Previously Documented Basin-localized Extension on Mercury
|
|
|
- Arline Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GSA DATA REPOSITORY Watters et al. Previously Documented Basin-localized Extension on Mercury The most widely distributed extensional landforms on Mercury seen in images from the Mariner 10 and MESSENGER flybys are within the ~1550-km-diameter Caloris basin (Solomon et al., 2008; Murchie et al., 2008). Although Mariner 10 imaged less than half of the basin, basin-concentric and basin-radial troughs interpreted as graben were identified on interior plains deposits inward of the basin rim (Strom et al., 1975; Melosh and McKinnon, 1988; Watters et al., 2005). MESSENGER s first flyby of Mercury confirmed that graben are present throughout the interior of Caloris and revealed that one system of graben, Pantheon Fossae, consists of troughs strongly radial to a point near the center of the basin (Solomon et al., 2008; Murchie et al., 2008; Head et al., 2008; Watters et al., 2009a, b). During its second flyby, MESSENGER imaged another system of basinradial and basin-concentric graben in the interior plains of the ~700-km-diameter Rembrandt basin (Watters et al., 2009c). Graben were also discovered in two smaller, comparatively young peak-ring basins, Raditladi and Rachmaninoff, both between 250 and 300 km in diameter (Solomon et al., 2008; Watters et al., 2009b; Prockter et al., 2010). Images obtained during the orbital phase of the MESSENGER mission revealed graben within the interior ring of the 230-km-diameter Mozart peak-ring basin (Blair et al., 2012). The extensional stresses that led to graben formation in the Caloris basin have been postulated to be the result of flexural uplift of the interior in response to loading by volcanic plains emplaced exterior to the basin (Melosh and McKinnon, 1988; Kennedy et al., 2008), inward flow of the lower crust in response to horizontal pressure gradients produced by differences in elevation and crustal thickness (Watters et al., 2005; Watters and Nimmo, 2010), or the radial propagation of vertical dikes from a subsurface magma body (Head et al., 2008). These flyby observations suggested that the formation and modification of impact basins has been a key factor in the localization of extensional tectonic activity on Mercury. Thermal contraction of cooling volcanic units may have played a role in the formation of graben in the basins on Mercury, particular the mid-sized, peak-ring basins. For an initial basin floor geometry with a central deep zone, circumferentially oriented graben such as those found in the Raditladi, Rachmaninoff, and Mozart peak-ring basins can have formed as a result of thermal contraction of interior plains material (Blair et al., 2012). The distribution and complex patterns of graben in the larger Caloris and Rembrandt basins are more difficult to match with thermal stresses alone. Page 1 of 4
2 Spatial Distribution of Wrinkle Ridge Graben Systems Buried craters and basins that contain wrinkle ridge graben systems are distributed throughout the northern plains of Mercury (Fig. DR1). To date, these tectonic systems have been found on the volcanic plains that bury 25 impact features, including ghost craters interior to buried basins, ranging in diameter from ~40 to 300 km. This population is in addition to a larger population (~120) of buried basins and craters in the northern plains that have a wide range of diameters but mostly lack evidence of extensional landforms (Fig. DR1). Wrinkle ridge graben systems associated with buried craters and basins are also seen in other volcanic plains provinces on Mercury. In the volcanic plains exterior to the Caloris basin, seven buried impact structures with wrinkle ridges and graben have been found to date (Fig. DR2). Although the global extent of buried impact features with wrinkle-ridge graben systems is not yet known, their presence in large volcanic provinces other than the northern plains suggests that the tectonic processes that formed them were not isolated to a few areas on Mercury. Finite Element Modeling We used the finite element code Abaqus [ to develop axisymmetric models of stress and deformation in a volcanically buried, 50-km-diameter impact crater in a partially filled, 200-km-diameter basin (values of model parameters are listed in Table 1). The crater and basin were assumed to have 1 and 4 km of volcanic fill at their respective centers, and the volcanic unit outside the basin was taken to be 1.5 km thick. For simulations of thermal contraction, the youngest cooling unit was assumed to be 0.5 km thick in the basin interior and 0.1 km thick outside the basin. Simulations of global contraction and thermal contraction were modeled to depths of 20 km and 300 km in radius, whereas models that involved lithospheric flexure, including isostatic uplift and lower crustal flow, extended to 200 km depth and 1000 km in radius from the basin center. Side and bottom boundaries were fixed in all models except for simulations of global contraction, for which a horizontal strain equivalent to 1 km of global radial contraction was applied. We considered models in which the elastic strength of the volcanic unit to that of the shallow underlying crust ranged between a factor of 1 and 10, but we found that different ratios influenced only the absolute magnitude of stresses in the volcanic unit and not the predicted style of faulting. In thermal contraction models, stresses were specified at the time when the youngest cooling unit reached background temperature, whereas stresses in uplift models were specified at the time when viscous regions reached a state of relaxation. The choice of thermal conductivity or viscosity did not influence the calculated stress state. Model results suggest that uplift of the basin in response either to isostatic forces or lower crustal flow can account for a lack of a preferred graben orientations near the basin center but not for circumferentially oriented graben. In addition, such uplift models 2
