Module 6 : Wave Guides. Lecture 40 : Introduction of Parallel Waveguide. Objectives. In this course you will learn the following
|
|
|
- Timothy Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide.
2 Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide Wave Guide is a structure which can guide Electro Magnetic Energy. A Wave guide is a prime component of a communication system. The Wave guide in structure should transport electro magnetic energy with as minimal loss as possible. In practice, we find two types of wave guide in structure which are as follows : Metallic Wave Guide : Is used in high frequency, microwaves and millimeter waves transmission. Co-axial cables and hollow rectangular or circular wave guide's fall in this category. Delectric Wave Guide : Is used at sub millimeter wavelenghts and optical frequencies. Optical fibres and thin film integrated optical devices fall in this category. The important feature of a wave guide in structure is the ' Modal Propagation'. The electro magnetic energy propagates inside the wave guide in the form of definite field patterns called ' MODES '. The electro magnetic fields inside a bound structure like the wave guide's can exist only in the form of MODES. The modal fields of a wave guide can be visualized either in the form of super position of plane waves or as a boundary value problem The decomposition of plane waves is possible for simple wave guide in structure like parallel plane wave guide or planer thin film wave guide's. For rectangular and circular wave guide one essentially has to solve the wave equation with appropriate boundary condition imposed by the wave guide walls. The second approach is more general where as, the first approach provides better physical understanding of the wave propagation inside the wave guide. A parallel wave guide is formed by two infinite parallel conducting planes. The electro magnetic energy is confined between the planes and moves in a direction parallel to the planes. The electro magnetic waves which can exists between the parallel planes can be of three types Transverse Electric Fields Transverse Magnetic Flelds Transverse Electomagnetic Fields For Transverse Electric Field, the electric field is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. That is to say that the electric field does not have any component in the direction of wave propagation. For Transverse Magnetic Field, the magnetic field is transverse to the direction. of wave propagation. That is to say that the electric field does not have any component in the direction of wave propagation. For Transverse Electromagnetic Fields, the electric and magnetic fields both do not have a component in the direction of wave propagation.
3 Parallel Plane Wave Guide (contd) Let us try to visualize the fields inside a parallel wave guide in the form of super position plane wave. Let us consider a single conducting plane on which a plane wave with perpendicular polarization is incident at an angle as shown in the figure below Since the conducting plane is ideal the wave is completely reflected back and the total electric and magnetic field in the medium can be written as and (6.1) (6.2)
4 Parallel Plane Wave Guide (contd) The electric field which is oriented in the -direction is parallel to the conducting plane. Naturally, the total electirc field should be zero at the conducting plane i.e at We can however note that the electric field is zero not only at but at any height which satisfies the condition (6.3) What that means is the fields are unaffected if we keep another conducting plane parallel to the original conducting plane at a height given by 6.3 while the field given by 6.1 and 6.2 are not disturbed. The structure however has now become a bound structure wihin which the electro magnetic fields are trapped. Inverting equation 6.3, we get (6.4) The equation implies that for a given separation for a two conducting planes (for a given height of parallel plane wave guide, ) the plane waves can propagate only at discrete angles given by 6.4 The plane wave cannot propagate any arbitrary angle whih does not satisfy the condition 6.4 The characteristics of the plane wave propagation between two parallel conducting planes can then be summarized as follows: (1) We have naturally migrated from the continuous domain of to the discrete domain. (2) Since is 1, there are finite number of angles for a given boundary separation ` ' and the frequency. (3) For is always greater than 1 even for the smallest value of. This imply that no wave can be launched between the two conducting planes, if the separation between them is less than. (4) As the separation between the boundaries increases or the wavelength decreases, the number of acceptable angles at which the wave can be launched, also increases.
