Set Notation and the Real Numbers
|
|
|
- Walter Mosley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Set Notation and the Real Numbers Oh, and some stuff on functions, too 1
2 Elementary Set Theory Vocabulary: Set Element Subset Union Intersection Set Difference Disjoint A intersects B Empty set or null set Symbols: a A {x x is } A B or A B A B A B Ø A B or A B AxB 2
3 Functions Vocabulary: Domain Range Image Identity function Inverse function Pre Image or Inverse Image Composition of Functions One to one Onto One to one correspondence Symbols: f(a) (a is an element) f(a) (A is a set) f 1 1 (Inverse function) f 1 (B) (B is a set) f 1 (b) (b is an element) f g 3
4 Functions For us, a function from a set A to a set B is a rule that assigns to each element x of A a unique element f(x) of B. The set A is the domain of the function, the set B is the range. For us, the domain and range are part of the definition of a function. Thus we would not say that f(x)=3x+7 defines a function until the domain and range were specified. 4
5 Functions 2 Thus, the function f : defined by f () x = x is not the same as the function g: [0, ) defined by gx 2 () = x. This is the real point of a function being onto or not; the function f is not onto, while the function g is onto. (So for us, the answer to the typical calculus problem that asks, what is the range? is, You tell me! ) 5
6 We use the real numbers in the axioms of our particular brand of geometry. For the most part, our ordinary everyday knowledge of real numbers (e.g. knowing how to order them and do arithmetic with them) will do. However, there are a few places where we will rely on their deeper properties. We will list a few of them here. 6
7 Trichotomy: Given any two real numbers x and y, exactly one of the following is true: x < y x = y, or x > y. This is equivalent to saying that every real number is either positive, negative or 0. We will use this when we prove that linear pairs are supplementary. 7
8 Density: Between every two real numbers a and b, there is a rational number between a and b, and there is an irrational number between a and b. This is equivalent to saying that both the rational numbers and irrational numbers are dense in the real numbers. 8
9 Archimedean Property: If M and ε are any two positive real numbers, then there exists a positive integer n such that nε > M. If you think of M as very big and ε as very small, this says simply that if you take enough (i.e. n) copies of something small (ε), you can get as big as you want (M). We will use this later in proving facts about similarity. il i 9
10 Completeness: Thecompleteness propertyofof the real numbers has several different equivalent formulations, some of which are better suited for some purposes than others. We need a couple of definitions: Definition: A number b is called an upper bound for a set A of real numbers provided x a for every real number a in A. 10
11 Definition: A number l is called the least upper bound for a set A provided it is an upper bound for A and l b for every other upper bound b of A. Now we can state a couple of equivalent versions of completeness: 11
12 (Least Upper Bound Property): Every nonempty set of real numbers that has an upper bound has a least upper bound. Every bounded increasing sequence of real numbers converges. Every Cauchy sequence of real numbers converges. 12
13 This basic property of real numbers assures us that limits exist, and is the foundation for calculus. We ll use these properties a few times, e.g. in the proof of circular continuity and theproof of the Saccheri Legendre Theorem. 13
Axioms for the Real Number System
 Axioms for the Real Number System Math 361 Fall 2003 Page 1 of 9 The Real Number System The real number system consists of four parts: 1. A set (R). We will call the elements of this set real numbers,
Axioms for the Real Number System Math 361 Fall 2003 Page 1 of 9 The Real Number System The real number system consists of four parts: 1. A set (R). We will call the elements of this set real numbers,
Sets and Functions. MATH 464/506, Real Analysis. J. Robert Buchanan. Summer Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Sets and Functions
 Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend N to the integers
 Chapter 1 The Real Numbers 1.1. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {1, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers 1.1. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {1, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need
In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend N to the integers
 Chapter The Real Numbers.. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend
Chapter The Real Numbers.. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend
THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4
 FOUNDATIONS OF ANALYSIS FALL 2008 TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4 (1) Every element in a field has a multiplicative inverse. (2) In a field the additive inverse of 1 is 0. (3) In a field
FOUNDATIONS OF ANALYSIS FALL 2008 TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4 (1) Every element in a field has a multiplicative inverse. (2) In a field the additive inverse of 1 is 0. (3) In a field
Consequences of the Completeness Property
 Consequences of the Completeness Property Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of the Completeness Property Today 1 / 10 Introduction In this section, we use the fact that R
Consequences of the Completeness Property Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of the Completeness Property Today 1 / 10 Introduction In this section, we use the fact that R
That is, there is an element
 Section 3.1: Mathematical Induction Let N denote the set of natural numbers (positive integers). N = {1, 2, 3, 4, } Axiom: If S is a nonempty subset of N, then S has a least element. That is, there is
