LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE DETECTION AND ANALYSES IN PLOVDIV, BULGARIA, BETWEEN 1986 AND 2000
|
|
|
- Alexandra Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE DETECTION AND ANALYSES IN PLOVDIV, BULGARIA, BETWEEN 1986 AND 2000 Boriana Pangelova, GIS Analyst CABRERA SERVICES 473 Silver Lane East Hartford, CT John Rogan, Assistant Professor of Geography Department of Geography Clark University 950 Main Street Worcester, MA ABSTRACT This paper compares three remote sensing techniques to monitor land-cover change in Plovdiv County, Bulgaria ( ) using multitemporal Landsat TM data. Following the fall of dictatorship in 1989, Bulgaria experienced major political and economic changes, not accompanied by the implementation of necessary instruments for managing land-use transitions. As a result, the country experienced rapid and widespread land-cover conversionsthe extent of which is still unknown. The context of the study is based on three major issues in remote sensing science: 1) Unsupervised classification algorithms are currently under-utilized in land-cover applications; 2) Many developing countries, such as Bulgaria, are data-poor and the main information source for proper land management and monitoring are non-spatial summary reports; 3) A lack of reliable ground reference data in these countries demands the development of alternative methodologies to address this paucity. Supervised and unsupervised classifications were used to map land-cover in 1986 and 2000 and postclassification comparison of map products produced maps of land- cover conversion. To assess land cover modifications, change vector analysis was then used to produce images of change direction and magnitude between the two dates based on two Kauth Thomas transformation features: brightness and greenness. Landscape pattern metrics were subsequently used to determine the status and trends in the condition of land-cover change process. The results indicate that there was a significant increase in urban areas and decrease in agriculture. The research demonstrated that the applied techniques were successful tools for monitoring land-cover change in countries with limited or inexistent spatial data, where the only available information is represented in reports provided by international organizations. Results also showed that the unsupervised classification provided better land-cover change estimation and accuracy in the study area. Overall accuracies of land cover change maps using unsupervised classification algorithm were higher (74-84%) then the accuracies achieved, when the supervised classification was applied (54-68%). KEYWORDS: land-cover change, classification, change vector analysis, landscape metrics. INTRODUCTION The underlying driving forces behind land cover dynamics may potentially be traced to political and economic factors (Berov et al., 1998). After 1989, Bulgaria experienced major political and economic changes, moving from a socialist political system to a free-market society. This change affected the structure of all the former cooperative farms, which were transformed into thousands of new private farms, without the implementation of a system that would provide the necessary technical and economic support for a rational and appropriate use and management of the natural and human agriculture resources. Also these political and economic changes were not accompanied by the implementation of necessary instruments for monitoring of land use; as a result Bulgaria experienced a decrease
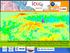
2 in the collection of information with respect to the use and management of major agriculture areas in the country (Berov et al., 1998). There is an increasing need to study the effects of these socio-economic changes in the land cover in Bulgaria. However, in order to do this it is necessary the existence of reliable spatial data. Bulgaria is of one of data-poor countries with very limited spatial data sources; therefore there is a need for development of approaches that would substitute this lack of information. The development of new models and algorithms of remote sensing science and GIS technology have made possible a more precise quantification of the spatial relationship between the two major components of the global environmental change: land cover and land use. Despite this progress remote sensing still faces serious challenges with respect to the monitoring of land cover change in countries with limited or inexistent spatial data, where the only available information are statistical reports elaborated by international organizations such as FAO. Given these limitations the question for scientists remains on how to accomplish this work and to how to support national land use management strategies in data-poor countries. In order to respond to this challenge it is necessary to develop of methodologies that integrate the existent remote sensing approaches. The wide variety of land cover changes that occur on the landscape between certain periods of time can be monitored by different change detection methods. There is a wide variety of methods in remote sensing to analyze these changes and these methods are related to different aspects of the land cover such as land cover conversion, change in vegetation growth, change in the landscape configuration and composition, etc. The aim of this research was to map land cover change in an area with limited ground data. In order to accomplish this, different change detection methods will be applied: Classification algorithms, Change Vector Analysis and Landscape metrics. The specific research objectives of this study were: To map land cover/use and estimate land cover conversion using remote sensing data and methods for the region of Plovdiv, Bulgaria, ; To determine which classification method (supervised or unsupervised) can more accurately map the study area; To assess the relationship between land cover/use changes and the transition from planned-centralized to free-market economy in Bulgaria over the period between 1986 and DATA AND METHODS Study Area The study area is Plovdiv County, Bulgaria (12,000 km 2 ) located in the central part of Southern Bulgaria (Figure 1) along one of the largest Bulgarian rivers ( Maritza). Elevation ranges from 15 to 625 m, the dominant slope is 15 degrees and the dominant aspect is 250 degrees. The average temperature ranges from 32 F in January to 75 F in July. The average annual precipitation is 1170 mm (Berov et al., 2003). According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAOSTAT) report the population growth, Plovdiv County decreased by 60% from 1970 to Plovdiv County is the second largest and second most populated county in Bulgaria. The area includes urban areas, agriculture fields, wetlands, forest and barren. The study region represents an interesting scenario of land cover change: a significant trend in urban growth and agricultural decline over the past 15 years. Figure 1. Study area of Plovdiv County, Bulgaria fg
3 DATA Satellite Data Two satellite images were acquired to map land cover changes in the Plovdiv County : Landsat 5 TM (May 22, 1986) and Landsat ETM+ 7 (June 21, 2000) (Figure 2). The spatial resolution of the satellite images was 28.5 m. Both images were registered to the UTM Zone 35 North Projection with less then 0.5 pixel root mean squared error. In order to reduce the variation in pixel digital number (DN), caused by non-surface factors as sun angle, earth-sun distance, detector calibration differences between various sensors systems, atmospheric condition and sun-targetsensor geometry (Jensen 1996), the bands from both images were radiometrically corrected using the dark object subtraction technique (Chavez, 1996). Haze was removed from each band and digital number (DN) values were transformed into reflectance values. The correction was performed according to the method designed by Markham and Barker (1985). The Solar azimuth for TM 1986 was degree and the solar azimuth for ETM 2000 was degree. The Solar elevation for 1986 was degree and the solar elevation for ETM 2000 was degree. Figure 2. The Plovdiv County Study Area. The images are false color composites of Landsat TM 5 and Landsat ETM +7 bands 2, 3, 4 for 1986 (left) and 2000 (right), which have been topographically and radiometrically corrected. Ancillary Data Slope and elevation spatial variables (Figure 3) were included with the spectral data as ancillary variables, because the results from previous studies indicated that including of these environmental variables in the classification process may help to improve the discrimination between classes and it may increase the overall accuracy of the final classified maps (Rogan et al., 2005). A 90m digital elevation model (DEM) was resampled 28.5 m and was used to produce the second environmental variable slope. Figure 3. Ancillary data: Slope and elevation
4 METHODOLOGY Unsupervised Classification ISOCLUST An unsupervised classification was performed on the data using the ISODATA clustering algorithm. Various experiments to determine the most efficient distinction between the different land cover classes were explored using 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 clusters. The best combination of classes was achieved deriving thirty clusters. The derived thirty classes were grouped into five desired categories: Agriculture, Barren, Forest, Water, Urban, using reference information from paper maps and readings and some prior knowledge of the area. Supervised Classification Using Neural Networks A supervised classification was performed using cluster-sampling approach (Rogan, 2004). Training sites were derived from the satellite images using reference maps. To deliver the appropriate support size of each category the required training set for each class was determine at least ten times the number of discriminating variables (e.g., wavebands) used in the classified map (Mather 1987; Piper 1992; Peddle 1993). A backpropagation Artificial Neural Network was used to compare each pixel to the classes from the training data and to label accordingly. The following land cover categories were produced: agriculture, barren, forest, water and urban (Table 2). Slope and elevation were chosen as the only ancillary variable, because the inclusion of these variables showed a increase in the overall accuracy of the produced classification maps for 1986 and 2000: 68% and 54% respectively. The incorporation of aspect decreased the value of overall accuracy by 5%. Change Vector analysis (CVA) In order to reduce redundancy in the data and highlight the vegetative qualities of the landscape, Tasseled Cap transformations (Kauth & Thomas, 1976) were performed on bands 1-5, and 7 for both satellite images. The transformation produced two new components, representing the biophysical properties of the landscape scene: brightness and greenness. Brightness represents variations in soil reflectance throughout the study area. Greenness is the contrast between the near infrared bands and the visible bands and it represents variation in vegetation cover. The inputs of brightness and greenness were used to generate images for the magnitude ands direction of variation among spectral change vectors between 1986 and These two transformed bands presented biophysically interpretable inputs for change vector analysis. The cross tabulation between these images showed the processes of cultivation, urbanization, and persistence between 1986 and Landscape Metrics To quantify landscape pattern two landscape metrics were calculated: Shannon evenness (SHEI) and fragmentation index. Each of these metrics is measured by producing images for both years. Shannon evenness indicates how evenly the proportion of cover types is distributed on the landscape. Values for SHEI range between 0 and 1. Values near to 0 indicate a landscape dominated by one category, while values near to 1 indicate that the proportions of each cover type are nearly equal. The Fragmentation index indicates the breaking up of a habit or cover type into smaller, disconnected parcels. Each metric refers to the thematic zones of the landscape for which the metric is calculated. Examining Land Cover Change The TM 1986 and ETM images were independently classified using Neural Net Classifier and ISOCLUST classifier in five categories (Agriculture, Barren, Forest, Water and Urban). All of the final classified land cover maps were filtered using a 3x3 majority filter in order to reduce noise in the classification. CVA direction and magnitude images were created from TM 1986 and ETM The images representing direction change were created according following: Angles measured between 90 and 180 indicate an increase in greenness and a decrease in brightness (Lorena et al., 2002). Angles measured between 270 and 360 indicate a decrease in greenness and an increase in brightness (Lorena et al., 2002). Angles measured between 0 and 90 and 180 and 270 indicate either increases or decreases in both bands of greenness and brightness (Lorena et al., 2002). The final map was classified into three categories of no change, increased greenness and decreased brightness and decreased greenness and increased brightness. The image representing magnitude change was classified also into three categories: no change, low change magnitude, and high change magnitude. These ranges were chosen,
