Objectives: Learn how to show Electron configuration using:
|
|
|
- Morgan Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4 WAYS to SHOW the Electron Configuration(Electron arrangement) Objectives: Learn how to show Electron configuration using: 1. Using Aufbau Energy Diagrams 2. Orbital Diagrams 3. Long hand Electron configuration 4. Short-hand Electron configuration
2 Filling Rules for Electron Orbitals Aufbau Principle: Electrons occupy the positions of the lowest energy until all the electrons of the atom have been accounted for. Pauli Exclusion Principle: An orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. that must spin in opposite directions. Hund s Rule: Electrons in the same sublevel occupy empty orbitals rather than pair up *Aufbau is German for building up
3 Periodic Patterns s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s d (n-1) 3d 4d 5d 6d p 2p 3p 4p 5p 6p 7p f (n-2) 6 7 5f 4f
4 Order in which subshells are filled with electrons (AUFBAU) 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4f 5s 5p 5d 5f 6s 6p 6d 7s s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d
5 Energy Energy Sublevels 6d 5f 7s 6p 5d 4f 6s 5p 4d 5s 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 7s 6s 5s 4s 3s 2s 6p 5p 4p 3p 2p 6d 5d 4d 3d 5f 4f n = 4 n = 3 n = 2 4f 4d 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s n = 1
6 Energy Sublevels s p d f s p d s p s n = 4 n = 3 4f 4d 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 n = 2 2p 2s n = 1
7 Aufbau Energy Level Diagram of an Atom 6s 6p 5d 4f 32 5s 5p 4d 18 4s 4p 3d Arbitrary Energy Scale 3s 3p s 2p 8 2 O Connor, Davis, MacNab, McClellan, CHEMISTRY Experiments and Principles 1982, page 177 NUCLEUS
8 Electron capacities Copyright 2006 Pearson Benjamin Cummings. All rights reserved.
9 Copyright 2007 Pearson Benjamin Cummings. All rights reserved
10 Energy General Rules Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Lazy Tenant Rule 6d 5f 7s 6p 5d 4f 6s 5p 4d 5s 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 7s 6s 5s 4s 3s 6p 5p 4p 3p 2p 6d 5d 4d 3d 5f 4f 2s Courtesy Christy Johannesson
11 Order in which subshells are filled with electrons (AUFBAU) 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4f 5s 5p 5d 5f 6s 6p 6d 7s s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d
12 LET s WATCH this SIMPLE VIDEO on how to use the AUFBAU diagram To WRITE ELECTRON configurations VIDEO LINK LET S DO IT! If you believe you haven t understood Anything so far here is a simple video. However, the electron config is WRONG For Lithium when she shows you. It is Li 2 2s 1
13 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p Electron Configuration NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS
14 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Hydrogen 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration H = 1
15 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Helium 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration He = 2
16 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Lithium 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration Li = 2 2s 1
17 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Carbon 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration C = 2 2s 2 2p 2
18 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Nitrogen 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p Hund s Rule maximum number of unpaired orbitals. NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration N = 2 2s 2 2p 3
19 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Fluorine 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration F = 2 2s 2 2p 5
20 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Aluminum 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration Al = 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 1
21 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Argon 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration Ar = 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6
22 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Iron 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration Fe = 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6
23 Arbitrary Energy Scale Energy Level Diagram 6s 6p 5d 4f Lanthanum 5s 5p 4d Bohr Model 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p N 2s 2p NUCLEUS H He Li C N Al Ar F Fe La CLICK ON ELEMENT TO FILL IN CHARTS Electron Configuration La = 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 5d 1
24 Electron Configurations Orbital Filling Electron Element 2s 2p x 2p y 2p z 3s Configuration H He Li C N O F Ne Na 1 2 NOT CORRECT Violates Hund s Rule 2 2s 1 2 2s 2 2p 2 2 2s 2 2p 3 2 2s 2 2p 4 2 2s 2 2p 5 2 2s 2 2p 6 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1
25 Electron Configurations Orbital Filling Electron Element 2s 2p x 2p y 2p z 3s Configuration H He Li C N O F Ne Na s 1 2 2s 2 2p 2 2 2s 2 2p 3 2 2s 2 2p 4 2 2s 2 2p 5 2 2s 2 2p 6 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1
26 Shorthand Configuration A neon's electron configuration ( 2 2s 2 2p 6 ) [Ne] 3s 1 B C third energy level one electron in the s orbital D orbital shape Na = [ 2 2s 2 2p 6 ] 3s 1 electron configuration
27 Shorthand Configuration Element symbol Ca V F Ag I Xe Electron configuration [Ar] 4s 2 [Ar] 4s 2 3d 3 [He] 2s 2 2p 5 [Kr] 5s 2 4d 9 [Kr] 5s 2 4d 10 5p 5 [Kr] 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 Fe [He] 2s[Ar] 2 2p 6 4s 3s 3d 3p 4s 2 3d 6 Sg [Rn] 7s 2 5f 14 6d 4
28 General Rules Pauli Exclusion Principle Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli Courtesy Christy Johannesson
29 General Rules Hund s Rule Within a sublevel, place one electron per orbital before pairing them. Empty Bus Seat Rule WRONG RIGHT Courtesy Christy Johannesson
30 Notation 8 O Orbital Diagram O 8e - 2s 2p Electron Configuration 2 2s 2 2p 4 Courtesy Christy Johannesson
31 Notation 16 S Longhand Configuration S 16e - 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4 Core Electrons Valence Electrons Shorthand Configuration S 16e - [Ne] 3s 2 3p 4 Courtesy Christy Johannesson
32 Periodic Patterns s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s d (n-1) 3d 4d 5d 6d p 2p 3p 4p 5p 6p 7p f (n-2) 6 7 5f 4f
33 Periodic Patterns Period # energy level (subtract for d & f) A/B Group # total # of valence e - Column within sublevel block # of e - in sublevel Courtesy Christy Johannesson
34 Periodic Patterns Example - Hydrogen st column of s-block t Period s-block Courtesy Christy Johannesson
35 Periodic Patterns Shorthand Configuration Core electrons: Go up one row and over to the Noble Gas. Valence electrons: On the next row, fill in the # of e - in each sublevel Courtesy Christy Johannesson
36 Periodic Patterns 32 Ge Example - Germanium [Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 2 Courtesy Christy Johannesson
37 Stability Full energy level Full sublevel (s, p, d, f) Half-full sublevel Courtesy Christy Johannesson
38 The Octet Rule Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until they have eight valence electrons. This fills the valence shell and tends to give the atom the stability of the inert gasses. 8 ONLY s- and p-orbitals are valence electrons.