5 Recap In this course you have learnt the following Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide.
Module 5 : Plane Waves at Media Interface. Lecture 39 : Electro Magnetic Waves at Conducting Boundaries. Objectives
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Reflection from a Conducting Boundary. Normal Incidence at Conducting Boundary. Reflection from a Conducting Boundary Let us consider a dielectric
Objectives In this course you will learn the following Reflection from a Conducting Boundary. Normal Incidence at Conducting Boundary. Reflection from a Conducting Boundary Let us consider a dielectric
Module 5 : Plane Waves at Media Interface. Lecture 36 : Reflection & Refraction from Dielectric Interface (Contd.) Objectives
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Reflection and Refraction with Parallel Polarization. Reflection and Refraction for Normal Incidence. Lossy Media Interface. Reflection and Refraction
Objectives In this course you will learn the following Reflection and Refraction with Parallel Polarization. Reflection and Refraction for Normal Incidence. Lossy Media Interface. Reflection and Refraction
Electromagnetic waves in free space
 Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides
 1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
Modal Analysis and Cutoff Condition of a Doubly Clad Cardioidic Waveguide
 Intl J ngg Sci Adv Research 5 Sep;():9-97 Modal Analysis and Cutoff Condition of a Doubly Clad Cardioidic Waveguide Ram Janma Department of Physics, University Institute of ngineering and Technology, Chhatrapati
Intl J ngg Sci Adv Research 5 Sep;():9-97 Modal Analysis and Cutoff Condition of a Doubly Clad Cardioidic Waveguide Ram Janma Department of Physics, University Institute of ngineering and Technology, Chhatrapati
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS
 UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
PHY3128 / PHYM203 (Electronics / Instrumentation) Transmission Lines
 Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
Module 2 : Transmission Lines. Lecture 1 : Transmission Lines in Practice. Objectives. In this course you will learn the following
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Point 1 Point 2 Point 3 Point 4 Point 5 Point 6 Point 7 Point 8 Point 9 Point 10 Point 11 Point 12 Various Types Of Transmission Line Explanation:
Objectives In this course you will learn the following Point 1 Point 2 Point 3 Point 4 Point 5 Point 6 Point 7 Point 8 Point 9 Point 10 Point 11 Point 12 Various Types Of Transmission Line Explanation:
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
Lecture 36 Date:
 Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Drawbacks in Metallic Waveguides. α f. Skin effect. Surface roughness Mono-mode operation Narrow band in metallic rectangular waveguide
 Drawbacks in Metallic Waveguides Skin effect α f Surface roughness Mono-mode operation 1 Narrow band in metallic rectangular waveguide 2 α f α 3 f 2 to f 5 2 Types of Dielectric Waveguide ε r2 (a) Circular
Drawbacks in Metallic Waveguides Skin effect α f Surface roughness Mono-mode operation 1 Narrow band in metallic rectangular waveguide 2 α f α 3 f 2 to f 5 2 Types of Dielectric Waveguide ε r2 (a) Circular
Lecture 5 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Lecture 5 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Waveguides Continued - In the previous lecture we made the assumption that
Lecture 5 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Waveguides Continued - In the previous lecture we made the assumption that
Super-reflection and Cloaking Based on Zero Index Metamaterial
 Super-reflection and Cloaking Based on Zero Index Metamaterial Jiaming Hao, Wei Yan, and Min Qiu Photonics and Microwave ngineering, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), lectrum 9, 164 4, Kista, Sweden
Super-reflection and Cloaking Based on Zero Index Metamaterial Jiaming Hao, Wei Yan, and Min Qiu Photonics and Microwave ngineering, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), lectrum 9, 164 4, Kista, Sweden
ONEMAG - Electromagnetic Waves
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE
Chapter 5 Cylindrical Cavities and Waveguides
 Chapter 5 Cylindrical Cavities and Waveguides We shall consider an electromagnetic field propagating inside a hollow (in the present case cylindrical) conductor. There are no sources inside the conductor,
Chapter 5 Cylindrical Cavities and Waveguides We shall consider an electromagnetic field propagating inside a hollow (in the present case cylindrical) conductor. There are no sources inside the conductor,
TC412 Microwave Communications. Lecture 8 Rectangular waveguides and cavity resonator
 TC412 Microwave Communications Lecture 8 Rectangular waveguides and cavity resonator 1 TM waves in rectangular waveguides Finding E and H components in terms of, WG geometry, and modes. From 2 2 2 xye
TC412 Microwave Communications Lecture 8 Rectangular waveguides and cavity resonator 1 TM waves in rectangular waveguides Finding E and H components in terms of, WG geometry, and modes. From 2 2 2 xye
Introduction to optical waveguide modes
 Chap. Introduction to optical waveguide modes PHILIPPE LALANNE (IOGS nd année) Chapter Introduction to optical waveguide modes The optical waveguide is the fundamental element that interconnects the various
Chap. Introduction to optical waveguide modes PHILIPPE LALANNE (IOGS nd année) Chapter Introduction to optical waveguide modes The optical waveguide is the fundamental element that interconnects the various
A RIGOROUS TWO-DIMENSIONAL FIELD ANALYSIS OF DFB STRUCTURES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 22, 197 212, 1999 A RIGOROUS TWO-DIMENSIONAL FIELD ANALYSIS OF DFB STRUCTURES M. Akbari, M. Shahabadi, and K. Schünemann Arbeitsbereich Hochfrequenztechnik Technische
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 22, 197 212, 1999 A RIGOROUS TWO-DIMENSIONAL FIELD ANALYSIS OF DFB STRUCTURES M. Akbari, M. Shahabadi, and K. Schünemann Arbeitsbereich Hochfrequenztechnik Technische
Power loss in a conducting surface in terms of linear surface current density and surface resistance.
