNC NSI matrix elements, calculated the ratio between the magnetic dipole hyperine structure (A) and the nuclear gyromagnetic (g) constants, neglecting isotope eects, and compared these with experimental results or Ra + rom ISOLDE [3, 4]. Our calculated value or [A I /g I (7S 1/ )A I /g I (7P 1/ )] 1/ diers by 3% rom the experimental value, which is a reasonable estimate or the dominant uncertainty in the atomic theory. Thus, our best value or the parity nonconserving E1 amplitude in Ra + is E1 PNC = 46.4(1.4) iea 0 ( Q W /N). It appears easible to push the accuracy o the atomic theory or Ra + to the sub-1% level. Improvements along several lines are in progress. The Breit interaction [5, 6] and QED corrections, which contribute around 1%, need to be included. The neutron-skin eect [7], which also contributes at the sub-1% level, has to be investigated. However, at the same time it is clear that experimental inormation to test the atomic theory is severely lacking. Not all relevant energy levels are known [1], there is no experimental inormation on the E1 transition strengths, nor on the lietimes o the D-states. It is highly desirable to have more experimental data on the magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole hyperine constants A and B or the various Ra + isotopes. The extraction o these constants [3, 4] is model dependent, and ideally one would like to use a single consistent ab initio ramework or this.
5 4 TABLE IV: The properties o the isotopes o Ra + suitable or a single-ion APNC experiment. A is the mass number, I is the nuclear spin, and τ 1/ the hal-lie time. A I τ 1/ Possible production reaction 13 1/.74(6) min 08 Pb + 1 C 13 Ra + 7n 3 3/ (5) d p + 3 Th 3 Ra + A X + an + bp (3) d p + 3 Th 4 Ra + A X + an + bp 5 1/ () d 9 Th 5 Ra + α (7) y Commercially available 7 3/ + 4.(5) min p + 3 Th 7 Ra + A X + an + bp At the TRIµP acility, radium isotopes can be produced in usion and evaporation or spallation reactions. The ions can be collected in a radio-requency trap where they can be laser-cooled on the 7s S 1/ 7p P 1/ resonance line at 468 nm, with repumping via the 6d D 3/ 7p P 1/ transition at 1.08 µm, or which strong lasers are available. They will then be transerred to a miniature trap or the single-ion experiment, where techniques similar to Res. [10, 11, 1] will be applied to perorm the measurements. In particular, the 7s S 1/ 7p P 3/ and 6d D 5/ 7p P 3/ transitions at 381 nm and 801 nm, respectively, can be used or shelving [10]. A list o the Ra + isotopes suitable or a single-ion experiment is shown in Table IV. A hal-lie o the order o seconds is required or a high-precision single-ion experiment, but, on the other hand, it should not exceed a ew days, so as to avoid long-lived radioactive contamination o the core equipment. Good candidates thereore are the odd isotopes 13 Ra + and 7 Ra +, and the even isotope 4 Ra +. (Since the odd isotopes have a nonzero nuclear spin, the nuclear spin-dependent weak interaction will contribute to E1 PNC [8]). The isotopes listed can all be produced at TRIµP, and the experimental data required to constrain the atomic theory can be measured there with laser spectroscopy. Since multiple Ra + isotopes will be available, the possibility exists to measure APNC in a chain o isotopes, which can help to eliminate remaining uncertainties in the atomic theory [9]. In conclusion, Ra + appears to be an excellent candidate or an APNC experiment, since E1 PNC is large, the required lasers are all at convenient wavelengths, and one can exploit the high-precision techniques o singleion trapping. The atomic theory needed or the interpretation o the experiment could reach an accuracy better than 1%, but precise experimental data or the relevant atomic properties are mandatory to achieve such a benchmark. The prospects or APNC in Ra + as a precise test o the SM look promising. Part o this work was supported by the Dutch Stichting voor Fundamenteel Onderzoek der Materie (FOM) under program 48 (TRIµP) and project 06PR499. The calculations were carried out using the Tera-lop Supercomputer in C-DAC, Bangalore. [1] M. A. Bouchiat and C. C. Bouchiat, Phys. Lett. B 48, 111 (1974). [] N. Fortson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 383 (1993). [3] C. S. Wood, S. C. Bennett, D. Cho, B. P. Masterson, J. L. Roberts, C. E. Tanner, and C. E. Wieman, Science 75, 1759 (1997). [4] S. C. Bennett and C. E. Wieman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 8, 484 (1999). [5] W. J. Marciano and J. L. Rosner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 963 (1990). [6] J. S. M. Ginges and V. V. Flambaum, Phys. Rep. 637, 63 (004). [7] J. Guéna, M. Lintz, and M.-A. Bouchiat, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 0, 375 (005). [8] M. Lintz, J. Guéna, and M.-A. Bouchiat, Eur. Phys. J. A 3, 55 (007). [9] E. Gomez, L. A. Orozco, and G. D. Sprouse, Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, 79 (006). [10] T. W. Koerber, M. Schacht, W. Nagourney, and E. N. Fortson, J. Phys. B 36, 637 (003). [11] J. A. Sherman, T. W. Koerber, A. Markhotok, W. Nagourney, and E. N. Fortson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, (005). [1] T. W. Koerber, M. H. Schacht, K. R. G. Hendrickson, W. Nagourney, and E. N. Fortson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, (00). [13] G. P. Berg et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 560, 169 (006). [14] E. Traykov et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 57, 580 (007). [15] radiumion. [16] B. K. Sahoo, R. K. Chaudhuri, B. P. Das, and D. Mukherjee, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, (006). [17] S. A. Blundell, J. Sapirstein, and W. R. Johnson, Phys. Rev. D 45, 160 (199). [18] R. K. Chaudhuri, P. K. Panda, and B. P. Das, Phys. Rev. A 59, 1187 (1999). [19] V. A. Dzuba, V. V. Flambaum, and J. S. M. Ginges, Phys. Rev. A 63, (001). [0] M. A. Bouchiat and C. C. Bouchiat, J. Phys. (Paris) 35, 899 (1974); ibid., 36, 493 (1975). [1] E. Rasmussen, Z. Phys. 86, 4 (1933). [] B. K. Sahoo, B. P. Das, R. K. Chaudhuri, D. Mukherjee, R. G. E. Timmermans, and K. Jungmann, Phys. Rev. A 76, (R) (007). [3] W. Neu, R. Neugart, E.-W. Otten, G. Passler, K. Wendt, B. Fricke, E. Arnold, H. J. Kluge, G. Ulm, and the ISOLDE collaboration, Z. Phys. D 11, 105 (1989). [4] K. Wendt, S. A. Ahmad, W. Klempt, R. Neugart, E. W. Otten, H. H. Stroke, and the ISOLDE collaboration, Z. Phys. D 4, 7 (1987). [5] A. Derevianko, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1618 (000). [6] V. A. Dzuba, V. V. Flambaum, and M. S. Saronova, Phys. Rev. A 73, 011 (006). [7] B. A. Brown, A. Derevianko, and V. V. Flambaum, arxiv v1 (008). [8] K. P. Geetha, A. D. Singh, B. P. Das, and C. S. Unnikrishnan, Phys. Rev. A 58, R16 (1998). [9] V. A. Dzuba, V. V. Flambaum, and I. B. Khriplovich, Z. Phys. D 1, 43 (1986).