39 THIS SLIDE IS ANIMATED IN FILLING ORDER 2.PPT H = 1 He = 2 Li = 2 2s 1 2s Be = 2 2s 2 2s C = 2 2s 2 2p 2 2s 2px 2py 2pz S = 2 2s 2 2p 4 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz
40 Fe = 1 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 Iron has 26 electrons. 2s 2p x 2p y 2p z 3s 3p x 3p y 3p z 4s 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d 6s 6p 5d 4f 32 5s 5p 4d e- e- e - e - e - e- e - e - e - e - e - e e - e - e - e e - e - - e - e - e - e - e - e e - e- - Arbitrary Energy Scale 4s 4p 3d 3s 3p 2s 2p NUCLEUS
41 Energy Level Diagram of a Many-Electron Atom 6s 6p 5d 4f 32 5s 5p 4d 18 4s 4p 3d Arbitrary Energy Scale 3s 3p s 2p 8 2 O Connor, Davis, MacNab, McClellan, CHEMISTRY Experiments and Principles 1982, page 177 NUCLEUS
42 Maximum of Electrons In Each Sublevel Maximum Number of Electrons In Each Sublevel Maximum Number Sublevel Number of Orbitals of Electrons s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 f 7 14 LeMay Jr, Beall, Robblee, Brower, Chemistry Connections to Our Changing World, 1996, page 146
43 Stability Electron Configuration Exceptions Copper EXPECT: [Ar] 4s 2 3d 9 ACTUALLY: [Ar] 4s 1 3d 10 Copper gains stability with a full d-sublevel. Courtesy Christy Johannesson
44 Stability Electron Configuration Exceptions Chromium EXPECT: [Ar] 4s 2 3d 4 ACTUALLY: [Ar] 4s 1 3d 5 Chromium gains stability with a half-full d-sublevel. Courtesy Christy Johannesson
45 Energy Electron Filling in Periodic Table s s 1 p 2 3 d 4 K 4s 1 Ca 4s 2 Sc 3d 1 Ti 3d 2 V 3d 3 Cr 3d 45 Mn 3d 5 Fe 3d 6 Co 3d 7 Ni 3d 8 Cu 3d 9 3d 10 Zn 3d 10 Ga 4p 1 Ge 4p 2 As 4p 3 Se 4p 4 Br 4p 5 Kr 4p 6 n = 4 n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 4f 4d 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s Cr 4s 1 3d 5 4s Cu 4s 1 3d 10 3d Cr 4s 1 3d 5 Cu 4s 1 3d 10 4s 3d
46 Stability Ion Formation Atoms gain or lose electrons to become more stable. Isoelectronic with the Noble Gases Courtesy Christy Johannesson
47 Stability Ion Electron Configuration Write the e - configuration for the closest Noble Gas EX: Oxygen ion O 2- Ne O 2-10e - [He] 2s 2 2p 6 Courtesy Christy Johannesson
48 Orbital Diagrams for Nickel 28 Ni s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Excited State 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Pauli Exclusion 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Hund s Rule 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d
49 Orbital Diagrams for Nickel 28 Ni s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Excited State s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d VIOLATES Pauli Exclusion 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d VIOLATES Hund s Rule 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d
50 Write out the complete electron configuration for the following: 1) An atom of nitrogen 2) An atom of silver 3) An atom of uranium POP (shorthand) Fill in the orbital boxes for an atom of nickel (Ni) QUIZ 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Which rule states no two electrons can spin the same direction in a single orbital? Extra credit: Draw a Bohr model of a Ti 4+ cation. Ti 4+ is isoelectronic to Argon.
51 Answer Key Write out the complete electron configuration for the following: 1) An atom of nitrogen 2 2s 2 2p 3 2) An atom of silver 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 9 3) An atom of uranium (shorthand) [Rn]7s 2 6d 1 5f 3 Fill in the orbital boxes for an atom of nickel (Ni) 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Which rule states no two electrons can spin the same direction in a single orbital? Pauli exclusion principle Extra credit: Draw a Bohr model of a Ti 4+ cation. n = 22+ n Ti 4+ is isoelectronic to Argon.
