Case study: AVO analysis in a high-impedance Atoka Sandstone (Pennsylvanian), North Arkoma Basin, McIntosh County, Oklahoma
|
|
|
- Barbra Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
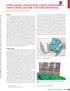
1 Case study: AVO analysis in a high-impedance Atoka Sandstone (Pennsylvanian), North Arkoma Basin, McIntosh County, Oklahoma MOHAMED A. EISSA, Tanta University, Egypt, and University of Oklahoma, Norman, U.S. JOHN P. CASTAGNA, University of Oklahoma, Norman, U.S. The variation of reflection coefficients with source-to-receiver spacing in multioffset seismic data is known to contain information about the lithology and pore-fluid content of subsurface rocks. However, such analysis is particularly challenging for thin, high-impedance reservoirs. In such instances, a key component of AVO analysis is a methodology for response calibration so that fluid properties can be interpreted vertically and laterally away from a borehole with a high degree of confidence. The use of AVO as a direct hydrocarbon indicator in clastic rocks is based on differences in the response of the compressional-wave (P-wave) velocity (V P ) and the shear-wave (S-wave) velocity (V S ) of a reservoir rock with the introduction of gas into the pore spaces. P-waves are sensitive to changes in pore fluids. The introduction of only a small amount of gas into the pore spaces of a rock can greatly reduce the P-wave velocity. In contrast, the S-wave velocity is only weakly dependent on pore fluid content. Thus, the introduction of hydrocarbons decreases the V P /V S ratio. This decrease, upon the introduction of gas into the pore space, changes the relative amplitudes of the reflections from the top and the base of the reservoir as a function of the angle of incidence. For thin beds (i.e., less than one-fourth wavelength) interference between reflections from the top and base of a reservoir may obscure the AVO response. The objective of this study is to determine if AVO analysis can be used to identify and delineate thin, highimpedance gas sands. The study area lies on the shelf of the northern Arkoma Basin in McIntosh County, Oklahoma, U.S. (Figure 1). The target reservoir is the Pennsylvanian Atoka Sand. Figure 2 shows the general stratigraphic column of the Oklahoma portion of the Arkoma basin. The Arkoma basin is an arcuate foreland trough stretching some 250 miles across southeast Oklahoma into central Arkansas. From Late Cambrian to Early Pennsylvanian (basal Atokan) time, the area now occupied by the basin was part of an Atlantic-type margin (shallow shelf) marking the southern edge of the Paleo-North American Figure 1. Location map for the study area. continent. A basic transgressive sequence, with significant interruptions, progressed from basal sands (Reagant) to a thick carbonate serious (Arbuckle group), to a mixture of carbonate, sand, and shale (Simpson, Viola, Sylvan, Hunton), and finally, to an episode of mainly shale deposition (Woodford, Caney). The entire sequence ends in a brief period (Latest Chesterian-basal Atokan) of shallow water sand and limestone sedimentation (Cromwell, Union Valley, Wapanucka, Spiro), which presumably reflects regression associated with the earliest stage of foreland basin formation. Subsequent subsidence during the Early-Mid Pennsylvanian was extremely rapid. In direct response to the major Ouachita collisional event, a thick flysch wedge (Atokan, lower Desmoinesian in the southern basin area) resulted, and then, with progressive shoaling of 988 THE LEADING EDGE OCTOBER 2003
2 Figure 2. Generalized stratigraphic column and subsurface nomenclature (right column) of the Arkoma Basin (modified from Hendrick). Figure 3. Petrophysical analysis for the target reservoirs within the Atoka interval in Wright Gas-bearing sands indicated by arrows. the basin, the southward progradation of major delta complexes (Hartshorne, Savanna, Boggy formations) and accompanying coal swamps occurred. In southeastern Oklahoma, total basin fill varies from around 5000 ft near the northern shelf edge to ft or more near the Choctaw thrust, the first major fault of the frontal Ouachita system with continuous surface expression. Atokan sediments, representing the main stage of foreland basin subsidence, increase rapidly in thickness from few hundred feet on the flanks of the Ozark Uplift to over ft in the vicinity of the Choctaw, a distance of some miles. Many folds and faults in the Arkoma basin were produced by horizontal compressive forces related to the Ouachita oregony. The compressive forces were directed north and northwest and decreased in intensity away from the Ouachita Mountains region. Nonetheless, anticlines and synclines are tightly folded and terminated by the thrust faults near the southern margin of the basin. Gas produced from the structures is typically dry, being approximately 95% methane. Well and seismic data. Well logs from Wright 1-15 (Figure 3) were available for this study. These included the gamma ray, deep and shallow resistivity, and porosity logs (neutron, density, 990 THE LEADING EDGE OCTOBER 2003
3 Figure 4. Neutron-density crossplot, showing lithology, porosity, and gas effect for the Atoka interval in Wright NPHI = porosity derived from compensated neutron log; RHOB = bulk density derived from formation density log. and sonic). The target reservoir is fluvial Pennsylvanian Lower Atokan sand at depths of ft. The perforated interval ( ft) showed initial production of ft 3 of gas per day (MCFGPD). Petrophysical analysis indicates that the target reservoir consists of sand and shaly sand with most production coming from the thin clean sand body at ft which exhibits an average porosity of 10% (Figure 3). The neutron-density crossplot shows that the pay interval log responses exhibit gas effects (Figure 4). Other sand bodies at 2350 ft (45 ft thick) and 2495 ft (30 ft thick) also show gas. A 2D seismic survey was taken along a north-south 3.5-mile line about 1300 ft from Wright The acquisition used a dynamite source (1 lb per shot) with a source depth of 5 ft and a source interval of 110 ft. Record length was 2 s and the sample rate was 2 ms. The geophone group interval was 110 ft and the geophone layout was 12 over 110 ft. The processing sequence included exponential gain correction, relative amplitude scaling, elevation and drift correction, surface consistent deconvolution, CDP sort, velocity analysis, NMO correction, automatic residual static, zero-phase spectral amplitude balancing, trim statics, fx Figure 5. Real data (a) before applying Radon filter, (b) after applying Radon filter, and (c) the subtracted-noise model. Figure 6. Extracted wavelet used in synthetic modeling. OCTOBER 2003 THE LEADING EDGE 991
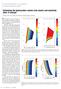
4 Figure 7. AVO brine synthetic-seismogram model of Wright Figure 8. AVO gas synthetic-seismogram model 1 for Wright 1-15, allowing V S to change in the gas interval. deconvolution, and prestack migration. Special processing for AVO included parabolic Radon filtering (Hampson-Russell invest procedure, Hz and time shifts from +80 to - 80 ms were passed) of supergathers consisting of 10 summed CDP gathers. Figure 5 shows real-data gathers before and after Radon filtering, and the subtracted-noise model. Seismic modeling and analysis. Primaries-only, ray-trace synthetic seismograms using sonic and density logs from Wright 1-15 were generated, using the extracted wavelet at the well (Figure 6). Synthetic gathers were NMO-corrected and calculated at the same offset as the real data ( ft) with no correction for spreading, transmission loss, attenuation, or geophonearray response. S-wave velocity was estimated using the mudrock equation for brine-saturated rocks. Figure 7, the brine model, displays an amplitude decrease with increasing offset at the target horizon. In the gas model, Poisson s ratio for the target reservoirs was changed to 0.1 in two ways: gas model 1 changed V S and kept V P fixed as measured (Figure 8) and gas model 2 changed V P and kept V S fixed (Figure 9). The top and the base of the 110-ft sand package are distinctly recognized in the synthetics. In the brine model, target reservoirs show no AVO anom- 992 THE LEADING EDGE OCTOBER 2003