Section 3.1: Mathematical Induction Let N denote the set of natural numbers (positive integers). N = {1, 2, 3, 4, } Axiom: If S is a nonempty subset of N, then S has a least element. That is, there is
MAS331: Metric Spaces Problems on Chapter 1
 MAS331: Metric Spaces Problems on Chapter 1 1. In R 3, find d 1 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)), d 2 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)) and d ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)). 2. In R 4, show that d 1 ((4, 4, 4, 6), (0, 0, 0, 0)) =
MAS331: Metric Spaces Problems on Chapter 1 1. In R 3, find d 1 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)), d 2 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)) and d ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)). 2. In R 4, show that d 1 ((4, 4, 4, 6), (0, 0, 0, 0)) =
Functions and relations
 Functions and relations Relations Set rules & symbols Sets of numbers Sets & intervals Functions Relations Function notation Hybrid functions Hyperbola Truncus Square root Circle Inverse functions 2 Relations
Functions and relations Relations Set rules & symbols Sets of numbers Sets & intervals Functions Relations Function notation Hybrid functions Hyperbola Truncus Square root Circle Inverse functions 2 Relations
2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom
 60 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom In this section, we use the fact that R is complete to establish some important results. First, we will prove that
60 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom In this section, we use the fact that R is complete to establish some important results. First, we will prove that
MIDTERM REVIEW FOR MATH The limit
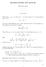 MIDTERM REVIEW FOR MATH 500 SHUANGLIN SHAO. The limit Define lim n a n = A: For any ε > 0, there exists N N such that for any n N, a n A < ε. The key in this definition is to realize that the choice of
MIDTERM REVIEW FOR MATH 500 SHUANGLIN SHAO. The limit Define lim n a n = A: For any ε > 0, there exists N N such that for any n N, a n A < ε. The key in this definition is to realize that the choice of
Problem Set 2: Solutions Math 201A: Fall 2016
 Problem Set 2: s Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. (a) Prove that a closed subset of a complete metric space is complete. (b) Prove that a closed subset of a compact metric space is compact. (c) Prove that
Problem Set 2: s Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. (a) Prove that a closed subset of a complete metric space is complete. (b) Prove that a closed subset of a compact metric space is compact. (c) Prove that
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition
 Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Discrete Mathematics. W. Ethan Duckworth. Fall 2017, Loyola University Maryland
 Discrete Mathematics W. Ethan Duckworth Fall 2017, Loyola University Maryland Contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Statements......................................... 4 1.2 Constructing Direct Proofs................................
Discrete Mathematics W. Ethan Duckworth Fall 2017, Loyola University Maryland Contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Statements......................................... 4 1.2 Constructing Direct Proofs................................
VCE. VCE Maths Methods 1 and 2 Pocket Study Guide
 VCE VCE Maths Methods 1 and 2 Pocket Study Guide Contents Introduction iv 1 Linear functions 1 2 Quadratic functions 10 3 Cubic functions 16 4 Advanced functions and relations 24 5 Probability and simulation
VCE VCE Maths Methods 1 and 2 Pocket Study Guide Contents Introduction iv 1 Linear functions 1 2 Quadratic functions 10 3 Cubic functions 16 4 Advanced functions and relations 24 5 Probability and simulation
Chapter 0: Sets and Numbers
 Haberman MTH 112 Section I: Periodic Functions and Trigonometry Chapter 0: Sets and Numbers DEFINITION: A set is a collection of objects specified in a manner that enables one to determine if a given object
Haberman MTH 112 Section I: Periodic Functions and Trigonometry Chapter 0: Sets and Numbers DEFINITION: A set is a collection of objects specified in a manner that enables one to determine if a given object
Sequences. Chapter 3. n + 1 3n + 2 sin n n. 3. lim (ln(n + 1) ln n) 1. lim. 2. lim. 4. lim (1 + n)1/n. Answers: 1. 1/3; 2. 0; 3. 0; 4. 1.
 Chapter 3 Sequences Both the main elements of calculus (differentiation and integration) require the notion of a limit. Sequences will play a central role when we work with limits. Definition 3.. A Sequence
Chapter 3 Sequences Both the main elements of calculus (differentiation and integration) require the notion of a limit. Sequences will play a central role when we work with limits. Definition 3.. A Sequence
HW 4 SOLUTIONS. , x + x x 1 ) 2
 HW 4 SOLUTIONS The Way of Analysis p. 98: 1.) Suppose that A is open. Show that A minus a finite set is still open. This follows by induction as long as A minus one point x is still open. To see that A
HW 4 SOLUTIONS The Way of Analysis p. 98: 1.) Suppose that A is open. Show that A minus a finite set is still open. This follows by induction as long as A minus one point x is still open. To see that A
NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination. Answer Key
 NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination Answer Key 1 1. [25 points] Let X be a set with 2 or more elements. Show that there are topologies U and V on X such that the identity map J : (X, U)
NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination Answer Key 1 1. [25 points] Let X be a set with 2 or more elements. Show that there are topologies U and V on X such that the identity map J : (X, U)
Describing the Real Numbers