5 based on the following threshold values from the image histograms: high (0 to 60), low (60-167) and persistence ( ). The change direction and magnitude values of the images were cross-tabulated and classified into three categories of urbanization, cultivation and persistence. Landscape metrics images were classified into three categories: increased landscape index, decreased landscape index and no change. Accuracy Assessment Accuracy Assessment using an error matrix was assessed for the 1986 and 2000 unsupervised and supervised classification using four measures of accuracy: overall accuracy, user s accuracy, producer s accuracy and Kappa coefficient: A topographic map for the Plovdiv City area was used as ground reference information for the classification of For 2000, the classified 1996 land use map was used. A total of 30 random points for each class were taken to determine the accuracy of the classification method. Accuracy was assessed in terms of errors of omission (producer s accuracy) and commission (user s accuracy) and Kappa coefficient. The overall map accuracy was calculated by dividing the total correct classified pixels, (major diagonal of the error matrix) by the total number of pixels in the error matrix. Overall accuracy did not take into account the proportion of agreement between datasets and it tends to overestimate classification accuracy (Congalton and Mead 1983). Producer s accuracy was calculated by dividing the total number of correct pixels in a category by total number of pixels of that category as derived from the reference data. Producer s accuracy indicates the probability of reference pixel being correctly classified and it is a measure of omission error (Jensen 1996). User s accuracy was calculated by dividing the total number of correct pixels in a category by the total number of pixels that are actually classified in that category. User s accuracy is the probability of classified pixel actually represents that category on the ground. User s accuracy is a measure of commission error (Jensen 1996). The Kappa Coefficient measures the proportional improvement of classification over purely random assignment to classes. This accuracy measure attempts to control for a chance agreement by incorporating the off-diagonal elements as a product of the row and column of the error matrix (Cohen 1960). RESULTS Figure 4. Land Cover Map 1986 and 2000 (Unsupervised Classification) Land cover change results from the land cover unsupervised (Figure 4) classification algorithm. The land cover maps obtained from the unsupervised classification of TM 1986 and ETM+2000 respectively. The land cover conversion result show a net change in the amount of land use between 1986 and 2000, indicating that urban areas increased by 9% representing an area of 1050 km 2. Agriculture decreased by 3.8% or 455 km 2. Forest decreased by 2.6% or 317 km 2. Barren decreased by 4.3% or 514 km 2 and Water increased by 1.6% or 203 km 2. The maps show a decrease in agriculture and forest and increase in urban from 1986 to 2000.
6 Figure 5. Land Cover Map 1986 and 2000 (Supervised Classification). The maps obtained from the supervised classification. Figure 5 shows the amount of change of each land category between 1986 and Urban areas are shown to increase by 19 % or 2,271 km 2. Agriculture decreased by 25% or 2971 km 2. Barren increased by 3.6% or 4241 km 2. Forest increased with 170 km 2 or 1.4%. Water did not change very much; it increased with 105 km 2 or 1%. The map results are showing trend of high level in urbanization and high level of decreased in agriculture. According this algorithm around 1% of the agriculture areas were converted into forest areas. The main reason for this change is closely related to the process of abandonment of agriculture fields after the political and economical transition of Bulgaria to free-market economy (Hristova et al., 2004) Figure 6. Direction of Vegetation Magnitude of Vegetation Change Classification Vegetation Change The result of Change in Direction Image (Figure 6) shows that the areas with decreased greenness and increased brightness are areas located along the Maritza River Basin in the North Part of the study area. This change in the biophysical properties of the scene represents process of high level of urbanization from 1986 to The result of Change Magnitude Image also shows the majority of areas with high magnitude in change are clustered to the north of the study area. The crosstabulation map between change direction map and change magnitude map was classified into three categories: no change, cultivation and urbanization. A total land area of 8061 km 2 representing 67% of the overall land area of 11,906 km 2 was classified as: no change. Urban areas increased by 30% or 3,637 km 2 while the area under cultivation increased by 1.74% or 207 km 2. Land classified as cultivation contained higher levels of vegetation in 2000 than in 1986, and land designated as urbanization contained lower levels of vegetation in 2000 than in 1986.
7 Figure 7. Shannon evenness image 1986 Shannon evenness image for 2000 Figure 8. Fragmentation image for 1986 Fragmentation image for 2000 Figure 7 and 8 show the land cover change results using landscape metrics. Figure 7 shows a change in Shannon Evenness (SHEI) obtained from relative richness maps of 1986 and The range of the image values is from 0 to 1. Values close to 0 indicated that the landscape is dominated by one cover type. Values closer to 1 indicated the presence of other land cover types. The values of SHEI for 1986 are close to 0, indicating that agriculture was the dominant land cover on the landscape. Values of SHEI for 2000 are close to 1, indicating that the number or land cover types increased as result from the urbanization process. Figure 8 shows a change in fragmentation obtained from fragmentation maps of 1986 and The values range from 0 to 1. The values close to 1, indicate that the landscape was more homogeneous, values close to 1, indicate the process of breaking land cover type into small parcels increased. The results show similar trend as SHEI. In 1986 the landscape can be characterized as more homogeneous then Accuracy Assessment Results The overall accuracy for 1986 was 84% and it was with 20% higher then the accuracy performed with the supervised algorithm for According to the unsupervised classification algorithm for 1986, agriculture had the highest producer s and relatively high user s accuracy of 100% and 81%. This implies that the 100% of pixels that were correctly identified as agriculture, 81% of those pixels were actually also labeled as agriculture. The urban areas had the lowest user s accuracy of 70% and relatively high producer s accuracy of 83%. This means that 83% of pixels that were correctly identified as urban, 70% of those pixels were labeled as urban. Barren areas had the lowest producer s accuracy 67% and relatively high user s accuracy 83%. This means that 67% of the pixels belong to barren class, but 83% were labeled as barren. The Kappa Coefficient for this map was 0.8. According the accuracy assessment results using supervised classification for 1986, agriculture had the lowest producer s and
8 user s accuracy of 67% and 57%. This means that the 67 % of pixels that are correctly identify as agriculture, 57% of those pixels were actually also labeled as agriculture. Urban also had low producer s and user s accuracy of 67% and 59%. The Kappa Coefficient was 0.6. The accuracy assessment results from unsupervised and the supervised classification for the ETM indicate similar results with the comparison between the two algorithms for 1986 that the producer s and user s accuracy for each class were lower using Supervised Classification Algorithm. The overall accuracy for unsupervised accuracy for 2000 was 74%, while for supervised was 54 %. According the accuracy assessment of unsupervised classification map for 2000 water had the highest user s and producer s accuracy of 90% and 77% respectively. Agriculture has the lowest producer s and user s accuracy of 60% and 67%. The result of the accuracy assessment of supervised classification algorithm for 2000 shows that urban had the highest producer s accuracy of 70% and the lowest user s accuracy of 40%. This means that the 70% of pixels that were correctly identified as urban, 40% of those pixels were actually also labeled as urban. DISCUSSION As there were no other remote sensing studies of Plovdiv County to compare the results of this study to, two reference materials were used for this purpose: results from the European Land Cover Change and FAOSTAT database information for Plovdiv County. The CORINE project (Co-ordination of Information on the Environment) was implemented from the European Commission. The aim of this project was to examine land cover change information during the period 1990 to 2000 for all the European countries using 44 land cover classes. Corine Land Cover project for Bulgaria was executed with the financial support of the European Environmental Agency and the Bulgarian Ministry of Environment and Water. The methodology of this project did not include classification algorithms and the interpretation process of land cover was performed with InterChange2 software-extension of ArcView3.2. Figure 9. Land Cover Change Comparison between Unsupervised Classification for Plovdiv area, Bulgaria and CORINE Classification for the entire country The comparison of the results from the CORINE classification for Bulgaria to the results from Unsupervised Classification for Plovdiv indicates a close similarity (Figure 9). Both classifications show a trend in increasing urbanization and decreasing agriculture. According to the CLC project, the agriculture sector decreased in 1.7% (unsupervised classification indicated 3.6% and supervised 25.0% decrease), urban areas increased 2.3% (unsupervised classification showed 8.9% and supervised 19.1% increase). The results from unsupervised classification show a greater increase in urbanization compared to the results of urbanization changes from Corine, the visual interpretation of Corine Classificaiton does not show the high level of urbanization in Plovdiv County. The difference in the results between the two studies can be explained by two main factors: First, the CLC project included the entire territory of the country, and second, the period of the analysis is four years shorter.