5 Figure 9. AVO gas synthetic-seismogram model 2 for Wright 1-15, allowing V P to change in the gas interval. a b Figure 10. (a) Near-offset stack and (b) far-offset stack, showing the AVO anomaly for the target reservoir. aly. In gas model 1 (Figure 8), however, the top of the main reservoir (at 480 ms two-way time or TWT) shows a strong peak in the near-offset traces which decrease its amplitude with increase of offset and leads to a change in polarity (at about 2000 ft) and an increase of the trough amplitude in the far-offset traces. The base of the reservoir is expressed in a trough at 497 ms TWT in the near offset, which has AVO behavior that is the reverse of the top. Notice similar AVO anomalies for sand bodies at 430 ms and 470 ms. The near and far offsets of the real data are more similar to the AVO response of gas model 2 (Figure 9). This suggests that the sonic logs are measuring P-wave velocities that are higher than those to which the seismic data are responding. The AVO response of the real data exhibit typical AVO behavior for class I sands with a polarity reversal with offset according to the Rutherford and Williams (1989) classification. Nearstack and far-stack sections (Figure 10) exhibit clearly anomalous AVO responses between CDPs 214 and 223 at 480 ms TWT. AVO inversion. The AVO inversion process aims to establish a quantitative 994 THE LEADING EDGE OCTOBER 2003
6 Figure 11. AVO inversion for near offsets allowing V P, density, and layer thickness to change and using original log with V S from mudrock trend model as starting model. Red log is after inversion and black log is before inversion. Figure 12. AVO inversion for near and far offsets allowing V S to change and using original log model as starting model. Red log is after inversion and black log is before inversion. model which is consistent with the real seismic record and relate to the true geology. The big concern with AVO inversion is nonuniqueness, in which many models match the real data. We applied a model-based AVO inversion technique. It was performed using an iterative and general linear inversion (GLI) algorithm that allows fixed constraints. It is one-dimensional modeling that requires a starting model with a known number of layers for V P, V S, density, and thickness. Then an accurate forward model can be established using ray tracing and the Zoeppritz equations. This generalized linear inversion uses initial assumptions of the answers and proceeds to refine that answer through a series of steps until the best fit between the synthetic and the real data is achieved. AVO inversion was performed using the brine model, gas model 1, and gas model 2 as starting models. The maximum amounts the inverted parameters were allowed to change were: V P, 5000 ft/s; density, 1.0 g/cm 3 ; layer thickness, 100 ft; V S, 5000 ft/s. The model consists of 63 layers. Brine-sand starting model: Figure 11 shows AVO inversion for near offsets, allowing only V P, density, and thickness to change from the starting brine OCTOBER 2003 THE LEADING EDGE 995
7 Figure 13. AVO inversion for near offsets, allowing V P, density, and layer thickness to change and using gas model 1 as starting model. Red log is after inversion and black log is before inversion. Figure 14. AVO inversion for near and far offsets, allowing V S to change and using gas model 1 as starting model. Red log is after inversion and black log is before inversion. Figure 15. AVO inversion for near offsets, allowing V P, density, and layer thickness to change and using gas model 2 as starting model. Red log is after inversion and black log is before inversion. Figure 16. AVO inversion for near and far offsets, allowing V S to change and using gas model 2 as starting model. Red log is after inversion and black log is before inversion. 996 THE LEADING EDGE OCTOBER 2003
8 model which employed the original well-log data. The V P and density values after inversion (red curves) show only minor changes. Figure 12 shows the AVO inversion for all offsets, allowing only V S to change and using the near-trace inversion results with V S predicted from trend curves as the starting model. Note that V S, after inversion (red curve), has slightly decreased in the lower part of the main gas intervals at ms TWT. An abnormal increase of V S is observed at 463 ms TWT (2495 ft), which indicates abnormal decrease in Poisson s ratio curve (0.12), presumably caused by the presence of gas. The Poisson s ratio curve slightly increases at the bottom of the main gas interval and exhibits a major decrease at 463 ms TWT (2495 ft). Gas-sand starting model 1: AVO inversion was also performed using gas model 1 as the starting model (Figure 13). V P and density reflect only minor changes after inversion for near offsets. These were used as the starting model for the full gather, allowing only V S to change (Figure 14). V S in the lower part of the main gas interval was decreased. No significant changes were evident in the top of the main reservoir. Note an abrupt increase of V S at 463 ms TWT (2495 ft). Poisson s ratio increases for the bottom part of the main gas interval. A major decrease in Poisson s ratio occurs at 463 ms TWT (2495 ft). An inverted Poisson ratio curve indicates no gas at 440 ms TWT (2350 ft) and 457 ms TWT (2460 ft). Gas-sand starting model 2: First, after allowing V P, density, and layer thickness to change (Figure 15), the inverted V P and density were shifted 9 ft upward, with an increase in the lower part of the main reservoir. Figure 16 shows the AVO inversion for the full gathers, using the near-trace inversion results as the starting model and allowing only V S to change. Inverted V S decreases in the lower part of the main gas intervals. Poisson s ratio increases at the base of the main reservoir and does not change at the top of the main reservoir. A Poisson s ratio drop to 0.1 at 463 ms TWT (2495 ft) indicates gas. Poisson s ratio indicates no gas in the other two intervals at 440 TWT (2350 ft) and 457 ms TWT (2460 ft). Both gas models confirm the presence of gas at the top of the main reservoir at 480 ms TWT (2590 ft). Another gas interval was detected by the inversion at 463 ms TWT (2495 ft). A gas interval at 440 ms TWT (2350 ft) was not apparent after the inversion. Conclusion. A lower Atoka (Pennsylvanian) high-impedance sand package has been shown to exhibit a class I AVO anomaly with a phase reversal. This suggests that AVO analysis may be a useful tool for detecting and delineating high impedance gas sands in the northern Arkoma Basin. AVO inversion indicates the presence of gas in this lower Atoka sand. Suggested reading. AVO inversion, theory and practice by Hampson (TLE, 1991). A model-based analysis of AVO in Sacramento Valley by Hong et al. (Offset-Dependent Reflectivity Theory and Practice of AVO Analysis, SEG, 1993). Vitrinite reflectance and deep Arbuckle maturation at Wilburton Field, Latimer County, Oklahoma by Hendrick (in Oklahoma Geological Survey Circular 93, 1992). TLE Acknowledgment: The authors thank Jerry Wilson, manager of Pathfinder LLC, for providing data and financial support. Corresponding author: meissa@ou.edu OCTOBER 2003 THE LEADING EDGE 997
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation. for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea. R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.
 Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
Search and Discovery Article #41255 (2014)** Posted February 11, 2014
 Correlating Porosity with Acoustic Impedance in Sandstone Gas Reservoirs: Examples from the Atokan Sandstones of the Arkoma Basin, Southeastern Oklahoma* Ibrahim Çemen 1, Jeff Fuchs 1, Bill Coffey 2, Rodney
Correlating Porosity with Acoustic Impedance in Sandstone Gas Reservoirs: Examples from the Atokan Sandstones of the Arkoma Basin, Southeastern Oklahoma* Ibrahim Çemen 1, Jeff Fuchs 1, Bill Coffey 2, Rodney
Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Seismic Inversion Techniques
 P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection
 A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma
 Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary The Woodford Shale is one of the more important resource
Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary The Woodford Shale is one of the more important resource
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks
 An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait
 Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion and Amplitude Versus Angle Modeling Reduces the Risk in Hydrocarbon Prospect Evaluation
 Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay. Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round
 New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round Multiclient data interpretation provides key deliverables
New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round Multiclient data interpretation provides key deliverables
Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field
 Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field Downloaded 09/12/14 to 84.215.159.82. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use
Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field Downloaded 09/12/14 to 84.215.159.82. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use
Seismic reservoir characterization of a U.S. Midcontinent fluvial system using rock physics, poststack seismic attributes, and neural networks
 CORNER INTERPRETER S Coordinated by Linda R. Sternbach Seismic reservoir characterization of a U.S. Midcontinent fluvial system using rock physics, poststack seismic attributes, and neural networks JOEL
CORNER INTERPRETER S Coordinated by Linda R. Sternbach Seismic reservoir characterization of a U.S. Midcontinent fluvial system using rock physics, poststack seismic attributes, and neural networks JOEL
AFI (AVO Fluid Inversion)
 AFI (AVO Fluid Inversion) Uncertainty in AVO: How can we measure it? Dan Hampson, Brian Russell Hampson-Russell Software, Calgary Last Updated: April 2005 Authors: Dan Hampson, Brian Russell 1 Overview
AFI (AVO Fluid Inversion) Uncertainty in AVO: How can we measure it? Dan Hampson, Brian Russell Hampson-Russell Software, Calgary Last Updated: April 2005 Authors: Dan Hampson, Brian Russell 1 Overview
Case History. 3-D AVO analysis and modeling applied to fracture detection in coalbed methane reservoirs. Antonio C. B. Ramos and Thomas L.
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 62, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1997); P. 1683 1695, 23 FIGS., 1 TABLE. Case History 3-D AVO analysis and modeling applied to fracture detection in coalbed methane reservoirs Antonio C. B.
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 62, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1997); P. 1683 1695, 23 FIGS., 1 TABLE. Case History 3-D AVO analysis and modeling applied to fracture detection in coalbed methane reservoirs Antonio C. B.
Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin
 P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
Derived Rock Attributes Analysis for Enhanced Reservoir Fluid and Lithology Discrimination
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 95-105 www.iosrjournals.org Derived Rock Attributes Analysis
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 95-105 www.iosrjournals.org Derived Rock Attributes Analysis
The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field
 P-305 The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field Summary V B Singh*, Mahendra Pratap, ONGC The objective of the modeling was to
P-305 The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field Summary V B Singh*, Mahendra Pratap, ONGC The objective of the modeling was to
Tim Carr - West Virginia University
 Tim Carr - West Virginia University Understanding Seismic Data Resolution (Vertical and Horizontal) Common Depth Points (CDPs) Two way time (TWT) Time versus depth Interpretation of Reflectors 2 Able to
Tim Carr - West Virginia University Understanding Seismic Data Resolution (Vertical and Horizontal) Common Depth Points (CDPs) Two way time (TWT) Time versus depth Interpretation of Reflectors 2 Able to
Practical aspects of AVO modeling
 Practical aspects of AVO modeling YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Canada JONATHAN DOWNTON, Veritas, Calgary, Canada, YONG XU, Arcis Corporation, Calgary, Canada AVO (amplitude variation with
Practical aspects of AVO modeling YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Canada JONATHAN DOWNTON, Veritas, Calgary, Canada, YONG XU, Arcis Corporation, Calgary, Canada AVO (amplitude variation with
Time lapse view of the Blackfoot AVO anomaly
 Time lapse view of the Blackfoot AVO anomaly Han-xing Lu, Gary F. Margrave and Colin C. Potter Time lapse view of the Blackfoot AVO SUMMARY In the Blackfoot field, southeast of Calgary there is an incised
Time lapse view of the Blackfoot AVO anomaly Han-xing Lu, Gary F. Margrave and Colin C. Potter Time lapse view of the Blackfoot AVO SUMMARY In the Blackfoot field, southeast of Calgary there is an incised
Downloaded 11/20/12 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 AVO crossplot analysis in unconsolidated sediments containing gas hydrate and free gas: Green Canyon 955, Gulf of Mexico Zijian Zhang* 1, Daniel R. McConnell 1, De-hua Han 2 1 Fugro GeoConsulting, Inc.,
AVO crossplot analysis in unconsolidated sediments containing gas hydrate and free gas: Green Canyon 955, Gulf of Mexico Zijian Zhang* 1, Daniel R. McConnell 1, De-hua Han 2 1 Fugro GeoConsulting, Inc.,
The reason why acoustic and shear impedances inverted