University of Groningen. Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste
 University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen On-line Excited-State Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Short-Lived $^+$ Ions Versolato, O. O.; Giri, G. S.; Wansbeek, L. W.; van den Berg, J.E.; van der Hoek, D.J.; Jungmann, Klaus-Peter;
University of Groningen On-line Excited-State Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Short-Lived $^+$ Ions Versolato, O. O.; Giri, G. S.; Wansbeek, L. W.; van den Berg, J.E.; van der Hoek, D.J.; Jungmann, Klaus-Peter;
Atomic Parity Violation
 Atomic Parity Violation Junghyun Lee APV proposes new physics beyond the standard model of elementary particles. APV is usually measured through the weak nuclear charge Q w, quantifying the strength of
Atomic Parity Violation Junghyun Lee APV proposes new physics beyond the standard model of elementary particles. APV is usually measured through the weak nuclear charge Q w, quantifying the strength of
Atomic Parity Non-Conservation in Francium: The FrPNC Experiment
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO Vol.?, N.?? Atomic Parity Non-Conservation in Francium: The FrPNC Experiment at TRIUMF S. Aubin( 1 ), E. Gomez( 2 ), J. A. Behr( 3 ), M. R. Pearson( 3 ), D. Sheng( 4 ), J. Zhang( 4 ),
IL NUOVO CIMENTO Vol.?, N.?? Atomic Parity Non-Conservation in Francium: The FrPNC Experiment at TRIUMF S. Aubin( 1 ), E. Gomez( 2 ), J. A. Behr( 3 ), M. R. Pearson( 3 ), D. Sheng( 4 ), J. Zhang( 4 ),
Tests of fundamental symmetries with atoms and molecules
 Tests of fundamental symmetries with atoms and molecules 1 Listening to an atom q Coulomb forces + Quantum Electro-Dynamics => a relatively simple interpretation q Unprecedented control over internal and
Tests of fundamental symmetries with atoms and molecules 1 Listening to an atom q Coulomb forces + Quantum Electro-Dynamics => a relatively simple interpretation q Unprecedented control over internal and
Towards a Precise Measurement of Atomic Parity Violation in a Single Ra + Ion
 Towards a Precise Measurement of Atomic Parity Violation in a Single + Ion TRIµP Program Trapped dioactive Isotopes: µ-laboratories for fundamental Physics Kernfysisch Versneller Instituut (KVI) University
Towards a Precise Measurement of Atomic Parity Violation in a Single + Ion TRIµP Program Trapped dioactive Isotopes: µ-laboratories for fundamental Physics Kernfysisch Versneller Instituut (KVI) University
ATOMIC PARITY VIOLATION
 ATOMIC PARITY VIOLATION OUTLINE Overview of the Atomic Parity Violation Theory: How to calculate APV amplitude? Analysis of Cs experiment and implications for search for physics beyond the Standard Model
ATOMIC PARITY VIOLATION OUTLINE Overview of the Atomic Parity Violation Theory: How to calculate APV amplitude? Analysis of Cs experiment and implications for search for physics beyond the Standard Model
Parity Nonconservation in Atoms: The Weak Charge and Anapole Moment of 133 Cs
 Parity Nonconservation in Atoms: The Weak Charge and Anapole Moment of 133 Cs Walter Johnson University of Notre Dame 1) Weak charge Q W of 133 Cs provides a test of the Standard Electroweak Model. 2)
Parity Nonconservation in Atoms: The Weak Charge and Anapole Moment of 133 Cs Walter Johnson University of Notre Dame 1) Weak charge Q W of 133 Cs provides a test of the Standard Electroweak Model. 2)
Citation for published version (APA): Martinus, G. H. (1998). Proton-proton bremsstrahlung in a relativistic covariant model s.n.
 University of Groningen Proton-proton bremsstrahlung in a relativistic covariant model Martinus, Gerard Henk IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Proton-proton bremsstrahlung in a relativistic covariant model Martinus, Gerard Henk IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
Triple excitations in the coupled-cluster method. Application to atomic properties.
