The return of geopolitics was more prominent outside departments of geography and took a clear conservative hue. US foreign policy officials and the
|
|
|
- Kelley Anthony
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GEOPOLITICS The study of the geographical factors in world politics and inter-state relations. The term is also used more generally to describe regional strategic relations, as in the geopolitics of the South China Sea. In the present day it covers much the same ground as International Relations, although with greater emphasis on geographical factors such as location, resources, and accessibility. Within this broad definition, there are many variants and the differences between them are significant. In part, these stem from the chequered history of the term geopolitics, which fell from favor across much of the Anglo-American world after the 1940s. Its original or traditional form arose towards the end of the 19th century. This imperial geopolitics can be thought of as the application of Social Darwinism to the state. Combining ideas of permanent national rivalry, the need for state expansion, environmental determinism, and racist ideas about civilizations, this geopolitics was consciously directed towards informing and aiding statecraft among the European imperial powers, as well as the USA. Admiral Alfred Thayer Mahan ( ) for example, warned the US government about the need to restore naval power in order to secure US trade interests. His ideas on sea power were adapted by Halford Mackinder, whose Heartland concept is regarded as the exemplar of this style of reasoning. Inspired by Friedrich Raztel and the Swedish geographer Rudolph Kjellén ( ) who coined the term geopolitics a school of geopolitik formed in Germany in the 1920s. Because of its close links with the subsequent Nazi regime, American and other geographers repudiated the term geopolitics, dismissing it as a pseudo-science of racism and crude environmental determinism. Although geographers such as Isaiah Bowman also addressed strategic relations at the world scale they generally described their work as political geography. A recognizable version of geopolitik did, however, thrive among military academies and military dictatorships in South America well into the 1970s. Those scholars who continued to develop and adapt Mackinder s ideas to the Cold War situation, notably Nicholas Spykman and later Saul Cohen, emphasized spatial themes rather than environmental or racial ones (see geostrategic region). But within academic geography in general, geopolitics had become a dirty word.
2 The return of geopolitics was more prominent outside departments of geography and took a clear conservative hue. US foreign policy officials and the intellectuals who sought to influence it, recycled and updated many of the ideas of imperial geopolitics from the 1970s onwards (see Clash of Civilizations; Pax Americana). Among geographers, there were two main responses. On the one hand, some argued for a restored geopolitics stripped of its imperial trappings and more attentive to the changing relations between geopolitical and geoeconomic relations in an era of globalization. In particular, this line of research recognized non-state political actors, including social movements and terrorist networks, and new issues such as global environmental change and the global media. A related but distinct response was the formation of critical geopolitics, which drew more on post-structuralist concepts of discourse and representation to interrogate the texts (e.g. speeches, newsreel, policy documents) of politicians and state-centered foreign policy. There are also a number of other strands in current geopolitics. Jennifer Hyndman outlined a feminist geopolitics, informed by feminist geographical ideas and focused beyond the scale of the state to consider the politics of social justice, harm, sexual violence, and the public/private divide (see fear). Popular geopolitics examines how political geographical ideas circulate through film, television, cartoons, and magazines. Anti-geopolitics describes the challenges to state-centered geopolitics from within civil society, including dissidents, social movements, and allied forms of resistance. Its aim is to oppose the idea that the interests of the state and its political allies are the same as the interests of communities. Gerry Kearns uses the term progressive geopolitics to refer to the ideas and practices in opposition to conservative geopolitics. It has more faith in international law and cosmopolitan ideals as ways of regulating the relations between states and people so as to avoid conflict. Castree, N., Kitchin, R., & Rogers, A. (2013). "Geopolitics." In A Dictionary of Human Geography. : Oxford University Press. Retrieved 14 Mar. 2017
3 Geopolitics What is "geopolitics"? More on Geopolitics Debate on the term Geopolitics The term geopolitics reflects the connection between power and interests, strategic decision-making, and geographic space. The contemporary use of the term deviates radically from its origin in the late 19th century. Originally "geopolitics" reflected an understanding of international affairs strongly influenced by Social Darwinism. It also signaled a cynical realist view of international affairs, with limited belief in the significance of multilateralism, global norms or international law. As used in this program, "geopolitics" denotes the interplay of natural resources, strategic dominance and geographic space on the one hand, and the various state and non-state actors pursuing individual as well as collective interests on the other. However, linkage to earlier usage of the term is not entirely broken. The growing use of the term in the public sphere signals a need for a term that reflects the renaissance of great power rivalry and the rise of multi-polarity in the early 21st century. The Reemergence of Geopolitics Geopolitics relates political power to geographical space. The word was coined by the Swedish political scientist Rudolph Kjellén at the dawn of the 19th century, epitomizing an organic conception of great power rivalry and expansion. While early Anglo-American geopolitical debate concerned the relative importance of land power and sea power, German discourse centered on interstate rivalry in continental space. The prominent geopolitician Halford Mackinder saw the end of European expansion overseas in the early 20th century. He termed this era the Columbian epoch and heralded a closed geopolitical system as expansion came to an end. Great power rivalry would now intensify, with the Heartland theory as a major perspective on global politics. The Heartland theory said that core of Eurasia was the key to world
4 dominance. The Molotov-Ribbentrop pact some decades later was a political manifestation of the strategic implications of this theory. In retrospect, Mackinder underestimated the long-term capabilities of offshore sea powers like the United States, as he underestimated how technological advances like submarines and intercontinental missiles could bolster the might of marine based powers. Military technology, certainly, goes into the geopolitical equation, but Mackinder and the heartland theorists had a rather static view of the importance of the steam engine and the railroad which had opened up Eurasia. The Western strategy of the Cold War was a rim land strategy for containment of the USSR by a string of military alliances around the Eurasian Soviet core ranging from NATO in the European north-west, CENTO in the Middle-East, SEATO in South-east Asia and ANZUS in the Pacific. Cold War strategies were modeled on classical geopolitical thought. The Columbian epoch was gradually brought to an end with the process of decolonization. A Post-Columbian era slowly emerged, half a century after Mackinder`s pioneering analysis. The voluntary dissolution of the USSR at Christmas Day 1991 seems like a spectacular negation the the Heartland theory. The political tenant to the Eurasian Core Area ended its ambitions for becoming a global hegemon. The Russian successor state was radically disadvantaged in terms of space and power to proceed with this ambition. On the other hand, Russia may launch new power projections towards the Arctic, due to oil and gas deposits in more accessible waters as the ice recedes. Eastern Eurasia, accordingly, is emerging as a geopolitical stronghold with the rise of China. The Heartland will remain geopolitically significant, but a unified power is less likely. The center of gravity in geopolitical terms is moving towards the North and the East. The geopolitical analysis of the dynamics of the High North should be precise and specific on the implications of these shifting coordinates. Geopolitical analysis has changed during the 20th century, no longer being tied up with fin-de-siècle social Darwinism, and also with perspectives on power and space at different orders of scale, from the global down to the local level. The Arctic is of medium-sized order with a typically circumpolar character spanning the rim lands of three continents and numerous states. The resources, transport routes and strategic importance of this circumpolar area are the geopolitical foci of analysis. More narrow
5 sections of this circumpolar area may certainly be blown up without losing the geopolitical point of view. Globalization and geopolitics are contrasting images of global developments after the end of the Cold War. While globalization indicates interdependence, transnational flows and obliterated state frontiers, geopolitics conjures great power games and power politics. The balance has tilted in favor of geopolitics with the rise of China and India, the reassertion of Russia, and the repercussions of 9/11. This balance does not only change over time. It also works out differently in various parts of the world. Again, the Arctic is a field of tension between contradictory force. In search of conceptual clarity by Michael Mayer In a 1964 US Supreme Court decision, Justice Potter Stewart argued that pornography was difficult to define, but he claimed: I know it when I see it. If only geopolitics were so simple. The concept of pornography has remained quite stable; its definition has become a matter of establishing social and legal boundaries. Unfortunately, the fundamental conceptualization of geopolitics has been constantly under revision, making the term so versatile that it nearly inverts Steward s definition: I see it, therefore I know it. Geopolitics is reemerging everywhere without a clear and commonly agreed upon idea of what the term implies. One region that most would agree clearly exhibits geopolitical tensions is Central Asia, though one could find wildly different reasoning behind such a claim. Some might argue, as Rudolph Kjellén would, that Russia and China are expanding into the region and attempting to absorb weaker states like a biological organism. Followers of Halford Mackinder would see continued competition over part of the Heartland. Henry Kissinger defined geopolitics as an approach that focused on finding equilibrium: Russia, China, India and the United States must therefore be acting to balance each other in the region. Thomas P.M Barnett recently drew the Pentagon s New Map of strategic interests, what the US has called the arc of instability : Central Asia features prominently. Finally, Colin Gray takes the broadest view by claiming that all politics is in fact geopolitics because politics always occurs within a particular geographical context.