9 Figure 10. Land Cover Change Comparison between Unsupervised Classification and Supervised Classificaiton and FAOSTAT data for Plovdiv county, Bulgaria The second reference dataset, FAOSTAT, is an online database that provides country, regional and world agricultural statistics. Statistics from FAOSTAT for Plovdiv County for the period are very similar to the results from the unsupervised classification (Figure 10). FAOSTAT showed a decreased of 3.0% in agriculture, compared to unsupervised classification 3.7% and supervised classification 25% decrease. In the urban sector FAOSTAT showed an increased of 7.0% compared to unsupervised classification 8.9% and supervised classification 19.1% increase. Forest decreased 5% and unsupervised and supervised classification 2.6% and 1.4% decrease respectively. The comparison of the accuracy analysis between unsupervised and supervised classification indicated that unsupervised classification outperformed supervised classification. The supervised method provided the lowest overall accuracy (68%, Kappa: 0.6 for 1986 and 54%, Kappa 0.43 for 2000), with higher errors in producer s and user s accuracy. The unsupervised classification increased accuracy to 84% (Kappa: 0.8) for 1986 and 74% (Kappa: 0.68) for 2000, but the producer s and user s accuracy for the land cover categories for 2000 were still low. The quantitative results of landscape metrics and Change Vector Analysis of land use dynamics presented in this study corroborated the findings of the classification method: a high urbanization trend in the Northwest and Northeast areas of Plovdiv County in Bulgaria during the period between 1986 and The results of these analyses also provided a solid foundation for the conclusion of agriculture land lost to this process. One of the important changes detected from this study within non-forestry land use, was the increased fragmentation of agricultural areas due to urbanization and increased crop loss in the remaining lowlands. The positive changes on forest area, detected by the supervised classification provided some evidence of ecological sustainability in the region. This finding signified to some extent the success of local communities in forest conservation activities. The comparison between both change detection methods showed that Change vector analyses performed better due to it s ability to not only detect the change but also to determine the nature of the disturbance. This method can allow resource managers to observe changes over large areas and provide long-term monitoring capabilities. The reports from FAOSTAT on Food and Agriculture Indicators for Bulgaria for the last 30 years showed a decreased of 30% in population growth and agriculture labor force. Agriculture exports decreased in 75% from 1979 to The agriculture production of wheat, milk and meat decreased in 30%. Between 1986 and 1990 agriculture was the largest source of income and employment for Plovdiv County. Given the information from FAOSTAT statistics and considering the results from this study it can be concluded that the transition from a centralized economy to free-market economy negatively affected the agriculture production of Plovdiv County from 1986 to The main driving force for this change being the economical and political changes related to the new structure of the Bulgarian society. Other possible driving forces of land cover changes in Plovdiv, Bulgaria between 1986 and 2000 could be the population change. Comparative assessments of population and land use suggest that population growth is negatively correlated with the expansion of agricultural land, and positively correlated with urban growth and land intensification.
10 Bulgaria's cities experienced rapid growth after In 1946 only Sofia and Plovdiv had populations numbering over 100,000, by 1990 there were ten cities having populations exceeding 250,000. In 1990 nearly onethird of Bulgaria's population lived in the ten largest cities; two-thirds of the population was urban. Although the urban birth rate declined after the mid-1970s, large-scale migration from rural areas to cities continued through At the same time, migration from cities to rural areas increased in more than double from the 1960s to the 1980s, mainly because more mechanical and service jobs became available in agriculture during that period. In cities such as Sofia and Plovdiv, where industrialization started earlier, the population stabilized and the repercussions of rapid population growth slowed down in the 1980s. The population of the average Bulgarian city grew by three to four times between 1950 and The rapidity of this growth caused some negative trends: the cities often lacked the resources to meet the needs of their growing populations, in particular, housing and social services could not grow fast enough. The cities' great need for social resources in turn diverted resources from smaller, more scattered population centers. The overall rural to urban migration pattern caused shortages of agricultural labor, especially in the villages surrounding large cities. The government discouraged new industries from locating in outlying areas because of the lack of workers. CONCLUSION This research project investigated land cover changes in Plovdiv County, Bulgaria from 1986 to The results from the applied change detection techniques indicate that there is a significant increase in urban areas and decrease in agriculture. An unsupervised classification algorithm was the most suitable approach to detect changes over large areas and to provide long-term capabilities for monitoring land cover change in data-poor regions. The similarity of results from this research and the official statistics from FAOSTAT proved that remote sensing methods provides reliable and cost effective information for land use mangers and planners. This study demonstrates that remote sensing offers great analytical tools to relate socio-economic and political changes in the society to land cover change. Both classification methods showed agreement with respect to identifying the areas of change, the change vector analysis and landscape metrics also proved this finding. The difference in the two classification methods lay in the estimated quantification of the land cover conversion. Supervised classification appeared to over-classify the pixels from the images due to a large variety of reflectance (especially urban areas). From a visual examination of the map of land change from the CORINE study it appears that their methodology misclassified the areas where land change occurred and it under-represented the magnitude of the changes. From these results it can be suggested that change detection methods applied in this study should be adopted for the land cover change analysis of large areas without reliable spatial data. REFERENCES Anderson, J.R., Hardy, E, E., Roach, J, T., and Witmer, R, E., 1976, A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data. Geological Survey Professional Paper No. 964, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. p. 28. Berov, J.R., 1998, The transition in Bulgaria specific features and results, problems and perspectives (an attempt at a sociological content-analysis), Series: Economics and Organization Vol. 2, No 1, 2003, pp Berov, J.R., 2004, Overview of the political transition in Bulgaria Chavez, P.S., Jr., 1996, Radiometric calibration of Landsat Thematic Mapper multispectral mages. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 55 (9), Carpenter, G.A., Gjaja, M.N., Gopal, S., Woodcock, C.E., 1997, ART neural networks for remote sensing: Vegetation classification from Landsat TM and terrain data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 35 (2): Cihlar, J., 2000, Landcover mapping of large areas from satellites: status and research priorities. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21 (6 & 7, ). Congalton, R.G., and Mead R. A., 1983., A quantitative method to test for consistency andncorrectness photointerpretation. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 49(1):