3 cannot explain why graben are confined within basins and do not extend beyond the basin rims, nor why graben generally have greater widths within ghost craters located inside basins. Models of thermal contraction similarly predict graben without a preferred orientation in the centers of craters and basins, but they also predict circumferential graben (radial stress more extensional than circumferential stress) in regions where the youngest cooling unit thins, consistent with observations of such graben orientations at the edges of buried craters and basins. Moreover, thermal contraction models predict that graben should form only where the youngest cooling unit is thick, e.g., within ghost basins where lavas pooled but not outside the basins. This conclusion follows from calculations of thermal strains, which are a factor of 5 greater for thicker cooling units than for thinner units in the models. The formation of wrinkle-ridge rings over buried basin rims is well matched by global contraction models, because horizontal compressive stresses are greatest where the volcanic unit is thinnest and the radial stress component is more compressive than the circumferential stress component at such locations. 3
4 Table DR1. Model parameters adopted for this analysis. Symbol Description Value Units ρ f Density of volcanic fill kg m -3 ρ c Density of crust 3200 kg m -3 ρ m Density of mantle 3400 kg m -3 E Young s modulus (in all regions unless Pa specified in the text) ν Poisson s ratio 0.25 η lc Viscosity of lower crust Pa s η a Viscosity of asthenosphere Pa s G Gravitational acceleration 3.7 m s -2 T i,s Surface temperature 0 C ΔT Background thermal gradient 10 C km -1 T i,f Elastic blocking temperature of fill 900 C κ f Thermal conductivity of fill 1.5 W m -1 K- 1 κ b Thermal conductivity of basement W m -1 K -1 η c Viscosity of compacting basement Pa s α f Volumetric coefficient of thermal expansion C -1 REFERENCES CITED Blair, D.M., Freed, A.M., Byrne, P.K., Klimczak, C, Solomon, S.C., Watters, T.R., Prockter, L.M., Melosh, H.J., and Zuber, M.T., 2012, Thermally induced graben in peak-ring basins and ghost craters on Mercury: Houston, Texas, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Lunar and Planetary Science 43, CD-ROM, abstract Freed, A. M., Herring, T., and Bürgmann, R., 2010, Steady-state laboratory flow laws alone fail to explain postseismic observations: Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v. 300, p Kennedy, P.J., Freed, A.M., and Solomon, S.C., 2008, Mechanisms of faulting in and around Caloris basin, Mercury: Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 113, E08004, doi: /2007JE
5 Figure DR1. Figure DR1. Distribution of buried impact craters and basins delineated by wrinkle-ridge rings in the northern plains. Blue circles mark the locations of buried impact features with wrinkle ridge graben systems, and pink circles mark the locations of buried impact features that lack graben. The locations of major graben are shown in red. The yellow outline marks the boundary of the northern plains.
6 Figure DR2. Figure DR2. Locations of known occurrences of buried impact features with wrinkle-ridge graben tectonic systems. Thus far, 32 buried impact craters and basins (red circles) have been documented in the northern plains and in the plains exterior to the Caloris basin. This distribution indicates that wrinkle-ridge graben systems occur in two of the largest contiguous expanses of volcanic plains material on Mercury. The central longitude of the projection is 180 E.
The origin of graben and ridges in Rachmaninoff, Raditladi, and Mozart basins, Mercury
 The origin of graben and ridges in Rachmaninoff, Raditladi, and Mozart basins, Mercury The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The origin of graben and ridges in Rachmaninoff, Raditladi, and Mozart basins, Mercury The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Deformation associated with ghost craters and basins in volcanic smooth plains on Mercury: Strain analysis and implications for plains evolution
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012je004100, 2012 Deformation associated with ghost craters and basins in volcanic smooth plains on Mercury: Strain analysis and implications for
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012je004100, 2012 Deformation associated with ghost craters and basins in volcanic smooth plains on Mercury: Strain analysis and implications for
(b) What is the amplitude at the altitude of a satellite of 400 km?
