Evaluation of landslide susceptibility using multivariate statistical methods: a case study in the Prahova subcarpathians, Romania
|
|
|
- Richard Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of landslide susceptibility using multivariate statistical methods: a case study in the Prahova subcarpathians, Romania Z. Chitu, I. Sandric, B. Mihai & I. Savulescu Faculty of Geography, University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania. ABSTRACT: The shallow landslides affect most of the hillslopes in the Prahova Subcarpathians and are mainly caused by the agriculture practices. Though, these processes do not imply immediately losses for human activity, the landslide susceptibility assessment is necessary to prevent terrain degradation. The evaluation of landslide susceptibility requires understanding of spatial distribution of the factors that control slope instability. It is known that the behavior of landslides is difficult to evaluate because of the various factors that trigger the mass movements. One of the most efficient methods to establish the importance of the factors in landslides susceptibility is the multivariate analysis, like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and logistic regression. For this study, the PCA was applied to remove the redundant information from the elements that control slope instability like lithology, faults, slope gradient, plan curvature, profile curvature, land use and land cover, soils etc. The PCA analysis had reduced the factors at six principal components and the first three components comprise over 85% of the information. The logistic regression analysis was used to correlate the presence of the past and actual landslides with the PCA components and derive a landslides susceptibility map. To validate the model we used the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. ROC shows a good correlation between the observed and predicted values of the validation dataset. 1 INTRODUCTION Landslide susceptibility is defined as the likelihood of a landslide occurring in an area on the basis of local terrain conditions (Brabb, 1984). The landslide susceptibility map must provide information about the areas affected by landslides and that may be affected by future landslides. Landslide susceptibility mapping have received special attention in the latest 25 years from various fields of science and several methods have been proposed. Though, there is no agreement for unique methodology, the landslide susceptibility mapping can be performed using one of the available methodologies: geomorhological mapping, heuristic approach, statistical methods or process based models (Guzzetti, 2005). Due to the large area of our study, the high number of variables and especially due to the redundancy in the information, we choose to apply multivariate statistical methods. This approach offers the possibility to handle a high number of layers, to establish the importance of factors in slope instability and the relation between this factors and the past and present distribution of landslides (Carrara 1995). The development of these quantitative techniques with GIS tools, make possible to obtain, in short time, landslide susceptibility maps for large areas (Santacana 2003). Complete overview of the use of GIS for landslide susceptibility assessment can be found in Carrara (1991, 1995), van Westen (1994) and Guzzetti (2005). In Romania, landslide susceptibility assessment is a recent field of research, some contributions were given by Sandric 2003, 2005, Mihai 2005; Micu, in prep. In this study the methodology used to assess shallow landslides susceptibility is principal component analysis and logistic regression, using the procedure implemented in IDRISI Kilimanjaro 2 STUDY AREA Landslides and especially shallow landslides are a common feature for the Romanian hills and plateaus landscapes (Ielenicz et al., 1999; 2005). The study area is located in the Prahova Subcarpathians, along the Prahova River and is the administrative area of Breaza (Fig. 1). 2.1 General presentation The area is characterized by high slope gradient values between 15-30, specific to most of the hill
2 slopes, medium drainage density, with values between km/km 2 (Popp 1939). The natural vegetation was replaced during the last two centuries by the secondary vegetation. The human activity has a relevant impact for this area, with a population density of about inhabitants/km 2. The local economy is dominated by agricultural activities, based mainly on grazing and orchards. The main factors that control the spatial distribution of landslides are: lithology, slope gradient, land-use and land-cover. (Surdeanu 1998). After heavy rainfalls, the Subcarpathian area is affected by landslides, usually superposing on older landslide bodies. Balteanu (1986, 1997) estimated an average denudation rate generated by landslides to mm/year. The shallow landslides are a frequent feature with an average recurrence of 5-7 years (Balteanu 1986). landslides have an important significance for the region, because of the losses caused annually in agriculture. The landslide inventory includes 156 landslides, mostly rotational slides (ca. 92%) and few translational slides (3%), complex landslides (3%) and earth flows (2%). The shallow landslides are spread especially in areas with small vegetation. The deep seated landslides are old landslides which extend over the entire hillslope (Fig. 2). They are either in a dormant state or have been partially reactivated during the rainfall events of 1982, 1997 and The methodology used to create the landslide inventory, is a combination between field observations and aerial image interpretation. The field observations were carried out for about three years ( ), using a Garmin GPS receiver and topographical maps at a scale 1:5000. The aerial images are color orthophotos (acquisition time: 2005), grayscale air-photos from 1972, 1978, 1986 and aerial photos obtained from two flights taken on May 7th and 15th 2008 from a small aircraft, model Cessna F172H, with a Canon 400D camera with 10Megapixels resolution and Tamron AF mm Di-II lens Figure 1. Location of the study area. 2.2 Geology From the geological point of view, the study area is composed from a nappe system. These nappes belong to the Cretaceous and the Paleogene flysch areas, as well as to the Upper Cretaceous and Lower Miocene post tectonic sedimentary covers. The faults, as an effect of the tectonic transformations, show a system of parallel synclines and anticlines, oriented from the East to the West (Damian 2003). The most affected lithostratigraphic units are: Gura Beliei marls (Upper Cretaceous post tectonic sedimentary covers) which produce rotational and translational slides and earthflow; molasses deposits of Doftana (marls, clays, sandstones of Lower Miocene post tectonic sedimentary cover), affected by rotational and translational slides; Pucioasa deposits (marls, clays of Paleogene Flysch) affected by earthflows, rotational and translational slides. 2.3 Landslide inventory We use the term shallow landslides to define the small size rotational and translational slides and earth flows (Santacana et al., 2003). The shallow Figure 2. Shallow and deep-seated landslides on the hillslopes between Prahova Valley and Târsa Valley, reactivated in 2007 by human activity; oblique aerial picture, May 15 th METHODOLOGY When many factors are available an issue of information redundancy is arising. To reduce the number of variables and to limit their interdependence we choose to use the PCA analysis (Carrara, 1995). It is well known that morphometrical parameters derived from DEM present a high interdependence, and this, often, leads to underestimation or overestimation of the results. The principal components analysis was used in order to reduce the redundant information from the variables and transform them from correlated variables into uncorrelated variables, named principal components (Gorsevski 2001). To model the susceptibility for -266-
