E. Dithianes (S,S-Acetals)
|
|
|
- Janice Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E. Dithianes (,-Acetals) bjectives By the end of this section you will be able to: 1) prepare,-acetals (dithianes) from aldehydes and ketones; 2) draw an arrow-pushing mechanism for the formation of dithianes from carbonyl compounds; 3) hydrolyse,-acetals back to the corresponding carbonyl compounds; 4) draw an arrow-pushing mechanism for this hydrolysis reaction; 5) use dithianes as acyl anion equivalents in synthesis; 6) rationalise the increased pk a of the α-c H in a dithiane compared with that in the corresponding,-acetal. Q? How might we synthesise an unsymmetrically substituted α-hydroxy ketone?
2 Retrosynthetic Analysis involving Polar Bond Disconnections The best polar bond disconnection in this type of molecule is obviously that between the two functional groups (i.e. the carbonyl group and the alcohol) as this breaks up the molecule into two of similar complexity. However, whichever disconnection we choose requires a reagent that displays the unnatural polarity of the functional group. ynthons that temporarily reverse the characteristic pattern of reactivity of a functional group are known as umpolung species. ne of the easiest methods for synthesising unsymmetrically substituted α-hydroxy ketones is to react an aldehyde or ketone (a so-called a 1 -synthon) with an acyl anion equivalent (a d 1 -synthon). Dithianes are one of the most important acyl anion equivalents; the,-acetal functionality serves as a temporary mask for the carbonyl functionality and permits formation of the requisite carbanion using a strong base (nbuli is most often used).
3 Dithianes as Acyl Anion Equivalents The pk a of an aldehyde C H is far too high (>45) for it to be abstracted by any commonly used base. Aldehydes and ketones are good electrophiles. ometimes we need to mask this reactivity pattern. We can do this by temporarily protecting the carbonyl group as an,-acetal. The pk a of the C H in an acetal is still too high for it to be abstracted by a base. However if we prepare the corresponding,-dithioacetal then we generate a species that possesses an α-c H that can now be abstracted, albeit with a strong base (e.g. nbuli).
4 We need to be able to rationalise the increased acidity of the α-c H in a dithiane compared with that in the corresponding,-acetal. There are a number of reasons why two sulfur atoms in the dithiane can more readily stabilise negative charge than can two (more electronegative) oxygen atoms in an acetal. 1) xygen in period 2 has no low-lying empty orbitals whereas sulfur in period 3 has empty 3d As allowing pπ dπ electron donation [order of carbanion stabilisation through this mechanism: CH 2 < < < e].
5 2) However, data suggest that the negative charge in lithiated dithiane is very localised on the carbon centre suggesting a more important mechanism for stabilising adjacent negative charge is through induced polarisation effects which are only significant on the larger group 6 atoms (, and even better, e). A Comparison between,-acetals and,-acetals,-acetals,-acetals hydrolytic stability formation pk a of α- hydrogen hydrolysis fairly acid labile readily formed from diol and cat. acid (under dehydrating conditions) too high to allow metallation readily hydrolysed back to C= compound under aqueous acidic conditions common protecting group for aldehydes and ketones hydrolytically fairly stable more difficult to form - normally use dithiol and a Lewis acid - removal of water less important pk a = 31 (dithiane) to 38 (substituted dithianes) - low enough to permit metallation with strong bases e.g. nbuli more difficult to hydrolyse - cannot normally use just aqueous acid rarely used as a simple protecting group - normally exploit its use as an acyl anion equivalent
6 Formation of,-acetals from Carbonyl Compounds Examples H TB Me Me Piv BF H H 3 Et 2 CH 2 Cl 2, 0 C, 1 h 95% TB Me Me Piv H H pta, HAc rt, 5 h, 99% chemoselective reaction 1,2-protection of enone
