Modern Atomic Theory. (a.k.a. the electron chapter!) Chemistry 1: Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 11
|
|
|
- Bernadette Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modern Atomic Theory (a.k.a. the electron chapter!) 1 Chemistry 1: Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 11
2 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION 2
3 Electromagnetic radiation. 3
4 4 Electromagnetic Radiation Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves.
5 5 Electromagnetic Radiation wavelength Visible light Amplitude wavelength Ultaviolet radiation Node
6 Electromagnetic Radiation 6 Waves have a frequency Use the Greek letter nu, ν, for frequency, and units are cycles per sec All radiation: λ ν = c where c = velocity of light = 3.00 x 10 8 m/sec
7 7 Electromagnetic Spectrum Long wavelength --> small frequency Short wavelength --> high frequency increasing frequency increasing wavelength
8 8 Electromagnetic Spectrum In increasing energy, ROY G BIV
9 Excited Gases & Atomic Structure 9
10 Atomic Line Emission 10 Spectra and Niels Bohr Niels Bohr ( ) Bohr s greatest contribution to science was in building a simple model of the atom. It was based on an understanding of the LINE EMISSION SPECTRA of excited atoms. Problem is that the model only works for H
11 Spectrum of White Light 11
12 12 Line Emission Spectra of Excited Atoms Excited atoms emit light of only certain wavelengths The wavelengths of emitted light depend on the element.
13 Spectrum of Excited Hydrogen Gas 13
14 Line Spectra of Other Elements 14
15 An excited lithium atom emitting a photon of red light to drop to a lower energy state. 15
16 An excited H atom returns to a lower energy level. 16
17 17 The Electric Pickle Excited atoms can emit light. Here the solution in a pickle is excited electrically. The Na + ions in the pickle juice give off light characteristic of that element.
18 Light Spectrum Lab! Slit that allows light inside 18 Scale Line up the slit so that it is parallel with the spectrum tube (light bulb)
19 Light Spectrum Lab! Slit that allows light inside Scale 19 Run electricity through various gases, creating light Look at the light using a spectroscope to separate the light into its component colors Using colored pencils, draw the line spectra (all of the lines) and determine the wavelength of the three brightest lines Once you line up the slit with the light, then look to the scale on the right. You should see the colored lines under the scale. Eyepiece
20 Light Spectrum Lab! 20
21 The Wave-Particle Nature of Light Light consists of waves and packets of energy called photons. Different wavelengths of light carry different amounts of energy. Red light less energy (long wavelengths, low frequency, slower) Blue light more energy (short wavelengths, higher frequency, faster) 21
22 Figure 11.6: Photons of red and blue light. Different wavelengths of light carry different amounts of energy. 22
23 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom. 23
24 24 Atomic Spectra One view of atomic structure in early 20th century was that an electron (e-) traveled about the nucleus in an orbit. + Electron orbit
25 25 Atomic Spectra and Bohr Bohr said classical view is wrong. Need a new theory now called QUANTUM or WAVE MECHANICS. e- can only exist in certain discrete orbits e- is restricted to QUANTIZED energy state (quanta = bundles of energy)
26 Quantum or Wave Mechanics 26 E. Schrodinger Schrodinger applied idea of e- behaving as a wave to the problem of electrons in atoms. He developed the WAVE EQUATION Solution gives set of math expressions called WAVE FUNCTIONS, Ψ
27 Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle 27 W. Heisenberg Problem of defining nature of electrons in atoms solved by W. Heisenberg. Cannot simultaneously define the position and momentum (= m v) of an electron. We define e- energy exactly but accept limitation that we do not know exact position.
28 Models of the Atom 28
29 Sublevels of the Principal Energy Levels s Groups 1 and 2 p Groups d Transition metals f Lanthanide and Actinide Series Blocks within the Periodic Table. 29
30 Sublevels of the Principal Energy Levels Sublevel Shape # orbitals # electrons s sphere 1 2 p dumbbell 3 6 d f
31 Arrangement of Sublevels 31
32 Principal Levels Divided into Sublevels 32
33 33 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electrons in atoms are arranged as LEVELS (n) SUBLEVELS (l) ORBITALS (m l )
34 QUANTUM NUMBERS 34 The shape, size, and energy of each orbital is a function of 3 quantum numbers which describe the location of an electron within an atom or ion n (principal) ---> energy level l (orbital) ---> shape of orbital m l (magnetic) ---> designates a particular suborbital The fourth quantum number is not derived from the wave function s (spin) ---> spin of the electron (clockwise or counterclockwise: ½ or ½)
35 QUANTUM NUMBERS 35 So if two electrons are in the same place at the same time, they must be repelling, so at least the spin quantum number is different! The Pauli Exclusion Principle says that no two electrons within an atom (or ion) can have the same four quantum numbers. If two electrons are in the same energy level, the same sublevel, and the same orbital, they must repel. Think of the 4 quantum numbers as the address of an electron Country > State > City > Street
36 36 Energy Levels Each energy level has a number called the PRINCIPAL QUANTUM NUMBER, n Currently n can be 1 thru 7, because there are 7 periods on the periodic table
37 37 Energy Levels n = 1 n = 2 n = 3 n = 4
38 Relative sizes of the spherical 1s, 2s, and 3s orbitals of hydrogen. 38
39 39 Types of Orbitals The most probable area to find these electrons takes on a shape So far, we have 4 shapes. They are named s, p, d, and f. No more than 2 e- assigned to an orbital one spins clockwise, one spins counterclockwise
40 Types of Orbitals (l) 40 s orbital p orbital d orbital
41 p Orbitals Typical p orbital 41 this is a p sublevel with 3 orbitals These are called x, y, and z planar node 3p y orbital There is a PLANAR NODE thru the nucleus, which is an area of zero probability of finding an electron
42 p Orbitals 42 The three p orbitals lie 90 o apart in space
43 d Orbitals typical d orbital 43 planar node d sublevel has 5 orbitals planar node
44 The shapes and labels of the five 3d orbitals. 44
45 45 f Orbitals For l = 3, ---> f sublevel with 7 orbitals
46 Diagonal Rule 46 Must be able to write it for the test! This will be question #1! Without it, you will not get correct answers! The diagonal rule is a memory device that helps you remember the order of the filling of the orbitals from lowest energy to highest energy Aufbau principle states that electrons fill from the lowest possible energy to the highest energy
47 s s 2p s 3p 3d Diagonal Rule s 4p 4d 4f Steps: s 5p 5d 5f 5g? 1. Write the energy levels top to bottom. s 6p 6d 6f 6g? 6h? s 7p 7d 7f 7g? 7h? 7i? Write the orbitals in s, p, d, f order. Write the same number of orbitals as the energy level. 3. Draw diagonal lines from the top right to the bottom left. 4. To get the correct order, follow the arrows! By this point, we are past the current periodic table so we can stop.
