ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
|
|
|
- Alisha Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modelling the population dynamics and file availability of a P2P file sharing system Riikka Susitaival, Samuli Aalto and Jorma Virtamo Helsinki University of Technology PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 1
2 Introduction 1. BitTorrent most popular p2p system now In October 2004, bittorrent accounted for 21 % of outgoing and 44 % of incoming traffic in Turku University network (all p2p protocols accounted for 62 % and 85 % of traffic) Idea: File divided into chunks peers download and upload concurrently chunk is typically 256 KB Measurements have shown three phases in life time of a file: flash crowd, steady state, and end phase PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 2
3 2. Some analytical models of BitTorrent-like p2p system done so far: Analysis of transient regime by a branching process and steady state time regime by a Markov model Performance modelling by a stochastic fluid model Modelling the network level latencies by delay of a single class open queueing network and peer level latencies by delay of M/G/1/K processor sharing queues. PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 3
4 Purpose of our study Modelling of bittorrent-like P2P system by stochastic models Population dynamics; evolution of number of downloaders and seeds Life time of file sharing process when availability of file is not guaranteed Effect of flash crowd to the population dynamics Single chunk versus multiple chunks PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 4
5 Basic assumptions Sharing of a single chunk New requests for the chunk arrive with rate λ A peer downloads the chunk with rate µ d After download the peer can upload the chunk with rate µ s Seeds leave the system with rate γ, also original one. If all seeds are left, system dies. Let x(t) be the number of downloaders and y(t) the number of seeds at time t λ x Min[µ sx,µ dy] y γ y PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 5
6 1. Deterministic fluid model Evolution of x(t) and y(t) can be described by a deterministic fluid model: dx(t) dt dy(t) dt = λ min{µ d x(t), µ s y(t)}, = min{µ d x(t), µ s y(t)} γy(t), If µ s γ, the steady state solution is x = λ/µ d and ȳ = λ/γ, otherwise x and y = 0. (1) PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 6
7 50 40 Number of downloaders Number of seeds t t Figure 1: The number of downloaders and seeds as a function of time, when λ/µ = 10 and λ/γ = 20. Solid line: fluid model, Gray lines: simulation. PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 7
8 2. Markov chain model To analyze evolution of x and y further a continuous time Markov process with state pair (x, y) and transition matrix Q constructed. The state transitions in the matrix Q are: q((x, y), (x + 1, y)) = λ, q((x, y), (x 1, y + 1)) = min{µ d x, µ s y}, if x > 0, q((x, y), (x, y 1)) = γy, if y > 0. (2) The states (x, y) with y = 0 are absorbing The mean life time of file sharing process: solve the absorbtion times of the system by a recursion PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 8
9 80 Absorbtion time Expected number of seeds Figure 2: The mean absorbtion time of the system as a function of λ/γ. Solid line: truncated Markov process, dots: simulation of infinite system. PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 9
10 Flash crowd Some measurement indicate that the peer arrival rate decreases over time. Proposed traffic model for p2p networks: λ(t) = λ 0 e t τ, where parameter τ describes the attenuation of the demand over time. As before, the system can be described by equations dx(t) dt dy(t) dt = λ 0 e t τ min{µd x(t), µ s y(t)}, = µ min{x(t), y(t)} γy(t). (3) PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 10
11 Arrival rate Number of downloaders Number of seeds t t t Figure 3: Arrival rate, number of downloaders and seeds as a function of time, when λ 0 = 10, τ = 50, µ = 1 and γ = 1/5. Solid line: fluid model, Gray lines: simulation. PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 11
12 Sharing of a file in multiple chunks Now the file of L bytes is divided into K chunks When a peer has downloaded the first (random) chunk, it can upload it to other peers as a leecher. Mean download time of a chunk is denoted by 1/(Kµ d ) If peer has all chunks it serves other peers as seed. Seeds leave the system with rate γ, also original one. If one of the chunks is missing, the system dies. PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 12
13 Case K = 2 In the system we have four types of peers x 0 (t) number of peers with no chunks x 1 (t) number of peers with chunk 1 x 2 (t) number of peers with chunk 2 y(t) number of peers with chunks 1 and 2 2µ p 1 x 0 x 1 2µ x 1 λ x 0 y γ y 2µ p 2 x 0 x 2 2µ x 2 PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 13
14 The system can be described by a four-dimensional Markov chain, which state is quartet (x 0, x 1, x 2, y) States (x 0, x 1, x 2, y) with y = 0 (x 1 = 0 x 2 = 0) are absorbing. The mean life can be calculated from the absorbtion times by a recursion K > 2: Only simulations PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 14
15 Figure 4: The mean life time of the system as a function of λ/γ. Left side: download constrained system, right side: capacity shared between downloaders. PANNET Seminar, 16th March Slide 15
Reprinted with kind permission of Springer Science+Business Media.