7 Reaction of Lithiated Dithianes Lithiated dithianes react with a variety of electrophiles: Carbonyl compounds. i) Reaction is more rapid with aldehydes than with ketones, which are less electrophilic. ii) Under normal conditions, lithiated dithianes react in a 1,2-fashion with enones and enals. Epoxides
8 Alkylating Reagents Double alkylation of commercially available dithiane provides a route to a masked form of an unsymmetrically substituted ketone: For useful references: 1) D. eebach, E. J. Corey, J. rg. Chem., 1975, 40, ; 2) P. C. Page, M. B. van Niel, J. C. Prodger, Tetrahedron 1989, 45, Hydrolysis of,-acetals to Unmask the Carbonyl Group,-Acetals are more difficult to hydrolyse than their oxygen congeners owing to i) the reduced Brønsted basicity of sulfur relative to oxygen, and ii) the higher barrier to formation of the thiocarbenium cationic intermediate. To facilitate deprotection it is necessary to enhance the nucleofugacity (i.e. the leaving group ability) of sulfur. This can be achieved in a number of ways: 1) Deprotection by Metal Coordination ulfur is a soft nucleophile/base (oxygen is a hard nucleophile/base) and therefore forms strong bonds with soft metals such as Hg(II), Ag(I), Tl(I) etc. Unmasking the carbonyl group in a dithiane is often carried out using heavy metal salts.
9 mechanism of deprotection The reaction is normally buffered using a base such as CaC 3 which can 'mop up' the liberated acid. Ag(I) and Tl(I) salts react similarly. 2) Alkylative Deprotection The leaving group ability of sulfur can be enhanced by alkylation. A variety of alkylating agents have been used e.g. MeI, Me 3 BF 4, Et 3 BF 4. The mechanism is similar to above. Example Piv Piv Piv Piv PhMe 2 i Me MeI, CaC 3 MeCN-H 2 12 h, 55 C 98% PhMe 2 i Me
10 3) xidative Deprotection xidation of the sulfur with a range of oxidising agents (e.g. Cl 2, Br 2, I 2, N-bromosuccinimide and mcpba) can also be used to facilitate dithiane hydrolysis. Example H TBDP Me Br N TBDP MeH 80% H Me For a review on the mechanism of hydrolysis of thioacetals: D. P. N. atchell, R.. atchell, Chem. oc. Rev., 1990, 19, ummary Dithianes, or dithioacetals, are formed by reacting a bis-thiol with an aldehyde or ketone, generally under Lewis acid catalysis. ince dithioacetals are not electrophilic species, this functional group can be used as a protecting group for an aldehyde or ketone. However since sulfur is more readily polarisable than oxygen, it can more efficiently stabilise proximal negative charge by setting up induced dipoles and through pπ-dπ bonding. As a result, the α-c H in a dithioacetal is much more acidic (pk a (dithiane) ~31) than the corresponding hydrogen in an,-acetal (pk a >40). This allows dithianes to be employed more usefully as acyl anion equivalents. Treatment of a dithiane with a strong base, such as nbuli, provides a nucleophilic acyl anion equivalent that reacts with a range of electrophiles including aldehydes and ketones, epoxides and reactive alkylating agents (R X). After the reaction, the carbonyl group can be unmasked by hydrolysis. In contrast to,-acetals that can be hydrolysed readily under aqueous acidic conditions, dithioacetals require modified conditions to effect this reaction. The sulfur has to be made into a better leaving group; this can be achieved by the use of heavy metals (e.g. Hg(II)), alkylating agents (e.g. Me 3 BF 4 ) or using oxidising agents (e.g. Cl 2 ).
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Lecture 15. More Carbonyl Chemistry. Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first O R'OH, H + OR" 2R"OH R + H 2 O OR" 3/8/16
 Lecture 15 More Carbonyl Chemistry R" R C + R' 2R" R C R" R' + 2 March 8, 2016 Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first R', + R R 1 emiacetal reacts further in acid to yield an acetal
Lecture 15 More Carbonyl Chemistry R" R C + R' 2R" R C R" R' + 2 March 8, 2016 Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first R', + R R 1 emiacetal reacts further in acid to yield an acetal
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH CARBOXYLIC ACIDS.