Unit 5: Light and Electron Configuration C H E M I S T R Y M R. R O N G
 Unit 5: Light and Electron Configuration C H E M I S T R Y 2 0 1 4-15 M R. R O N G Historical Models of the Atom Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr What do you notice about where the electrons are? Bohr Model
Unit 5: Light and Electron Configuration C H E M I S T R Y 2 0 1 4-15 M R. R O N G Historical Models of the Atom Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr What do you notice about where the electrons are? Bohr Model
General Rules. Pauli Exclusion Principle. Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli
 General Rules Pauli Exclusion Principle Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli General Rules Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Lazy Tenant
General Rules Pauli Exclusion Principle Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli General Rules Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Lazy Tenant
When I lecture we will add more info, so leave spaces in your notes
 Title and Highlight Topic: EQ: Date Reflect Question: Reflect on the material by asking a question (its not suppose to be answered from notes) NOTES: Write out the notes from my website. Use different
Title and Highlight Topic: EQ: Date Reflect Question: Reflect on the material by asking a question (its not suppose to be answered from notes) NOTES: Write out the notes from my website. Use different
Unit Two: Elements & Matter. February 1, 2016
 Unit Two: Elements & Matter February 1, 2016 Warm-Up: 2/1/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Ca 2+ Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron 34 36 Mass Num. 2. Identify which family the
Unit Two: Elements & Matter February 1, 2016 Warm-Up: 2/1/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Ca 2+ Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron 34 36 Mass Num. 2. Identify which family the
[3.3] Energy Level Diagrams and Configurations
![[3.3] Energy Level Diagrams and Configurations [3.3] Energy Level Diagrams and Configurations](/thumbs/87/96003907.jpg) [3.3] Energy Level Diagrams and Configurations 1 Energy Level Diagrams Energy level diagrams are used to represent the electron arrangement in an atom 2 Pauli s Exclusion Principle No two electrons have
[3.3] Energy Level Diagrams and Configurations 1 Energy Level Diagrams Energy level diagrams are used to represent the electron arrangement in an atom 2 Pauli s Exclusion Principle No two electrons have
The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. orbital 3s 3p 3d. Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n.
 Shells and Subshells The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. n=3 orbital 3s 3p 3d Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n n=3 3s 3p 3d Subshell: all orbitals with the same value
Shells and Subshells The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. n=3 orbital 3s 3p 3d Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n n=3 3s 3p 3d Subshell: all orbitals with the same value
Electron Configurations
 Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Where are the s, p, d, f orbitals located on the periodic table? Identify them on the diagram below.
 Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Section 3: Electron Configuration Objectives: Be able to define: Aufbau Principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle, Hund s rule. Be able to list the number of electrons
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Section 3: Electron Configuration Objectives: Be able to define: Aufbau Principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle, Hund s rule. Be able to list the number of electrons
Unit 4B- Electron Configuration- Guided Notes
 Unit 4B- Electron Configuration- Guided Notes Atomic Structure Electrons are arranged in or around the nucleus of an atom o First shell can hold a maximum of electrons o Second shell can hold a maximum
Unit 4B- Electron Configuration- Guided Notes Atomic Structure Electrons are arranged in or around the nucleus of an atom o First shell can hold a maximum of electrons o Second shell can hold a maximum
Electron Configuration. The electron configuration of an atom tells us how the electrons are distributed among the various atomic orbitals.
 Electron Configuration The electron configuration of an atom tells us how the electrons are distributed among the various atomic orbitals. Spin Quantum Number, m s In the 1920s, it was discovered that
Electron Configuration The electron configuration of an atom tells us how the electrons are distributed among the various atomic orbitals. Spin Quantum Number, m s In the 1920s, it was discovered that
Unit 8: Atomic Theory. Quantum Mechanics
 Unit 8: Atomic Theory Quantum Mechanics 1 Unit 8: Atomic Theory 1. Historical Views of the Atom 2. The 'New' Look Atom 3. Electron Configurations 4. Electron Configurations & the Periodic Table 5. Quantum
Unit 8: Atomic Theory Quantum Mechanics 1 Unit 8: Atomic Theory 1. Historical Views of the Atom 2. The 'New' Look Atom 3. Electron Configurations 4. Electron Configurations & the Periodic Table 5. Quantum
Unit 8: Atomic Theory. Quantum Mechanics
 Unit 8: Atomic Theory Quantum Mechanics 1 Unit 8: Atomic Theory 1. Historical Views of the Atom 2. The 'New' Look Atom 3. Electron Configurations 4. Electron Configurations & the Periodic Table 5. Quantum
Unit 8: Atomic Theory Quantum Mechanics 1 Unit 8: Atomic Theory 1. Historical Views of the Atom 2. The 'New' Look Atom 3. Electron Configurations 4. Electron Configurations & the Periodic Table 5. Quantum
Electron Configuration & Orbitals
 Electron Configuration & Orbitals 2 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 6 Continuous spectrum (results when white light is passed through a prism) contains
Electron Configuration & Orbitals 2 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 6 Continuous spectrum (results when white light is passed through a prism) contains
Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions
 Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions Section 3.5 The Periodic Table is like a MAP that describes the arrangement of electrons within their orbitals. Orbital diagrams represent
Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions Section 3.5 The Periodic Table is like a MAP that describes the arrangement of electrons within their orbitals. Orbital diagrams represent
6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)
 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 317 Orbital n l m l degeneracy Radial nodes (no.) 4f 4 3 7 0 4p 4 1 3 2 7f 7 3 7 3 5d 5 2 5 2 Check Your Learning How many orbitals have
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 317 Orbital n l m l degeneracy Radial nodes (no.) 4f 4 3 7 0 4p 4 1 3 2 7f 7 3 7 3 5d 5 2 5 2 Check Your Learning How many orbitals have
Electron Configurations
 Electron Configurations Parts of the atom Protons identify the element. Neutrons add mass and help glue the nucleus together ( all those protons are NOT happy being stuck next to each other). Parts of
Electron Configurations Parts of the atom Protons identify the element. Neutrons add mass and help glue the nucleus together ( all those protons are NOT happy being stuck next to each other). Parts of
LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL Did not explain the chemical properties of atoms For example, it could not explain why metals or compounds of metals give off characteristic
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL Did not explain the chemical properties of atoms For example, it could not explain why metals or compounds of metals give off characteristic
5. N. 9. Cl 2. Pb. 6. Ag. c. 4f d. 3d
 Brief Instructions An electron configuration is a method of indicating the arrangement of electrons about a nucleus. A typical electron configuration consists of numbers, letters, and superscripts with
Brief Instructions An electron configuration is a method of indicating the arrangement of electrons about a nucleus. A typical electron configuration consists of numbers, letters, and superscripts with
Unit 1 Part 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Introduction to Atomic Structure UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC STRUCTURE Contents 1. Protons, Neutrons and Electrons 2. Early Models of the Atom 3. Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4. Atoms and Ions
UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC STRUCTURE Contents 1. Protons, Neutrons and Electrons 2. Early Models of the Atom 3. Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4. Atoms and Ions
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
Chapter 7 The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends
 Chapter 7 The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electrons in atoms are arranged as SHELLS (n) SUBSHELLS (l) ORBITALS
Chapter 7 The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electrons in atoms are arranged as SHELLS (n) SUBSHELLS (l) ORBITALS
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Use the Venn Diagram to compare and contrast the Bohr Model of the atom with the Quantum Mechanical Model of atom
 Use the Venn Diagram to compare and contrast the Bohr Model of the atom with the Quantum Mechanical Model of atom Bohr Model Quantum Model Energy level Atomic orbital Quantum Atomic number Quantum mechanical
Use the Venn Diagram to compare and contrast the Bohr Model of the atom with the Quantum Mechanical Model of atom Bohr Model Quantum Model Energy level Atomic orbital Quantum Atomic number Quantum mechanical
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
 ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS Electron Spin The electron: spins around its own axis acts as an tiny magnet (any moving electrical charge creates a magnetic field around itself) can spin in either of 2
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS Electron Spin The electron: spins around its own axis acts as an tiny magnet (any moving electrical charge creates a magnetic field around itself) can spin in either of 2
Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends
 Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 11.01 The Bohr Model of the Atom
Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 11.01 The Bohr Model of the Atom
Topic 2 Atomic Structure. IB Chemistry SL Coral Gables Senior High School Ms. Kiely
 Topic 2 Atomic Structure IB Chemistry SL Coral Gables Senior High School Ms. Kiely Bell Ringer (i) Calculate the number of neutrons and electrons in one atom of ⁶⁵Cu. (ii) State one difference in the physical
Topic 2 Atomic Structure IB Chemistry SL Coral Gables Senior High School Ms. Kiely Bell Ringer (i) Calculate the number of neutrons and electrons in one atom of ⁶⁵Cu. (ii) State one difference in the physical
Electron Configuration
 Electron Configuration Electrons as Waves Review Louis de Broglie (1924) Applied wave-particle theory to electrons ELECTRONS EXHIBIT WAVE PROPERTIES Louis de Broglie ~1924 QUANTIZED WAVELENGTHS 200 Fundamental
Electron Configuration Electrons as Waves Review Louis de Broglie (1924) Applied wave-particle theory to electrons ELECTRONS EXHIBIT WAVE PROPERTIES Louis de Broglie ~1924 QUANTIZED WAVELENGTHS 200 Fundamental
Electronic configuration
 Electronic configuration The energy of electrons The electrons of an atom all have the same charge and the same mass, but each electron has a different amount of energy. Electrons that have the lowest
Electronic configuration The energy of electrons The electrons of an atom all have the same charge and the same mass, but each electron has a different amount of energy. Electrons that have the lowest
1. Electronic Structure 2. Electron Configuration 3. Core Notation 4. EC Relationship to Periodic Table 5. Electron Configuration of Ions
 Pre-AP Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory II Name: Date: Block: 1. Electronic Structure 2. Electron Configuration 3. Core Notation 4. EC Relationship to Periodic Table 5. Electron Configuration of Ions Electronic
Pre-AP Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory II Name: Date: Block: 1. Electronic Structure 2. Electron Configuration 3. Core Notation 4. EC Relationship to Periodic Table 5. Electron Configuration of Ions Electronic
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
 Page III-6b- / Chapter Six Part II Lecture Notes The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends Chapter Six Part Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electrons in atoms are arranged as SHELLS (n) SUBSHELLS (l)
Page III-6b- / Chapter Six Part II Lecture Notes The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends Chapter Six Part Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electrons in atoms are arranged as SHELLS (n) SUBSHELLS (l)
POGIL: Electron Configurations
 Name DUE DATE Period Chemistry POGIL: Electron Configurations Why? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in molecules,
Name DUE DATE Period Chemistry POGIL: Electron Configurations Why? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in molecules,
LABELING ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
 Date: Name: LABELING ELECTRONS IN ATOMS The location of each electron in an atom is determined by a few different factors. Each factor is represented by a QUANTUM NUMBER. Prediction: What do you think
Date: Name: LABELING ELECTRONS IN ATOMS The location of each electron in an atom is determined by a few different factors. Each factor is represented by a QUANTUM NUMBER. Prediction: What do you think
Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory
 Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
 Electronic configurations, Auf-bau principle, Pauli principle, Hunds rule 1. Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct? 1) 3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than
Electronic configurations, Auf-bau principle, Pauli principle, Hunds rule 1. Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct? 1) 3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than
Arrangement of Electrons. Chapter 4
 Arrangement of Electrons Chapter 4 Properties of Light -Light s interaction with matter helps to understand how electrons behave in atoms -Light travels through space & is a form of electromagnetic radiation
Arrangement of Electrons Chapter 4 Properties of Light -Light s interaction with matter helps to understand how electrons behave in atoms -Light travels through space & is a form of electromagnetic radiation
UNIT 2 PART 1: ELECTRONS