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following The Poynting theorem and the concept of Poynting vector. Average Poynting vector( A true measure of power flow). Conditions for average power flow.
Objectives In this course you will learn the following The Poynting theorem and the concept of Poynting vector. Average Poynting vector( A true measure of power flow). Conditions for average power flow.
Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines
 Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers
 Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers Tushar Biswas 1, Shyamal K. Bhadra 1 1 Fiber optics and Photonics Division, CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute *196, Raja
Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers Tushar Biswas 1, Shyamal K. Bhadra 1 1 Fiber optics and Photonics Division, CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute *196, Raja
Introduction Introduction
 1 Introduction This book is an introduction to the theory of charged particle acceleration. It has two primary roles: 1.A unified, programmed summary of the principles underlying all charged particle accelerators.
1 Introduction This book is an introduction to the theory of charged particle acceleration. It has two primary roles: 1.A unified, programmed summary of the principles underlying all charged particle accelerators.
GRATING CLASSIFICATION
 GRATING CLASSIFICATION SURFACE-RELIEF GRATING TYPES GRATING CLASSIFICATION Transmission or Reflection Classification based on Regime DIFFRACTION BY GRATINGS Acousto-Optics Diffractive Optics Integrated
GRATING CLASSIFICATION SURFACE-RELIEF GRATING TYPES GRATING CLASSIFICATION Transmission or Reflection Classification based on Regime DIFFRACTION BY GRATINGS Acousto-Optics Diffractive Optics Integrated
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
GUIDED MICROWAVES AND OPTICAL WAVES
 Chapter 1 GUIDED MICROWAVES AND OPTICAL WAVES 1.1 Introduction In communication engineering, the carrier frequency has been steadily increasing for the obvious reason that a carrier wave with a higher
Chapter 1 GUIDED MICROWAVES AND OPTICAL WAVES 1.1 Introduction In communication engineering, the carrier frequency has been steadily increasing for the obvious reason that a carrier wave with a higher
Analysis of Single Mode Step Index Fibres using Finite Element Method. * 1 Courage Mudzingwa, 2 Action Nechibvute,
 Analysis of Single Mode Step Index Fibres using Finite Element Method. * 1 Courage Mudzingwa, 2 Action Nechibvute, 1,2 Physics Department, Midlands State University, P/Bag 9055, Gweru, Zimbabwe Abstract
Analysis of Single Mode Step Index Fibres using Finite Element Method. * 1 Courage Mudzingwa, 2 Action Nechibvute, 1,2 Physics Department, Midlands State University, P/Bag 9055, Gweru, Zimbabwe Abstract
Electromagnetic wave propagation through ultra-narrow channels filled
 31st October, HKUST, Hong-Kong Electromagnetic wave propagation through ultra-narrow channels filled with an ENZ material Mário G. Silveirinha How to have ε-nearε zero (ENZ) Media? 2 ω p ε r ~1 ω ω ( +
31st October, HKUST, Hong-Kong Electromagnetic wave propagation through ultra-narrow channels filled with an ENZ material Mário G. Silveirinha How to have ε-nearε zero (ENZ) Media? 2 ω p ε r ~1 ω ω ( +
FINAL EXAM IN FYS-3007
 Page 1 of 4 pages + chart FINAL EXAM IN FYS-007 Exam in : Fys-007 Microwave Techniques Date : Tuesday, May 1, 2011 Time : 09.00 1.00 Place : Åsgårdveien 9 Approved remedies : All non-living and non-communicating
Page 1 of 4 pages + chart FINAL EXAM IN FYS-007 Exam in : Fys-007 Microwave Techniques Date : Tuesday, May 1, 2011 Time : 09.00 1.00 Place : Åsgårdveien 9 Approved remedies : All non-living and non-communicating
A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 2008 296 A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index S. Haxha 1 and F. AbdelMalek 2 1 Photonics Group, Department of Electronics, University
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 2008 296 A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index S. Haxha 1 and F. AbdelMalek 2 1 Photonics Group, Department of Electronics, University
If we assume that sustituting (4) into (3), we have d H y A()e ;j (4) d +! ; Letting! ;, (5) ecomes d d + where the independent solutions are Hence, H
 W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes. Innite Parallel Plate Waveguide. y σ σ 0 We have studied TEM (transverse electromagnetic) waves etween two pieces of parallel conductors in the transmission line theory.
