Dark Matter Searches WIMPs
|
|
|
- Ann Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dark Matter Searches WIMPs Marc Schumann U Freiburg The Future of Non-Collider-Physics Mainz, April 27, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de with input from K. Eitel, M. Lindner, F. Petricca, T. Pollmann, S. Schönert, C. Weinheimer 1
2 Direct Detection in Germany U Münster (XENON / DARWIN) TU Dresden (DARWIN) U Mainz (XENON / DARWIN) MPIK Heidelberg (XENON, DARWIN) KIT (EDELWEISS / DARWIN) U Tübingen (CRESST) U Freiburg (XENON / DARWIN) MPP München (CRESST) TU München (CRESST) 2
3 Direct WIMP Search WIMP Elastic Scattering of WIMPs off target nuclei nuclear recoil WIMP v ~ 230 km/s Nuclear Recoil ER ~ O(10 kevnr) Detectable Signal Electronic Recoil Recoil Spectra: Xenon Germanium A² Argon Silicon form factor m =100 GeV/c² =4x10 43 cm² 3
4 Direct WIMP Search How to build a WIMP detector? Elastic Scattering of WIMPs off target nuclei nuclear recoil Recoil Spectra: large total mass, high A very low energy threshold ultra low background good signal / background discrimination Xenon Germanium A² Argon Silicon form factor m =100 GeV/c² =4x10 43 cm² 4
5 Background Sources muons muoninduced neutrons pp+7be neutrinos ER signature high-e neutrinos CNNS bg NR signature neutrons from (α,n) and sf natural γ-bg natural γ-bg neutrons from (α,n) and sf target-intrinsic bg: α-, β-, γ-radiation, n; activation, impurities, 2νββ Electronic Recoils Nuclear Recoils (gamma, beta) (neutron, WIMPs) 6
6 Avoid Backgrounds Shielding deep underground location large shield (Pb, water, poly) active veto (µ, coincidence) self shielding fiducialization Astropart. Phys. 35, 573 (2012) Background Suppression Use of radiopure materials Use knowledge about expected WIMP signal WIMPs interact only once single scatter selection requires some position resolution WIMPs interact with target nuclei nuclear recoils exploit different de/dx from signal and background Examples: scintillation pulse shape charge/light ratio ionization yield 8
7 Direct WIMP Detection Crystals (NaI, Ge, Si) Cryogenic Detectors Liquid Noble Gases Tracking: DRIFT, DMTPC MIMAC, NEWS NEWAGE CUORE Phonons SuperCDMS EDELWEISS CoGeNT CDEX Malbek DAMIC NEWS (gas) CRESST COSINUS Charge Superheated Liquids: PICO SIMPLE Light XENON, LUX/LZ ArDM, Panda-X DarkSide, DARWIN DEAP-3600, CLEAN DAMA, KIMS XMASS, COSINE ANAIS, SABRE 9
8 The WIMP Parameter Space spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions coupling unknown asymmetric dark matter coupling strength unknown MPs I W c i r gene m SUSY) (e.g. fro WIMP mass unknown 10
9 Current Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions some results are missing... 11
10 Neutrino Floor spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions neutrino floor PRD 89, (2014) some results are missing... 13
11 Neutrino Floor JCAP 01, 044 (2014) spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions neutrino floor PRD 89, (2014) Interactions from coherent neutrino-nucleus scattering (CNNS) will dominate ultimate background for direct detection some results are missing... 14
12 High WIMP Masses spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions For higher WIMP masses, simply extrapolate limits Search dominated by liquid noble gas TPCs: massive detectors filled with liquid Xe or Ar some results are missing... 15
13 Low WIMP Masses Current CRESST limits go down to 500 kev/c² spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions Search dominated by cryogenic detectors: crystals cooled down to mk temperatures some results are missing... 16
14 Cryogenic Detectors measure charge or light and heat (phonons) in crystals: Ge, (Si), CaWO4 E deposition temperature rise ΔT ~ μk ( TES) requires detecors with low heat capacity at mk temperatures Ge: SuperCDMS, EDELWEISS, CDEX CaWO4: CRESST Re co il n ec tro El Very good discrimination BUT: need to reject surface events Ionization Charge and heat measurement s 600 g very low threshold in HV mode Nu rr clea Heat ls ec oi Light and heat measurement very good discrimination multi-isotope target 17
15 Ge: Very low WIMP masses very low threshold for sensitivity to very low-mass WIMPs: amplify signal HV operation: Neganov-Luke effect to amplify charge signal convert work done by E-field on e -hole pairs to phonons E bias voltage initial recoil 3 ev/pair CDMSlite PRL 116, (2016) 625 g izip detector, 70 kg d exposure Vb=69 V, 56 evee threshold! 14 evee resolution no ionization measured no ER rejection kev 18
16 Cryogenic Detectors: Status Modane mm IZPs (1.4 kg Ge) results on low-mass LNGS The low mass record PRL 112, (2014) new low-threshold result: - 8 Ge detectors - lowest thresholds ( kevnr) no significant excess 40 better than 5 GeV/c² CaWO4: CRESST Soudan BDT: JCAP 05, 019 (2016) PL: EPJ C 76, 548 (2016) Not operational anymore! PRL 116, (2016) Soudan - target: CaWO4 multi-element material - bg reduced successfully data taking , 52 kg d - new result EPJ C, 76, 25 (2016) 300 g crystal with 307 evnr threshold EPJ C, 76, 25 (2016) lowest threshold lowest background EPJ C 74, 3184 (2014) 1 GeV/c² 19