 Triple excitations in the coupled-cluster method. Application to atomic properties. Sergey G. Porsev 1 and Andrei Derevianko 2 1 Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute Gatchina, Russia 2 University of Nevada
Triple excitations in the coupled-cluster method. Application to atomic properties. Sergey G. Porsev 1 and Andrei Derevianko 2 1 Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute Gatchina, Russia 2 University of Nevada
current status And future prospects
 September 20, 2007 Rare Isotopes & Fundamental symmetries workshop Atomic pnc theory: current status And future prospects marianna safronova outline Motivation & Summary of experiment Nuclear spin-independent
September 20, 2007 Rare Isotopes & Fundamental symmetries workshop Atomic pnc theory: current status And future prospects marianna safronova outline Motivation & Summary of experiment Nuclear spin-independent
Theoretical study of lifetimes and polarizabilities in Ba +
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 78, 012508 2008 Theoretical study of lifetimes and polarizabilities in Ba + E. Iskrenova-Tchoukova and M. S. Safronova Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark,
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 78, 012508 2008 Theoretical study of lifetimes and polarizabilities in Ba + E. Iskrenova-Tchoukova and M. S. Safronova Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark,
Parity and Time Reversal Violations in Atoms: Present Status and Future Prospects. Bhanu Pratap Das
 Parity and Time Reversal Violations in Atoms: Present Status and Future Prospects Bhanu Pratap Das Non-Accelerator Particle Physics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore 560 034, India Outline
Parity and Time Reversal Violations in Atoms: Present Status and Future Prospects Bhanu Pratap Das Non-Accelerator Particle Physics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore 560 034, India Outline
Nuclear structure and the anapole moment in francium; experiments and proposals. Luis A. Orozco UMD
 Nuclear structure and the anapole moment in francium; experiments and proposals. Luis A. Orozco UMD Work done in collaboration with Prof. Gene Sprouse from SUNYSB And Prof. David DeMille from Yale University.
Nuclear structure and the anapole moment in francium; experiments and proposals. Luis A. Orozco UMD Work done in collaboration with Prof. Gene Sprouse from SUNYSB And Prof. David DeMille from Yale University.
CURRENT STATUS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS
 AMO seminar - Berkeley March 18, 2008 ATOMIC PNC THEORY: CURRENT STATUS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA OUTLINE Motivation & Summary of experiment Nuclear spin-independent PNC & weak charge How
AMO seminar - Berkeley March 18, 2008 ATOMIC PNC THEORY: CURRENT STATUS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA OUTLINE Motivation & Summary of experiment Nuclear spin-independent PNC & weak charge How
High-precision calculation of the parity-nonconserving amplitude in francium
 High-precision calculation of the parity-nonconserving amplitude in francium M. S. Safronova and W. R. Johnson Department of Physics, Notre Dame University, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556 Received 6 December
High-precision calculation of the parity-nonconserving amplitude in francium M. S. Safronova and W. R. Johnson Department of Physics, Notre Dame University, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556 Received 6 December
Proposed experiment for the anapole measurement in francium. Luis A. Orozco Joint Quantum Institute University of Maryland
 Proposed experiment for the anapole measurement in francium Luis A. Orozco Joint Quantum Institute University of Maryland FrPNC collaboration: S. Aubin, J. A. Behr, V. Flambaum, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, K.
Proposed experiment for the anapole measurement in francium Luis A. Orozco Joint Quantum Institute University of Maryland FrPNC collaboration: S. Aubin, J. A. Behr, V. Flambaum, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, K.
Citation for published version (APA): Hoekstra, S. (2005). Atom Trap Trace Analysis of Calcium Isotopes s.n.
 University of Groningen Atom Trap Trace Analysis of Calcium Isotopes Hoekstra, Steven IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Atom Trap Trace Analysis of Calcium Isotopes Hoekstra, Steven IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Apr 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Apr 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Apr 2013](/thumbs/90/101607363.jpg) Calculation of parity non-conserving optical rotation in iodine at 1315 nm G. E. Katsoprinakis, L. Bougas and T. P. Rakitzis Institute of Electronic Structure and Lasers, Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas,
Calculation of parity non-conserving optical rotation in iodine at 1315 nm G. E. Katsoprinakis, L. Bougas and T. P. Rakitzis Institute of Electronic Structure and Lasers, Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas,
Theory of Electric Dipole Moments of Atoms and Molecules Bhanu Pratap Das
 Theory of Electric Dipole Moments of Atoms and Molecules Bhanu Pratap Das Theoretical Physics and Astrophysics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore Collaborators: H. S. Nataraj, B. K. Sahoo,
Theory of Electric Dipole Moments of Atoms and Molecules Bhanu Pratap Das Theoretical Physics and Astrophysics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore Collaborators: H. S. Nataraj, B. K. Sahoo,
University of Groningen. Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh
 University of Groningen Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
Parity non-conservation in thallium
 Parity non-conservation in thallium M. G. Kozlov and S. G. Porsev Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, Gatchina, 188300, Russia W. R. Johnson Department of Physics, Notre Dame University, Notre Dame,
Parity non-conservation in thallium M. G. Kozlov and S. G. Porsev Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, Gatchina, 188300, Russia W. R. Johnson Department of Physics, Notre Dame University, Notre Dame,
arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 12 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 12 Apr 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 12 Apr 2015](/thumbs/74/70163729.jpg) Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Lifetime measurement of the 5d 2 D 5/2 state in Ba + Amita Mohanty, Elwin A. Dijck, Mayerlin Nuñez Portela, Nivedya Valappol, Andrew T. Grier, Thomas
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Lifetime measurement of the 5d 2 D 5/2 state in Ba + Amita Mohanty, Elwin A. Dijck, Mayerlin Nuñez Portela, Nivedya Valappol, Andrew T. Grier, Thomas