6 How can one then meaningfully speak of geopolitics in a region? Despite historical references to Kjellén, Mackinder and Kissinger, common usage of the term geopolitics seem to be purely descriptive in nature. Østerud defines it as relating political power to geographical space, a concise definition that captures the term s essence but not its complexity. Much of the conceptual contents of geopolitics remains implicit and therefore in need of unpacking. More than the relationship between power politics and geography, the term (as commonly used) incorporates a number of underlying assumptions: states are the primary actors in the system, a military-economic competition exists between them for the raw materials needed for national power, that states and alliances are able to balance one another either through physical occupation or by securing political influence within a geographical space, and that geography represents perhaps the greatest determinant of political relationships. Strategy is crucial. The political significance of geography is directly related to, if not defined by, its strategic importance. Some analysts therefore refer instead to geostrategy. During the Cold War, a strategy of containing the Soviet Union combined with geopolitical assumptions of falling dominoes led American political leaders to regard Southeast Asia as geopolitically decisive the region s importance without the marriage of those two concepts would have been minimal. The geopolitical relevance of the Arctic will be determined by states perceptions of their strategic interests rather than the innate qualities of the region. Few discuss the geopolitics of the North Sea despite its resources or the English Channel despite the narrow choke point through which much shipping must pass. Geographic entities must be strategically contested to have geopolitical relevance. While the Arctic countries may, as Osterud claims, view the geopolitical center of gravity as shifting north and east, they must be aware that the rest of the world increasingly focuses south and east. The Arctic remains a promise of future resource riches and transport corridors. Russia, economically and demographically weakened, appears just as engaged with European relations, military forays in the Caucasus, and securing gas supplies from Central Asia. Other military-economic powers the United States, India and China seem more concerned with emerging markets in South America and Africa, not to mention emerging power relationships and tensions in the Middle East and South Asia. The economic aspects of national power are the principle drivers of these developments, as a subset of each actor s broader political and strategic interests.
7 In this regard, the dichotomy between globalization and geopolitics is a false one. The militaryeconomic competition that inspires geopolitical reasoning necessarily incorporates the processes of globalization. This is part of the playing field on which states and non-state actors compete. States are forced to take these trends into consideration, and in many cases use them for strategic gain. In many of today s bilateral strategic relationships, non-state globalization processes, state corporations and national economic policies interact in complex ways. States both shape the relationships through these processes and are also shaped by them. This is how Mackinder re-enters the picture. His heartland theory posited that controlling Eurasia was the source of world power because rail networks allowed for the efficient extraction of the region s raw materials while shielded from adversarial maritime powers ( would permit the use of vast continental resources for fleet-building, and the empire of the world would then be in sight ). It was not Eurasia per se, but its strategic resources and the geographic advantages it afforded. Over a century later, the sources of material power have shifted, as have the means of extracting them. The Mackinder of today should look to the current sources of national power: demographics, economic strength, technological advantages, state structures that allow for the efficient wielding of national power (including military power), and so on. As is the case with many historical texts, the reasoning remains relevant but must be reapplied to the features of the current strategic environment. Tomorrow s Heartland may lie in the Arctic, South Asia, Africa or even in outer space.
NATIONAL RESEARCH UNIVERSITY HIGHER SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY
 NATIONAL RESEARCH UNIVERSITY HIGHER SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Course syllabus HSE and UoL Parallel-degree Programme International Relations Lecturer and Class Teacher: Dr. Andrei Skriba Course
NATIONAL RESEARCH UNIVERSITY HIGHER SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Course syllabus HSE and UoL Parallel-degree Programme International Relations Lecturer and Class Teacher: Dr. Andrei Skriba Course
CONTENTS. Acknowledgements... i-ii Contents... iii-viii List of Tables, Maps, Graphs & Figures... ix-x Abbreviations... xi-xiii Preface...
 CONTENTS Acknowledgements... i-ii Contents... iii-viii List of Tables, Maps, Graphs & Figures... ix-x Abbreviations... xi-xiii Preface... xiv-xvi CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... l-40 1.1 Background... 1-4 1.2
CONTENTS Acknowledgements... i-ii Contents... iii-viii List of Tables, Maps, Graphs & Figures... ix-x Abbreviations... xi-xiii Preface... xiv-xvi CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... l-40 1.1 Background... 1-4 1.2
Iceland and the Arctic: The Politics of Territoriality. Valur Ingimundaron Professor of Contemporary History, University of Iceland
 Iceland and the Arctic: The Politics of Territoriality Valur Ingimundaron Professor of Contemporary History, University of Iceland Drivers of Icelandic Arctic Policies Geostrategic Position Economic Interests
Iceland and the Arctic: The Politics of Territoriality Valur Ingimundaron Professor of Contemporary History, University of Iceland Drivers of Icelandic Arctic Policies Geostrategic Position Economic Interests
Third Annual Climate Science and Policy Conference, UC Santa Cruz: Earth s Climate Future: Unchartered Territory
 Third Annual Climate Science and Policy Conference, UC Santa Cruz: Earth s Climate Future: Unchartered Territory Geopolitics of Climate Change: The Arctic Case Steven L. Lamy, PhD Vice Dean for Academic
Third Annual Climate Science and Policy Conference, UC Santa Cruz: Earth s Climate Future: Unchartered Territory Geopolitics of Climate Change: The Arctic Case Steven L. Lamy, PhD Vice Dean for Academic
Dr. Steven Lamy Sophie Cottle
 Dr. Steven Lamy Sophie Cottle The Circumpolar North has begun to acquire an identity of its own in the minds of policymakers and scholars alike. Yet this region cannot be understood properly as a cockpit
Dr. Steven Lamy Sophie Cottle The Circumpolar North has begun to acquire an identity of its own in the minds of policymakers and scholars alike. Yet this region cannot be understood properly as a cockpit
PENNSYLVANIA ACADEMIC STANDARDS
 PENNSYLVANIA ACADEMIC STANDARDS ARTS AND HUMANITIES 9.2 Historical and Cultural Contexts A. Explain historical, cultural and social context of an individual work in the arts B. Relate works in the arts
PENNSYLVANIA ACADEMIC STANDARDS ARTS AND HUMANITIES 9.2 Historical and Cultural Contexts A. Explain historical, cultural and social context of an individual work in the arts B. Relate works in the arts
Geopolitics - Exam Notes
 1 Geopolitics - Exam Notes Definitions Gottman defines geopolitics as the influence of geographical factors on political action Physical geography: relates to the surface of the earth Cultural geography:
1 Geopolitics - Exam Notes Definitions Gottman defines geopolitics as the influence of geographical factors on political action Physical geography: relates to the surface of the earth Cultural geography:
Global Studies A and B Mr. Lord
 1. ARRIVE ON TIME. Global Studies A and B Mr. Lord michael.lord@orecity.k12.or.us Global Studies A and B Classroom Rules and Grading Expectations 2. BE PREPARED BOTH MENTALLY AND PHYSICALLY FOR CLASS.