 Describing the Real Numbers Anthony Várilly Math 25a, Fall 2001 1 Introduction The goal of these notes is to uniquely describe the real numbers by taking certain statements as axioms. This exercise might
Describing the Real Numbers Anthony Várilly Math 25a, Fall 2001 1 Introduction The goal of these notes is to uniquely describe the real numbers by taking certain statements as axioms. This exercise might
Essential Background for Real Analysis I (MATH 5210)
 Background Material 1 Essential Background for Real Analysis I (MATH 5210) Note. These notes contain several definitions, theorems, and examples from Analysis I (MATH 4217/5217) which you must know for
Background Material 1 Essential Background for Real Analysis I (MATH 5210) Note. These notes contain several definitions, theorems, and examples from Analysis I (MATH 4217/5217) which you must know for
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES. Contents. 1. Sets Functions Countability Axiom of choice Equivalence relations 9
 MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
DR.RUPNATHJI( DR.RUPAK NATH )
 Contents 1 Sets 1 2 The Real Numbers 9 3 Sequences 29 4 Series 59 5 Functions 81 6 Power Series 105 7 The elementary functions 111 Chapter 1 Sets It is very convenient to introduce some notation and terminology
Contents 1 Sets 1 2 The Real Numbers 9 3 Sequences 29 4 Series 59 5 Functions 81 6 Power Series 105 7 The elementary functions 111 Chapter 1 Sets It is very convenient to introduce some notation and terminology
Structure of R. Chapter Algebraic and Order Properties of R
 Chapter Structure of R We will re-assemble calculus by first making assumptions about the real numbers. All subsequent results will be rigorously derived from these assumptions. Most of the assumptions
Chapter Structure of R We will re-assemble calculus by first making assumptions about the real numbers. All subsequent results will be rigorously derived from these assumptions. Most of the assumptions
Introduction to Proofs in Analysis. updated December 5, By Edoh Y. Amiran Following the outline of notes by Donald Chalice INTRODUCTION
 Introduction to Proofs in Analysis updated December 5, 2016 By Edoh Y. Amiran Following the outline of notes by Donald Chalice INTRODUCTION Purpose. These notes intend to introduce four main notions from
Introduction to Proofs in Analysis updated December 5, 2016 By Edoh Y. Amiran Following the outline of notes by Donald Chalice INTRODUCTION Purpose. These notes intend to introduce four main notions from
POL502: Foundations. Kosuke Imai Department of Politics, Princeton University. October 10, 2005
 POL502: Foundations Kosuke Imai Department of Politics, Princeton University October 10, 2005 Our first task is to develop the foundations that are necessary for the materials covered in this course. 1
POL502: Foundations Kosuke Imai Department of Politics, Princeton University October 10, 2005 Our first task is to develop the foundations that are necessary for the materials covered in this course. 1
Properties of the Integers
 Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
a + b = b + a and a b = b a. (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) and (a b) c = a (b c). a (b + c) = a b + a c and (a + b) c = a c + b c.
 Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Theorem. For every positive integer n, the sum of the positive integers from 1 to n is n(n+1)
 Week 1: Logic Lecture 1, 8/1 (Sections 1.1 and 1.3) Examples of theorems and proofs Theorem (Pythagoras). Let ABC be a right triangle, with legs of lengths a and b, and hypotenuse of length c. Then a +
Week 1: Logic Lecture 1, 8/1 (Sections 1.1 and 1.3) Examples of theorems and proofs Theorem (Pythagoras). Let ABC be a right triangle, with legs of lengths a and b, and hypotenuse of length c. Then a +
A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY
 A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY 1. NOTATION Before we begin some notational definitions are useful. (1) Z = {, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, }is the set of integers. (2) Q = { a b : aεz, bεz {0}} is the set
A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY 1. NOTATION Before we begin some notational definitions are useful. (1) Z = {, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, }is the set of integers. (2) Q = { a b : aεz, bεz {0}} is the set
Economics 204 Fall 2012 Problem Set 3 Suggested Solutions
 Economics 204 Fall 2012 Problem Set 3 Suggested Solutions 1. Give an example of each of the following (and prove that your example indeed works): (a) A complete metric space that is bounded but not compact.
Economics 204 Fall 2012 Problem Set 3 Suggested Solutions 1. Give an example of each of the following (and prove that your example indeed works): (a) A complete metric space that is bounded but not compact.
Practice Test III, Math 314, Spring 2016
 Practice Test III, Math 314, Spring 2016 Dr. Holmes April 26, 2016 This is the 2014 test reorganized to be more readable. I like it as a review test. The students who took this test had to do four sections
Practice Test III, Math 314, Spring 2016 Dr. Holmes April 26, 2016 This is the 2014 test reorganized to be more readable. I like it as a review test. The students who took this test had to do four sections
Lecture 2: A crash course in Real Analysis
 EE5110: Probability Foundations for Electrical Engineers July-November 2015 Lecture 2: A crash course in Real Analysis Lecturer: Dr. Krishna Jagannathan Scribe: Sudharsan Parthasarathy This lecture is
EE5110: Probability Foundations for Electrical Engineers July-November 2015 Lecture 2: A crash course in Real Analysis Lecturer: Dr. Krishna Jagannathan Scribe: Sudharsan Parthasarathy This lecture is
Number Axioms. P. Danziger. A Group is a set S together with a binary operation (*) on S, denoted a b such that for all a, b. a b S.
