Problem-Based Learning at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine: Self-Assessment of Performance in Postdoctoral Training
|
|
|
- Myles Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problem-Based Learning at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine: Self-Assessment of Performance in Postdoctoral Training Kewalin Thammasitboon, D.D.S., D.M.Sc.; Cortino Sukotjo, D.D.S., Ph.D, M.M.Sc.; Howard Howell, D.D.S.; Nadeem Karimbux, D.M.D., M.M.Sc. Abstract: Problem-based learning (PBL) was implemented into the dental curriculum at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine (HSDM) in 1994 with an expectation that this pedagogy would enhance students critical thinking and communication skills as well as general professional competencies. Previous studies have described several aspects of the outcome of PBL curricula at the predoctoral level. However, there is no information available on the perceptions and performance of PBL graduates during their postdoctoral training in dentistry. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of PBL methodology on the performance of HSDM graduates during their postdoctoral training in comparison with their non-hsdm (traditional) co-residents. Surveys containing traditional knowledge-based criteria, preclinical and clinical criteria, and PBL criteria were sent to HSDM graduates from the classes of 2002 through 2004 who were in postgraduate training programs. The HSDM and traditional graduates were asked to evaluate and compare their performance in selected areas with those of their co-residents from either a PBL curriculum or a traditional curriculum. The directors of each program were also asked to assess HSDM graduates relative to other graduates in the program based on the same aspects. Overall, HSDM graduates rated themselves more highly than non-hsdm graduates on all competencies. No significant difference between HSDM and non-hsdm responses was found in general dental knowledge, specialty specific knowledge, preclinical skills, clinical skills, communication with staff, and patient education, whereas significant differences (p<0.05) were found for communication with patients, critical thinking, independent learning, performance in small group settings, self-assessment, and teamwork. The data obtained from the program directors revealed corresponding results. The HSDM graduates capacity for independent learning was rated as excellent by percent of the directors and percent of the HSDM graduates themselves. These findings suggest that the performance of HSDM graduates during their postdoctoral training met expectations and were similar to non-hsdm graduates for traditional residency program competencies. However, the PBL training appears to provide HSDM graduates with enhanced abilities in independent learning, communication, and cooperation skills. Dr. Thammasitboon is an Instructor, Division of Endodontology, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Prince of Songkla University; Dr. Sukotjo is an Instructor, Department of Restorative and Biomaterial Sciences, Harvard School of Dental Medicine; Dr. Howell is Professor of Periodontology and Dean of Dental Education, Harvard School of Dental Medicine; and Dr. Karimbux is Associate Professor of Periodontology and Assistant Dean of Dental Education, Harvard School of Dental Medicine. Direct correspondence and requests for reprints to Dr. Nadeem Karimbux, Office of Dental Education, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, 188 Longwood Ave., Boston, MA 02115; fax; nadeem_karimbux@hsdm.harvard.edu. Key words: problem-based learning, dental, performance, graduate, postdoctoral, resident, independent learning Submitted for publication 10/16/06; accepted 4/20/07 Problem-based learning (PBL) began in the McMaster University medical program in 1965 with a goal of improving students ability to apply knowledge in clinical contexts, increase retention of information, and develop lifelong learning habits. 1 Many health profession schools have adopted various forms of PBL methods, including Harvard University where a PBL-integrated New Pathway program (NP) was introduced into the medical school in Numerous studies have compared the effects of PBL and a traditional curriculum on the satisfaction in learning environment, perception, and performance of both faculties and students. 3 The data revealed both pros and cons of PBL methods. However, the conclusion drawn from these studies indicated positive effects 4-9 or, otherwise, neutral effects of the PBL method PBL was first implemented in dental classes at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine (HSDM) in fall The HSDM predoctoral curriculum has transitioned from a traditional curriculum to a PBLhybrid curriculum in both preclinical and clinical education, with an expectation that this pedagogy would enhance the students critical and interdisciplinary thinking and communication skills as well as their general professional competencies. 4,14 Previously published studies have reported several aspects of the effects of PBL methodology on the competencies of HSDM students. These studies demonstrated that PBL has been effective at increas Journal of Dental Education Volume 71, Number 8
2 ing National Board Dental Examination (NBDE) Part I scores, graduation rates, and percentage of graduates entering postgraduate education programs, as well as decreasing attrition rates. 4 However, the implementation of PBL at HSDM has not universally increased student productivity in research. 11 Several studies in medical education have shown the positive effect of PBL on the performance of graduates during their practice or residency training. A randomized controlled trial study conducted at Harvard Medical School showed that residents who graduated from the PBL-integrated New Pathway program rated their preparation to practice humanistic medicine higher than did traditional students and expressed more confidence in their ability to manage patients with psychosocial problems. A study by Antepohl et al. showed that PBL graduates tended to pursue a higher education and they were satisfied with their undergraduate education and preparation for communication with patients, collaboration with other health professionals, and development of critical thinking as well as scientific attitudes. 3 Results from several studies carried out in other institutes also indicated superior performance of the graduates from PBL medical programs in professional practice or postdoctoral training especially in the areas of self-directed, lifelong learning, communication with patients, 15 cooperation skill, problem-solving skill, and ability to work independently. 16 Despite the differences between characteristics of PBL and non-pbl graduates, a recent study showed that there were no differences with respect to the main occupation (clinician or others), practice location (urban or rural), or employment sector (public or private) after graduation between medical student graduates from traditional and nontraditional curricula. 17 It has been accepted that resident evaluation is more reliable if the assessments are based on impressions derived from multiple sources of information, for example, direct observation interactions as well as from more than one evaluator. Supervisors evaluation of residents performance has been included in several medical education studies 15,18,19 and has been shown to be valuable in resident performance evaluation. 19,20 However, the investigators were not able to identify any articles in the dental literature that reported the use of multiple evaluators in a PBL outcome study. The goal of this study was to extend the information on the outcomes of PBL education by examining the performance of HSDM graduates during their postdoctoral training. The study was designed to test the hypothesis that HSDM graduates perform well during their postdoctoral training, especially in the areas considered to be enhanced by PBL curricula including critical thinking, teamwork, communication skills, and self-directed learning. To test this hypothesis, two types of data were collected and analyzed: 1) comparison of competency self-assessments completed by HSDM graduates and graduates of other schools, and 2) comparison of self-assessments completed by HSDM graduates and graduate program directors ratings of the competency of residents from HSDM. In addition, graduates future plans were collected to determine whether HSDM and non-hsdm graduates had different preferences for their future careers. Methods A questionnaire was distributed in January 2005 to eighty-four HSDM graduates from the classes of 2002, 2003, and 2004 who were in postgraduate training across the United States. These graduates represented percent of the total population who graduated from HSDM during those three years. A co-resident of each of these eighty-four HSDM graduates who went to a non-hsdm, non- PBL, lecture-based school was also asked to fill out the questionnaire and served as the control group. In addition, the program directors (fifty-eight directors) of each HSDM graduate s postgraduate program were asked to complete a questionnaire comparing HSDM graduates to other residents who were graduates of traditional dental education programs that did not employ PBL. A questionnaire was created and approved by the Harvard Medical School Office for Research Subject Protection. The questionnaire was a modification of a questionnaire created for a previous study by Santos-Gomez et al. 15 and also was based on a questionnaire developed for the ACGME Outcomes Project by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME). The questionnaire asked HSDM graduates to rate themselves in comparison with other residents (co-residents) in their advanced graduate programs who had graduated from non-pbl, lecture-based dental schools other than HSDM on twelve selected competencies on a four-point scale, which consisted of excellent, good, fair, and poor. These twelve competencies were organized into three categories. The first category includes competencies expected to be enhanced by August 2007 Journal of Dental Education 1081