17 Upcoming Projects basically funded CRESST-II EDELWEISS SuperCDMS Germanium 25t d some results are missing... 20
18 Ge/Si: SuperCDMS PRD 95, (2017) selected by NSF-DOE downselection ~50 kg target (upgrade to 400 kg possible) low threshold focus on 1-10 GeV/c² mass range Move Soudan SNOLAB: deeper lab, better materials & shield, improved resolution, electronics, mm IZPs (1.4 kg Ge, 0.6 kg Si) Timeline: /19: construction - comissioning/science by beyond 2024:upgrade mass? until then: - CUTE detector R&D platform at SNOLAB cryostat oversized: offers prime real-estate with <40 mk, ultra low-noise, ultra-low background 21
19 Ge: EDELWEISS-III continue operatation of a few kg of Ge detectors in Modane Lab (F) 800 g Ge crystals measure ionization and heat (NTD sensors) interdigitized electrodes: fiducialization (~600 g) focus on low-mass WIMPs (HV or lite mode) Strategy beyond 2019: potential to cooperate with SNOLAB 22
20 CaWO4: CRESST-III CRESST-III: lower threshold to 100 evnr Lead technologies by German groups 500eV pulse arxiv: smaller, cleaner, self-grown crystals (300 g 25 g) - all-scintillating detector design avoid partial energy depositions - improve signal-to-noise - still able to discriminate ER/NR Status: Prototype exceeds design goal: 50 evnr threshold 6 modules with <100 ev threshold LNGS CRESST-III Timeline Phase 1 (2017): faster than SuperCDMS 50 kg days (1 y), design goal threshold (100 ev) Phase 2 (>2019): approaching the neutrino floor 1000 kg days (2 y, 100 detectors) background reduced by factor evnr threshold Beyond CRESST-III: depends on WIMP results CRESST detectors sensitive to CNNS etc. 23
21 Technical Challenges CRESST (CaWO4) EDELWEISS / SuperCDMS (Ge) at which energy does ER/NR discrimination not work anymore? no ER rejection in HV mode background challenging detection experiment or always background limited? phonon resolution crucial environmental noise reduction (no photons created in 10 ev regime) smaller crystals lower threshold technical challenge to reach required large exposure radiopurity of crystals becomes very important background: many small crystals: small S/V ratio bg from instrumentation/cables etc? heat-only events in EDW: dominant and reproducible low-e background currently not fully understood (stress from gluing?) L. ICHEP 2016 factor 100 reduction required HV detector background dominated by cosmogenic activation Ge isotopes 3H production in Ge/Si Astropart. Phys. 91, 51 (2017) 25
22 High WIMP Masses spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions some results are missing... 26
23 Liquid Noble Gases: Detector Concepts Single Phase Detector Time Projection Chamber PMT pos HV gas E S1 Time + no high voltage, very high light yield M. O(cm) resolution, no double scatter rejection Schumann (Freiburg) Direct WIMP Searches Amplitude Amplitude liquid target neg HV S1 S2 Time + O(mm) resolution, S2/S1 NR rejection technical challenges (HV), less light 27
24 Noble Liquid Targets Target LXe LAr Atomic Number Atomic mass Boiling Point Tb [K] Liq. Tb [g/cm³] Fraction in Atmosphere Price 0.09 $$$ 9340 ($) Scintillator Scint. Wavelength [nm] Ionizer W (E to generate e-ion pair) [ev] Radioactive Isotopes ER Rejection Odd Isotopes ( SD couplings) 136 Xe (2νββ) ok (2-phase only) 50% (129Xe, 131Xe) 39 Scalability Projects [running, in preparation] ~4 ~2½ no consumable; can be re-used Ar-depleted gas: $$$ 39 Ar (~1 Bq/kg) great (high-e only) 28
25 ER Background Rejection LAr Pulse shape discrimination (PSD): Lifetimes of singlet and triplet states: Ar: 5 ns, 1.6 µs Xe: 4 ns, 22 ns Ratio Ntrip/Nsing depends on de/dx the interaction type LAr: excellent ~ irrelevant Nuclear Recoils Electronic Recoils PRC 78, (2008) LXe: ~ high threshold required NIM A 612, 328 (2010) Charge-Light-Ratio (S2/S1): Signal partition in light/charge depends on de/dx the interaction type NR PRL 107, (2011) ER Astropart. Phys. 85, 23 (2016) Edrift [kv/cm] 122 kev NR acc ER rej [PE/keV] [%] [%] XENON XENON LUX ZEPLIN-III < K. Ni APP14 works down to low-e threshold works for LXe and LAr significant loss of acceptance 29
26 Relevant Backgrounds LXe LAr Radioactivity Laboratory (ER, NR) Muon-induced neutrons Detector materials Gamma (ER) Neutrons (NR) Target Intrinsic isotopes (ER) 39 Ar 85 Kr 222 Rn price: high threshold price: high threshold Neutrinos NR: 8B, atmospheric ER: pp, 7Be threshold too high for 8B ER rejection mandatory Artefacts???? all experiments are underground and sufficiently shielded all TPCs employ fiducialization and multiple-scatter rejection 30
27 DarkSide: Ar-depleted Argon 39 content: M. Wada, Moriond 2017 extract underground Ar (UAr) in CO2 well in Colorado cryogenic FNAL Ar reduced by factor ~1400! 155 kg UAr produced in 6 years effort 39 Future: mass-production planned Colorado extract 100 kg/day Sardegna Result: DarkSide t d exposure PRD 93, (2016) column: 350m high, 1.5m OD isotopic depletion 31