 SPECIAL The Rocky SECTION: Mountain The Rocky region Mountain region Comparison of shear impedances inverted from stacked PS and SS data: Example from Rulison Field, Colorado ELDAR GULIYEV, Occidental
SPECIAL The Rocky SECTION: Mountain The Rocky region Mountain region Comparison of shear impedances inverted from stacked PS and SS data: Example from Rulison Field, Colorado ELDAR GULIYEV, Occidental
Amplitude variation with offset AVO. and. Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators DHI. Reflection at vertical incidence. Reflection at oblique incidence
 Amplitude variation with offset AVO and Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators DHI Reflection at vertical incidence Reflection coefficient R(p) c α 1 S wavespeed β 1 density ρ 1 α 2 S wavespeed β 2 density ρ 2
Amplitude variation with offset AVO and Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators DHI Reflection at vertical incidence Reflection coefficient R(p) c α 1 S wavespeed β 1 density ρ 1 α 2 S wavespeed β 2 density ρ 2
FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON
 FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 10 14 July 2017 Jakarta The course is aimed at teaching the physical concepts involved in the application of seismic
FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 10 14 July 2017 Jakarta The course is aimed at teaching the physical concepts involved in the application of seismic
Analysis of multicomponent walkaway vertical seismic profile data
 Analysis of multicomponent walkaway vertical seismic profile data Bona Wu, Don C. Lawton, and Kevin W. Hall ABSTRACT A multicomponent walkaway VSP data processed for PP and PS imaging as well to study
Analysis of multicomponent walkaway vertical seismic profile data Bona Wu, Don C. Lawton, and Kevin W. Hall ABSTRACT A multicomponent walkaway VSP data processed for PP and PS imaging as well to study
INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION
 INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 31 July 4 August 2017 Jakarta COURSE OUTLINE The course is aimed at imparting working knowledge
INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 31 July 4 August 2017 Jakarta COURSE OUTLINE The course is aimed at imparting working knowledge
Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration
 Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration ABSTRACT Yong Xu*, Satinder Chopra Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division, 301,400-3rd Ave SW, Calgary, AB, T2P 4H2 yxu@corelab.ca Summary
Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration ABSTRACT Yong Xu*, Satinder Chopra Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division, 301,400-3rd Ave SW, Calgary, AB, T2P 4H2 yxu@corelab.ca Summary
We apply a rock physics analysis to well log data from the North-East Gulf of Mexico
 Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
A031 Porosity and Shale Volume Estimation for the Ardmore Field Using Extended Elastic Impedance
 A31 Porosity and Shale Volume Estimation for the Ardmore Field Using Extended Elastic Impedance A.M. Francis* (Earthworks Environment & Resources Ltd) & G.J. Hicks (Earthworks Environment & Resources Ltd)
A31 Porosity and Shale Volume Estimation for the Ardmore Field Using Extended Elastic Impedance A.M. Francis* (Earthworks Environment & Resources Ltd) & G.J. Hicks (Earthworks Environment & Resources Ltd)
Elements of 3D Seismology Second Edition
 Elements of 3D Seismology Second Edition Copyright c 1993-2003 All rights reserved Christopher L. Liner Department of Geosciences University of Tulsa August 14, 2003 For David and Samantha And to the memory
Elements of 3D Seismology Second Edition Copyright c 1993-2003 All rights reserved Christopher L. Liner Department of Geosciences University of Tulsa August 14, 2003 For David and Samantha And to the memory
SEG/San Antonio 2007 Annual Meeting. Summary
 A comparison of porosity estimates obtained using post-, partial-, and prestack seismic inversion methods: Marco Polo Field, Gulf of Mexico. G. Russell Young* and Mrinal K. Sen, The Institute for Geophysics
A comparison of porosity estimates obtained using post-, partial-, and prestack seismic inversion methods: Marco Polo Field, Gulf of Mexico. G. Russell Young* and Mrinal K. Sen, The Institute for Geophysics
Pre-stack (AVO) and post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data
 Pre-stack (AVO) and post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data A.Nassir Saeed, Gary F. Margrave and Laurence R. Lines ABSTRACT Post-stack and pre-stack (AVO) inversion were performed
Pre-stack (AVO) and post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data A.Nassir Saeed, Gary F. Margrave and Laurence R. Lines ABSTRACT Post-stack and pre-stack (AVO) inversion were performed
An overview of AVO and inversion
 P-486 An overview of AVO and inversion Brian Russell, Hampson-Russell, CGGVeritas Company Summary The Amplitude Variations with Offset (AVO) technique has grown to include a multitude of sub-techniques,
P-486 An overview of AVO and inversion Brian Russell, Hampson-Russell, CGGVeritas Company Summary The Amplitude Variations with Offset (AVO) technique has grown to include a multitude of sub-techniques,
Delineating a sandstone reservoir at Pikes Peak, Saskatchewan using 3C seismic data and well logs
 Delineating a sandston reservoir at Pikes Peak Delineating a sandstone reservoir at Pikes Peak, Saskatchewan using 3C seismic data and well logs Natalia L. Soubotcheva and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT To
Delineating a sandston reservoir at Pikes Peak Delineating a sandstone reservoir at Pikes Peak, Saskatchewan using 3C seismic data and well logs Natalia L. Soubotcheva and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT To
RC 1.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1307
 from seismic AVO Xin-Gong Li,University of Houston and IntSeis Inc, De-Hua Han, and Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Donn McGuire, Anadarko Petroleum Corp Summary A new inversion method is tested to directly
from seismic AVO Xin-Gong Li,University of Houston and IntSeis Inc, De-Hua Han, and Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Donn McGuire, Anadarko Petroleum Corp Summary A new inversion method is tested to directly
OTC OTC PP. Abstract
 OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
A.K. Khanna*, A.K. Verma, R.Dasgupta, & B.R.Bharali, Oil India Limited, Duliajan.