11 Copping, P., Jonckheere, I., Muys, B., and Lambin, E., 2002, Digital change detection methods in natural ecosystem monitoring. In proceedings of the First Annual Workshop on the Analysis of Multi-temporal Remote Sensing Images, L. Bruzzone, and P. Smits (Eds.), World Scientific Publishing Co., Pte. Ltd., 440 p. DeFries, R.S., Townshed, J.R.G., and Hansen, M., 1999, Continuous fields of vegetation characteristics at the global scale. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104: Franklin, S. E., and Wulder, M.A., 2002, Remote Sensing methods in medium spatial resolution satellite data land cover classification of large areas. Progress in Physical Geography, 26 (2): Franklin, J., Phinn, S.R., Woodcock, C.E., and Rogan, J., 2003, Multi-attribute vegetation maps of Forest Service lands in California supporting resource management decision. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 6, Gong, P., Xu, B., 2003, Remote Sensing of forests over time: Change types, methods, and opportunities. In Wulder, M and Franklin, S.E. editors Methods and applications for remote sensing of forests Concepts and case studies, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp Jensen, J.R., 1996, Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective Jensen, J.R., Rutchey, K., Koch, M.S., Narumalani, S., 1995, Inland wetland change detection in the Everglades Water Conservation Area 2A using time series of normalized remotely sensed data. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 61: Langevin, C., and Stow, D.A., in press. Identifying change in dynamic urban landscape: A neural network approach to map updating. Progress in Planning. Lorena, R. B., J. R. dos Santos, Y. E. Shimabukuro, I. F. Brown, H. J. H. Kux, A change vector analysis technique to monitor land use/land cover change in SW Brazilan Amazon: Acre Site. Proceeding from Integrated Remote Sensing at the Global, Regional, and Local Scale: ISPRS Commission I Mid-Term Symposium in conjunction with Pecora 15/Land Satellite Information IV Conference, November 10-15, Lunetta, R.S., 1998, Project formulation and analysis approaches. In Lunetta, R.S., Elvidge C.D., editors, Remote Sensing change detection environmental monitoring methods and applications, An arbor Press, Chelsea, MI, 318 pp. Lunetta, R.S., Johnson, D.M., Lyon, J.G., Grotwell, J., 2003, Impacts of imagery temporal frequency on land-cover change detection monitoring. Remote Sensing of Environment 89 (2004) Maingi J.K and Marsh, S.E. 2001, Assessment of environmental impacts of river basin development on the riverine forests of eastern Kenya using multi-temporal satellite data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2001, 14, Mather, P.M., 1987, Computer Processing of Remotely-Sensed Images (Chichester: Wiley). Markham, B. L. and Barker, J. L., eds., 1985, Landsat Image Data Quality Special Issue, Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 51 (9): Moody, A., Gopal, S., Strahler, A.H., 1996, Artificial neural network response to mixed pixels in coarse-resolution satellite data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 58: Serra, P., Pons, X., Sauri, D. 2002, Post-Classification Change detection with data from different sensors: some accuracy considerations. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2003v.24, no.16, Seto, K.C., and Liu, W., 2003, Comparing ARTMAP neural network with maximum likelihood classifier for detecting urban change. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 69 (9), Skidmore, A.K., and Turner, B.J., Forest mapping accuracies are improved using a supervised nonparametric classifier with SPOT data. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 54, Skole, D.L., Justice, C.O., Townshend, J.R.G., Janestos, A.C.,1997, A Land Cover Change Monitoring Program: Strategy for an International Effort. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change 2: Stahler, A.H., 1980, The use of prior probabilities in maximum likelihood classification of remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 10, Rogan, J., Franklin, J., Roberts, D.A., 2002, A comparison of methods for monitoring multitemporal vegetation change using Thematic Mapper imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 80,
Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction in Tabriz
 Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM
 Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM Kalpana G. Bastakoti Department of Geography, University of Calgary, kalpanagb@gmail.com Abstract This paper presents a study of detecting
Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM Kalpana G. Bastakoti Department of Geography, University of Calgary, kalpanagb@gmail.com Abstract This paper presents a study of detecting
A Method to Improve the Accuracy of Remote Sensing Data Classification by Exploiting the Multi-Scale Properties in the Scene
 Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Spatial Accuracy Assessment in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences Shanghai, P. R. China, June 25-27, 2008, pp. 183-188 A Method to Improve the
Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Spatial Accuracy Assessment in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences Shanghai, P. R. China, June 25-27, 2008, pp. 183-188 A Method to Improve the
Use of Corona, Landsat TM, Spot 5 images to assess 40 years of land use/cover changes in Cavusbasi
 New Strategies for European Remote Sensing, Olui (ed.) 2005 Millpress, Rotterdam, ISBN 90 5966 003 X Use of Corona, Landsat TM, Spot 5 images to assess 40 years of land use/cover changes in Cavusbasi N.
New Strategies for European Remote Sensing, Olui (ed.) 2005 Millpress, Rotterdam, ISBN 90 5966 003 X Use of Corona, Landsat TM, Spot 5 images to assess 40 years of land use/cover changes in Cavusbasi N.
Yanbo Huang and Guy Fipps, P.E. 2. August 25, 2006
 Landsat Satellite Multi-Spectral Image Classification of Land Cover Change for GIS-Based Urbanization Analysis in Irrigation Districts: Evaluation in Low Rio Grande Valley 1 by Yanbo Huang and Guy Fipps,
Landsat Satellite Multi-Spectral Image Classification of Land Cover Change for GIS-Based Urbanization Analysis in Irrigation Districts: Evaluation in Low Rio Grande Valley 1 by Yanbo Huang and Guy Fipps,
IMPROVING REMOTE SENSING-DERIVED LAND USE/LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION WITH THE AID OF SPATIAL INFORMATION
 IMPROVING REMOTE SENSING-DERIVED LAND USE/LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION WITH THE AID OF SPATIAL INFORMATION Yingchun Zhou1, Sunil Narumalani1, Dennis E. Jelinski2 Department of Geography, University of Nebraska,
IMPROVING REMOTE SENSING-DERIVED LAND USE/LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION WITH THE AID OF SPATIAL INFORMATION Yingchun Zhou1, Sunil Narumalani1, Dennis E. Jelinski2 Department of Geography, University of Nebraska,
ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA
 PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, NR. 4, 2010 ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA Mara Pilloni
PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, NR. 4, 2010 ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA Mara Pilloni
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July-2015 1428 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover /Land Use Mapping Using Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery Paliwal M.C &.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July-2015 1428 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover /Land Use Mapping Using Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery Paliwal M.C &.
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity
 Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
KNOWLEDGE-BASED CLASSIFICATION OF LAND COVER FOR THE QUALITY ASSESSEMENT OF GIS DATABASE. Israel -
 KNOWLEDGE-BASED CLASSIFICATION OF LAND COVER FOR THE QUALITY ASSESSEMENT OF GIS DATABASE Ammatzia Peled a,*, Michael Gilichinsky b a University of Haifa, Department of Geography and Environmental Studies,
KNOWLEDGE-BASED CLASSIFICATION OF LAND COVER FOR THE QUALITY ASSESSEMENT OF GIS DATABASE Ammatzia Peled a,*, Michael Gilichinsky b a University of Haifa, Department of Geography and Environmental Studies,
M.C.PALIWAL. Department of Civil Engineering NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING & RESEARCH, BHOPAL (M.P.), INDIA
 INVESTIGATIONS ON THE ACCURACY ASPECTS IN THE LAND USE/LAND COVER MAPPING USING REMOTE SENSING SATELLITE IMAGERY By M.C.PALIWAL Department of Civil Engineering NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS
INVESTIGATIONS ON THE ACCURACY ASPECTS IN THE LAND USE/LAND COVER MAPPING USING REMOTE SENSING SATELLITE IMAGERY By M.C.PALIWAL Department of Civil Engineering NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai
 Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TOOL FOR LAND USE / LAND COVER ANALYSIS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD AND MINIMUM DISTANCE METHOD
 IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TOOL FOR LAND USE / LAND COVER ANALYSIS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD AND MINIMUM DISTANCE METHOD Manisha B. Patil 1, Chitra G. Desai 2 and * Bhavana N. Umrikar 3 1 Department
IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TOOL FOR LAND USE / LAND COVER ANALYSIS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD AND MINIMUM DISTANCE METHOD Manisha B. Patil 1, Chitra G. Desai 2 and * Bhavana N. Umrikar 3 1 Department
This is trial version
 Journal of Rangeland Science, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2 J. Barkhordari and T. Vardanian/ 459 Contents available at ISC and SID Journal homepage: www.rangeland.ir Full Paper Article: Using Post-Classification
Journal of Rangeland Science, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2 J. Barkhordari and T. Vardanian/ 459 Contents available at ISC and SID Journal homepage: www.rangeland.ir Full Paper Article: Using Post-Classification
LAND COVER CATEGORY DEFINITION BY IMAGE INVARIANTS FOR AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION
 LAND COVER CATEGORY DEFINITION BY IMAGE INVARIANTS FOR AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION Nguyen Dinh Duong Environmental Remote Sensing Laboratory Institute of Geography Hoang Quoc Viet Rd., Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
LAND COVER CATEGORY DEFINITION BY IMAGE INVARIANTS FOR AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION Nguyen Dinh Duong Environmental Remote Sensing Laboratory Institute of Geography Hoang Quoc Viet Rd., Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
The Wide Dynamic Range Vegetation Index and its Potential Utility for Gap Analysis