28 LXe: Krypton Removal Two methods: cryogenic distillation (XMASS, XENON) chromatography (LUX) Example: XENON1T nat goal: Kr/Xe = 0.2 ppt (below level of pp-neutrinos) achieved by novel online distillation: nat Kr/Xe = (0.36±0.06) ppt achieved lowest value in LXe experiments ever E R P I M LI N Y R A XENON1T column has produced large gas sample <0.048 ppt = (90% CL) 4x cleaner than needed arxiv:
29 LXe: Radon Background WIMP ROI: 1 12 kev interval PR EL IM IN AR Y XENON1T JCAP 04, 027 (2016) Current Strategy Example: goal XENON1T measured avoid Rn emanation by selecting clean materials 10 µbq/kg (11±2) µbq/kg prelim. arxiv: Future Strategy active Rn removal Example: cryogenic distillation XENON1T distillation column XENON100 demonstrated reduction factor >27 (@ 95% CL) 33
30 Noble Gas: Single Phase Detectors Kamioka (JP) LXe LAr light pulse-shape for discrimination 3.6t liquid argon target; high 39Ar background in natar (~1 Bq/kg) data taking right now... high light yield, results expected for TAUP 2017 sensitivity: GeV/c² F. Retiere (LIDINE 2015) 832 kg LXe target, 642 PMTs very high light yield, low threshold (0.5 kevee) BUT: no possibility to reject NRs many results: summary: arxiv: background limited! stable data taking since >2 years SNOLAB (CA) 34
31 Running dual phase detectors LNGS (IT) LAr PRD 93, (2016) - 46 kg LAr, which is 39 Ar-depleted by a factor d 37kg exposure - no event in ROI - still taking data (mid March: >35 kg y data) CJPL (CN) LXe LNGS (IT) LXe PRL 117, (2016) JCAP 04, 027 (2016) - 60cm 60cm, 500 kg target - 2nd largest operational LXe TPC - 96cm 96cm, 2.0 t target - largest LXe TPC taking data - Rn and Kr background goals basically achieved New result July 2016: - combines data from 2 runs (85Kr differs by factor 10) Expect first result soon! kg d = 0.1 t y exposure - no signal excess - best limit above ~4.5 GeV/c² - still taking data aim for 2 years of data 50 PE ~ 25 kevr Goal: < GeV/c² Finished projects: LNGS (IT), SURF (USA) LXe 36
32 Upcoming Projects basically funded some results are missing... 37
33 DarkSide-20k LAr scale up DS-50 by factor 400: 30t LAr total 20t fiducial focus on high-mass region >400 GeV/c² keep strategy for background-free search with 100 t y exposure large amount of underground Ar: URANIA (+ARIA) pulse-shape discrimination high LY needed Readout by two arrays liquid scintillator neutron veto of grouped SiPMs: 14 m² total start LNGS within 2021 Requirements: PDE: 45% Dark Count Rate: 0.1 Hz/mm² 39
34 LZ LUX/ZEPLIN LXe arxiv: LZ = LUX+ZEPLIN selected by 2014 US DOE-NSF downselection to be SURF (USA) 50 larger than LUX 10t total LXe mass, 7t active target, 5.6t fiducial target 488 R11410 PMTs 2015: started procurement of xenon gas, PMTs,... 06/2020: start commisioning goal: ~50 GeV/c² after 15 t y exposure 40
35 XENONnT LNGS using XENON1T systems - 6.0t active target ~8t total mass R11410 PMTs - projected to start science in goal: factor 10 better than XENON1T ~140cm FC sensitivity ~50 GeV/c² (conservative, no background subtraction) XENON1T XENONnT LZ increase sensitivity by an order of magnitude LZ information from: LXe JCAP 04, 027 (2016) Existing/operational: Muon Veto Cryostat Support Outer Cryostat in-lxe Cabling LXe storage system Cryogenic system Purification system Kr removal responsibility or participation DAQ 95% of Electronics Calibration System 260 PMTs >8t of LXe Screening facilities Started: 230 new PMTs ordered TPC/Cryostat design first material orders Screening campaign Neutron veto studies 2nd storage vessel ordered Rn reduction system design purification improvements etc. 41
36 Spin-dependent WIMP Couplings WIMP-neutron scattering: dominated by LXe TPCs also: Ge, NaI, CsI, CF3I, C3F8 WIMP-proton scattering: dominated by bubble chambers (CF3I, C3F8) also: Xe, NaI, CsI PRL 116, (2016) LUX LUX nt / ON N E X LZ excellent complementarity to LHC searches (ATLAS, CMS) PICO-60 XENONnT / LZ excellent complementarity to indirect searches (IceCube, SuperK) 42
37 Towards the Neutrino Floor LXe LAr 260 cm DARWIN ~50t total LXe ~40 t LXe TPC aim for 200 t y exposure start operations at LNGS by 2026?? lots of sensitivity studies darwin observatory.org M. Moriond 2017 JCAP 11, 017 (2016) ARGO ~300t depleted Ar TPC aim for 1000 t y exposure background-free start operations at LNGS by 2027?? 43
38 Technical Challenges 50 t LXe TPC LXe size: 2.6m (~2.7 XENON1T, ~2 XENONnT/LZ) procurement of LXe no consumable! high voltage for drift field gas purification for high e-lifetime photosensors: long-term stability of PMTs? alternatives? (GPMs, hybrid, etc) JCAP 10, 016 (2015) backgrounds in WIMP ROI = 0.1 ppt of natkr 0.5 XENON1T goal; 0.03 ppt achieved EPJ C 74 (2014) 2746 = 0.1 µbq/kg of 222Rn 0.01 XENON1T goal; main challenge challenging Rn background ER rejection is required need high LY challenge: keep large LXe inventory clean unexpected artefacts? 300 t LAr TPC LAr size: 6.5m (~18 DS-50, ~2.5 DarkSide-20k) DAr: isotopic depletion by cryogenic distillation (never demonstrated for 39Ar) high voltage for drift field gas purification for high e-lifetime single-phase better option? light detection: PSD requires lots of photons very high LY, high threshold ( 6x more gas) attenuation/scatt. length XUV photons? wavelength shifters: long-term stability SiPMs: reduce channels by tiling: huge number of channels; large capacitance leads to rapidly decreasing signal-2-noise ratio radiopurity? neutrons? backgrounds in WIMP ROI 39Ar PSD; PSD with pile-up? neutrons? Rn plate-out? challenge: keep large UAr inventory clean unexpected artefacts? 44