W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes. Innite Parallel Plate Waveguide. y σ σ 0 We have studied TEM (transverse electromagnetic) waves etween two pieces of parallel conductors in the transmission line theory.
Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition
 Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition Sourangsu Banerji Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, RCC Institute of Information
Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition Sourangsu Banerji Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, RCC Institute of Information
Chapter 5 Cylindrical Cavities and Waveguides
 Chapter 5 Cylindrical Cavities and Waveguides We shall consider an electromagnetic field propagating inside a hollow (in the present case cylindrical) conductor. There are no sources inside the conductor,
Chapter 5 Cylindrical Cavities and Waveguides We shall consider an electromagnetic field propagating inside a hollow (in the present case cylindrical) conductor. There are no sources inside the conductor,
Physics 3312 Lecture 7 February 6, 2019
 Physics 3312 Lecture 7 February 6, 2019 LAST TIME: Reviewed thick lenses and lens systems, examples, chromatic aberration and its reduction, aberration function, spherical aberration How do we reduce spherical
Physics 3312 Lecture 7 February 6, 2019 LAST TIME: Reviewed thick lenses and lens systems, examples, chromatic aberration and its reduction, aberration function, spherical aberration How do we reduce spherical
Light Waves and Polarization
 Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction
 Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
444 Index Boundary condition at transmission line short circuit, 234 for normal component of B, 170, 180 for normal component of D, 169, 180 for tange
 Index A. see Magnetic vector potential. Acceptor, 193 Addition of complex numbers, 19 of vectors, 3, 4 Admittance characteristic, 251 input, 211 line, 251 Ampere, definition of, 427 Ampere s circuital
Index A. see Magnetic vector potential. Acceptor, 193 Addition of complex numbers, 19 of vectors, 3, 4 Admittance characteristic, 251 input, 211 line, 251 Ampere, definition of, 427 Ampere s circuital
Constructing Potential Energy Diagrams
 potential ENERGY diagrams Visual Quantum Mechanics Teaching Guide ACTIVITY 2B Constructing Potential Energy Diagrams Goal In this activity, you will explore energy diagrams for magnets in repulsive configurations.
potential ENERGY diagrams Visual Quantum Mechanics Teaching Guide ACTIVITY 2B Constructing Potential Energy Diagrams Goal In this activity, you will explore energy diagrams for magnets in repulsive configurations.