48 48 Why are d and f orbitals always in lower energy levels? d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy It s better (lower in energy) to skip a sublevel that requires a large amount of energy (d and f orbtials) for one in a higher level but lower energy This is the reason for the diagonal rule! BE SURE TO FOLLOW THE ARROWS IN ORDER!
49 How many electrons can be in a sublevel? 49 Remember: A maximum of two electrons can be placed in an orbital. s orbitals p orbitals d orbitals f orbitals Number of orbitals Number of electrons
50 Electron Configurations 50 A list of all the electrons in an atom (or ion) Must go in order (Aufbau principle) 2 electrons per orbital, maximum We need electron configurations so that we can determine the number of electrons in the outermost energy level. These are called valence electrons. The number of valence electrons determines how many and what this atom (or ion) can bond to in order to make a molecule 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 etc.
51 Electron Configurations 51 4 Energy Level Sublevel Number of electrons in the sublevel 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 etc.
52 Let s Try It! 52 Write the electron configuration for the following elements: H Li N Ne K Zn Pb
53 Let s Try It! 53 Write the electron configuration for the following elements: H 1s 1 Li 1s 2 2s 1 N 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3 Ne 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 K 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 1 Zn 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 Pb 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 2
54 Orbitals and the Periodic Table 54 Orbitals grouped in s, p, d, and f orbitals (sharp, proximal, diffuse, and fundamental) s orbitals d orbitals p orbitals f orbitals
55 Shorthand Notation 55 A way of abbreviating long electron configurations Since we are only concerned about the outermost electrons, we can skip to places we know are completely full (noble gases), and then finish the configuration
56 Shorthand Notation 56 Step 1: It s the Showcase Showdown! Find the closest noble gas to the atom (or ion), WITHOUT GOING OVER the number of electrons in the atom (or ion). Write the noble gas in brackets [ ]. Step 2: Find where to resume by finding the next energy level. Step 3: Resume the configuration until it s finished.
57 57 Shorthand Notation Chlorine Longhand is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5 You can abbreviate the first 10 electrons with a noble gas, Neon. [Ne] replaces 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 The next energy level after Neon is 3 So you start at level 3 on the diagonal rule (all levels start with s) and finish the configuration by adding 7 more electrons to bring the total to 17 [Ne] 3s 2 3p 5
58 58 Practice Shorthand Notation Write the shorthand notation for each of the following atoms: Cl [Ne] 3s 2 3p 5 K [Ar] 4s 1 Ca [Ar] 4s 2 I [Kr] 5s 2 4d 10 5p 5 Bi [Xe] 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 3
59 Valence Electrons 59 Electrons are divided between core and valence electrons B 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1 Core = [He], valence = 2s 2 2p 1 Br [Ar] 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5 Core = [Ar] 3d 10, valence = 4s 2 4p 5
60 Rules of the Game 60 No. of valence electrons of a main group atom = Group number (for A groups) Atoms like to either empty or fill their outermost level. Since the outer level contains two s electrons and six p electrons (d & f are always in lower levels), the optimum number of electrons is eight. This is called the octet rule.
61 61 Keep an Eye On Those Ions! Electrons are lost or gained like they always are with ions negative ions have gained electrons, positive ions have lost electrons The electrons that are lost or gained should be added/removed from the highest energy level (not the highest orbital in energy!)
62 62 Keep an Eye On Those Ions! Tin Atom: [Kr] 5s 2 4d 10 5p 2 Sn +4 ion: [Kr] 4d 10 Sn +2 ion: [Kr] 5s 2 4d 10 Note that the electrons came out of the highest energy level, not the highest energy orbital!
63 63 Keep an Eye On Those Ions! Bromine Atom: [Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 5 Br - ion: [Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 Note that the electrons went into the highest energy level, not the highest energy orbital!
64 Try Some Ions! 64 Write the longhand notation for these: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 F - Li + Mg +2 Write the shorthand notation for these: Br - [Kr] [Xe] Ba +2 Al +3 1s 2 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 note this is the same as F - this is called isoelectronic [Ne]
65 65 Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle Remember d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy If we can t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d 4 and d 9 For the purposes of this class, we are going to assume that ALL atoms (or ions) that end in d 4 or d 9 are exceptions to the rule. This may or may not be true, it just depends on the atom.
66 Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle d 4 is one electron short of being HALF full In order to become more stable (require less energy), one of the closest s electrons will actually go into the d, making it d 5 instead of d 4. For example: Cr would be [Ar] 4s 2 3d 4, but since this ends exactly with a d 4 it is an exception to the rule. Thus, Cr should be [Ar] 4s 1 3d 5. Procedure: Find the closest s orbital. Steal one electron from it, and add it to the d. 66
67 Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle d 9 is one electron short of being full Just like d 4, one of the closest s electrons will go into the d, this time making it d 10 instead of d 9. For example: Au would be [Xe] 6s 2 4f 14 5d 9, but since this ends exactly with a d 9 it is an exception to the rule. Thus, Au should be [Xe] 6s 1 4f 14 5d 10. Procedure: Same as before! Find the closest s orbital. Steal one electron from it, and add it to the d. 67
68 68 Try These! Write the shorthand notation for: Cu W Au [Ar] 4s 1 3d 10 [Xe] 6s 1 4f 14 5d 5 [Xe] 6s 1 4f 14 5d 10
69 Orbital Diagrams 69 Graphical representation of an electron configuration One arrow represents one electron Shows spin and which orbital within a sublevel Same rules as before (Aufbau principle, d 4 and d 9 exceptions, two electrons in each orbital, etc. etc.)