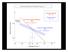
3 landslides we used the logistic regression analysis, which calculates the probability that an individual pixel will contain a landslide. 3.1 Materials The data used to assess the landslide susceptibility is composed from: a DEM with a cell size of 10m, lithology, faults density, drainage density, land-use and land-cover, landslide inventory and several terrain parameters derived from DEM: slope gradient, aspect, profile curvature, plan curvature, energy of the relief. The digital elevation model was obtained by interpolation of contour lines and point elevation. The contour lines and elevation points were digitized from the topographical maps at a scale of 1:5000. The lithology and the faults were digitized from the geological maps at scales ranging from 1:25000 up to 1: Land-use and land-cover was mapped by image interpretation from the color orthophotos (acquisition time: 2005) and from field surveys. The morphometrical parameters like slope gradient, plan curvature etc were derived from the DEM using Idrisi Kilimanjaro GIS software. 3.2 PCA analysis The PCA analysis was used to reduce de number of variables and to eliminate de redundant information from these variables. A number of 15 variables, represented by various topographical attributes, land-use and land-cover, lithology etc were introduced in the PCA analysis and only six principal components were obtained. The variables were previously classified and the classes were created to maximize the information and minimize the variance inside a class. Component 1 has 35.31%, component 2 has 28.33%, component 3 has 21.27% of the information, summarizing together ~85% of the information. The next three principal components have 8.73%, 5.08% and 1.28% of the information, summarizing together ~15% from the total information. The first four components have together 93.64% of the information and if we add the fifth component it reaches 98.72%. 3.3 Logistic regression analysis Logistic regression was applied for three different combination of the principal components obtained from the PCA analysis. The principal components were used as independent variables and the past and present shallow landslides as dependent variable. We have combined the first three components, then the first four components and the first fifth components. The result was the landslides susceptibility map for each of the combination, indicating the probability that a pixel will contain a landslide. 3.4 ROC analysis ROC analysis is suitable to assess the validity of a model that predicts the location of the occurrence of a class by comparing the predicted image with the actual presence of the class (Pontius, 2001). The ROC analysis was used to validate the results obtained from the logistic regression analysis (Gorsevski, 2001). The susceptibility map was introduced as the image to be validated and the past and present landslides were used as the reference image (Pontius, 2001). The ROC analysis was used for each susceptibility map obtained from the three logistic regression equations using three, four and five components Figure 3. ROC graph showing the validation of the three susceptibility maps 4 RESULTS Upon examination of the normalized eigenvectors, the elements with the absolute largest value indicated that the first principal component has a strong relationship with the slope gradient and the relief energy, the second principal component has a strong relationship with land-use, land-cover and lithology, the third principal component with width drainage density and plan curvature, the fourth principal component with aspect and the fifth principal component with the profile curvature and fault density. Logistic regression analysis has produced a series of three landslide susceptibility. The logistic regression for the combinations of the first three, four and five principal components with the past and present shallow landslides are: -267-
4 Figure 4. Susceptibility map for shallow landslides. Administrative area of Breaza, Prahova Subcarpathians, Romania
5 logit(sl)= *PC *PC *PC3 (1) logit(sl)= *PC *PC *PC *PC4 (2) logit(sl)= *PC *PC *PC *PC *PC5 (3) From all the equations from above we can observe that the susceptibility is increasing by a value of ~0.6 when the PC1 is present and by a value of ~0.3 when the PC2 is present and is decreasing by a value of ~-0.1 when the PC3 is present. By adding PC4 (Equation 2) the susceptibility is decreasing by a value of ~-0.3, but PC5 is increasing the susceptibility value by ~0.35. All three equations have produced susceptibility maps with a ROC value very similar ( ). Figure 3 plots the ROC values for each susceptibility map. The best results were obtained by combining the first four principal components, having the highest ROC value of 0.75 (Fig. 3). The highest susceptibility values are present on the hillslopes of Tarsa River and on the left hand side of Prahova River. These area correspond marls and clay deposits, small vegetation and slope gradients between 10⁰ and 25⁰(Fig. 4) Low susceptibility areas correspond to flat areas on top of the terraces with deposits of sand and gravel and under the forest vegetation from the hillsslopes of Tarsa River. The cutting threshold between low susceptibility and high susceptibility is set by the logistic regression at 0.06 (Fig. 4). 5 DISCUSSION The map presented in the Figure 4 represents the landslides susceptibility for shallow landslides in the administrative area of Breaza. The map accurately describes areas that are prone to shallow landslides, but it also presents areas that are not prone to shallow landslides or are affected by deep-seated landslides. The terrace scarp of Prahova, on the east part of Breaza de Sus city, are partially identified with high susceptibility for shallow landslides, but these areas are covered by old deep-seated landslides, with a latent state of activity. The areas correctly identified with high susceptibility for shallow landslides are on the hillslopes of Tarsa River, between Irimesti village in the south and Valea Tarsei village in the north and at east of Surdesti village. The values of ROC are higher than 0.5, which indicate a random fir. The ROC value of 0.75 is comparable with ROC values reported in other fields are ranging from 0.71 to 0.89 for weather forecasting, from 0.75 to 0.97 for library information retrieval, 0.81 to 0.93 for medical imaging diagnosis, from 0.68 to 0.93 for material strength testing and from 0.55 to 0.93 for polygraph lie detection (Pontius, 2001). Special attention must be given to the criteria used in variables classification, so the maximum of information is retained in the class with minimum variance between classes. 6 CONCLUSION The PCA analysis can be used to identify the shallow landslides susceptibility with satisfactory results. ROC analysis enables scientist to validate a model ability to identify a specific location. The ROC values obtained are comparable with ROC values reported by scientist from other research fields. REFERENCES Balteanu, D The importance of mass movements in the Romanian Subcarpathians. Zeitschrift fur Geomorphologie. Suppl. Bd.58: Balteanu, D Romania. In C. Embleton & C. Embleton- Hamann (eds.), Geomorphological hazards of Europe: Amsterdam: Elsevier. Brabb, E Innovative approaches for landslide hazard evaluation in IV International Symposium on Landslides, 1: , Toronto. Carrara, A., Cardinali, M., Detti, R., Guzzetti, F., Pasqui, V., Reichenbach, P GIS techniques and statistical models in evaluating landslide hazard. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 16: Carrara, A., Cardinali, M., Guzzetti, F., Reichenbach, P GIS technology in mapping landslide hazard. In Carrara, A. & Guzzetti, F. (eds.). Geographic Information Systems in Assessing Natural Hazards: Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers. Damian, R In Armas et al. Vulnerabilitatea versantilor la alunecari de teren in sectorul subcarpatic al Vaii Prahova, Bucuresti, Fundatia Romania de Maine. Ielenicz, M.,Patru, Ileana, Mihai, B Some geomorphic types of landslides in Romania, Transactions.Japanese Geomorphological Union., 20(3) : Ielenicz, M., Ghincea (Clius) M., Patru, I.G Subcarpatii Romaniei. Bucuresti: Universitara. Gorsevski, P Statistical modeling of landslide hazard using GIS, Proceedings of the Seventh Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conference, March 25 to 29, 2001, Reno, Nevada.: Guzzetti, F Landslide hazard and risk assessment. PhD dissertation. Bonn, Germany Mihai, B Muntii Timisului (Carpatii Curburii). Potential geomorfologic si amenajarea spatiului montan, Bucuresti: Universitatii din Bucuresti. Pontius, R., Schneider, L.C Land-cover change model validation by an ROC method for the Ipswich watershed, Massachusetts, USA. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 85: Popp, N Subcarpatii dintre Prahova si Dambovita. Studiu geomorfologic, Bucuresti: Societatea Regala Romana de Geografie -269-