1. ARRIVE ON TIME. Global Studies A and B Mr. Lord michael.lord@orecity.k12.or.us Global Studies A and B Classroom Rules and Grading Expectations 2. BE PREPARED BOTH MENTALLY AND PHYSICALLY FOR CLASS.
SOCIAL SCIENCES. WORLD GEOGRAPHY LH Grade(s): 9 Pre-Req: N/A
 SOCIAL SCIENCES WORLD GEOGRAPHY 21033000 Grade(s): 9 The World Cultural Geography course consists of the following content area strands: American History, World History, Geography, Humanities, Civics and
SOCIAL SCIENCES WORLD GEOGRAPHY 21033000 Grade(s): 9 The World Cultural Geography course consists of the following content area strands: American History, World History, Geography, Humanities, Civics and
A Cold War Map and Image Gallery
 A Cold War Map and Image Gallery Visualizing Global Geopolitics Presented by The California Geographic Alliance and The San Diego State University Geography Department This handout provides information
A Cold War Map and Image Gallery Visualizing Global Geopolitics Presented by The California Geographic Alliance and The San Diego State University Geography Department This handout provides information
GE 331: Political Geography Spring Office Hours: Tuesday, Thursday 11-12:30; Wednesday 1-2 Phone:
 GE 331: Political Geography Spring 2007 Instructor: Professor Bill Anderson Office: CAS 439f Office Hours: Tuesday, Thursday 11-12:30; Wednesday 1-2 Phone: 358-0208 email: bander@bu.edu Lectures: Tuesday,
GE 331: Political Geography Spring 2007 Instructor: Professor Bill Anderson Office: CAS 439f Office Hours: Tuesday, Thursday 11-12:30; Wednesday 1-2 Phone: 358-0208 email: bander@bu.edu Lectures: Tuesday,
The study of Geography and the use of geographic tools help us view the world in new ways.
 S How does Geography help us understand our world? What factors shape the Earth s different environments? 7.1.9 7.2.9 BIG IDEAS COMPETENCIES Text pages or The study of Geography and the use of geographic
S How does Geography help us understand our world? What factors shape the Earth s different environments? 7.1.9 7.2.9 BIG IDEAS COMPETENCIES Text pages or The study of Geography and the use of geographic
Social Studies Framework K-12 ( ) 1
 RIVERVIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT NO. 407 STRAND CIVICS (GOVERNMENT) ECONOMICS HISTORY GEOGRAPHY Grade K Me & My Community Working together Purpose of rules Being a community contributor Compare/contrast needs
RIVERVIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT NO. 407 STRAND CIVICS (GOVERNMENT) ECONOMICS HISTORY GEOGRAPHY Grade K Me & My Community Working together Purpose of rules Being a community contributor Compare/contrast needs
Central Valley School District Social Studies Curriculum Map Grade 7. August - September
 August - September Geographical/Historical Skills Identify and analyze timelines. Construct and use cause and effect charts. Differentiate between fact and opinion. Use of word webs, flip charts, outlines
August - September Geographical/Historical Skills Identify and analyze timelines. Construct and use cause and effect charts. Differentiate between fact and opinion. Use of word webs, flip charts, outlines
LEARNING OUTCOMES SST (G1-G12)
 LEARNING OUTCOMES SST (G1-G12) Grade 1 Learning Outcomes Students will be expected to: - demonstrate an understanding of the importance of interactions between people - demonstrate an understanding of
LEARNING OUTCOMES SST (G1-G12) Grade 1 Learning Outcomes Students will be expected to: - demonstrate an understanding of the importance of interactions between people - demonstrate an understanding of
ILLINOIS CERTIFICATION TESTING SYSTEM
 ILLINOIS CERTIFICATION TESTING SYSTEM FIELD 113 SOCIAL SCIENCE: GEOGRAPHY November 2003 Illinois Certification Testing System FIELD 113 SOCIAL SCIENCE: GEOGRAPHY November 2003 Subarea Range of Objectives
ILLINOIS CERTIFICATION TESTING SYSTEM FIELD 113 SOCIAL SCIENCE: GEOGRAPHY November 2003 Illinois Certification Testing System FIELD 113 SOCIAL SCIENCE: GEOGRAPHY November 2003 Subarea Range of Objectives
Social Studies Continuum
 Historical Skills chronological thinking understand that we can learn about the past from different sorts of evidence begin to use historical resources apply research skills by investigating a topic in
Historical Skills chronological thinking understand that we can learn about the past from different sorts of evidence begin to use historical resources apply research skills by investigating a topic in
GRADE 8 LEAP SOCIAL STUDIES ASSESSMENT STRUCTURE. Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment Structure
 Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment Structure 1 In 2013-2014, the grade 8 LEAP test continues to assess Louisiana s social studies benchmarks. The design of the multiple-choice sessions of the test remains
Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment Structure 1 In 2013-2014, the grade 8 LEAP test continues to assess Louisiana s social studies benchmarks. The design of the multiple-choice sessions of the test remains
MILITARY ASPECTS OF MONGOLIAN GEOPOLITICS
 ARTICLES MILITARY ASPECTS OF MONGOLIAN GEOPOLITICS R.Bold* Three big events have taken place in Mongolia during the last 4 years which are now determining new directions in the na-tional defense policy.
ARTICLES MILITARY ASPECTS OF MONGOLIAN GEOPOLITICS R.Bold* Three big events have taken place in Mongolia during the last 4 years which are now determining new directions in the na-tional defense policy.