 UNIT 2 PART 1: ELECTRONS Electrons in an Atom Bohr s Model: Electrons resided in an allowed orbit. Quantum Mechanics Model: Probability of finding an electron in an area around the nucleus. This area around
UNIT 2 PART 1: ELECTRONS Electrons in an Atom Bohr s Model: Electrons resided in an allowed orbit. Quantum Mechanics Model: Probability of finding an electron in an area around the nucleus. This area around
Atomic Theory. Quantum Mechanics
 Atomic Theory Quantum Mechanics Quantum Mechanics The ol solar system model of the atom does have some practical uses It tells us that protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are in orbitals
Atomic Theory Quantum Mechanics Quantum Mechanics The ol solar system model of the atom does have some practical uses It tells us that protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are in orbitals
Name Chemistry-PAP Period. Notes: Electrons. Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics:
 Name Chemistry-PAP Period The Wave Nature of Light Notes: Electrons Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength (λ): the distance between 2 consecutive crests
Name Chemistry-PAP Period The Wave Nature of Light Notes: Electrons Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength (λ): the distance between 2 consecutive crests
Chapter 6 Part 3; Many-electron atoms
 Chapter 6 Part 3; Many-electron atoms Read: BLB 6.7 6.9 HW: BLB 6:59,63,64,67,71b-d,74,75,90,97; Packet 6:10 14 Know: s & atoms with many electrons Spin quantum number m s o Pauli exclusion principle o
Chapter 6 Part 3; Many-electron atoms Read: BLB 6.7 6.9 HW: BLB 6:59,63,64,67,71b-d,74,75,90,97; Packet 6:10 14 Know: s & atoms with many electrons Spin quantum number m s o Pauli exclusion principle o
2 e. 14 e. # e # orbitals. 10 e 5. sublevel. shape of orbital. Orbital Shapes. Notes Orbital Notation; e Config; NGN.
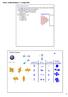 How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
Electrons! Chapter 5, Part 2
 Electrons! Chapter 5, Part 2 3. Contained within sublevels are orbitals: pairs of electrons each having a different space or region they occupy a. Each sublevel contains certain orbitals: i. s sublevel
Electrons! Chapter 5, Part 2 3. Contained within sublevels are orbitals: pairs of electrons each having a different space or region they occupy a. Each sublevel contains certain orbitals: i. s sublevel
Model 1: Orbitals. 1. What is an atomic orbital? What are the four different orbitals?
 Name: Date: Period: POGIL: Electron Configuration and Orbitals Model 1: Orbitals The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron
Name: Date: Period: POGIL: Electron Configuration and Orbitals Model 1: Orbitals The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron
Mendeleev s Periodic Law
 Mendeleev s Periodic Law Periodic Law When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain sets of properties recur periodically. Mendeleev s Periodic Law allows us to predict what
Mendeleev s Periodic Law Periodic Law When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain sets of properties recur periodically. Mendeleev s Periodic Law allows us to predict what
Chap 7 Part 2Tc.notebook November 02, 2017
 Chapter 7 Section 4 11 Quantum mechanics electrons are organized in atoms in very specific ways energy levels represent distances from the nucleus inside energy levels are orbitals that can hold 2 electrons
Chapter 7 Section 4 11 Quantum mechanics electrons are organized in atoms in very specific ways energy levels represent distances from the nucleus inside energy levels are orbitals that can hold 2 electrons
Komperda. Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation
 Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation Dmitri Mendeleyev Father of the Modern P.T. Periods and Group Period horizontal row on P.T. Each period represents an energy level (think back to models of the
Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation Dmitri Mendeleyev Father of the Modern P.T. Periods and Group Period horizontal row on P.T. Each period represents an energy level (think back to models of the
Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom. Aim: To write orbital notation and electron configurations representing the wave mechanical model of the atom.
 Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Aim: To write orbital notation and electron configurations representing the wave mechanical model of the atom. Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Atoms contain protons,
Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Aim: To write orbital notation and electron configurations representing the wave mechanical model of the atom. Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Atoms contain protons,
Creating Energy-Level Diagrams Aufbau (building up) Principle Electrons are added to the lowest energy orbital available.
 3.6 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Bohr's Theory Was Incorrect Because... Only explained the line spectrum of hydrogen Position and motion of an e cannot be specified (since the e is so small,
3.6 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Bohr's Theory Was Incorrect Because... Only explained the line spectrum of hydrogen Position and motion of an e cannot be specified (since the e is so small,
Orbital Diagram Rules: 1. The Aufbau Principle: Under normal condition, each electron occupies the
 Honors Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Orbital Diagram Rules: 1. The Aufbau Principle: Under normal condition, each electron occupies the 2. The Pauli Exclusion Principle: a maximum of can occupy an orbital
Honors Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Orbital Diagram Rules: 1. The Aufbau Principle: Under normal condition, each electron occupies the 2. The Pauli Exclusion Principle: a maximum of can occupy an orbital
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5
 Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 Helpful Videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-djeilynje Quantum Mechanics Better than any previous model, quantum mechanics does explain how the atom behaves. Quantum
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 Helpful Videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-djeilynje Quantum Mechanics Better than any previous model, quantum mechanics does explain how the atom behaves. Quantum
An Electron s Address: Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration
 AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block An Electron s Address: Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that
AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block An Electron s Address: Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that
Electron Arrangement - Part 2
 Brad Collins Electron Arrangement - Part 2 Chapter 9 Some images Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Review Energy Levels Multi-electron 4d 4d 4d 4d 4d n = 4 4s 4p 4p 4p 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d n=3, l = 2
Brad Collins Electron Arrangement - Part 2 Chapter 9 Some images Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Review Energy Levels Multi-electron 4d 4d 4d 4d 4d n = 4 4s 4p 4p 4p 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d n=3, l = 2
5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms > Happy Thursday!