Back to basics : Maxwell equations & propagation equations
 The step index planar waveguide Back to basics : Maxwell equations & propagation equations Maxwell equations Propagation medium : Notations : linear Real fields : isotropic Real inductions : non conducting
The step index planar waveguide Back to basics : Maxwell equations & propagation equations Maxwell equations Propagation medium : Notations : linear Real fields : isotropic Real inductions : non conducting
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
Power Loss. dp loss = 1 = 1. Method 2, Ohmic heating, power lost per unit volume. Agrees with method 1. c = 2 loss per unit area is dp loss da
 How much power is dissipated (per unit area?). 2 ways: 1) Flow of energy into conductor: Energy flow given by S = E H, for real fields E H. so 1 S ( ) = 1 2 Re E H, dp loss /da = ˆn S, so dp loss = 1 µc
How much power is dissipated (per unit area?). 2 ways: 1) Flow of energy into conductor: Energy flow given by S = E H, for real fields E H. so 1 S ( ) = 1 2 Re E H, dp loss /da = ˆn S, so dp loss = 1 µc
 E.M.WAVES 1. Taller the antenna longer is the coverage of television broadcast. Justify this statement with the help of a figure. 2.If v g, v x v m represents the speed of gamma rays, X-rays microwaves
E.M.WAVES 1. Taller the antenna longer is the coverage of television broadcast. Justify this statement with the help of a figure. 2.If v g, v x v m represents the speed of gamma rays, X-rays microwaves
Enhancing the Rate of Spontaneous Emission in Active Core-Shell Nanowire Resonators
 Chapter 6 Enhancing the Rate of Spontaneous Emission in Active Core-Shell Nanowire Resonators 6.1 Introduction Researchers have devoted considerable effort to enhancing light emission from semiconductors
Chapter 6 Enhancing the Rate of Spontaneous Emission in Active Core-Shell Nanowire Resonators 6.1 Introduction Researchers have devoted considerable effort to enhancing light emission from semiconductors
Microwave Network Analysis
 Prof. Dr. Mohammad Tariqul Islam titareq@gmail.my tariqul@ukm.edu.my Microwave Network Analysis 1 Text Book D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering, 3 rd edition, 2005 by John-Wiley & Sons. Fawwaz T. ILABY,
Prof. Dr. Mohammad Tariqul Islam titareq@gmail.my tariqul@ukm.edu.my Microwave Network Analysis 1 Text Book D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering, 3 rd edition, 2005 by John-Wiley & Sons. Fawwaz T. ILABY,
PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Spring Final Exam Wednesday, 6 May 2009
 Name: PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Spring 2009 Final Exam Wednesday, 6 May 2009 This exam has two parts. Part I has 20 multiple choice questions, worth two points each. Part II consists of six relatively
Name: PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Spring 2009 Final Exam Wednesday, 6 May 2009 This exam has two parts. Part I has 20 multiple choice questions, worth two points each. Part II consists of six relatively
NR/RR. Set No. 2 CODE NO: NR/RR210204
 Set No. 2 II B.Tech I Semester Examinations,May 2011 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Electrical And Electronics Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Set No. 2 II B.Tech I Semester Examinations,May 2011 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Electrical And Electronics Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
Dielectric Waveguides and their Use in Solar Cells. Zachariah Peterson
 Dielectric Waveguides and their Use in Solar Cells Zachariah Peterson ABSTRACT In this paper, I discuss a brief history of waveguide technologies, followed by a derivation of the behavior of light in a
Dielectric Waveguides and their Use in Solar Cells Zachariah Peterson ABSTRACT In this paper, I discuss a brief history of waveguide technologies, followed by a derivation of the behavior of light in a
TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide
 1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff
 Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Bragg reflection waveguides with a matching layer
 Bragg reflection waveguides with a matching layer Amit Mizrahi and Levi Schächter Electrical Engineering Department, Technion IIT, Haifa 32, ISRAEL amitmiz@tx.technion.ac.il Abstract: It is demonstrated
Bragg reflection waveguides with a matching layer Amit Mizrahi and Levi Schächter Electrical Engineering Department, Technion IIT, Haifa 32, ISRAEL amitmiz@tx.technion.ac.il Abstract: It is demonstrated
Transmission Lines. Plane wave propagating in air Y unguided wave propagation. Transmission lines / waveguides Y. guided wave propagation
 Transmission Lines Transmission lines and waveguides may be defined as devices used to guide energy from one point to another (from a source to a load). Transmission lines can consist of a set of conductors,
Transmission Lines Transmission lines and waveguides may be defined as devices used to guide energy from one point to another (from a source to a load). Transmission lines can consist of a set of conductors,
Joel A. Shapiro January 21, 2010
 Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 21, 20 rmation Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 21, 20 rmation Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics
 Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light
 1. Objective Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light Understanding the definition of polarized and un-polarized light. Understanding polarizer and analzer definition, Maluse s law. Retarding
1. Objective Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light Understanding the definition of polarized and un-polarized light. Understanding polarizer and analzer definition, Maluse s law. Retarding
Plasmonics. The long wavelength of light ( μm) creates a problem for extending optoelectronics into the nanometer regime.