70 Orbital Diagrams 70 One additional rule: Hund s Rule In orbitals of EQUAL ENERGY (p, d, and f), place one electron in each orbital before making any pairs All single electrons must spin the same way I nickname this rule the Monopoly Rule In Monopoly, you have to build houses EVENLY. You can not put 2 houses on a property until all the properties has at least 1 house.
71 Notation Orbital Diagram (use arrows) O 8e - 1s 2s 2p 71
72 Hund s Rule Within a sublevel, place one e - per orbital before pairing them. Empty Bus Seat Rule WRONG RIGHT 72
73 Lithium 73 Group 1A Atomic number = 3 1s 2 2s 1 ---> 3 total electrons 3s 2s 3p 2p 1s
74 Carbon 74 3s 2s 1s 3p 2p Group 4A Atomic number = 6 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 ---> 6 total electrons Here we see for the first time HUND S RULE. When placing electrons in a set of orbitals having the same energy, we place them singly as long as possible.
75 Lanthanide Element Configurations 75 4f orbitals used for Ce - Lu and 5f for Th - Lr
76 76 Draw these orbital diagrams! Oxygen (O) Chromium (Cr) Mercury (Hg)
77 77 Oxygen 3s 3p Group 6A Atomic number = 8 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 ---> 8 total electrons 2s 2p 1s
78 Chromium 78
79 Mercury 79
80 Ion Configurations 80 To form anions from elements, add 1 or more e- from the highest sublevel. P [Ne] 3s 2 3p 3 + 3e- ---> P 3- [Ne] 3s 2 3p 6 or [Ar] 3s 3p 3s 3p 2p 2p 2s 2s 1s 1s
81 General Periodic Trends 81 Atomic and ionic size Ionization energy Electronegativity Higher effective nuclear charge Electrons held more tightly Larger orbitals. Electrons held less tightly.
82 82 Atomic Size Size goes UP on going down a group. Because electrons are added further from the nucleus, there is less attraction. This is due to 1) additional energy levels and 2) the shielding effect. Each additional energy level shields the electrons from being pulled in toward the nucleus. Size goes UP going Right to Left across a period.
83 83 Atomic Size Size decreases across a period owing to increase in the positive charge from the protons. Each added electron feels a greater and greater + charge because the protons are pulling in the same direction, where the electrons are scattered. Large Small
84 84 Which is Bigger? Na or K? Na or Mg? Al or I? K Na I
85 Ion Sizes 85 Li,152 pm 3e and 3p Does + the size go up Li + or down, 60 pm when 2e and 3 losing p an electron to form a cation?
86 Ion Sizes 86 Li,152 pm 3e and 3p + Li +, 78 pm 2e and 3 p Forming a cation. CATIONS are SMALLER than the atoms from which they come. The electron/proton attraction has gone UP and so size DECREASES.
87 Ion Sizes 87 F,64 pm 9e and 9p Does the size go up or - down when gaining an electron to form an F -, 136 pm 10 anion? e and 9 p
88 Ion Sizes 88 F, 71 pm 9e and 9p - F -, 133 pm 10 e and 9 p Forming an anion. ANIONS are LARGER than the atoms from which they come. The electron/proton attraction has gone DOWN and so size INCREASES. Trends in ion sizes are the same as atom sizes.
89 Trends in Ion Sizes 89 Figure 8.13
90 90 Which is Bigger? Cl or Cl -? K + or K? Ca or Ca +2? I - or Br -? Cl - K Ca I -
91 Ionization Energy 91 IE = energy required to remove an electron from an atom (in the gas phase). Mg (g) kj ---> Mg + (g) + e- This is called the FIRST ionization energy because we removed only the OUTERMOST electron Mg + (g) kj ---> Mg 2+ (g) + e- This is the SECOND IE.
92 Trends in Ionization Energy 92 IE increases across a period because the positive charge increases. Metals lose electrons more easily than nonmetals. Nonmetals lose electrons with difficulty (they like to GAIN electrons).
93 93 Trends in Ionization Energy IE increases UP a group Because size increases (Shielding Effect & Increased Distance from Nucleus)
94 Which has a higher 1 st ionization energy? 94 Mg or Ca? Al or S? Cs or Ba? Mg S Ba
95 95 Electronegativity, χ χ is a measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Concept proposed by Linus Pauling
96 Periodic Trends: Electronegativity In a group: Atoms with fewer energy levels can attract electrons better (less shielding), and are closer to the nucleus. So, electronegativity increases UP a group of elements. In a period: More protons, while the energy levels are the same, means atoms can better attract electrons. So, electronegativity increases RIGHT in a period of elements. 96
97 Electronegativity 97
98 98 Which is more electronegative? F or Cl? Na or K? Sn or I? F Na I
99 The End!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 99
ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS... WHY BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS JUST WON T CUT IT ANYMORE!
 ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS... WHY BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS JUST WON T CUT IT ANYMORE! REPRESENTING ELECTRONS... Now that you know what an orbital is, you need to be able to use that to describe the electronic
ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS... WHY BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS JUST WON T CUT IT ANYMORE! REPRESENTING ELECTRONS... Now that you know what an orbital is, you need to be able to use that to describe the electronic
Where are the s, p, d, f orbitals located on the periodic table? Identify them on the diagram below.
 Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Section 3: Electron Configuration Objectives: Be able to define: Aufbau Principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle, Hund s rule. Be able to list the number of electrons
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Section 3: Electron Configuration Objectives: Be able to define: Aufbau Principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle, Hund s rule. Be able to list the number of electrons
ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS, ORBITAL DIAGRAMS, AUFBAU PRINCIPLE, HUND S RULE
 ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS, ORBITAL DIAGRAMS, AUFBAU PRINCIPLE, HUND S RULE REPRESENTING ELECTRONS... Now that you know what an orbital is, you need to be able to use that to describe
ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS, ORBITAL DIAGRAMS, AUFBAU PRINCIPLE, HUND S RULE REPRESENTING ELECTRONS... Now that you know what an orbital is, you need to be able to use that to describe
Unit Two: Elements & Matter. February 1, 2016
 Unit Two: Elements & Matter February 1, 2016 Warm-Up: 2/1/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Ca 2+ Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron 34 36 Mass Num. 2. Identify which family the
Unit Two: Elements & Matter February 1, 2016 Warm-Up: 2/1/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Ca 2+ Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron 34 36 Mass Num. 2. Identify which family the
Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table. Unit 6 Honors Chemistry
 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table Unit 6 Honors Chemistry Wave Theory of Light James Clerk Maxwell Electromagnetic waves a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through
Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table Unit 6 Honors Chemistry Wave Theory of Light James Clerk Maxwell Electromagnetic waves a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through
Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE
 Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE What Makes Red Light Red? (4.1) Electromagnetic Radiation: energy that travels in waves (light) Waves Amplitude: height
Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE What Makes Red Light Red? (4.1) Electromagnetic Radiation: energy that travels in waves (light) Waves Amplitude: height
The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol λ.
 CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity 1 The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol
CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity 1 The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol
To review Rutherford s model of the atom To explore the nature of electromagnetic radiation To see how atoms emit light
 Objectives To review Rutherford s model of the atom To explore the nature of electromagnetic radiation To see how atoms emit light 1 A. Rutherford s Atom.but there is a problem here!! 2 Using Rutherford
Objectives To review Rutherford s model of the atom To explore the nature of electromagnetic radiation To see how atoms emit light 1 A. Rutherford s Atom.but there is a problem here!! 2 Using Rutherford
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms. 4.1 The Development of a New Atomic Model
 Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms 4.1 The Development of a New Atomic Model Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation: EM radiation are forms of energy which move through space as waves There
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms 4.1 The Development of a New Atomic Model Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation: EM radiation are forms of energy which move through space as waves There
Light. Light (con t.) 2/28/11. Examples
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5)
 Name Per. Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to
Name Per. Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to
Chemistry 111 Dr. Kevin Moore
 Chemistry 111 Dr. Kevin Moore Black Body Radiation Heated objects emit radiation based on its temperature Higher temperatures produce higher frequencies PhotoElectric Effect Light on a clean metal surface
Chemistry 111 Dr. Kevin Moore Black Body Radiation Heated objects emit radiation based on its temperature Higher temperatures produce higher frequencies PhotoElectric Effect Light on a clean metal surface
White Light. Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom
 Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Electromagnetic Radiation and Energy The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom The Modern Model of the Atom Periodicity of Electron Configurations Valence Electrons for
Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Electromagnetic Radiation and Energy The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom The Modern Model of the Atom Periodicity of Electron Configurations Valence Electrons for
ELEMENTS & MATTER. September 7, 2016
 ELEMENTS & MATTER September 7, 2016 Review Problems: 9/7/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron Mass Num. Atomic Mass 34 36 Ca 2+ 2. Identify which
ELEMENTS & MATTER September 7, 2016 Review Problems: 9/7/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron Mass Num. Atomic Mass 34 36 Ca 2+ 2. Identify which
Chapter 9: Electrons and the Periodic Table
 C h e m i s t r y 1 2 C h 9 : E l e c t r o n s a n d P e r i o d i c T a b l e P a g e 1 Chapter 9: Electrons and the Periodic Table Work on MasteringChemistry assignments What we have learned: Dalton
C h e m i s t r y 1 2 C h 9 : E l e c t r o n s a n d P e r i o d i c T a b l e P a g e 1 Chapter 9: Electrons and the Periodic Table Work on MasteringChemistry assignments What we have learned: Dalton
: the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. In, this Greek philosopher suggested that the universe was made of.
 Notes: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Atomic Structure: : the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. From the early concept of the atom to the modern atomic theory, scientists have built
Notes: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Atomic Structure: : the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. From the early concept of the atom to the modern atomic theory, scientists have built
CHAPTER 4 10/11/2016. Properties of Light. Anatomy of a Wave. Components of a Wave. Components of a Wave
 Properties of Light CHAPTER 4 Light is a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior and travels at the speed of light. Together, all
Properties of Light CHAPTER 4 Light is a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior and travels at the speed of light. Together, all
Quantum Model & Configurations
 Quantum Model & Configurations Bohr s Energy Levels: Bohr was able to tell us the electrons are found in layers around the nucleus based on the following: Each element gives off a unique emission spectrum
Quantum Model & Configurations Bohr s Energy Levels: Bohr was able to tell us the electrons are found in layers around the nucleus based on the following: Each element gives off a unique emission spectrum
Chapter 11 Modern Atomic Theory Notes
 Chapter 11 Modern Atomic Theory Notes Electromagnetic radiation energy that travels through space as waves. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength ( lambda) distance between two consecutive
Chapter 11 Modern Atomic Theory Notes Electromagnetic radiation energy that travels through space as waves. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength ( lambda) distance between two consecutive
Electrons and Periodic Table (Ch. 4 & 5) OTHS Academic Chemistry
 Name Objectives: Per. Electrons and Periodic Table (Ch. 4 & 5) OTHS Academic Chemistry Express the arrangement of electrons in atoms through electron configurations Understand the electromagnetic spectrum
Name Objectives: Per. Electrons and Periodic Table (Ch. 4 & 5) OTHS Academic Chemistry Express the arrangement of electrons in atoms through electron configurations Understand the electromagnetic spectrum
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE. Light and Energy. Chapter Nine
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Chapter Nine Light and Energy! Electromagnetic radiation (EM) is an especially important form of energy for scientific study.! Many types of radiant energy are
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Chapter Nine Light and Energy! Electromagnetic radiation (EM) is an especially important form of energy for scientific study.! Many types of radiant energy are
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table. How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation
 Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
CHAPTER 4. Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms 4.1 Part I Development of a New Atomic Model 4.1 Objectives 1. Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic
CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms 4.1 Part I Development of a New Atomic Model 4.1 Objectives 1. Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic
LIGHT AND THE QUANTUM MODEL
 LIGHT AND THE QUANTUM MODEL WAVES Wavelength ( ) - length of one complete wave Frequency ( ) - # of waves that pass a point during a certain time period hertz (Hz) = 1/s Amplitude (A) - distance from the
LIGHT AND THE QUANTUM MODEL WAVES Wavelength ( ) - length of one complete wave Frequency ( ) - # of waves that pass a point during a certain time period hertz (Hz) = 1/s Amplitude (A) - distance from the
Arrangement of Electrons. Chapter 4
 Arrangement of Electrons Chapter 4 Properties of Light -Light s interaction with matter helps to understand how electrons behave in atoms -Light travels through space & is a form of electromagnetic radiation
Arrangement of Electrons Chapter 4 Properties of Light -Light s interaction with matter helps to understand how electrons behave in atoms -Light travels through space & is a form of electromagnetic radiation
5.1 Light & Quantized Energy
 5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Objectives: 1. Describe electromagnetic (EM) wave properties & measures 2. Relate visible light to areas of the EM spectrum with higher & lower energy 3. Know the relationship
5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Objectives: 1. Describe electromagnetic (EM) wave properties & measures 2. Relate visible light to areas of the EM spectrum with higher & lower energy 3. Know the relationship
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior
 Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior Models of the Atom I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior Models of the Atom I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The
Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms
 Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms Importance of Electrons Draw a complete Bohr model of the atom. Write an element s electron configuration. Know how the symbols used in ECs relate to electron properties
Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms Importance of Electrons Draw a complete Bohr model of the atom. Write an element s electron configuration. Know how the symbols used in ECs relate to electron properties
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY
 Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Wave
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Wave
4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS
 4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS Bohr s Model Contradicts Common Sense If only certain orbits with definite energies are allowed and the electrons constantly gives off radiation,
4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS Bohr s Model Contradicts Common Sense If only certain orbits with definite energies are allowed and the electrons constantly gives off radiation,
LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL Did not explain the chemical properties of atoms For example, it could not explain why metals or compounds of metals give off characteristic
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL Did not explain the chemical properties of atoms For example, it could not explain why metals or compounds of metals give off characteristic
Atomic Structure Part II Electrons in Atoms
 Atomic Structure Part II Electrons in Atoms Radiant energy travels in the form of waves that have both electrical and magnetic properties. These electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space, as
Atomic Structure Part II Electrons in Atoms Radiant energy travels in the form of waves that have both electrical and magnetic properties. These electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space, as
Atomic Structure Part II. Electrons in Atoms
 Atomic Structure Part II Electrons in Atoms Radiant energy travels in the form of waves that have both electrical and magnetic properties. These electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space, as
Atomic Structure Part II Electrons in Atoms Radiant energy travels in the form of waves that have both electrical and magnetic properties. These electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space, as
s or Hz J atom J mol or -274 kj mol CHAPTER 4. Practice Exercises ΔE atom = ΔE mol =
 CHAPTER 4 Practice Exercises 4.1 10 1 2.1410 s or Hz 4.3 ΔE atom = ΔE mol = 4.5610 J atom 19 1 2.7410 J mol or -274 kj mol 5 1-1 4.5 excitation energy = 471 kj mol 1 + 275 kj mol 1 = 746 kj mol 1 Hg 4.7
CHAPTER 4 Practice Exercises 4.1 10 1 2.1410 s or Hz 4.3 ΔE atom = ΔE mol = 4.5610 J atom 19 1 2.7410 J mol or -274 kj mol 5 1-1 4.5 excitation energy = 471 kj mol 1 + 275 kj mol 1 = 746 kj mol 1 Hg 4.7
Elements and the Periodic Table
 CHAPTER 6 Elements and the Periodic Table 6.1 The Periodic Table Are you made of star dust? Are you made of star dust? The Big Bang produced hydrogen and helium and a tiny bit of lithium Are you made of
CHAPTER 6 Elements and the Periodic Table 6.1 The Periodic Table Are you made of star dust? Are you made of star dust? The Big Bang produced hydrogen and helium and a tiny bit of lithium Are you made of
Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Chapter 6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms
 Chapter 6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light To understand the electronic structure of atoms, one must understand the nature of electromagnetic radiation Visible light is an example
Chapter 6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light To understand the electronic structure of atoms, one must understand the nature of electromagnetic radiation Visible light is an example
Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends
 Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 11.01 The Bohr Model of the Atom
Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 11.01 The Bohr Model of the Atom
Honors Unit 6 Notes - Atomic Structure
 Name: Honors Unit 6 Notes - Atomic Structure Objectives: 1. Students will have a general understanding of the wave nature of light and the interrelationship between frequency, wavelength, and speed of
Name: Honors Unit 6 Notes - Atomic Structure Objectives: 1. Students will have a general understanding of the wave nature of light and the interrelationship between frequency, wavelength, and speed of
Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes
 Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes There are several important atomic characteristics that show predictable that you should know. Atomic Radius The first and
Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes There are several important atomic characteristics that show predictable that you should know. Atomic Radius The first and
Modern Atomic Theory
 Modern Atomic Theory In science, often times chemical or physical behavior can not be seen with the naked eye (nor with the use of some other device). Consequently, an understanding and explanation of
Modern Atomic Theory In science, often times chemical or physical behavior can not be seen with the naked eye (nor with the use of some other device). Consequently, an understanding and explanation of
Ch 9 Electrons in Atoms & the Periodic Table Study Sheet Acc. Chemistry SCANTRON. Name /99. 3) Light is a type of matter. 3)
 Ch 9 Electrons in Atoms & the Periodic Table Study Sheet Acc. Chemistry SCANTRON Name /99 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When the elements are arranged
Ch 9 Electrons in Atoms & the Periodic Table Study Sheet Acc. Chemistry SCANTRON Name /99 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When the elements are arranged
General Rules. Pauli Exclusion Principle. Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli
 General Rules Pauli Exclusion Principle Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli General Rules Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Lazy Tenant
General Rules Pauli Exclusion Principle Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli General Rules Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Lazy Tenant
Unit Five Practice Test (Part I) PT C U5 P1
 Unit Five Practice Test (Part I) PT C U5 P1 Name Period LPS Standard(s): --- State Standard(s): 12.3.1 Short Answers. Answer the following questions. (5 points each) 1. Write the electron configuration
Unit Five Practice Test (Part I) PT C U5 P1 Name Period LPS Standard(s): --- State Standard(s): 12.3.1 Short Answers. Answer the following questions. (5 points each) 1. Write the electron configuration
Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity
 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity The Periodic Table Periodic law (Mendeleev, Meyer, 1870) periodic reoccurrence of similar physical and chemical properties of the elements arranged by increasing
Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity The Periodic Table Periodic law (Mendeleev, Meyer, 1870) periodic reoccurrence of similar physical and chemical properties of the elements arranged by increasing
Chapter 7. Characteristics of Atoms. 7.1 Electromagnetic Radiation. Chapter 7 1. The Quantum Mechanical Atom. Atoms: How do we study atoms?
 Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Atom 1 Characteristics of Atoms Atoms: possess mass contain positive nuclei contain electrons occupy volume have various properties attract one another combine to form
Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Atom 1 Characteristics of Atoms Atoms: possess mass contain positive nuclei contain electrons occupy volume have various properties attract one another combine to form
Modern Atomic Theory CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Chapter 3B Modern Atomic Theory 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Waves Electromagnetic Radiation Dual Nature of Light Bohr Model of Atom Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Electron Configuration Electron Configuration
Chapter 3B Modern Atomic Theory 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Waves Electromagnetic Radiation Dual Nature of Light Bohr Model of Atom Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Electron Configuration Electron Configuration
Atoms and Periodic Properties
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Unit 01 (Chp 6,7): Atoms and Periodic Properties John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Unit 01 (Chp 6,7): Atoms and Periodic Properties John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College
Warm-up For sulfur: 1. How many valence electrons does it have? 2. What ion does this typically form? 3. Write the electron configuration for the ion.
 Warm-up For sulfur: 1. How many valence electrons does it have? 2. What ion does this typically form? 3. Write the electron configuration for the ion. Nucleus Contains 99.9% of the mass of an atom Found
Warm-up For sulfur: 1. How many valence electrons does it have? 2. What ion does this typically form? 3. Write the electron configuration for the ion. Nucleus Contains 99.9% of the mass of an atom Found
8. Which of the following could be an isotope of chlorine? (A) 37 Cl 17 (B) 17 Cl 17 (C) 37 Cl 17 (D) 17 Cl 37.5 (E) 17 Cl 37
 Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
Creating Energy-Level Diagrams Aufbau (building up) Principle Electrons are added to the lowest energy orbital available.
 3.6 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Bohr's Theory Was Incorrect Because... Only explained the line spectrum of hydrogen Position and motion of an e cannot be specified (since the e is so small,
3.6 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Bohr's Theory Was Incorrect Because... Only explained the line spectrum of hydrogen Position and motion of an e cannot be specified (since the e is so small,
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior
 Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The energy of the electron
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The energy of the electron
Light. October 16, Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms Honors Chemistry. Bohr Model
 Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms Honors Chemistry Bohr Model Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist and a student of Rutherford improved Rutherford's model. Bohr proposed that an electron is found only in specific
Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms Honors Chemistry Bohr Model Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist and a student of Rutherford improved Rutherford's model. Bohr proposed that an electron is found only in specific
CHAPTER 5 Electrons in Atoms
 CHAPTER 5 Electrons in Atoms 5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Was the Nuclear Atomic model incomplete? To most scientists, the answer was yes. The arrangement of electrons was not determined > Remember...the
CHAPTER 5 Electrons in Atoms 5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Was the Nuclear Atomic model incomplete? To most scientists, the answer was yes. The arrangement of electrons was not determined > Remember...the
Chapter 5. The Electromagnetic Spectrum. What is visible light? What is visible light? Which of the following would you consider dangerous?
 Which of the following would you consider dangerous? X-rays Radio waves Gamma rays UV radiation Visible light Microwaves Infrared radiation Chapter 5 Periodicity and Atomic Structure 2 The Electromagnetic
Which of the following would you consider dangerous? X-rays Radio waves Gamma rays UV radiation Visible light Microwaves Infrared radiation Chapter 5 Periodicity and Atomic Structure 2 The Electromagnetic
Electrons in Atoms. Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy
 Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Chapter 7 The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends
 Chapter 7 The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electrons in atoms are arranged as SHELLS (n) SUBSHELLS (l) ORBITALS
Chapter 7 The Structure of Atoms and Periodic Trends Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electrons in atoms are arranged as SHELLS (n) SUBSHELLS (l) ORBITALS
Unit 1 Part 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Introduction to Atomic Structure UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC STRUCTURE Contents 1. Protons, Neutrons and Electrons 2. Early Models of the Atom 3. Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4. Atoms and Ions
UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC STRUCTURE Contents 1. Protons, Neutrons and Electrons 2. Early Models of the Atom 3. Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4. Atoms and Ions
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5
 Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 DO NOW - Finish coloring your periodic tables! (5 min) State at Room Temperature Appearance Conductivity Malleability and Ductility Metals - solid except for mercury
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 DO NOW - Finish coloring your periodic tables! (5 min) State at Room Temperature Appearance Conductivity Malleability and Ductility Metals - solid except for mercury
Unit 4. Electrons in Atoms
 Unit 4 Electrons in Atoms When were most of the subatomic particles discovered? Who discovered densely packed nucleus surrounded by fast moving electrons? Rutherford s Model Major development Lacked detail
Unit 4 Electrons in Atoms When were most of the subatomic particles discovered? Who discovered densely packed nucleus surrounded by fast moving electrons? Rutherford s Model Major development Lacked detail
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms
 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Electronic Structure Electronic structure the arrangement and energy of electrons 1 st lets talk about waves Why? Extremely small particles have properties that
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Electronic Structure Electronic structure the arrangement and energy of electrons 1 st lets talk about waves Why? Extremely small particles have properties that
Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory
 Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity
 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity Electron Spin The 4 th quantum number is known as the spin quantum number and is designated by m s. It can have the value of either + ½ or ½ It roughly translates
Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity Electron Spin The 4 th quantum number is known as the spin quantum number and is designated by m s. It can have the value of either + ½ or ½ It roughly translates
Electrons in Atoms. So why does potassium explode in water? Quantum Mechanics Periodic Trends Chemical Bonding
 Electrons in Atoms So why does potassium explode in water? Quantum Mechanics Periodic Trends Chemical Bonding 12.1 Development of Atomic Models Dalton s Thompson s Rutherford s Bohr s carbon Quantum Model
Electrons in Atoms So why does potassium explode in water? Quantum Mechanics Periodic Trends Chemical Bonding 12.1 Development of Atomic Models Dalton s Thompson s Rutherford s Bohr s carbon Quantum Model
Atomic Theory. H. Cannon, C. Clapper and T. Guillot Klein High School
 Atomic Theory Unit 3 Development of the Atomic Theory 1. Where is the mass of the atom concentrated? 2. What is located in the nucleus? 3. What is the negative particle that orbits the nucleus? 4. What
Atomic Theory Unit 3 Development of the Atomic Theory 1. Where is the mass of the atom concentrated? 2. What is located in the nucleus? 3. What is the negative particle that orbits the nucleus? 4. What
Chapter 4. Table of Contents. Section 1 The Development of a New Atomic Model. Section 2 The Quantum Model of the Atom
 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Table of Contents Section 1 The Development of a New Atomic Model Section 2 The Quantum Model of the Atom Section 3 Electron Configurations Section 1 The Development of
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Table of Contents Section 1 The Development of a New Atomic Model Section 2 The Quantum Model of the Atom Section 3 Electron Configurations Section 1 The Development of
Made the FIRST periodic table
 Made the FIRST periodic table 1869 Mendeleev organized the periodic table based on the similar properties and relativities of certain elements Later, Henri Moseley organized the elements by increasing
Made the FIRST periodic table 1869 Mendeleev organized the periodic table based on the similar properties and relativities of certain elements Later, Henri Moseley organized the elements by increasing
A photon checks into a hotel and the bell hop asks, Can I help you with your luggage? The photon replies, I don t have any. I m traveling light.