 Riikka Susitaival and Samuli Aalto. Modelling the population dynamics and the file availability in a BitTorrent like P2P system with decreasing peer arrival rate. In Proceedings of the International Workshop
Riikka Susitaival and Samuli Aalto. Modelling the population dynamics and the file availability in a BitTorrent like P2P system with decreasing peer arrival rate. In Proceedings of the International Workshop
Dynamics of content propagation in BitTorrent-like P2P file exchange systems
 211 5th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC) Orlando, FL, USA, December 12-15, 211 Dynamics of content propagation in BitTorrent-like P2P file exchange systems
211 5th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC) Orlando, FL, USA, December 12-15, 211 Dynamics of content propagation in BitTorrent-like P2P file exchange systems
Optimal Server Scheduling in Hybrid P2P Networks
 Performance Evaluation Performance Evaluation (21) 1 19 Optimal Server Scheduling in Hybrid P2P Networks Bo Zhang a, Sem C. Borst b,c, Martin I. Reiman b a School of Industrial and Systems Engineering,
Performance Evaluation Performance Evaluation (21) 1 19 Optimal Server Scheduling in Hybrid P2P Networks Bo Zhang a, Sem C. Borst b,c, Martin I. Reiman b a School of Industrial and Systems Engineering,
P2P Video-on-Demand: Steady State and Scalability
 P2P Video-on-Demand: Steady State and Scalability Niklas Raatikainen, Sasu Tarkoma, Petri Savolainen Helsinki Institute for Information Technology Email: firstname.lastname@hiit.fi Samuli Aalto, Pasi Lassila
P2P Video-on-Demand: Steady State and Scalability Niklas Raatikainen, Sasu Tarkoma, Petri Savolainen Helsinki Institute for Information Technology Email: firstname.lastname@hiit.fi Samuli Aalto, Pasi Lassila
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Modeling and Performance Analysis of BitTorrent-Like Peer-to-Peer Networks
 Modeling and Performance Analysis of BitTorrent-Like Peer-to-Peer Networks regular paper, ID: 444 Abstract In this paper, we develop simple models to study the performance of BitTorrent, a second generation
Modeling and Performance Analysis of BitTorrent-Like Peer-to-Peer Networks regular paper, ID: 444 Abstract In this paper, we develop simple models to study the performance of BitTorrent, a second generation
Asymptotic behavior of a class of Processor Sharing queues with applications to P2P modelling
 Asymptotic behavior of a class of Processor Sharing queues with applications to P2P modelling Andrés Ferragut Fernando Paganini Universidad ORT Uruguay Noviembre 2011 Contents 1 Introduction and Motivation
Asymptotic behavior of a class of Processor Sharing queues with applications to P2P modelling Andrés Ferragut Fernando Paganini Universidad ORT Uruguay Noviembre 2011 Contents 1 Introduction and Motivation
Modeling and Performance Analysis of BitTorrent-Like Peer-to-Peer Networks
 Modeling and Performance Analysis of BitTorrent-Like Peer-to-Peer Networks Dongyu Qiu and R. Srikant Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 68 {dqiu, rsrikant}@uiuc.edu
Modeling and Performance Analysis of BitTorrent-Like Peer-to-Peer Networks Dongyu Qiu and R. Srikant Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 68 {dqiu, rsrikant}@uiuc.edu
Stochastic Differential Equation Approach to Model BitTorrent-like P2P Systems
 Stochastic Differential Equation Approach to Model BitTorrent-like P2P Systems Bin Fan Dept. of Computer Science & Eng. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Email: bfan@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Dah-Ming Chiu Dept.
Stochastic Differential Equation Approach to Model BitTorrent-like P2P Systems Bin Fan Dept. of Computer Science & Eng. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Email: bfan@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Dah-Ming Chiu Dept.