3 PBL including communication with patients and staff, critical thinking, independent learning, performance in small group settings, patient education, self-assessment, and teamwork. The second category includes competencies known to be equal between PBL and non-hsdm students including general dental knowledge and knowledge that is specific for a specialty area; and the final category includes competencies that are speculated to be strengths of a traditional curriculum including preclinical and clinical skills. The competencies were placed in a random order in the questionnaire to control bias. The HSDM graduates were asked to randomly give the questionnaire to one co-resident in the program who had been trained in a non-hsdm dental school. Each co-resident was asked to assess himself or herself on the twelve competencies. The director of each program was also asked to assess HSDM graduate(s) in the program on the selected competencies. The questionnaire included an overall evaluation in which the directors were asked to rate the HSDM graduates comprehensively, considering all aspects of performance, using a scale that consisted of superior, satisfactory, marginal, and unsatisfactory. The questionnaire completed by the HSDM and non-hsdm graduates also included a question on the graduates future career plans with the response options being full-time clinical instructor, full-time researcher, part-time clinical instructor, part-time researcher, and private practitioner. The graduates were allowed to select more than one option that is in their plan. To prevent misinterpretation, definitions of the competencies were enclosed with the questionnaire. Follow-up letters were sent to the HSDM graduates who did not respond one month after the first letters were sent. Differences between the responses provided by HSDM and non-hsdm residents were analyzed Table 1. Survey response and return rates Number of Questionnaires HSDM Non-HSDM Director Sent Responded * Returned ** % of Response 57% 43% 67% *Subjects who answered and sent back the questionnaire. **Unopened questionnaires that were returned either because of an address change or because the graduates were no longer in the program. with the Mann-Whitney test with significance set at p<0.05. The responses by HSDM-trained residents and their directors were paired and analyzed with the Wilcoxon signed ranks test to determine the degree of correspondence and to investigate the direction of any differences that were identified from analysis of the responses. Results Of the subjects who were sent the questionnaires, responses were available for forty-two respondents from HSDM, thirty-eight from non-hsdm, and fifty-one from program directors (response rates are shown in Table 1). Figure 1 shows the distribution of the respondents by the type of residency program. More than 45 percent of the respondents were in orthodontic advanced graduate programs, and about 24 percent of the respondents were in periodontal programs. The others were in prosthodontics, endodontics, pediatric dentistry, oral surgery, or General Practice Residency/Advanced Education in General Dentistry (GPR/AEGD) programs. However, since there was only one AEGD resident who graduated from HSDM responding to the questionnaire and there was no matched non-hsdm resident, those data were excluded. Results of the graduates selfassessments are shown in Table 2, which displays the percentages of the total number of responses in the four rating categories: excellent, good, fair, poor. The non-applicable responses were not included. The competencies expected to be enhanced by PBL are marked with asterisks in Table 2 and are highlighted in subsequent tables. Overall, HSDM graduates rated themselves more highly than non-hsdm graduates on all competencies. For the eight items expected to be enhanced by PBL, the differences between HSDM and non-hsdm graduates responses were statistically significant for six of these competencies. HSDM graduates rated themselves the highest for the competency independent learning ; percent self-assessed their skill level as excellent for this item. In contrast, percent of the non- HSDM believed they were excellent in independent learning. The highest rating for the non-hsdm graduates was ability in communication with staff ; percent self-assessed their skill level as excellent for this item. Table 3 compares the self-assessment ratings for all forty-one HSDM and thirty-eight non-hsdm 1082 Journal of Dental Education Volume 71, Number 8
4 HSDM Non-HSDM % Graduate AEGD/GPR Endodontics Oral Surgery Orthodontics Program Pedodontics Periodontics Prosthodontics Figure 1. Program distribution of the HSDM and non-hsdm respondents (n=80), shown in percentage of graduates residents combined without regard to type of postgraduate program. The statistical analysis displayed in Table 3 showed that there was no significant difference found for general dental knowledge, knowledge specific for specialty, preclinical skills, clinical skills, communication with staff, and patient education. However, there was a significant difference (p<0.05) comparing HSDM and non-hsdm ratings in communication with patients, critical thinking, independent learning, performance in small group settings, self-assessment, and teamwork. Table 4 shows responses from the graduate program directors who were asked to evaluate HSDM graduates performance in their program. The directors highest rating was in the category of independent learning, where percent of the HSDM graduates were evaluated to be excellent. The statistical analysis shown in Table 5 shows no significant difference (p>0.05) between the directors evaluations and HSDM graduates self-assessments in twenty-seven instances where responses were available from both director and resident. However, there were seven competencies where the directors rated HSDM graduates less favorably than the HSDM graduates self-assessment, and there were five competencies where the directors rated HSDM graduates more favorably than the HSDM graduates self-assessment. However, none of these differences between residency director and HSDM graduates ratings were significantly different. The program directors evaluation of the HSDM graduates overall performance showed that percent were rated as superior, percent were rated satisfactory, 6.67 percent were rated as marginal, and 2.22 percent were rated as unsatisfactory. Residents future career plans are shown in Figure 2. Most of the HSDM and non-hsdm residents planned to pursue their careers either as full-time private practitioners (57.58 percent of all non-hsdm and percent of all HSDM respondents) or as part-time private practitioners who also worked as part-time clinical instructors in dental schools (33.33 percent of all non-hsdm and percent of all HSDM respondents). Interestingly, percent of the HSDM graduates expected to be involved in the academic field, either full-time or part-time, whereas percent of non-hsdm respondents planned to work in academia. August 2007 Journal of Dental Education 1083
5 Table 2. Results of self-assessment of HSDM and non-hsdm graduates in each postgraduate program Program (n=hsdm/non-hsdm) % of HSDM Graduates % of Non-HSDM Graduates ORTHODONTICS (n=19/19) Poor Fair Good Excellent Poor Fair Good Excellent p-value General dental knowledge Knowledge specific for specialty Communication with patients* Communication with staff* Independent learning* Teamwork* Patient education* Preclinical skills Clinical skills Critical thinking* Performance in small group settings* Self-assessment* PERIODONTICS (n=11/9) Poor Fair Good Excellent Poor Fair Good Excellent p-value General dental knowledge Knowledge specific for specialty Communication with patients* Communication with staff* Independent learning* Teamwork* Patient education* Preclinical skills Clinical skills Critical thinking* Performance in small group settings* Self-assessment* ENDODONTICS (n=4/4) Poor Fair Good Excellent Poor Fair Good Excellent p-value General dental knowledge Knowledge specific for specialty Communication with patients* Communication with staff* Independent learning* Teamwork* Patient education* Preclinical kills Clinical skills Critical thinking* Performance in small group settings* Self-assessment* Journal of Dental Education Volume 71, Number 8
6 PEDODONTICS (n=4/4) Poor Fair Good Excellent Poor Fair Good Excellent p-value General dental knowledge Knowledge specific for specialty Communication with patients* Communication with staff* Independent learning* Teamwork* Patient education* Preclinical skills Clinical skills Critical thinking* Performance in small group settings* Self-assessment* PROSTHODONTICS (n=1/1) Poor Fair Good Excellent Poor Fair Good Excellent p-value General dental knowledge Knowledge specific for specialty Communication with patients* Communication with staff* Independent learning* Teamwork* Patient education* Preclinical skills Clinical skills Critical thinking* Performance in small group settings* Self-assessment* ORAL SURGERY (n=2/1) Poor Fair Good Excellent Poor Fair Good Excellent p-value General dental knowledge Knowledge specific for specialty Communication with patients* Communication with staff* Independent learning* Teamwork* Patient education* Preclinical skills Clinical skills Critical thinking* Performance in small group settings* Self-assessment* *Competencies expected to be enhanced by PBL. August 2007 Journal of Dental Education 1085
7 Discussion PBL has been implemented in the predoctoral curriculum at HSDM for twelve years. Earlier studies conducted at HSDM demonstrated the benefits of this system. Our study was interested in the performance of HSDM graduates during their postdoctoral training, to examine if these students retained characteristics expected of a PBL student. This study focused on the competencies relevant to professional practice, which could be categorized into three groups: the competencies expected to be enhanced by PBL, the competencies known to be equal between PBL and non-hsdm students, and the competencies speculated to be stronger in traditional curricula. The results from self-assessment showed that HSDM graduates rated themselves more highly than non-hsdm graduates on all competencies. This implies a higher confidence in their abilities. Statisti- Table 3. Comparison of self-assessment by all HSDM (n=41) and all non-hsdm (n=38) residents % of HSDM graduates % of non-hsdm graduates p-value Poor Fair Good Excellent Poor Fair Good Excellent Independent learning* Communication with patients* Teamwork* Communication with staff Performance in small group settings* Critical thinking* Self-assessment* Patient education Knowledge specific for specialty Clinical skills General dental knowledge Preclinical skills *Items where the differences between HSDM and non-hsdm graduates responses were statistically significant. Results of self-assessment of HSDM (n=41) and non-hsdm (n=38) graduates on selected competencies sorted by the percentage of excellent results of HSDM graduates. The competencies expected to be enhanced by PBL are screened. Table 4. Program directors (n=51) evaluation of HSDM graduates performance in postdoctoral training program % of HSDM Graduates Rated in Each Performance Category Poor Fair Good Excellent Independent learning Communication with patients Teamwork Communication with staff Performance in small group settings Critical thinking Self-assessment Patient education Knowledge specific for specialty Clinical skills General dental knowledge Preclinical skills Results of the program director evaluation (n=51) of HSDM graduates performance in postdoctoral training program. The competencies expected to be enhanced by PBL are screened Journal of Dental Education Volume 71, Number 8