 Quantum Mechanics A photon checks into a hotel and the bell hop asks, Can I help you with your luggage? The photon replies, I don t have any. I m traveling light. Electron Density Based on Heisenberg uncertainty
Quantum Mechanics A photon checks into a hotel and the bell hop asks, Can I help you with your luggage? The photon replies, I don t have any. I m traveling light. Electron Density Based on Heisenberg uncertainty
Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table 1. What are the three primary particles found in an atom? A) neutron, positron, and electron B) electron, neutron, and proton C) electron, proton,
Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table 1. What are the three primary particles found in an atom? A) neutron, positron, and electron B) electron, neutron, and proton C) electron, proton,
Chapter 6. Electronic. Electronic Structure of Atoms Pearson Education
 Chapter 6 Laser: step-like energy transition 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light 6.2 Quantized Energy and Photons 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model 6.4 The Wave Behavior of Matter 6.5 Quantum Mechanics and
Chapter 6 Laser: step-like energy transition 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light 6.2 Quantized Energy and Photons 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model 6.4 The Wave Behavior of Matter 6.5 Quantum Mechanics and
MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 C10 04/19/2013 13:34:14 Page 114 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is
C10 04/19/2013 13:34:14 Page 114 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is
Atomic Structure. Part 3: Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom. Key Question: How does the wave mechanical model explain the location of electrons?
 Name Chemistry Atomic Structure Essential Question: How was the structure of the atom determined? Vocabulary: bright-line spectrum electron configuration excited state ground state orbital wave-mechanical
Name Chemistry Atomic Structure Essential Question: How was the structure of the atom determined? Vocabulary: bright-line spectrum electron configuration excited state ground state orbital wave-mechanical
Development of the Periodic Table. Chapter 5. Light and the EM Spectrum. Light
 Chapter 5 Periodic Table Song Periodicity and Atomic Structure Development of the Periodic Table Mid-1800 s, several scientists placed known elements in order based on different criteria. Mendeleev s and
Chapter 5 Periodic Table Song Periodicity and Atomic Structure Development of the Periodic Table Mid-1800 s, several scientists placed known elements in order based on different criteria. Mendeleev s and
The Electron Cloud. Here is what we know about the electron cloud:
 The Electron Cloud Here is what we know about the electron cloud: It contains the subatomic particles called electrons This area accounts for most of the volume of the atom ( empty space) These electrons
The Electron Cloud Here is what we know about the electron cloud: It contains the subatomic particles called electrons This area accounts for most of the volume of the atom ( empty space) These electrons
9/13/2011. The Greek Philosophers. Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table. Dalton s Atomic Theory. J. J. Thomson. Thomson s Experiment
 Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table The Greek Philosophers Democritus believed that all matter is made up of tiny particles that could not be divided Aristotle -- thought that matter was made of only
Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table The Greek Philosophers Democritus believed that all matter is made up of tiny particles that could not be divided Aristotle -- thought that matter was made of only
WARM-UP. Draw each of the three models of the atom that we learned about last unit. Who came up with each? What was wrong with each?
 WARM-UP Draw each of the three models of the atom that we learned about last unit. Who came up with each? What was wrong with each? 1:59 1:58 1:57 1:56 1:55 1:54 1:53 1:52 1:51 1:50 1:49 1:48 1:47 1:46
WARM-UP Draw each of the three models of the atom that we learned about last unit. Who came up with each? What was wrong with each? 1:59 1:58 1:57 1:56 1:55 1:54 1:53 1:52 1:51 1:50 1:49 1:48 1:47 1:46
Frequency and wavelength are mathematically related to each other by the equation: c = λν.
 Chemistry I Unit 3: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Properties of Light The Wave Description of Light Electromagnetic radiation- a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels
Chemistry I Unit 3: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Properties of Light The Wave Description of Light Electromagnetic radiation- a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels
Chapter 8: Electrons in Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation
 Chapter 8: Electrons in Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy transmission modeled as waves moving through space. (see below left) Electromagnetic Radiation
Chapter 8: Electrons in Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy transmission modeled as waves moving through space. (see below left) Electromagnetic Radiation
- Light has properties of WAVES such as DIFFRACTION (it bends around small obstructions).