Delta School District 1
 Delta School District Social Studies Curriculum Scope and Sequence K-12 GLE Principles of Constitutional Democracy K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9-12 1. Knowledge of the principles expressed in documents shaping constitutional
Delta School District Social Studies Curriculum Scope and Sequence K-12 GLE Principles of Constitutional Democracy K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9-12 1. Knowledge of the principles expressed in documents shaping constitutional
Policy framework The Netherlands and the Polar Regions, Summary and priorities
 Policy framework The Netherlands and the Polar Regions, 2011-2015 Summary and priorities The policy outlined in this Policy Framework for the Polar Regions (2011-2015) is part of the government s orientation
Policy framework The Netherlands and the Polar Regions, 2011-2015 Summary and priorities The policy outlined in this Policy Framework for the Polar Regions (2011-2015) is part of the government s orientation
Stillwater Area Schools Curriculum Guide for Elementary Social Studies
 Stillwater Area Schools Curriculum Guide for Elementary Social Studies Grade Four Draft March 21, 2006 Minnesota and the St. Croix Valley I. Historical Skills A. The student will acquire skills of chronological
Stillwater Area Schools Curriculum Guide for Elementary Social Studies Grade Four Draft March 21, 2006 Minnesota and the St. Croix Valley I. Historical Skills A. The student will acquire skills of chronological
Prentice Hall World Cultures: A Global Mosaic 2004 Correlated to: Wisconsin Model Academic Standards for Social Studies (By the end of Grade 12)
 Wisconsin Model Academic Standards for Social Studies (By the end of Grade 12) A. Geography: People, Places, and Environments A.12.1 Use various types of atlases and appropriate vocabulary to describe
Wisconsin Model Academic Standards for Social Studies (By the end of Grade 12) A. Geography: People, Places, and Environments A.12.1 Use various types of atlases and appropriate vocabulary to describe
Economic Interests, Environmental Concerns, and Multilateral Governance The German Approach to the Arctic
 Economic Interests, Environmental Concerns, and Multilateral Governance The German Approach to the Arctic Dr. Markus Kaim German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Berlin Carleton University,
Economic Interests, Environmental Concerns, and Multilateral Governance The German Approach to the Arctic Dr. Markus Kaim German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Berlin Carleton University,
LOUISIANA STUDENT STANDARDS FOR SOCIAL STUDIES THAT CORRELATE WITH A FIELD TRIP TO DESTREHAN PLANTATION KINDERGARTEN
 LOUISIANA STUDENT STANDARDS FOR SOCIAL STUDIES THAT CORRELATE WITH A FIELD TRIP TO DESTREHAN PLANTATION KINDERGARTEN Standard 2 Historical Thinking Skills Students distinguish between events, people, and
LOUISIANA STUDENT STANDARDS FOR SOCIAL STUDIES THAT CORRELATE WITH A FIELD TRIP TO DESTREHAN PLANTATION KINDERGARTEN Standard 2 Historical Thinking Skills Students distinguish between events, people, and
End of Geopolitics and the Beginnings of Geopolinomics: United States in Central and Southwest Asia
 End of Geopolitics and the Beginnings of Geopolinomics: United States in Central and Southwest Asia By Aftab Kazi, PhD (Pittsburgh), Senior Fellow Central Asia-Caucasus Institute & Silk Road Studies Program
End of Geopolitics and the Beginnings of Geopolinomics: United States in Central and Southwest Asia By Aftab Kazi, PhD (Pittsburgh), Senior Fellow Central Asia-Caucasus Institute & Silk Road Studies Program
The following objectives were taken from the K-12 Skills Competency Goals
 Seventh Grade Social Studies Crosswalk World Geography, History and Culture: Patterns of Continuity and Change The Great Global Convergence (1400-1800) to the Present - Represents the last five Eras of
Seventh Grade Social Studies Crosswalk World Geography, History and Culture: Patterns of Continuity and Change The Great Global Convergence (1400-1800) to the Present - Represents the last five Eras of
A Correlation of. Eastern Hemisphere. Ohio s Learning Standards Social Studies: K-12 Grade 6
 A Correlation of Eastern Hemisphere To Grade 6 to,, Grade 6 Introduction This document demonstrates how, Eastern Hemisphere, Ohio Edition, meets : K-12 Social Studies for Grade 6. Correlation page references
A Correlation of Eastern Hemisphere To Grade 6 to,, Grade 6 Introduction This document demonstrates how, Eastern Hemisphere, Ohio Edition, meets : K-12 Social Studies for Grade 6. Correlation page references
A Correlation of Prentice Hall World History The Modern Era 2014
 A Correlation of Prentice Hall World History The Modern Era 2014 To the College, Career, & Civic Life (C3) Framework for Social Studies State Standards Dimension 2 Disciplinary Indicators Introduction
A Correlation of Prentice Hall World History The Modern Era 2014 To the College, Career, & Civic Life (C3) Framework for Social Studies State Standards Dimension 2 Disciplinary Indicators Introduction
Investigaciones Regionales ISSN: Asociación Española de Ciencia Regional España
 Investigaciones Regionales ISSN: 1695-7253 investig.regionales@uah.es Asociación Española de Ciencia Regional España Bailey, David Reseña de "Handbook of Industrial Districts" de Giacomo Becattini, Marco
Investigaciones Regionales ISSN: 1695-7253 investig.regionales@uah.es Asociación Española de Ciencia Regional España Bailey, David Reseña de "Handbook of Industrial Districts" de Giacomo Becattini, Marco
Centre for International Politics, Organization and Disarmament School of International Studies Jawaharlal Nehru University
 Centre for International Politics, Organization and Disarmament School of International Studies Jawaharlal Nehru University Programme- M.Phil Course Title- CONCEPTS AND ISSUES IN GEOPOLITICS Semester-
Centre for International Politics, Organization and Disarmament School of International Studies Jawaharlal Nehru University Programme- M.Phil Course Title- CONCEPTS AND ISSUES IN GEOPOLITICS Semester-
Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural
 SS6G10 Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural resources of Germany, the United Kingdom and
SS6G10 Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural resources of Germany, the United Kingdom and
I CAN STATEMENTS 6TH GRADE SOCIAL STUDIES
 6TH GRADE SOCIAL STUDIES I can compare historical issues involving rights, roles and statues of individuals. I can describe the relationships among specialization, division of labor, productivity of workers
6TH GRADE SOCIAL STUDIES I can compare historical issues involving rights, roles and statues of individuals. I can describe the relationships among specialization, division of labor, productivity of workers
Norwich City Schools Social Studies 6
 Social Studies 6 Topic: Maps and Globes and Graphs and Time Transferable Concepts: change 3: Geography Geography Geographers use maps, globes, and graphs to study the Earth and everything on it. Types
Social Studies 6 Topic: Maps and Globes and Graphs and Time Transferable Concepts: change 3: Geography Geography Geographers use maps, globes, and graphs to study the Earth and everything on it. Types
