Little s result. T = average sojourn time (time spent) in the system N = average number of customers in the system. Little s result says that
|
|
|
- Reginald Walker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Virtamo Queueing Theory / Little s result 1 Little s result The result Little s result or Little s theorem is a very simple (but fundamental) relation between the arrival rate of customers, average number of customers in the system and the mean sojourn time of customers in the system. Consider any system as a black box and define = average arrival rate (average number of customers arriving per time unit) T = average sojourn time (time spent) in the system N = average number of customers in the system T Little s result says that N = T The result is very useful because of its generality Nothing is assumed about the system any part of the system can be considered as a black box The arrival process can be anything in particular, one need not assume it to be a Poisson process the process, however, has to be stationary
2 J. Virtamo Queueing Theory / Little s result 2 The use of Little s result In queueing theory it is often simpler to derive a result concerning the average number of customers in the system. Then Little s can be used to calculate the corresponding time in system (sojourn time), N T. Sometimes the result is used in the converse direction, i.e. starting from the average sojourn time one deduces the average number in system, T N.
3 J. Virtamo Queueing Theory / Little s result 3 Justification of Little s result The number in system N t forms a stochastic process. Its average value over a long period of time t can be calculated by dividing the shaded area in the figure by the length of the period t. N(t) N little 2 0 t On average, each customer contributes to the area by the amount T. The average number of customers arriving in interval t is t. The area is thus (t) T N = T. Intuitive reasoning: Assume that each customer is charged a fee of (T /min) mk, i.e. one mark per each minute stayed in the system. The average income rate of the system is thus T mk/min, but it is also N mk/min since each customer in the system generates a income rate 1 mk/min.
4 J. Virtamo Queueing Theory / Little s result 4 Application: traffic intensity (load) Consider some elements in a network, e.g. trunks, ports or any logical units such that each customer in the system reserves one such element. Let = the arrival rate of customers into the system T = average holding time of an element The quantity a = T is called the (offered) traffic intensity or load of the traffic. Traffic intensity is a pure number, but in order to emphasize the context one often denotes as its unit erlang or erl (as a tribute to the Danish pioneer of traffic theory, A.K. Erlang). By Little s result, the traffic intensity is the same as the average number of simultaneously reserved elements. Example. In the trunk group from a PBX (private branch exchange) to the central office there are on the average 150 calls per hour. The mean holding time of a call is on 3 min. The traffic intensity is a = 150 h 1 3min=7.5 erl In other words, in the trunk group there are on the average 7.5 calls in progress simultaneously.
5 J. Virtamo Queueing Theory / Little s result 5 Offered, blocked and carried traffic All real systems have a finite capacity and some of the customers requesting service have to be refused (blocked). Therefore, we have to distinguish the following concepts b c = offered traffic stream (arrival rate) = blocked traffic stream = carried traffic stream b N, T c Little s result applies to the stream of customers admitted into the system N = c T traffic intensity of the carried traffic Little s result can also be applied by extending the boundary of the system as shown in the figure. Then all the customers enter the system (arrival rate ), but part of the customers receive a harsh service (immediate kick out). The average time in system is now T = b 0+ c T = c T Little s result gives N = T = c T b N, T T' c which is the same result as previously.
6 J. Virtamo Queueing Theory / Little s result 6 Traffic intensity of the carried traffic in a singel server system X Consider a single server system, i.e. a system which can accommodate only one customer at a time. = the carried traffic stream passing through the server (served customers) X = average service time By Little s result we have N = X. On the other hand, the average occupancy can be calculated 1 directly 0 N = p 0 0+p 1 1=p 1 t p 0 p 1 = probability that the server is free = probability that the server is occupied; the usage of the server, ρ a = X = ρ In a single server system, the carried traffic intensity is the same as the usage of the server (proportion of time the server is being used).
7 J. Virtamo Queueing Theory / Little s result 7 Little s result: example In the system there are N system places in total K servers, mean service time X N K waiting places N-K odotuspaikkaa K palvelinta N systeemipaikkaa Assume that the arrival rate is so high that the system si always saturated (all palces occupied). Denote by the rate of the carried customer stream. Question: What is the mean sojourn time in system T? We apply Little s result twice: first to the set of servers and then to the whole system 1. Set of servers Mean time spent in a server = X K = X = K X 2. The whole system N = T T = N = N K X T = N K X
Non Markovian Queues (contd.)
 MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Session-Based Queueing Systems
 Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
CS 798: Homework Assignment 3 (Queueing Theory)
 1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling. Hamilton Institute, Summer 2010
 Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance
 Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
λ λ λ In-class problems
 In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
Chapter 10. Queuing Systems. D (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines.
 Chapter 10 Queuing Systems D. 10. 1. (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines. D. 10.. (Queuing System) A ueuing system consists of 1. a user source.
Chapter 10 Queuing Systems D. 10. 1. (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines. D. 10.. (Queuing System) A ueuing system consists of 1. a user source.
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
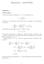 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
CS418 Operating Systems
 CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
QUEUING SYSTEM. Yetunde Folajimi, PhD
 QUEUING SYSTEM Yetunde Folajimi, PhD Part 2 Queuing Models Queueing models are constructed so that queue lengths and waiting times can be predicted They help us to understand and quantify the effect of
QUEUING SYSTEM Yetunde Folajimi, PhD Part 2 Queuing Models Queueing models are constructed so that queue lengths and waiting times can be predicted They help us to understand and quantify the effect of
MARKOV DECISION PROCESSES
 J. Virtamo 38.3141 Teletraffic Theory / Markov decision processes 1 MARKOV DECISION PROCESSES In studying Markov processes we have up till now assumed that the system, its states and transition probabilities
J. Virtamo 38.3141 Teletraffic Theory / Markov decision processes 1 MARKOV DECISION PROCESSES In studying Markov processes we have up till now assumed that the system, its states and transition probabilities
Link Models for Circuit Switching
 Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours)
 1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017
 CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
Classical Queueing Models.
 Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
11 The M/G/1 system with priorities
 11 The M/G/1 system with priorities In this chapter we analyse queueing models with different types of customers, where one or more types of customers have priority over other types. More precisely we
11 The M/G/1 system with priorities In this chapter we analyse queueing models with different types of customers, where one or more types of customers have priority over other types. More precisely we
MAT SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions.
 MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
Markov processes and queueing networks
 Inria September 22, 2015 Outline Poisson processes Markov jump processes Some queueing networks The Poisson distribution (Siméon-Denis Poisson, 1781-1840) { } e λ λ n n! As prevalent as Gaussian distribution
Inria September 22, 2015 Outline Poisson processes Markov jump processes Some queueing networks The Poisson distribution (Siméon-Denis Poisson, 1781-1840) { } e λ λ n n! As prevalent as Gaussian distribution
Solutions to Homework Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 2011
 Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models
 Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models Some General Queueing Models Discouraged Arrivals Impatient Arrivals Bulk Service and Bulk Arrivals OR37-Dr.Khalid Al-Nowibet 1 5.1 General Queueing Models 1.
Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models Some General Queueing Models Discouraged Arrivals Impatient Arrivals Bulk Service and Bulk Arrivals OR37-Dr.Khalid Al-Nowibet 1 5.1 General Queueing Models 1.
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective. Ward Whitt. IEOR Department. Columbia University
 Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Quality of Real-Time Streaming in Wireless Cellular Networks : Stochastic Modeling and Analysis
 Quality of Real-Time Streaming in Wireless Cellular Networs : Stochastic Modeling and Analysis B. Blaszczyszyn, M. Jovanovic and M. K. Karray Based on paper [1] WiOpt/WiVid Mai 16th, 2014 Outline Introduction
Quality of Real-Time Streaming in Wireless Cellular Networs : Stochastic Modeling and Analysis B. Blaszczyszyn, M. Jovanovic and M. K. Karray Based on paper [1] WiOpt/WiVid Mai 16th, 2014 Outline Introduction
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
An M/M/1/N Queuing system with Encouraged Arrivals
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISS 0973-1768 Volume 13, umber 7 (2017), pp. 3443-3453 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com An M/M/1/ Queuing system with Encouraged
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISS 0973-1768 Volume 13, umber 7 (2017), pp. 3443-3453 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com An M/M/1/ Queuing system with Encouraged
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems
 GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
Quiz Queue II. III. ( ) ( ) =1.3333
 Quiz Queue UMJ, a mail-order company, receives calls to place orders at an average of 7.5 minutes intervals. UMJ hires one operator and can handle each call in about every 5 minutes on average. The inter-arrival
Quiz Queue UMJ, a mail-order company, receives calls to place orders at an average of 7.5 minutes intervals. UMJ hires one operator and can handle each call in about every 5 minutes on average. The inter-arrival
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV PROCESSES
 QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Computer Systems Modelling
 Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Master thesis. Multi-class Fork-Join queues & The stochastic knapsack problem
 Master thesis Multi-class Fork-Join queues & The stochastic knapsack problem Sihan Ding August 26th, 2011 Supervisor UL: Dr. Floske Spieksma Supervisors CWI: Drs. Chrétien Verhoef Prof.dr. Rob van der
Master thesis Multi-class Fork-Join queues & The stochastic knapsack problem Sihan Ding August 26th, 2011 Supervisor UL: Dr. Floske Spieksma Supervisors CWI: Drs. Chrétien Verhoef Prof.dr. Rob van der
Continuous Time Processes
 page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
7 Variance Reduction Techniques
 7 Variance Reduction Techniques In a simulation study, we are interested in one or more performance measures for some stochastic model. For example, we want to determine the long-run average waiting time,
7 Variance Reduction Techniques In a simulation study, we are interested in one or more performance measures for some stochastic model. For example, we want to determine the long-run average waiting time,
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H 2 b /s queue
 An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/6/16. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
IE 581 Introduction to Stochastic Simulation. Three pages of hand-written notes, front and back. Closed book. 120 minutes.