 170 LIGHT wavelength Diffraction frequency = wavelengths / time = - Light has properties of WAVES such as DIFFRACTION (it bends around small obstructions). - Einstein noted that viewing light as a particle
170 LIGHT wavelength Diffraction frequency = wavelengths / time = - Light has properties of WAVES such as DIFFRACTION (it bends around small obstructions). - Einstein noted that viewing light as a particle
Unit 7. Atomic Structure
 Unit 7. Atomic Structure Upon successful completion of this unit, the students should be able to: 7.1 List the eight regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in the designated order and perform calculations
Unit 7. Atomic Structure Upon successful completion of this unit, the students should be able to: 7.1 List the eight regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in the designated order and perform calculations
Problems with the Wave Theory of Light (Photoelectric Effect)
 CHEM101 NOTES Properties of Light Found that the wave theory could not work for some experiments e.g. the photovoltaic effect This is because the classic EM view of light could not account for some of
CHEM101 NOTES Properties of Light Found that the wave theory could not work for some experiments e.g. the photovoltaic effect This is because the classic EM view of light could not account for some of
Provide a short and specific definition in YOUR OWN WORDS. Do not use the definition from the book. Electromagnetic Radiation
 Name: Provide a short and specific definition in YOUR OWN WORDS. Do not use the definition from the book Additional Notes: Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength Frequency Photoelectric
Name: Provide a short and specific definition in YOUR OWN WORDS. Do not use the definition from the book Additional Notes: Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength Frequency Photoelectric
How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas?
 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine to moles chlorine using formula weight 2 - Convert moles
EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine to moles chlorine using formula weight 2 - Convert moles
Particle Behavior of Light 1. Calculate the energy of a photon, mole of photons 2. Find binding energy of an electron (know KE) 3. What is a quanta?
 Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A EOC review II Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. atomic orbital d. ground state b. aufbau principle e. Pauli exclusion principle c. electron configuration
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A EOC review II Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. atomic orbital d. ground state b. aufbau principle e. Pauli exclusion principle c. electron configuration
Name Chemistry-PAP Period. Notes: Electrons. Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics:
 Name Chemistry-PAP Period The Wave Nature of Light Notes: Electrons Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength (λ): the distance between 2 consecutive crests
Name Chemistry-PAP Period The Wave Nature of Light Notes: Electrons Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength (λ): the distance between 2 consecutive crests
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms What is the origin of color in matter? Demo: flame tests What does this have to do with the atom? Why are atomic properties periodic? 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms What is the origin of color in matter? Demo: flame tests What does this have to do with the atom? Why are atomic properties periodic? 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms 5 Section 5.1 Section Section 5.3 Table Of Contents Light and Quantized Energy Electron Configuration Compare the wave and particle natures of
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms 5 Section 5.1 Section Section 5.3 Table Of Contents Light and Quantized Energy Electron Configuration Compare the wave and particle natures of
Electrons and Molecular Forces
 Electrons and Molecular Forces Chemistry 30 Ms. Hayduk Electron Configuration Atomic Structure Atomic Number Number of protons in the nucleus Defines the element Used to organize the periodic table 1 Bohr
Electrons and Molecular Forces Chemistry 30 Ms. Hayduk Electron Configuration Atomic Structure Atomic Number Number of protons in the nucleus Defines the element Used to organize the periodic table 1 Bohr
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
 p. 99 p. 98 p. 98 Electromagnetic Spectrum Image Atomic Structure and Periodicity Chemistry Zumdahl Chapter 7 Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation: a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior
p. 99 p. 98 p. 98 Electromagnetic Spectrum Image Atomic Structure and Periodicity Chemistry Zumdahl Chapter 7 Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation: a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior
Chapter 11: MODERN ATOMIC THEORY
 Chapter 11: MODERN ATOMIC THEORY LIGHT: Electromagnetic Radiation Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, a type of energy that travels through space at a constant speed, known as the speed of light
Chapter 11: MODERN ATOMIC THEORY LIGHT: Electromagnetic Radiation Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, a type of energy that travels through space at a constant speed, known as the speed of light
Ch 6 Atomic Spectra. Masterson & Hurley
 Ch 6 Atomic Spectra Masterson & Hurley 1 Joule = 1 kg m 2 s 2 Ch 6.1 Light, Photon Energies, & Atomic Spectra What scientists know about light, scientists are able to explain the structure of the atom.
Ch 6 Atomic Spectra Masterson & Hurley 1 Joule = 1 kg m 2 s 2 Ch 6.1 Light, Photon Energies, & Atomic Spectra What scientists know about light, scientists are able to explain the structure of the atom.
2 e. 14 e. # e # orbitals. 10 e 5. sublevel. shape of orbital. Orbital Shapes. Notes Orbital Notation; e Config; NGN.
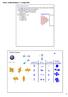 How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
Duncan. Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3
 Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Light Calculation Notes Here s how the type/form of EM radiation can be determined The amount
Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Light Calculation Notes Here s how the type/form of EM radiation can be determined The amount
Quantum Theory and Electron Configurations
 Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and Electron Configurations It s all about color In terms of atomic models, so far: Dalton (1803) = Tiny, solid particle Thomson (1897) = Plum Pudding model Electrons
Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and Electron Configurations It s all about color In terms of atomic models, so far: Dalton (1803) = Tiny, solid particle Thomson (1897) = Plum Pudding model Electrons
Light. Chapter 7. Parts of a wave. Frequency = ν. Kinds of EM waves. The speed of light
 Chapter 7 Atomic Structure Light Made up of electromagnetic radiation Waves of electric and magnetic fields at right angles to each other. 1 2 Parts of a wave Wavelength λ Frequency = ν Frequency = number
Chapter 7 Atomic Structure Light Made up of electromagnetic radiation Waves of electric and magnetic fields at right angles to each other. 1 2 Parts of a wave Wavelength λ Frequency = ν Frequency = number
SCH4U1 Atomic & Molecular Structure Test Review
 SCH4U1 Atomic & Molecular Structure Test Review 1. Which object(s) would you use to describe the shape of the 2p orbital? a. a dumb-bell b. a circle c. a sphere d. two perpendicular dumb-bells e. a doughnut
SCH4U1 Atomic & Molecular Structure Test Review 1. Which object(s) would you use to describe the shape of the 2p orbital? a. a dumb-bell b. a circle c. a sphere d. two perpendicular dumb-bells e. a doughnut