Closed-shell Atomic Electric Dipole Moments. K. V. P. Latha Angom Dilip Kumar Singh B. P. Das Rajat Chaudhuri
 Closed-shell Atomic Electric Dipole Moments K. V. P. Latha Angom Dilip Kumar Singh B. P. Das Rajat Chaudhuri An observation of EDM of a non-degenerate physical system is a direct unambiguous evidence of
Closed-shell Atomic Electric Dipole Moments K. V. P. Latha Angom Dilip Kumar Singh B. P. Das Rajat Chaudhuri An observation of EDM of a non-degenerate physical system is a direct unambiguous evidence of
Theoretical simulation of nonlinear spectroscopy in the liquid phase La Cour Jansen, Thomas
 University of Groningen Theoretical simulation of nonlinear spectroscopy in the liquid phase La Cour Jansen, Thomas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Theoretical simulation of nonlinear spectroscopy in the liquid phase La Cour Jansen, Thomas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen. Radium Ion Spectroscopy Giri, Gouri Shankar
 University of Groningen Radium Ion Spectroscopy Giri, Gouri Shankar IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Radium Ion Spectroscopy Giri, Gouri Shankar IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 22 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 22 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 22 Jul 2007](/thumbs/79/80319606.jpg) Theoretical determination of lifetimes of metastable states in Sc III and Y III B. K. Sahoo Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems, arxiv:0707.3282v1 [physics.atom-ph] 22 Jul 2007 Nöthnitzer
Theoretical determination of lifetimes of metastable states in Sc III and Y III B. K. Sahoo Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems, arxiv:0707.3282v1 [physics.atom-ph] 22 Jul 2007 Nöthnitzer
Determination of electric-dipole matrix elements in K and Rb from Stark shift measurements
 Determination of electric-dipole matrix elements in K and Rb from Stark shift measurements Bindiya Arora and M. S. Safronova Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware
Determination of electric-dipole matrix elements in K and Rb from Stark shift measurements Bindiya Arora and M. S. Safronova Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen beta-decay and the electric dipole moment Wilschut, Henricus; Van Der Hoek, D. J.; Jungmann, Klaus-Peter; Kruithof, W.; Onderwater, Cornelis; Santra, B.; Shidling, P. D.; Willmann,
University of Groningen beta-decay and the electric dipole moment Wilschut, Henricus; Van Der Hoek, D. J.; Jungmann, Klaus-Peter; Kruithof, W.; Onderwater, Cornelis; Santra, B.; Shidling, P. D.; Willmann,
Nuclear electric dipole moment in the Gaussian expansion method
 Nuclear electric dipole moment in the Gaussian expansion method Nodoka Yamanaka (ithes Group, RIKEN) In collaboration with E. Hiyama (RIKEN), T. Yamada (Kanto-Gakuin Univ.), Y. Funaki (RIKEN) 2015/10/12
Nuclear electric dipole moment in the Gaussian expansion method Nodoka Yamanaka (ithes Group, RIKEN) In collaboration with E. Hiyama (RIKEN), T. Yamada (Kanto-Gakuin Univ.), Y. Funaki (RIKEN) 2015/10/12
The FrPNC Experiment, weak interaction studies in Francium at TRIUMF
 The FrPNC Experiment, weak interaction studies in Francium at TRIUMF E Gomez 1, S Aubin 2, R Collister 3, J A Behr 4, G Gwinner 3, L A Orozco 5, M R Pearson 4, M Tandecki 3, D Sheng 5, J Zhang 5 1 Institute
The FrPNC Experiment, weak interaction studies in Francium at TRIUMF E Gomez 1, S Aubin 2, R Collister 3, J A Behr 4, G Gwinner 3, L A Orozco 5, M R Pearson 4, M Tandecki 3, D Sheng 5, J Zhang 5 1 Institute
Parity Nonconservation in Cesium: Is the Standard Model in Trouble?
 Parity Nonconservation in Cesium: Is the Standard Model in Trouble? Walter Johnson Department of Physics Notre Dame University http://www.nd.edu/ johnson May 10, 2001 Abstract This is a brief review of
Parity Nonconservation in Cesium: Is the Standard Model in Trouble? Walter Johnson Department of Physics Notre Dame University http://www.nd.edu/ johnson May 10, 2001 Abstract This is a brief review of
Superfluid helium and cryogenic noble gases as stopping media for ion catchers Purushothaman, Sivaji
 University of Groningen Superfluid helium and cryogenic noble gases as stopping media for ion catchers Purushothaman, Sivaji IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Superfluid helium and cryogenic noble gases as stopping media for ion catchers Purushothaman, Sivaji IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen. Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste
 University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen. Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya
 University of Groningen Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Jan 2012](/thumbs/84/90866394.jpg) Electric dipole moment enhancement factor of thallium S. G. Porsev 1,2, M. S. Safronova 1, and M. G. Kozlov 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA
Electric dipole moment enhancement factor of thallium S. G. Porsev 1,2, M. S. Safronova 1, and M. G. Kozlov 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA
Nuclear Anapole Moments and the Parity-nonconserving Nuclear Interaction
 Nuclear Anapole Moments and the Parity-nonconserving Nuclear Interaction Cheng-Pang Liu TRIUMF Research Facility, 4004 Wesbrook Mall, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T 2A3 Abstract. The anapole moment is a parity-odd
Nuclear Anapole Moments and the Parity-nonconserving Nuclear Interaction Cheng-Pang Liu TRIUMF Research Facility, 4004 Wesbrook Mall, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T 2A3 Abstract. The anapole moment is a parity-odd
Two-photon spectroscopy of the francium 8S 1/2 level
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 59, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 1999 Two-photon spectroscopy of the francium 8S 1/2 level J. E. Simsarian, W. Z. Zhao, L. A. Orozco, and G. D. Sprouse Department of Physics and Astronomy,
PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 59, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 1999 Two-photon spectroscopy of the francium 8S 1/2 level J. E. Simsarian, W. Z. Zhao, L. A. Orozco, and G. D. Sprouse Department of Physics and Astronomy,
ATOMIC CALCULATIONS FOR TESTS OF FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS
 University of Virginia Colloquium ATOMIC CALCULATIONS FOR TESTS OF FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA November 11, 2011 OUTLINE Atomic physics tests of fundamental physics Parity violation Search for
University of Virginia Colloquium ATOMIC CALCULATIONS FOR TESTS OF FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA November 11, 2011 OUTLINE Atomic physics tests of fundamental physics Parity violation Search for
Breit interaction in heavy atoms