 Three pages of hand-written notes, front and back. Closed book. 120 minutes. 1. SIMLIB. True or false. (2 points each. If you wish, write an explanation of your thinking.) (a) T F The time of the next
Three pages of hand-written notes, front and back. Closed book. 120 minutes. 1. SIMLIB. True or false. (2 points each. If you wish, write an explanation of your thinking.) (a) T F The time of the next
P (L d k = n). P (L(t) = n),
 4 M/G/1 queue In the M/G/1 queue customers arrive according to a Poisson process with rate λ and they are treated in order of arrival The service times are independent and identically distributed with
4 M/G/1 queue In the M/G/1 queue customers arrive according to a Poisson process with rate λ and they are treated in order of arrival The service times are independent and identically distributed with
Dynamic resource sharing
 J. Virtamo 38.34 Teletraffic Theory / Dynamic resource sharing and balanced fairness Dynamic resource sharing In previous lectures we have studied different notions of fair resource sharing. Our focus
J. Virtamo 38.34 Teletraffic Theory / Dynamic resource sharing and balanced fairness Dynamic resource sharing In previous lectures we have studied different notions of fair resource sharing. Our focus
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory
 CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
Queuing Networks. - Outline of queuing networks. - Mean Value Analisys (MVA) for open and closed queuing networks
 Queuing Networks - Outline of queuing networks - Mean Value Analisys (MVA) for open and closed queuing networks 1 incoming requests Open queuing networks DISK CPU CD outgoing requests Closed queuing networks
Queuing Networks - Outline of queuing networks - Mean Value Analisys (MVA) for open and closed queuing networks 1 incoming requests Open queuing networks DISK CPU CD outgoing requests Closed queuing networks
Queueing. Chapter Continuous Time Markov Chains 2 CHAPTER 5. QUEUEING
 2 CHAPTER 5. QUEUEING Chapter 5 Queueing Systems are often modeled by automata, and discrete events are transitions from one state to another. In this chapter we want to analyze such discrete events systems.
2 CHAPTER 5. QUEUEING Chapter 5 Queueing Systems are often modeled by automata, and discrete events are transitions from one state to another. In this chapter we want to analyze such discrete events systems.
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains
 Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Readings: Finish Section 5.2
 LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Fall Exam Review
 IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Fall 2017 Exam Review Nirmalya Roy Department of Information Systems University of Maryland Baltimore County www.umbc.edu Exam When: Tuesday (11/28) 7:10pm
IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Fall 2017 Exam Review Nirmalya Roy Department of Information Systems University of Maryland Baltimore County www.umbc.edu Exam When: Tuesday (11/28) 7:10pm
Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty
 Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty Assaf Zeevi Graduate School of Business Columbia University Stochastic Processing Networks Conference, August 2009 based on joint work with Mike Harrison Achal
Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty Assaf Zeevi Graduate School of Business Columbia University Stochastic Processing Networks Conference, August 2009 based on joint work with Mike Harrison Achal
Queuing Theory. The present section focuses on the standard vocabulary of Waiting Line Models.