6 Sandric, I. in Armas et al. Vulnerabilitatea versantilor la alunecari de teren in sectorul subcarpatic al Vaii Prahova, Bucuresti, Fundatia Romania de Maine. Sandric, I., 2005, Aplicatii ale teoriei probabilitatilor conditionate in geomorfologie, Analele Universitatii Bucuresti, Anul LIV-2005 Santacana, N., Baeza, B., Corominas, J., De Paz, A., Marturia, J A GIS-based multivariate statistical analysis for shallow landslide susceptibility mapping in la Pobla de Lillet area (Easter Pyrenees, Spain). Natural Hazards 30: Surdeanu, V Geografia terenurilor degradate. I. Alunecarile de teren: Cluj-Napoca: Presa Universitara Clujeana van Westen, C.J GIS in landslide hazard zonation: A review with examples from the Andes of Colombia. In Price, M.F. & Heywood, D.I. (eds.), Mountain Environments and Geographic Information Systems: Taylor and Francis Publishers
Landslide Hazard Assessment Methodologies in Romania
 A Scientific Network for Earthquake, Landslide and Flood Hazard Prevention SciNet NatHazPrev Landslide Hazard Assessment Methodologies in Romania In the literature the terms of susceptibility and landslide
A Scientific Network for Earthquake, Landslide and Flood Hazard Prevention SciNet NatHazPrev Landslide Hazard Assessment Methodologies in Romania In the literature the terms of susceptibility and landslide
STATISTICAL MODELING OF LANDSLIDE HAZARD USING GIS
 STATISTICAL MODELING OF LANDSLIDE HAZARD USING GIS By Peter V. Gorsevski, Department of Forest Resources College of Natural Resources University of Idaho; Randy B. Foltz, U.S. Forest Service, Rocky Mountain
STATISTICAL MODELING OF LANDSLIDE HAZARD USING GIS By Peter V. Gorsevski, Department of Forest Resources College of Natural Resources University of Idaho; Randy B. Foltz, U.S. Forest Service, Rocky Mountain
Landslide hazards zonation using GIS in Khoramabad, Iran
 Journal of Geotechnical Geology Winter 04, Vol. 9, No. 4: 4- www.geo-tech.ir Landslide hazards zonation using GIS in Khoramabad, Iran G. R. Khanlari *, Y. Abdilor & R. Babazadeh ) Associate Prof., Department
Journal of Geotechnical Geology Winter 04, Vol. 9, No. 4: 4- www.geo-tech.ir Landslide hazards zonation using GIS in Khoramabad, Iran G. R. Khanlari *, Y. Abdilor & R. Babazadeh ) Associate Prof., Department
Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods: A Critical Review
 International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 215-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods:
International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 215-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods:
TESTING ON THE TIME-ROBUSTNESS OF A LANDSLIDE PREDICTION MODEL. Hirohito Kojima* and Chang-Jo F. Chung**
 TESTING ON THE TIME-ROBUSTNESS OF A LANDSLIDE PREDICTION MODEL Hirohito Kojima* and Chang-Jo F. Chung** *: Science University of Tokyo, Remote Sensing Lab., Dept. of Civil Engineering 2641 Yamazaki, Noda-City,
TESTING ON THE TIME-ROBUSTNESS OF A LANDSLIDE PREDICTION MODEL Hirohito Kojima* and Chang-Jo F. Chung** *: Science University of Tokyo, Remote Sensing Lab., Dept. of Civil Engineering 2641 Yamazaki, Noda-City,
GEOMORPHOLOGY APPROACH IN LANDSLIDE VULNERABILITY, TANJUNG PALAS TENGAH, EAST KALIMANTAN, INDONESIA
 GEOMORPHOLOGY APPROACH IN LANDSLIDE VULNERABILITY, TANJUNG PALAS TENGAH, EAST KALIMANTAN, INDONESIA *Twin H. W. Kristyanto Geology Study Program, FMIPA UI, Universitas Indonesia *Author for Correspondence:
GEOMORPHOLOGY APPROACH IN LANDSLIDE VULNERABILITY, TANJUNG PALAS TENGAH, EAST KALIMANTAN, INDONESIA *Twin H. W. Kristyanto Geology Study Program, FMIPA UI, Universitas Indonesia *Author for Correspondence:
SPATIAL MODELS FOR THE DEFINITION OF LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY AND LANDSLIDE HAZARD. J.L. Zêzere Centre of Geographical Studies University of Lisbon
 SPATIAL MODELS FOR THE DEFINITION OF LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY AND LANDSLIDE HAZARD J.L. Zêzere Centre of Geographical Studies University of Lisbon CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF LANDSLIDE RISK Dangerous Phenomena
SPATIAL MODELS FOR THE DEFINITION OF LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY AND LANDSLIDE HAZARD J.L. Zêzere Centre of Geographical Studies University of Lisbon CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF LANDSLIDE RISK Dangerous Phenomena
Gully erosion and associated risks in the Tutova basin Moldavian Plateau
 Landform Analysis, Vol. 17: 193 197 (2011) Gully erosion and associated risks in the Tutova basin Moldavian Plateau University Alexandru Ioan Cuza of Iasi, Department of Geography, Romania, e-mail: catiul@yahoo.com
Landform Analysis, Vol. 17: 193 197 (2011) Gully erosion and associated risks in the Tutova basin Moldavian Plateau University Alexandru Ioan Cuza of Iasi, Department of Geography, Romania, e-mail: catiul@yahoo.com
Landslide susceptibility assessment for propose the best variant of road network (North of Iran)
 1 Landslide susceptibility assessment for propose the best variant of road network (North of Iran) Mehrdad Safaei 1, Husaini Omar 2, Bujang K Huat 3, Maryam Fattahi 4 1, 2,3 Mountainous Terrain Development
1 Landslide susceptibility assessment for propose the best variant of road network (North of Iran) Mehrdad Safaei 1, Husaini Omar 2, Bujang K Huat 3, Maryam Fattahi 4 1, 2,3 Mountainous Terrain Development
Using Weather and Climate Information for Landslide Prevention and Mitigation
 Using Weather and Climate Information for Landslide Prevention and Mitigation Professor Roy C. Sidle Disaster Prevention Research Institute Kyoto University, Japan International Workshop on Climate and
Using Weather and Climate Information for Landslide Prevention and Mitigation Professor Roy C. Sidle Disaster Prevention Research Institute Kyoto University, Japan International Workshop on Climate and
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE.
 PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
GIS Application in Landslide Hazard Analysis An Example from the Shihmen Reservoir Catchment Area in Northern Taiwan
 GIS Application in Landslide Hazard Analysis An Example from the Shihmen Reservoir Catchment Area in Northern Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, No.300, Jungda
GIS Application in Landslide Hazard Analysis An Example from the Shihmen Reservoir Catchment Area in Northern Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, No.300, Jungda
Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India
 Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India Ajay Kumar Sharma & Anand Mohan Singh Overview Landslide - movement of a mass of rock,
Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India Ajay Kumar Sharma & Anand Mohan Singh Overview Landslide - movement of a mass of rock,
STRATEGY ON THE LANDSLIDE TYPE ANALYSIS BASED ON THE EXPERT KNOWLEDGE AND THE QUANTITATIVE PREDICTION MODEL
 STRATEGY ON THE LANDSLIDE TYPE ANALYSIS BASED ON THE EXPERT KNOWLEDGE AND THE QUANTITATIVE PREDICTION MODEL Hirohito KOJIMA*, Chang-Jo F. CHUNG**, Cees J.van WESTEN*** * Science University of Tokyo, Remote