 Happy Thursday! Please take out your homework problems for me to check for a grade. Keep them out since we will be going over them. Also, take out your notes packet! 1 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1
Happy Thursday! Please take out your homework problems for me to check for a grade. Keep them out since we will be going over them. Also, take out your notes packet! 1 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1
Chapter 5. Periodicity and the Electronic Structure of Atoms
 Chapter 5 Periodicity and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Electron Spin experiments by Stern and Gerlach showed a beam of silver atoms is split in two by a magnetic field the experiment reveals that
Chapter 5 Periodicity and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Electron Spin experiments by Stern and Gerlach showed a beam of silver atoms is split in two by a magnetic field the experiment reveals that
Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
HL Chemistry Topic 12 Atomic Structure
 Define: ionization energy - 1 - Trends in Ionization Energy in the Periodic Table Why do these trends in ionization energy occur? Background information: Understand the concept of effective nuclear charge
Define: ionization energy - 1 - Trends in Ionization Energy in the Periodic Table Why do these trends in ionization energy occur? Background information: Understand the concept of effective nuclear charge
Full file at
 16 Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element. a.
16 Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element. a.
1.1 Atomic structure. The Structure of the Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation Energies
 1.1 Atomic structure The Structure of the Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation Energies a) Protons, neutrons and electrons THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM Atoms are made up of three fundamental
1.1 Atomic structure The Structure of the Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation Energies a) Protons, neutrons and electrons THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM Atoms are made up of three fundamental
Page 1 of 9. Website: Mobile:
 Question 1: Did Dobereiner s triads also exist in the columns of Newlands Octaves? Compare and find out. Only one triad of Dobereiner s triads exists in the columns of Newlands octaves. The triad formed
Question 1: Did Dobereiner s triads also exist in the columns of Newlands Octaves? Compare and find out. Only one triad of Dobereiner s triads exists in the columns of Newlands octaves. The triad formed
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Electron Configuration Vocabulary: atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule, electron configuration, Hund s rule, orbital, Pauli exclusion
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Electron Configuration Vocabulary: atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule, electron configuration, Hund s rule, orbital, Pauli exclusion
ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS... WHY BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS JUST WON T CUT IT ANYMORE!
 ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS... WHY BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS JUST WON T CUT IT ANYMORE! REPRESENTING ELECTRONS... Now that you know what an orbital is, you need to be able to use that to describe the electronic
ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS... WHY BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS JUST WON T CUT IT ANYMORE! REPRESENTING ELECTRONS... Now that you know what an orbital is, you need to be able to use that to describe the electronic
Section 3 Electron Configurations. Chapter 4. Preview
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Electron Configurations Rules Governing Electron Configurations Representing Electron Configurations Elements of the Second Period Elements of the Third Period Elements
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Electron Configurations Rules Governing Electron Configurations Representing Electron Configurations Elements of the Second Period Elements of the Third Period Elements
Particle Behavior of Light 1. Calculate the energy of a photon, mole of photons 2. Find binding energy of an electron (know KE) 3. What is a quanta?
 Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
ATOMIC ORBITALS AND ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS
 ATOMIC ORBITALS AND ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS Quantum Mechanics Better than any previous model, quantum mechanics does explain how the atom behaves. Quantum mechanics treats electrons not as particles, but
ATOMIC ORBITALS AND ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS Quantum Mechanics Better than any previous model, quantum mechanics does explain how the atom behaves. Quantum mechanics treats electrons not as particles, but
Chemistry- Unit 3. Section II - Chapter 7 ( , 7.11) Quantum Mechanics
 Chemistry- Unit 3 Section II - Chapter 7 (7.6-7.8, 7.11) Quantum Mechanics Atomic Review What subatomic particles do you get to play with? Protons Neutrons Electrons NO! It would change the element Don
Chemistry- Unit 3 Section II - Chapter 7 (7.6-7.8, 7.11) Quantum Mechanics Atomic Review What subatomic particles do you get to play with? Protons Neutrons Electrons NO! It would change the element Don
MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 C10 04/19/2013 13:34:14 Page 114 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is
C10 04/19/2013 13:34:14 Page 114 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is
Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element.
Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element.
Chapter 8. Periodic Properties of the Elements
 Chapter 8 Periodic Properties of the Elements Mendeleev (1834 1907) Ordered elements by atomic mass. Saw a repeating pattern of properties. Periodic Law When the elements are arranged in order of increasing
Chapter 8 Periodic Properties of the Elements Mendeleev (1834 1907) Ordered elements by atomic mass. Saw a repeating pattern of properties. Periodic Law When the elements are arranged in order of increasing
Modern Atomic Theory CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Chapter 3B Modern Atomic Theory 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Waves Electromagnetic Radiation Dual Nature of Light Bohr Model of Atom Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Electron Configuration Electron Configuration
Chapter 3B Modern Atomic Theory 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Waves Electromagnetic Radiation Dual Nature of Light Bohr Model of Atom Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Electron Configuration Electron Configuration
Electron Configurations: Assigning each electron in an atom to the energy level and sublevel it occupies in the atom. Number of Electrons
 First some terms and more information about the structure of the atom: 1) Energy level is no longer an orbit but more like a boundary or maximum distance from the nucleus that electrons occupy. 1, 2, 3
First some terms and more information about the structure of the atom: 1) Energy level is no longer an orbit but more like a boundary or maximum distance from the nucleus that electrons occupy. 1, 2, 3
Electronic Structure of Atoms and the Periodic table. Electron Spin Quantum # m s
 Electronic Structure of Atoms and the Periodic table Chapter 6 & 7, Part 3 October 26 th, 2004 Homework session Wednesday 3:00 5:00 Electron Spin Quantum # m s Each electron is assigned a spinning motion
Electronic Structure of Atoms and the Periodic table Chapter 6 & 7, Part 3 October 26 th, 2004 Homework session Wednesday 3:00 5:00 Electron Spin Quantum # m s Each electron is assigned a spinning motion
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY
 Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
#9 Modern Atomic Theory Quantitative Chemistry
 Name #9 Modern Atomic Theory Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: What is the current model of the atom? Key Learning: The current model of the atom is based on the quantum mechanical model.