 Plasmonics The long wavelength of light ( μm) creates a problem for extending optoelectronics into the nanometer regime. A possible way out is the conversion of light into plasmons. They have much shorter
Plasmonics The long wavelength of light ( μm) creates a problem for extending optoelectronics into the nanometer regime. A possible way out is the conversion of light into plasmons. They have much shorter
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
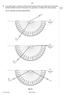 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC
 FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC WAVEGUIDES Chin-ping Yu (1) and Hung-chun Chang (2) (1) Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei,
FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC WAVEGUIDES Chin-ping Yu (1) and Hung-chun Chang (2) (1) Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei,
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
Chapter 5. Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice
 Chapter 5 Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice In chapter 3 and 4, we have demonstrated that the deformed rods, rotational rods and perturbation
Chapter 5 Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice In chapter 3 and 4, we have demonstrated that the deformed rods, rotational rods and perturbation
The Dielectric Function of a Metal ( Jellium )
 The Dielectric Function of a Metal ( Jellium ) Total reflection Plasma frequency p (10 15 Hz range) Why are Metals Shiny? An electric field cannot exist inside a metal, because metal electrons follow the
The Dielectric Function of a Metal ( Jellium ) Total reflection Plasma frequency p (10 15 Hz range) Why are Metals Shiny? An electric field cannot exist inside a metal, because metal electrons follow the
Exam in TFY4240 Electromagnetic Theory Wednesday Dec 9, :00 13:00
 NTNU Page 1 of 5 Institutt for fysikk Contact during the exam: Paul Anton Letnes Telephone: Office: 735 93 648, Mobile: 98 62 08 26 Exam in TFY4240 Electromagnetic Theory Wednesday Dec 9, 2009 09:00 13:00
NTNU Page 1 of 5 Institutt for fysikk Contact during the exam: Paul Anton Letnes Telephone: Office: 735 93 648, Mobile: 98 62 08 26 Exam in TFY4240 Electromagnetic Theory Wednesday Dec 9, 2009 09:00 13:00
Prof. Dr. Magdi El-Saadawi
 Electromagnetic Field Theory 2nd Year EE Students Prof. Dr. Magdi El-Saadawi www.saadawi1.net saadawi1@gmail.com 2015/2016 1 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction and Course Objectives Chapter 2 Vector Algebra
Electromagnetic Field Theory 2nd Year EE Students Prof. Dr. Magdi El-Saadawi www.saadawi1.net saadawi1@gmail.com 2015/2016 1 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction and Course Objectives Chapter 2 Vector Algebra
Imaging Chain. Imaging Chain. Imaging Chain. 1. Light source. 2. Object interactions. 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors)
 1. Light source λ [nm] sunset blue sky 2. Object interactions 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors) 1 Optics: Lenses Objects Images Optics: Mirrors Object Image 4. Detector or Sensor Photographic
1. Light source λ [nm] sunset blue sky 2. Object interactions 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors) 1 Optics: Lenses Objects Images Optics: Mirrors Object Image 4. Detector or Sensor Photographic
Dispersion Properties of Photonic Crystal Fiber with Four cusped Hypocycloidal Air Holes in Cladding
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 1, Issue 1, Ver. III (Jan.-Feb. 17), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Dispersion Properties of
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 1, Issue 1, Ver. III (Jan.-Feb. 17), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Dispersion Properties of
Teaching Electromagnetic Waves in Effective and Enjoyable Fashion
 Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Teaching Electromagnetic Waves in Effective and Enjoyable Fashion Raghunath K Shevgaonkar IIT Bombay Presented at IEEE-INAE
Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Teaching Electromagnetic Waves in Effective and Enjoyable Fashion Raghunath K Shevgaonkar IIT Bombay Presented at IEEE-INAE
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light
 Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
ELECTROMAGNETIC ENVIRONMENT GENERATED IN A TEM CELL FOR BIOLOGICAL DOSIMETRY APPLICATIONS
 ISEF 2007 XIII International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering Prague, Czech Republic, September 13-15, 2007 ELECTROMAGNETIC ENVIRONMENT GENERATED
ISEF 2007 XIII International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering Prague, Czech Republic, September 13-15, 2007 ELECTROMAGNETIC ENVIRONMENT GENERATED
Waveguide Principles
 CHAPTER 8 Waveguide Principles In Chapter 6, we introduced transmission lines, and in Chapter 7, we studied their analysis. We learned that transmission lines are made up of two (or more) parallel conductors.