 Appendix A Number Axioms P. Danziger 1 Number Axioms 1.1 Groups Definition 1 A Group is a set S together with a binary operation (*) on S, denoted a b such that for all a, b and c S 0. (Closure) 1. (Associativity)
Appendix A Number Axioms P. Danziger 1 Number Axioms 1.1 Groups Definition 1 A Group is a set S together with a binary operation (*) on S, denoted a b such that for all a, b and c S 0. (Closure) 1. (Associativity)
Some Background Material
 Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
MAT 417, Fall 2017, CRN: 1766 Real Analysis: A First Course
 MAT 47, Fall 207, CRN: 766 Real Analysis: A First Course Prerequisites: MAT 263 & MAT 300 Instructor: Daniel Cunningham What is Real Analysis? Real Analysis is the important branch of mathematics that
MAT 47, Fall 207, CRN: 766 Real Analysis: A First Course Prerequisites: MAT 263 & MAT 300 Instructor: Daniel Cunningham What is Real Analysis? Real Analysis is the important branch of mathematics that
1 Chapter 1: SETS. 1.1 Describing a set
 1 Chapter 1: SETS set is a collection of objects The objects of the set are called elements or members Use capital letters :, B, C, S, X, Y to denote the sets Use lower case letters to denote the elements:
1 Chapter 1: SETS set is a collection of objects The objects of the set are called elements or members Use capital letters :, B, C, S, X, Y to denote the sets Use lower case letters to denote the elements:
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers
 Chapter 1 The Real Numbers In a beginning course in calculus, the emphasis is on introducing the techniques of the subject;i.e., differentiation and integration and their applications. An advanced calculus
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers In a beginning course in calculus, the emphasis is on introducing the techniques of the subject;i.e., differentiation and integration and their applications. An advanced calculus
2.1 Sets. Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R.
 2. Basic Structures 2.1 Sets Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R. Definition 2 Objects in a set are called elements or members of the set. A set is
2. Basic Structures 2.1 Sets Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R. Definition 2 Objects in a set are called elements or members of the set. A set is
Continuity. Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
FRACTAL GEOMETRY, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND CHAOS
 FRACTAL GEOMETRY, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND CHAOS MIDTERM SOLUTIONS. Let f : R R be the map on the line generated by the function f(x) = x 3. Find all the fixed points of f and determine the type of their
FRACTAL GEOMETRY, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND CHAOS MIDTERM SOLUTIONS. Let f : R R be the map on the line generated by the function f(x) = x 3. Find all the fixed points of f and determine the type of their
MAT115A-21 COMPLETE LECTURE NOTES
 MAT115A-21 COMPLETE LECTURE NOTES NATHANIEL GALLUP 1. Introduction Number theory begins as the study of the natural numbers the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...}, Z = { 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}, and sometimes
MAT115A-21 COMPLETE LECTURE NOTES NATHANIEL GALLUP 1. Introduction Number theory begins as the study of the natural numbers the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...}, Z = { 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}, and sometimes
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project
 Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
Continuity. Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
Economics 204 Fall 2011 Problem Set 2 Suggested Solutions
 Economics 24 Fall 211 Problem Set 2 Suggested Solutions 1. Determine whether the following sets are open, closed, both or neither under the topology induced by the usual metric. (Hint: think about limit
Economics 24 Fall 211 Problem Set 2 Suggested Solutions 1. Determine whether the following sets are open, closed, both or neither under the topology induced by the usual metric. (Hint: think about limit
1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
Why write proofs? Why not just test and repeat enough examples to confirm a theory?
 P R E F A C E T O T H E S T U D E N T Welcome to the study of mathematical reasoning. The authors know that many students approach this material with some apprehension and uncertainty. Some students feel
P R E F A C E T O T H E S T U D E N T Welcome to the study of mathematical reasoning. The authors know that many students approach this material with some apprehension and uncertainty. Some students feel
MATH 131A: REAL ANALYSIS (BIG IDEAS)
 MATH 131A: REAL ANALYSIS (BIG IDEAS) Theorem 1 (The Triangle Inequality). For all x, y R we have x + y x + y. Proposition 2 (The Archimedean property). For each x R there exists an n N such that n > x.
MATH 131A: REAL ANALYSIS (BIG IDEAS) Theorem 1 (The Triangle Inequality). For all x, y R we have x + y x + y. Proposition 2 (The Archimedean property). For each x R there exists an n N such that n > x.
Due date: Monday, February 6, 2017.