STRATEGY ON THE LANDSLIDE TYPE ANALYSIS BASED ON THE EXPERT KNOWLEDGE AND THE QUANTITATIVE PREDICTION MODEL Hirohito KOJIMA*, Chang-Jo F. CHUNG**, Cees J.van WESTEN*** * Science University of Tokyo, Remote
Practical reliability approach to urban slope stability
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Practical reliability approach to urban slope stability R. Chowdhury
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Practical reliability approach to urban slope stability R. Chowdhury
Landslide Susceptibility, Hazard, and Risk Assessment. Twin Hosea W. K. Advisor: Prof. C.T. Lee
 Landslide Susceptibility, Hazard, and Risk Assessment Twin Hosea W. K. Advisor: Prof. C.T. Lee Date: 2018/05/24 1 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION LANDSLIDE HAZARD ASSESSTMENT LOGISTIC REGRESSION IN LSA STUDY CASE
Landslide Susceptibility, Hazard, and Risk Assessment Twin Hosea W. K. Advisor: Prof. C.T. Lee Date: 2018/05/24 1 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION LANDSLIDE HAZARD ASSESSTMENT LOGISTIC REGRESSION IN LSA STUDY CASE
Available online at Analele Stiintifice ale Universitatii Al. I. Cuza din Iasi Seria Geologie 59 (2) (2013) 61 68
 Available online at http://geology.uaic.ro/auig/ Analele Stiintifice ale Universitatii Al. I. Cuza din Iasi Seria Geologie 59 (2) (2013) 61 68 AUI GEOLOGIE Lithostratigraphical characterization of the
Available online at http://geology.uaic.ro/auig/ Analele Stiintifice ale Universitatii Al. I. Cuza din Iasi Seria Geologie 59 (2) (2013) 61 68 AUI GEOLOGIE Lithostratigraphical characterization of the
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: April, 2016
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
Hendra Pachri, Yasuhiro Mitani, Hiro Ikemi, and Ryunosuke Nakanishi
 21 2nd International Conference on Geological and Civil Engineering IPCBEE vol. 8 (21) (21) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 1.7763/IPCBEE. 21. V8. 2 Relationships between Morphology Aspect and Slope Failure
21 2nd International Conference on Geological and Civil Engineering IPCBEE vol. 8 (21) (21) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 1.7763/IPCBEE. 21. V8. 2 Relationships between Morphology Aspect and Slope Failure
Fuzzy Logic Method for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping, Rio Blanco, Nicaragua
 Fuzzy Logic Method for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping, Rio Blanco, Nicaragua H. Schernthanner 1 1 University of Potsdam, Institute of Geography, GIS department, Karl-Liebknecht-Str. 24/25, 14476 Golm
Fuzzy Logic Method for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping, Rio Blanco, Nicaragua H. Schernthanner 1 1 University of Potsdam, Institute of Geography, GIS department, Karl-Liebknecht-Str. 24/25, 14476 Golm
How do humans interact with their environment in residential areas prone to landsliding - a case-study from the Flemish Ardennes -
 Landslide processes: from geomorphologic mapping to dynamic modelling. A tribute to Prof. Dr. Theo van Asch miet.vandeneeckhaut@ees.kuleuven.be Strasbourg, France, February 6-7 th 2009 How do humans interact
Landslide processes: from geomorphologic mapping to dynamic modelling. A tribute to Prof. Dr. Theo van Asch miet.vandeneeckhaut@ees.kuleuven.be Strasbourg, France, February 6-7 th 2009 How do humans interact
Combined landslide inventory and susceptibility assessment based on different mapping units: an example from the Flemish Ardennes, Belgium
 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Combined landslide inventory and susceptibility assessment based on
Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Combined landslide inventory and susceptibility assessment based on
Criteria for identification of areas at risk of landslides in Europe: the Tier 1 approach
 Criteria for identification of areas at risk of landslides in Europe: the Tier 1 approach Andreas Günther 1, Paola Reichenbach 2, Fausto Guzzetti 2, Andreas Richter 1 1 Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften
Criteria for identification of areas at risk of landslides in Europe: the Tier 1 approach Andreas Günther 1, Paola Reichenbach 2, Fausto Guzzetti 2, Andreas Richter 1 1 Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften
3D Slope Stability Analysis for Slope Failure Probability in Sangun mountainous, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan
 3D Slope Stability Analysis for Slope Failure Probability in Sangun mountainous, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan Hendra PACHRI (1), Yasuhiro MITANI (1), Hiro IKEMI (1), and Wenxiao JIANG (1) (1) Graduate School
3D Slope Stability Analysis for Slope Failure Probability in Sangun mountainous, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan Hendra PACHRI (1), Yasuhiro MITANI (1), Hiro IKEMI (1), and Wenxiao JIANG (1) (1) Graduate School
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS
 LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
2013 Esri Europe, Middle East and Africa User Conference October 23-25, 2013 Munich, Germany
 2013 Esri Europe, Middle East and Africa User Conference October 23-25, 2013 Munich, Germany Environmental and Disaster Management System in the Valles Altos Region in Carabobo / NW-Venezuela Prof.Dr.habil.Barbara
2013 Esri Europe, Middle East and Africa User Conference October 23-25, 2013 Munich, Germany Environmental and Disaster Management System in the Valles Altos Region in Carabobo / NW-Venezuela Prof.Dr.habil.Barbara
Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures. Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS
 Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS Natural hazards: physical phenomena, active in geological time capable of producing
Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS Natural hazards: physical phenomena, active in geological time capable of producing
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Landslide Hazard Mapping with New Topographic Factors: A Study Case of Penang Island, Malaysia
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(4) Special 014, Pages: 387-39 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Landslide
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(4) Special 014, Pages: 387-39 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Landslide
Landslide hazard assessment in the Khelvachauri area, Georgia
 Report on the project of AES Geohazards Stream Landslide hazard assessment in the Khelvachauri area, Georgia May 2010 George Jianping Panisara Gaprindashvili Guo Daorueang Institute of Geo-Information
Report on the project of AES Geohazards Stream Landslide hazard assessment in the Khelvachauri area, Georgia May 2010 George Jianping Panisara Gaprindashvili Guo Daorueang Institute of Geo-Information
INTRODUCTION. Climate
 INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
Floodplain modeling. Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece
 Floodplain modeling Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece Scientific Staff: Dr Carmen Maftei, Professor, Civil Engineering Dept. Dr Konstantinos
Floodplain modeling Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece Scientific Staff: Dr Carmen Maftei, Professor, Civil Engineering Dept. Dr Konstantinos
MANAGEMENT OF LARGE MUDSLIDES
 36 MANAGEMENT OF LARGE MUDSLIDES Three large and active mudslides Poche, 1860?, Super-Sauze, 1960?, La Valette, March 1982, 1 M m 3 900,000 m 3 4-5 M m 3 37 Three large and active mudslides Type of development:
36 MANAGEMENT OF LARGE MUDSLIDES Three large and active mudslides Poche, 1860?, Super-Sauze, 1960?, La Valette, March 1982, 1 M m 3 900,000 m 3 4-5 M m 3 37 Three large and active mudslides Type of development:
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan
 Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
WATERCOURSE HARNESSING BANK EROSION AND CONSOLIDATION
 GUVERNUL MINISTERUL POSDRU MUNCII, FAMILIEI ŞI WATERCOURSE HARNESSING BANK EROSION AND CONSOLIDATION PhD. student: ALUPOAE Daniel Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, Faculty of Civil Engineering