 Practice final quiz 2015 Geodynamics 2015 1 a) Complete the following table. parameter symbol units temperature T C or K thermal conductivity heat capacity density coefficient of thermal expansion volumetric)
Practice final quiz 2015 Geodynamics 2015 1 a) Complete the following table. parameter symbol units temperature T C or K thermal conductivity heat capacity density coefficient of thermal expansion volumetric)
Surface changes caused by erosion and sedimentation were treated by solving: (2)
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
Thrust faults and the global contraction of Mercury
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L04701, doi:10.1029/2003gl019171, 2004 Thrust faults and the global contraction of Mercury Thomas R. Watters Center for Earth and Planetary Studies, National Air
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L04701, doi:10.1029/2003gl019171, 2004 Thrust faults and the global contraction of Mercury Thomas R. Watters Center for Earth and Planetary Studies, National Air
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry. Planetary Surfaces
 Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Received 15 June 2013; revised 7 September 2013; accepted 11 September 2013; published 3 October 2013.
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: PLANETS, VOL. 118, 2030 2044, doi:10.1002/jgre.20157, 2013 Insights into the subsurface structure of the Caloris basin, Mercury, from assessments of mechanical layering
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: PLANETS, VOL. 118, 2030 2044, doi:10.1002/jgre.20157, 2013 Insights into the subsurface structure of the Caloris basin, Mercury, from assessments of mechanical layering
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Evidence for Young Volcanism on Mercury from the Third MESSENGER Flyby
 Evidence for Young Volcanism on Mercury from the Third MESSENGER Flyby Louise M. Prockter, 1 * Carolyn M. Ernst, 1 Brett W. Denevi, 2 Clark R. Chapman, 3 James W. Head III, 4 Caleb I. Fassett, 4 William
Evidence for Young Volcanism on Mercury from the Third MESSENGER Flyby Louise M. Prockter, 1 * Carolyn M. Ernst, 1 Brett W. Denevi, 2 Clark R. Chapman, 3 James W. Head III, 4 Caleb I. Fassett, 4 William
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Recent extensional tectonics on the Moon revealed by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera Thomas R. Watters 1, Mark S. Robinson 2, Maria E. Banks 1, Thanh Tran 2, Brett W. Denevi 3 1. Center for Earth
Recent extensional tectonics on the Moon revealed by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera Thomas R. Watters 1, Mark S. Robinson 2, Maria E. Banks 1, Thanh Tran 2, Brett W. Denevi 3 1. Center for Earth
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Icarus 209 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Icarus. journal homepage:
 Icarus 29 (21) 262 27 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Evaluation of the origin hypotheses of Pantheon Fossae, central Caloris basin, Mercury
Icarus 29 (21) 262 27 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Evaluation of the origin hypotheses of Pantheon Fossae, central Caloris basin, Mercury
Tectonics. Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust
 Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Gravitational constraints
 Gravitational constraints Reading: Fowler p172 187 Gravity anomalies Free-air anomaly: g F = g g( λ ) + δg obs F Corrected for expected variations due to the spheroid elevation above the spheroid Bouguer
Gravitational constraints Reading: Fowler p172 187 Gravity anomalies Free-air anomaly: g F = g g( λ ) + δg obs F Corrected for expected variations due to the spheroid elevation above the spheroid Bouguer
NAME IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY INTRUSION OF MAGMA
 NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY INTRUSION OF MAGMA 1. The summit of Mauna Loa is 8192 m above the floor of the Pacific Ocean, but only 4169 m of this is above sea level. About 150 m of ocean-floor
NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY INTRUSION OF MAGMA 1. The summit of Mauna Loa is 8192 m above the floor of the Pacific Ocean, but only 4169 m of this is above sea level. About 150 m of ocean-floor
Geotherms. Reading: Fowler Ch 7. Equilibrium geotherms One layer model
 Geotherms Reading: Fowler Ch 7 Equilibrium geotherms One layer model (a) Standard model: k = 2.5 W m -1 C -1 A = 1.25 x 10-6 W m -3 Q moho = 21 x 10-3 W m -2 shallow T-gradient: 30 C km -1 deep T-gradient:
Geotherms Reading: Fowler Ch 7 Equilibrium geotherms One layer model (a) Standard model: k = 2.5 W m -1 C -1 A = 1.25 x 10-6 W m -3 Q moho = 21 x 10-3 W m -2 shallow T-gradient: 30 C km -1 deep T-gradient:
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far. Interiors of Terrestrial Planets. The Terrestrial Planets
 Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Geologic history of the Mead impact basin, Venus
 Geologic history of the Mead impact basin, Venus Robert R. Herrick Virgil L. Sharpton Lunar and Planetary Institute, 3600 Bay Area Boulevard, Houston, Texas 77058 ABSTRACT The geologic history of the Mead
Geologic history of the Mead impact basin, Venus Robert R. Herrick Virgil L. Sharpton Lunar and Planetary Institute, 3600 Bay Area Boulevard, Houston, Texas 77058 ABSTRACT The geologic history of the Mead
Forces That Shape Earth. How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle?
 Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Mohr's Circle and Earth Stress (The Elastic Earth)
 Lect. 1 - Mohr s Circle and Earth Stress 6 Mohr's Circle and Earth Stress (The Elastic Earth) In the equations that we derived for Mohr s circle, we measured the angle, θ, as the angle between σ 1 and
Lect. 1 - Mohr s Circle and Earth Stress 6 Mohr's Circle and Earth Stress (The Elastic Earth) In the equations that we derived for Mohr s circle, we measured the angle, θ, as the angle between σ 1 and
The influence of short wavelength variations in viscosity on subduction dynamics
 1 Introduction Deformation within the earth, driven by mantle convection due primarily to cooling and subduction of oceanic lithosphere, is expressed at every length scale in various geophysical observations.
1 Introduction Deformation within the earth, driven by mantle convection due primarily to cooling and subduction of oceanic lithosphere, is expressed at every length scale in various geophysical observations.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1828 Projectile Remnants in Central Peaks of Lunar Impact Craters Authors: Z. Yue 1, 2, B. C. Johnson 3, D. A. Minton 2, H. J. Melosh 2,3 *, K. Di 1, W. Hu 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1828 Projectile Remnants in Central Peaks of Lunar Impact Craters Authors: Z. Yue 1, 2, B. C. Johnson 3, D. A. Minton 2, H. J. Melosh 2,3 *, K. Di 1, W. Hu 1,
Tectonic landforms. Global distribution Extension. Compression. Strike-slip faults Outlook: Implications for geophysics
 Tectonic landforms Global distribution Extension Long and narrow graben ( simple grabens ) Complex graben systems ( rifts ) Compression Wrinkle ridges Lobate scarps Strike-slip faults Outlook: Implications
Tectonic landforms Global distribution Extension Long and narrow graben ( simple grabens ) Complex graben systems ( rifts ) Compression Wrinkle ridges Lobate scarps Strike-slip faults Outlook: Implications
Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages )
 Name Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages 676 683) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth s plates move about quickly on top of
Name Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages 676 683) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth s plates move about quickly on top of
Earth and Planetary Science Letters
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 285 (2009) 251 262 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Earth and Planetary Science Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Evidence for intrusive
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 285 (2009) 251 262 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Earth and Planetary Science Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Evidence for intrusive
Mountains are then built by deforming crust: Deformation & Mountain Building. Mountains form where stresses are high!
 Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Plate Tectonics. Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist
 Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric Plate
Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric Plate
Data Repository Hampel et al., page 1/5
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2138 Data Repositor Hampel et al., page 1/5 SETUP OF THE FINITE-ELEMENT MODEL The finite-element models were created with the software ABAQUS and consist of a 1-km-thick lithosphere,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2138 Data Repositor Hampel et al., page 1/5 SETUP OF THE FINITE-ELEMENT MODEL The finite-element models were created with the software ABAQUS and consist of a 1-km-thick lithosphere,
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression. 1. Introduction
 Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
Earth as a planet: Interior and Surface layers
 Earth as a planet: Interior and Surface layers Bibliographic material: Langmuir & Broecker (2012) How to build a habitable planet Internal structure of the Earth: Observational techniques Seismology Analysis
Earth as a planet: Interior and Surface layers Bibliographic material: Langmuir & Broecker (2012) How to build a habitable planet Internal structure of the Earth: Observational techniques Seismology Analysis
CURRICULUM VITAE 1. CONTACT INFORMATION 2. EDUCATION 3. RESEARCH INTERESTS 4. PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE
 CURRICULUM VITAE 1. CONTACT INFORMATION Christian Klimczak, Ph.D. Department of Terrestrial Magnetism Carnegie Institution of Washington 5241 Broad Branch Road, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20015-1305 Email:
CURRICULUM VITAE 1. CONTACT INFORMATION Christian Klimczak, Ph.D. Department of Terrestrial Magnetism Carnegie Institution of Washington 5241 Broad Branch Road, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20015-1305 Email:
Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions. Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions
 Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions Cooling of oceanic lithosphere also increases rock strength and seismic velocity. Thus
Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions Cooling of oceanic lithosphere also increases rock strength and seismic velocity. Thus
Shape Earth. Plate Boundaries. Building. Building
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Crustal Activity. Plate Tectonics - Plates - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones
 Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Planetary and Space Science
 Planetary and Space Science 59 (2011) 1932 1948 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Planetary and Space Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pss The transition from complex crater to
Planetary and Space Science 59 (2011) 1932 1948 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Planetary and Space Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pss The transition from complex crater to
block tectonics on Venus
 block tectonics on Venus p a u l b y r n e r i c h a r d g h a i l a. m. c e l â l s e n g ö r c h r i s t i a n k l i m c z a k r e b e c c a h a h n s e a n s o l o m o n VEXAG meeting #15 byrne et al.