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
STOCHASTIC MODELS FOR RELIABILITY, AVAILABILITY, AND MAINTAINABILITY
 STOCHASTIC MODELS FOR RELIABILITY, AVAILABILITY, AND MAINTAINABILITY Ph.D. Assistant Professor Industrial and Systems Engineering Auburn University RAM IX Summit November 2 nd 2016 Outline Introduction
STOCHASTIC MODELS FOR RELIABILITY, AVAILABILITY, AND MAINTAINABILITY Ph.D. Assistant Professor Industrial and Systems Engineering Auburn University RAM IX Summit November 2 nd 2016 Outline Introduction
Multiclass P2P Networks: Static Resource Allocation for Service Differentiation and Bandwidth Diversity
 Multiclass P2P Networks: Static Resource Allocation for Service Differentiation and Bandwidth Diversity Florence Clévenot-Perronnin Philippe Nain Keith W. Ross Abstract We propose a multiclass fluid model
Multiclass P2P Networks: Static Resource Allocation for Service Differentiation and Bandwidth Diversity Florence Clévenot-Perronnin Philippe Nain Keith W. Ross Abstract We propose a multiclass fluid model
Stochastic Analysis and File Availability Enhancement for BT-like File Sharing Systems. John.C.S.Lui The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Stochastic Analysis and File Availability Enhancement for BT-like File Sharing Systems John.C.S.Lui The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 Outline 2 Outline Introduction 2 Outline Introduction Modeling
Stochastic Analysis and File Availability Enhancement for BT-like File Sharing Systems John.C.S.Lui The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 Outline 2 Outline Introduction 2 Outline Introduction Modeling
Provably stable, distributed file sharing protocols
 Provably stable, distributed file sharing protocols Barlas Oguz Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-2012-6 http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/pubs/techrpts/2012/eecs-2012-6.html
Provably stable, distributed file sharing protocols Barlas Oguz Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-2012-6 http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/pubs/techrpts/2012/eecs-2012-6.html
Supply chains models
 Supply chains models Maria Ivanova Technische Universität München, Department of Mathematics, Haupt Seminar 2016 Garching, Germany July 3, 2016 Overview Introduction What is Supply chain? Traffic flow
Supply chains models Maria Ivanova Technische Universität München, Department of Mathematics, Haupt Seminar 2016 Garching, Germany July 3, 2016 Overview Introduction What is Supply chain? Traffic flow
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits. IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015
 Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
A.Piunovskiy. University of Liverpool Fluid Approximation to Controlled Markov. Chains with Local Transitions. A.Piunovskiy.
 University of Liverpool piunov@liv.ac.uk The Markov Decision Process under consideration is defined by the following elements X = {0, 1, 2,...} is the state space; A is the action space (Borel); p(z x,
University of Liverpool piunov@liv.ac.uk The Markov Decision Process under consideration is defined by the following elements X = {0, 1, 2,...} is the state space; A is the action space (Borel); p(z x,
NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
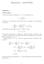 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017
 CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
Optimal Peer-Assisted File Distribution: Single and Multi-Class Problems
 Optimal Peer-Assisted ile Distribution: Single and Multi-Class Problems Rakesh Kumar, Keith Ross Abstract With the emergence of BitTorrent, Swarmcast, and CDNs, peer-assisted file distribution has become
Optimal Peer-Assisted ile Distribution: Single and Multi-Class Problems Rakesh Kumar, Keith Ross Abstract With the emergence of BitTorrent, Swarmcast, and CDNs, peer-assisted file distribution has become
Network management and QoS provisioning - Network Calculus
 Network Calculus Network calculus is a metodology to study in a deterministic approach theory of queues. First a linear modelization is needed: it means that, for example, a system like: ρ can be modelized
Network Calculus Network calculus is a metodology to study in a deterministic approach theory of queues. First a linear modelization is needed: it means that, for example, a system like: ρ can be modelized
Dynamic Atomic Congestion Games with Seasonal Flows
 Dynamic Atomic Congestion Games with Seasonal Flows Marc Schröder Marco Scarsini, Tristan Tomala Maastricht University Department of Quantitative Economics Scarsini, Schröder, Tomala Dynamic Atomic Congestion
Dynamic Atomic Congestion Games with Seasonal Flows Marc Schröder Marco Scarsini, Tristan Tomala Maastricht University Department of Quantitative Economics Scarsini, Schröder, Tomala Dynamic Atomic Congestion
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance
 Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Dynamic resource sharing
 J. Virtamo 38.34 Teletraffic Theory / Dynamic resource sharing and balanced fairness Dynamic resource sharing In previous lectures we have studied different notions of fair resource sharing. Our focus
J. Virtamo 38.34 Teletraffic Theory / Dynamic resource sharing and balanced fairness Dynamic resource sharing In previous lectures we have studied different notions of fair resource sharing. Our focus
Stochastic Network Calculus
 Stochastic Network Calculus Assessing the Performance of the Future Internet Markus Fidler joint work with Amr Rizk Institute of Communications Technology Leibniz Universität Hannover April 22, 2010 c
Stochastic Network Calculus Assessing the Performance of the Future Internet Markus Fidler joint work with Amr Rizk Institute of Communications Technology Leibniz Universität Hannover April 22, 2010 c
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
Markov Processes and Queues
 MIT 2.853/2.854 Introduction to Manufacturing Systems Markov Processes and Queues Stanley B. Gershwin Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity Massachusetts Institute of Technology Markov Processes
MIT 2.853/2.854 Introduction to Manufacturing Systems Markov Processes and Queues Stanley B. Gershwin Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity Massachusetts Institute of Technology Markov Processes
Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty
 Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty Assaf Zeevi Graduate School of Business Columbia University Stochastic Processing Networks Conference, August 2009 based on joint work with Mike Harrison Achal
Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty Assaf Zeevi Graduate School of Business Columbia University Stochastic Processing Networks Conference, August 2009 based on joint work with Mike Harrison Achal
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3. Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, Announcements
 Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Analytical Model for Mesh-based P2PVoD
 Analytical Model for Mesh-based P2PVoD Yue Lu, Jan David Mol, Fernando Kuipers, Piet Van Mieghem Delft University of Technology {Y.Lu, J.J.D.Mol, F.A.Kuipers, P.F.A.VanMieghem}@tudelft.nl Abstract Recently,
Analytical Model for Mesh-based P2PVoD Yue Lu, Jan David Mol, Fernando Kuipers, Piet Van Mieghem Delft University of Technology {Y.Lu, J.J.D.Mol, F.A.Kuipers, P.F.A.VanMieghem}@tudelft.nl Abstract Recently,
A Coalition Formation Game in Partition Form for Peer-to-Peer File Sharing Networks
 Author manuscript, published in "IEEE GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS CONFERENCE (IEEE GLOBECOM 2010), United States (2010)" A Coalition Formation Game in Partition Form for Peer-to-Peer File Sharing Networks Walid
Author manuscript, published in "IEEE GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS CONFERENCE (IEEE GLOBECOM 2010), United States (2010)" A Coalition Formation Game in Partition Form for Peer-to-Peer File Sharing Networks Walid
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 30-1 Overview Queueing Notation
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 30-1 Overview Queueing Notation
Little s result. T = average sojourn time (time spent) in the system N = average number of customers in the system. Little s result says that
 J. Virtamo 38.143 Queueing Theory / Little s result 1 Little s result The result Little s result or Little s theorem is a very simple (but fundamental) relation between the arrival rate of customers, average
J. Virtamo 38.143 Queueing Theory / Little s result 1 Little s result The result Little s result or Little s theorem is a very simple (but fundamental) relation between the arrival rate of customers, average
Page 0 of 5 Final Examination Name. Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam.
 Final Examination Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam. To receive full credit, show enough work to indicate your logic. Do not spend time calculating. You will receive full credit
Final Examination Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam. To receive full credit, show enough work to indicate your logic. Do not spend time calculating. You will receive full credit
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/6/16. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
Design of IP networks with Quality of Service
 Course of Multimedia Internet (Sub-course Reti Internet Multimediali ), AA 2010-2011 Prof. Pag. 1 Design of IP networks with Quality of Service 1 Course of Multimedia Internet (Sub-course Reti Internet
Course of Multimedia Internet (Sub-course Reti Internet Multimediali ), AA 2010-2011 Prof. Pag. 1 Design of IP networks with Quality of Service 1 Course of Multimedia Internet (Sub-course Reti Internet
A review of Continuous Time MC STA 624, Spring 2015
 A review of Continuous Time MC STA 624, Spring 2015 Ruriko Yoshida Dept. of Statistics University of Kentucky polytopes.net STA 624 1 Continuous Time Markov chains Definition A continuous time stochastic
A review of Continuous Time MC STA 624, Spring 2015 Ruriko Yoshida Dept. of Statistics University of Kentucky polytopes.net STA 624 1 Continuous Time Markov chains Definition A continuous time stochastic
Methodology for Computer Science Research Lecture 4: Mathematical Modeling
 Methodology for Computer Science Research Andrey Lukyanenko Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science and Technology andrey.lukyanenko@tkk.fi Definitions and Goals
Methodology for Computer Science Research Andrey Lukyanenko Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science and Technology andrey.lukyanenko@tkk.fi Definitions and Goals
Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, :12 PM
 stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
MS&E 321 Spring Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10. x n+1 = f(x n ),
 MS&E 321 Spring 12-13 Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10 Section 4: Steady-State Theory Contents 4.1 The Concept of Stochastic Equilibrium.......................... 1 4.2
MS&E 321 Spring 12-13 Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10 Section 4: Steady-State Theory Contents 4.1 The Concept of Stochastic Equilibrium.......................... 1 4.2
Fluid models in performance analysis
 Fluid models in performance analysis Miklós Telek Dept. of Telecom., Technical University of Budapest SFM-07:PE, May 31, 2007 Bertinoro, Italy Joint work with Marco Gribaudo Dip. di Informatica, Università
Fluid models in performance analysis Miklós Telek Dept. of Telecom., Technical University of Budapest SFM-07:PE, May 31, 2007 Bertinoro, Italy Joint work with Marco Gribaudo Dip. di Informatica, Università
Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network. Haifa Statistics Seminar May 5, 2008
 Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network Yoni Nazarathy Gideon Weiss Haifa Statistics Seminar May 5, 2008 1 Outline 1 Preview of Results 2 Introduction Queueing
Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network Yoni Nazarathy Gideon Weiss Haifa Statistics Seminar May 5, 2008 1 Outline 1 Preview of Results 2 Introduction Queueing
Readings: Finish Section 5.2
 LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
Differential and Difference LTI systems
 Signals and Systems Lecture: 6 Differential and Difference LTI systems Differential and difference linear time-invariant (LTI) systems constitute an extremely important class of systems in engineering.