 Summary StatMod provides an easy-to-use and inexpensive tool for spatially applying the classification rules generated from the CT algorithm in S-PLUS. While the focus of this article was to use StatMod
Summary StatMod provides an easy-to-use and inexpensive tool for spatially applying the classification rules generated from the CT algorithm in S-PLUS. While the focus of this article was to use StatMod
LAND USE MAPPING AND MONITORING IN THE NETHERLANDS (LGN5)
 LAND USE MAPPING AND MONITORING IN THE NETHERLANDS (LGN5) Hazeu, Gerard W. Wageningen University and Research Centre - Alterra, Centre for Geo-Information, The Netherlands; gerard.hazeu@wur.nl ABSTRACT
LAND USE MAPPING AND MONITORING IN THE NETHERLANDS (LGN5) Hazeu, Gerard W. Wageningen University and Research Centre - Alterra, Centre for Geo-Information, The Netherlands; gerard.hazeu@wur.nl ABSTRACT
Application of Remote Sensing Techniques for Change Detection in Land Use/ Land Cover of Ratnagiri District, Maharashtra
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 2015), PP 55-60 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Remote Sensing
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 2015), PP 55-60 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Remote Sensing
Deriving Uncertainty of Area Estimates from Satellite Imagery using Fuzzy Land-cover Classification
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 10 (2013), pp. 1059-1066 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Deriving
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 10 (2013), pp. 1059-1066 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Deriving
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl
 Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
Data Fusion and Multi-Resolution Data
 Data Fusion and Multi-Resolution Data Nature.com www.museevirtuel-virtualmuseum.ca www.srs.fs.usda.gov Meredith Gartner 3/7/14 Data fusion and multi-resolution data Dark and Bram MAUP and raster data Hilker
Data Fusion and Multi-Resolution Data Nature.com www.museevirtuel-virtualmuseum.ca www.srs.fs.usda.gov Meredith Gartner 3/7/14 Data fusion and multi-resolution data Dark and Bram MAUP and raster data Hilker
Land Cover Classification Over Penang Island, Malaysia Using SPOT Data
 Land Cover Classification Over Penang Island, Malaysia Using SPOT Data School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Penang, Malaysia. Tel: +604-6533663, Fax: +604-6579150 E-mail: hslim@usm.my, mjafri@usm.my,
Land Cover Classification Over Penang Island, Malaysia Using SPOT Data School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Penang, Malaysia. Tel: +604-6533663, Fax: +604-6579150 E-mail: hslim@usm.my, mjafri@usm.my,
An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT)
 An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT) Prepared for Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri Department of Conservation 07-01-2000-12-31-2001 Submitted by
An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT) Prepared for Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri Department of Conservation 07-01-2000-12-31-2001 Submitted by
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE
 SEMINAR ON A REVIEW OF CHANGE DETECTION TECHNIQUES INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE PRESENTED BY:- ABHISHEK BHATT RESEARCH SCHOLAR abhishekbhatt.iitr@gmail.com OUTLINE This seminar is organized into
SEMINAR ON A REVIEW OF CHANGE DETECTION TECHNIQUES INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE PRESENTED BY:- ABHISHEK BHATT RESEARCH SCHOLAR abhishekbhatt.iitr@gmail.com OUTLINE This seminar is organized into
Land Use/Land Cover Mapping in and around South Chennai Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques ABSTRACT
 Land Use/Land Cover Mapping in and around South Chennai Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques *K. Ilayaraja, Abhishek Singh, Dhiraj Jha, Kriezo Kiso, Amson Bharath institute of Science and Technology
Land Use/Land Cover Mapping in and around South Chennai Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques *K. Ilayaraja, Abhishek Singh, Dhiraj Jha, Kriezo Kiso, Amson Bharath institute of Science and Technology
MULTI-SOURCE IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
 MULTI-SOURCE IMAGE CLASSIFICATION Hillary Tribby, James Kroll, Daniel Unger, I-Kuai Hung, Hans Williams Corresponding Author: Daniel Unger (unger@sfasu.edu Arthur Temple College of Forestry and Agriculture
MULTI-SOURCE IMAGE CLASSIFICATION Hillary Tribby, James Kroll, Daniel Unger, I-Kuai Hung, Hans Williams Corresponding Author: Daniel Unger (unger@sfasu.edu Arthur Temple College of Forestry and Agriculture
Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite Multitemporal Data over Abeokuta, Nigeria
 International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
Spanish national plan for land observation: new collaborative production system in Europe
 ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.103/5/Add.1 Economic and Social Affairs 9 July 2013 Tenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for the Americas New York, 19-23, August 2013 Item
ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.103/5/Add.1 Economic and Social Affairs 9 July 2013 Tenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for the Americas New York, 19-23, August 2013 Item
Geospatial Information for Urban Sprawl Planning and Policies Implementation in Developing Country s NCR Region: A Study of NOIDA City, India
 Geospatial Information for Urban Sprawl Planning and Policies Implementation in Developing Country s NCR Region: A Study of NOIDA City, India Dr. Madan Mohan Assistant Professor & Principal Investigator,
Geospatial Information for Urban Sprawl Planning and Policies Implementation in Developing Country s NCR Region: A Study of NOIDA City, India Dr. Madan Mohan Assistant Professor & Principal Investigator,
2 Dr.M.Senthil Murugan
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 11, November-2013 186 Comparative Study On Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images Classification Approaches 1 R.Priya 2 Dr.M.Senthil
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 11, November-2013 186 Comparative Study On Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images Classification Approaches 1 R.Priya 2 Dr.M.Senthil
DEVELOPMENT OF DIGITAL CARTOGRAPHIC DATABASE FOR MANAGING THE ENVIRONMENT AND NATURAL RESOURCES IN THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA
 DEVELOPMENT OF DIGITAL CARTOGRAPHIC BASE FOR MANAGING THE ENVIRONMENT AND NATURAL RESOURCES IN THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA Dragutin Protic, Ivan Nestorov Institute for Geodesy, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
DEVELOPMENT OF DIGITAL CARTOGRAPHIC BASE FOR MANAGING THE ENVIRONMENT AND NATURAL RESOURCES IN THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA Dragutin Protic, Ivan Nestorov Institute for Geodesy, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 OBJECTIVE
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
 SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING of NATURAL RESOURCES David L. Verbyla LEWIS PUBLISHERS Boca Raton New York London Tokyo Contents CHAPTER 1. SATELLITE IMAGES 1 Raster Image Data 2 Remote Sensing Detectors 2 Analog
SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING of NATURAL RESOURCES David L. Verbyla LEWIS PUBLISHERS Boca Raton New York London Tokyo Contents CHAPTER 1. SATELLITE IMAGES 1 Raster Image Data 2 Remote Sensing Detectors 2 Analog
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-Temporal changes of Land
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-Temporal changes of Land
LAND COVER CHANGES IN ROMANIA BASED ON CORINE LAND COVER INVENTORY
 LAND COVER CHANGES IN ROMANIA BASED ON CORINE LAND COVER INVENTORY 1990 2012 JENICĂ HANGANU, ADRIAN CONSTANTINESCU * Key-words: CORINE Land Cover inventory, Land cover changes, GIS. Abstract. From 1990
LAND COVER CHANGES IN ROMANIA BASED ON CORINE LAND COVER INVENTORY 1990 2012 JENICĂ HANGANU, ADRIAN CONSTANTINESCU * Key-words: CORINE Land Cover inventory, Land cover changes, GIS. Abstract. From 1990
A NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE VEGETATION INDEX (NDVI) TIME-SERIES OF IDLE AGRICULTURE LANDS: A PRELIMINARY STUDY
 A NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE VEGETATION INDEX (NDVI) TIME-SERIES OF IDLE AGRICULTURE LANDS: A PRELIMINARY STUDY Chaichoke Vaiphasa 1*, Supawee Piamduaytham 2, Tanasak Vaiphasa 3, and Andrew K. Skidmore 4 1
A NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE VEGETATION INDEX (NDVI) TIME-SERIES OF IDLE AGRICULTURE LANDS: A PRELIMINARY STUDY Chaichoke Vaiphasa 1*, Supawee Piamduaytham 2, Tanasak Vaiphasa 3, and Andrew K. Skidmore 4 1
A SURVEY OF REMOTE SENSING IMAGE CLASSIFICATION APPROACHES
 IJAMML 3:1 (2015) 1-11 September 2015 ISSN: 2394-2258 Available at http://scientificadvances.co.in DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18642/ijamml_7100121516 A SURVEY OF REMOTE SENSING IMAGE CLASSIFICATION APPROACHES
IJAMML 3:1 (2015) 1-11 September 2015 ISSN: 2394-2258 Available at http://scientificadvances.co.in DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18642/ijamml_7100121516 A SURVEY OF REMOTE SENSING IMAGE CLASSIFICATION APPROACHES
1. Introduction. Chaithanya, V.V. 1, Binoy, B.V. 2, Vinod, T.R. 2. Publication Date: 8 April DOI: https://doi.org/ /cloud.ijarsg.