block tectonics on Venus p a u l b y r n e r i c h a r d g h a i l a. m. c e l â l s e n g ö r c h r i s t i a n k l i m c z a k r e b e c c a h a h n s e a n s o l o m o n VEXAG meeting #15 byrne et al.
Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels.
 Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels. Rugged Terra Rugged terra are mountainous regions of the moon. Wrinkle Ridges Wrinkle Ridges are created through
Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels. Rugged Terra Rugged terra are mountainous regions of the moon. Wrinkle Ridges Wrinkle Ridges are created through
GS388 Handout: Radial density distribution via the Adams-Williamson equation 1
 GS388 Handout: Radial density distribution via the Adams-Williamson equation 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS ADIABATIC COMPRESSION: THE ADAMS WILLIAMSON EQUATION...1 EFFECT OF NON-ADIABATIC TEMPERATURE GRADIENT...3
GS388 Handout: Radial density distribution via the Adams-Williamson equation 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS ADIABATIC COMPRESSION: THE ADAMS WILLIAMSON EQUATION...1 EFFECT OF NON-ADIABATIC TEMPERATURE GRADIENT...3
12 Gravity and Topography
 12. Gravity and Topography 126 12 Gravity and Topography In the limit of perfect hydrostatic equilibrium, there is an exact relationship between gravity and topography... and no new information emerges:
12. Gravity and Topography 126 12 Gravity and Topography In the limit of perfect hydrostatic equilibrium, there is an exact relationship between gravity and topography... and no new information emerges:
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Topics. Magma Ascent and Emplacement. Magma Generation. Magma Rise. Energy Sources. Instabilities. How does magma ascend? How do dikes form?
 Magma Ascent and Emplacement Reading: Encyclopedia of Volcanoes: Physical Properties of Magmas (pp. 171-190) Magma Chambers (pp. 191-206) Plumbing Systems (pp. 219-236) Magma ascent at shallow levels (pp.237-249)
Magma Ascent and Emplacement Reading: Encyclopedia of Volcanoes: Physical Properties of Magmas (pp. 171-190) Magma Chambers (pp. 191-206) Plumbing Systems (pp. 219-236) Magma ascent at shallow levels (pp.237-249)
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Defining the former elevation and shape of the lithosphere, in particular the elevation of the Earth s surface,
 Isostasy in Move Defining the former elevation and shape of the lithosphere, in particular the elevation of the Earth s surface, is important in the restoration of a model as it aids in reducing uncertainty
Isostasy in Move Defining the former elevation and shape of the lithosphere, in particular the elevation of the Earth s surface, is important in the restoration of a model as it aids in reducing uncertainty
UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS
 UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS CONTINENTAL DRIFT Alfred Wegner proposed the theory that the crustal plates are moving over the mantle. He argued that today s continents once formed a single landmass, called Pangaea
UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS CONTINENTAL DRIFT Alfred Wegner proposed the theory that the crustal plates are moving over the mantle. He argued that today s continents once formed a single landmass, called Pangaea
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
The distribution and origin of smooth plains on Mercury
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: PLANETS, VOL. 118, 891 907, doi:10.1002/jgre.20075, 2013 The distribution and origin of smooth plains on Mercury Brett W. Denevi, 1 Carolyn M. Ernst, 1 Heather M. Meyer,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: PLANETS, VOL. 118, 891 907, doi:10.1002/jgre.20075, 2013 The distribution and origin of smooth plains on Mercury Brett W. Denevi, 1 Carolyn M. Ernst, 1 Heather M. Meyer,
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Earth s Continents and Seafloors. GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor
 Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Planetary and Space Science
 Planetary and Space Science 59 (2011) 1960 1967 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Planetary and Space Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pss Mercury crater statistics from MESSENGER
Planetary and Space Science 59 (2011) 1960 1967 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Planetary and Space Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pss Mercury crater statistics from MESSENGER
Long-term survival of the axial valley morphology at abandoned slow-spreading centers