Human Geography: Places and Regions in Global Context Sixth Edition. Political Geographies. Chapter 9 Lecture
 Chapter 9 Lecture Human Geography: Places and Regions in Global Context Sixth Edition Political Geographies Wendy A. Mitteager State University of New York, Oneonta Key Concepts Geopolitics Territories
Chapter 9 Lecture Human Geography: Places and Regions in Global Context Sixth Edition Political Geographies Wendy A. Mitteager State University of New York, Oneonta Key Concepts Geopolitics Territories
REGIONAL SDI DEVELOPMENT
 REGIONAL SDI DEVELOPMENT Abbas Rajabifard 1 and Ian P. Williamson 2 1 Deputy Director and Senior Research Fellow Email: abbas.r@unimelb.edu.au 2 Director, Professor of Surveying and Land Information, Email:
REGIONAL SDI DEVELOPMENT Abbas Rajabifard 1 and Ian P. Williamson 2 1 Deputy Director and Senior Research Fellow Email: abbas.r@unimelb.edu.au 2 Director, Professor of Surveying and Land Information, Email:
Will Russia and China Jointly Deter the United States? Nikita Perfilyev PhD Candidate, University of Vienna
 Will Russia and China Jointly Deter the United States? Nikita Perfilyev PhD Candidate, University of Vienna Nuclear Deterrence Relations } Traditionally dyads } Emphasis on US-Russian, US-Chinese nuclear
Will Russia and China Jointly Deter the United States? Nikita Perfilyev PhD Candidate, University of Vienna Nuclear Deterrence Relations } Traditionally dyads } Emphasis on US-Russian, US-Chinese nuclear
Strand 1: Principles of Constitutional Democracy. Strand 2: Principles and Processes of Governance Systems
 Social Studies GLE S - Grade 4 Strand 1: Principles of Constitutional Democracy 1. Knowledge of the principles expressed in documents shaping constitutional democracy in the United States A. Knowledge
Social Studies GLE S - Grade 4 Strand 1: Principles of Constitutional Democracy 1. Knowledge of the principles expressed in documents shaping constitutional democracy in the United States A. Knowledge
Social Studies Curriculum Sixth Grade
 Social Studies Curriculum Sixth Grade A. History Students will examine the key historic movements, events, and figures that contributed to the development of modern Europe and American nations from early
Social Studies Curriculum Sixth Grade A. History Students will examine the key historic movements, events, and figures that contributed to the development of modern Europe and American nations from early
Chapter 8. Political Geography
 Chapter 8 Political Geography Nations of the World Today human geographers emphasize a thematic approach, concerned with the location of activities in the world, the reasons for particular spatial distributions,
Chapter 8 Political Geography Nations of the World Today human geographers emphasize a thematic approach, concerned with the location of activities in the world, the reasons for particular spatial distributions,
Korea's Nord Politics and New Direction of Geography Education in Korea
 Korea's Nord Politics and New Direction of Geography Education in Korea Ki-Suk Lee Seoul National University The recent geography education at level of middle and high school in Korea is facing two inevitable
Korea's Nord Politics and New Direction of Geography Education in Korea Ki-Suk Lee Seoul National University The recent geography education at level of middle and high school in Korea is facing two inevitable
MINORITY CULTURES IN CATALAN CULTURE
 MINORITY CULTURES IN SPAIN. CATALONIA AND THE CATALAN CULTURE Dr. Joan Tort Oulun Yliopisto, Suomi/Finland 24th April, 2008 Key words: Catalonia/Spain/Europe Old Europe Territorial i identities Managing
MINORITY CULTURES IN SPAIN. CATALONIA AND THE CATALAN CULTURE Dr. Joan Tort Oulun Yliopisto, Suomi/Finland 24th April, 2008 Key words: Catalonia/Spain/Europe Old Europe Territorial i identities Managing
OIB GEOGRAPHY SYLLABUS. Theme
 OIB GEOGRAPHY SYLLABUS Summary of Themes Theme 1) Different views and interpretations of world organisation through the study of maps focusing on issues of globalisation and development; to include a critical
OIB GEOGRAPHY SYLLABUS Summary of Themes Theme 1) Different views and interpretations of world organisation through the study of maps focusing on issues of globalisation and development; to include a critical
Paasi, Anssi: Review on Monmonier, M: No dig, no fly, no go: how maps restrict and
 Paasi, Anssi: Review on Monmonier, M: No dig, no fly, no go: how maps restrict and control. Progress in Human Geography 36:2 (2012), pp. 282-289. Mark Monmonier, a distinguished professor of geography
Paasi, Anssi: Review on Monmonier, M: No dig, no fly, no go: how maps restrict and control. Progress in Human Geography 36:2 (2012), pp. 282-289. Mark Monmonier, a distinguished professor of geography
CONNECTED WORLDS: THE CARIBBEAN, ORIGIN OF MODERN WORLD (CONNECCARIBBEAN )
 CONNECTED WORLDS: THE CARIBBEAN, ORIGIN OF MODERN WORLD (CONNECCARIBBEAN-823846) This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie
CONNECTED WORLDS: THE CARIBBEAN, ORIGIN OF MODERN WORLD (CONNECCARIBBEAN-823846) This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie
PROGRAM OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION CHAIRMANSHIP OF THE ARCTIC COUNCIL IN
 PROGRAM OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION CHAIRMANSHIP OF THE ARCTIC COUNCIL IN 2004-2006 The Arctic Council is a unique forum for interaction between the governments of the Arctic States, the Permanent Participants
PROGRAM OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION CHAIRMANSHIP OF THE ARCTIC COUNCIL IN 2004-2006 The Arctic Council is a unique forum for interaction between the governments of the Arctic States, the Permanent Participants
Chapter-Two Geopolitics: A Conceptual Analysis
 Chapter-Two Geopolitics: A Conceptual Analysis Foreign policy behaviour of nation-states is always shaped by the domestic and external settings and is designed to serve their national interests. It can
Chapter-Two Geopolitics: A Conceptual Analysis Foreign policy behaviour of nation-states is always shaped by the domestic and external settings and is designed to serve their national interests. It can
CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE
 CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE Course Name(s): World Area Studies Grade(s): 9-11 Department: Social Studies Course Length: 1 Semester Pre-requisite: None Textbook/Key Resource: No Primary Textbook Course Description:
CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE Course Name(s): World Area Studies Grade(s): 9-11 Department: Social Studies Course Length: 1 Semester Pre-requisite: None Textbook/Key Resource: No Primary Textbook Course Description:
September 14, 2013 Objective: How does geography impact history? What important features exist that have shaped societies?
 Lowenhaupt 1 September 14, 2013 Objective: How does geography impact history? What important features exist that have shaped societies? Warm-Up: In your binder, answer the following question: Imagine you
Lowenhaupt 1 September 14, 2013 Objective: How does geography impact history? What important features exist that have shaped societies? Warm-Up: In your binder, answer the following question: Imagine you
Blooms: Knowledge Learning Objective: Understand how states and nations are organized.