 Modern Analysis Homework 3 Solutions Due date: Monday, February 6, 2017. 1. If A R define A = {x R : x A}. Let A be a nonempty set of real numbers, assume A is bounded above. Prove that A is bounded below
Modern Analysis Homework 3 Solutions Due date: Monday, February 6, 2017. 1. If A R define A = {x R : x A}. Let A be a nonempty set of real numbers, assume A is bounded above. Prove that A is bounded below
3.1 Basic properties of real numbers - continuation Inmum and supremum of a set of real numbers
 Chapter 3 Real numbers The notion of real number was introduced in section 1.3 where the axiomatic denition of the set of all real numbers was done and some basic properties of the set of all real numbers
Chapter 3 Real numbers The notion of real number was introduced in section 1.3 where the axiomatic denition of the set of all real numbers was done and some basic properties of the set of all real numbers
METRIC SPACES KEITH CONRAD
 METRIC SPACES KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction As calculus developed, eventually turning into analysis, concepts first explored on the real line (e.g., a limit of a sequence of real numbers) eventually extended
METRIC SPACES KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction As calculus developed, eventually turning into analysis, concepts first explored on the real line (e.g., a limit of a sequence of real numbers) eventually extended
P-adic Functions - Part 1
 P-adic Functions - Part 1 Nicolae Ciocan 22.11.2011 1 Locally constant functions Motivation: Another big difference between p-adic analysis and real analysis is the existence of nontrivial locally constant
P-adic Functions - Part 1 Nicolae Ciocan 22.11.2011 1 Locally constant functions Motivation: Another big difference between p-adic analysis and real analysis is the existence of nontrivial locally constant
Walker Ray Econ 204 Problem Set 3 Suggested Solutions August 6, 2015
 Problem 1. Take any mapping f from a metric space X into a metric space Y. Prove that f is continuous if and only if f(a) f(a). (Hint: use the closed set characterization of continuity). I make use of
Problem 1. Take any mapping f from a metric space X into a metric space Y. Prove that f is continuous if and only if f(a) f(a). (Hint: use the closed set characterization of continuity). I make use of
One-to-one functions and onto functions
 MA 3362 Lecture 7 - One-to-one and Onto Wednesday, October 22, 2008. Objectives: Formalize definitions of one-to-one and onto One-to-one functions and onto functions At the level of set theory, there are
MA 3362 Lecture 7 - One-to-one and Onto Wednesday, October 22, 2008. Objectives: Formalize definitions of one-to-one and onto One-to-one functions and onto functions At the level of set theory, there are
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project
 Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement. sentential connectives. negation. conjunction. disjunction
 Copyright & License Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement sentential connectives negation conjunction disjunction implication or conditional antecedant & consequent hypothesis
Copyright & License Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement sentential connectives negation conjunction disjunction implication or conditional antecedant & consequent hypothesis
18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions
 18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Extension theorems Characterizing measures on R d Random variables Outline Extension theorems Characterizing
18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Extension theorems Characterizing measures on R d Random variables Outline Extension theorems Characterizing
Analysis I. Classroom Notes. H.-D. Alber
 Analysis I Classroom Notes H-D Alber Contents 1 Fundamental notions 1 11 Sets 1 12 Product sets, relations 5 13 Composition of statements 7 14 Quantifiers, negation of statements 9 2 Real numbers 11 21
Analysis I Classroom Notes H-D Alber Contents 1 Fundamental notions 1 11 Sets 1 12 Product sets, relations 5 13 Composition of statements 7 14 Quantifiers, negation of statements 9 2 Real numbers 11 21
Numbers 1. 1 Overview. 2 The Integers, Z. John Nachbar Washington University in St. Louis September 22, 2017
 John Nachbar Washington University in St. Louis September 22, 2017 1 Overview. Numbers 1 The Set Theory notes show how to construct the set of natural numbers N out of nothing (more accurately, out of
John Nachbar Washington University in St. Louis September 22, 2017 1 Overview. Numbers 1 The Set Theory notes show how to construct the set of natural numbers N out of nothing (more accurately, out of
Math 105A HW 1 Solutions
 Sect. 1.1.3: # 2, 3 (Page 7-8 Math 105A HW 1 Solutions 2(a ( Statement: Each positive integers has a unique prime factorization. n N: n = 1 or ( R N, p 1,..., p R P such that n = p 1 p R and ( n, R, S
Sect. 1.1.3: # 2, 3 (Page 7-8 Math 105A HW 1 Solutions 2(a ( Statement: Each positive integers has a unique prime factorization. n N: n = 1 or ( R N, p 1,..., p R P such that n = p 1 p R and ( n, R, S
Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics. Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics
 Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics An Introductory Single Variable Real Analysis: A Learning Approach through Problem Solving Marcel B. Finan c All Rights
Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics An Introductory Single Variable Real Analysis: A Learning Approach through Problem Solving Marcel B. Finan c All Rights
Real Analysis Notes. Thomas Goller
 Real Analysis Notes Thomas Goller September 4, 2011 Contents 1 Abstract Measure Spaces 2 1.1 Basic Definitions........................... 2 1.2 Measurable Functions........................ 2 1.3 Integration..............................
Real Analysis Notes Thomas Goller September 4, 2011 Contents 1 Abstract Measure Spaces 2 1.1 Basic Definitions........................... 2 1.2 Measurable Functions........................ 2 1.3 Integration..............................
Maths 212: Homework Solutions
 Maths 212: Homework Solutions 1. The definition of A ensures that x π for all x A, so π is an upper bound of A. To show it is the least upper bound, suppose x < π and consider two cases. If x < 1, then
Maths 212: Homework Solutions 1. The definition of A ensures that x π for all x A, so π is an upper bound of A. To show it is the least upper bound, suppose x < π and consider two cases. If x < 1, then
Chapter One. The Real Number System
 Chapter One. The Real Number System We shall give a quick introduction to the real number system. It is imperative that we know how the set of real numbers behaves in the way that its completeness and
Chapter One. The Real Number System We shall give a quick introduction to the real number system. It is imperative that we know how the set of real numbers behaves in the way that its completeness and
Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics.
 MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
Mathematics-I Prof. S.K. Ray Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Lecture 1 Real Numbers
 Mathematics-I Prof. S.K. Ray Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 1 Real Numbers In these lectures, we are going to study a branch of mathematics called
Mathematics-I Prof. S.K. Ray Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 1 Real Numbers In these lectures, we are going to study a branch of mathematics called
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes
 Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
MAS3706 Topology. Revision Lectures, May I do not answer enquiries as to what material will be in the exam.
 MAS3706 Topology Revision Lectures, May 208 Z.A.Lykova It is essential that you read and try to understand the lecture notes from the beginning to the end. Many questions from the exam paper will be similar
MAS3706 Topology Revision Lectures, May 208 Z.A.Lykova It is essential that you read and try to understand the lecture notes from the beginning to the end. Many questions from the exam paper will be similar
Supplementary Material for MTH 299 Online Edition
 Supplementary Material for MTH 299 Online Edition Abstract This document contains supplementary material, such as definitions, explanations, examples, etc., to complement that of the text, How to Think
Supplementary Material for MTH 299 Online Edition Abstract This document contains supplementary material, such as definitions, explanations, examples, etc., to complement that of the text, How to Think
Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 5 Friday July 29, 2011
 Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 5 Friday July 29, 2011 Section 2.6 (cont.) Properties of Real Functions Here we first study properties of functions from R to R, making use of the additional structure
Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 5 Friday July 29, 2011 Section 2.6 (cont.) Properties of Real Functions Here we first study properties of functions from R to R, making use of the additional structure
Chapter Summary. Sets The Language of Sets Set Operations Set Identities Functions Types of Functions Operations on Functions Computability
 Chapter 2 1 Chapter Summary Sets The Language of Sets Set Operations Set Identities Functions Types of Functions Operations on Functions Computability Sequences and Summations Types of Sequences Summation
Chapter 2 1 Chapter Summary Sets The Language of Sets Set Operations Set Identities Functions Types of Functions Operations on Functions Computability Sequences and Summations Types of Sequences Summation
 1 of 8 7/15/2009 3:43 PM Virtual Laboratories > 1. Foundations > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6. Cardinality Definitions and Preliminary Examples Suppose that S is a non-empty collection of sets. We define a relation
1 of 8 7/15/2009 3:43 PM Virtual Laboratories > 1. Foundations > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6. Cardinality Definitions and Preliminary Examples Suppose that S is a non-empty collection of sets. We define a relation
Finite and infinite sets, and cardinality
 (1/17) MA180/186/190 : Semester 2 Calculus http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ma180-2 Niall Madden (Niall.Madden@NUIGalway.ie) Finite and infinite sets, and cardinality Lecture 02: Tuesday, 8 January 2013 Today:
(1/17) MA180/186/190 : Semester 2 Calculus http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ma180-2 Niall Madden (Niall.Madden@NUIGalway.ie) Finite and infinite sets, and cardinality Lecture 02: Tuesday, 8 January 2013 Today:
MATH 23b, SPRING 2005 THEORETICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA AND MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Midterm (part 1) Solutions March 21, 2005
 MATH 23b, SPRING 2005 THEORETICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA AND MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Midterm (part 1) Solutions March 21, 2005 1. True or False (22 points, 2 each) T or F Every set in R n is either open or closed
MATH 23b, SPRING 2005 THEORETICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA AND MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Midterm (part 1) Solutions March 21, 2005 1. True or False (22 points, 2 each) T or F Every set in R n is either open or closed
Numbers, sets, and functions
 Chapter 1 Numbers, sets, and functions 1.1. The natural numbers, integers, and rational numbers We assume that you are familiar with the set of natural numbers the set of integers and the set of rational
Chapter 1 Numbers, sets, and functions 1.1. The natural numbers, integers, and rational numbers We assume that you are familiar with the set of natural numbers the set of integers and the set of rational
INFINITY: CARDINAL NUMBERS
 INFINITY: CARDINAL NUMBERS BJORN POONEN 1 Some terminology of set theory N := {0, 1, 2, 3, } Z := {, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, } Q := the set of rational numbers R := the set of real numbers C := the set of complex
INFINITY: CARDINAL NUMBERS BJORN POONEN 1 Some terminology of set theory N := {0, 1, 2, 3, } Z := {, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, } Q := the set of rational numbers R := the set of real numbers C := the set of complex
Suppose R is an ordered ring with positive elements P.