Signals and Systems Lecture: 6 Differential and Difference LTI systems Differential and difference linear time-invariant (LTI) systems constitute an extremely important class of systems in engineering.
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Impact of traffic mix on caching performance
 Impact of traffic mix on caching performance Jim Roberts, INRIA/RAP joint work with Christine Fricker, Philippe Robert, Nada Sbihi BCAM, 27 June 2012 A content-centric future Internet most Internet traffic
Impact of traffic mix on caching performance Jim Roberts, INRIA/RAP joint work with Christine Fricker, Philippe Robert, Nada Sbihi BCAM, 27 June 2012 A content-centric future Internet most Internet traffic
Birth-Death Processes
 Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues
 Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
Irreducibility. Irreducible. every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that. Absorbing state: p jj =1
 Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Stochastic process. X, a series of random variables indexed by t
 Stochastic process X, a series of random variables indexed by t X={X(t), t 0} is a continuous time stochastic process X={X(t), t=0,1, } is a discrete time stochastic process X(t) is the state at time t,
Stochastic process X, a series of random variables indexed by t X={X(t), t 0} is a continuous time stochastic process X={X(t), t=0,1, } is a discrete time stochastic process X(t) is the state at time t,
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective. Ward Whitt. IEOR Department. Columbia University
 Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
ANALYSIS OF P2P FILE TRANSFERRING SYSTEM BY STOCHASTIC QUEUE MODELS JI ZHU THESIS
 c 2010 Ji Zhu ANALYSIS OF P2P FILE TRANSFERRING SYSTEM BY STOCHASTIC QUEUE MODELS BY JI ZHU THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Electrical
c 2010 Ji Zhu ANALYSIS OF P2P FILE TRANSFERRING SYSTEM BY STOCHASTIC QUEUE MODELS BY JI ZHU THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Electrical
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks
 A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks by Doo Il Choi, Charles Knessl and Charles Tier University of Illinois at Chicago 85 South
A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks by Doo Il Choi, Charles Knessl and Charles Tier University of Illinois at Chicago 85 South
Statistics 150: Spring 2007
 Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
Stochastic2010 Page 1
 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, April 02, 2010 2:03 PM Long-time properties for branching processes Clearly state 0 is an absorbing state, forming its own recurrent
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, April 02, 2010 2:03 PM Long-time properties for branching processes Clearly state 0 is an absorbing state, forming its own recurrent
Simulation. Where real stuff starts
 Simulation Where real stuff starts March 2019 1 ToC 1. What is a simulation? 2. Accuracy of output 3. Random Number Generators 4. How to sample 5. Monte Carlo 6. Bootstrap 2 1. What is a simulation? 3
Simulation Where real stuff starts March 2019 1 ToC 1. What is a simulation? 2. Accuracy of output 3. Random Number Generators 4. How to sample 5. Monte Carlo 6. Bootstrap 2 1. What is a simulation? 3
MARKOV DECISION PROCESSES
 J. Virtamo 38.3141 Teletraffic Theory / Markov decision processes 1 MARKOV DECISION PROCESSES In studying Markov processes we have up till now assumed that the system, its states and transition probabilities
J. Virtamo 38.3141 Teletraffic Theory / Markov decision processes 1 MARKOV DECISION PROCESSES In studying Markov processes we have up till now assumed that the system, its states and transition probabilities
Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales. Rolf Riedi
 Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales Rolf Riedi Dept of Statistics Stochastic Systems and Modelling in Networking and Finance Part II Dependable Adaptive Systems and Mathematical Modeling Kaiserslautern,
Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales Rolf Riedi Dept of Statistics Stochastic Systems and Modelling in Networking and Finance Part II Dependable Adaptive Systems and Mathematical Modeling Kaiserslautern,
Markov Model. Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states
 Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
On the stability of two-chunk file-sharing systems
 On the stability of two-chunk file-sharing systems Ilkka Norros, Hannu Reittu, Timo Eirola To cite this version: Ilkka Norros, Hannu Reittu, Timo Eirola. On the stability of two-chunk file-sharing systems.