 Human Geography, 11 th edition Practice Questions Chapter 08 1. Geographers define as the study of the political organization of the world. A. the United Nations B. political science C. political economy
Human Geography, 11 th edition Practice Questions Chapter 08 1. Geographers define as the study of the political organization of the world. A. the United Nations B. political science C. political economy
2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies
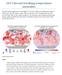 2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies June 2015 global temperature was the highest in 136 (since 1880) years reaching an average of 0.88 C above the 20 th century average. This is an increase of 0.12
2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies June 2015 global temperature was the highest in 136 (since 1880) years reaching an average of 0.88 C above the 20 th century average. This is an increase of 0.12
Dr. Emily A. Fogarty, Coordinator History, Politics and Geography Dept School of Arts & Sciences
 Geography Dr. Emily A. Fogarty, Coordinator History, Politics and Geography Dept. Emily.Fogarty@farmingdale.edu 631-420-2739 School of Arts & Sciences The History, Politics and Geography Department offers
Geography Dr. Emily A. Fogarty, Coordinator History, Politics and Geography Dept. Emily.Fogarty@farmingdale.edu 631-420-2739 School of Arts & Sciences The History, Politics and Geography Department offers
MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4
 MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4 Course Title: Social Studies Brief Description Overview: Students will explore the history, geography, government, and economy of the United States with
MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4 Course Title: Social Studies Brief Description Overview: Students will explore the history, geography, government, and economy of the United States with
Proposed AKS for 6 th Grade Social Studies
 Proposed AKS for 6 th Grade Social Studies A. Map and Globe Skills 1. use cardinal directions 2. use intermediate directions 3. use a letter/number grid system to determine location 4. compare and contrast
Proposed AKS for 6 th Grade Social Studies A. Map and Globe Skills 1. use cardinal directions 2. use intermediate directions 3. use a letter/number grid system to determine location 4. compare and contrast
What Are Cities for? Changhyun Kim Seoul National University
 Localities, Vol. 2, 2012, pp. 371-377 Cities for People, Not for Profit: Critical Urban Theory and the Right to the City, by Neil Brenner, Peter Marcuse, and Margit Mayer eds., Routledge, 2012, 296pp.
Localities, Vol. 2, 2012, pp. 371-377 Cities for People, Not for Profit: Critical Urban Theory and the Right to the City, by Neil Brenner, Peter Marcuse, and Margit Mayer eds., Routledge, 2012, 296pp.
Introduction to the subject area Differing understandings of geopolitics Discussion of seminar structure and student research topics
 GEOG 607 SEMINAR: GEOPOLITICS Instructor: Alexander B. Murphy Fall 2012 Mondays, 14:00-16:50 Condon 207 This graduate geography seminar explores the concept of geopolitics a term with widely varying connotations
GEOG 607 SEMINAR: GEOPOLITICS Instructor: Alexander B. Murphy Fall 2012 Mondays, 14:00-16:50 Condon 207 This graduate geography seminar explores the concept of geopolitics a term with widely varying connotations
Territorial Cooperation within the Northern Periphery and the Arctic
 Territorial Cooperation within the Northern Periphery and the Arctic 12 March 2013 / By Silvia Curbelo Betancort North charr project, Landösjön lake, Sweden. Source: North Periphery Programme Today we
Territorial Cooperation within the Northern Periphery and the Arctic 12 March 2013 / By Silvia Curbelo Betancort North charr project, Landösjön lake, Sweden. Source: North Periphery Programme Today we
GACE Middle Grades Social Science Assessment Test at a Glance
 GACE Middle Grades Social Science Assessment Test at a Glance Updated June 2017 See the GACE Middle Grades Social Science Assessment Study Companion for practice questions and preparation resources. Assessment
GACE Middle Grades Social Science Assessment Test at a Glance Updated June 2017 See the GACE Middle Grades Social Science Assessment Study Companion for practice questions and preparation resources. Assessment
Alleghany County Schools Curriculum Guide GRADE/COURSE: World Geography
 GRADE/COURSE: World 2013-14 GRADING PERIOD: 1 st Six Weeks Time Frame Unit/SOLs SOL # Strand Resource Assessment 8 days* The student will use maps, globes, satellite images, photographs, or diagrams to
GRADE/COURSE: World 2013-14 GRADING PERIOD: 1 st Six Weeks Time Frame Unit/SOLs SOL # Strand Resource Assessment 8 days* The student will use maps, globes, satellite images, photographs, or diagrams to
Grade 7 Social Studies
 Standard 1: History Students will examine the major movements, events, and figures that contributed to the development of nations in modern Africa, Asia, and the Southwest Pacific from acient civilizations
Standard 1: History Students will examine the major movements, events, and figures that contributed to the development of nations in modern Africa, Asia, and the Southwest Pacific from acient civilizations
EU s Role IN THE ARCTIC
 EU s Role IN THE ARCTIC Cautionary note! The EU is extremely complex policy entity The Arctic is very heterogeneous policy environment Both are changing, and fast 1 + 1= even more complexity Another cautionary
EU s Role IN THE ARCTIC Cautionary note! The EU is extremely complex policy entity The Arctic is very heterogeneous policy environment Both are changing, and fast 1 + 1= even more complexity Another cautionary
Supplementary Appendix for Power, Proximity, and Democracy: Geopolitical Competition in the International System
 Supplementary Appendix for Power, Proximity, and Democracy: Geopolitical Competition in the International System S1. The Need for a Country-Level Measure of Geopolitical Competition Previous scholarship
Supplementary Appendix for Power, Proximity, and Democracy: Geopolitical Competition in the International System S1. The Need for a Country-Level Measure of Geopolitical Competition Previous scholarship
Grade 5: Social Studies Practices
 Grade 5: Social Studies Practices A. Gathering and Using Evidence 1. Develop questions to help identify evidence about topics related to the historical events occurring in the Western Hemisphere that can
Grade 5: Social Studies Practices A. Gathering and Using Evidence 1. Develop questions to help identify evidence about topics related to the historical events occurring in the Western Hemisphere that can
Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do?
 Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do? Lesson 1.1 What is History? I. Why Study History? A. History is the study of the of the past. History considers both the way things
Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do? Lesson 1.1 What is History? I. Why Study History? A. History is the study of the of the past. History considers both the way things
Report. Workshop 5: How can atlases help to organise and promote the seas?
 Workshop 5: How can atlases help to organise and promote the seas? Report 1. Three key messages included on the reporting slide for the last plenary session Atlases help people to visualise intuitively
Workshop 5: How can atlases help to organise and promote the seas? Report 1. Three key messages included on the reporting slide for the last plenary session Atlases help people to visualise intuitively
UNIT 4: POLITICAL ORGANIZATION OF SPACE
 UNIT 4: POLITICAL ORGANIZATION OF SPACE Advanced Placement Human Geography Session 1 ADVANCED PLACEMENT HUMAN GEOGRAPHY REVIEW SESSIONS: UNIT FOUR By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study
UNIT 4: POLITICAL ORGANIZATION OF SPACE Advanced Placement Human Geography Session 1 ADVANCED PLACEMENT HUMAN GEOGRAPHY REVIEW SESSIONS: UNIT FOUR By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study
Curriculum Unit. Instructional Unit #1
 Curriculum Unit Name of Course: AP Human Geography Grade Level(s): 9-12 Brief Description (Course Catalog): The purpose of the AP Human Geography course is to introduce students to the systematic study
Curriculum Unit Name of Course: AP Human Geography Grade Level(s): 9-12 Brief Description (Course Catalog): The purpose of the AP Human Geography course is to introduce students to the systematic study
The importance of international university and project cooperation in science
 The importance of international university and project cooperation in science The Role of Science in Arctic Social and Business Development Arctic Frontiers Science January 25, 2017 Dr. Marina Kalinina
The importance of international university and project cooperation in science The Role of Science in Arctic Social and Business Development Arctic Frontiers Science January 25, 2017 Dr. Marina Kalinina
GEOPOLITICS OF NORTH EAST ASIA: THE U.S. PERSPECTIVE
 GEOPOLITICS OF NORTH EAST ASIA: THE U.S. PERSPECTIVE AUTHOR: 1 MASASHI OKUYAMA University of Reading DATE: May 2005 In the post-cold War era, the defence elites in the United States consider North East
GEOPOLITICS OF NORTH EAST ASIA: THE U.S. PERSPECTIVE AUTHOR: 1 MASASHI OKUYAMA University of Reading DATE: May 2005 In the post-cold War era, the defence elites in the United States consider North East
The Region in Canadian Geography
 The Region in Canadian Geography Reading Course website (www.yorku.ca/anderson) Lists today s reading Laliberté et al (2015) Teaching the geographies of Canada: Reflections on pedagogy, curriculum, and
The Region in Canadian Geography Reading Course website (www.yorku.ca/anderson) Lists today s reading Laliberté et al (2015) Teaching the geographies of Canada: Reflections on pedagogy, curriculum, and
Water and Geopolitical Imperatives
 Water and Geopolitical Imperatives March 6, 2017 Access to and control over water is a strategic imperative that has been the impetus of conflict throughout history. Originally produced on Feb. 27, 2017
Water and Geopolitical Imperatives March 6, 2017 Access to and control over water is a strategic imperative that has been the impetus of conflict throughout history. Originally produced on Feb. 27, 2017
Comprehensive Curriculum for 8 th Grade Social Studies. Unit GLE s Guiding Questions Can students do the following (?) Allotted Time Chapters 1
 Unit GLE s Guiding Questions Can students do the following (?) Allotted Time Chapters 1 Physical and Cultural Geography of Louisiana 1. Time Zones 2. Place Location 3. Map Construction 4. Chart/Graph Construction
Unit GLE s Guiding Questions Can students do the following (?) Allotted Time Chapters 1 Physical and Cultural Geography of Louisiana 1. Time Zones 2. Place Location 3. Map Construction 4. Chart/Graph Construction
Name three countries in Europe.