 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Breit interaction in heavy atoms M G Kozlov, SGPorsev, and I I Tupitsyn Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, 188350, Gatchina, Russia E-mail: mgk@mf1309.spb.edu St. Petersburg State
LETTER TO THE EDITOR Breit interaction in heavy atoms M G Kozlov, SGPorsev, and I I Tupitsyn Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, 188350, Gatchina, Russia E-mail: mgk@mf1309.spb.edu St. Petersburg State
Status of Atomic PNC: Experiment/Theory
 Status of Atomic PNC: Experiment/Theory W. R. Johnson University of Notre Dame Abstract Atomic PNC measurements and calculations are reviewed with emphasis on the 6s 7s transition in cesium and the corresponding
Status of Atomic PNC: Experiment/Theory W. R. Johnson University of Notre Dame Abstract Atomic PNC measurements and calculations are reviewed with emphasis on the 6s 7s transition in cesium and the corresponding
Lifetime measurement of the 5d 2 D 5/2 state in Ba +
 Hyperfine Interact (2015) 233:113 119 DOI 10.1007/s10751-015-1161-9 Lifetime measurement of the 5d 2 D 5/2 state in Ba + Amita Mohanty 1 Elwin A. Dijck 1 Mayerlin Nuñez Portela 1 Nivedya Valappol 1 Andrew
Hyperfine Interact (2015) 233:113 119 DOI 10.1007/s10751-015-1161-9 Lifetime measurement of the 5d 2 D 5/2 state in Ba + Amita Mohanty 1 Elwin A. Dijck 1 Mayerlin Nuñez Portela 1 Nivedya Valappol 1 Andrew
Nuclear Structure V: Application to Time-Reversal Violation (and Atomic Electric Dipole Moments)
 T Symmetry EDM s Octupole Deformation Other Nuclei Nuclear Structure V: Application to Time-Reversal Violation (and Atomic Electric Dipole Moments) J. Engel University of North Carolina June 16, 2005 T
T Symmetry EDM s Octupole Deformation Other Nuclei Nuclear Structure V: Application to Time-Reversal Violation (and Atomic Electric Dipole Moments) J. Engel University of North Carolina June 16, 2005 T
Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga
 Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
ON THE THEORY OF NUCLEAR ANAPOLE MOMENTS. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia
 ON THE THEORY OF NUCLEAR ANAPOLE MOMENTS V.F. Dmitriev 1, and I.B. Khriplovich 2 Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract We discuss the present state of the theory of nuclear
ON THE THEORY OF NUCLEAR ANAPOLE MOMENTS V.F. Dmitriev 1, and I.B. Khriplovich 2 Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract We discuss the present state of the theory of nuclear
What we know about Francium. University of Science and Technology of China Hefei, China July 2018 Luis A. Orozco
 What we know about Francium University of Science and Technology of China Hefei, China July 2018 Luis A. Orozco www.jqi.umd.edu The slides are available at: http://www.physics.umd.edu/rgroups/amo/orozco/results/2018/results18.htm
What we know about Francium University of Science and Technology of China Hefei, China July 2018 Luis A. Orozco www.jqi.umd.edu The slides are available at: http://www.physics.umd.edu/rgroups/amo/orozco/results/2018/results18.htm
Contents. Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition
 Contents Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition Notes xiii xv xvii 1 Basic Concepts 1 1.1 History 1 1.1.1 The Origins of Nuclear Physics 1 1.1.2 The Emergence of Particle Physics: the
Contents Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition Notes xiii xv xvii 1 Basic Concepts 1 1.1 History 1 1.1.1 The Origins of Nuclear Physics 1 1.1.2 The Emergence of Particle Physics: the
Effects of Neutron Spatial Distributions on Atomic Parity Nonconservation in Cesium.
 Effects of Neutron Spatial Distributions on Atomic Parity Nonconservation in Cesium. S. J. Pollock and M. C. Welliver Dep t of Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder CO 80309 (July 12, 1999) We have
Effects of Neutron Spatial Distributions on Atomic Parity Nonconservation in Cesium. S. J. Pollock and M. C. Welliver Dep t of Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder CO 80309 (July 12, 1999) We have
University of Groningen. Hollow-atom probing of surfaces Limburg, Johannes
 University of Groningen Hollow-atom probing of surfaces Limburg, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Hollow-atom probing of surfaces Limburg, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM. Spin. Pseudo-scalar. s d
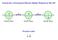 Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin Pseudo-scalar s d C. S. Wu 1912-1997 Parity (space reversal) x, y, z -x, -y, -z z y Parity z x x y Pseudo-scalar
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin Pseudo-scalar s d C. S. Wu 1912-1997 Parity (space reversal) x, y, z -x, -y, -z z y Parity z x x y Pseudo-scalar
Excitation energies, polarizabilities, multipole transition rates, and lifetimes of ions along the francium isoelectronic sequence
 Excitation energies, polarizabilities, multipole transition rates, and lifetimes of ions along the francium isoelectronic sequence U. I. Safronova* Physics Department, University of Nevada, Reno, Nevada
Excitation energies, polarizabilities, multipole transition rates, and lifetimes of ions along the francium isoelectronic sequence U. I. Safronova* Physics Department, University of Nevada, Reno, Nevada
Efficient inter-trap transfer of cold francium atoms
 Hyperfine Interact (2016) 237:150 DOI 10.1007/s10751-016-1347-9 Efficient inter-trap transfer of cold francium atoms J. Zhang 1 R. Collister 2 K. Shiells 2 M. Tandecki 3 S. Aubin 4 J. A. Behr 3 E. Gomez
Hyperfine Interact (2016) 237:150 DOI 10.1007/s10751-016-1347-9 Efficient inter-trap transfer of cold francium atoms J. Zhang 1 R. Collister 2 K. Shiells 2 M. Tandecki 3 S. Aubin 4 J. A. Behr 3 E. Gomez
Electric quadrupole moments of metastable states of Ca +,Sr +, and Ba +
 Electric quadrupole moments of metastable states of Ca +,Sr +, and Ba + Dansha Jiang and Bindiya Arora Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716-2570, USA M. S.
Electric quadrupole moments of metastable states of Ca +,Sr +, and Ba + Dansha Jiang and Bindiya Arora Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716-2570, USA M. S.
Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.
![Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen. Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.](/thumbs/95/126078116.jpg) University of Groningen Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries Wang, Yanan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries Wang, Yanan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen. Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano
 University of Groningen Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Citation for published version (APA): Mollema, A. K. (2008). Laser cooling, trapping and spectroscopy of calcium isotopes s.n.