8 cal analysis showed significant differences (p<0.05) between the HSDM and non-hsdm graduate selfratings for almost all of the competencies expected to be enhanced by the PBL method including ability in communication with patients, critical thinking, independent learning, self-assessment, teamwork, and performance in small group settings. On all of these competencies, HSDM graduates rated themselves one to two scores higher than non- HSDM graduates. In particular, more than 80 percent of HSDM graduates considered themselves to be excellent in conducting independent learning. These results correspond with previous self-assessment studies, which also showed that the PBL graduates gave themselves higher ratings for these areas, especially in communication and independent learning skills as well as the ability to collaborate with others. 15,21,22 However, a significant difference was not found in communications with staff and patient education, which are expected to be one of the strengths of a PBL curriculum. The results also showed that HSDM and non- HSDM graduates believed that they performed equally well in general dental knowledge and knowledge specific for their chosen dental specialty. It has been demonstrated in previous studies that the performance of PBL students in these areas is typically equivalent but not superior in comparison to traditionally educated students. 21,22 These results, which are generally consistent with previous research, indicate that the HSDM and non-hsdm students probably did not overestimate or underestimate their level of competency when completing the self-assessment surveys. More importantly, no significant differences were found between HSDM and traditional graduates for preclinical skills or clinical skills. There has been speculation that HSDM graduates level of competency in procedural skills would be adversely affected by the reduction of laboratory time resulting from implementation of the PBL program at Harvard. The results presented here confirm findings from an- Table 5. Statistical comparison of the HSDM graduates self-assessment and program directors evaluation (n=27) % of Response p value Same Higher Lower Independent learning Communication with patients Teamwork Communication with staff Performance in small group settings Critical thinking Self-assessment Patient education Knowledge specific for specialty Clinical skills General dental knowledge Preclinical skills Statistical results of the comparison between the HSDM graduate self-assessment and program director evaluation (n=27): Same (the directors and HSDM graduates rated the performance similarly); Higher (the directors rated HSDM graduates more highly than the graduates did); Lower (the directors rated HSDM graduates less favorably than the graduates did). The competencies expected to be enhanced by PBL are screened. other as yet unpublished study conducted at HSDM that showed the reduction of laboratory preclinical exercises at HSDM did not affect students didactic and clinical performance. The HSDM graduates self-assessments and the evaluations completed by the program directors were generally similar. Program directors also rated HSDM graduates to be excellent in independent learning. However, the directors gave less favorable ratings compared to the graduates self-assessments in a few areas. These results are not consistent with several studies that have shown that directors tend to be more lenient evaluators than residents, 23 and poor correlations between director and resident self-evaluations have been reported. 15,18 One explanation that has been proposed is that supervisors ratings of residents are usually based on an overall impression instead of actual performance, while self-assessment tends to examine performance in discrete areas. 15 However, most of the dental postdoctoral programs have considerably smaller size than medical residency programs. This could result in more stringent evaluations or more similar responses between self- and directors evaluations, which were found in our study. In regard to future career plans, there was no statistically significant difference between HSDM and non-hsdm residents, which is consistent with previous findings. 2,17 However, the data suggested that HSDM graduates appear to be more likely August 2007 Journal of Dental Education 1087
9 HSDM Non-HSDM % Resident ftc ftr ptc ptr ptc/ptr ptc/pp ptc/ptr/pp PP Others Future plan Figure 2. Residents future career plans ftc (full-time clinical instructor); ftr (full-time researcher); ptc (part-time clinical instructor); ptr (part-time researcher); PP (private practitioner) to get involved in academia as part-time clinical instructors. The findings in our study suggest that some characteristics of the PBL curriculum appear to remain with graduates in their postdoctoral training. However, there may also be some confounding variables. Performance of the graduates might reflect other factors unrelated to the PBL method. For example, the selection procedures of Harvard University that target candidates who have specific characteristics and attributes may preferentially sort students by PBL characteristics prior to exposure to the PBL environment in HSDM. It is also possible that the prestige of Harvard University creates high confidence in its graduates, resulting in higher selfassessment ratings by HSDM graduates. In addition, the majority of the respondents were in orthodontic and periodontal programs. The findings of the study might have represented unique characteristics of the residents in these programs rather than characteristics of the PBL graduates. However, significant differences for certain competencies were found between HSDM and non-hsdm graduates within the same program including orthodontic and periodontal programs. It is also possible that the positive responses by the HSDM subjects in this study reflect their gratitude to their school or their faculties. Similarly, the directors responses could be influenced by their relationship with HSDM or by their global impression of Harvard as a high-quality academic institution, which may have produced halo effect ratings for residents known to be HSDM graduates. Despite the positive results, interpretation of the data in the present study was limited by the small sample size as well as the low response rate and the inherent disadvantages of using a questionnaire with a rating scale because respondents may avoid using the extreme ends of a rating scale. It is also possible that responses were subjective or biased. An evaluation of the effectiveness of a PBL curriculum was challenging because it is difficult to recruit subjects from a parallel traditional education track that could serve as better controls. More importantly, the results from self-assessment reflect the subjects perceptions of their own performance, which may or may not demonstrate their true performance. Even though the present study illustrates the experience of a select group of dental residents who graduated from only one PBL program the Harvard 1088 Journal of Dental Education Volume 71, Number 8
10 School of Dental Medicine these findings extend the results of earlier studies and hopefully will be informative for dental faculty who desire to implement a PBL curriculum in other schools. REFERENCES 1. Saarinen-Rahiika H, Binkley JM. Problem-based learning in physical therapy: a review of the literature and overview of the McMaster University experience. Phys Ther 1998;78(2): ; discussion Peters AS, Greenberger-Rosovsky R, Crowder C, Block SD, Moore GT. Long-term outcomes of the New Pathway Program at Harvard Medical School: a randomized controlled trial. Acad Med 2000;75(5): Antepohl W, Domeij E, Forsberg P, Ludvigsson J. A follow-up of medical graduates of a problem-based learning curriculum. Med Educ 2003;37(2): Susarla SM, Medina-Martinez N, Howell TH, Karimbux NY. Problem-based learning: effects on standard outcomes. J Dent Educ 2003;67(9): Baig LA, Asad F. Introducing problem-based learning in a medical school with traditional/conventional curriculum. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2003;13(7): Fincham AG, Baehner R, Chai Y, Crowe DL, Fincham C, Iskander M, et al. Problem-based learning at the University of Southern California School of Dentistry. J Dent Educ 1997;61(5): Fincham AG, Shuler CF. The changing face of dental education: the impact of PBL. J Dent Educ 2001;65(5): Fasce E, Calderon M, Braga L, De Orue M, Mayer H, Wagemann H, et al. [Problem-based learning in the teaching of physics to medical students: comparison with traditional teaching]. Rev Med Chil 2001;129(9): Iputo JE, Kwizera E. Problem-based learning improves the academic performance of medical students in South Africa. Med Educ 2005;39(4): Hsu SC, Ong GH. Evaluation of problem-based learning: a lecturer s perspective. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2001;30(5): Susarla SM, Bergman AV, Howell TH, Karimbux NY. Problem-based learning and research at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine: a ten-year follow-up. J Dent Educ 2004;68(1): Garvey MT, O Sullivan M, Blake M. Multidisciplinary case-based learning for undergraduate students. Eur J Dent Educ 2000;4(4): Herzig S, Linke RM, Marxen B, Borner U, Antepohl W. Long-term follow up of factual knowledge after a single, randomised problem-based learning course. BMC Med Educ 2003;3(3). 14. Howell TH, Matlin K. Damn the torpedoes innovations for the future: the new curriculum at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine. J Dent Educ 1995;59(9): Santos-Gomez L, Kalishman S, Rezler A, Skipper B, Mennin SP. Residency performance of graduates from a problem-based and a conventional curriculum. Med Educ 1990;24(4): Kelly M, McCartan BE, Schmidt HG. Cognitive learning theory and its application in the dental curriculum. Eur J Dent Educ 1999;3(Suppl 1): Pearson SA, Rolfe I, Ringland C, Kay-Lambkin F. A comparison of practice outcomes of graduates from traditional and non-traditional medical schools in Australia. Med Educ 2002;36(10): Davis JD. Comparison of faculty, peer, self, and nurse assessment of obstetrics and gynecology residents. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99(4): Joshi R, Ling FW, Jaeger J. Assessment of a 360- degree instrument to evaluate residents competency in interpersonal and communication skills. Acad Med 2004;79(5): Gray J. Global rating scales in residency education. Acad Med 1996;71(1 Suppl):S Schmidt HG, van der Molen HT. Self-reported competency ratings of graduates of a problem-based medical curriculum. Acad Med 2001;76(5): Prince KJ, van Eijs PW, Boshuizen HP, van der Vleuten CP, Scherpbier AJ. General competencies of problembased learning (PBL) and non-pbl graduates. Med Educ 2005;39(4): Keck JW, Arnold L, Willoughby L, Calkins V. Efficacy of cognitive/noncognitive measures in predicting resident-physician performance. J Med Educ 1979;54(10): August 2007 Journal of Dental Education 1089
ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING Department of Geology University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez. Progress Report
 ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING Department of Geology University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez Progress Report Period of Report August to December of 2004. Purpose of our Assessment The fundamental purpose
ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING Department of Geology University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez Progress Report Period of Report August to December of 2004. Purpose of our Assessment The fundamental purpose
Tulare County Office of Education BTSA Induction Consortium
 Tulare County Office of Education BTSA Induction Consortium Biennial Report 5/17/10 Page 1 of 15 Local Educational Agency CD Code 54-10546 Section A, Part I: Contextual Information Biennial Report Contextual
Tulare County Office of Education BTSA Induction Consortium Biennial Report 5/17/10 Page 1 of 15 Local Educational Agency CD Code 54-10546 Section A, Part I: Contextual Information Biennial Report Contextual
Change the narrative for Chemistry, and change the major and minor requirements for Chemistry
 APC Document 37 Change the narrative for Chemistry, and change the major and minor requirements for Chemistry Effective Date: Fall 2016 1. Delete: On page 99-101, the Chemistry narrative, and the major
APC Document 37 Change the narrative for Chemistry, and change the major and minor requirements for Chemistry Effective Date: Fall 2016 1. Delete: On page 99-101, the Chemistry narrative, and the major
Dr. Amel Ibrahim Faragalla Yaagoub September, Curriculum Vitae. Amel/ Ibrahim Fragalla Yaagoub
 Curriculum Vitae Personal information First name(s)/ Surname(s) Address Amel/ Ibrahim Fragalla Yaagoub King Khalid University College of Dentistry Department of Periodontology Cell Phone 00966558744317
Curriculum Vitae Personal information First name(s)/ Surname(s) Address Amel/ Ibrahim Fragalla Yaagoub King Khalid University College of Dentistry Department of Periodontology Cell Phone 00966558744317
LEHMAN COLLEGE OF THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY CURRICULUM CHANGE
 LEHMAN COLLEGE OF THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY CURRICULUM CHANGE Name of Program and Degree Award: Chemistry BS Hegis Number: 1905 Program Code: 02663 Effective Term: Fall 2015
LEHMAN COLLEGE OF THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY CURRICULUM CHANGE Name of Program and Degree Award: Chemistry BS Hegis Number: 1905 Program Code: 02663 Effective Term: Fall 2015
Transforming Chemistry Education through the Green Chemistry Commitment. Amy S. Cannon, Ph.D. Executive Director Beyond Benign
 Transforming Chemistry Education through the Green Chemistry Commitment Amy S. Cannon, Ph.D. Executive Director Beyond Benign Headquarters located in Wilmington, MA Co-founded by John Warner and Amy Cannon
Transforming Chemistry Education through the Green Chemistry Commitment Amy S. Cannon, Ph.D. Executive Director Beyond Benign Headquarters located in Wilmington, MA Co-founded by John Warner and Amy Cannon
AS AN. Prepared by the. ASBOG Committee on Academic Assessment Randy L. Kath, Ph.D., PG, Chairman Richard K. Spruill, Ph.D., PG, Committee Member
 NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF STATE BOARDS OF GEOLOGY (ASBOG ) FUNDAMENTALS OF GEOLOGY (FG) EXAMINATION AS AN "ASSESSMENT EXAMINATION" Prepared by the ASBOG Committee on Academic Assessment Randy L. Kath, Ph.D.,
NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF STATE BOARDS OF GEOLOGY (ASBOG ) FUNDAMENTALS OF GEOLOGY (FG) EXAMINATION AS AN "ASSESSMENT EXAMINATION" Prepared by the ASBOG Committee on Academic Assessment Randy L. Kath, Ph.D.,
Mission Statement. Program outcomes
 Department: Geology Assessment coordinator: Sue DeBari During the 2009-2010 academic year, faculty and staff of the Geology Department engaged themselves in a review of our assessment procedures and materials,
Department: Geology Assessment coordinator: Sue DeBari During the 2009-2010 academic year, faculty and staff of the Geology Department engaged themselves in a review of our assessment procedures and materials,
RSC Analytical Division Strategy
 RSC Analytical Division Strategy 2013-2017 The Analytical Division aims to promote and support analytical chemistry at all levels from public outreach and school education to the most innovative and cutting
RSC Analytical Division Strategy 2013-2017 The Analytical Division aims to promote and support analytical chemistry at all levels from public outreach and school education to the most innovative and cutting
Grace College Department of Graduate Counseling Vital Statistics and Program Evaluation Outcomes Vital Statistics
 Grace College Department of Graduate Counseling Vital Statistics and Program Evaluation Outcomes 2017-2018 Vital Statistics 2017-2018 Enrollment as of 4/1/2018 (full-time) 113 Graduates (Summer 2017-Spring
Grace College Department of Graduate Counseling Vital Statistics and Program Evaluation Outcomes 2017-2018 Vital Statistics 2017-2018 Enrollment as of 4/1/2018 (full-time) 113 Graduates (Summer 2017-Spring
Programme Specification MSc in Cancer Chemistry
 Programme Specification MSc in Cancer Chemistry 1. COURSE AIMS AND STRUCTURE Background The MSc in Cancer Chemistry is based in the Department of Chemistry, University of Leicester. The MSc builds on the
Programme Specification MSc in Cancer Chemistry 1. COURSE AIMS AND STRUCTURE Background The MSc in Cancer Chemistry is based in the Department of Chemistry, University of Leicester. The MSc builds on the
Update on Green Chemistry Education
 Update on Green Chemistry Education IGSS 09 Carl Lecher, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Chemistry Director of the Marian University Institute for Green and Sustainable Science June 29 th -July 31 st, 2009
Update on Green Chemistry Education IGSS 09 Carl Lecher, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Chemistry Director of the Marian University Institute for Green and Sustainable Science June 29 th -July 31 st, 2009
Diffusion of GIS in Public Policy Doctoral Program
 Diffusion of GIS in Public Policy Doctoral Program By Fulbert Namwamba PhD Southern University This presentation demonstrate how GIS was introduced in the Public Policy Doctoral Program at Southern University,
Diffusion of GIS in Public Policy Doctoral Program By Fulbert Namwamba PhD Southern University This presentation demonstrate how GIS was introduced in the Public Policy Doctoral Program at Southern University,
Green Chemistry Commitment
 Info Kit Green Chemistry Commitment What is the Green Chemistry Commitment? The Green Chemistry Commitment (GCC) is a consortium program that unites the green chemistry community around shared goals and
Info Kit Green Chemistry Commitment What is the Green Chemistry Commitment? The Green Chemistry Commitment (GCC) is a consortium program that unites the green chemistry community around shared goals and
Grade 11 Student Electives Guidelines for 2015/16
 Grade 11 Student Guidelines for 2015/16 Overview As part of Abu Dhabi Education Council s continuous improvements efforts towards raising the standard of education in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, the Cycle
Grade 11 Student Guidelines for 2015/16 Overview As part of Abu Dhabi Education Council s continuous improvements efforts towards raising the standard of education in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, the Cycle
SOUTH DAKOTA BOARD OF REGENTS. Academic and Student Affairs ******************************************************************************
 SOUTH DAKOTA BOARD OF REGENTS Academic and Student Affairs AGENDA ITEM: 7 C (4) DATE: June 28-30, 2016 ****************************************************************************** SUBJECT: New Minor:
SOUTH DAKOTA BOARD OF REGENTS Academic and Student Affairs AGENDA ITEM: 7 C (4) DATE: June 28-30, 2016 ****************************************************************************** SUBJECT: New Minor:
Proposal Submission Data Quarterly Report Published: July Proposals by Sponsor Type
 Proposals by Sponsor Type Sponsors Federal 154 280 251 212 897 168 330 229 211 938 196 289 268 154 907 DHHS 45 114 111 108 378 57 122 114 97 390 62 103 109 87 361 NSF 63 108 96 43 310 67 162 73 47 349
Proposals by Sponsor Type Sponsors Federal 154 280 251 212 897 168 330 229 211 938 196 289 268 154 907 DHHS 45 114 111 108 378 57 122 114 97 390 62 103 109 87 361 NSF 63 108 96 43 310 67 162 73 47 349
Non-parametric methods
 Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Medicine Biostatistics course Non-parametric methods March 4&7, 2016 Instructor: Dr. Nimet İlke Akçay (ilke.cetin@emu.edu.tr) Learning Objectives 1. Distinguish
Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Medicine Biostatistics course Non-parametric methods March 4&7, 2016 Instructor: Dr. Nimet İlke Akçay (ilke.cetin@emu.edu.tr) Learning Objectives 1. Distinguish
PROGRAM EVALUATION PRELIMINARY REPORT. The following information is organized by program specialty areas for
 PROGRAM EVALUATION PRELIMINARY REPORT For the 2016-2017 academic year, DePaul Counseling Program faculty conducted a program evaluation by reviewing available data and surveying stakeholders. The following
PROGRAM EVALUATION PRELIMINARY REPORT For the 2016-2017 academic year, DePaul Counseling Program faculty conducted a program evaluation by reviewing available data and surveying stakeholders. The following
Table of Contents. The High 5s Project Interim Report
 Annexes Table of Contents Annex 1 The High 5s Project and LTAs websites... 127 Annex 2 Culture survey: international comparative report... 129 Annex 3 Context survey report: Med Rec... 165 Annex 4A Event
Annexes Table of Contents Annex 1 The High 5s Project and LTAs websites... 127 Annex 2 Culture survey: international comparative report... 129 Annex 3 Context survey report: Med Rec... 165 Annex 4A Event
Geospatial Science and Technology Model Courses and Certificate:
 Geospatial Science and Technology Model Courses and Certificate: Guidelines and Tools to Align Curriculum to Workforce Needs Ann Johnson Associate Director gisajohnson@delmar.edu Funded by National Science
Geospatial Science and Technology Model Courses and Certificate: Guidelines and Tools to Align Curriculum to Workforce Needs Ann Johnson Associate Director gisajohnson@delmar.edu Funded by National Science
Programme title: MChem Chemistry (Mathematical and Computational Chemistry)
 Faculty of Life Sciences Programme Specification Programme title: MChem Chemistry (Mathematical and Computational Chemistry) Academic Year: 2018/19 Degree Awarding Body: Final and interim award(s): University
Faculty of Life Sciences Programme Specification Programme title: MChem Chemistry (Mathematical and Computational Chemistry) Academic Year: 2018/19 Degree Awarding Body: Final and interim award(s): University
University of Cape Town
 1 University of Cape Town CHED Employment Equity Plan (draft): April 2015- March 2020 Name of Department/Faculty Department Centre for Higher Education Development (CHED) Transformation Committee Date
1 University of Cape Town CHED Employment Equity Plan (draft): April 2015- March 2020 Name of Department/Faculty Department Centre for Higher Education Development (CHED) Transformation Committee Date
PROGRAM EVALUATION REPORT The following information is organized by CACREP-Accredited Program Specialty Areas for
 PROGRAM EVALUATION REPORT 2016-2017 For the 2016-2017 academic year, DePaul Counseling Program faculty conducted a program evaluation by reviewing available data and surveying stakeholders. The following
PROGRAM EVALUATION REPORT 2016-2017 For the 2016-2017 academic year, DePaul Counseling Program faculty conducted a program evaluation by reviewing available data and surveying stakeholders. The following
INTEGRATING GEOSPATIAL PERSPECTIVES IN THE ANTHROPOLOGY CURRICULUM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO (UNM)
 INTEGRATING GEOSPATIAL PERSPECTIVES IN THE ANTHROPOLOGY CURRICULUM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO (UNM) VERONICA ARIAS HEATHER RICHARDS JUDITH VAN DER ELST DEPARTMENT OF ANTHROPOLOGY MARCH 2005 INTEGRATING
INTEGRATING GEOSPATIAL PERSPECTIVES IN THE ANTHROPOLOGY CURRICULUM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO (UNM) VERONICA ARIAS HEATHER RICHARDS JUDITH VAN DER ELST DEPARTMENT OF ANTHROPOLOGY MARCH 2005 INTEGRATING
ACGME Milestones/CCC. Content ACGME 3/9/2015. By the end of this session, the learner will be able to:
 ACGME Milestones/CCC A McLaren MD Banner Orthopaedic Residency Disclosures no monetary or administrative conflicts of interest related to this program or presentation Phoenix AZ By the end of this session,
ACGME Milestones/CCC A McLaren MD Banner Orthopaedic Residency Disclosures no monetary or administrative conflicts of interest related to this program or presentation Phoenix AZ By the end of this session,
Education for Tourism Development
 Abstract: Education for Tourism Development David Airey 1 University of Surrey, UK Successful tourist development depends in part upon appropriate education provision. At the same time, the needs of tourist
Abstract: Education for Tourism Development David Airey 1 University of Surrey, UK Successful tourist development depends in part upon appropriate education provision. At the same time, the needs of tourist
2016 ChE Undergraduate Advising Sessions Program
 2016 ChE Undergraduate Advising Sessions Program Educational Objectives During the first few years after graduation, a successful graduate of the program will: 1. Demonstrate achievement by applying a
2016 ChE Undergraduate Advising Sessions Program Educational Objectives During the first few years after graduation, a successful graduate of the program will: 1. Demonstrate achievement by applying a
BASIC PAY EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, /
 or BASIC PAY EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 00 1/ Cumulative Years of Service O- / 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 15.70 15.0 17.0.0 O-9 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
or BASIC PAY EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 00 1/ Cumulative Years of Service O- / 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 15.70 15.0 17.0.0 O-9 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
GEOGRAPHY MA, ASSESSMENT REPORT AY
 GEOGRAPHY MA, ASSESSMENT REPORT AY2012-2013 Programs: Geography MA Options Department: GSHAA Assessment Instruments and Student Outcomes This is an assessment report on three MA options in Geography in
GEOGRAPHY MA, ASSESSMENT REPORT AY2012-2013 Programs: Geography MA Options Department: GSHAA Assessment Instruments and Student Outcomes This is an assessment report on three MA options in Geography in
CHEMISTRY, B.S. (SCIENCE)
 Chemistry, B.S. (Science) 1 CHEMISTRY, B.S. (SCIENCE) Begin Campus: Any Penn State Campus End Campus: University Park Program Description This major provides a strong foundation in the theory and practice
Chemistry, B.S. (Science) 1 CHEMISTRY, B.S. (SCIENCE) Begin Campus: Any Penn State Campus End Campus: University Park Program Description This major provides a strong foundation in the theory and practice
UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY Department of CHEMISTRY UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM ASSESSMENT PLAN
 UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY Department of CHEMISTRY UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM ASSESSMENT PLAN 1. Introduction Assessment Plan for Bachelor in Arts and Bachelor in Science in the A&S Department of Chemistry Unit
UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY Department of CHEMISTRY UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM ASSESSMENT PLAN 1. Introduction Assessment Plan for Bachelor in Arts and Bachelor in Science in the A&S Department of Chemistry Unit
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES PROGRAM FOR THE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEGREE IN NATURAL SCIENCE Interdisciplinary Science (Option I)
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES PROGRAM FOR THE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEGREE IN NATURAL SCIENCE Interdisciplinary Science (Option I) Student Name: Email address: GE Year / Major Year: CIN: Phone:
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES PROGRAM FOR THE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEGREE IN NATURAL SCIENCE Interdisciplinary Science (Option I) Student Name: Email address: GE Year / Major Year: CIN: Phone:
On ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE in CBME: Assessment, Strategies and Pitfalls
 On ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE in CBME: Assessment, Strategies and Pitfalls Inf e r e n t i a l L e a p ASSESSMENT CONTEXT FUTURE CLINICAL PERFORMANCE LATENT ATTRIBUTES Inf e r e n t i a l L e a p Walter Tavares,
On ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE in CBME: Assessment, Strategies and Pitfalls Inf e r e n t i a l L e a p ASSESSMENT CONTEXT FUTURE CLINICAL PERFORMANCE LATENT ATTRIBUTES Inf e r e n t i a l L e a p Walter Tavares,
department of chemistry
 department of chemistry Why Chemistry? You enjoy problem solving. You want to learn about how the world works at the molecular level. Chemistry provides excellent preparation for graduate and professional
department of chemistry Why Chemistry? You enjoy problem solving. You want to learn about how the world works at the molecular level. Chemistry provides excellent preparation for graduate and professional
CHEMISTRY. Careers in Chemistry. Faculty. The Chemistry Department. Programs Offered. Repeat Policy
 CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT OFFICE Darwin Hall 300 (707) 664-2119 www.sonoma.edu/chemistry DEPARTMENT CHAIR Carmen Works Darwin 312 (707) 664-3084 Works@sonoma.edu Faculty Bogdan Negru Steven Farmer Jon M. Fukuto
CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT OFFICE Darwin Hall 300 (707) 664-2119 www.sonoma.edu/chemistry DEPARTMENT CHAIR Carmen Works Darwin 312 (707) 664-3084 Works@sonoma.edu Faculty Bogdan Negru Steven Farmer Jon M. Fukuto
Substantive Program Modification Form
 SOUTH DAKOTA BOARD OF REGENTS ACADEMIC AFFAIRS FORMS Substantive Program Modification Form UNIVERSITY: SDSU CURRENT PROGRAM TITLE: Pharmaceutical Sciences (B.S.) [S.BSPHS.PHS] CIP CODE: 51.001 UNIVERSITY
SOUTH DAKOTA BOARD OF REGENTS ACADEMIC AFFAIRS FORMS Substantive Program Modification Form UNIVERSITY: SDSU CURRENT PROGRAM TITLE: Pharmaceutical Sciences (B.S.) [S.BSPHS.PHS] CIP CODE: 51.001 UNIVERSITY
TPS for Problem Solving Dr. Edward Prather
 TPS for Problem Solving Dr. Edward Prather University of Arizona Center for Astronomy Education (CAE) http://astronomy101.jpl.nasa.gov Insights from the Univ. of Arizona AAU STEM reform effort in Physics
TPS for Problem Solving Dr. Edward Prather University of Arizona Center for Astronomy Education (CAE) http://astronomy101.jpl.nasa.gov Insights from the Univ. of Arizona AAU STEM reform effort in Physics
DFG form /18 page 1 of Valid for proposals submitted as of 1 January
 form 50.03 01/18 page 1 of 10 Guidelines Heisenberg Programme - Valid for proposals submitted as of 1 January 2018 - As a result of a resolution of the Joint Committee dated 4 July 2017, the Heisenberg
form 50.03 01/18 page 1 of 10 Guidelines Heisenberg Programme - Valid for proposals submitted as of 1 January 2018 - As a result of a resolution of the Joint Committee dated 4 July 2017, the Heisenberg
CHEMISTRY. Faculty. The Chemistry Department. Programs Offered. Repeat Policy. Careers in Chemistry
 CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT OFFICE Darwin Hall 300 (707) 664-2119 www.sonoma.edu/chemistry DEPARTMENT CHAIR Jennifer Whiles Lillig Faculty Steven Farmer Jon M. Fukuto Monica Lares Jennifer Whiles Lillig Mark
CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT OFFICE Darwin Hall 300 (707) 664-2119 www.sonoma.edu/chemistry DEPARTMENT CHAIR Jennifer Whiles Lillig Faculty Steven Farmer Jon M. Fukuto Monica Lares Jennifer Whiles Lillig Mark
Requirement for the Major in Chemistry with a Concentration in Biochemistry
 Department Chair: R. LaFever Department Office: Science Building II, Room 273 Telephone: (661) 654-3027 email: aparks@csub.edu Website: www.csub.edu/chemistry/ Faculty: K. Cohn, M.L. Dutton, A. Gebauer,
Department Chair: R. LaFever Department Office: Science Building II, Room 273 Telephone: (661) 654-3027 email: aparks@csub.edu Website: www.csub.edu/chemistry/ Faculty: K. Cohn, M.L. Dutton, A. Gebauer,
Space Syntax: Architecture and Cities MRes This programme information sheet includes details of the structure and content of the course.