Name #9 Modern Atomic Theory Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: What is the current model of the atom? Key Learning: The current model of the atom is based on the quantum mechanical model.
4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS
 4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS Bohr s Model Contradicts Common Sense If only certain orbits with definite energies are allowed and the electrons constantly gives off radiation,
4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS Bohr s Model Contradicts Common Sense If only certain orbits with definite energies are allowed and the electrons constantly gives off radiation,
KWL CHART--ELECTRONS
 KWL CHART--ELECTRONS WHAT DO I ALREADY KNOW ABOUT ELECTRONS? WHAT DO I WANT TO KNOW CONCERNING ELECTRONS? WHAT HAVE I LEARNED TODAY ABOUT ELECTRONS? GPS STANDARD SC3. Students will use the modern atomic
KWL CHART--ELECTRONS WHAT DO I ALREADY KNOW ABOUT ELECTRONS? WHAT DO I WANT TO KNOW CONCERNING ELECTRONS? WHAT HAVE I LEARNED TODAY ABOUT ELECTRONS? GPS STANDARD SC3. Students will use the modern atomic
Electron Configurations
 Electron Configurations Electron Arrangement in an Atom The arrangement of electrons in an atom is its electron configuration. It is impossible to know where an electron is or how fast it is traveling
Electron Configurations Electron Arrangement in an Atom The arrangement of electrons in an atom is its electron configuration. It is impossible to know where an electron is or how fast it is traveling
Note that the protons and neutrons are each almost 2,000 times more massive than an electron; What is the approximate diameter of an atom?
 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
The Rutherford s model of the atom did not explain how an atom can emit light or the chemical properties of an atom.
 The Rutherford s model of the atom did not explain how an atom can emit light or the chemical properties of an atom. Plum Pudding Model Rutherford s Model Niels Bohr studied the hydrogen atom because it
The Rutherford s model of the atom did not explain how an atom can emit light or the chemical properties of an atom. Plum Pudding Model Rutherford s Model Niels Bohr studied the hydrogen atom because it
Practice with Electron Configurations
 Practice with Electron Configurations Prelab Assignment Read the entire lab and write an objective and possible hazards in your laboratory notebook. Answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook
Practice with Electron Configurations Prelab Assignment Read the entire lab and write an objective and possible hazards in your laboratory notebook. Answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook
CDO AP Chemistry Unit 5
 1. a. Calculate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 5.56 MHz. b. Calculate the frequency of electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength equal to 667 nm. 2. Electromagnetic
1. a. Calculate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 5.56 MHz. b. Calculate the frequency of electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength equal to 667 nm. 2. Electromagnetic
Electron Configuration & Periodicity Unit 3
 Name: Electron Configuration & Periodicity Unit 3 (seven class periods) Unit 3.1: First Ionization Energy & Photoelectron Spectroscopy 1) Coulombs Law a) The force of attraction between two charged objects
Name: Electron Configuration & Periodicity Unit 3 (seven class periods) Unit 3.1: First Ionization Energy & Photoelectron Spectroscopy 1) Coulombs Law a) The force of attraction between two charged objects
Atomic Emission Spectra, & Electron Configuration. Unit 1 Coral Gables Senior High Ms. Kiely Pre-IB Chemistry I
 Atomic Emission Spectra, & Electron Configuration Unit 1 Coral Gables Senior High Ms. Kiely Pre-IB Chemistry I Bell-Ringer What does Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle state? Answer Heisenberg s Uncertainty
Atomic Emission Spectra, & Electron Configuration Unit 1 Coral Gables Senior High Ms. Kiely Pre-IB Chemistry I Bell-Ringer What does Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle state? Answer Heisenberg s Uncertainty
ORBITAL DIAGRAM - A graphical representation of the quantum number "map" of electrons around an atom.