 RGANIC - BRWN 8E CH. 17 - CARBXYLIC ACIDS!! www.clutchprep.com RGANIC - BRWN 8E CH. 17 - CARBXYLIC ACIDS CNCEPT: CARBXYLIC ACID NMENCLATURE IUPAC: Replace alkane -e with Substituents are located using
RGANIC - BRWN 8E CH. 17 - CARBXYLIC ACIDS!! www.clutchprep.com RGANIC - BRWN 8E CH. 17 - CARBXYLIC ACIDS CNCEPT: CARBXYLIC ACID NMENCLATURE IUPAC: Replace alkane -e with Substituents are located using
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Advanced Organic Synthesis
 به نام خدا 3 Advanced Organic Synthesis Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran SYNTHETIC DESIGN 1. Retrosynthetic Analysis 2. Reversal of the Carbonyl Group Polarity (Umpolung)
به نام خدا 3 Advanced Organic Synthesis Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran SYNTHETIC DESIGN 1. Retrosynthetic Analysis 2. Reversal of the Carbonyl Group Polarity (Umpolung)
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
ANSWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMINATIONS CHEMISTRY 249H
 AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
Effect of nucleophile on reaction
 1 Effect of nucleophile on reaction X DS c X c c X DS c + X cleophile not involved in DS of S N 1 so does not effect the reaction (well obviously it controls the formula of the product!) cleophile has
1 Effect of nucleophile on reaction X DS c X c c X DS c + X cleophile not involved in DS of S N 1 so does not effect the reaction (well obviously it controls the formula of the product!) cleophile has
CHEM J-4 June 2013
 CHEM110 013-J-4 June 013 Describe the periodic trends exhibited by atomic radii. Justify these trends in terms of principal quantum number, n, and effective nuclear charge, Z eff. Atomic radius decreases
CHEM110 013-J-4 June 013 Describe the periodic trends exhibited by atomic radii. Justify these trends in terms of principal quantum number, n, and effective nuclear charge, Z eff. Atomic radius decreases
Advanced Organic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis
 123.312 Advanced rganic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis Tutorial Question 1. Propose a retrosynthetic analysis of the following two compounds. Your answer should include both the synthons, showing your thinking,
123.312 Advanced rganic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis Tutorial Question 1. Propose a retrosynthetic analysis of the following two compounds. Your answer should include both the synthons, showing your thinking,
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION
 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
p Bonds as Electrophiles
 Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Paper No and Title 14: Organic Chemistry IV (Advance Organic Synthesis and Supramolecular Chemistry and carbocyclic rings)
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title 14: Organic Chemistry IV (Advance Organic Synthesis and Supramolecular Chemistry and carbocyclic Module No and 5: C-C disconnections of alcohols Title Module Tag CHE_P14_M5
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title 14: Organic Chemistry IV (Advance Organic Synthesis and Supramolecular Chemistry and carbocyclic Module No and 5: C-C disconnections of alcohols Title Module Tag CHE_P14_M5
CHEMISTRY Topic #8: Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert:
 Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
18.8 Oxidation. Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium
 18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Structure of Ketones and Aldehydes Structure:
 Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Chapter 16. Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group. Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones. Synthesis of Aldehydes
 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Relative Reactivity of carbonyls: Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
 Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Aldehydes and Ketones
 Reading Chapter 12: 12.1-12.3, 12.6-12.9 Practice problems: in text problems and 19, 21-24, 28 Carbonyl Compounds II: Reactions of More Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives The Structure of 1 The Structure
Reading Chapter 12: 12.1-12.3, 12.6-12.9 Practice problems: in text problems and 19, 21-24, 28 Carbonyl Compounds II: Reactions of More Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives The Structure of 1 The Structure
Suggested solutions for Chapter 41