On the stability of two-chunk file-sharing systems Ilkka Norros, Hannu Reittu, Timo Eirola To cite this version: Ilkka Norros, Hannu Reittu, Timo Eirola. On the stability of two-chunk file-sharing systems.
MODELING WEBCHAT SERVICE CENTER WITH MANY LPS SERVERS
 MODELING WEBCHAT SERVICE CENTER WITH MANY LPS SERVERS Jiheng Zhang Oct 26, 211 Model and Motivation Server Pool with multiple LPS servers LPS Server K Arrival Buffer. Model and Motivation Server Pool with
MODELING WEBCHAT SERVICE CENTER WITH MANY LPS SERVERS Jiheng Zhang Oct 26, 211 Model and Motivation Server Pool with multiple LPS servers LPS Server K Arrival Buffer. Model and Motivation Server Pool with
A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue
 A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue Robert C. Hampshire Heinz School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University hamp@andrew.cmu.edu William A. Massey Department of
A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue Robert C. Hampshire Heinz School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University hamp@andrew.cmu.edu William A. Massey Department of
DELAY, MEMORY, AND MESSAGING TRADEOFFS IN DISTRIBUTED SERVICE SYSTEMS
 DELAY, MEMORY, AND MESSAGING TRADEOFFS IN DISTRIBUTED SERVICE SYSTEMS By David Gamarnik, John N. Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5 th September, 2017 We consider the
DELAY, MEMORY, AND MESSAGING TRADEOFFS IN DISTRIBUTED SERVICE SYSTEMS By David Gamarnik, John N. Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5 th September, 2017 We consider the
Asymptotic Coupling of an SPDE, with Applications to Many-Server Queues
 Asymptotic Coupling of an SPDE, with Applications to Many-Server Queues Mohammadreza Aghajani joint work with Kavita Ramanan Brown University March 2014 Mohammadreza Aghajanijoint work Asymptotic with
Asymptotic Coupling of an SPDE, with Applications to Many-Server Queues Mohammadreza Aghajani joint work with Kavita Ramanan Brown University March 2014 Mohammadreza Aghajanijoint work Asymptotic with
Gibbsian On-Line Distributed Content Caching Strategy for Cellular Networks
 Gibbsian On-Line Distributed Content Caching Strategy for Cellular Networks Arpan Chattopadhyay, Bartłomiej Błaszczyszyn, H. Paul Keeler arxiv:1610.02318v2 [cs.ni] 6 Nov 2017 Abstract In this paper, we
Gibbsian On-Line Distributed Content Caching Strategy for Cellular Networks Arpan Chattopadhyay, Bartłomiej Błaszczyszyn, H. Paul Keeler arxiv:1610.02318v2 [cs.ni] 6 Nov 2017 Abstract In this paper, we
SAMPLING AND INVERSION
 SAMPLING AND INVERSION Darryl Veitch dveitch@unimelb.edu.au CUBIN, Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne Workshop on Sampling the Internet, Paris 2005 A TALK WITH TWO
SAMPLING AND INVERSION Darryl Veitch dveitch@unimelb.edu.au CUBIN, Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne Workshop on Sampling the Internet, Paris 2005 A TALK WITH TWO
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV PROCESSES
 QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
Output Analysis for a Single Model
 Output Analysis for a Single Model Output Analysis for a Single Model Output analysis is the examination of data generated by a simulation. Its purpose is to predict the performance of a system or to compare
Output Analysis for a Single Model Output Analysis for a Single Model Output analysis is the examination of data generated by a simulation. Its purpose is to predict the performance of a system or to compare
Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem
 Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Heterogeneous download times in a homogeneous BitTorrent swarm
 Heterogeneous download times in a homogeneous BitTorrent swarm Fabricio Murai a, Antonio A. de A. Rocha b,, Daniel R. Figueiredo a, Edmundo A. de Souza e Silva a a COPPE/Systems Engineering and Computer
Heterogeneous download times in a homogeneous BitTorrent swarm Fabricio Murai a, Antonio A. de A. Rocha b,, Daniel R. Figueiredo a, Edmundo A. de Souza e Silva a a COPPE/Systems Engineering and Computer
MULTITRACK: A DELAY AND COST AWARE P2P OVERLAY ARCHITECTURE. A Thesis VINITH KUMAR REDDY PODDUTURI
 MULTITRACK: A DELAY AND COST AWARE P2P OVERLAY ARCHITECTURE A Thesis by VINITH KUMAR REDDY PODDUTURI Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
MULTITRACK: A DELAY AND COST AWARE P2P OVERLAY ARCHITECTURE A Thesis by VINITH KUMAR REDDY PODDUTURI Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Predator-Prey Population Dynamics
 Predator-Prey Population Dynamics Gonzalo Mateos Dept. of ECE and Goergen Institute for Data Science University of Rochester gmateosb@ece.rochester.edu http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~gmateosb/ October 2,
Predator-Prey Population Dynamics Gonzalo Mateos Dept. of ECE and Goergen Institute for Data Science University of Rochester gmateosb@ece.rochester.edu http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~gmateosb/ October 2,
4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes
 Math Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Page 1 4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Introduction A stochastic model is one in which random effects are incorporated into the model.