39 Science Channels LXe 50 t LXe TPC LAr 300 t LAr TPC Nuclear Recoil Interactions WIMP dark matter spin-independent mid/high mass spin-independent high mass spin-dependent Phys.Dark Univ. 9-10, 51 (2015) complementary with LHC, indirect search various inelastic models (χ, n, MiDM, ) JCAP 10, 016 (2015) Coherent neutrino-nucleon scattering (CNNS) 8B neutrinos (low E), atmospheric (high E) atmospheric (high E) JCAP 1611, 017 (2016) supernova neutrinos PRD 89, (2014), PRD 94, (2016) Electronic Recoil Interactions Non-WIMP dark matter and neutrino physics axions, ALPs JCAP 1611, 017 (2016) sterile neutrinos pp, 7Be: precision flux measurements <1% JCAP 01, 044 (2014) 7Be, pep, CNO flux measurements 2% 10% 15% JCAP 1608, 017 (2016) Rare nuclear events 0νββ (136Xe), 2νEC (134Xe),... JCAP 01, 044 (2014) 45
40 WIMP Spectroscopy Parameter Reconstruction Target Complementarity LXe: 200 t y JCAP 11, 017 (2016) Capability to reconstruct WIMP parameters m =20, 100, 500 GeV/c² χ due to flat WIMP spectra, no target can reconstruct masses >500 GeV/c² PRD 83, (2011) Reconstruction improves considerably by adding Ge-data to Xe. Only minimal improvement for Ar. If there is no hint for DM from direct detection + LHC? Do we proceed with multi-ton scale projects R&D has to continue to be ready! 47
41 Summary Germanium 25t d 48
42 Question 1: Science I What are the primary scientific questions of the field? Direct detection of WIMP dark matter What is the nature of the WIMP? (mass, X-section, couplings)? Which experimental options exist to answer them and when? Direct measurement of WIMP-induced nuclear recoils Different experimental approaches (different targets) cryogenic low mass: lowest threshold, low exposure, mediocre background higher masses: high exposure, low background, mediocre threshold/resolution different targets are sensitive to different couplings, WIMP models (SI: all targets, SD/inelastic: Xe, Ge, F) Important complementarity with indirect detection: mainly spin-dependent (F, Xe, Ge) but also spin-independent (Super-K) collider searches: mainly spin-dependent (Xe, F, Ge) 49
43 Question 1: Science II For proposed projects: Important results guaranteed, likely or possible? WIMP-detection depends on nature's choice. Future experiments will scan well-motivated parameter space However: even limits are high-impact results! big impact on validity of models! Which secondary topics are covered by the project and what are its chances for success? CNNS not yet detected (Ge, CaWO4, Xe) yes! Supernova neutrinos (Xe) complementarity with large detectors yes if SN Solar neutrinos: low-e (Xe), high-e (Ar) yes! neutrinoless double beta decay (Xe)?? Axions, ALPs, SuperWIMPs, dark photons, etc.?? (Xe, Ge, Si, CaWO4 experiments need ER sensitivity = low ER background) fractional charges (Ge, Si)?? etc etc etc 50
44 Question 2 Estimate of the time scales, costs (invest) and structures (collaboration size and international composition) time scale: next generation ( basically funded ) have results by ~ ultimate detectors: TDRs needed in 5-6 years operation in mid 2020s cost: n/a structures: sufficient size (moderate increase) for next generation projects more manpower/funding needed for ultimate detectors Which risks exist? see various technical challenges unknown and fastly changing Chinese projects competition don't lose European leadership Which competing projects exist world-wide for the physics question, taking also realistic schedules and progress into account? see talk 51
45 Question 3 Where is the specific German interest? Do special strengths of German groups play a role? Are there enough interested groups/people for a meaningful contribution? Currently two activities pursued in Germany: Low-mass with cryogenic detectors (CRESST: CaWO 4, EDELWEISS: Ge) CRESST is a German project (75% manpower, expertise) High-mass with LXe TPC (XENON, DARWIN) DE groups are largest community (with US), major contributions to project special expertise: background reduction DARWIN pushed forward by German PIs Special Opportunity: DARWIN is largely European project! (66% EU, 25% D) Unique possibility for leadership! Will the participation create synergies and international visibility? It does already. How does the required funding fit to the German funding structures? CRESST: XENON: DARWIN: BMBF, SFB, MPG BMBF, MPG currently: Universities, MPG, ERC future: BMBF 52