 Long-term survival of the axial valley morphology at abandoned slow-spreading centers Andrew M. Freed Department of Geosciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721 Jian Lin Peter R. Shaw Woods
Long-term survival of the axial valley morphology at abandoned slow-spreading centers Andrew M. Freed Department of Geosciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721 Jian Lin Peter R. Shaw Woods
Directed Reading. Section: How Mountains Form MOUNTAIN RANGES AND SYSTEMS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Large impact basins on Mercury: Global distribution, characteristics, and modification history from MESSENGER orbital data
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012je004154, 2012 Large impact basins on Mercury: Global distribution, characteristics, and modification history from MESSENGER orbital data Caleb
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012je004154, 2012 Large impact basins on Mercury: Global distribution, characteristics, and modification history from MESSENGER orbital data Caleb
Correction to Localized gravity/topography admittance and correlation spectra on Mars: Implications for regional and global evolution
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004je002286, 2004 Correction to Localized gravity/topography admittance and correlation spectra on Mars: Implications for regional and global evolution
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004je002286, 2004 Correction to Localized gravity/topography admittance and correlation spectra on Mars: Implications for regional and global evolution
The Importance of Impact Melts
 The Importance of Impact Melts Constrain bombardment histories [Chapman et al. (2007)] Ar-Ar age dating [e.g. Norman et al. (2006)] Identify type of impactor Highly Siderophile Elements (HSE) [e.g. Puchtel
The Importance of Impact Melts Constrain bombardment histories [Chapman et al. (2007)] Ar-Ar age dating [e.g. Norman et al. (2006)] Identify type of impactor Highly Siderophile Elements (HSE) [e.g. Puchtel
Community Involvement - NASA Review Panels
 CURRICULUM VITAE Christian Klimczak, Assistant Professor Department of Geology University of Georgia Geography-Geology Building, Room 310 210 Field Street; Athens, GA 30602-2501 Email: klimczak@uga.edu
CURRICULUM VITAE Christian Klimczak, Assistant Professor Department of Geology University of Georgia Geography-Geology Building, Room 310 210 Field Street; Athens, GA 30602-2501 Email: klimczak@uga.edu
Amazing Orientale Peaks and Valleys
 LROC Image Browser - M1124173129LR http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc_browse/view/m1124173129lr 1 of 1 7/19/2013 11:04 PM Amazing Orientale Peaks and Valleys Image Data Time Orbit 17842 Center Longitude 264.72
LROC Image Browser - M1124173129LR http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc_browse/view/m1124173129lr 1 of 1 7/19/2013 11:04 PM Amazing Orientale Peaks and Valleys Image Data Time Orbit 17842 Center Longitude 264.72
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Tectonic plates of the world
 Mountain Building Tectonic plates of the world ISOSTACY Isostatic Rebound crust rises as a result of removal of mass This iceberg also demonstrates the process of isostatic rebound. Types of Mountains
Mountain Building Tectonic plates of the world ISOSTACY Isostatic Rebound crust rises as a result of removal of mass This iceberg also demonstrates the process of isostatic rebound. Types of Mountains
Section 2: How Mountains Form
 Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Plate Tectonics. Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist
 Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric
Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric
Lecture 2: Tectonics of Rocky Planets
 Lecture 2: Tectonics of Rocky Planets Lithosphere is a thermal boundary layer where heat transport is Lithosphere is a dominated by conduction. On Earth, this layer is treated as a rigid layer from which
Lecture 2: Tectonics of Rocky Planets Lithosphere is a thermal boundary layer where heat transport is Lithosphere is a dominated by conduction. On Earth, this layer is treated as a rigid layer from which
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7. Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 11/11/2010. Seismology: study of earthquakes and related phenomena
 Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 8. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 8 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 8 The Moon and Mercury Units of Chapter 8 8.1 Orbital Properties 8.2 Physical Properties 8.3 Surface Features on the Moon