Math Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Page 1 4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Introduction A stochastic model is one in which random effects are incorporated into the model.
On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems
 On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems David Gamarnik MIT Joint work with Patrick Eschenfeldt, John Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia (MIT) High level comments High level comments
On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems David Gamarnik MIT Joint work with Patrick Eschenfeldt, John Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia (MIT) High level comments High level comments
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.070J Fall 2013 Lecture 22 12/09/2013. Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.7J Fall 213 Lecture 22 12/9/213 Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion Content. 1. G/G/1 queueing system 2. One dimensional reflection mapping
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.7J Fall 213 Lecture 22 12/9/213 Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion Content. 1. G/G/1 queueing system 2. One dimensional reflection mapping
Latency analysis for Distributed Storage
 Latency analysis for Distributed Storage Parimal Parag Archana Bura Jean-François Chamberland Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas
Latency analysis for Distributed Storage Parimal Parag Archana Bura Jean-François Chamberland Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas
A Simple Memoryless Proof of the Capacity of the Exponential Server Timing Channel
 A Simple Memoryless Proof of the Capacity of the Exponential Server iming Channel odd P. Coleman ECE Department Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois colemant@illinois.edu Abstract his
A Simple Memoryless Proof of the Capacity of the Exponential Server iming Channel odd P. Coleman ECE Department Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois colemant@illinois.edu Abstract his
SIMULATION STUDIES OF A FLUID QUEUING SYSTEM
 SIMULATION STUDIES OF A FLUID QUEUING SYSTEM BY YUAN YAO THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Electrical and Computer Engineering in the Graduate
SIMULATION STUDIES OF A FLUID QUEUING SYSTEM BY YUAN YAO THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Electrical and Computer Engineering in the Graduate
Hyperbolic Models for Large Supply Chains. Christian Ringhofer (Arizona State University) Hyperbolic Models for Large Supply Chains p.
 Hyperbolic Models for Large Supply Chains Christian Ringhofer (Arizona State University) Hyperbolic Models for Large Supply Chains p. /4 Introduction Topic: Overview of conservation law (traffic - like)
Hyperbolic Models for Large Supply Chains Christian Ringhofer (Arizona State University) Hyperbolic Models for Large Supply Chains p. /4 Introduction Topic: Overview of conservation law (traffic - like)
All models are wrong / inaccurate, but some are useful. George Box (Wikipedia). wkc/course/part2.pdf
 PART II (3) Continuous Time Markov Chains : Theory and Examples -Pure Birth Process with Constant Rates -Pure Death Process -More on Birth-and-Death Process -Statistical Equilibrium (4) Introduction to
PART II (3) Continuous Time Markov Chains : Theory and Examples -Pure Birth Process with Constant Rates -Pure Death Process -More on Birth-and-Death Process -Statistical Equilibrium (4) Introduction to
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Stochastic Processes
 Stochastic Processes 8.445 MIT, fall 20 Mid Term Exam Solutions October 27, 20 Your Name: Alberto De Sole Exercise Max Grade Grade 5 5 2 5 5 3 5 5 4 5 5 5 5 5 6 5 5 Total 30 30 Problem :. True / False
Stochastic Processes 8.445 MIT, fall 20 Mid Term Exam Solutions October 27, 20 Your Name: Alberto De Sole Exercise Max Grade Grade 5 5 2 5 5 3 5 5 4 5 5 5 5 5 6 5 5 Total 30 30 Problem :. True / False
Liquidation in Limit Order Books. LOBs with Controlled Intensity
 Limit Order Book Model Power-Law Intensity Law Exponential Decay Order Books Extensions Liquidation in Limit Order Books with Controlled Intensity Erhan and Mike Ludkovski University of Michigan and UCSB
Limit Order Book Model Power-Law Intensity Law Exponential Decay Order Books Extensions Liquidation in Limit Order Books with Controlled Intensity Erhan and Mike Ludkovski University of Michigan and UCSB
Heterogeneous download times in a homogeneous BitTorrent swarm
 Heterogeneous download times in a homogeneous BitTorrent swarm arxiv:112.361v2 [cs.ni] 18 Feb 211 Fabrício Murai, Antonio A de A Rocha Daniel R. Figueiredo and Edmundo de Souza e Silva {fabricio, arocha,
Heterogeneous download times in a homogeneous BitTorrent swarm arxiv:112.361v2 [cs.ni] 18 Feb 211 Fabrício Murai, Antonio A de A Rocha Daniel R. Figueiredo and Edmundo de Souza e Silva {fabricio, arocha,
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions
 J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
Queuing Theory. Using the Math. Management Science
 Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
Queuing Networks. - Outline of queuing networks. - Mean Value Analisys (MVA) for open and closed queuing networks
 Queuing Networks - Outline of queuing networks - Mean Value Analisys (MVA) for open and closed queuing networks 1 incoming requests Open queuing networks DISK CPU CD outgoing requests Closed queuing networks
Queuing Networks - Outline of queuing networks - Mean Value Analisys (MVA) for open and closed queuing networks 1 incoming requests Open queuing networks DISK CPU CD outgoing requests Closed queuing networks
Content Dynamics in P2P Networks from Queueing and Fluid Perspectives.