46 Question 4 Where could the project be realized? Direct WIMP searches need large underground laboratories, which do not exist in Germany. CRESST and XENON are installed at LNGS (IT) and will continue there. DARWIN: a LOI/space request has been submitted to LNGS SuperCDMS (Ge, Si) will be hosted by SNOLAB (CA) EDELWEISS groups might join Argon: DarkSide-20k will be realized at LNGS. no concrete proposal for ARGO yet. Maybe LNGS? Maybe SNOLAB (merger with DEAP??) Unknowns: China (Ge/Xe), Japan (Xe) 53
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids
 Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
The XENON1T experiment
 The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments
 Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program. Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli
 DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli UCLA DM Conference Los Angeles February 23, 2018 The case for DarkSide-20k
DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli UCLA DM Conference Los Angeles February 23, 2018 The case for DarkSide-20k
DarkSide. Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1
 DarkSide Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1 DARKSIDE MAIN FEATURES Dark Matter direct detection WIMP induced nuclear recoils Double
DarkSide Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1 DARKSIDE MAIN FEATURES Dark Matter direct detection WIMP induced nuclear recoils Double
Status of DM Direct Detection. Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science
 Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
XENON100. Marc Schumann. Physik Institut, Universität Zürich. IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th,
 XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program
 Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
XENONNT AND BEYOND. Hardy Simgen. WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg. Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg
 XENONNT AND BEYOND Hardy Simgen Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg THE XENON PROGRAM FOR DIRECT DARK MATTER SEARCH 1 THE PRESENT: XENON1T! LXe TPC under construction
XENONNT AND BEYOND Hardy Simgen Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg THE XENON PROGRAM FOR DIRECT DARK MATTER SEARCH 1 THE PRESENT: XENON1T! LXe TPC under construction
Direct Dark Matter Searches
 Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids
 DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
DarkSide-20k and the Darkside Program for Dark Matter Searches
 DarkSide-20k and the Darkside Program for Dark Matter Searches Cristiano Galbiati Princeton University APC Paris Diderot GDR Neutrinos LPSC Grenoble June 6, 2016 DarkSide-20k Institutions [cm 2 ] σ 41
DarkSide-20k and the Darkside Program for Dark Matter Searches Cristiano Galbiati Princeton University APC Paris Diderot GDR Neutrinos LPSC Grenoble June 6, 2016 DarkSide-20k Institutions [cm 2 ] σ 41
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T
 Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Darkside-50, DarkSide-20k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon
 Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments
 Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector. WIMP Search. Mani Tripathi, INPAC Meeting. Berkeley, May 5, 2007
 LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano
 School and Workshop on Dark Matter and Neutrino Detection Dark Matter Direct Detection Lecture 3 Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano!113 Outline Lecture 1: The dark matter problem WIMP and WIMP-like DM detection
School and Workshop on Dark Matter and Neutrino Detection Dark Matter Direct Detection Lecture 3 Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano!113 Outline Lecture 1: The dark matter problem WIMP and WIMP-like DM detection
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS
 SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Dark Matter Direct Detection
 Dark Matter Direct Detection Laura Baudis, UZH Jocelyn Monroe, RHUL Outline 1) Scientific Context 2) Community Input: 5-10 year Horizon for Direct Detection in Europe 3) APPEC GA Considerations for Discussion
Dark Matter Direct Detection Laura Baudis, UZH Jocelyn Monroe, RHUL Outline 1) Scientific Context 2) Community Input: 5-10 year Horizon for Direct Detection in Europe 3) APPEC GA Considerations for Discussion
Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN
 Via Lactea 2 (2008) Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN NASA/WMAP 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs, and WISPs Chicago, 21-July-2012 http://xenon.physik.uni-mainz.de
Via Lactea 2 (2008) Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN NASA/WMAP 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs, and WISPs Chicago, 21-July-2012 http://xenon.physik.uni-mainz.de
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project
 Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Dark Matter Search with XENON
 Dark Matter Search with XENON Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Universität Mainz, Seminar, May 2, 2012 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 Baryonic Matter Dark Matter? Dark Energy????