 Name three countries in Europe. I will be able to identify the 5 themes of geography for Europe and locate the countries and capitals of Europe and the major physical features. People: Past: Through the
Name three countries in Europe. I will be able to identify the 5 themes of geography for Europe and locate the countries and capitals of Europe and the major physical features. People: Past: Through the
USING MAPS Designed by Catherine Denial Assistant Professor of History Knox College, Galesburg IL
 USING MAPS Designed by Catherine Denial Assistant Professor of History Knox College, Galesburg IL Most college-level textbooks contain numerous maps related to key historical events westward expansion;
USING MAPS Designed by Catherine Denial Assistant Professor of History Knox College, Galesburg IL Most college-level textbooks contain numerous maps related to key historical events westward expansion;
CANADA S ROLE IN THE GLOBAL SPACE AND ANTARCTIC GOVERNANCE. SAMUEL ADENIJI AUGUST 14, 2017.
 CANADA S ROLE IN THE GLOBAL SPACE AND ANTARCTIC GOVERNANCE. SAMUEL ADENIJI AUGUST 14, 2017. Generally, the global commons have been defined as those areas of the planet that fall outside national jurisdictions
CANADA S ROLE IN THE GLOBAL SPACE AND ANTARCTIC GOVERNANCE. SAMUEL ADENIJI AUGUST 14, 2017. Generally, the global commons have been defined as those areas of the planet that fall outside national jurisdictions
Essential Questions Content Skills Assessments Standards/PIs
 Map: GLOBAL 10 Type: Consensus Grade Level: 10 School Year: 2007-2008 Author: Jeff Fogler District/Building: Minisink Valley CSD/High School Created: 11/06/2007 Last Updated: 11/06/2007
Map: GLOBAL 10 Type: Consensus Grade Level: 10 School Year: 2007-2008 Author: Jeff Fogler District/Building: Minisink Valley CSD/High School Created: 11/06/2007 Last Updated: 11/06/2007
Fourth Grade Social Studies Crosswalk
 Fourth Grade Social Studies Crosswalk This crosswalk document compares the 2010 K-12 Social Studies Essential Standards and the 2006 North Carolina Social Studies Standard Course of Study (SCOS) and provides
Fourth Grade Social Studies Crosswalk This crosswalk document compares the 2010 K-12 Social Studies Essential Standards and the 2006 North Carolina Social Studies Standard Course of Study (SCOS) and provides
HPISD CURRICULUM (SOCIAL STUDIES, WORLD GEOGRAPHY)
 HPISD CURRICULUM (SOCIAL STUDIES, WORLD GEOGRAPHY) EST. NUMBER OF DAYS: 14 UNIT NAME Unit Overview UNIT 7 SOUTH WEST ASIA/NORTH AFRICA SWANA s geography has led to economic and cultural differences. Students
HPISD CURRICULUM (SOCIAL STUDIES, WORLD GEOGRAPHY) EST. NUMBER OF DAYS: 14 UNIT NAME Unit Overview UNIT 7 SOUTH WEST ASIA/NORTH AFRICA SWANA s geography has led to economic and cultural differences. Students
Arizona Educator Proficiency Assessments (AEPA ) FIELD 04: GEOGRAPHY TEST OBJECTIVES
 Arizona Educator Proficiency Assessments (AEPA ) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Range of Objectives Approximate Test Proportions I. Geographic Concepts and Skills 1 6 25% II. World Geography 7 14 34% III. United
Arizona Educator Proficiency Assessments (AEPA ) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Range of Objectives Approximate Test Proportions I. Geographic Concepts and Skills 1 6 25% II. World Geography 7 14 34% III. United
Peoples, Places and Cultures in Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific
 GRADE 7 Peoples, Places and Cultures in Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific Course 0470-07 Students in seventh grade explore the history, geography, government, economic systems, current issues, and
GRADE 7 Peoples, Places and Cultures in Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific Course 0470-07 Students in seventh grade explore the history, geography, government, economic systems, current issues, and
The Arctic Council - 20 years Anniversary
 The Arctic Council - 20 years Anniversary The Arctic Council in a Global Context - the Road Ahead Norræna húsið, 9. september 2016 Panel discussion Lilja Alfreðsdóttir, Minister for Foreign Affairs of
The Arctic Council - 20 years Anniversary The Arctic Council in a Global Context - the Road Ahead Norræna húsið, 9. september 2016 Panel discussion Lilja Alfreðsdóttir, Minister for Foreign Affairs of
WORLD GEOGRAPHY GRADE 10
 Parent / Student Course Information SOCIAL STUDIES WORLD GEOGRAPHY GRADE 10 Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents may arrange to meet
Parent / Student Course Information SOCIAL STUDIES WORLD GEOGRAPHY GRADE 10 Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents may arrange to meet
Item Specifications Summary 7 th grade World Geography Assessment
 Item Specifications Summary 7 th grade World Geography Assessment 2013-14 Structure: 65 multiple choice questions (15 field test items) Minimum of 6 questions per standard At least 75% of objectives have
Item Specifications Summary 7 th grade World Geography Assessment 2013-14 Structure: 65 multiple choice questions (15 field test items) Minimum of 6 questions per standard At least 75% of objectives have
The National Spatial Strategy
 Purpose of this Consultation Paper This paper seeks the views of a wide range of bodies, interests and members of the public on the issues which the National Spatial Strategy should address. These views
Purpose of this Consultation Paper This paper seeks the views of a wide range of bodies, interests and members of the public on the issues which the National Spatial Strategy should address. These views
Content Area: Social Studies Course: Grade 7 Social Studies Grade Level: Seventh R14 The Seven Cs of Learning
 Content Area: Social Studies Course: Grade 7 Social Studies Grade Level: Seventh R14 The Seven Cs of Learning Collaboration Character Communication Citizenship Critical Thinking Creativity Curiosity Unit
Content Area: Social Studies Course: Grade 7 Social Studies Grade Level: Seventh R14 The Seven Cs of Learning Collaboration Character Communication Citizenship Critical Thinking Creativity Curiosity Unit
AP Human Geography. Course Outline Geography: Its Nature and Perspectives: Weeks 1-4
 AP Human Geography The Course The AP Human Geography course is designed to provide secondary students with the equivalent of one semester of a college introductory human geography class. The purpose of
AP Human Geography The Course The AP Human Geography course is designed to provide secondary students with the equivalent of one semester of a college introductory human geography class. The purpose of
Canadian and World Studies