 University of Groningen Laser cooling, trapping and spectroscopy of calcium isotopes Mollema, Albert Kornelis IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Laser cooling, trapping and spectroscopy of calcium isotopes Mollema, Albert Kornelis IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS
 DAMOP 2010 May 29, 2010 DEVELOPMENT OF A CONFIGURATION-INTERACTION INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA MIKHAIL KOZLOV PNPI, RUSSIA DANSHA JIANG UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
DAMOP 2010 May 29, 2010 DEVELOPMENT OF A CONFIGURATION-INTERACTION INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA MIKHAIL KOZLOV PNPI, RUSSIA DANSHA JIANG UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 University of Groningen Direct observation of the spin-dependent Peltier effect Flipse, J.; Bakker, F. L.; Slachter, A.; Dejene, F. K.; van Wees, Bart Published in: Nature Nanotechnology DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.2
University of Groningen Direct observation of the spin-dependent Peltier effect Flipse, J.; Bakker, F. L.; Slachter, A.; Dejene, F. K.; van Wees, Bart Published in: Nature Nanotechnology DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.2
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Nonlinear optical properties of one-dimensional organic molecular aggregates in nanometer films Markov, R.V.; Plekhanov, A.I.; Shelkovnikov, V.V.; Knoester, Jasper Published in:
University of Groningen Nonlinear optical properties of one-dimensional organic molecular aggregates in nanometer films Markov, R.V.; Plekhanov, A.I.; Shelkovnikov, V.V.; Knoester, Jasper Published in:
TOWARDS AN OPTICAL NUCLEAR CLOCK WITH THORIUM-229
 TOWARDS AN OPTICAL NUCLEAR CLOCK WITH THORIUM- A. G. Radnaev, C. J. Campbell, and A. Kuzmich School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0430, USA Alexander.Radnaev@gatech.edu
TOWARDS AN OPTICAL NUCLEAR CLOCK WITH THORIUM- A. G. Radnaev, C. J. Campbell, and A. Kuzmich School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0430, USA Alexander.Radnaev@gatech.edu
FYS 3510 Subatomic physics with applications in astrophysics. Nuclear and Particle Physics: An Introduction
 FYS 3510 Subatomic physics with applications in astrophysics Nuclear and Particle Physics: An Introduction Nuclear and Particle Physics: An Introduction, 2nd Edition Professor Brian Martin ISBN: 978-0-470-74275-4
FYS 3510 Subatomic physics with applications in astrophysics Nuclear and Particle Physics: An Introduction Nuclear and Particle Physics: An Introduction, 2nd Edition Professor Brian Martin ISBN: 978-0-470-74275-4
Radium Atom. Electron and Nuclear EDM s. Trapped Radioactive Isotopes: µ icro laboratories for Fundamental Physics
 Radium Atom Electron and Nuclear EDM s TRIµ P: Trapped Radioactive Isotopes: µ icro laboratories for Fundamental Physics Lorenz Willmann, University of Groningen, KVI PandT2008, Heidelberg, 9 June 2008
Radium Atom Electron and Nuclear EDM s TRIµ P: Trapped Radioactive Isotopes: µ icro laboratories for Fundamental Physics Lorenz Willmann, University of Groningen, KVI PandT2008, Heidelberg, 9 June 2008
EDM. Spin. ν e. β - Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics
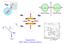 T + - + - He Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin β - θ ν e He Kr 6 He 6 Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin
T + - + - He Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin β - θ ν e He Kr 6 He 6 Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin
Prospects for Atomic Parity Violation Experiments
 Prospects for Atomic Parity Violation Experiments Konstantin Tsigutkin and Dima Budker http://socrates.berkeley.edu/~budker socrates.berkeley.edu/~budker/ Outline A brief story of parity violation in atoms
Prospects for Atomic Parity Violation Experiments Konstantin Tsigutkin and Dima Budker http://socrates.berkeley.edu/~budker socrates.berkeley.edu/~budker/ Outline A brief story of parity violation in atoms
Atomic electric dipole moment calculation with perturbed coupled cluster method
 Atomic electric dipole moment calculation with perturbed coupled cluster method D. Angom Theoretical Physics Division, Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad 380 009 Symposium on 50 Years of Coupled Cluster
Atomic electric dipole moment calculation with perturbed coupled cluster method D. Angom Theoretical Physics Division, Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad 380 009 Symposium on 50 Years of Coupled Cluster
Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540
 Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540 Questions about organization Second quantization Questions about last class? Comments? Similar strategy N-particles Consider Two-body operators in Fock
Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540 Questions about organization Second quantization Questions about last class? Comments? Similar strategy N-particles Consider Two-body operators in Fock
Atomic Clocks and the Search for Variation of Fundamental Constants
 January 22, 2015 Atomic Clocks and the Search for Variation of Fundamental Constants MARIANNA SAFRONOVA University of Maryland Outline Blackbody radiation shifts in atomic clocks: Al +, Yb, Sr Theoretical
January 22, 2015 Atomic Clocks and the Search for Variation of Fundamental Constants MARIANNA SAFRONOVA University of Maryland Outline Blackbody radiation shifts in atomic clocks: Al +, Yb, Sr Theoretical
Status of the Search for an EDM of 225 Ra
 Status of the Search for an EDM of 225 Ra I. Ahmad, K. Bailey, J. Guest, R. J. Holt, Z.-T. Lu, T. O Connor, D. H. Potterveld, N. D. Scielzo Roy Holt Lepton Moments 2006 Cape Cod Outline Why is an EDM interesting?
Status of the Search for an EDM of 225 Ra I. Ahmad, K. Bailey, J. Guest, R. J. Holt, Z.-T. Lu, T. O Connor, D. H. Potterveld, N. D. Scielzo Roy Holt Lepton Moments 2006 Cape Cod Outline Why is an EDM interesting?