 Space Syntax: Architecture and Cities MRes 2018-19 This programme information sheet includes details of the structure and content of the course. CONTENTS Overview 3 Structure 4 Content 5 Staff 6 Opportunities
Space Syntax: Architecture and Cities MRes 2018-19 This programme information sheet includes details of the structure and content of the course. CONTENTS Overview 3 Structure 4 Content 5 Staff 6 Opportunities
EMPLOYER SURVEY 2001 of the UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS
 EMPLOYER SURVEY 2001 of the UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS INTRODUCTION An employer survey was conducted as part of a series of surveys undertaken to meet the accreditation
EMPLOYER SURVEY 2001 of the UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS INTRODUCTION An employer survey was conducted as part of a series of surveys undertaken to meet the accreditation
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2011 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE
 COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2011 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: POSTDOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Clicking a table title will automatically direct you to that table in this document *Programs that combine two
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2011 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: POSTDOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Clicking a table title will automatically direct you to that table in this document *Programs that combine two
Cover/Signature Page - Abbreviated Template/Abbreviated Template with Curriculum
 Cover/Signature Page - Abbreviated Template/Abbreviated Template with Curriculum Institution Submitting Request: University of Utah Proposed Title: Astronomy & Astrophysics Emphasis for Physics BA/BS Currently
Cover/Signature Page - Abbreviated Template/Abbreviated Template with Curriculum Institution Submitting Request: University of Utah Proposed Title: Astronomy & Astrophysics Emphasis for Physics BA/BS Currently
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2014 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE
 COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2014 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: POSTDOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Clicking a table title will automatically direct you to that table in this document *Programs that combine two
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2014 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: POSTDOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Clicking a table title will automatically direct you to that table in this document *Programs that combine two
Master Syllabus Department of Geography GEOG 121: Geography of the Cultural Environment Course Description
 Master Syllabus Department of Geography GEOG 121: Geography of the Cultural Environment Course Description Geography of the Cultural Environment utilizes qualitative methods to investigate relationships
Master Syllabus Department of Geography GEOG 121: Geography of the Cultural Environment Course Description Geography of the Cultural Environment utilizes qualitative methods to investigate relationships
Chemistry Brigham Young University Idaho
 Department of Chemistry Chemistry Introduction Chemistry is the study of matter, energy, and their transformations. The principles of this discipline serve as a theoretical basis for a wide variety of
Department of Chemistry Chemistry Introduction Chemistry is the study of matter, energy, and their transformations. The principles of this discipline serve as a theoretical basis for a wide variety of
The Practice of Geospatial Leadership
 The Practice of Geospatial Leadership John P. Wilson, Ph.D. Professor of Spatial Sciences, Sociology, Architecture, Civil & Environmental Engineering, and Computer Science Founding Director, Spatial Sciences
The Practice of Geospatial Leadership John P. Wilson, Ph.D. Professor of Spatial Sciences, Sociology, Architecture, Civil & Environmental Engineering, and Computer Science Founding Director, Spatial Sciences
The 17 th Annual Graduate Student Research Symposium
 The University at Buffalo Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering Presents The 17 th Annual Graduate Student Research Symposium Single Molecule Tracking at Wet Interfaces Daniel K. Schwartz Chair
The University at Buffalo Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering Presents The 17 th Annual Graduate Student Research Symposium Single Molecule Tracking at Wet Interfaces Daniel K. Schwartz Chair
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET
 Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
Curriculum: The Impact of MCAT 2015
 American Chemical Society Chemistry and the Premedical Curriculum: The Impact of MCAT 2015 Chemical Sciences Roundtable May 22, 2013 Joel Shulman University of Cincinnati AAMC-HHMI Report on Scientific
American Chemical Society Chemistry and the Premedical Curriculum: The Impact of MCAT 2015 Chemical Sciences Roundtable May 22, 2013 Joel Shulman University of Cincinnati AAMC-HHMI Report on Scientific
Chemistry. Chemistry. Brigham Young University Idaho Department of
 Department of Introduction is the study of matter, energy, and their transformations. The principles of this discipline serve as a theoretical basis for a wide variety of fields such as agriculture, biology,
Department of Introduction is the study of matter, energy, and their transformations. The principles of this discipline serve as a theoretical basis for a wide variety of fields such as agriculture, biology,
So How Does Professional Licensure in Geoscience Impact Me?
 So How Does Professional Licensure in Geoscience Impact Me? Christopher C. Mathewson, PhD, PE, PG Regents Professor, Emeritus, TAMU Department of Geology & Geophysics Subject Matter Expert, Council of
So How Does Professional Licensure in Geoscience Impact Me? Christopher C. Mathewson, PhD, PE, PG Regents Professor, Emeritus, TAMU Department of Geology & Geophysics Subject Matter Expert, Council of
MEMO. SUBJECT: 2004 Annual Assessment Reports for BS Chemistry
 MEMO May 31,2004 TO: Dr. Richard Rakos, College of Science, - FROM: Robert Wei, Coordinator of Assessment for BS Chemistry /Z,LALL./ 11/4 - ( SUBJECT: 2004 Annual Assessment Reports for BS Chemistry Over
MEMO May 31,2004 TO: Dr. Richard Rakos, College of Science, - FROM: Robert Wei, Coordinator of Assessment for BS Chemistry /Z,LALL./ 11/4 - ( SUBJECT: 2004 Annual Assessment Reports for BS Chemistry Over
Advancing Green Chemistry Practices in Business
 Green Chemistry and Commerce Council: 6 th Annual GC3 Innovators Roundtable Advancing Green Chemistry Practices in Business Barbara Peterson, Ph.D. Marty Mulvihill, Ph.D. Program Director Executive Director,
Green Chemistry and Commerce Council: 6 th Annual GC3 Innovators Roundtable Advancing Green Chemistry Practices in Business Barbara Peterson, Ph.D. Marty Mulvihill, Ph.D. Program Director Executive Director,
PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS Degree: Bachelor of Science Major: Chemistry
 2017-2018 PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS Degree: Bachelor of Science Major: Chemistry About This Major... Chemistry students gain a unique perspective on the composition, properties, and reactivity of the substances
2017-2018 PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS Degree: Bachelor of Science Major: Chemistry About This Major... Chemistry students gain a unique perspective on the composition, properties, and reactivity of the substances
Academic Affairs Assessment of Student Learning Report for Academic Year
 Academic Affairs Assessment of Student Learning Report for Academic Year 2017-2018. Department/Program Chemistry Assessment Coordinator s Name: Micheal Fultz Assessment Coordinator s Email Address: mfultz@wvstateu.edu
Academic Affairs Assessment of Student Learning Report for Academic Year 2017-2018. Department/Program Chemistry Assessment Coordinator s Name: Micheal Fultz Assessment Coordinator s Email Address: mfultz@wvstateu.edu
Proposal for a new Minor in Geophysics
 1. Why the minor is needed: Proposal for a new Minor in Geophysics Geophysics is a major branch of the physical sciences that has until now been neglected by the University of Maryland. Geophysicists make
1. Why the minor is needed: Proposal for a new Minor in Geophysics Geophysics is a major branch of the physical sciences that has until now been neglected by the University of Maryland. Geophysicists make
Data Visualization (CSE 578) About this Course. Learning Outcomes. Projects
 (CSE 578) Note: Below outline is subject to modifications and updates. About this Course Visual representations generated by statistical models help us to make sense of large, complex datasets through
(CSE 578) Note: Below outline is subject to modifications and updates. About this Course Visual representations generated by statistical models help us to make sense of large, complex datasets through
CHEM 1413 Course Syllabus (CurricUNET) Course Syllabus
 Semester with Course Reference Number (CRN) CHEM 1413 Course Syllabus (CurricUNET) Course Syllabus College Chemistry I CHEM 1413 Instructor contact information (phone number and email address) Office Location
Semester with Course Reference Number (CRN) CHEM 1413 Course Syllabus (CurricUNET) Course Syllabus College Chemistry I CHEM 1413 Instructor contact information (phone number and email address) Office Location
geographic patterns and processes are captured and represented using computer technologies
 Proposed Certificate in Geographic Information Science Department of Geographical and Sustainability Sciences Submitted: November 9, 2016 Geographic information systems (GIS) capture the complex spatial
Proposed Certificate in Geographic Information Science Department of Geographical and Sustainability Sciences Submitted: November 9, 2016 Geographic information systems (GIS) capture the complex spatial
DEPARTMENT of CHEMISTRY AND BIOCHEMISTRY
 DEPARTMENT of CHEMISTRY AND BIOCHEMISTRY ACADEMIC GUIDANCE 2015-2016 PROGRAMS B.S. in Chemistry B.A. in Chemistry B.S. in Biochemistry B.S. in Physical Sciences with specialization in Chemistry or Physics
DEPARTMENT of CHEMISTRY AND BIOCHEMISTRY ACADEMIC GUIDANCE 2015-2016 PROGRAMS B.S. in Chemistry B.A. in Chemistry B.S. in Biochemistry B.S. in Physical Sciences with specialization in Chemistry or Physics
Department of Chemistry Learning Outcomes Assessment Report
 Department of Chemistry Learning Outcomes Assessment Report 2008-2009 I. Introduction: The chemistry department is a department characterized by a relatively young faculty, most of which have been hired
Department of Chemistry Learning Outcomes Assessment Report 2008-2009 I. Introduction: The chemistry department is a department characterized by a relatively young faculty, most of which have been hired
Microscale Chemistry Technology Exchange at Argonne National Laboratory - East
 Microscale Chemistry Technology Exchange at Argonne National Laboratory - East Rose Pausma (rpausma@depanlgov) and Deon Ettinger (dettinger@dep anlgov) Division of Educational Programs + Argonne National
Microscale Chemistry Technology Exchange at Argonne National Laboratory - East Rose Pausma (rpausma@depanlgov) and Deon Ettinger (dettinger@dep anlgov) Division of Educational Programs + Argonne National
Department Of Geography. MSc Applied GIS.