CHAPTER 8 Waveguide Principles In Chapter 6, we introduced transmission lines, and in Chapter 7, we studied their analysis. We learned that transmission lines are made up of two (or more) parallel conductors.
Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves
 Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves Wave equations Why do electromagnetic waves arise? What are their properties? How do they transport energy from place to place? Recap (1) In a region of space containing
Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves Wave equations Why do electromagnetic waves arise? What are their properties? How do they transport energy from place to place? Recap (1) In a region of space containing
Module 9 : Infinite Series, Tests of Convergence, Absolute and Conditional Convergence, Taylor and Maclaurin Series
 Module 9 : Infinite Series, Tests of Convergence, Absolute and Conditional Convergence, Taylor and Maclaurin Series Lecture 27 : Series of functions [Section 271] Objectives In this section you will learn
Module 9 : Infinite Series, Tests of Convergence, Absolute and Conditional Convergence, Taylor and Maclaurin Series Lecture 27 : Series of functions [Section 271] Objectives In this section you will learn
Constructing Potential Energy Diagrams
 potential ENERGY diagrams Visual Quantum Mechanics Teac eaching Guide ACTIVITY 2 Constructing Potential Energy Diagrams Goal In this activity, you will explore energy diagrams for magnets in repulsive
potential ENERGY diagrams Visual Quantum Mechanics Teac eaching Guide ACTIVITY 2 Constructing Potential Energy Diagrams Goal In this activity, you will explore energy diagrams for magnets in repulsive
Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236. Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization
 Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236 Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization 1 Electromagnetic Radiation The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source to illuminate the target.
Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236 Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization 1 Electromagnetic Radiation The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source to illuminate the target.
Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. #07 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation in Plasma Today, I begin a new topic that is electromagnetic
Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. #07 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation in Plasma Today, I begin a new topic that is electromagnetic
USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION
 October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
SURFACE PLASMONS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS IN ELECTRO-OPTICAL DEVICES
 SURFACE PLASMONS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS IN ELECTRO-OPTICAL DEVICES Igor Zozouleno Solid State Electronics Department of Science and Technology Linöping University Sweden igozo@itn.liu.se http://www.itn.liu.se/meso-phot
SURFACE PLASMONS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS IN ELECTRO-OPTICAL DEVICES Igor Zozouleno Solid State Electronics Department of Science and Technology Linöping University Sweden igozo@itn.liu.se http://www.itn.liu.se/meso-phot
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
COMSOL Design Tool: Simulations of Optical Components Week 6: Waveguides and propagation S matrix
 COMSOL Design Tool: Simulations of Optical Components Week 6: Waveguides and propagation S matrix Nikola Dordevic and Yannick Salamin 30.10.2017 1 Content Revision Wave Propagation Losses Wave Propagation
COMSOL Design Tool: Simulations of Optical Components Week 6: Waveguides and propagation S matrix Nikola Dordevic and Yannick Salamin 30.10.2017 1 Content Revision Wave Propagation Losses Wave Propagation
CONTROL OF MICROWAVE HEATING IN RECTANGULAR WAVEGUIDE
 ISTP-16, 2005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA CONTROL OF MICROWAVE HEATING IN RECTANGULAR WAVEGUIDE Kazuo AOKI*, Masatoshi AKAHORI*, Kenji OSHIMA** and Masato MORITA* *Nagaoka
ISTP-16, 2005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA CONTROL OF MICROWAVE HEATING IN RECTANGULAR WAVEGUIDE Kazuo AOKI*, Masatoshi AKAHORI*, Kenji OSHIMA** and Masato MORITA* *Nagaoka
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F)
 B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
TASK A. TRANSMISSION LINE AND DISCONTINUITIES
 TASK A. TRANSMISSION LINE AND DISCONTINUITIES Task A. Transmission Line and Discontinuities... 1 A.I. TEM Transmission Line... A.I.1. Circuit Representation of a Uniform Transmission Line... A.I.. Time
TASK A. TRANSMISSION LINE AND DISCONTINUITIES Task A. Transmission Line and Discontinuities... 1 A.I. TEM Transmission Line... A.I.1. Circuit Representation of a Uniform Transmission Line... A.I.. Time
Module 5 : MODERN PHYSICS Lecture 23 : Particle and Waves
 Module 5 : MODERN PHYSICS Lecture 23 : Particle and Waves Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Radiation (light) exhibits both wave and particle nature. Laws governing black body radiation,