GUVERNUL MINISTERUL POSDRU MUNCII, FAMILIEI ŞI WATERCOURSE HARNESSING BANK EROSION AND CONSOLIDATION PhD. student: ALUPOAE Daniel Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, Faculty of Civil Engineering
2014 Summer Training Courses on Slope Land Disaster Reduction Hydrotech Research Institute, National Taiwan University, Taiwan August 04-15, 2014
 Final Project Report 2014 Summer Training Courses on Slope Land Disaster Reduction Hydrotech Research Institute, National Taiwan University, Taiwan August 04-15, 2014 Landslides in Mt. Umyeon Susceptibility
Final Project Report 2014 Summer Training Courses on Slope Land Disaster Reduction Hydrotech Research Institute, National Taiwan University, Taiwan August 04-15, 2014 Landslides in Mt. Umyeon Susceptibility
BASIC DETAILS. Morphometric features for landslide zonation A case study for Ooty Mettupalayam highway
 BASIC DETAILS Paper reference number : MWF PN 121 Title of the paper Name of the Presenter Author affiliation Mailing address Email address : Extraction of Topographic and Morphometric features for landslide
BASIC DETAILS Paper reference number : MWF PN 121 Title of the paper Name of the Presenter Author affiliation Mailing address Email address : Extraction of Topographic and Morphometric features for landslide
A GIS-based statistical model for landslide susceptibility mapping: A case study in the Taleghan watershed, Iran
 Biological Forum An International Journal 7(2): 862-868(2015) ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 A GIS-based statistical model for landslide susceptibility mapping: A case study in
Biological Forum An International Journal 7(2): 862-868(2015) ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 A GIS-based statistical model for landslide susceptibility mapping: A case study in
Directed Reading. Section: Types of Maps
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Types of Maps 1. What are some of the characteristics of an area shown on maps used by Earth scientists? a. types of animals, types of plants, types of minerals
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Types of Maps 1. What are some of the characteristics of an area shown on maps used by Earth scientists? a. types of animals, types of plants, types of minerals
BUCHAREST UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF GEOGRAPHY
 Landscape and Water Resources Management (LWRM) BUCHAREST UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF GEOGRAPHY Dr. Liliana ZAHARIA Tourism Studies and Forecast Research Center (TSFRC) RESEARCH CENTERS Center for Geomorphological
Landscape and Water Resources Management (LWRM) BUCHAREST UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF GEOGRAPHY Dr. Liliana ZAHARIA Tourism Studies and Forecast Research Center (TSFRC) RESEARCH CENTERS Center for Geomorphological
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data -
 ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
Landslide Susceptibility Model of Tualatin Mountains, Portland Oregon. By Tim Cassese and Colby Lawrence December 10, 2015
 Landslide Susceptibility Model of Tualatin Mountains, Portland Oregon By Tim Cassese and Colby Lawrence December 10, 2015 Landslide Closes Highway 30 at St. John's Bridge Introduction: Study Area: Tualatin
Landslide Susceptibility Model of Tualatin Mountains, Portland Oregon By Tim Cassese and Colby Lawrence December 10, 2015 Landslide Closes Highway 30 at St. John's Bridge Introduction: Study Area: Tualatin
Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan
 Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Graduate Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, Taiwan Seismology Forum 27: Natural Hazards and Surface
Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Graduate Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, Taiwan Seismology Forum 27: Natural Hazards and Surface
Stability analysis of the Vallcebre translational slide, Eastern Pyrenees (Spain) by means of a GIS
 Natural Hazards 30: 473 485, 2003. 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 473 Stability analysis of the Vallcebre translational slide, Eastern Pyrenees (Spain) by means of a GIS JORDI
Natural Hazards 30: 473 485, 2003. 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 473 Stability analysis of the Vallcebre translational slide, Eastern Pyrenees (Spain) by means of a GIS JORDI
Debris flow hazard mapping with a random walk model in Korea
 Risk Analysis VII PI-627 Debris flow hazard mapping with a random walk model in Korea H.-J. Youn, C.-W. Lee & C.-S. Woo Korea Forest Research Institute, Korea Abstract Recently, the sediment-related disasters,
Risk Analysis VII PI-627 Debris flow hazard mapping with a random walk model in Korea H.-J. Youn, C.-W. Lee & C.-S. Woo Korea Forest Research Institute, Korea Abstract Recently, the sediment-related disasters,
Landslide Computer Modeling Potential
 Landslide Computer Modeling Potential Michael D. Dixon, P.E. Civil Engineer Payette National Forest The Payette National Forest selected the Stability Index Mapping (SINMAP) model for use in identifying
Landslide Computer Modeling Potential Michael D. Dixon, P.E. Civil Engineer Payette National Forest The Payette National Forest selected the Stability Index Mapping (SINMAP) model for use in identifying
INDICATIVE HAZARD MAPS FOR LANDSLIDES IN STYRIA; AUSTRIA
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18509/agb.2016.10 UDC:528.88:551.311.24(436) COBISS: INDICATIVE HAZARD MAPS FOR LANDSLIDES IN STYRIA; AUSTRIA Herwig Proske 1 & Christian Bauer 1/2 1 Joanneum Research, Graz, Austria
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18509/agb.2016.10 UDC:528.88:551.311.24(436) COBISS: INDICATIVE HAZARD MAPS FOR LANDSLIDES IN STYRIA; AUSTRIA Herwig Proske 1 & Christian Bauer 1/2 1 Joanneum Research, Graz, Austria
Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model. John Rogers & Lauren McKinney
 Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model John Rogers & Lauren McKinney Columbia River Gorge at Risk: Using LiDAR and GIS-based predictive modeling for regional-scale erosion susceptibility
Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model John Rogers & Lauren McKinney Columbia River Gorge at Risk: Using LiDAR and GIS-based predictive modeling for regional-scale erosion susceptibility
Assessment of Urban Geomorphological Hazard in the North-East of Cairo City, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. G. Albayomi
 Assessment of Urban Geomorphological Hazard in the North-East of Cairo City, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques G. Albayomi Geography Department, Faculty of Arts, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt Gehan_albayomi@arts.helwan.edu.eg
Assessment of Urban Geomorphological Hazard in the North-East of Cairo City, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques G. Albayomi Geography Department, Faculty of Arts, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt Gehan_albayomi@arts.helwan.edu.eg
Multicriteria GIS Modelling of Terrain Susceptibility to Gully Erosion, using the Example of the Island of Pag
 14th International Conference on Geoinformation and Cartography Zagreb, September 27-29, 2018. Multicriteria GIS Modelling of Terrain Susceptibility to Gully Erosion, using the Example of the Island of
14th International Conference on Geoinformation and Cartography Zagreb, September 27-29, 2018. Multicriteria GIS Modelling of Terrain Susceptibility to Gully Erosion, using the Example of the Island of
Landslide Mapping and Hazard Analysis for a Natural Gas Pipeline Project
 CIVIL GOVERNMENT SERVICES MINING & METALS OIL, GAS & CHEMICALS POWER Albert Kottke, Mark Lee, & Matthew Waterman Landslide Mapping and Hazard Analysis for a Natural Gas Pipeline Project Technical Innovation
CIVIL GOVERNMENT SERVICES MINING & METALS OIL, GAS & CHEMICALS POWER Albert Kottke, Mark Lee, & Matthew Waterman Landslide Mapping and Hazard Analysis for a Natural Gas Pipeline Project Technical Innovation
Scientific registration n : 2180 Symposium n : 35 Presentation : poster MULDERS M.A.