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
STUDY OF NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE BUILT-UP (NDBI) INDEX IN AUTOMATICALLY MAPPING URBAN AREAS FROM LANDSAT TM IMAGERY
 STUDY OF NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE BUILT-UP (NDBI) INDEX IN AUTOMATICALLY MAPPING URBAN AREAS FROM LANDSAT TM IMAGERY Dr. Hari Krishna Karanam Professor, Civil Engineering, Dadi Institute of Engineering &
STUDY OF NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE BUILT-UP (NDBI) INDEX IN AUTOMATICALLY MAPPING URBAN AREAS FROM LANDSAT TM IMAGERY Dr. Hari Krishna Karanam Professor, Civil Engineering, Dadi Institute of Engineering &
Online publication date: 22 January 2010 PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: On: 29 January 2010 Access details: Access Details: Free Access Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered
This article was downloaded by: On: 29 January 2010 Access details: Access Details: Free Access Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered
GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING
 GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING Ryutaro Tateishi, Cheng Gang Wen, and Jong-Geol Park Center for Environmental Remote Sensing (CEReS), Chiba University 1-33 Yayoi-cho Inage-ku Chiba
GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING Ryutaro Tateishi, Cheng Gang Wen, and Jong-Geol Park Center for Environmental Remote Sensing (CEReS), Chiba University 1-33 Yayoi-cho Inage-ku Chiba
GeoComputation 2011 Session 4: Posters Accuracy assessment for Fuzzy classification in Tripoli, Libya Abdulhakim khmag, Alexis Comber, Peter Fisher ¹D
 Accuracy assessment for Fuzzy classification in Tripoli, Libya Abdulhakim khmag, Alexis Comber, Peter Fisher ¹Department of Geography, University of Leicester, Leicester, LE 7RH, UK Tel. 446252548 Email:
Accuracy assessment for Fuzzy classification in Tripoli, Libya Abdulhakim khmag, Alexis Comber, Peter Fisher ¹Department of Geography, University of Leicester, Leicester, LE 7RH, UK Tel. 446252548 Email:
A Logistic Regression Method for Urban growth modeling Case Study: Sanandaj City in IRAN
 A Logistic Regression Method for Urban growth modeling Case Study: Sanandaj City in IRAN Sassan Mohammady GIS MSc student, Dept. of Surveying and Geomatics Eng., College of Eng. University of Tehran, Tehran,
A Logistic Regression Method for Urban growth modeling Case Study: Sanandaj City in IRAN Sassan Mohammady GIS MSc student, Dept. of Surveying and Geomatics Eng., College of Eng. University of Tehran, Tehran,
Object-based classification of residential land use within Accra, Ghana based on QuickBird satellite data
 International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 28, No. 22, 20 November 2007, 5167 5173 Letter Object-based classification of residential land use within Accra, Ghana based on QuickBird satellite data D.
International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 28, No. 22, 20 November 2007, 5167 5173 Letter Object-based classification of residential land use within Accra, Ghana based on QuickBird satellite data D.
Understanding and Measuring Urban Expansion
 VOLUME 1: AREAS AND DENSITIES 21 CHAPTER 3 Understanding and Measuring Urban Expansion THE CLASSIFICATION OF SATELLITE IMAGERY The maps of the urban extent of cities in the global sample were created using
VOLUME 1: AREAS AND DENSITIES 21 CHAPTER 3 Understanding and Measuring Urban Expansion THE CLASSIFICATION OF SATELLITE IMAGERY The maps of the urban extent of cities in the global sample were created using
CHAPTER 1 THE UNITED STATES 2001 NATIONAL LAND COVER DATABASE
 CHAPTER 1 THE UNITED STATES 2001 NATIONAL LAND COVER DATABASE Collin Homer*, Jon Dewitz, Joyce Fry, and Nazmul Hossain *U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science
CHAPTER 1 THE UNITED STATES 2001 NATIONAL LAND COVER DATABASE Collin Homer*, Jon Dewitz, Joyce Fry, and Nazmul Hossain *U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data -
 ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
Environmental Impact Assessment Land Use and Land Cover CISMHE 7.1 INTRODUCTION
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens. Title. Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki. Citation Japan.
 Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
MODULE 5 LECTURE NOTES 5 PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS
 MODULE 5 LECTURE NOTES 5 PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS. (PCA) Principal component analysis (PCA), also known as Karhunen-Loeve analysis, transforms the information inherent in multispectral remotely sensed
MODULE 5 LECTURE NOTES 5 PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS. (PCA) Principal component analysis (PCA), also known as Karhunen-Loeve analysis, transforms the information inherent in multispectral remotely sensed
GEOGRAPHY (GE) Courses of Instruction
 GEOGRAPHY (GE) GE 102. (3) World Regional Geography. The geographic method of inquiry is used to examine, describe, explain, and analyze the human and physical environments of the major regions of the
GEOGRAPHY (GE) GE 102. (3) World Regional Geography. The geographic method of inquiry is used to examine, describe, explain, and analyze the human and physical environments of the major regions of the
Preparation of LULC map from GE images for GIS based Urban Hydrological Modeling
 International Conference on Modeling Tools for Sustainable Water Resources Management Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad: 28-29 December 2014 Abstract Preparation
International Conference on Modeling Tools for Sustainable Water Resources Management Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad: 28-29 December 2014 Abstract Preparation
Land Use/Cover Changes & Modeling Urban Expansion of Nairobi City
 Land Use/Cover Changes & Modeling Urban Expansion of Nairobi City Overview Introduction Objectives Land use/cover changes Modeling with Cellular Automata Conclusions Introduction Urban land use/cover types
Land Use/Cover Changes & Modeling Urban Expansion of Nairobi City Overview Introduction Objectives Land use/cover changes Modeling with Cellular Automata Conclusions Introduction Urban land use/cover types
Comparative Analysis of Supervised and
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol.,, no., 68-69 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.988/ams.. Comparative Analysis of Supervised and Unsupervised Classification on Multispectral Data Asmala
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol.,, no., 68-69 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.988/ams.. Comparative Analysis of Supervised and Unsupervised Classification on Multispectral Data Asmala
Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover Classification in Jodhpur City Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover Classification in Jodhpur City Using Remote Sensing and GIS S.L. Borana 1, S.K.Yadav 1 Scientist, RSG, DL, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India 1 Abstract: A This study examines
Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover Classification in Jodhpur City Using Remote Sensing and GIS S.L. Borana 1, S.K.Yadav 1 Scientist, RSG, DL, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India 1 Abstract: A This study examines
AUTOMATED BUILDING DETECTION FROM HIGH-RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGE FOR UPDATING GIS BUILDING INVENTORY DATA
 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 678 AUTOMATED BUILDING DETECTION FROM HIGH-RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGE FOR UPDATING GIS BUILDING INVENTORY
13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 678 AUTOMATED BUILDING DETECTION FROM HIGH-RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGE FOR UPDATING GIS BUILDING INVENTORY
AN INVESTIGATION OF AUTOMATIC CHANGE DETECTION FOR TOPOGRAPHIC MAP UPDATING
 AN INVESTIGATION OF AUTOMATIC CHANGE DETECTION FOR TOPOGRAPHIC MAP UPDATING Patricia Duncan 1 & Julian Smit 2 1 The Chief Directorate: National Geospatial Information, Department of Rural Development and
AN INVESTIGATION OF AUTOMATIC CHANGE DETECTION FOR TOPOGRAPHIC MAP UPDATING Patricia Duncan 1 & Julian Smit 2 1 The Chief Directorate: National Geospatial Information, Department of Rural Development and
Advanced Image Analysis in Disaster Response
 Advanced Image Analysis in Disaster Response Creating Geographic Knowledge Thomas Harris ITT The information contained in this document pertains to software products and services that are subject to the
Advanced Image Analysis in Disaster Response Creating Geographic Knowledge Thomas Harris ITT The information contained in this document pertains to software products and services that are subject to the
GIS AND REMOTE SENSING FOR WATER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 GIS AND REMOTE SENSING FOR WATER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT G. GHIANNI, G. ADDEO, P. TANO CO.T.IR. Extension and experimental station for irrigation technique - Vasto (Ch) Italy. E-mail : ghianni@cotir.it, addeo@cotir.it,