Dark Matter Search with XENON Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Universität Mainz, Seminar, May 2, 2012 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 Baryonic Matter Dark Matter? Dark Energy????
PoS(EPS-HEP2017)074. Darkside Status and Prospects. Charles Jeff Martoff Temple University
 Temple University E-mail: cmartoff@gmail.com The DarkSide Dark Matter Search Program is a direct-detection search for dark matter using a Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber. The detector is designed
Temple University E-mail: cmartoff@gmail.com The DarkSide Dark Matter Search Program is a direct-detection search for dark matter using a Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber. The detector is designed
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN
 WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T
 Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector
 XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
DARWIN. Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich. Aspera Technology Forum 2010, October 21-22, 2010
 21-22 DARWIN Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Aspera Technology Forum 2010, October 21-22, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Dark Matter: Evidence & Detection NASA/WMAP
21-22 DARWIN Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Aspera Technology Forum 2010, October 21-22, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Dark Matter: Evidence & Detection NASA/WMAP
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results
 Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
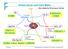 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection!
 BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection Jeremy Mock, on behalf of Cecilia Levy and Matthew Szydagis SUNY Albany Direct DM Search Today 3 detection channels (light, charge, heat):
BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection Jeremy Mock, on behalf of Cecilia Levy and Matthew Szydagis SUNY Albany Direct DM Search Today 3 detection channels (light, charge, heat):
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment. Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH
 Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
DarkSide new results and prospects
 DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search
 Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector. David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012
 Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search
 Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Dark Matter Search * in China
 Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
The Direct Search for Dark Matter
 picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration. Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016
 Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
The XENON1T Experiment
 The XENON1T Experiment Ranny Budnik Columbia University On behalf of the XENON1T collaboration 1 Status in WIMP DM Sensitivities (2012) Spin-independent Spin-dependent, n-coupling preliminary Spin-dependent,
The XENON1T Experiment Ranny Budnik Columbia University On behalf of the XENON1T collaboration 1 Status in WIMP DM Sensitivities (2012) Spin-independent Spin-dependent, n-coupling preliminary Spin-dependent,
PandaX Dark Matter Search
 PandaX Dark Matter Search Xiangdong Ji Shanghai Jiao Tong University University of Maryland On Behalf of the PandaX Collaboration 2017/8/7 1 Outline Introduction to WIMP search and liquid xenon experiments
PandaX Dark Matter Search Xiangdong Ji Shanghai Jiao Tong University University of Maryland On Behalf of the PandaX Collaboration 2017/8/7 1 Outline Introduction to WIMP search and liquid xenon experiments
Axion search with Dark Matter detector
 Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Low Energy Particles in Noble Liquids
 Low Energy Particles in Noble Liquids Antonio J. Melgarejo Fernandez Columbia University Invisibles School, July 14th 2013, Durham Explaining the title I Noble gases are a group of elements found at the
Low Energy Particles in Noble Liquids Antonio J. Melgarejo Fernandez Columbia University Invisibles School, July 14th 2013, Durham Explaining the title I Noble gases are a group of elements found at the
Experimental Searches for Neutrinoless Double-Beta Decays in 76-Ge Alan Poon
 Experimental Searches for Neutrinoless Double-Beta Decays in 76-Ge Alan Poon Institute for Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics Nuclear Science Division 1 Outline Introduction - 0νββ decay (see Agostini s
Experimental Searches for Neutrinoless Double-Beta Decays in 76-Ge Alan Poon Institute for Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics Nuclear Science Division 1 Outline Introduction - 0νββ decay (see Agostini s
The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC. SURF South Dakota
 The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC SURF South Dakota 1 LUX - ZEPLIN 31 Institutions, ~200 people 7 ton LXe TPC ( tons LXe total) University of Alabama University at Albany SUNY Berkeley Lab (LBNL), UC Berkeley
The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC SURF South Dakota 1 LUX - ZEPLIN 31 Institutions, ~200 people 7 ton LXe TPC ( tons LXe total) University of Alabama University at Albany SUNY Berkeley Lab (LBNL), UC Berkeley
Dark Matter and the XENON Experiment
 Dark Matter and the XENON Experiment Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Lunch Seminar, Weizmann Institute of Science, November 4th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 3 95%
Dark Matter and the XENON Experiment Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Lunch Seminar, Weizmann Institute of Science, November 4th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 3 95%
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status. Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN Heidelberg
 LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN-2015. Heidelberg 1 LZ = LUX + ZEPLIN 29 institutions currently About 160 people Continuing to expand internationally
LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN-2015. Heidelberg 1 LZ = LUX + ZEPLIN 29 institutions currently About 160 people Continuing to expand internationally
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run
 DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Future DM Direct Detection Experiments
 Future DM Direct Detection Experiments Javier Tiffenberg April 20, 2017 Fermi National Laboratory 1 Alps 2017 April 20, 2017 Talk index This talk.. Why we need Future Direct Detection Experiments? Direct
Future DM Direct Detection Experiments Javier Tiffenberg April 20, 2017 Fermi National Laboratory 1 Alps 2017 April 20, 2017 Talk index This talk.. Why we need Future Direct Detection Experiments? Direct
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results
 A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search. Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University Seminar at KEK, Tsukuba Japan 3 February, 2011 Jin Ping Laboratory Newly constructed deep underground lab In the
PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University Seminar at KEK, Tsukuba Japan 3 February, 2011 Jin Ping Laboratory Newly constructed deep underground lab In the
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS
 Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
New Physics Results from DarkSide-50. Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide-50 Collaboration Feb
 New Physics Results from DarkSide5 Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide5 Collaboration Feb. 8 Lake Louise Winter Institute 8 DETECTOR DARKSIDE 5 Radonfree (Rn levels < 5 mbq/m )
New Physics Results from DarkSide5 Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide5 Collaboration Feb. 8 Lake Louise Winter Institute 8 DETECTOR DARKSIDE 5 Radonfree (Rn levels < 5 mbq/m )
TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON. Henrique Araújo Imperial College London
 TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON Henrique Araújo Imperial College London Oxford University 18 th October 2016 OUTLINE Two-phase xenon for (dark) radiation detection Instrumenting a liquid
TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON Henrique Araújo Imperial College London Oxford University 18 th October 2016 OUTLINE Two-phase xenon for (dark) radiation detection Instrumenting a liquid
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1](/thumbs/95/125151835.jpg) DPF2015-240 November 4, 2015 Status and Results from DarkSide-50 arxiv:1511.00676v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1 Physics and Astronomy Department University of California, Los Angeles, CA
DPF2015-240 November 4, 2015 Status and Results from DarkSide-50 arxiv:1511.00676v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1 Physics and Astronomy Department University of California, Los Angeles, CA
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment
 Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Dark Matter Search. Dark Matter
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective
 The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective A. Rizzo a on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Department of Astrophysics, Columbia University in the City of New York, USA Abstract.
The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective A. Rizzo a on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Department of Astrophysics, Columbia University in the City of New York, USA Abstract.
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection
 COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination
 Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
CANDLES Experiment Current Status and Future Plan. X. Li for the CANDLES Collaboration
 CANDLES Experiment Current Status and Future Plan X. Li for the CANDLES Collaboration 1 Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay (0νββ) 2νββ decay 0νββ decay (A, Z) => (A, Z+2) + 2e - process beyond Standard Model
CANDLES Experiment Current Status and Future Plan X. Li for the CANDLES Collaboration 1 Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay (0νββ) 2νββ decay 0νββ decay (A, Z) => (A, Z+2) + 2e - process beyond Standard Model
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON
 LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
Recent results and status of the XENON program
 on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Subatech, Ecole des Mines de Nantes, CNRS/In2p3, Université de Nantes, Nantes, France E-mail: julien.masbou@subatech.in2p3.fr The XENON program aims at the direct detection
on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Subatech, Ecole des Mines de Nantes, CNRS/In2p3, Université de Nantes, Nantes, France E-mail: julien.masbou@subatech.in2p3.fr The XENON program aims at the direct detection
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST
 Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future
 Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future -Ge detectors at LN temperature Lin, Shin-Ted / Sichuan University On behalf of CDEX Collaboration Oct. 19, 2015 (Materials Provided by Prof. Qian
Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future -Ge detectors at LN temperature Lin, Shin-Ted / Sichuan University On behalf of CDEX Collaboration Oct. 19, 2015 (Materials Provided by Prof. Qian
Outline. Dark Matter Physics at SNOLAB: And Future Prospects. Overview of SNOLAB DarkMatter Program. Status of Current Experiments
 Outline Dark Matter Physics at SNOLAB: And Future Prospects Overview of SNOLAB DarkMatter Program Status of Current Experiments The G2 Down Select Process Crystal Ball Gazing where will we be in 2020?