 Department Of Geography. MSc Applied GIS. This is a really exciting time to be in GIS, with new tools and new software allowing the application of GIS techniques to an ever-increasing range of fields.
Department Of Geography. MSc Applied GIS. This is a really exciting time to be in GIS, with new tools and new software allowing the application of GIS techniques to an ever-increasing range of fields.
Part 2: Data Collection and Analysis
 Part 2: Data Collection and Analysis STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOME 1: Possess an understanding of theoretical chemistry appropriate for a baccalaureate candidate. Criterion 1.1: Student performance in upper
Part 2: Data Collection and Analysis STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOME 1: Possess an understanding of theoretical chemistry appropriate for a baccalaureate candidate. Criterion 1.1: Student performance in upper
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2012 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE
 COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2012 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: POSTDOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Clicking a table title will automatically direct you to that table in this document *Programs that combine two
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2012 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: POSTDOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Clicking a table title will automatically direct you to that table in this document *Programs that combine two
Dave C. Swalm School of Chemical Engineering
 Mississippi State University 1 Dave C. Swalm School of Chemical Engineering Interim Director: Bill Elmore Office: 330 Swalm Chemical Engineering Building Chemical Engineering Chemical Engineering is a
Mississippi State University 1 Dave C. Swalm School of Chemical Engineering Interim Director: Bill Elmore Office: 330 Swalm Chemical Engineering Building Chemical Engineering Chemical Engineering is a
LEHMAN COLLEGE OF THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK. 1. Type of Change: Change in Degree Requirements
 Alpha Number: Hegis Code 1214 Program Code: 30600 1. Type of Change: Change in Degree Requirements 2. From: [The curriculum consists of 45 graduate credits and includes core courses, an area of specialization,
Alpha Number: Hegis Code 1214 Program Code: 30600 1. Type of Change: Change in Degree Requirements 2. From: [The curriculum consists of 45 graduate credits and includes core courses, an area of specialization,
= 1 i. normal approximation to χ 2 df > df
 χ tests 1) 1 categorical variable χ test for goodness-of-fit ) categorical variables χ test for independence (association, contingency) 3) categorical variables McNemar's test for change χ df k (O i 1
χ tests 1) 1 categorical variable χ test for goodness-of-fit ) categorical variables χ test for independence (association, contingency) 3) categorical variables McNemar's test for change χ df k (O i 1
NHS Occupational Health Workforce Survey 2009
 NHS Occupational Health Workforce Survey 2009 Analysed by the Workforce Review Team NHS Occupational Health Workforce Survey 2009 Table of Contents 1. Foreword... 7 2. NHS Plus... 8 3. Executive summary...
NHS Occupational Health Workforce Survey 2009 Analysed by the Workforce Review Team NHS Occupational Health Workforce Survey 2009 Table of Contents 1. Foreword... 7 2. NHS Plus... 8 3. Executive summary...
NERCHE Self-Assessment Rubric for the Institutionalization of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in Higher Education
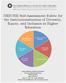 NERCHE Self-Assessment Rubric for the Institutionalization of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in Higher Education College of Education and Human Development University of Massachusetts Boston 100 Morrissey
NERCHE Self-Assessment Rubric for the Institutionalization of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in Higher Education College of Education and Human Development University of Massachusetts Boston 100 Morrissey
EASTERN OREGON UNIVERSITY Chemistry-Biochemistry
 EASTERN OREGON UNIVERSITY Chemistry-Biochemistry PROGRAM OBJECTIVES The chemistry-biochemistry degree offered by the Department of Chemistry-Biochemistry prepares chemistry majors for graduate work in
EASTERN OREGON UNIVERSITY Chemistry-Biochemistry PROGRAM OBJECTIVES The chemistry-biochemistry degree offered by the Department of Chemistry-Biochemistry prepares chemistry majors for graduate work in
Department of Chemistry
 Department of Chemistry Brandon University Department of Chemistry Phone (204) 727-9677 Faculty of Science Fax (204) 728-7346 www.brandonu.ca/chemistry Mission Statement To provide a high quality of education
Department of Chemistry Brandon University Department of Chemistry Phone (204) 727-9677 Faculty of Science Fax (204) 728-7346 www.brandonu.ca/chemistry Mission Statement To provide a high quality of education
Chemistry. Faculty Kent Davis, chair; Pablo Hilario, Denise Lee-Haye, Marie Pak, Robert Wilson Departmental Office: 355 Chan Shun Hall; (707)
 Faculty Kent Davis, chair; Pablo Hilario, Denise Lee-Haye, Marie Pak, Robert Wilson Departmental Office: 355 Chan Shun Hall; (707) 965-7597 Degrees and Programs Chemistry, B.S....77 Chemistry, B.A....78
Faculty Kent Davis, chair; Pablo Hilario, Denise Lee-Haye, Marie Pak, Robert Wilson Departmental Office: 355 Chan Shun Hall; (707) 965-7597 Degrees and Programs Chemistry, B.S....77 Chemistry, B.A....78
Georgia Preceptor Tax Incentive Program (GA-PTIP)
 Georgia Preceptor Tax Incentive Program (GA-PTIP) O B J E C T I V E S Understand how academic programs help reward communitybased physician preceptors with the tax incentive Describe the preceptor/rotation
Georgia Preceptor Tax Incentive Program (GA-PTIP) O B J E C T I V E S Understand how academic programs help reward communitybased physician preceptors with the tax incentive Describe the preceptor/rotation
Chemists. A guide for newcomers to British Columbia
 Contents 1. Working as a Chemist... 2 2. Skills, Education and Experience... 6 3. Finding Jobs... 7 4. Applying for a Job... 9 5. Getting Help from Industry Sources... 10 1. Working as a Chemist Job Description
Contents 1. Working as a Chemist... 2 2. Skills, Education and Experience... 6 3. Finding Jobs... 7 4. Applying for a Job... 9 5. Getting Help from Industry Sources... 10 1. Working as a Chemist Job Description
SCHOOL OF NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY. CURRICULUM Since: August Degree: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE Credits: 153. Program: MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
 SCHOOL OF NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY Degree: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE Credits: 5 CURRICULUM Since: August 08 Program: MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY Description: The Bachelor of Science with a Major in Medical Technology
SCHOOL OF NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY Degree: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE Credits: 5 CURRICULUM Since: August 08 Program: MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY Description: The Bachelor of Science with a Major in Medical Technology
Internal Audit Report
 Internal Audit Report Right of Way Mapping TxDOT Internal Audit Division Objective To determine the efficiency and effectiveness of district mapping procedures. Opinion Based on the audit scope areas reviewed,
Internal Audit Report Right of Way Mapping TxDOT Internal Audit Division Objective To determine the efficiency and effectiveness of district mapping procedures. Opinion Based on the audit scope areas reviewed,
Content Descriptions Based on the Common Core Georgia Performance Standards (CCGPS) CCGPS Coordinate Algebra
 Content Descriptions Based on the Common Core Georgia Performance Standards (CCGPS) CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Introduction The State Board of Education is required by Georgia law (A+ Educational Reform
Content Descriptions Based on the Common Core Georgia Performance Standards (CCGPS) CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Introduction The State Board of Education is required by Georgia law (A+ Educational Reform
Fair and Square Computation of Inverse -Transforms of Rational Functions
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EDUCATION, VOL. 55, NO. 2, MAY 2012 285 Fair and Square Computation of Inverse -Transforms of Rational Functions Marcos Vicente Moreira and João Carlos Basilio Abstract All methods
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EDUCATION, VOL. 55, NO. 2, MAY 2012 285 Fair and Square Computation of Inverse -Transforms of Rational Functions Marcos Vicente Moreira and João Carlos Basilio Abstract All methods
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET
 Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
PROGRAM MODIFICATION PROGRAM AREA
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY CHANNEL ISLANDS PROGRAM MODIFICATION PROGRAM AREA BIOLOGY Please use the following format to modify any existing program. Any deletions from an existing program need to be underlined
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY CHANNEL ISLANDS PROGRAM MODIFICATION PROGRAM AREA BIOLOGY Please use the following format to modify any existing program. Any deletions from an existing program need to be underlined
Informal Translation
 Informal Translation Examination regulations for the consecutive Master's program Geodetic Engineering in the Faculty of Agriculture at the University of Bonn On September 11, 2017 47th issue No. 25 September
Informal Translation Examination regulations for the consecutive Master's program Geodetic Engineering in the Faculty of Agriculture at the University of Bonn On September 11, 2017 47th issue No. 25 September
CHEMISTRY, BS. Degree Requirements. Admissions. Policies. Requirements. Admissions & Policies. Teacher Licensure. BS without Concentration
 Chemistry, BS CHEMISTRY, BS Banner Code: SC-BS-CHEM Academic Advising Phone: 70-99-07 Email: sslayden@gmu.edu Website: cos.gmu.edu/chemistry/undergraduate-programs/ This program is approved by the American
Chemistry, BS CHEMISTRY, BS Banner Code: SC-BS-CHEM Academic Advising Phone: 70-99-07 Email: sslayden@gmu.edu Website: cos.gmu.edu/chemistry/undergraduate-programs/ This program is approved by the American
Technical Review of the Analytical Benefits to be Gained from Collecting Staff-Level Data on ECEC
 Technical Review of the Analytical Benefits to be Gained from Collecting Staff-Level Data on ECEC Thomas Bäumer University of Bamberg 14th Meeting of the OECD Network on ECEC: "Curriculum and Child Development"
Technical Review of the Analytical Benefits to be Gained from Collecting Staff-Level Data on ECEC Thomas Bäumer University of Bamberg 14th Meeting of the OECD Network on ECEC: "Curriculum and Child Development"
B.S. Degrees from the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
 B.S. Degrees from the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 2015-2016 The Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry offers two B.S. degrees: a B.S. degree in Chemistry, and a B.S. degree in Biochemistry
B.S. Degrees from the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 2015-2016 The Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry offers two B.S. degrees: a B.S. degree in Chemistry, and a B.S. degree in Biochemistry
PROFESSIONAL-CLERICAL RATIO REPORT
 PROFESSIONAL-CLERICAL RATIO REPORT UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I FY 2009-10 University Budget Office University of Hawai i August 2010 File Reference: Management and Planning Support Folder, Faculty/Staff Reports
PROFESSIONAL-CLERICAL RATIO REPORT UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I FY 2009-10 University Budget Office University of Hawai i August 2010 File Reference: Management and Planning Support Folder, Faculty/Staff Reports
Shift Scheduling in Pediatric Emergency Medicine
 Shift Scheduling in Pediatric Emergency Medicine Presenter : Young-Chae Hong M.S.E. Co-Authors : Amy Cohn, Ph.D. & Ed O'Brien M.D. University of Michigan INFOMS at San Francisco 11 / 10 / 2014 Collaborators
Shift Scheduling in Pediatric Emergency Medicine Presenter : Young-Chae Hong M.S.E. Co-Authors : Amy Cohn, Ph.D. & Ed O'Brien M.D. University of Michigan INFOMS at San Francisco 11 / 10 / 2014 Collaborators
CALIFORNIA STATE POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY, POMONA ACADEMIC SENATE ACADEMIC PROGRAMS COMMITTEE REPORT TO THE ACADEMIC SENATE AP
 CALIFORNIA STATE POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY, POMONA ACADEMIC SENATE ACADEMIC PROGRAMS COMMITTEE REPORT TO THE ACADEMIC SENATE AP-009-167 BS IN GEOGRAPHY GEOSPATIAL ANALYSIS OPTION Academic Programs Committee
CALIFORNIA STATE POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY, POMONA ACADEMIC SENATE ACADEMIC PROGRAMS COMMITTEE REPORT TO THE ACADEMIC SENATE AP-009-167 BS IN GEOGRAPHY GEOSPATIAL ANALYSIS OPTION Academic Programs Committee
COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS OF MANITOBA INQUIRY PANEL DECISION
 COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS OF MANITOBA INQUIRY PANEL DECISION INQUIRY: IC2459 DR. RANDY RAYMOND ALLAN On November 10, 2016, a hearing was convened before an Inquiry Panel (the Panel ) of the College
COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS OF MANITOBA INQUIRY PANEL DECISION INQUIRY: IC2459 DR. RANDY RAYMOND ALLAN On November 10, 2016, a hearing was convened before an Inquiry Panel (the Panel ) of the College
SOLVING EQUATIONS AND DEVELOPING THE FOUNDATION FOR PROOFS
 SOLVING EQUATIONS AND DEVELOPING THE FOUNDATION FOR PROOFS 6.EE.6 and 6.EE.7 CONTENTS The types of documents contained in the unit are listed below. Throughout the unit, the documents are arranged by lesson.
SOLVING EQUATIONS AND DEVELOPING THE FOUNDATION FOR PROOFS 6.EE.6 and 6.EE.7 CONTENTS The types of documents contained in the unit are listed below. Throughout the unit, the documents are arranged by lesson.
Children s Understanding of Generalisation Transformations
 Children s Understanding of Generalisation Transformations V. Filippakopoulou, B. Nakos, E. Michaelidou Cartography Laboratory, Faculty of Rural and Surveying Engineering National Technical University
Children s Understanding of Generalisation Transformations V. Filippakopoulou, B. Nakos, E. Michaelidou Cartography Laboratory, Faculty of Rural and Surveying Engineering National Technical University
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2017 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE
 COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2017 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: DOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Table titles are hyperlinks to the tables within this document INTRODUCTION The Annual Report was created in 1998
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION 2017 ANNUAL REPORT ONLINE SUMMARY DATA: DOCTORAL PROGRAMS ^Table titles are hyperlinks to the tables within this document INTRODUCTION The Annual Report was created in 1998
T test for two Independent Samples. Raja, BSc.N, DCHN, RN Nursing Instructor Acknowledgement: Ms. Saima Hirani June 07, 2016
 T test for two Independent Samples Raja, BSc.N, DCHN, RN Nursing Instructor Acknowledgement: Ms. Saima Hirani June 07, 2016 Q1. The mean serum creatinine level is measured in 36 patients after they received
T test for two Independent Samples Raja, BSc.N, DCHN, RN Nursing Instructor Acknowledgement: Ms. Saima Hirani June 07, 2016 Q1. The mean serum creatinine level is measured in 36 patients after they received
Purpose Study conducted to determine the needs of the health care workforce related to GIS use, incorporation and training.
 GIS and Health Care: Educational Needs Assessment Cindy Gotz, MPH, CHES Janice Frates, Ph.D. Suzanne Wechsler, Ph.D. Departments of Health Care Administration & Geography California State University Long
GIS and Health Care: Educational Needs Assessment Cindy Gotz, MPH, CHES Janice Frates, Ph.D. Suzanne Wechsler, Ph.D. Departments of Health Care Administration & Geography California State University Long
Report for the Masters of Counseling at Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary Hamilton
 1 2016-2017 Report for the Masters of Counseling at Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary Hamilton 1. Annual reviews of current students MACO students are reviewed once annually, either for an Annual or
1 2016-2017 Report for the Masters of Counseling at Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary Hamilton 1. Annual reviews of current students MACO students are reviewed once annually, either for an Annual or
Duke University. Duke Biostatistics and Bioinformatics (B&B) Working Paper Series. Randomized Phase II Clinical Trials using Fisher s Exact Test
 Duke University Duke Biostatistics and Bioinformatics (B&B) Working Paper Series Year 2010 Paper 7 Randomized Phase II Clinical Trials using Fisher s Exact Test Sin-Ho Jung sinho.jung@duke.edu This working
Duke University Duke Biostatistics and Bioinformatics (B&B) Working Paper Series Year 2010 Paper 7 Randomized Phase II Clinical Trials using Fisher s Exact Test Sin-Ho Jung sinho.jung@duke.edu This working
ADVENTURES IN THE FLIPPED CLASSROOM FOR INTRODUCTORY
 ADVENTURES IN THE FLIPPED CLASSROOM FOR INTRODUCTORY A M Y N U S S B A U M A N D M O N N I E M C G E E STATISTICS S R C O S J U N E 5, 2 0 1 3 Amy Nussbaum and Monnie McGee SRCOS, June 5, 2013 FLIPPED
ADVENTURES IN THE FLIPPED CLASSROOM FOR INTRODUCTORY A M Y N U S S B A U M A N D M O N N I E M C G E E STATISTICS S R C O S J U N E 5, 2 0 1 3 Amy Nussbaum and Monnie McGee SRCOS, June 5, 2013 FLIPPED