Module 5 : MODERN PHYSICS Lecture 23 : Particle and Waves Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Radiation (light) exhibits both wave and particle nature. Laws governing black body radiation,
feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field matching
 CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
UNIT 1. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Electronics & Communication Engineering Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun
 UNIT 1 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Electronics & Communication Engineering Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus Introduction: Demand of Information Age, Block Diagram
UNIT 1 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Electronics & Communication Engineering Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus Introduction: Demand of Information Age, Block Diagram
CHAPTER 2. COULOMB S LAW AND ELECTRONIC FIELD INTENSITY. 2.3 Field Due to a Continuous Volume Charge Distribution
 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light
 Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Novel Features of Computational EM and Particle-in-Cell Simulations. Shahid Ahmed. Illinois Institute of Technology
 Novel Features of Computational EM and Particle-in-Cell Simulations Shahid Ahmed Illinois Institute of Technology Outline Part-I EM Structure Motivation Method Modes, Radiation Leakage and HOM Damper Conclusions
Novel Features of Computational EM and Particle-in-Cell Simulations Shahid Ahmed Illinois Institute of Technology Outline Part-I EM Structure Motivation Method Modes, Radiation Leakage and HOM Damper Conclusions
Supplementary Information
 S1 Supplementary Information S2 Forward Backward Forward Backward Normalized to Normalized to Supplementary Figure 1 Maximum local field ratio and transmission coefficient. Maximum local field ratio (green
S1 Supplementary Information S2 Forward Backward Forward Backward Normalized to Normalized to Supplementary Figure 1 Maximum local field ratio and transmission coefficient. Maximum local field ratio (green
Lecture 2 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Lecture Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Dispersion Introduction - An electromagnetic wave with an arbitrary wave-shape
Lecture Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Dispersion Introduction - An electromagnetic wave with an arbitrary wave-shape
Plane Wave: Introduction
 Plane Wave: Introduction According to Mawell s equations a timevarying electric field produces a time-varying magnetic field and conversely a time-varying magnetic field produces an electric field ( i.e.
Plane Wave: Introduction According to Mawell s equations a timevarying electric field produces a time-varying magnetic field and conversely a time-varying magnetic field produces an electric field ( i.e.
DIELECTRIC waveguides and dielectric-loaded metallic
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL 46, NO 7, JULY 1998 975 Transfer Matrix Function (TMF) for Wave Propagation in Dielectric Waveguides With Arbitrary Transverse Profiles Zion Menachem
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL 46, NO 7, JULY 1998 975 Transfer Matrix Function (TMF) for Wave Propagation in Dielectric Waveguides With Arbitrary Transverse Profiles Zion Menachem
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS
 L21-1 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS Free-Space Propagation: Similar to radiowaves (but more absorption by clouds, haze) Same expressions: antenna gain, effective area, power received Examples: TV controllers,
L21-1 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS Free-Space Propagation: Similar to radiowaves (but more absorption by clouds, haze) Same expressions: antenna gain, effective area, power received Examples: TV controllers,
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R.K. Shevagaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R.K. Shevagaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 02 Basics of Light In the last lecture, we discuss the
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R.K. Shevagaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 02 Basics of Light In the last lecture, we discuss the
School of Electronics Engineering (SENSE)
 School of Electronics Engineering (SENSE) B.Tech (Electronics & Communication Engineering) CURRICULUM [Curriculum for Applied Learning (CAL)] Sl. No Category Total number of Credits 1 University Core (UC)
School of Electronics Engineering (SENSE) B.Tech (Electronics & Communication Engineering) CURRICULUM [Curriculum for Applied Learning (CAL)] Sl. No Category Total number of Credits 1 University Core (UC)
Thin Ribbon Tapered Coupler for Dielectric Waveguide/Optical Fiber?
 Thin Ribbon Tapered Coupler for Dielectric Waveguide/Optical Fiber? C. Yeh * and T, Y. Otoski Jet Propulsion Laboratory California nstitute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 F.. Shimabukuro Aerospace Corporation
Thin Ribbon Tapered Coupler for Dielectric Waveguide/Optical Fiber? C. Yeh * and T, Y. Otoski Jet Propulsion Laboratory California nstitute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 F.. Shimabukuro Aerospace Corporation