Nuclear Schiff moment
 Nuclear Schiff moment V.F. Dmitriev, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia R.A. Sen'kov, I.B. Khriplovich, V.V. Flambaum Schiff theorem The energy of a neutral atom with a point like
Nuclear Schiff moment V.F. Dmitriev, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia R.A. Sen'kov, I.B. Khriplovich, V.V. Flambaum Schiff theorem The energy of a neutral atom with a point like
Peptide folding in non-aqueous environments investigated with molecular dynamics simulations Soto Becerra, Patricia
 University of Groningen Peptide folding in non-aqueous environments investigated with molecular dynamics simulations Soto Becerra, Patricia IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen Peptide folding in non-aqueous environments investigated with molecular dynamics simulations Soto Becerra, Patricia IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
Atomic Parity Violation in Ytterbium
 Atomic Parity Violation in Ytterbium K. Tsigutkin, D. Dounas-Frazer, A. Family, and D. Budker http://budker.berkeley.edu Atomic PV: important landmarks! 1959 Ya. B. Zel dovich: APV (Neutr. Current) Opt.
Atomic Parity Violation in Ytterbium K. Tsigutkin, D. Dounas-Frazer, A. Family, and D. Budker http://budker.berkeley.edu Atomic PV: important landmarks! 1959 Ya. B. Zel dovich: APV (Neutr. Current) Opt.
Lecture 4. Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects
 Lecture 4 Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects Plan of the lecture Reminder from the last lecture: Bound-state solutions of Dirac equation Higher-order corrections to Dirac energies: Radiative
Lecture 4 Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects Plan of the lecture Reminder from the last lecture: Bound-state solutions of Dirac equation Higher-order corrections to Dirac energies: Radiative
Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J.
 University of Groningen Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J. Published in: Default journal IMPORTANT
University of Groningen Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J. Published in: Default journal IMPORTANT
Model for the spacetime evolution of 200A GeV Au-Au collisions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 021903(R) (2004) Model or the spacetime evolution o 200A GeV Au-Au collisions Thorsten Renk Department o Physics, Duke University, P.O. Box 90305, Durham, North Carolina 27708, USA
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 021903(R) (2004) Model or the spacetime evolution o 200A GeV Au-Au collisions Thorsten Renk Department o Physics, Duke University, P.O. Box 90305, Durham, North Carolina 27708, USA
Citation for published version (APA): Andogah, G. (2010). Geographically constrained information retrieval Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Geographically constrained information retrieval Andogah, Geoffrey IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Geographically constrained information retrieval Andogah, Geoffrey IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 21 Hyperfine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms
 Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 21 Hyperfine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms Hyperfine effects in atomic physics are due to the interaction of the atomic electrons with the electric and magnetic multipole
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 21 Hyperfine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms Hyperfine effects in atomic physics are due to the interaction of the atomic electrons with the electric and magnetic multipole
Blackbody radiation shift, multipole polarizabilities, oscillator strengths, lifetimes, hyperfine constants, and excitation energies in Ca +
 Blackbody radiation shift, multipole polarizabilities, oscillator strengths, lifetimes, hyperfine constants, and excitation energies in Ca + M. S. Safronova 1 and U. I. Safronova 2,3 1 Department of Physics
Blackbody radiation shift, multipole polarizabilities, oscillator strengths, lifetimes, hyperfine constants, and excitation energies in Ca + M. S. Safronova 1 and U. I. Safronova 2,3 1 Department of Physics
Precision calculations of atoms with few valence electrons
 Precision calculations of atoms with few valence electrons arxiv:physics/0306061v1 [physics.atom-ph] 7 Jun 2003 M.G.Kozlov Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, Gatchina, 188300, Russia E-mail:mgk@MF1309.spb.edu
Precision calculations of atoms with few valence electrons arxiv:physics/0306061v1 [physics.atom-ph] 7 Jun 2003 M.G.Kozlov Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, Gatchina, 188300, Russia E-mail:mgk@MF1309.spb.edu
Citation for published version (APA): Sok, R. M. (1994). Permeation of small molecules across a polymer membrane: a computer simulation study s.n.
 University of Groningen Permeation of small molecules across a polymer membrane Sok, Robert Martin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Permeation of small molecules across a polymer membrane Sok, Robert Martin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Determination of the static polarizability of the 8s 2 S 1/2 state of atomic cesium
 Determination of the static polarizability of the 8s 2 S 1/2 state of atomic cesium Mevan Gunawardena School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 4797, USA
Determination of the static polarizability of the 8s 2 S 1/2 state of atomic cesium Mevan Gunawardena School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 4797, USA
Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.
![Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n. Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.](/thumbs/95/124821987.jpg) University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
2. ETA EVALUATIONS USING WEBER FUNCTIONS. Introduction
 . ETA EVALUATIONS USING WEBER FUNCTIONS Introduction So ar we have seen some o the methods or providing eta evaluations that appear in the literature and we have seen some o the interesting properties
. ETA EVALUATIONS USING WEBER FUNCTIONS Introduction So ar we have seen some o the methods or providing eta evaluations that appear in the literature and we have seen some o the interesting properties
13. Basic Nuclear Properties
 13. Basic Nuclear Properties Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 13. Basic Nuclear Properties 1 In this section... Motivation for study The strong nuclear force Stable nuclei Binding
13. Basic Nuclear Properties Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 13. Basic Nuclear Properties 1 In this section... Motivation for study The strong nuclear force Stable nuclei Binding
Chaotic scattering from hydrogen atoms in a circularly polarized laser field
 Chaotic scattering rom hydrogen atoms in a circularly polarized laser ield Elias Okon, William Parker, Will Chism, and Linda E. Reichl Center or Studies in Statistical Mechanics and Complex Systems, The
Chaotic scattering rom hydrogen atoms in a circularly polarized laser ield Elias Okon, William Parker, Will Chism, and Linda E. Reichl Center or Studies in Statistical Mechanics and Complex Systems, The
Sakura Pascarelli European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble, France
 X-RAY ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY: FUNDAMENTALS AND SIMPLE MODEL OF EXAFS Sakura Pascarelli European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble, France Part I: Fundamentals o X-ray Absorption Fine Structure:
X-RAY ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY: FUNDAMENTALS AND SIMPLE MODEL OF EXAFS Sakura Pascarelli European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble, France Part I: Fundamentals o X-ray Absorption Fine Structure:
Anderson impurity in a semiconductor
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 54, NUMBER 12 Anderson impurity in a semiconductor 15 SEPTEMBER 1996-II Clare C. Yu and M. Guerrero * Department o Physics and Astronomy, University o Caliornia, Irvine, Caliornia
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 54, NUMBER 12 Anderson impurity in a semiconductor 15 SEPTEMBER 1996-II Clare C. Yu and M. Guerrero * Department o Physics and Astronomy, University o Caliornia, Irvine, Caliornia
LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES
 LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES A.E. Barzakh, D.V. Fedorov, A.M. Ionan, V.S. Ivanov, F.V. Moroz, K.A. Mezilev, S.Yu. Orlov, V.N. Panteleev, Yu.M. Volkov
LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES A.E. Barzakh, D.V. Fedorov, A.M. Ionan, V.S. Ivanov, F.V. Moroz, K.A. Mezilev, S.Yu. Orlov, V.N. Panteleev, Yu.M. Volkov
Citation for published version (APA): Kootstra, F. (2001). Time-dependent density functional theory for periodic systems s.n.