 Scientific registration n : 2180 Symposium n : 35 Presentation : poster GIS and Remote sensing as tools to map soils in Zoundwéogo (Burkina Faso) SIG et télédétection, aides à la cartographie des sols
Scientific registration n : 2180 Symposium n : 35 Presentation : poster GIS and Remote sensing as tools to map soils in Zoundwéogo (Burkina Faso) SIG et télédétection, aides à la cartographie des sols
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 1, 2010
 An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
Investigation of landslide based on high performance and cloud-enabled geocomputation
 Investigation of landslide based on high performance and cloud-enabled geocomputation Jun Liu 1, Shuguang Liu 2,*, Qiming Zhou 3, Jing Qian 1 1 Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy
Investigation of landslide based on high performance and cloud-enabled geocomputation Jun Liu 1, Shuguang Liu 2,*, Qiming Zhou 3, Jing Qian 1 1 Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy
Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model
 Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model Amal Markhi: Phd Student Supervisor: Pr :N.Laftrouhi Contextualization Facing
Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model Amal Markhi: Phd Student Supervisor: Pr :N.Laftrouhi Contextualization Facing
Assessment of the Incidence of Landslides Using Numerical Information
 PAPER Assessment of the Incidence of Landslides Using Numerical Information Atsushi HASEGAWA Takehiro OHTA, Dr. Sci. Assistant Senior Researcher, Senior Researcher, Laboratory Head, Geology Laboratory,
PAPER Assessment of the Incidence of Landslides Using Numerical Information Atsushi HASEGAWA Takehiro OHTA, Dr. Sci. Assistant Senior Researcher, Senior Researcher, Laboratory Head, Geology Laboratory,
LANDSLIDE HAZARD MAPPING BY USING GIS IN THE LILLA EDET PROVINCE OF SWEDEN
 LANDSLIDE HAZARD MAPPING BY USING GIS IN THE LILLA EDET PROVINCE OF SWEDEN Arzu ERENER 1, Suzanne LACASSE 2, Amir M. KAYNIA 3 1 Geodetic and Geographic Information Technologies, Middle East Technical University,
LANDSLIDE HAZARD MAPPING BY USING GIS IN THE LILLA EDET PROVINCE OF SWEDEN Arzu ERENER 1, Suzanne LACASSE 2, Amir M. KAYNIA 3 1 Geodetic and Geographic Information Technologies, Middle East Technical University,
Response on Interactive comment by Anonymous Referee #1
 Response on Interactive comment by Anonymous Referee #1 Sajid Ali First, we would like to thank you for evaluation and highlighting the deficiencies in the manuscript. It is indeed valuable addition and
Response on Interactive comment by Anonymous Referee #1 Sajid Ali First, we would like to thank you for evaluation and highlighting the deficiencies in the manuscript. It is indeed valuable addition and
IDENTIFICATION OF LANDSLIDE-PRONE AREAS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES IN SILLAHALLAWATERSHED, NILGIRIS DISTRICT,TAMILNADU,INDIA
 IDENTIFICATION OF LANDSLIDE-PRONE AREAS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES IN SILLAHALLAWATERSHED, NILGIRIS DISTRICT,TAMILNADU,INDIA J.Jayanthi 1, T.Naveen Raj 2, M.Suresh Gandhi 3, 1 Research Scholar, Department
IDENTIFICATION OF LANDSLIDE-PRONE AREAS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES IN SILLAHALLAWATERSHED, NILGIRIS DISTRICT,TAMILNADU,INDIA J.Jayanthi 1, T.Naveen Raj 2, M.Suresh Gandhi 3, 1 Research Scholar, Department
LANDSLIDE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION ANALYSIS USING GIS. CASE STUDY SECAȘELOR PLATEAU
 RISCURI ŞI CATASTROFE, NR. XVI, VOL. 20, NR. 1/2017 LANDSLIDE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION ANALYSIS USING GIS. CASE STUDY SECAȘELOR PLATEAU GH.ROŞIAN 1, CS.HORVATH 2, A.NIȚĂ 3, ROZALIA BENEDEK 4 Abstract: - Spatial
RISCURI ŞI CATASTROFE, NR. XVI, VOL. 20, NR. 1/2017 LANDSLIDE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION ANALYSIS USING GIS. CASE STUDY SECAȘELOR PLATEAU GH.ROŞIAN 1, CS.HORVATH 2, A.NIȚĂ 3, ROZALIA BENEDEK 4 Abstract: - Spatial
Landslide hazard and risk management in the Barcelonnette Basin: some case studies
 Intensive Course Barcelona, UPC, 1-4 September 2008 Landslide hazard and risk management in the Barcelonnette Basin: some case studies J.-P. Malet 1, A. Remaître 1, Y. Thiery 1 O. Maquaire 2, M. Peyron
Intensive Course Barcelona, UPC, 1-4 September 2008 Landslide hazard and risk management in the Barcelonnette Basin: some case studies J.-P. Malet 1, A. Remaître 1, Y. Thiery 1 O. Maquaire 2, M. Peyron
AN APPROACH TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF SLOPE MOVEMENTS
 Training/workshop on Earthquake Vulnerability and Multi-Hazard Risk Assessment: Geospatial Tools for Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Effort 13 31 March 2006, Islamabad, Pakistan AN APPROACH TO THE CLASSIFICATION
Training/workshop on Earthquake Vulnerability and Multi-Hazard Risk Assessment: Geospatial Tools for Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Effort 13 31 March 2006, Islamabad, Pakistan AN APPROACH TO THE CLASSIFICATION
Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid
 Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid Landslide Hazard Dr. Arvind Phukan, P.E. Cosultant/Former Professor of Civil Engineering University of Alaska, Anchorage, USA RI District Governor
Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid Landslide Hazard Dr. Arvind Phukan, P.E. Cosultant/Former Professor of Civil Engineering University of Alaska, Anchorage, USA RI District Governor
LANLDSIDE HAZARD, SOCIAL-ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY AND PHYSICAL (BUILDINGS) RISK ASSESMENT SAGAREJO MUNICIPALITY CASE STUDY (PROJECT)
 LANLDSIDE HAZARD, SOCIAL-ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY AND PHYSICAL (BUILDINGS) RISK ASSESMENT SAGAREJO MUNICIPALITY CASE STUDY (PROJECT) - 1 - 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. USED DATA 4 3. METHODOLOGY 5 3.1 Work flow
LANLDSIDE HAZARD, SOCIAL-ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY AND PHYSICAL (BUILDINGS) RISK ASSESMENT SAGAREJO MUNICIPALITY CASE STUDY (PROJECT) - 1 - 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. USED DATA 4 3. METHODOLOGY 5 3.1 Work flow
GIS-aided Statistical Landslide Susceptibility Modeling And Mapping Of Antipolo Rizal (Philippines)
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS GIS-aided Statistical Landslide Susceptibility Modeling And Mapping Of Antipolo Rizal (Philippines) To cite this article: A J Dumlao
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS GIS-aided Statistical Landslide Susceptibility Modeling And Mapping Of Antipolo Rizal (Philippines) To cite this article: A J Dumlao
Topographical Change Monitoring for Susceptible Landslide Area Determination by Using Multi-Date Digital Terrain Models and LiDAR
 Topographical Change Monitoring for Susceptible Landslide Area Determination by Using Multi-Date Digital Terrain Models and Chanist PRASERTBURANAKUL 1, Parkorn SUWANICH 2, Kanchana NAKHAPAKORN 3, and Sukit
Topographical Change Monitoring for Susceptible Landslide Area Determination by Using Multi-Date Digital Terrain Models and Chanist PRASERTBURANAKUL 1, Parkorn SUWANICH 2, Kanchana NAKHAPAKORN 3, and Sukit
Virtual Reality Modeling of Landslide for Alerting in Chiang Rai Area Banphot Nobaew 1 and Worasak Reangsirarak 2
 Virtual Reality Modeling of Landslide for Alerting in Chiang Rai Area Banphot Nobaew 1 and Worasak Reangsirarak 2 1 Banphot Nobaew MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand 2 Worasak Reangsirarak MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand
Virtual Reality Modeling of Landslide for Alerting in Chiang Rai Area Banphot Nobaew 1 and Worasak Reangsirarak 2 1 Banphot Nobaew MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand 2 Worasak Reangsirarak MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand
Viale della Fiera 8 Bologna - Italy
 Assessment of landslides susceptibility and reactivation likelihood in the Emilia Romagna region (Italy) Mauro Generali e Marco Pizziolo Regione Emilia-Romagna Geological Survey Viale della Fiera 8 Bologna
Assessment of landslides susceptibility and reactivation likelihood in the Emilia Romagna region (Italy) Mauro Generali e Marco Pizziolo Regione Emilia-Romagna Geological Survey Viale della Fiera 8 Bologna
THE IMPACT OF LANDSLIDE AREAS ON MUNICIPAL SPATIAL PLANNING
 THE IMPACT OF LANDSLIDE AREAS ON MUNICIPAL SPATIAL PLANNING Jarosław Bydłosz, PhD Faculty of Mining Surveying and Environmental Engineering AGH University of Science and Technology e-mail: bydlosz@agh.edu.pl
THE IMPACT OF LANDSLIDE AREAS ON MUNICIPAL SPATIAL PLANNING Jarosław Bydłosz, PhD Faculty of Mining Surveying and Environmental Engineering AGH University of Science and Technology e-mail: bydlosz@agh.edu.pl
LANDSLIDES ANALYSIS USING GEOLOGICAL,
 Construcţii Landslides analysis based on experimental measurements C. Dobrescu, E. Calarasu, M. Stoica LANDSLIDES ANALYSIS USING GEOLOGICAL, GEOTECHNICAL AND GEOPHYSICAL DATA FROM EXPERIMENTAL MEASUREMENTS
Construcţii Landslides analysis based on experimental measurements C. Dobrescu, E. Calarasu, M. Stoica LANDSLIDES ANALYSIS USING GEOLOGICAL, GEOTECHNICAL AND GEOPHYSICAL DATA FROM EXPERIMENTAL MEASUREMENTS
The Geomorphological Processes of The Three Gorges Section of the Changjiang River. PhD. Zhou Bin Prof. Yang Da-yuan
 The Geomorphological Processes of The Three Gorges Section of the Changjiang River PhD. Zhou Bin Prof. Yang Da-yuan Geomorphological Processes is knowledge of land development process. Its emphasis is
The Geomorphological Processes of The Three Gorges Section of the Changjiang River PhD. Zhou Bin Prof. Yang Da-yuan Geomorphological Processes is knowledge of land development process. Its emphasis is
Photogrammetric Methods for Monitoring Cliffs with Low Retreat Rate
 Journal of Coastal Research SI 56 1577-1581 ICS2009 (Proceedings) Portugal ISSN 0749-0258 Photogrammetric Methods for Monitoring Cliffs with Low Retreat Rate P. Redweik, R. Matildes, F. Marques and L.
Journal of Coastal Research SI 56 1577-1581 ICS2009 (Proceedings) Portugal ISSN 0749-0258 Photogrammetric Methods for Monitoring Cliffs with Low Retreat Rate P. Redweik, R. Matildes, F. Marques and L.
PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS. Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES. Faulting. Folding 9/6/2012. TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS GRADATIONAL TECTONIC
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
A Combined Model for Landslide Susceptibility, Hazard and Risk Assessment
 AUT Journal of Civil Engineering AUT J. Civil Eng., 2(1) (2018) 11-28 DOI: 10.22060/ajce.2018.14235.5465 A Combined Model for Landslide Susceptibility, Hazard and Risk Assessment R. Talaei* Soil Conservation
AUT Journal of Civil Engineering AUT J. Civil Eng., 2(1) (2018) 11-28 DOI: 10.22060/ajce.2018.14235.5465 A Combined Model for Landslide Susceptibility, Hazard and Risk Assessment R. Talaei* Soil Conservation
Georeferencing and Satellite Image Support: Lessons learned, Challenges and Opportunities
 Georeferencing and Satellite Image Support: Lessons learned, Challenges and Opportunities Shirish Ravan shirish.ravan@unoosa.org UN-SPIDER United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) UN-SPIDER
Georeferencing and Satellite Image Support: Lessons learned, Challenges and Opportunities Shirish Ravan shirish.ravan@unoosa.org UN-SPIDER United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) UN-SPIDER
Preparing Landslide Inventory Maps using Virtual Globes
 Introduction: A landslide is the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope, under the influence of gravity. Landslides can be caused by different phenomena, including intense or prolonged
Introduction: A landslide is the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope, under the influence of gravity. Landslides can be caused by different phenomena, including intense or prolonged
SLOPE HAZARD AND RISK MAPPING: A TECHNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE
 International Symposium on Multi-Hazard and Risk 2015 23-24 March 2015, UTM Kuala Lumpur SLOPE HAZARD AND RISK MAPPING: A TECHNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Very high resolution DTM derived from LiDAR LiDAR Ortho
International Symposium on Multi-Hazard and Risk 2015 23-24 March 2015, UTM Kuala Lumpur SLOPE HAZARD AND RISK MAPPING: A TECHNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Very high resolution DTM derived from LiDAR LiDAR Ortho
Tatsuo Sekiguchi* and Hiroshi Sato*
 by Tatsuo Sekiguchi* and Hiroshi Sato* ABSTRACT Landslides induced by heavy rainfall and earthquakes may result in disaster by destroying homes and buildings. High-fluidity landslides caused by liquefied
by Tatsuo Sekiguchi* and Hiroshi Sato* ABSTRACT Landslides induced by heavy rainfall and earthquakes may result in disaster by destroying homes and buildings. High-fluidity landslides caused by liquefied
Deep-Seated Landslides and Landslide Dams Characteristics Caused by Typhoon Talas at Kii Peninsula, Japan
 Deep-Seated Landslides and Landslide Dams Characteristics Caused by Typhoon Talas at Kii Peninsula, Japan Hefryan Sukma KHARISMALATRI*,1, Hitomi KIKUCHI 1, Yoshiharu ISHIKAWA 1, Takashi GOMI 1, Katsushige
Deep-Seated Landslides and Landslide Dams Characteristics Caused by Typhoon Talas at Kii Peninsula, Japan Hefryan Sukma KHARISMALATRI*,1, Hitomi KIKUCHI 1, Yoshiharu ISHIKAWA 1, Takashi GOMI 1, Katsushige
depression above scarp scarp
 1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
12 th International Symposium on Landslides June 2016, Napoli (Italy)
 12 th International Symposium on s 12-19 June 2016, Napoli (Italy) use of thematic for landslide susceptibility assessment by means of statistical : case study of shallow landslides in fine grained soils
12 th International Symposium on s 12-19 June 2016, Napoli (Italy) use of thematic for landslide susceptibility assessment by means of statistical : case study of shallow landslides in fine grained soils
Geomorphology and Landslide Hazard Models
 Geomorphology and Landslide Hazard Models Steve Parry GeoRisk Solutions Key component of interpreting geomorphology and therefore hazard at a site is the use of API The purpose of this talk is not to try
Geomorphology and Landslide Hazard Models Steve Parry GeoRisk Solutions Key component of interpreting geomorphology and therefore hazard at a site is the use of API The purpose of this talk is not to try
ENGRG Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki March 17, 2014 Lecture 08: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki March 17, 2014 Lecture 08: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia
 Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia N. Lakmal Deshapriya 1, Udhi Catur Nugroho 2, Sesa Wiguna 3, Manzul Hazarika 1, Lal Samarakoon 1 1 Geoinformatics
Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia N. Lakmal Deshapriya 1, Udhi Catur Nugroho 2, Sesa Wiguna 3, Manzul Hazarika 1, Lal Samarakoon 1 1 Geoinformatics
GEOGRAPHY (029) CLASS XI ( ) Part A: Fundamentals of Physical Geography. Map and Diagram 5. Part B India-Physical Environment 35 Marks
 GEOGRAPHY (029) CLASS XI (207-8) One Theory Paper 70 Marks 3 Hours Part A Fundamentals of Physical Geography 35 Marks Unit-: Geography as a discipline Unit-3: Landforms Unit-4: Climate Unit-5: Water (Oceans)
GEOGRAPHY (029) CLASS XI (207-8) One Theory Paper 70 Marks 3 Hours Part A Fundamentals of Physical Geography 35 Marks Unit-: Geography as a discipline Unit-3: Landforms Unit-4: Climate Unit-5: Water (Oceans)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70. Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills
 Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Introduction-Overview. Why use a GIS? What can a GIS do? Spatial (coordinate) data model Relational (tabular) data model
 Introduction-Overview Why use a GIS? What can a GIS do? How does a GIS work? GIS definitions Spatial (coordinate) data model Relational (tabular) data model intro_gis.ppt 1 Why use a GIS? An extension
Introduction-Overview Why use a GIS? What can a GIS do? How does a GIS work? GIS definitions Spatial (coordinate) data model Relational (tabular) data model intro_gis.ppt 1 Why use a GIS? An extension