 s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
Lecture 1: Chemistry of the Carbonyl Group
 Lecture 1: Chemistry of the Carbonyl Group bjectives: By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1. identify and name all major carbonyl functional groups; 2. use a molecular orbital approach to describe
Lecture 1: Chemistry of the Carbonyl Group bjectives: By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1. identify and name all major carbonyl functional groups; 2. use a molecular orbital approach to describe
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
Suggested solutions for Chapter 27
 uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
Acids and Bases. Acids and Bases
 BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
Lecture 18. Oxidation and Reduction. Oxidation. Reduction O CH 4 CH 3 OH H C H. Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 18 xidation and Reduction C 4 C 3 C C C xidation Reduction March 27, 2018 Suppose you want to make this compound????? C + BrC 2 C 2 C?? CC 2 C 2 C 4-ydroxy-4-phenylbutanal It s an alcohol. Use
Lecture 18 xidation and Reduction C 4 C 3 C C C xidation Reduction March 27, 2018 Suppose you want to make this compound????? C + BrC 2 C 2 C?? CC 2 C 2 C 4-ydroxy-4-phenylbutanal It s an alcohol. Use
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols
 Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALCOHOLS AND CARBONYL COMPOUNDS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRO TO REDOX Oxidation reactions involve an increase in the content of a molecule Reduction reactions involve an increase in the content of a molecule EXAMPLE: Label the
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRO TO REDOX Oxidation reactions involve an increase in the content of a molecule Reduction reactions involve an increase in the content of a molecule EXAMPLE: Label the
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Still More Carbonyl Chemistry
 Lecture 17 Still More arbonyl hemistry ' ' A B P( 6 5 ) 3 A P( 6 5 ) 3 B March 22, 2018 eaction Theme The most common reaction of a carbonyl group is addition of a nucleophile to form a tetrahedral addition
Lecture 17 Still More arbonyl hemistry ' ' A B P( 6 5 ) 3 A P( 6 5 ) 3 B March 22, 2018 eaction Theme The most common reaction of a carbonyl group is addition of a nucleophile to form a tetrahedral addition
Chapter 2 Acids and Bases. Arrhenius Acid and Base Theory. Brønsted-Lowry Acid and Base Theory
 hapter 2 Acids and Bases A significant amount of chemistry can be described using different theories of acids and bases. We ll consider three different acid-base theories (listed in order of increasing
hapter 2 Acids and Bases A significant amount of chemistry can be described using different theories of acids and bases. We ll consider three different acid-base theories (listed in order of increasing
Alcohols. Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
 Alcohols Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group Uses: synthetic intermediate, cleanser, cosmetics, fuel, alcoholic beverages, etc. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
Alcohols Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group Uses: synthetic intermediate, cleanser, cosmetics, fuel, alcoholic beverages, etc. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides
 Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Synthesis Using Aromatic Materials
 Chapter 10 Synthesis Using Aromatic Materials ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION AND DIRECTED ORTHO METALATION Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 10.2 p Bonds Acting as Nucleophiles Copyright
Chapter 10 Synthesis Using Aromatic Materials ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION AND DIRECTED ORTHO METALATION Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 10.2 p Bonds Acting as Nucleophiles Copyright
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORKSHEET 1
 EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 2 - COVALENT BONDING AND CHEMICAL REACTIVITY
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: Acids and Bases
 There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chem 263 March 28, 2006
 Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
EWG EWG EWG EDG EDG EDG
 Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Alkenes and benzene both react with bromine but alkenes are much more reactive.