 University of Groningen Time-dependent density functional theory for periodic systems Kootstra, Freddie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Time-dependent density functional theory for periodic systems Kootstra, Freddie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
Modern Ab-initio Calculations Based on Tomas-Fermi-Dirac Theory with High-Pressure Environment
 American Journal o Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Spectroscopy 016; 1(1): 7-1 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajqcms doi: 10.11648/j.ajqcms.0160101.1 Modern Ab-initio Calculations Based on Tomas-Fermi-Dirac
American Journal o Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Spectroscopy 016; 1(1): 7-1 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajqcms doi: 10.11648/j.ajqcms.0160101.1 Modern Ab-initio Calculations Based on Tomas-Fermi-Dirac
PoS(CKM2016)100. Measurement of γ from time-dependent analysis of. Agnieszka Dziurda. CERN
 Measurement o γ rom time-dependent analysis o B s D s K ± CERN E-mail: agnieszka.dziurda@cern.ch We report the measurement o the time-dependent CP violating observables in B s D s K ± decays. The study
Measurement o γ rom time-dependent analysis o B s D s K ± CERN E-mail: agnieszka.dziurda@cern.ch We report the measurement o the time-dependent CP violating observables in B s D s K ± decays. The study
Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.
![Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n. Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.](/thumbs/95/124821981.jpg) University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 22 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 22 Jun 2012 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 22 Jun 2012](/thumbs/80/81601032.jpg) Electroweak hadron structure in point-form dynamics heavy-light systems arxiv:1206.5150v1 [hep-ph] 22 Jun 2012 and Wolfgang Schweiger Institut für Physik, Universität Graz, A-8010 Graz, Austria E-mail:
Electroweak hadron structure in point-form dynamics heavy-light systems arxiv:1206.5150v1 [hep-ph] 22 Jun 2012 and Wolfgang Schweiger Institut für Physik, Universität Graz, A-8010 Graz, Austria E-mail:
Dual photo- and redox- active molecular switches for smart surfaces Ivashenko, Oleksii
 University of Groningen Dual photo- and redox- active molecular switches for smart surfaces Ivashenko, Oleksii IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Dual photo- and redox- active molecular switches for smart surfaces Ivashenko, Oleksii IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
Evolution Of Shell Structure, Shapes & Collective Modes. Dario Vretenar
 Evolution Of Shell Structure, Shapes & Collective Modes Dario Vretenar vretenar@phy.hr 1. Evolution of shell structure with N and Z A. Modification of the effective single-nucleon potential Relativistic
Evolution Of Shell Structure, Shapes & Collective Modes Dario Vretenar vretenar@phy.hr 1. Evolution of shell structure with N and Z A. Modification of the effective single-nucleon potential Relativistic
Atomic structure and dynamics
 Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Apr 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Apr 2015](/thumbs/73/69579006.jpg) Electric dipole moment of 225 Ra due to P- and T-violating weak interactions Yashpal Singh and B. K. Sahoo Theoretical Physics Division, Physical Research Laboratory, Navrangpura, hmedabad - 380009, India
Electric dipole moment of 225 Ra due to P- and T-violating weak interactions Yashpal Singh and B. K. Sahoo Theoretical Physics Division, Physical Research Laboratory, Navrangpura, hmedabad - 380009, India
Reconciliation of experimental and theoretical electric tensor polarizabilities of the cesium ground state
 Europhysics Letters PREPRINT Reconciliation of experimental and theoretical electric tensor polarizabilities of the cesium ground state S. Ulzega ( ), A. Hofer, P. Moroshkin and A. Weis Physics Department,
Europhysics Letters PREPRINT Reconciliation of experimental and theoretical electric tensor polarizabilities of the cesium ground state S. Ulzega ( ), A. Hofer, P. Moroshkin and A. Weis Physics Department,
Spin caloritronics in magnetic/non-magnetic nanostructures and graphene field effect devices Dejene, Fasil
 University of Groningen Spin caloritronics in magnetic/non-magnetic nanostructures and graphene field effect devices Dejene, Fasil DOI: 10.1038/nphys2743 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
University of Groningen Spin caloritronics in magnetic/non-magnetic nanostructures and graphene field effect devices Dejene, Fasil DOI: 10.1038/nphys2743 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
Geometrical Methods for Data Analysis I: Dalitz Plots and Their Uses
 Geometrical Methods for Data Analysis I: Dalitz Plots and Their Uses History of the Dalitz Plot Dalitz s original plot non-relativistic; in terms of kinetic energies applied to the τ-θ puzzle Modern-day
Geometrical Methods for Data Analysis I: Dalitz Plots and Their Uses History of the Dalitz Plot Dalitz s original plot non-relativistic; in terms of kinetic energies applied to the τ-θ puzzle Modern-day
Citation for published version (APA): Raimond, J. J. (1934). The coefficient of differential galactic absorption Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen The coefficient of differential galactic absorption Raimond, Jean Jacques IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen The coefficient of differential galactic absorption Raimond, Jean Jacques IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