LAND DEGRADATION IN THE CARIBBEAN: QUATERNARY GEOLOGICAL PROCESSES. RAFI AHMAD
 EXTENDED TASK FORCE MEETING OF PARTICIPATING AGENCIES AND LATIN AMERICAN COUNTRIES FOR ENHANCING SOUTH-SOUTH COOPERATION BETWEEN LAC-CARIBBEAN SIDS PARTNERSHIP INITIATIVE ON LAND DEGRADATION AND SUSTAINABLE
EXTENDED TASK FORCE MEETING OF PARTICIPATING AGENCIES AND LATIN AMERICAN COUNTRIES FOR ENHANCING SOUTH-SOUTH COOPERATION BETWEEN LAC-CARIBBEAN SIDS PARTNERSHIP INITIATIVE ON LAND DEGRADATION AND SUSTAINABLE
INDIRECT ASSESSMENT OF RIVER-TORRENTIAL EROSION BY MEASURING THE ERODED VOLUM CASE STUDY: THE REGHIU STREAM
 INDIRECT ASSESSMENT OF RIVER-TORRENTIAL EROSION BY MEASURING THE ERODED VOLUM CASE STUDY: THE REGHIU STREAM NICULAE LUCICA 1 ABSTRACT. Indirect assessment of river-torrential erosion by measuring the eroded
INDIRECT ASSESSMENT OF RIVER-TORRENTIAL EROSION BY MEASURING THE ERODED VOLUM CASE STUDY: THE REGHIU STREAM NICULAE LUCICA 1 ABSTRACT. Indirect assessment of river-torrential erosion by measuring the eroded
SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEGRADATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES IN RIVER LIKODRA WATERSHED
 Soil Erosion Modelling JRC Ispra 20-21-22 March 2017 University of Belgrade, Faculty of Forestry Department for Ecological Engineering in Protection of Soil and Water Resources SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL ANALYSIS
Soil Erosion Modelling JRC Ispra 20-21-22 March 2017 University of Belgrade, Faculty of Forestry Department for Ecological Engineering in Protection of Soil and Water Resources SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL ANALYSIS
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Ecological Site Descriptions ESDs : NRCS Site-based Approach to Land Classification and Evaluation. Nels Barrett, NRCS Ecologist SSSSNE 20
 Ecological Site Descriptions ESDs : NRCS Site-based Approach to Land Classification and Evaluation Nels Barrett, NRCS Ecologist SSSSNE 20 Overview Definition of Ecological Sites, ES Content of Ecological
Ecological Site Descriptions ESDs : NRCS Site-based Approach to Land Classification and Evaluation Nels Barrett, NRCS Ecologist SSSSNE 20 Overview Definition of Ecological Sites, ES Content of Ecological
MAP STUDY: INTERPRETATION OF SURVEY MAPS
 MAP STUDY: INTERPRETATION OF SURVEY MAPS Types and Elements of Maps Maps are drawn to represent the Earth on a piece of paper. Maps are used widely to represent the Earth. Maps use signs and symbols in
MAP STUDY: INTERPRETATION OF SURVEY MAPS Types and Elements of Maps Maps are drawn to represent the Earth on a piece of paper. Maps are used widely to represent the Earth. Maps use signs and symbols in
Remote Sensing and GIS Contribution to. Tsunami Risk Sites Detection. of Coastal Areas in the Mediterranean
 The Third International Conference on Early Warning (EWC III), 26.-29.March 2006 in Bonn Remote Sensing and GIS Contribution to Tsunami Risk Sites Detection of Coastal Areas in the Mediterranean BARBARA
The Third International Conference on Early Warning (EWC III), 26.-29.March 2006 in Bonn Remote Sensing and GIS Contribution to Tsunami Risk Sites Detection of Coastal Areas in the Mediterranean BARBARA
RAINFALL AGGRESSIVENESS EVALUATION
 RISCURI ŞI CATASTROFE, NR. XV, VOL. 18, NR. 1/2016 RAINFALL AGGRESSIVENESS EVALUATION IN REGHIN HILLS USING FOURNIER INDEX J. SZILAGYI 1, I. A. IRIMUȘ 1, C. TOGĂNEL 1, EMILIA SZILAGYI 1 Abstract: Aggressiveness
RISCURI ŞI CATASTROFE, NR. XV, VOL. 18, NR. 1/2016 RAINFALL AGGRESSIVENESS EVALUATION IN REGHIN HILLS USING FOURNIER INDEX J. SZILAGYI 1, I. A. IRIMUȘ 1, C. TOGĂNEL 1, EMILIA SZILAGYI 1 Abstract: Aggressiveness
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal
 Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
Pedometric Techniques in Spatialisation of Soil Properties for Agricultural Land Evaluation
 Bulletin UASVM Agriculture, 67(1)/2010 Print ISSN 1843-5246; Electronic ISSN 1843-5386 Pedometric Techniques in Spatialisation of Soil Properties for Agricultural Land Evaluation Iuliana Cornelia TANASĂ
Bulletin UASVM Agriculture, 67(1)/2010 Print ISSN 1843-5246; Electronic ISSN 1843-5386 Pedometric Techniques in Spatialisation of Soil Properties for Agricultural Land Evaluation Iuliana Cornelia TANASĂ
Crystal Moncada. California State University San Bernardino. January- July Brett R. Goforth- Department of Geography and Environmental Studies
 A Geographical Information System (GIS) Based Evaluation of Landslide Susceptibility Mapped on the Harrison Mountain Quadrangle of the Santa Ana River Watershed Crystal Moncada California State University
A Geographical Information System (GIS) Based Evaluation of Landslide Susceptibility Mapped on the Harrison Mountain Quadrangle of the Santa Ana River Watershed Crystal Moncada California State University
Topographic Maps. Take Notes as you view the slides
 Topographic Maps Take Notes as you view the slides Lesson Objectives Define a topographic map and state its uses. Describe how contour lines show the elevations, shape, and slope of the land. Identify
Topographic Maps Take Notes as you view the slides Lesson Objectives Define a topographic map and state its uses. Describe how contour lines show the elevations, shape, and slope of the land. Identify
Phil Flentje. in collaboration with Industry Partners Wollongong City Council Roads and Traffic Authority Rail Corporation HAZARD AND RISK
 Dr. Phil Flentje, Senior Research Fellow (Engineering Geologist) Civil, Mining, and Environmental Engineering email: pflentje@uow.edu.au GIS-based Landslide Inventory, Susceptibility and Hazard zoning
Dr. Phil Flentje, Senior Research Fellow (Engineering Geologist) Civil, Mining, and Environmental Engineering email: pflentje@uow.edu.au GIS-based Landslide Inventory, Susceptibility and Hazard zoning
Data Mining Approach For Landslide Susceptibility Mapping For Kundhapallam Watershed, Nilgiris, TamilNadu Dr. P. Rajesh Prasanna 1, S.
 Data Mining Approach For Landslide Susceptibility Mapping For Kundhapallam Watershed, Nilgiris, TamilNadu Dr. P. Rajesh Prasanna 1, S.Evany Nithya 2 1 Professor, Anna University Tiruchirappalli 2 Asst.
Data Mining Approach For Landslide Susceptibility Mapping For Kundhapallam Watershed, Nilgiris, TamilNadu Dr. P. Rajesh Prasanna 1, S.Evany Nithya 2 1 Professor, Anna University Tiruchirappalli 2 Asst.