 1. The real numbers. 1.1. Ordered rings. Definition 1.1. By an ordered commutative ring with unity we mean an ordered sextuple (R, +, 0,, 1, P ) such that (R, +, 0,, 1) is a commutative ring with unity
1. The real numbers. 1.1. Ordered rings. Definition 1.1. By an ordered commutative ring with unity we mean an ordered sextuple (R, +, 0,, 1, P ) such that (R, +, 0,, 1) is a commutative ring with unity
Cauchy Sequences. x n = 1 ( ) 2 1 1, . As you well know, k! n 1. 1 k! = e, = k! k=0. k = k=1
 Cauchy Sequences The Definition. I will introduce the main idea by contrasting three sequences of rational numbers. In each case, the universal set of numbers will be the set Q of rational numbers; all
Cauchy Sequences The Definition. I will introduce the main idea by contrasting three sequences of rational numbers. In each case, the universal set of numbers will be the set Q of rational numbers; all
Principles of Real Analysis I Fall I. The Real Number System
 21-355 Principles of Real Analysis I Fall 2004 I. The Real Number System The main goal of this course is to develop the theory of real-valued functions of one real variable in a systematic and rigorous
21-355 Principles of Real Analysis I Fall 2004 I. The Real Number System The main goal of this course is to develop the theory of real-valued functions of one real variable in a systematic and rigorous
Exercises for Unit VI (Infinite constructions in set theory)
 Exercises for Unit VI (Infinite constructions in set theory) VI.1 : Indexed families and set theoretic operations (Halmos, 4, 8 9; Lipschutz, 5.3 5.4) Lipschutz : 5.3 5.6, 5.29 5.32, 9.14 1. Generalize
Exercises for Unit VI (Infinite constructions in set theory) VI.1 : Indexed families and set theoretic operations (Halmos, 4, 8 9; Lipschutz, 5.3 5.4) Lipschutz : 5.3 5.6, 5.29 5.32, 9.14 1. Generalize
REVIEW FOR THIRD 3200 MIDTERM
 REVIEW FOR THIRD 3200 MIDTERM PETE L. CLARK 1) Show that for all integers n 2 we have 1 3 +... + (n 1) 3 < 1 n < 1 3 +... + n 3. Solution: We go by induction on n. Base Case (n = 2): We have (2 1) 3 =
REVIEW FOR THIRD 3200 MIDTERM PETE L. CLARK 1) Show that for all integers n 2 we have 1 3 +... + (n 1) 3 < 1 n < 1 3 +... + n 3. Solution: We go by induction on n. Base Case (n = 2): We have (2 1) 3 =
Topology. Xiaolong Han. Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA address:
 Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
1.3. The Completeness Axiom.
 13 The Completeness Axiom 1 13 The Completeness Axiom Note In this section we give the final Axiom in the definition of the real numbers, R So far, the 8 axioms we have yield an ordered field We have seen
13 The Completeness Axiom 1 13 The Completeness Axiom Note In this section we give the final Axiom in the definition of the real numbers, R So far, the 8 axioms we have yield an ordered field We have seen
2.23 Theorem. Let A and B be sets in a metric space. If A B, then L(A) L(B).
 2.23 Theorem. Let A and B be sets in a metric space. If A B, then L(A) L(B). 2.24 Theorem. Let A and B be sets in a metric space. Then L(A B) = L(A) L(B). It is worth noting that you can t replace union
2.23 Theorem. Let A and B be sets in a metric space. If A B, then L(A) L(B). 2.24 Theorem. Let A and B be sets in a metric space. Then L(A B) = L(A) L(B). It is worth noting that you can t replace union
CHAPTER 3: THE INTEGERS Z
 CHAPTER 3: THE INTEGERS Z MATH 378, CSUSM. SPRING 2009. AITKEN 1. Introduction The natural numbers are designed for measuring the size of finite sets, but what if you want to compare the sizes of two sets?
CHAPTER 3: THE INTEGERS Z MATH 378, CSUSM. SPRING 2009. AITKEN 1. Introduction The natural numbers are designed for measuring the size of finite sets, but what if you want to compare the sizes of two sets?
MATH 220 (all sections) Homework #12 not to be turned in posted Friday, November 24, 2017
 MATH 220 (all sections) Homework #12 not to be turned in posted Friday, November 24, 2017 Definition: A set A is finite if there exists a nonnegative integer c such that there exists a bijection from A
MATH 220 (all sections) Homework #12 not to be turned in posted Friday, November 24, 2017 Definition: A set A is finite if there exists a nonnegative integer c such that there exists a bijection from A
Real Analysis Math 131AH Rudin, Chapter #1. Dominique Abdi
 Real Analysis Math 3AH Rudin, Chapter # Dominique Abdi.. If r is rational (r 0) and x is irrational, prove that r + x and rx are irrational. Solution. Assume the contrary, that r+x and rx are rational.
Real Analysis Math 3AH Rudin, Chapter # Dominique Abdi.. If r is rational (r 0) and x is irrational, prove that r + x and rx are irrational. Solution. Assume the contrary, that r+x and rx are rational.
Outline. We will now investigate the structure of this important set.
 The Reals Outline As we have seen, the set of real numbers, R, has cardinality c. This doesn't tell us very much about the reals, since there are many sets with this cardinality and cardinality doesn't
The Reals Outline As we have seen, the set of real numbers, R, has cardinality c. This doesn't tell us very much about the reals, since there are many sets with this cardinality and cardinality doesn't
DO FIVE OUT OF SIX ON EACH SET PROBLEM SET
 DO FIVE OUT OF SIX ON EACH SET PROBLEM SET 1. THE AXIOM OF FOUNDATION Early on in the book (page 6) it is indicated that throughout the formal development set is going to mean pure set, or set whose elements,
DO FIVE OUT OF SIX ON EACH SET PROBLEM SET 1. THE AXIOM OF FOUNDATION Early on in the book (page 6) it is indicated that throughout the formal development set is going to mean pure set, or set whose elements,
3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS
 3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS Definition 3.1 Let X be a topological space. A subset D of X is dense in X iff D = X. X is separable iff it contains a countable dense subset. X satisfies the first
3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS Definition 3.1 Let X be a topological space. A subset D of X is dense in X iff D = X. X is separable iff it contains a countable dense subset. X satisfies the first
School of the Art Institute of Chicago. Calculus. Frank Timmes. flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.