Lecture Outlines Chapter 8 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 8 The Moon and Mercury Units of Chapter 8 8.1 Orbital Properties 8.2 Physical Properties 8.3 Surface Features on the Moon
4. Basins due to orogenic loading
 4. Basins due to orogenic loading Orogenic loading and lithospheric flexure: peripheral vs. retroarc foreland basin Elastic vs. viscoelastic models Gravity anomalies, foreland flexure, and the development
4. Basins due to orogenic loading Orogenic loading and lithospheric flexure: peripheral vs. retroarc foreland basin Elastic vs. viscoelastic models Gravity anomalies, foreland flexure, and the development
3. PLATE TECTONICS LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Class Date. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere c. asthenosphere d. mesosphere
 Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. The formation of lunar mascon basins from impact to contemporary form
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We modeled the evolution of lunar basins from impact to contemporary form The evolution of basins results from crater
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We modeled the evolution of lunar basins from impact to contemporary form The evolution of basins results from crater
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
EDIMENTARY BASINS. What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour
 EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
GEOL104: Exploring the Planets LAB 5: PLANETARY TECTONICS
 GEOL104: Exploring the Planets LAB 5: PLANETARY TECTONICS OBJECTIVES: I. Understand the three basic types of tectonic interactions that can occur II. Identify tectonic interactions on other planets MATERIALS:
GEOL104: Exploring the Planets LAB 5: PLANETARY TECTONICS OBJECTIVES: I. Understand the three basic types of tectonic interactions that can occur II. Identify tectonic interactions on other planets MATERIALS:
High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation
 High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation L.L.A. Vermeersen (1), H. Schotman (1), M.-W. Jansen (1), R. Riva (1) and R. Sabadini (2) (1) DEOS,
High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation L.L.A. Vermeersen (1), H. Schotman (1), M.-W. Jansen (1), R. Riva (1) and R. Sabadini (2) (1) DEOS,
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global geophysics and wave propagation
 Global geophysics and wave propagation Reading: Fowler p76 83 Remote sensing Geophysical methods Seismology Gravity and bathymetry Magnetics Heat flow Seismology: Directly samples the physical properties
Global geophysics and wave propagation Reading: Fowler p76 83 Remote sensing Geophysical methods Seismology Gravity and bathymetry Magnetics Heat flow Seismology: Directly samples the physical properties
Plume-induced topography and geoid anomalies and their implications for the Tharsis rise on Mars
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003je002226, 2004 Plume-induced topography and geoid anomalies and their implications for the Tharsis rise on Mars James H. Roberts Department of
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003je002226, 2004 Plume-induced topography and geoid anomalies and their implications for the Tharsis rise on Mars James H. Roberts Department of
Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS. asthenosphere uplift continental drift. known as. tectonic plates move. object. UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Unit Topics. Topic 1: Earth s Interior Topic 2: Continental Drift Topic 3: Crustal Activity Topic 4: Crustal Boundaries Topic 5: Earthquakes
 The Dynamic Earth Unit Topics Topic 1: Earth s Interior Topic 2: Continental Drift Topic 3: Crustal Activity Topic 4: Crustal Boundaries Topic 5: Earthquakes Topic 1: Earth s Interior Essential Question:
The Dynamic Earth Unit Topics Topic 1: Earth s Interior Topic 2: Continental Drift Topic 3: Crustal Activity Topic 4: Crustal Boundaries Topic 5: Earthquakes Topic 1: Earth s Interior Essential Question:
Which lettered location has the highest elevation? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. New York State's highest peak, Mt. Marcy, is located at approximately A) 44 10' N 74 05' W B) 44 05' N 73 55' W C) 73 55' N 44 10' W D) 74 05' N 44 05' W 2. Four locations, A, B, C, and D, are represented
1. New York State's highest peak, Mt. Marcy, is located at approximately A) 44 10' N 74 05' W B) 44 05' N 73 55' W C) 73 55' N 44 10' W D) 74 05' N 44 05' W 2. Four locations, A, B, C, and D, are represented
Strike-Slip Faults. ! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.
 Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice
 Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates
 Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates Crust Mantle Dynamics Introductory Geology Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Isostasy and Tectonics Laboratory Topics
Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates Crust Mantle Dynamics Introductory Geology Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Isostasy and Tectonics Laboratory Topics
Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet
 Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet In today s class, we want to look at those characteristics of the Earth that are also important in our understanding of the other terrestrial planets. This is
Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet In today s class, we want to look at those characteristics of the Earth that are also important in our understanding of the other terrestrial planets. This is
Klaus Gessner, Chris Wijns, Louis Moresi, Fabio Boschetti and Alison Ord
 Flow partitioning in the lithosphere during core complex formation: An interactive evolutionary computation approach using particle-in-cell finite elements Klaus Gessner, Chris Wijns, Louis Moresi, Fabio
Flow partitioning in the lithosphere during core complex formation: An interactive evolutionary computation approach using particle-in-cell finite elements Klaus Gessner, Chris Wijns, Louis Moresi, Fabio
Geodynamics Lecture 5 Basics of elasticity
 Geodynamics Lecture 5 Basics of elasticity Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi! 16.9.2014 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce linear elasticity! Look at the
Geodynamics Lecture 5 Basics of elasticity Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi! 16.9.2014 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce linear elasticity! Look at the
Supplementary information on the West African margin
 Huismans and Beaumont 1 Data repository Supplementary information on the West African margin Interpreted seismic cross-sections of the north Angolan to south Gabon west African passive margins 1-3, including
Huismans and Beaumont 1 Data repository Supplementary information on the West African margin Interpreted seismic cross-sections of the north Angolan to south Gabon west African passive margins 1-3, including
Camden Fairview NASA Lunar Research Team PowerPoint. October 27, 2011
 Camden Fairview NASA Lunar Research Team PowerPoint October 27, 2011 Introduction to the Moon The Moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth and was formed about the same time, over 4.5 billion years
Camden Fairview NASA Lunar Research Team PowerPoint October 27, 2011 Introduction to the Moon The Moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth and was formed about the same time, over 4.5 billion years
11.1 Rock Deformation
 Tarbuck Lutgens Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock
Tarbuck Lutgens Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
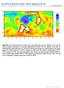 doi:10.1038/nature12280 Figure S1. The map shows the crater density (for craters larger than 25 km in diameter, N(25), per 10 6 km 2 ) on Mercury calculated in a moving neighborhood of radius 500 km, updated
doi:10.1038/nature12280 Figure S1. The map shows the crater density (for craters larger than 25 km in diameter, N(25), per 10 6 km 2 ) on Mercury calculated in a moving neighborhood of radius 500 km, updated
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES GENERAL SUBJECTS. GEODESY and GRAVITY
 COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
LIGO sees binary neutron star merger on August 17, 2017
 LIGO sees binary neutron star merger on August 17, 2017 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Multi-Messenger Astronomy This
LIGO sees binary neutron star merger on August 17, 2017 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Multi-Messenger Astronomy This
EARTH S SURFACE MOVEMENTS - introduction. Josef Stemberk, Institute of Rock Structure nad Mechanics CAS
 EARTH S SURFACE MOVEMENTS - introduction Josef Stemberk, Institute of Rock Structure nad Mechanics CAS Why is necessary to study dynamic (engineering) geology? There are known catastrophic events from
EARTH S SURFACE MOVEMENTS - introduction Josef Stemberk, Institute of Rock Structure nad Mechanics CAS Why is necessary to study dynamic (engineering) geology? There are known catastrophic events from
Earth Science ENR Plate Boundaries Notes
 Name Earth Science ENR Plate Boundaries Notes Per Tchr Plate Boundary Types: 1) Divergent Plate Boundary (Seafloor Spreading Centers) 2) Divergent Plate Boundary (Continental Rift Valley) 3) Transform
Name Earth Science ENR Plate Boundaries Notes Per Tchr Plate Boundary Types: 1) Divergent Plate Boundary (Seafloor Spreading Centers) 2) Divergent Plate Boundary (Continental Rift Valley) 3) Transform
THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
 UNIT 1 THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH 1.1.Earth s interior layers The interior of the Earth can be divided into layers according to: -Composition layers ( organized in order of increasing density
UNIT 1 THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH 1.1.Earth s interior layers The interior of the Earth can be divided into layers according to: -Composition layers ( organized in order of increasing density
Timing of water plume eruptions on Enceladus explained by interior viscosity structure
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2475 Timing of water plume eruptions on Enceladus explained by interior viscosity structure Marie Běhounková 1, Gabriel Tobie 2, Ondřej Čadek 1, Gaël Choblet
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2475 Timing of water plume eruptions on Enceladus explained by interior viscosity structure Marie Běhounková 1, Gabriel Tobie 2, Ondřej Čadek 1, Gaël Choblet
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny
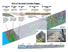 Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
Captain s Tryouts 2017
 Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