 P-92 Application of Spectral Decomposition for identification of Channel Sand Body in OIL s operational area in Upper Assam Shelf Basin, India - A Case study A.K. Khanna*, A.K. Verma, R.Dasgupta, & B.R.Bharali,
P-92 Application of Spectral Decomposition for identification of Channel Sand Body in OIL s operational area in Upper Assam Shelf Basin, India - A Case study A.K. Khanna*, A.K. Verma, R.Dasgupta, & B.R.Bharali,
Sensitivity Analysis of Pre stack Seismic Inversion on Facies Classification using Statistical Rock Physics
 Sensitivity Analysis of Pre stack Seismic Inversion on Facies Classification using Statistical Rock Physics Peipei Li 1 and Tapan Mukerji 1,2 1 Department of Energy Resources Engineering 2 Department of
Sensitivity Analysis of Pre stack Seismic Inversion on Facies Classification using Statistical Rock Physics Peipei Li 1 and Tapan Mukerji 1,2 1 Department of Energy Resources Engineering 2 Department of
Interpretation of baseline surface seismic data at the Violet Grove CO 2 injection site, Alberta
 Violet Grove seismic interpretation Interpretation of baseline surface seismic data at the Violet Grove CO 2 injection site, Alberta Fuju Chen and Don Lawton ABSTRACT Time-lapse seismic technology has
Violet Grove seismic interpretation Interpretation of baseline surface seismic data at the Violet Grove CO 2 injection site, Alberta Fuju Chen and Don Lawton ABSTRACT Time-lapse seismic technology has
THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS
 THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS Cuesta, Julián* 1, Pérez, Richard 1 ; Hernández, Freddy 1 ; Carrasquel, Williams 1 ; Cabrera,
THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS Cuesta, Julián* 1, Pérez, Richard 1 ; Hernández, Freddy 1 ; Carrasquel, Williams 1 ; Cabrera,
Rock-Physics and Seismic-Inversion Based Reservoir Characterization of AKOS FIELD, Coastal Swamp Depobelt, Niger Delta, Nigeria
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 59-67 www.iosrjournals.org Rock-Physics and Seismic-Inversion
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 59-67 www.iosrjournals.org Rock-Physics and Seismic-Inversion
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting. that the project results can correctly interpreted.
 Calibration of Pre-Stack Simultaneous Impedance Inversion using Rock Physics Scott Singleton and Rob Keirstead, Rock Solid Images Log Conditioning and Rock Physics Modeling Summary Geophysical Well Log
Calibration of Pre-Stack Simultaneous Impedance Inversion using Rock Physics Scott Singleton and Rob Keirstead, Rock Solid Images Log Conditioning and Rock Physics Modeling Summary Geophysical Well Log
Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study
 Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study Suresh Thampi, Aqeel Ahmed, Yahya Al-Ansari, Ali Shehab, Ahmed Fateh, Anindya Ghosh, Ghada Almoulani. The
Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study Suresh Thampi, Aqeel Ahmed, Yahya Al-Ansari, Ali Shehab, Ahmed Fateh, Anindya Ghosh, Ghada Almoulani. The
AVO analysis of 3-D seismic data at G-field, Norway
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(5):148-164 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC AVO analysis of 3-D seismic data at G-field, Norway Fredrick
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(5):148-164 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC AVO analysis of 3-D seismic data at G-field, Norway Fredrick
PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%)
 PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%) Your answers should be brief (just a few words) and may be written on these pages if you wish. Remember to hand these pages in with your other exam pages!
PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%) Your answers should be brief (just a few words) and may be written on these pages if you wish. Remember to hand these pages in with your other exam pages!
Summary. Seismic Field Example
 Water-saturation estimation from seismic and rock-property trends Zhengyun Zhou*, Fred J. Hilterman, Haitao Ren, Center for Applied Geosciences and Energy, University of Houston, Mritunjay Kumar, Dept.
Water-saturation estimation from seismic and rock-property trends Zhengyun Zhou*, Fred J. Hilterman, Haitao Ren, Center for Applied Geosciences and Energy, University of Houston, Mritunjay Kumar, Dept.
Comparative Study of AVO attributes for Reservoir Facies Discrimination and Porosity Prediction
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-004, India PP 498-50 Comparative Study of AVO attributes for Reservoir Facies Discrimination and Porosity Prediction Y. Hanumantha Rao & A.K.
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-004, India PP 498-50 Comparative Study of AVO attributes for Reservoir Facies Discrimination and Porosity Prediction Y. Hanumantha Rao & A.K.
Quantifying Bypassed Pay Through 4-D Post-Stack Inversion*
 Quantifying Bypassed Pay Through 4-D Post-Stack Inversion* Robert Woock 1, Sean Boerner 2 and James Gamble 1 Search and Discovery Article #40799 (2011) Posted August 12, 2011 *Adapted from oral presentation
Quantifying Bypassed Pay Through 4-D Post-Stack Inversion* Robert Woock 1, Sean Boerner 2 and James Gamble 1 Search and Discovery Article #40799 (2011) Posted August 12, 2011 *Adapted from oral presentation
Acoustic impedance inversion analysis: Croatia offshore and onshore case studies
 Acoustic impedance inversion analysis: Croatia offshore and onshore case studies Domagoj Vukadin, mag. ing. geol. Stipica Brnada, mag. geol. SPE Conference Hungarian Section Visegrád, November, 19. 2015
Acoustic impedance inversion analysis: Croatia offshore and onshore case studies Domagoj Vukadin, mag. ing. geol. Stipica Brnada, mag. geol. SPE Conference Hungarian Section Visegrád, November, 19. 2015
3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history
 P-290 3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history N. B. R. Prasad, ONGC Summary In recent years, there has been a growing interest in shear- wave exploration for hydrocarbons as it facilitates to
P-290 3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history N. B. R. Prasad, ONGC Summary In recent years, there has been a growing interest in shear- wave exploration for hydrocarbons as it facilitates to
Oil and Gas Research Institute Seismic Analysis Center Faults Detection Using High-Resolution Seismic Reflection Techniques
 Oil and Gas Research Institute Seismic Analysis Center Faults Detection Using High-Resolution Seismic Reflection Techniques Ghunaim T. Al-Anezi (KACST) March 2013 1 Objectives The objective of the survey