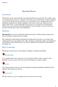 Queuing Theory Introduction Waiting lines are the most frequently encountered problems in everyday life. For example, queue at a cafeteria, library, bank, etc. Common to all of these cases are the arrivals
Queuing Theory Introduction Waiting lines are the most frequently encountered problems in everyday life. For example, queue at a cafeteria, library, bank, etc. Common to all of these cases are the arrivals
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/25/17. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
Markov Chains. X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2 <... < t k < t k+1. If X(t) is discrete-valued. If X(t) is continuous-valued
 Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
S Queueing Theory, II/2007 Exercises. Virtamo / Penttinen. 10th December Discrete and Continuous Distributions 1
 S-38.343 Queueing Theory, II/007 Exercises Virtamo / Penttinen 0th December 007 Contents Discrete and Continuous Distributions Distributions and Markov Chains 5 3 Birth&death- and Poisson-processes, Little
S-38.343 Queueing Theory, II/007 Exercises Virtamo / Penttinen 0th December 007 Contents Discrete and Continuous Distributions Distributions and Markov Chains 5 3 Birth&death- and Poisson-processes, Little
One billion+ terminals in voice network alone
 Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Waiting Time Analysis of A Single Server Queue in an Out- Patient Clinic
 IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. V (May - Jun. 2015), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Waiting Time Analysis of A Single Server Queue in
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. V (May - Jun. 2015), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Waiting Time Analysis of A Single Server Queue in
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman
 IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
Elementary queueing system
 Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue M/M/1 with preemptive-resume priority M/M/1 with non-preemptive priority 1 History of queueing theory An old
Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue M/M/1 with preemptive-resume priority M/M/1 with non-preemptive priority 1 History of queueing theory An old
Retrial queue for cloud systems with separated processing and storage units
 Retrial queue for cloud systems with separated processing and storage units Tuan Phung-Duc Department of Mathematical and Computing Sciences Tokyo Institute of Technology Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Retrial queue for cloud systems with separated processing and storage units Tuan Phung-Duc Department of Mathematical and Computing Sciences Tokyo Institute of Technology Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, Japan
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997
 57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
Computer Systems Modelling
 Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Lent Term 2010/11 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Lent Term 2010/11 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH , YEAR APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS)
 YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Instructor : Dr. Igor Poliakov MATH 4570 6.0, YEAR 2006-07 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS) March 29, 2007 Name (print)
YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Instructor : Dr. Igor Poliakov MATH 4570 6.0, YEAR 2006-07 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS) March 29, 2007 Name (print)
Erlang loss bounds for OT ICU systems
 Queueing Syst (2009) 63: 253 280 DOI 10.1007/s11134-009-9149-2 Erlang loss bounds for OT ICU systems N.M. van Dijk N. Kortbeek Received: 22 December 2008 / Revised: 30 October 2009 / Published online:
Queueing Syst (2009) 63: 253 280 DOI 10.1007/s11134-009-9149-2 Erlang loss bounds for OT ICU systems N.M. van Dijk N. Kortbeek Received: 22 December 2008 / Revised: 30 October 2009 / Published online:
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Queues and Queueing Networks
 Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Kendall notation. PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue
 Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue 1 History of queueing theory An old research area Started in 1909, by Agner Erlang (to model the Copenhagen
Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue 1 History of queueing theory An old research area Started in 1909, by Agner Erlang (to model the Copenhagen
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse567-11/
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse567-11/
Multiaccess Problem. How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users?
 Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Contents Preface The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process Introduction to Renewal Theory
 Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
Data analysis and stochastic modeling
 Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue
 Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 30-1 Overview Queueing Notation
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 30-1 Overview Queueing Notation
Answers to selected exercises
 Answers to selected exercises A First Course in Stochastic Models, Henk C. Tijms 1.1 ( ) 1.2 (a) Let waiting time if passengers already arrived,. Then,, (b) { (c) Long-run fraction for is (d) Let waiting
Answers to selected exercises A First Course in Stochastic Models, Henk C. Tijms 1.1 ( ) 1.2 (a) Let waiting time if passengers already arrived,. Then,, (b) { (c) Long-run fraction for is (d) Let waiting
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
Control of Fork-Join Networks in Heavy-Traffic
 in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
Waiting time characteristics in cyclic queues
 Waiting time characteristics in cyclic queues Sanne R. Smits, Ivo Adan and Ton G. de Kok April 16, 2003 Abstract In this paper we study a single-server queue with FIFO service and cyclic interarrival and
Waiting time characteristics in cyclic queues Sanne R. Smits, Ivo Adan and Ton G. de Kok April 16, 2003 Abstract In this paper we study a single-server queue with FIFO service and cyclic interarrival and
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION MH4702/MAS446/MTH437 Probabilistic Methods in OR
 NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2013-201 MH702/MAS6/MTH37 Probabilistic Methods in OR December 2013 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2013-201 MH702/MAS6/MTH37 Probabilistic Methods in OR December 2013 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains
COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational Analysis and Workload Characterisation COMP9334 1 Last lecture Modelling of computer systems using Queueing Networks Open
COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational Analysis and Workload Characterisation COMP9334 1 Last lecture Modelling of computer systems using Queueing Networks Open
λ, µ, ρ, A n, W n, L(t), L, L Q, w, w Q etc. These
 Queuing theory models systems with servers and clients (presumably waiting in queues). Notation: there are many standard symbols like λ, µ, ρ, A n, W n, L(t), L, L Q, w, w Q etc. These represent the actual
Queuing theory models systems with servers and clients (presumably waiting in queues). Notation: there are many standard symbols like λ, µ, ρ, A n, W n, L(t), L, L Q, w, w Q etc. These represent the actual
Classification of Queuing Models
 Classification of Queuing Models Generally Queuing models may be completely specified in the following symbol form:(a/b/c):(d/e)where a = Probability law for the arrival(or inter arrival)time, b = Probability
Classification of Queuing Models Generally Queuing models may be completely specified in the following symbol form:(a/b/c):(d/e)where a = Probability law for the arrival(or inter arrival)time, b = Probability
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues
 Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
The Erlang Model with non-poisson Call Arrivals
 The Erlang Model with non-poisson Call Arrivals Thomas Bonald To cite this version: Thomas Bonald. The Erlang Model with non-poisson Call Arrivals. Sigmetrics / Performance 2006 - Joint International Conference
The Erlang Model with non-poisson Call Arrivals Thomas Bonald To cite this version: Thomas Bonald. The Erlang Model with non-poisson Call Arrivals. Sigmetrics / Performance 2006 - Joint International Conference
TOWARDS BETTER MULTI-CLASS PARAMETRIC-DECOMPOSITION APPROXIMATIONS FOR OPEN QUEUEING NETWORKS
 TOWARDS BETTER MULTI-CLASS PARAMETRIC-DECOMPOSITION APPROXIMATIONS FOR OPEN QUEUEING NETWORKS by Ward Whitt AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974-0636 March 31, 199 Revision: November 9, 199 ABSTRACT
TOWARDS BETTER MULTI-CLASS PARAMETRIC-DECOMPOSITION APPROXIMATIONS FOR OPEN QUEUEING NETWORKS by Ward Whitt AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974-0636 March 31, 199 Revision: November 9, 199 ABSTRACT
Queueing Theory. VK Room: M Last updated: October 17, 2013.
 Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
CHAPTER 4. Networks of queues. 1. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.1. Arrivals
 CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling
 NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
Probability and Statistics Concepts
 University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
Analysis of an M/G/1 queue with customer impatience and an adaptive arrival process
 Analysis of an M/G/1 queue with customer impatience and an adaptive arrival process O.J. Boxma 1, O. Kella 2, D. Perry 3, and B.J. Prabhu 1,4 1 EURANDOM and Department of Mathematics & Computer Science,
Analysis of an M/G/1 queue with customer impatience and an adaptive arrival process O.J. Boxma 1, O. Kella 2, D. Perry 3, and B.J. Prabhu 1,4 1 EURANDOM and Department of Mathematics & Computer Science,
An M/M/1 Queue in Random Environment with Disasters
 An M/M/1 Queue in Random Environment with Disasters Noam Paz 1 and Uri Yechiali 1,2 1 Department of Statistics and Operations Research School of Mathematical Sciences Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978,
An M/M/1 Queue in Random Environment with Disasters Noam Paz 1 and Uri Yechiali 1,2 1 Department of Statistics and Operations Research School of Mathematical Sciences Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978,
Networks of Queues Models with Several. Classes of Customers and Exponential. Service Times
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 2015, no. 76, 3789-3796 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2015.53287 Networks of Queues Models with Several Classes of Customers and Exponential
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 2015, no. 76, 3789-3796 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2015.53287 Networks of Queues Models with Several Classes of Customers and Exponential
Link Models for Packet Switching
 Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2
 1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem. Wade Trappe
 Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Name of the Student:
 SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