 Content Dynamics in P2P Networks from Queueing and Fluid Perspectives. Andres Ferragut and Fernando Paganini Universidad ORT Uruguay, Montevideo, Uruguay Abstract In this paper we analyze the dynamics
Content Dynamics in P2P Networks from Queueing and Fluid Perspectives. Andres Ferragut and Fernando Paganini Universidad ORT Uruguay, Montevideo, Uruguay Abstract In this paper we analyze the dynamics
A monotonic property of the optimal admission control to an M/M/1 queue under periodic observations with average cost criterion
 A monotonic property of the optimal admission control to an M/M/1 queue under periodic observations with average cost criterion Cao, Jianhua; Nyberg, Christian Published in: Seventeenth Nordic Teletraffic
A monotonic property of the optimal admission control to an M/M/1 queue under periodic observations with average cost criterion Cao, Jianhua; Nyberg, Christian Published in: Seventeenth Nordic Teletraffic
Outlines. Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC)
 Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
A Mathematical Model of the Skype VoIP Congestion Control Algorithm
 A Mathematical Model of the Skype VoIP Congestion Control Algorithm Luca De Cicco, S. Mascolo, V. Palmisano Dipartimento di Elettrotecnica ed Elettronica, Politecnico di Bari 47th IEEE Conference on Decision
A Mathematical Model of the Skype VoIP Congestion Control Algorithm Luca De Cicco, S. Mascolo, V. Palmisano Dipartimento di Elettrotecnica ed Elettronica, Politecnico di Bari 47th IEEE Conference on Decision
Exercises Solutions. Automation IEA, LTH. Chapter 2 Manufacturing and process systems. Chapter 5 Discrete manufacturing problems
 Exercises Solutions Note, that we have not formulated the answers for all the review questions. You will find the answers for many questions by reading and reflecting about the text in the book. Chapter
Exercises Solutions Note, that we have not formulated the answers for all the review questions. You will find the answers for many questions by reading and reflecting about the text in the book. Chapter
Part II: continuous time Markov chain (CTMC)
 Part II: continuous time Markov chain (CTMC) Continuous time discrete state Markov process Definition (Markovian property) X(t) is a CTMC, if for any n and any sequence t 1
Part II: continuous time Markov chain (CTMC) Continuous time discrete state Markov process Definition (Markovian property) X(t) is a CTMC, if for any n and any sequence t 1
Answers to selected exercises
 Answers to selected exercises A First Course in Stochastic Models, Henk C. Tijms 1.1 ( ) 1.2 (a) Let waiting time if passengers already arrived,. Then,, (b) { (c) Long-run fraction for is (d) Let waiting
Answers to selected exercises A First Course in Stochastic Models, Henk C. Tijms 1.1 ( ) 1.2 (a) Let waiting time if passengers already arrived,. Then,, (b) { (c) Long-run fraction for is (d) Let waiting
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 2. Markov Processes
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 2. Markov Processes Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/28 Outline 2/28 1 Definition
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 2. Markov Processes Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/28 Outline 2/28 1 Definition
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling. Hamilton Institute, Summer 2010
 Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Markov decision processes with threshold-based piecewise-linear optimal policies
 1/31 Markov decision processes with threshold-based piecewise-linear optimal policies T. Erseghe, A. Zanella, C. Codemo Dept. of Information Engineering, University of Padova, Italy Padova, June 2, 213
1/31 Markov decision processes with threshold-based piecewise-linear optimal policies T. Erseghe, A. Zanella, C. Codemo Dept. of Information Engineering, University of Padova, Italy Padova, June 2, 213