 School of the Art Institute of Chicago Calculus Frank Timmes ftimmes@artic.edu flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.shtml Syllabus 1 Aug 29 Pre-calculus 2 Sept 05 Rates and areas 3 Sept 12 Trapezoids
School of the Art Institute of Chicago Calculus Frank Timmes ftimmes@artic.edu flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.shtml Syllabus 1 Aug 29 Pre-calculus 2 Sept 05 Rates and areas 3 Sept 12 Trapezoids
Sets and Functions. (As we will see, in describing a set the order in which elements are listed is irrelevant).
 Sets and Functions 1. The language of sets Informally, a set is any collection of objects. The objects may be mathematical objects such as numbers, functions and even sets, or letters or symbols of any
Sets and Functions 1. The language of sets Informally, a set is any collection of objects. The objects may be mathematical objects such as numbers, functions and even sets, or letters or symbols of any
Chapter 5. Measurable Functions
 Chapter 5. Measurable Functions 1. Measurable Functions Let X be a nonempty set, and let S be a σ-algebra of subsets of X. Then (X, S) is a measurable space. A subset E of X is said to be measurable if
Chapter 5. Measurable Functions 1. Measurable Functions Let X be a nonempty set, and let S be a σ-algebra of subsets of X. Then (X, S) is a measurable space. A subset E of X is said to be measurable if
MATH 2400: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1
 MATH 2400: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1 PETE L. CLARK 1) Find all real numbers x such that x 3 = x. Prove your answer! Solution: If x 3 = x, then 0 = x 3 x = x(x + 1)(x 1). Earlier we showed using the
MATH 2400: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1 PETE L. CLARK 1) Find all real numbers x such that x 3 = x. Prove your answer! Solution: If x 3 = x, then 0 = x 3 x = x(x + 1)(x 1). Earlier we showed using the
Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall F(x) = 1 x. f(t)dt. t 1 2. tf 2 (t)dt. and g(t, x) = 2 t. 2 t
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall 2. Let f L 2 (, ) be given. (a) Prove that ( x 2 f(t) dt) 2 x x t f(t) 2 dt. (b) Given part (a), prove that F L 2 (, ) 2 f L 2 (, ), where F(x) = x (a) Using
Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall 2. Let f L 2 (, ) be given. (a) Prove that ( x 2 f(t) dt) 2 x x t f(t) 2 dt. (b) Given part (a), prove that F L 2 (, ) 2 f L 2 (, ), where F(x) = x (a) Using
Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students
 Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students Anthony M. Marino Department of Finance and Business Economics Marshall School of Business Lecture 1: Introductory Material Sets The Real Number System Functions,
Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students Anthony M. Marino Department of Finance and Business Economics Marshall School of Business Lecture 1: Introductory Material Sets The Real Number System Functions,
6-2. Absolute Value, Square Roots, and Quadratic Equations. Vocabulary. Lesson. Example 1 Solve for x: x - 4 = 8.1. Mental Math
 Chapter 6 Lesson 6-2 Absolute Value, Square Roots, and Quadratic Equations BIG IDEA Geometrically, the absolute value of a number is its distance on a number line from 0. Algebraically, the absolute value
Chapter 6 Lesson 6-2 Absolute Value, Square Roots, and Quadratic Equations BIG IDEA Geometrically, the absolute value of a number is its distance on a number line from 0. Algebraically, the absolute value
STRONGLY CONNECTED SPACES
 Undergraduate Research Opportunity Programme in Science STRONGLY CONNECTED SPACES Submitted by Dai Bo Supervised by Dr. Wong Yan-loi Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore Academic
Undergraduate Research Opportunity Programme in Science STRONGLY CONNECTED SPACES Submitted by Dai Bo Supervised by Dr. Wong Yan-loi Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore Academic
3 Hausdorff and Connected Spaces
 3 Hausdorff and Connected Spaces In this chapter we address the question of when two spaces are homeomorphic. This is done by examining two properties that are shared by any pair of homeomorphic spaces.
3 Hausdorff and Connected Spaces In this chapter we address the question of when two spaces are homeomorphic. This is done by examining two properties that are shared by any pair of homeomorphic spaces.
2. Two binary operations (addition, denoted + and multiplication, denoted
 Chapter 2 The Structure of R The purpose of this chapter is to explain to the reader why the set of real numbers is so special. By the end of this chapter, the reader should understand the difference between
Chapter 2 The Structure of R The purpose of this chapter is to explain to the reader why the set of real numbers is so special. By the end of this chapter, the reader should understand the difference between