 160 ORBITAL DIAGRAM - A graphical representation of the quantum number "map" of electrons around an atom. 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s Each blank represents an ORBITAL, and can hold two electrons. The 4s subshell
160 ORBITAL DIAGRAM - A graphical representation of the quantum number "map" of electrons around an atom. 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s Each blank represents an ORBITAL, and can hold two electrons. The 4s subshell
Remember Bohr s Explanation: Energy Levels of Hydrogen: The Electronic Structure of the Atom 11/28/2011
 The Electronic Structure of the Atom Bohr based his theory on his experiments with hydrogen he found that when energy is added to a sample of hydrogen, energy is absorbed and reemitted as light When passed
The Electronic Structure of the Atom Bohr based his theory on his experiments with hydrogen he found that when energy is added to a sample of hydrogen, energy is absorbed and reemitted as light When passed
Bohr Model of Atom: electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun energy levels for electrons are quantized
 Chemistry I: Quantum Mechanics Notes Bohr Model of Atom: electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun energy levels for electrons are quantized Major developments that put
Chemistry I: Quantum Mechanics Notes Bohr Model of Atom: electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun energy levels for electrons are quantized Major developments that put
Name: Date: Period: ELECTRON ORBITAL ACTIVITY
 ELECTRON ORBITAL ACTIVITY Background Information: The arrangement of electrons within the orbitals of an atom is known as the electron configuration. The most stable arrangement is called the ground-state
ELECTRON ORBITAL ACTIVITY Background Information: The arrangement of electrons within the orbitals of an atom is known as the electron configuration. The most stable arrangement is called the ground-state
Electrons and Periodic Behavior. Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net
 Electrons and Periodic Behavior Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Wave-Particle Duality JJ Thomson won the Nobel prize for describing the electron as a particle. His son, George Thomson won the Nobel
Electrons and Periodic Behavior Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Wave-Particle Duality JJ Thomson won the Nobel prize for describing the electron as a particle. His son, George Thomson won the Nobel
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
Quantum theory predicts that an atom s electrons are found in: To account that orbitals hold two electrons, we need:
 Quantum theory predicts that an atom s electrons are found in: To account that orbitals hold two electrons, we need: Shells (principle quantum number, n) Subshells (angular momentum, l) Orbitals (magnetic
Quantum theory predicts that an atom s electrons are found in: To account that orbitals hold two electrons, we need: Shells (principle quantum number, n) Subshells (angular momentum, l) Orbitals (magnetic
Atoms and Periodic Properties
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Unit 01 (Chp 6,7): Atoms and Periodic Properties John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Unit 01 (Chp 6,7): Atoms and Periodic Properties John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College
Quantum Numbers and Electronic Configuration.
 Quantum Numbers and Electronic Configuration. F Scullion: www.justchemy.com 1 Each electron has a set of four numbers, called quantum numbers, that specify it completely; no two electrons in the same atom
Quantum Numbers and Electronic Configuration. F Scullion: www.justchemy.com 1 Each electron has a set of four numbers, called quantum numbers, that specify it completely; no two electrons in the same atom
Atomic Emission Spectra. and. Flame Tests. Burlingame High School Chemistry
 Atomic Structure Atomic Emission Spectra and Flame Tests Flame Tests Sodium potassium lithium When electrons are excited they bump up to a higher energy level. As they bounce back down they release energy
Atomic Structure Atomic Emission Spectra and Flame Tests Flame Tests Sodium potassium lithium When electrons are excited they bump up to a higher energy level. As they bounce back down they release energy
-"l" also contributes ENERGY. Higher values for "l" mean the electron has higher energy.
 170 - Giving the four parameters will uniquely identify an electron around an atom. No two electrons in the same atom can share all four. These parameters are called QUANTUM NUMBERS. PRINCIPAL QUANTUM
170 - Giving the four parameters will uniquely identify an electron around an atom. No two electrons in the same atom can share all four. These parameters are called QUANTUM NUMBERS. PRINCIPAL QUANTUM
Additional Problem 1.13
 Task 1 Due: 11:59pm on Friday, April 27, 2018 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Additional Problem 1.13 Classify each of the following as a pure
Task 1 Due: 11:59pm on Friday, April 27, 2018 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Additional Problem 1.13 Classify each of the following as a pure
October 30 November 3. Daily Log
 October 30 November 3 Daily Log October 30 th Bellwork In general there is a decrease in atomic radii as you move from left to right across a period. This trend, is caused by the increasing positive charge
October 30 November 3 Daily Log October 30 th Bellwork In general there is a decrease in atomic radii as you move from left to right across a period. This trend, is caused by the increasing positive charge
Modern Atomic Theory. (a.k.a. the electron chapter!) Chemistry 1: Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 11
 Modern Atomic Theory (a.k.a. the electron chapter!) 1 Chemistry 1: Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION 2 Electromagnetic radiation. 3 4 Electromagnetic Radiation
Modern Atomic Theory (a.k.a. the electron chapter!) 1 Chemistry 1: Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION 2 Electromagnetic radiation. 3 4 Electromagnetic Radiation
Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presenting Teach Yourself High School Chemistry in 4 Hours 1/56 http://www.rapidlearningcenter.com Atomic Structure and
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presenting Teach Yourself High School Chemistry in 4 Hours 1/56 http://www.rapidlearningcenter.com Atomic Structure and
7.1 Ions > Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding. 7.1 Ions. 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 7.3 Bonding in Metals
 Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU What
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU What
A bit of review. Atoms are made of 3 different SUB-ATOMIC PARTICLES: 1. ELECTRONS 2. PROTONS 3. NEUTRONS
 Chemistry in Action A bit of review Chemistry is the study of MATTER and ENERGY. Matter is anything that has MASS. All matter is made of super small particles called ATOMS. Atoms are made of 3 different
Chemistry in Action A bit of review Chemistry is the study of MATTER and ENERGY. Matter is anything that has MASS. All matter is made of super small particles called ATOMS. Atoms are made of 3 different
Chapter 5. Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
 Chapter 5 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Light Dual Nature of Light: Light can act like, and as particles. Light is one type of which is a form of Energy that has wavelike behaviour Other types of em
Chapter 5 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Light Dual Nature of Light: Light can act like, and as particles. Light is one type of which is a form of Energy that has wavelike behaviour Other types of em
Early Chemistry. Early Chemists only believed in 1 element: Dirt. Later Chemists believed in 4 elements:
 Early Chemistry Early Chemists only believed in 1 element: Dirt Later Chemists believed in 4 elements: Air Earth Fire Water Various combinations of these produced various compounds Atomic Structure All
Early Chemistry Early Chemists only believed in 1 element: Dirt Later Chemists believed in 4 elements: Air Earth Fire Water Various combinations of these produced various compounds Atomic Structure All