Outline Dark Matter Physics at SNOLAB: And Future Prospects Overview of SNOLAB DarkMatter Program Status of Current Experiments The G2 Down Select Process Crystal Ball Gazing where will we be in 2020?
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search
 Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Recent Progress from the DEAP-3600 Dark Matter Direct Detection Experiment
 Recent Progress from the DEAP-3600 Dark Matter Direct Detection Experiment Jocelyn Monroe, Royal Holloway University of London IPA2014 August 22, 2014 Outline 1. DEAP-3600 Detector 2. Experimental Technique
Recent Progress from the DEAP-3600 Dark Matter Direct Detection Experiment Jocelyn Monroe, Royal Holloway University of London IPA2014 August 22, 2014 Outline 1. DEAP-3600 Detector 2. Experimental Technique
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches
 Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Dark Matter Detection with XENON100 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future
 Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
After LUX: The LZ Program. David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011
 After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
The CUTE Facility. Ryan Underwood Queen s University, TRIUMF WNPPC 2019
 The CUTE Facility Ryan Underwood Queen s University, TRIUMF WNPPC 2019 Dark Matter Strong evidence for a nonluminous, gravitationally interacting kind of matter; Dark Matter Interaction with normal matter
The CUTE Facility Ryan Underwood Queen s University, TRIUMF WNPPC 2019 Dark Matter Strong evidence for a nonluminous, gravitationally interacting kind of matter; Dark Matter Interaction with normal matter
Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100
 Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100 IDM08, Stockholm, August 19, 2008 Laura Baudis University of Zurich For the XENON100 Collaboration LNGS collaboration meeting, Oct. 2007 1 ??? The
Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100 IDM08, Stockholm, August 19, 2008 Laura Baudis University of Zurich For the XENON100 Collaboration LNGS collaboration meeting, Oct. 2007 1 ??? The
Dark Matter Direct Detection: the state-of-the-art KMI School, Nagoya, Japan February 28, 2018
 Dark Matter Direct Detection: the state-of-the-art KMI School, Nagoya, Japan February 28, 2018 Elena Aprile, Columbia University Columbia University DES: NGC 1398 NGC 1398 xenon1t.org 1 Outline of Lecture
Dark Matter Direct Detection: the state-of-the-art KMI School, Nagoya, Japan February 28, 2018 Elena Aprile, Columbia University Columbia University DES: NGC 1398 NGC 1398 xenon1t.org 1 Outline of Lecture
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments
 Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON. Kaixuan Ni (Columbia)
 Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Results from DarkSide-50 with underground argon
 Dark Matter 2016 Los Angeles, CA 17-19 February 2016 Results from DarkSide-50 with underground argon Alden Fan UCLA for the DarkSide collaboration 1 DarkSide WIMP dark matter search using direct detection
Dark Matter 2016 Los Angeles, CA 17-19 February 2016 Results from DarkSide-50 with underground argon Alden Fan UCLA for the DarkSide collaboration 1 DarkSide WIMP dark matter search using direct detection
Direct dark matter search with XMASS. K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration
 Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Luca Grandi.
 Luca Grandi http://warp.pv.infn.it idm2004 - September 2004 Wimp Argon Programme Collaboration R. Brunetti, E. Calligarich, M. Cambiaghi, C. De Vecchi, R. Dolfini, L. Grandi, A. Menegolli, C. Montanari,
Luca Grandi http://warp.pv.infn.it idm2004 - September 2004 Wimp Argon Programme Collaboration R. Brunetti, E. Calligarich, M. Cambiaghi, C. De Vecchi, R. Dolfini, L. Grandi, A. Menegolli, C. Montanari,
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase. Elena Aprile Columbia University
 The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
Rare Event Searches and the Underground
 Rare Event Searches and the Underground session intro cosmogenics signal background > 1 but...begin to see your environment! session intro direct DM detection : measurement of nuclear RECOIL events in
Rare Event Searches and the Underground session intro cosmogenics signal background > 1 but...begin to see your environment! session intro direct DM detection : measurement of nuclear RECOIL events in
Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter
 Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter Rouven Essig C.N. Yang Institute for Theoretical Physics, Stony Brook Sackler Conference, Harvard, May 18, 2014 An ongoing program Direct Detection of sub-gev Dark
Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter Rouven Essig C.N. Yang Institute for Theoretical Physics, Stony Brook Sackler Conference, Harvard, May 18, 2014 An ongoing program Direct Detection of sub-gev Dark
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background
 Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100
 The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
Recent Results from the PandaX Experiment
 Recent Results from the PandaX Experiment Changbo Fu Shanghai Jiao Tong University On Behalf of Collaboration 25May2017 1 Outline 1. Introduciton Dark Matter: WIMPs, Axion, PandaX at China Jinping Underground
Recent Results from the PandaX Experiment Changbo Fu Shanghai Jiao Tong University On Behalf of Collaboration 25May2017 1 Outline 1. Introduciton Dark Matter: WIMPs, Axion, PandaX at China Jinping Underground
ANAIS: Status and prospects
 LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III
 The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