GIS AND REMOTE SENSING FOR WATER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT G. GHIANNI, G. ADDEO, P. TANO CO.T.IR. Extension and experimental station for irrigation technique - Vasto (Ch) Italy. E-mail : ghianni@cotir.it, addeo@cotir.it,
Analysis of Landuse, Landcover Change and Urban Expansion in Akure, Nigeria (pp )
 Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Sciences 2(4), June, 2011. ISSN : 2141-8225. http://www.grpjournal.org. Printed in Nigeria. All rights researved. Global Research Publishing, 2011. Analysis
Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Sciences 2(4), June, 2011. ISSN : 2141-8225. http://www.grpjournal.org. Printed in Nigeria. All rights researved. Global Research Publishing, 2011. Analysis
ASSESSING THEMATIC MAP USING SAMPLING TECHNIQUE
 1 ASSESSING THEMATIC MAP USING SAMPLING TECHNIQUE University of Tehran, Faculty of Natural Resources, Karaj-IRAN E-Mail: adarvish@chamran.ut.ac.ir, Fax: +98 21 8007988 ABSTRACT The estimation of accuracy
1 ASSESSING THEMATIC MAP USING SAMPLING TECHNIQUE University of Tehran, Faculty of Natural Resources, Karaj-IRAN E-Mail: adarvish@chamran.ut.ac.ir, Fax: +98 21 8007988 ABSTRACT The estimation of accuracy
Application of Satellite Images and GIS in Evaluation of Green Space Destruction in Urban Area (Case study: Boukan City)
 Application of Satellite Images and GIS in Evaluation of Green Space Destruction in Urban Area (Case study: oukan City) Himan Shahabi * 1, Hasan Zabihian 2, and Afsaneh Shikhi 1 1 Department of Remote
Application of Satellite Images and GIS in Evaluation of Green Space Destruction in Urban Area (Case study: oukan City) Himan Shahabi * 1, Hasan Zabihian 2, and Afsaneh Shikhi 1 1 Department of Remote
Module 2.1 Monitoring activity data for forests using remote sensing
 Module 2.1 Monitoring activity data for forests using remote sensing Module developers: Frédéric Achard, European Commission (EC) Joint Research Centre (JRC) Jukka Miettinen, EC JRC Brice Mora, Wageningen
Module 2.1 Monitoring activity data for forests using remote sensing Module developers: Frédéric Achard, European Commission (EC) Joint Research Centre (JRC) Jukka Miettinen, EC JRC Brice Mora, Wageningen
Page 1 of 8 of Pontius and Li
 ESTIMATING THE LAND TRANSITION MATRIX BASED ON ERRONEOUS MAPS Robert Gilmore Pontius r 1 and Xiaoxiao Li 2 1 Clark University, Department of International Development, Community and Environment 2 Purdue
ESTIMATING THE LAND TRANSITION MATRIX BASED ON ERRONEOUS MAPS Robert Gilmore Pontius r 1 and Xiaoxiao Li 2 1 Clark University, Department of International Development, Community and Environment 2 Purdue
AssessmentofUrbanHeatIslandUHIusingRemoteSensingandGIS
 Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: B Geography, GeoSciences, Environmental Science & Disaster Management Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal
Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: B Geography, GeoSciences, Environmental Science & Disaster Management Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal
Land Accounts - The Canadian Experience
 Land Accounts - The Canadian Experience Development of a Geospatial database to measure the effect of human activity on the environment Who is doing Land Accounts Statistics Canada (national) Component
Land Accounts - The Canadian Experience Development of a Geospatial database to measure the effect of human activity on the environment Who is doing Land Accounts Statistics Canada (national) Component
EFFECT OF ANCILLARY DATA ON THE PERFORMANCE OF LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION USING A NEURAL NETWORK MODEL. Duong Dang KHOI.
 EFFECT OF ANCILLARY DATA ON THE PERFORMANCE OF LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION USING A NEURAL NETWORK MODEL Duong Dang KHOI 1 10 Feb, 2011 Presentation contents 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Results 4. Discussion
EFFECT OF ANCILLARY DATA ON THE PERFORMANCE OF LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION USING A NEURAL NETWORK MODEL Duong Dang KHOI 1 10 Feb, 2011 Presentation contents 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Results 4. Discussion
Spatial Geotechnologies and GIS tools for urban planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115.
 planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques.
 Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Fouad K. Mashee, Ahmed A. Zaeen & Gheidaa S. Hadi Remote
Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Fouad K. Mashee, Ahmed A. Zaeen & Gheidaa S. Hadi Remote
ASSESSMENT OF NDVI FOR DIFFERENT LAND COVERS BEFORE AND AFTER ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTIONS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 7 (56) No. 1-2014 ASSESSMENT OF NDVI FOR DIFFERENT LAND COVERS BEFORE AND AFTER ATMOSPHERIC
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 7 (56) No. 1-2014 ASSESSMENT OF NDVI FOR DIFFERENT LAND COVERS BEFORE AND AFTER ATMOSPHERIC
Abstract. TECHNOFAME- A Journal of Multidisciplinary Advance Research. Vol.2 No. 2, (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct.
 Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
Dynamic Expansion and Urbanization of Greater Cairo Metropolis, Egypt Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan
 Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan (MSc Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan, Institue of Landscape Ecology, Muenster University, Robert-Koch Straße 28, D-48149 Münster, Germany, ahmedahalim@uni-muenster.de) 1 ABSTRACT
Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan (MSc Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan, Institue of Landscape Ecology, Muenster University, Robert-Koch Straße 28, D-48149 Münster, Germany, ahmedahalim@uni-muenster.de) 1 ABSTRACT
DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL
 DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL Paulo M. Barbosa, Mário R. Caetano, and Teresa G. Santos Centro Nacional de Informação Geográfica (CNIG), Portugal barp@cnig.pt, mario@cnig.pt,
DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL Paulo M. Barbosa, Mário R. Caetano, and Teresa G. Santos Centro Nacional de Informação Geográfica (CNIG), Portugal barp@cnig.pt, mario@cnig.pt,
IDENTIFICATION OF TRENDS IN LAND USE/LAND COVER CHANGES IN THE MOUNT CAMEROON FOREST REGION
 IDENTIFICATION OF TRENDS IN LAND USE/LAND COVER CHANGES IN THE MOUNT CAMEROON FOREST REGION By Nsorfon Innocent F. April 2008 Content Introduction Problem Statement Research questions/objectives Methodology
IDENTIFICATION OF TRENDS IN LAND USE/LAND COVER CHANGES IN THE MOUNT CAMEROON FOREST REGION By Nsorfon Innocent F. April 2008 Content Introduction Problem Statement Research questions/objectives Methodology
USING HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGERY
 USING HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGERY AND LIDAR DATA TO DETECT PLANT INVASIONS 2016 ESRI CANADA SCHOLARSHIP APPLICATION CURTIS CHANCE M.SC. CANDIDATE FACULTY OF FORESTRY UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA CURTIS.CHANCE@ALUMNI.UBC.CA
USING HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGERY AND LIDAR DATA TO DETECT PLANT INVASIONS 2016 ESRI CANADA SCHOLARSHIP APPLICATION CURTIS CHANCE M.SC. CANDIDATE FACULTY OF FORESTRY UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA CURTIS.CHANCE@ALUMNI.UBC.CA
The Positional and Thematic Accuracy for Analysis of Multi-Temporal Satellite Images on Mangrove Areas
 The Positional and Thematic Accuracy for Analysis of Multi-Temporal Satellite Images on Mangrove Areas Paulo Rodrigo Zanin¹, Carlos Antonio O. Vieira² ¹Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Campus Universitário
The Positional and Thematic Accuracy for Analysis of Multi-Temporal Satellite Images on Mangrove Areas Paulo Rodrigo Zanin¹, Carlos Antonio O. Vieira² ¹Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Campus Universitário
Geographically weighted methods for examining the spatial variation in land cover accuracy
 Geographically weighted methods for examining the spatial variation in land cover accuracy Alexis Comber 1, Peter Fisher 1, Chris Brunsdon 2, Abdulhakim Khmag 1 1 Department of Geography, University of
Geographically weighted methods for examining the spatial variation in land cover accuracy Alexis Comber 1, Peter Fisher 1, Chris Brunsdon 2, Abdulhakim Khmag 1 1 Department of Geography, University of
Optimizing unsupervised classifications of remotely sensed imagery with a data-assisted labeling approach
 Computers & Geosciences 34 (2008) 1877 1885 www.elsevier.com/locate/cageo Optimizing unsupervised classifications of remotely sensed imagery with a data-assisted labeling approach Ruili Lang, Guofan Shao,
Computers & Geosciences 34 (2008) 1877 1885 www.elsevier.com/locate/cageo Optimizing unsupervised classifications of remotely sensed imagery with a data-assisted labeling approach Ruili Lang, Guofan Shao,
Critical Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics Using Multi-Temporal Satellite Images
 Environments 2015, 2, 61-90; doi:10.3390/environments2010061 OPEN ACCESS environments ISSN 2076-3298 www.mdpi.com/journal/environments Article Critical Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics Using