 Canadian and World Studies World History since 1900: Global and Regional Interactions CHT3O1 This course focuses on major developments in world history from 1900 to the present. Students will explore the
Canadian and World Studies World History since 1900: Global and Regional Interactions CHT3O1 This course focuses on major developments in world history from 1900 to the present. Students will explore the
Towards international cooperation in the development of Marine Spatial Plans for the North Pacific: economic, social, and environmental dimensions
 Towards international cooperation in the development of Marine Spatial Plans for the North Pacific: economic, social, and environmental dimensions A.V. Sereda, V.B. Lobanov V.I. Il ichev Pacific Oceanological
Towards international cooperation in the development of Marine Spatial Plans for the North Pacific: economic, social, and environmental dimensions A.V. Sereda, V.B. Lobanov V.I. Il ichev Pacific Oceanological
Groveport Madison Local School District Sixth Grade Social Studies Content Standards Planning Sheets
 Standard: Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities A. Show the relationship between civic participation and attainment of civic and public goals. 1. Explain how opportunities for citizens to participate
Standard: Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities A. Show the relationship between civic participation and attainment of civic and public goals. 1. Explain how opportunities for citizens to participate
SOCIAL STUDIES Grade 6 Standard: History
 Standard: History Chronology A. Interpret relationships between events shown on multipletier 1. Construct a multiple-tier time line from a list of events time lines. and interpret the relationships between
Standard: History Chronology A. Interpret relationships between events shown on multipletier 1. Construct a multiple-tier time line from a list of events time lines. and interpret the relationships between
The Geopolitics of Containment
 The Geopolitics of Containment Reappraising American Foreign Policy During the Early Cold War, 1945-1953 Master's Thesis Thomas W. Bottelier 303010 23-08-2011 Supervisor: dr. B. Wubs Global History & International
The Geopolitics of Containment Reappraising American Foreign Policy During the Early Cold War, 1945-1953 Master's Thesis Thomas W. Bottelier 303010 23-08-2011 Supervisor: dr. B. Wubs Global History & International
Seventh Grade Social Studies Curriculum Map
 Semester Unit Unit Focus NC Essential Standards Social Studies Literacy in History/ Social Studies 1 1st Unit 1 Intro to Geography Culture Explorers Constitution Day Terrorism (9-11) 1st Unit 2 Renaissance
Semester Unit Unit Focus NC Essential Standards Social Studies Literacy in History/ Social Studies 1 1st Unit 1 Intro to Geography Culture Explorers Constitution Day Terrorism (9-11) 1st Unit 2 Renaissance
POLITICAL SYSTEMS. (ps ) Evaluate positions taken regarding the necessity of government and the purposes of government.
 Baltimore City Public School System Social Studies Content Standards (Grade 8) POLITICAL SYSTEMS In the context of U.S. History through 1877, at the end of grade 8, students know and are able to do everything
Baltimore City Public School System Social Studies Content Standards (Grade 8) POLITICAL SYSTEMS In the context of U.S. History through 1877, at the end of grade 8, students know and are able to do everything
World Studies
 World Studies 200 2013 2014 Instructor: Rick Rogers Prep Hour: 4th e mail:rogerric@crandon.k12.wi.us Phone: (715) 478 3339 Room: 65 Text/Materials: World History, by Jackson J. Spielvogel, Ph.D., McGraw
World Studies 200 2013 2014 Instructor: Rick Rogers Prep Hour: 4th e mail:rogerric@crandon.k12.wi.us Phone: (715) 478 3339 Room: 65 Text/Materials: World History, by Jackson J. Spielvogel, Ph.D., McGraw
MAJOR IN INTERNATIONAL STUDIES, EUROPEAN STUDIES CONCENTRATION
 Major in International Studies, European Studies Concentration 1 MAJOR IN INTERNATIONAL STUDIES, EUROPEAN STUDIES CONCENTRATION Requirements Effective Fall 2018 Freshman ANTH 200 Cultures and the Global
Major in International Studies, European Studies Concentration 1 MAJOR IN INTERNATIONAL STUDIES, EUROPEAN STUDIES CONCENTRATION Requirements Effective Fall 2018 Freshman ANTH 200 Cultures and the Global
DRAFT - PLEASE DO NOT QUOTE OR CITE THE RESECURITIZATION OF THE ARCTIC IN A CHANGING WORLD
 THE RESECURITIZATION OF THE ARCTIC IN A CHANGING WORLD Juliano Cesar Shishido Góes 1 Abstract: The Arctic has received more attention in recent years since the Cold War period, especially in relation to
THE RESECURITIZATION OF THE ARCTIC IN A CHANGING WORLD Juliano Cesar Shishido Góes 1 Abstract: The Arctic has received more attention in recent years since the Cold War period, especially in relation to
GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS CORRELATION NOTATIONS
 Book Title: World Studies: The Eastern Hemisphere 2005 Grade Level: 6 Publisher: Pearson Prentice Hall Subject/Course: Social Studies, Grade 6 Geography The World in Spatial Terms Grade 6 1. Use latitude
Book Title: World Studies: The Eastern Hemisphere 2005 Grade Level: 6 Publisher: Pearson Prentice Hall Subject/Course: Social Studies, Grade 6 Geography The World in Spatial Terms Grade 6 1. Use latitude
Cultural Geography. Chapter 1
 Cultural Geography Chapter 1 What is Geography? The study of the interaction of all physical and human phenomenon at individual places, and how interactions among places form patterns and organize space.
Cultural Geography Chapter 1 What is Geography? The study of the interaction of all physical and human phenomenon at individual places, and how interactions among places form patterns and organize space.
Introduction to Human Geography. Unit 1: It s Nature and Perspective
 Introduction to Human Geography Unit 1: It s Nature and Perspective Questions that Geography addresses: Where are things located? Why are they important? How are places related? How are places connected?
Introduction to Human Geography Unit 1: It s Nature and Perspective Questions that Geography addresses: Where are things located? Why are they important? How are places related? How are places connected?
The Arctic Cold War The battle to control resources while the future of the earth hangs in the balance.
 The Arctic Cold War The battle to control resources while the future of the earth hangs in the balance. 1 The Arctic Cold War The battle to control resources while the future of the earth hangs in the
The Arctic Cold War The battle to control resources while the future of the earth hangs in the balance. 1 The Arctic Cold War The battle to control resources while the future of the earth hangs in the