 2 Answer all the questions. 1 Alkenes and benzene both react with bromine but alkenes are much more reactive. (a) Explain the relative resistance to bromination of benzene compared with alkenes. In your
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Alkenes and benzene both react with bromine but alkenes are much more reactive. (a) Explain the relative resistance to bromination of benzene compared with alkenes. In your
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hem A225 Notes Page 67 I. Introduction hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (=) with no other heteroatoms attached. An aldehyde has at least one hydrogen attached;
hem A225 Notes Page 67 I. Introduction hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (=) with no other heteroatoms attached. An aldehyde has at least one hydrogen attached;
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
S N 2 and E2 Mechanisms (strong base/nucleophile competition reacting at a carbon or reacting at a proton)
 Electrophile (Lewis Acid) = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor (can also be an acidic proton = onsted acid) ucleophile (Lewis Base) = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron pair
Electrophile (Lewis Acid) = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor (can also be an acidic proton = onsted acid) ucleophile (Lewis Base) = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron pair
OUTLINE 535 LECTURE 4 (2003) Page 31
 UTLINE 535 LECTURE 4 (2003) Page 31 Protecting Groups in rganic Chemistry for xygen-based functionality. References: 1.1. Comprehensive Synthetic rganic Chemistry, 6, 631-701. 1.2. Protective Groups in
UTLINE 535 LECTURE 4 (2003) Page 31 Protecting Groups in rganic Chemistry for xygen-based functionality. References: 1.1. Comprehensive Synthetic rganic Chemistry, 6, 631-701. 1.2. Protective Groups in
S N 1 Displacement Reactions
 S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
Chapter 12. Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds Oxidation-Reduction & Organometallic Compounds. Structure
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Reactions of Chapter 10 Worksheet and Key
 1) Alcohol Fermentation Reactions of Chapter 10 Worksheet and Key Alcohol fermentation is a series of chemical reaction that convert sugar molecules, such a glucose, into ethanol and C 2. The overall reaction
1) Alcohol Fermentation Reactions of Chapter 10 Worksheet and Key Alcohol fermentation is a series of chemical reaction that convert sugar molecules, such a glucose, into ethanol and C 2. The overall reaction
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones
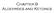 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones 9.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al The aldehyde functional group is always carbon
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones 9.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al The aldehyde functional group is always carbon
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
Chapter 2 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Polar Reactions. Indian Institute of Technology Madras CH 3 OH 2 -H 2 O CH 2. HCl. H 3 C CH 3 neopentyl alcohol CH 3 CH 3. 1,2-shift -H + H 3 C
 Polar Reactions Important points to be discussed in this module: 1. Chemistry of Carbocations with respect to: a. 1,2-shifts of carbocations b. Pinacol-pinacolone rearrangement c. Semipinacolone rearrangement
Polar Reactions Important points to be discussed in this module: 1. Chemistry of Carbocations with respect to: a. 1,2-shifts of carbocations b. Pinacol-pinacolone rearrangement c. Semipinacolone rearrangement
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours)
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Chem 263 Nov 24, Properties of Carboxylic Acids
 Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
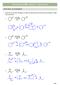 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
Nomenclature Question
 Topic 13: i-licker Slides Beauchamp 1 omenclature Question 2 2 a. 1,2-diamino-5,11-dioxo-6-isopropoxy-7-hydroxy-9-cyanoundec-3E-en-1-one b. 3-cyano-5-hydroxy-6-isopropoxy-7,11-dioxo-10,11-diaminoundec-8E-enal
Topic 13: i-licker Slides Beauchamp 1 omenclature Question 2 2 a. 1,2-diamino-5,11-dioxo-6-isopropoxy-7-hydroxy-9-cyanoundec-3E-en-1-one b. 3-cyano-5-hydroxy-6-isopropoxy-7,11-dioxo-10,11-diaminoundec-8E-enal
Chemical tests to distinguish carbonyl compounds
 R hemistry A 432 arbonyl ompounds arbonyl hemistry arbonyl compounds are those which contain >= - aldehydes - ketones - carboxylic acids - esters You should recall how to name aldehydes and ketones: 3
R hemistry A 432 arbonyl ompounds arbonyl hemistry arbonyl compounds are those which contain >= - aldehydes - ketones - carboxylic acids - esters You should recall how to name aldehydes and ketones: 3