Environments 2015, 2, 61-90; doi:10.3390/environments2010061 OPEN ACCESS environments ISSN 2076-3298 www.mdpi.com/journal/environments Article Critical Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics Using
A comparison of pixel and object-based land cover classification: a case study of the Asmara region, Eritrea
 Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution III 233 A comparison of pixel and object-based land cover classification: a case study of the Asmara region, Eritrea Y. H. Araya 1 & C. Hergarten 2 1 Student of
Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution III 233 A comparison of pixel and object-based land cover classification: a case study of the Asmara region, Eritrea Y. H. Araya 1 & C. Hergarten 2 1 Student of
CORINE LAND COVER CROATIA
 CORINE LAND COVER CROATIA INTRO Primary condition in making decisions directed to land cover and natural resources management is presence of knowledge and high quality information about biosphere and its
CORINE LAND COVER CROATIA INTRO Primary condition in making decisions directed to land cover and natural resources management is presence of knowledge and high quality information about biosphere and its
CHAPTER-7 INTERFEROMETRIC ANALYSIS OF SPACEBORNE ENVISAT-ASAR DATA FOR VEGETATION CLASSIFICATION
 147 CHAPTER-7 INTERFEROMETRIC ANALYSIS OF SPACEBORNE ENVISAT-ASAR DATA FOR VEGETATION CLASSIFICATION 7.1 INTRODUCTION: Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) is a rapidly evolving SAR remote
147 CHAPTER-7 INTERFEROMETRIC ANALYSIS OF SPACEBORNE ENVISAT-ASAR DATA FOR VEGETATION CLASSIFICATION 7.1 INTRODUCTION: Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) is a rapidly evolving SAR remote
International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations
 ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques with Satellite Imagery in A Part of Narmada River Basin of Madhya Pradesh, India
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 013, Volume, Issue 1, pp. 130-137, Article ID Tech-96 ISS 30-043 Research Article Open Access Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 013, Volume, Issue 1, pp. 130-137, Article ID Tech-96 ISS 30-043 Research Article Open Access Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques
Possible links between a sample of VHR images and LUCAS
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-1: Farms, agro-environment and rural development CPSA/LCU/08 Original: EN (available in EN) WORKING PARTY "LAND COVER/USE
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-1: Farms, agro-environment and rural development CPSA/LCU/08 Original: EN (available in EN) WORKING PARTY "LAND COVER/USE
Change Detection Across Geographical System of Land using High Resolution Satellite Imagery
 IJCTA, 9(40), 2016, pp. 129-139 International Science Press Closed Loop Control of Soft Switched Forward Converter Using Intelligent Controller 129 Change Detection Across Geographical System of using
IJCTA, 9(40), 2016, pp. 129-139 International Science Press Closed Loop Control of Soft Switched Forward Converter Using Intelligent Controller 129 Change Detection Across Geographical System of using
Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
The Road to Data in Baltimore
 Creating a parcel level database from high resolution imagery By Austin Troy and Weiqi Zhou University of Vermont, Rubenstein School of Natural Resources State and local planning agencies are increasingly
Creating a parcel level database from high resolution imagery By Austin Troy and Weiqi Zhou University of Vermont, Rubenstein School of Natural Resources State and local planning agencies are increasingly
1. Introduction. S.S. Patil 1, Sachidananda 1, U.B. Angadi 2, and D.K. Prabhuraj 3
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 525-531, Article ID Tech-249 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Machine Learning Technique
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 525-531, Article ID Tech-249 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Machine Learning Technique
Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015)
 Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) Extracting Land Cover Change Information by using Raster Image and Vector Data Synergy Processing Methods Tao
Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) Extracting Land Cover Change Information by using Raster Image and Vector Data Synergy Processing Methods Tao
Accuracy analysis of remote sensing change detection by rule-based rationality evaluation with post-classification comparison
 INT. J. REMOTE SENSING, 10MARCH, 2004, VOL. 25, NO. 5, 1037 1050 Accuracy analysis of remote sensing change detection by rule-based rationality evaluation with post-classification comparison H. LIU Department
INT. J. REMOTE SENSING, 10MARCH, 2004, VOL. 25, NO. 5, 1037 1050 Accuracy analysis of remote sensing change detection by rule-based rationality evaluation with post-classification comparison H. LIU Department
LANDSCAPE PATTERN AND PER-PIXEL CLASSIFICATION PROBABILITIES. Scott W. Mitchell,
 LANDSCAPE PATTERN AND PER-PIXEL CLASSIFICATION PROBABILITIES Scott W. Mitchell, Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Carleton University, Loeb Building B349, 1125 Colonel By Drive, Ottawa,
LANDSCAPE PATTERN AND PER-PIXEL CLASSIFICATION PROBABILITIES Scott W. Mitchell, Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Carleton University, Loeb Building B349, 1125 Colonel By Drive, Ottawa,
DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF LAND-USE/LAND-COVER CHANGES IN NAY PYI TAW, MYANMAR USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING IMAGES
 DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF LAND-USE/LAND-COVER CHANGES IN NAY PYI TAW, MYANMAR USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING IMAGES Kay Khaing Oo 1, Eiji Nawata 1, Kiyoshi Torii 2 and Ke-Sheng Cheng 3 1 Division of Environmental
DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF LAND-USE/LAND-COVER CHANGES IN NAY PYI TAW, MYANMAR USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING IMAGES Kay Khaing Oo 1, Eiji Nawata 1, Kiyoshi Torii 2 and Ke-Sheng Cheng 3 1 Division of Environmental
CHAPTER 2 REMOTE SENSING IN URBAN SPRAWL ANALYSIS
 9 CHAPTER 2 REMOTE SENSING IN URBAN SPRAWL ANALYSIS 2.1. REMOTE SENSING Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually being in contact with it. This
9 CHAPTER 2 REMOTE SENSING IN URBAN SPRAWL ANALYSIS 2.1. REMOTE SENSING Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually being in contact with it. This
The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural production
 The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural production Artur Łączyński Central Statistical Office, Agriculture Department Niepodległości 208 Warsaw, Poland E-mail a.laczynski@stat.gov.pl DOI:
The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural production Artur Łączyński Central Statistical Office, Agriculture Department Niepodległości 208 Warsaw, Poland E-mail a.laczynski@stat.gov.pl DOI:
Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery
 Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery Deanne Rogers*, Katherine Schwarting, and Gilbert Hanson Dept. of Geosciences, Stony Brook University,
Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery Deanne Rogers*, Katherine Schwarting, and Gilbert Hanson Dept. of Geosciences, Stony Brook University,
USING LANDSAT IN A GIS WORLD
 USING LANDSAT IN A GIS WORLD RACHEL MK HEADLEY; PHD, PMP STEM LIAISON, ACADEMIC AFFAIRS BLACK HILLS STATE UNIVERSITY This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under
USING LANDSAT IN A GIS WORLD RACHEL MK HEADLEY; PHD, PMP STEM LIAISON, ACADEMIC AFFAIRS BLACK HILLS STATE UNIVERSITY This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 1, 2013
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 1, 2013 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-temporal analysis of land
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 1, 2013 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-temporal analysis of land
West meets East: Monitoring and modeling urbanization in China Land Cover-Land Use Change Program Science Team Meeting April 3, 2012
 West meets East: Monitoring and modeling urbanization in China Land Cover-Land Use Change Program Science Team Meeting April 3, 2012 Annemarie Schneider Center for Sustainability and the Global Environment,
West meets East: Monitoring and modeling urbanization in China Land Cover-Land Use Change Program Science Team Meeting April 3, 2012 Annemarie Schneider Center for Sustainability and the Global Environment,
The Effects of Haze on the Accuracy of. Satellite Land Cover Classification
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 215, no. 49, 2433-2443 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.215.52157 The Effects of Haze on the Accuracy of Satellite Land Cover ification
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 215, no. 49, 2433-2443 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.215.52157 The Effects of Haze on the Accuracy of Satellite Land Cover ification