Oil and Gas Research Institute Seismic Analysis Center Faults Detection Using High-Resolution Seismic Reflection Techniques Ghunaim T. Al-Anezi (KACST) March 2013 1 Objectives The objective of the survey
Recent advances in application of AVO to carbonate reservoirs: case histories
 Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition
 Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition X. Qin* (University of Houston) & D. Han (University of Houston) SUMMARY In this study, we strive to understand unloading
Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition X. Qin* (University of Houston) & D. Han (University of Houston) SUMMARY In this study, we strive to understand unloading
Improved image aids interpretation: A case history
 Ye Zheng, Scott Cheadle (Veritas GeoServices, Calgary, Canada) Glenn M. Rising (Perez Companc Norcen Corod, Venezuela) SUMMARY The Oritupano-Leona 3D of Eastern Venezuela was originally acquired and processed
Ye Zheng, Scott Cheadle (Veritas GeoServices, Calgary, Canada) Glenn M. Rising (Perez Companc Norcen Corod, Venezuela) SUMMARY The Oritupano-Leona 3D of Eastern Venezuela was originally acquired and processed
USING 3-D SEISMIC INVERSION DATA AS A TOOL FOR PREDICTING POROSITY IN THE WILBURTON GAS FIELD, ARKOMA BASIN, SOUTHEASTERN OKLAHOMA
 USING 3-D SEISMIC INVERSION DATA AS A TOOL FOR PREDICTING POROSITY IN THE WILBURTON GAS FIELD, ARKOMA BASIN, SOUTHEASTERN OKLAHOMA by JEFFREY CHARLES FUCHS IBRAHIM ÇEMEN, COMMITTEE CHAIR ANDREW GOODLIFFE
USING 3-D SEISMIC INVERSION DATA AS A TOOL FOR PREDICTING POROSITY IN THE WILBURTON GAS FIELD, ARKOMA BASIN, SOUTHEASTERN OKLAHOMA by JEFFREY CHARLES FUCHS IBRAHIM ÇEMEN, COMMITTEE CHAIR ANDREW GOODLIFFE
INT 4.5. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 821
 Kathleen Baker* and Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines, Richard Gibson, Texas A&M University Summary There have been many studies of how Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators (DHIs) can help or hurt us when
Kathleen Baker* and Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines, Richard Gibson, Texas A&M University Summary There have been many studies of how Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators (DHIs) can help or hurt us when
Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data
 Inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Patricia E. Gavotti, Don C. Lawton, Gary F. Margrave and J. Helen Isaac ABSTRACT The Hussar
Inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Patricia E. Gavotti, Don C. Lawton, Gary F. Margrave and J. Helen Isaac ABSTRACT The Hussar
OTC Paper Number 15248
 OTC Paper Number 15248 The Vp/Vs Inversion Procedure: A Methodology for Shallow Water Flow (SWF) Prediction from Seismic Analysis of Multicomponent Data. Carlos Moreno* / The University of Oklahoma, John
OTC Paper Number 15248 The Vp/Vs Inversion Procedure: A Methodology for Shallow Water Flow (SWF) Prediction from Seismic Analysis of Multicomponent Data. Carlos Moreno* / The University of Oklahoma, John
Downloaded 01/29/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 An integrated study of a Mississippian tripolitic chert reservoir Osage County, Oklahoma, USA Benjamin L. Dowdell*, Atish Roy, and Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary With the advent of
An integrated study of a Mississippian tripolitic chert reservoir Osage County, Oklahoma, USA Benjamin L. Dowdell*, Atish Roy, and Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary With the advent of
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc.
 Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Instantaneous Spectral Analysis Applied to Reservoir Imaging and Producibility Characterization
 Instantaneous Spectral Analysis Applied to Reservoir Imaging and Producibility Characterization Feng Shen 1* and Gary C. Robinson 1, Tao jiang 2 1 EP Tech, Centennial, CO, 80112, 2 PetroChina Oil Company,
Instantaneous Spectral Analysis Applied to Reservoir Imaging and Producibility Characterization Feng Shen 1* and Gary C. Robinson 1, Tao jiang 2 1 EP Tech, Centennial, CO, 80112, 2 PetroChina Oil Company,
Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains
 Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Application of High Resolution Seismic Survey in CBM Exploration A Case study, Sohagpur West Block, Madhya Pradesh
 P - 421 Application of High Resolution Seismic Survey in CBM Exploration A Case study, Sohagpur West Block, Madhya Pradesh T. Seshunarayana, D.Viswaja*, K.N.S.S.S. Srinivas, P. Srinivasa Rao, S. Trupti,
P - 421 Application of High Resolution Seismic Survey in CBM Exploration A Case study, Sohagpur West Block, Madhya Pradesh T. Seshunarayana, D.Viswaja*, K.N.S.S.S. Srinivas, P. Srinivasa Rao, S. Trupti,
Seismic reservoir characterization using the multiattribute rotation scheme: Case study in the South Falkland Basin
 Seismic reservoir characterization using the multiattribute rotation scheme: Case study in the South Falkland Basin Pedro Alvarez 1, Bruce Farrer 2, and Doyin Oyetunji 1 Downloaded 08/15/16 to 50.207.209.154.
Seismic reservoir characterization using the multiattribute rotation scheme: Case study in the South Falkland Basin Pedro Alvarez 1, Bruce Farrer 2, and Doyin Oyetunji 1 Downloaded 08/15/16 to 50.207.209.154.
Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
Multiattribute seismic analysis on AVO-derived parameters A case study
 Multiattriute seismic analysis on AVO-derived parameters A case study SATINDER CHOPRA, Core La Reservoir Technologies, Calgary, Canada DOUG PRUDEN, GEDCO, Calgary, Canada Prospecting for reservoir zones
Multiattriute seismic analysis on AVO-derived parameters A case study SATINDER CHOPRA, Core La Reservoir Technologies, Calgary, Canada DOUG PRUDEN, GEDCO, Calgary, Canada Prospecting for reservoir zones
Impact of Phase Variations on Quantitative AVO Analysis
 Impact of Phase Variations on Quantitative AVO Analysis Summary A.K. Srivastava, V. Singh*, D.N. Tiwary and V. Rangachari GEOPIC, ONGC, Dehradun Email: ak_sri3@rediffmail.com Effectiveness of AVO techniques
Impact of Phase Variations on Quantitative AVO Analysis Summary A.K. Srivastava, V. Singh*, D.N. Tiwary and V. Rangachari GEOPIC, ONGC, Dehradun Email: ak_sri3@rediffmail.com Effectiveness of AVO techniques
Geological Framework for Active Resource Plays in Oklahoma. Edith Newton Wilson, PhD Rock Whisperer LLC March 4, 2014
 Geological Framework for Active Resource Plays in Oklahoma Edith Newton Wilson, PhD Rock Whisperer LLC March 4, 2014 Oklahoma Oil Production 2000: 200,000 bopd* 2013: 300,000 bopd** 10 6 What Oklahoma
Geological Framework for Active Resource Plays in Oklahoma Edith Newton Wilson, PhD Rock Whisperer LLC March 4, 2014 Oklahoma Oil Production 2000: 200,000 bopd* 2013: 300,000 bopd** 10 6 What Oklahoma