Suggested solutions for Chapter 30
 s for Chapter 30 30 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this synthesis of a tricyclic aromatic heterocycle. 2 Cl base A simple exercise in the synthesis of a pyridine fused to a pyrrole (or an indole with
s for Chapter 30 30 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this synthesis of a tricyclic aromatic heterocycle. 2 Cl base A simple exercise in the synthesis of a pyridine fused to a pyrrole (or an indole with
Week 6 notes CHEM
 Week 6 notes EM1002 2009 Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 1 Note
Week 6 notes EM1002 2009 Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 1 Note
CHAPTER 2. Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
 CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction
 P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
Ethers can be symmetrical or not:
 Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
CHAPTER 20: MORE ABOUT OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS Oxidation Reduction Reactions of Organic Compounds: An Overview
 CHAPTER 20: MORE ABOUT OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS In an oxidation-reduction reaction (redox reaction), one species loses electrons and one gains electrons. The species that loses electrons is oxidized,
CHAPTER 20: MORE ABOUT OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS In an oxidation-reduction reaction (redox reaction), one species loses electrons and one gains electrons. The species that loses electrons is oxidized,
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides. Chapter Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry
 Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Chapter 17-18 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Introduction Structure and Bonding Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH) bonded to an sp 3 hybridized carbon. 2
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Chapter 17-18 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Introduction Structure and Bonding Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH) bonded to an sp 3 hybridized carbon. 2
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides
 Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids. Acids Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids.
 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are abundant in nature and in pharmaceuticals. 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids The US produces over 2.5 million tons of acetic acid per year, which
21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are abundant in nature and in pharmaceuticals. 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids The US produces over 2.5 million tons of acetic acid per year, which
Hour Examination # 1
 CHEM 2410 Organic Chemistry 1 Fall 2017 Exam # 1 Problem Booklet Page 1 of 11 CHEM 2410 Organic Chemistry 1 Fall 2017 Exam Booklet No. Instructors: Paul Bracher & Erin Whitteck Hour Examination # 1 Wednesday,
CHEM 2410 Organic Chemistry 1 Fall 2017 Exam # 1 Problem Booklet Page 1 of 11 CHEM 2410 Organic Chemistry 1 Fall 2017 Exam Booklet No. Instructors: Paul Bracher & Erin Whitteck Hour Examination # 1 Wednesday,
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key
 CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
Synthetic Organic Chemistry Final Exam Resit (6KM33) Thursday, 26th June, 2014, 9:00 12:00 (3 h)
 Synthetic rganic Chemistry Final Exam Resit (6KM33) Thursday, 26th June, 2014, 9:00 12:00 (3 h) This is an open-book written exam. The course textbooks (Warren & Wyatt, 2 nd Ed.) with personal notes and
Synthetic rganic Chemistry Final Exam Resit (6KM33) Thursday, 26th June, 2014, 9:00 12:00 (3 h) This is an open-book written exam. The course textbooks (Warren & Wyatt, 2 nd Ed.) with personal notes and
Organocopper Reagents
 rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
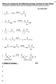 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH. 3 - ACIDS AND BASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 4 types of common chemical reactions that we need to be familiar with in organic chemistry 1. Acid-Base Reactions: Two molecules
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 4 types of common chemical reactions that we need to be familiar with in organic chemistry 1. Acid-Base Reactions: Two molecules
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher. Quiz # 4. Due in Monsanto Hall 103 by: Friday, April 4 th, 2014, 7:00 p.m.
 CHEM 347 Quiz # 4 Spring 2014 Page 1 of 9 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 4 Due in Monsanto Hall 103 by: Friday, April 4 th, 2014, 7:00 p.m. Student Name (Printed)
CHEM 347 Quiz # 4 Spring 2014 Page 1 of 9 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 4 Due in Monsanto Hall 103 by: Friday, April 4 th, 2014, 7:00 p.m. Student Name (Printed)