Static Corrections for Seismic Reflection Surveys
 Static Corrections for Seismic Reflection Surveys MIKE COX Volume Editors: Series Editor: Eugene F. Scherrer Roland Chen Eugene F. Scherrer Society of Exploration Geophysicists Tulsa, Oklahoma Contents
Static Corrections for Seismic Reflection Surveys MIKE COX Volume Editors: Series Editor: Eugene F. Scherrer Roland Chen Eugene F. Scherrer Society of Exploration Geophysicists Tulsa, Oklahoma Contents
The elastic properties such as velocity, density, impedance,
 SPECIAL SECTION: Rr ock Physics physics Lithology and fluid differentiation using rock physics template XIN-GANG CHI AND DE-HUA HAN, University of Houston The elastic properties such as velocity, density,
SPECIAL SECTION: Rr ock Physics physics Lithology and fluid differentiation using rock physics template XIN-GANG CHI AND DE-HUA HAN, University of Houston The elastic properties such as velocity, density,
AVO responses for varying Gas saturation sands A Possible Pathway in Reducing Exploration Risk
 P 420 AVO responses for varying Gas saturation sands A Possible Pathway in Reducing Exploration Risk Naina Gupta*, Debajyoti Guha, Ashok Yadav, Santan Kumar, Ashutosh Garg *Reliance Industries Limited,
P 420 AVO responses for varying Gas saturation sands A Possible Pathway in Reducing Exploration Risk Naina Gupta*, Debajyoti Guha, Ashok Yadav, Santan Kumar, Ashutosh Garg *Reliance Industries Limited,
Integrating Rock Physics into the Seismic Image
 Government-Funded Exploration License Competition The project: Mid North Sea High Integrating Rock Physics into the Seismic Image Kinga Wroblewska, Geophysicist Geop4ysics Ltd Petex, 17 November 2016 Integrating
Government-Funded Exploration License Competition The project: Mid North Sea High Integrating Rock Physics into the Seismic Image Kinga Wroblewska, Geophysicist Geop4ysics Ltd Petex, 17 November 2016 Integrating
Downloaded 10/02/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Multi-scenario, multi-realization seismic inversion for probabilistic seismic reservoir characterization Kester Waters* and Michael Kemper, Ikon Science Ltd. Summary We propose a two tiered inversion strategy
Multi-scenario, multi-realization seismic inversion for probabilistic seismic reservoir characterization Kester Waters* and Michael Kemper, Ikon Science Ltd. Summary We propose a two tiered inversion strategy
Rock Physics Perturbational Modeling: Carbonate case study, an intracratonic basin Northwest/Saharan Africa
 Rock Physics Perturbational Modeling: Carbonate case study, an intracratonic basin Northwest/Saharan Africa Franklin Ruiz, Carlos Cobos, Marcelo Benabentos, Beatriz Chacon, and Roberto Varade, Luis Gairifo,
Rock Physics Perturbational Modeling: Carbonate case study, an intracratonic basin Northwest/Saharan Africa Franklin Ruiz, Carlos Cobos, Marcelo Benabentos, Beatriz Chacon, and Roberto Varade, Luis Gairifo,
Unconventional reservoir characterization using conventional tools
 Ritesh K. Sharma* and Satinder Chopra Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS, Calgary, Canada Summary Shale resources characterization has gained attention in the last decade or so, after the Mississippian Barnett
Ritesh K. Sharma* and Satinder Chopra Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS, Calgary, Canada Summary Shale resources characterization has gained attention in the last decade or so, after the Mississippian Barnett
Seismic reservoir characterization in offshore Nile Delta.
 Seismic reservoir characterization in offshore Nile Delta. Part II: Probabilistic petrophysical-seismic inversion M. Aleardi 1, F. Ciabarri 2, B. Garcea 2, A. Mazzotti 1 1 Earth Sciences Department, University
Seismic reservoir characterization in offshore Nile Delta. Part II: Probabilistic petrophysical-seismic inversion M. Aleardi 1, F. Ciabarri 2, B. Garcea 2, A. Mazzotti 1 1 Earth Sciences Department, University
The Geology of the Arbuckle Group in the Midcontinent: Sequence Stratigraphy, Reservoir Development, and the Potential for Hydrocarbon Exploration*
 The Geology of the Arbuckle Group in the Midcontinent: Sequence Stratigraphy, Reservoir Development, and the Potential for Hydrocarbon Exploration* Richard D. Fritz 1, Patrick Medlock 2, Michael J. Kuykendall
The Geology of the Arbuckle Group in the Midcontinent: Sequence Stratigraphy, Reservoir Development, and the Potential for Hydrocarbon Exploration* Richard D. Fritz 1, Patrick Medlock 2, Michael J. Kuykendall
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES ABSTRACT
 ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
Prestack amplitude analysis methodology and application to seismic bright spots in the PO Valley, Italy
 GEOPHYSICS. VOL. 55. NO. 2 (FEBRUARY 1990); P. 157-166, 14 FIGS Prestack amplitude analysis methodology and application to seismic bright spots in the PO Valley, Italy Alfred0 Mazzotti* ABSTRACT The amplitude-versus-offset
GEOPHYSICS. VOL. 55. NO. 2 (FEBRUARY 1990); P. 157-166, 14 FIGS Prestack amplitude analysis methodology and application to seismic bright spots in the PO Valley, Italy Alfred0 Mazzotti* ABSTRACT The amplitude-versus-offset
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes
 Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
Bandlimited impedance inversion: using well logs to fill low frequency information in a non-homogenous model
 Bandlimited impedance inversion: using well logs to fill low frequency information in a non-homogenous model Heather J.E. Lloyd and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT An acoustic bandlimited impedance inversion
Bandlimited impedance inversion: using well logs to fill low frequency information in a non-homogenous model Heather J.E. Lloyd and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT An acoustic bandlimited impedance inversion
Downloaded 11/02/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at Summary.
 in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
Impact of the CDP Gathers and Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion in the Prospect Evaluation, Onshore Nile Delta, Egypt
 S Open Access Journal of Geology and Geoscience Research Article Impact of the CDP Gathers and Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion in the Prospect Evaluation, Onshore Nile Delta, Egypt Ahmed S Abu El Ata¹, Mohamed
S Open Access Journal of Geology and Geoscience Research Article Impact of the CDP Gathers and Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion in the Prospect Evaluation, Onshore Nile Delta, Egypt Ahmed S Abu El Ata¹, Mohamed
Bulletin of Earth Sciences of Thailand. Controls on Reservoir Geometry and Distribution, Tantawan Field, Gulf of Thailand.
 Controls on Reservoir Geometry and Distribution, Tantawan Field, Gulf of Thailand Atchara Praidee Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Controls on Reservoir Geometry and Distribution, Tantawan Field, Gulf of Thailand Atchara Praidee Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 375-379 Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History D. Srinivas, T.R. Murali Mohan, Ashwani Lamba,
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 375-379 Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History D. Srinivas, T.R. Murali Mohan, Ashwani Lamba,
Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions
 Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions Folke Engelmark* PGS Multi-Transient EM, Asia-Pacific, Singapore folke.engelmark@pgs.com Summary Successful as
Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions Folke Engelmark* PGS Multi-Transient EM, Asia-Pacific, Singapore folke.engelmark@pgs.com Summary Successful as
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd., VRC(Panvel), WOB, ONGC, Mumbai. 1
 P-259 Summary Data for identification of Porosity Behaviour in Oligocene Lime Stone of D18 Area Of Western Offshore, India V.K. Baid*, P.H. Rao, P.S. Basak, Ravi Kant, V. Vairavan 1, K.M. Sundaram 1, ONGC
P-259 Summary Data for identification of Porosity Behaviour in Oligocene Lime Stone of D18 Area Of Western Offshore, India V.K. Baid*, P.H. Rao, P.S. Basak, Ravi Kant, V. Vairavan 1, K.M. Sundaram 1, ONGC
The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc.
 The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc. While the application of new geophysical and petrophysical technology separately can
The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc. While the application of new geophysical and petrophysical technology separately can
Structural Geology of the Mountains
 Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Seismic interpretation. Principles of seismic stratigraphic interpretation
 Seismic interpretation Principles of seismic stratigraphic interpretation Seismic interpretation Seismic stratigraphy is a technical for interpreting stratigraphic information from seismic data. The resolution
Seismic interpretation Principles of seismic stratigraphic interpretation Seismic interpretation Seismic stratigraphy is a technical for interpreting stratigraphic information from seismic data. The resolution
Benefits of Integrated Seismic and Gravity Exploration: An example from Norman Wells, NWT
 Benefits of Integrated Seismic and Gravity Exploration: An example from Norman Wells, NWT J. Helen Isaac* and Donald C. Lawton Fold-Fault Research Project, University of Calgary 2500 University Drive NW,
Benefits of Integrated Seismic and Gravity Exploration: An example from Norman Wells, NWT J. Helen Isaac* and Donald C. Lawton Fold-Fault Research Project, University of Calgary 2500 University Drive NW,
Reflection Seismic Method
 Reflection Seismic Method Data and Image sort orders; Seismic Impedance; -D field acquisition geometries; CMP binning and fold; Resolution, Stacking charts; Normal Moveout and correction for it; Stacking;
Reflection Seismic Method Data and Image sort orders; Seismic Impedance; -D field acquisition geometries; CMP binning and fold; Resolution, Stacking charts; Normal Moveout and correction for it; Stacking;
Inversion and interpretation of multicomponent seismic data: Willesden Green, Alberta
 Willesden Green Inversion and interpretation of multicomponent seismic data: Willesden Green, Alberta Roxana M. Varga, Robert R. Stewart and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT In this paper, 2D multicomponent seismic
Willesden Green Inversion and interpretation of multicomponent seismic data: Willesden Green, Alberta Roxana M. Varga, Robert R. Stewart and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT In this paper, 2D multicomponent seismic
ZONGE GEOSCIENCES, INC.
 ZONGE GEOSCIENCES, INC. GEOPHYSICAL INVESTIGATION REPORT 2D Seismic Reflection Survey Crump Geyser Geothermal Prospect Warner Valley, Oregon Prepared for: John Casteel District Geologist Nevada Geothermal
ZONGE GEOSCIENCES, INC. GEOPHYSICAL INVESTIGATION REPORT 2D Seismic Reflection Survey Crump Geyser Geothermal Prospect Warner Valley, Oregon Prepared for: John Casteel District Geologist Nevada Geothermal
Quantitative interpretation using inverse rock-physics modeling on AVO data
 Quantitative interpretation using inverse rock-physics modeling on AVO data Erling Hugo Jensen 1, Tor Arne Johansen 2, 3, 4, Per Avseth 5, 6, and Kenneth Bredesen 2, 7 Downloaded 08/16/16 to 129.177.32.62.
Quantitative interpretation using inverse rock-physics modeling on AVO data Erling Hugo Jensen 1, Tor Arne Johansen 2, 3, 4, Per Avseth 5, 6, and Kenneth Bredesen 2, 7 Downloaded 08/16/16 to 129.177.32.62.
Sadewa Field is in Kutei Basin in the Makassar Strait between
 SPECIAL Asia SECTION: Pacific A s i a P acific Distinguishing gas sand from shale/brine sand using elastic impedance data and the determination of the lateral extent of channel reservoirs using amplitude
SPECIAL Asia SECTION: Pacific A s i a P acific Distinguishing gas sand from shale/brine sand using elastic impedance data and the determination of the lateral extent of channel reservoirs using amplitude
The Attribute for Hydrocarbon Prediction Based on Attenuation
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS The Attribute for Hydrocarbon Prediction Based on Attenuation To cite this article: Maman Hermana et al 214 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS The Attribute for Hydrocarbon Prediction Based on Attenuation To cite this article: Maman Hermana et al 214 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
Lithology prediction and fluid discrimination in Block A6 offshore Myanmar
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 141 Lithology prediction and fluid discrimination in Block A6 offshore Myanmar Hanumantha Rao. Y *, Loic Michel, Hampson-Russell, Kyaw Myint, Ko Ko,
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 141 Lithology prediction and fluid discrimination in Block A6 offshore Myanmar Hanumantha Rao. Y *, Loic Michel, Hampson-Russell, Kyaw Myint, Ko Ko,
Shallow Gas Prospect Evaluation in Shahbazpur Structure Using Seismic Attributes Analysis - a Case Study for Bhola Island, Southern Bangladesh
 Dhaka Univ. J. Sci. 64(2): 135-140, 2016 (July) Shallow Gas Prospect Evaluation in Shahbazpur Structure Using Seismic Attributes Analysis - a Case Study for Bhola Island, Southern Bangladesh Morshedur
Dhaka Univ. J. Sci. 64(2): 135-140, 2016 (July) Shallow Gas Prospect Evaluation in Shahbazpur Structure Using Seismic Attributes Analysis - a Case Study for Bhola Island, Southern Bangladesh Morshedur
SEISMIC INVERSION OVERVIEW
 DHI CONSORTIUM SEISMIC INVERSION OVERVIEW Rocky Roden September 2011 NOTE: Terminology for inversion varies, depending on the different contractors and service providers, emphasis on certain approaches,
DHI CONSORTIUM SEISMIC INVERSION OVERVIEW Rocky Roden September 2011 NOTE: Terminology for inversion varies, depending on the different contractors and service providers, emphasis on certain approaches,
Kurt Marfurt Arnaud Huck THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS
 The Society of Exploration Geophysicists and GeoNeurale announce Kurt Marfurt Arnaud Huck THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization
The Society of Exploration Geophysicists and GeoNeurale announce Kurt Marfurt Arnaud Huck THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization
