Geochemical mobility of chemical elements in saline lake systems in Khakassia (Russia)
|
|
|
- Louise Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 7 ( 2013 ) Water Rock Interaction [WRI 14] Geochemical mobility of chemical elements in saline lake systems in Khakassia (Russia) N. Guseva*, Y. Kopylova Institute of Natural Resourses, Tomsk Polytechnic University, Lenin Ave. 30, Tomsk, Russia. Abstract Saline lakes were sampled from the semi-arid region of the Russian Federation (Khakassia). The water and salt sediment samples were collected from 4 lakes: Khamiskol, Terpikol, Uskol, and Tus. The total dissolved solids (TDS) of the various lakes ranges from 7.9 to g/l. The ph values lie mostly in the range of The anionic composition of saline lakes is varied. The cationic composition of lakes is not so varied as the anionic one. Sodium is the dominant cation in the water composition of these lakes, whereas the Tus contains magnesium and sodium in equal proportions. The chemical element enrichment of water is regulated by the formation of significant quantities of secondary mineral phases. The Khakassia saline lakes are saturated with respect to carbonate minerals such as calcite, dolomite, magnesite, and are undersaturated in terms of natrite, anhydrite, thenardite, and halite. Geochemical mobility coefficients can be used to evaluate the geochemical mobility of major elements in the saline lake waters. Geochemical mobility coefficients suggest that trace elements tend to accumulate in secondary phases, which are consolidated by secondary mineral precipitation and sorption processes The Authors. Published by Elsevier by Elsevier B.V. Open B.V. access under CC BY-NC-ND license. Selection and/or peer-review under under responsibility of the Organizing of and Scientific and Scientific Committee Committee of WRI 14 of WRI Keywords: saline lakes, semi-arid region, geochemical mobility, water-rock interaction. 1. Introduction Saline lakes are a typical feature of an arid region. Khakassia is one of the unique regions of the Russian Federation in which saline lakes are mainly located. These lakes have been studied by Russian scientists and not only of them [1-3]. However there are still many unsolved problems such as chemical conditions that conduct to elements accumulation in water and secondary minerals crystallized in the lakes. The problem of chemical composition formation cannot be solved without an explanation of the chemical elements redistribution mechanism during water-rock interaction processes. Water chemical elements enrichment is a complex process that depends on the extent and form of element input, specific * Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: guseva24@yandex.ru The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. Open access under CC BY-NC-ND license. Selection and/or peer-review under responsibility of the Organizing and Scientific Committee of WRI doi: /j.proeps
2 326 N. Guseva and Y. Kopylova / Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 7 ( 2013 ) features of aquatic species and the output through the secondary minerals precipitation. The water-rock interaction processes are characterized by elements spreading in a water solution and by trapping in the secondary minerals. This fact was ignored in the previous study and the chemical elements migration intensity has been estimated without evaluating processes of chemical elements output by precipitated secondary mineral phases. Today we have an opportunity to estimate geochemical mobility of chemical elements during water-rock interaction at a new level. The main aim of this work is to study chemical elements mobility in Khakassia saline lake systems. These lakes illustrate very well the water-rock interaction processes because they are salt-forming. 2. Sampling and methods The sampling area is located in the South-Central Siberia, within the region of the Altai-Sayan Mountains. Detailed geological, climatic and geographic descriptions of region characteristics are given by Banks et al. [3]. This study is based on the results obtained from the saline lakes sampling. In , 4 samples of water and salt sediments were taken from the 4 lakes: Khamiskol, Terpikol, Uskol, and Tus. The ph, temperature and Eh values were measured by water test in the field. Water samples were investigated by the following methods: tytrimetric (НСО 3, СО 3 2, Cl, Ca 2+, Mg 2+ ), turbidimetric (SO 4 2 ), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (trace elements). Evaporate crust samples issue from the lake shore were collected in clean plastic bags; For these latter, salt were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. All these analysis were fulfilled at the Hydrogeochemical Laboratory of Tomsk Polytechnic University. 3. Results and discussion Results of the chemical composition analysis and field measurements are presented in Table 1. The waters of the lakes are distinct by their TDS ranged from 7.9 to g/l. The highest TDS mg/l is observed at the Tus (Table 1). The TDS of the Khamiskol is the lowest among considerable lakes. Measured ph values lay mostly in the range Table 1. Main hydrochemical characteristics of Khakasia saline lakes. ph CO 3 2 HCO 3 SO 4 2 Cl Ca 2+ Mg 2+ Na + K + TDS mg/l g/l Khamiskol Terpekol Uskol Tus The anionic composition of saline lakes is various. Chloride is the major anion in the Khamiskol water composition, whereas the bicarbonate (plus carbonate) and sulphate content exceeds 20 %, expressed as equivalents. The Terpekol water contains all anionic species (bicarbonate, carbonate, sulphate, chloride) in the equal ratio. The Uskol is mainly sulphate-containing, but the chloride content is 27 % expressed as equivalents. Sulphates and chlorides are present in the same proportions in the Tus, which correspond to 49 % expressed as equivalents respectively. Chloride and sulphate content tend to increase with TDS. Content of cationic species is not so variable than the anionic species in all lakes. Sodium is the dominating cation of these lakes, whereas the Tus contains also magnesium and sodium in equal proportions. The trace element composition of Khakassia saline lakes is restituted in Table 2. A comparison between the saline lakes and the continental salinization province groundwater, considered as one of the sources of chemical element for these lakes, indicated that all
3 N. Guseva and Y. Kopylova / Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 7 ( 2013 ) elements, except one, are expressed in lower concentrations in the lakes. All lakes are enriched in strontium compared with the continental salinization province groundwater. Another tendency is evidenced by comparing the chemical composition of lakes with seawater. Comparable TDS values are characteristic for both water types. The lakes are characterized by higher aluminum, zinc and barium concentrations. Lithium, silicon, strontium concentrations are higher in seawater. The trace elements concentration doesn t increase with an increase in mineralization of the lakes. Table 2. Trace elements composition of the Khakasia saline lakes. Li Al Si Zn Sr Ba TDS mg/l g/l Khamiskol Terpekol Uskol Tus Groundwater of the continental salinization province [4] Seawater [5] The accumulation of chemical elements in the lakes can be explained mainly by water rock interaction processes. The processes of chemical elements accumulation in water are controlled by secondary mineral phase formation in significant quantities. This process decreases the element mobility. For example calcium mobility is limited by calcium-bearing minerals precipitation such as calcite, dolomite, gypsum and etc. The saline lakes of Khakasia are saturated with respect to carbonate minerals such as calcite, dolomite, magnesite, the values of saturation index are presented in table 3. It is shown that geochemical mobility of calcium and magnesium decrease due to their concentration in secondary mineral phases, chemical composition of which is shown in Table 4. Chemical composition of evaporate crust from all lake shores presents mainly of lithophile elements such as aluminum, sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium (Table 4), with one exception this is Tus. The main element of the evaporate crust from the Tus is sodium, because in contrast to all considered lakes his mineral composition consists of only from thenardite. The concentrations of the rest elements in the Tus are lower than those in others lakes. The saturation with natrite, anhydrite, thenardite, and halite is not observed for the saline lakes, so the sodium accumulation in the saline lake is not limited by any secondary minerals. Table 3. Saturation index values for the calcite, dolomite, magnesite, natrite, anhydrite, thenardite, halite minerals. Saturation index CaCO 3 CaMg(CO 3) 2 MgCO 3 Na 2CO 3 CaSO 4 Na 2SO 4 NaCl Khamiskol Terpekol Uskol Tus Mobility of major element contained in water may be evaluated knowing their respective mineral bearing. However, it becomes very difficult to proceed with the same approach for trace elements, because they are trapped in few amount in the secondary minerals and are rarely detected. The geochemical mobility coefficient can be used to evaluate the geochemical mobility of trace elements in the saline lakes. The geochemical mobility coefficient can be calculated using the following expression: т х *100 К =, (1) а * п х
4 328 N. Guseva and Y. Kopylova / Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 7 ( 2013 ) а is the TDS (g/l), m x is the «х» element concentration in water (g/l), n x is the «х» element concentration in secondary mineral phases (%). Table 4. Evaporate crust chemical composition from the saline lake shores, mg/kg. Elements Khamiskol Terpekol Uskol Tus Na Ca <5.0 K Mg Al Ba Sr Si Li Zn Geochemical mobility coefficients are presented in table 5. The elements having a large geochemical mobility coefficient values tend to be stay solubilized in water, for example sodium. Geochemical mobility coefficients of strontium and barium decrease with an increase in TDS. The low values of this coefficient indicate that the elements are immobilized in secondary phases, for example magnesium and calcium. This fact was noted early in this article during analysis of water-rock interaction processes. Giving that trace elements indicate low geochemical mobility coefficient values, they are considered accumulated in the secondary phases. It can be connected with processes of the secondary mineral precipitation and sorption. Table 5. Geochemical mobility coefficient values of the Khakassia saline lakes TDS Na К Mg Са Sr Si Ва Zn Li Khamiskol Terpekol Uskol Tus Conclusion According to our investigation, water enrichment in chemical elements is regulated by formation of the secondary mineral phases. Values of the geochemical mobility coefficient can be considered as a quantitative measure of this process. The Khakassia saline lakes are saturated with respect to carbonate minerals such as calcite, dolomite, magnesite, and are undersaturated for natrite, anhydrite, thenardite and halite. As the data of geochemical mobility of the Khakassia saline lakes show that such elements as sodium and potassium are spread in water, the other elements are trapped in the secondary minerals. References [1] Parnachev VP, Vishnevezky II, Makarenko NA, Petrov AI, Kopilova JG, Smetanina IV, et al. Natural water of Shira region of Khakassia Republic. Tomsk: Tomsk State University Press, 2003 (In Russian). [2] Guseva N, Kopylova JG, Khvashevskaya AA, Smetanina IV. Salt composition of saline lakes of Severo-Minusinskaya depression, Khakassia. Proceedings of Tomsk politechnic universitet 2012 (In Russian). [3] Banks D, Parnachev VP, Frengstad B, Holden W, Karnachuk OV, Vedernikov AA. The evoluation of alkaline, saline groundand surface waters in the southern Siberian steppes. Appl Geochem 2004; 19: [4] Shvartsev SL. Geochemistry of Fresh Groundwater in the Main Landscape Zones of the Earth. Geochemistry International 2008; 13:
5 N. Guseva and Y. Kopylova / Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 7 ( 2013 ) [5] Turekian KK. The Oceans, streams and Atmosphere. In Wedepohl KH. Springer editors. Handbook of Geochemistry, Berlin and New York; 1969, p
9. Faryab: Groundwater Hydrochemical Types
 9. Faryab: Groundwater Hydrochemical Types 9.1 Ion Balance Error In 2013, 132 wells, boreholes and springs were sampled in Kohistan, Qaysar, Gurziwan, Bilchiragh and the four northern districts around
9. Faryab: Groundwater Hydrochemical Types 9.1 Ion Balance Error In 2013, 132 wells, boreholes and springs were sampled in Kohistan, Qaysar, Gurziwan, Bilchiragh and the four northern districts around
Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 13 ( 2015 ) th Applied Isotope Geochemistry Conference, AIG-11 BRGM
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 13 ( 2015 ) 47 51 11th Applied Isotope Geochemistry Conference, AIG-11 BRGM Halogen isotopes ( 37 Cl and 81
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 13 ( 2015 ) 47 51 11th Applied Isotope Geochemistry Conference, AIG-11 BRGM Halogen isotopes ( 37 Cl and 81
Ground and Intermediate Water Equilibrium with Water- Bearing Rock Minerals (Moldova) under Anthropogenic Impact
 Ground and Intermediate Water Equilibrium with Water- Bearing Rock Minerals (Moldova) under Anthropogenic Impact А N Timoshenkova 1, C Ye Moraru 2, Ye Yu Pasechnik 3, О G Tokarenko 4 and V А Butoshina
Ground and Intermediate Water Equilibrium with Water- Bearing Rock Minerals (Moldova) under Anthropogenic Impact А N Timoshenkova 1, C Ye Moraru 2, Ye Yu Pasechnik 3, О G Tokarenko 4 and V А Butoshina
Lect. 2: Chemical Water Quality
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department M.Sc. Water Resources Water Quality Management (ENGC 6304) Lect. 2: Chemical Water Quality ١ Chemical water quality parameters
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department M.Sc. Water Resources Water Quality Management (ENGC 6304) Lect. 2: Chemical Water Quality ١ Chemical water quality parameters
(4) Give an example of important reactions that are responsible for the composition of river water.
 Lecture 12 Global Biogeochemical Cycles (1) If rivers are the chief source of the dissolved salts in seawater, why is seawater not simply a concentrated version of average composition of all rivers? The
Lecture 12 Global Biogeochemical Cycles (1) If rivers are the chief source of the dissolved salts in seawater, why is seawater not simply a concentrated version of average composition of all rivers? The
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Salinity. foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m. Length. Area m 2 square feet ~0.09m2. Volume m 3 US pint ~ 0.47 L fl. oz. ~0.02 L.
 Length m foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m Area m 2 square feet ~0.09m2 Volume m 3 US pint ~ 0.47 L, L (liters) fl. oz. ~0.02 L Speed m/s mph Acceleration m/s 2 mph/s Weight kg, gram pound ~0.45kg Temperature
Length m foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m Area m 2 square feet ~0.09m2 Volume m 3 US pint ~ 0.47 L, L (liters) fl. oz. ~0.02 L Speed m/s mph Acceleration m/s 2 mph/s Weight kg, gram pound ~0.45kg Temperature
Name: Period: Date: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: What are polyatomic ions and why would you reverse the criss- cross?
 Name: Period: Date: UNIT 4: BONDING Lesson 4: Polyatomic s and Reverse Criss Cross. By the end of today, you will have an answer to: What are polyatomic ions and why would you reverse the criss- cross?
Name: Period: Date: UNIT 4: BONDING Lesson 4: Polyatomic s and Reverse Criss Cross. By the end of today, you will have an answer to: What are polyatomic ions and why would you reverse the criss- cross?
Hydrochemical Formation Mechanisms and Quality Assessment of Groundwater with Improved TOPSIS Method in Pengyang County Northwest China
 ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E-Journal of Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(3), 1164-1173 Hydrochemical Formation Mechanisms and Quality Assessment of Groundwater with Improved TOPSIS Method
ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E-Journal of Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(3), 1164-1173 Hydrochemical Formation Mechanisms and Quality Assessment of Groundwater with Improved TOPSIS Method
Salinity. See Appendix 1 of textbook x10 3 = See Appendix 1 of textbook
 Length Area Volume m m m foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m square feet ~0.09m2 US pint ~ 0.47 L fl. oz. ~0.02 L Speed m/s mph Acceleration m/s mph/s Weight kg, gram pound ~0.45kg Temperature o o See Appendix
Length Area Volume m m m foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m square feet ~0.09m2 US pint ~ 0.47 L fl. oz. ~0.02 L Speed m/s mph Acceleration m/s mph/s Weight kg, gram pound ~0.45kg Temperature o o See Appendix
5. Pb(IO 3) BaCO 3 8. (NH 4) 2SO 3
 Chemistry 11 Solution Chemistry II Name: Date: Block: 1. Ions in Solutions 2. Solubility Table 3. Separating Ions Ions in Solutions Ionization Equation - Represents the salt breaking apart into ions. Practice:
Chemistry 11 Solution Chemistry II Name: Date: Block: 1. Ions in Solutions 2. Solubility Table 3. Separating Ions Ions in Solutions Ionization Equation - Represents the salt breaking apart into ions. Practice:
Where is all the water?
 Where is all the water? The distribution of water at the Earth's surface % of total Oceans 97.25 Ice caps and glaciers 2.05 Groundwater 0.68 Lakes 0.01 Soils 0.005 Atmosphere (as vapour) 0.001 Rivers 0.0001
Where is all the water? The distribution of water at the Earth's surface % of total Oceans 97.25 Ice caps and glaciers 2.05 Groundwater 0.68 Lakes 0.01 Soils 0.005 Atmosphere (as vapour) 0.001 Rivers 0.0001
Downloaded from
 Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The s-block Elements Top concepts. The s-block elements of the periodic table are those in which the last electron enters the outermost s-orbital. Elements of group
Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The s-block Elements Top concepts. The s-block elements of the periodic table are those in which the last electron enters the outermost s-orbital. Elements of group
Hydrochemical Assessment of The Devonian Keg River Formation
 Hydrochemical Assessment of The Devonian Keg River Formation Francisco Castrillon-Munoz, MSc., P.Geol. Senior Hydrogeologist Worley Parsons Canada Thinks are not always what they seem MACBETH W. Shakespeare
Hydrochemical Assessment of The Devonian Keg River Formation Francisco Castrillon-Munoz, MSc., P.Geol. Senior Hydrogeologist Worley Parsons Canada Thinks are not always what they seem MACBETH W. Shakespeare
Modeling the interaction of mine brines with chloride minerals of potassium-magnesium deposits
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Modeling the interaction of mine brines with chloride minerals of potassium-magnesium deposits To cite this article: V V Fetisov
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Modeling the interaction of mine brines with chloride minerals of potassium-magnesium deposits To cite this article: V V Fetisov
Department of Evaluation of Natural Resources, Environmental Studies and Research Institute, University of Sadat City, Sadat, Egypt
 Hydrology 2017; 5(1): 7-14 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/hyd doi: 10.11648/j.hyd.20170501.12 ISSN: 2330-7609 (Print); ISSN: 2330-7617 (Online) Applications of Hydrogeochemical Modeling to Assessment
Hydrology 2017; 5(1): 7-14 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/hyd doi: 10.11648/j.hyd.20170501.12 ISSN: 2330-7609 (Print); ISSN: 2330-7617 (Online) Applications of Hydrogeochemical Modeling to Assessment
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Chemistry 10 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Chemistry 10 (2014 ) 162 167 XV International Scientific Conference Chemistry and Chemical Engineering in XXI century dedicated to professor
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Chemistry 10 (2014 ) 162 167 XV International Scientific Conference Chemistry and Chemical Engineering in XXI century dedicated to professor
Quartz or opaline silica solubility
 Quartz or opaline silica solubility The simplest process that might regulate the concentration of an element in solution is equilibrium with respect to a solid phase containing the element as a major component.
Quartz or opaline silica solubility The simplest process that might regulate the concentration of an element in solution is equilibrium with respect to a solid phase containing the element as a major component.
Field Trips. Field Trips
 Field Trips Saturday field trips have been scheduled October 9, October 23 and December 4 Last all day (9:00 AM to 4:00 PM) Bus transportation provided from campus Joint with GG101 laboratory, GG101 Section
Field Trips Saturday field trips have been scheduled October 9, October 23 and December 4 Last all day (9:00 AM to 4:00 PM) Bus transportation provided from campus Joint with GG101 laboratory, GG101 Section
SOLUBILITY REVIEW QUESTIONS
 Solubility Problem Set 1 SOLUBILITY REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. What is the solubility of calcium sulphate in M, g/l, and g/100 ml? 2. What is the solubility of silver chromate? In a saturated solution of silver
Solubility Problem Set 1 SOLUBILITY REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. What is the solubility of calcium sulphate in M, g/l, and g/100 ml? 2. What is the solubility of silver chromate? In a saturated solution of silver
GEOCHEMISTRY OF FRESH GROUND WATER OF
 GEOCHEMISTRY OF FRESH GROUND WATER OF ARTESIAN BASINS IN THE RUSSIAN PART OF PRIAMURYE KULAKOV VALERY V. Institute of Water and Ecology Problems FEB RAS, Khabarovsk, Russia Ground waters with increased
GEOCHEMISTRY OF FRESH GROUND WATER OF ARTESIAN BASINS IN THE RUSSIAN PART OF PRIAMURYE KULAKOV VALERY V. Institute of Water and Ecology Problems FEB RAS, Khabarovsk, Russia Ground waters with increased
CEE 680 Lecture #2 1/23/2016
 Updated: 23 January 2016 Print version Lecture #2 Intro: Water & Thermodynamics: Fundamentals and Definitions (Stumm & Morgan, Chapt.1 & 3.4 ) (Pg. 4 11; 97 105) (Pankow, Chapt. 2.8) (Benjamin, 1.2-1.5)
Updated: 23 January 2016 Print version Lecture #2 Intro: Water & Thermodynamics: Fundamentals and Definitions (Stumm & Morgan, Chapt.1 & 3.4 ) (Pg. 4 11; 97 105) (Pankow, Chapt. 2.8) (Benjamin, 1.2-1.5)
Uranium and thorium behavior in groundwater of the natural spa area Choygan mineral water (East Tuva)
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Uranium and thorium behavior in groundwater of the natural spa area Choygan mineral water (East Tuva) To cite this article: Y Kopylova
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Uranium and thorium behavior in groundwater of the natural spa area Choygan mineral water (East Tuva) To cite this article: Y Kopylova
Lecture 4 What Controls the Composition of Seawater
 Lecture 4 What Controls the Composition of Seawater Seawater is salty! Why? What controls the composition of seawater? Do Chemical Equilibrium reactions control the composition of the Ocean? What is meant
Lecture 4 What Controls the Composition of Seawater Seawater is salty! Why? What controls the composition of seawater? Do Chemical Equilibrium reactions control the composition of the Ocean? What is meant
Unit 3: Solubility. Chem 12 Solubility Notes. I) Ionic & Covalent Solutions What is a solution?
 Unit 3: Solubility I) Ionic & Covalent Solutions What is a solution? What are some examples of different types of solutions? solid solid: liquid solid: liquid liquid: liquid gas: gas gas: Jul 23 2:07 PM
Unit 3: Solubility I) Ionic & Covalent Solutions What is a solution? What are some examples of different types of solutions? solid solid: liquid solid: liquid liquid: liquid gas: gas gas: Jul 23 2:07 PM
NEW DIAGRAM USEFUL FOR CLASSIFICATION OF GROUNDWATER QUALITY
 NEW DIAGRAM USEFUL FOR CLASSIFICATION OF GROUNDWATER QUALITY Elhag A.B Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, King Khalid University, Saudi ABSTRACT: Due to human and human activities
NEW DIAGRAM USEFUL FOR CLASSIFICATION OF GROUNDWATER QUALITY Elhag A.B Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, King Khalid University, Saudi ABSTRACT: Due to human and human activities
QUESTIONSHEETS GROUPS 1 AND 2 REACTIONS OF THE ELEMENTS WITH WATER REACTIONS OF THE ELEMENTS WITH DILUTE ACIDS
 CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS AS Level AS TOPIC 10 GROUPS 1 AND 2 Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet 7 Questionsheet 8 Questionsheet
CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS AS Level AS TOPIC 10 GROUPS 1 AND 2 Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet 7 Questionsheet 8 Questionsheet
Hydrological Cycle Rain and rivers OUTLINE
 Hydrological Cycle Rain and rivers The Hydrosphere Rain and rivers OUTLINE 1 Generalizations (non-political conservatism) Conservative (not affected) and Non-Conservative (affected) Ions Distinction: whether
Hydrological Cycle Rain and rivers The Hydrosphere Rain and rivers OUTLINE 1 Generalizations (non-political conservatism) Conservative (not affected) and Non-Conservative (affected) Ions Distinction: whether
1. Forming a Precipitate 2. Solubility Product Constant (One Source of Ions)
 Chemistry 12 Solubility Equilibrium II Name: Date: Block: 1. Forming a Precipitate 2. Solubility Product Constant (One Source of Ions) Forming a Precipitate Example: A solution may contain the ions Ca
Chemistry 12 Solubility Equilibrium II Name: Date: Block: 1. Forming a Precipitate 2. Solubility Product Constant (One Source of Ions) Forming a Precipitate Example: A solution may contain the ions Ca
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material
 Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
Table 1. Solubility of gypsum and anhydrite adopted in this research and the predicted SI values
 Supporting information: Table 1. Solubility of gypsum and anhydrite adopted in this research and the predicted SI values Sample T ID # ( o C) 16, 65, 74 P NaCl CaSO 4 nh 2 O SI System (psi) (mol/kg H 2
Supporting information: Table 1. Solubility of gypsum and anhydrite adopted in this research and the predicted SI values Sample T ID # ( o C) 16, 65, 74 P NaCl CaSO 4 nh 2 O SI System (psi) (mol/kg H 2
Groundwater Geochemistry (Hydrogeochemistry) Wan Zuhairi Wan Yaacob (PhD, Assoc. Prof) Program Geologi, UKM
 Groundwater Geochemistry (Hydrogeochemistry) Wan Zuhairi Wan Yaacob (PhD, Assoc. Prof) Program Geologi, UKM Geochemistry Water / rock interactions in unsaturated/saturated zones Geochemistry is important
Groundwater Geochemistry (Hydrogeochemistry) Wan Zuhairi Wan Yaacob (PhD, Assoc. Prof) Program Geologi, UKM Geochemistry Water / rock interactions in unsaturated/saturated zones Geochemistry is important
SET #7 SOLONCHAKS SOLONETZ GYPSISOLS DURISOLS CALCISOLS
 SET #7 Soils in arid and semi-arid regions. Redistribution of calcium carbonate and gypsum is an important mechanism of horizon differentiation in soils in the dry zone. Soluble salts may accumulate at
SET #7 Soils in arid and semi-arid regions. Redistribution of calcium carbonate and gypsum is an important mechanism of horizon differentiation in soils in the dry zone. Soluble salts may accumulate at
Water Treatment Rules of Thumb Myths or Useful Tools
 Water Treatment Rules of Thumb Myths or Useful Tools Robert J. Ferguson French Creek Software, Inc. 1298 Hares Hill Road P.O. Box 684 Kimberton, PA 19442-0684 U.S.A. (610) 935-8337 Voice (610) 935-1008
Water Treatment Rules of Thumb Myths or Useful Tools Robert J. Ferguson French Creek Software, Inc. 1298 Hares Hill Road P.O. Box 684 Kimberton, PA 19442-0684 U.S.A. (610) 935-8337 Voice (610) 935-1008
Chemical Hydrogeology
 Physical hydrogeology: study of movement and occurrence of groundwater Chemical hydrogeology: study of chemical constituents in groundwater Chemical Hydrogeology Relevant courses General geochemistry [Donahoe]
Physical hydrogeology: study of movement and occurrence of groundwater Chemical hydrogeology: study of chemical constituents in groundwater Chemical Hydrogeology Relevant courses General geochemistry [Donahoe]
May 09, Ksp.notebook. Ksp = [Li + ] [F + ] Find the Ksp for the above reaction.
![May 09, Ksp.notebook. Ksp = [Li + ] [F + ] Find the Ksp for the above reaction. May 09, Ksp.notebook. Ksp = [Li + ] [F + ] Find the Ksp for the above reaction.](/thumbs/85/92550924.jpg) example: Constant Product K sp Solubility Product Constant Some compounds dissolve in water Some compounds dissolve better than others The more that a compound can dissolve, the more soluble the compound
example: Constant Product K sp Solubility Product Constant Some compounds dissolve in water Some compounds dissolve better than others The more that a compound can dissolve, the more soluble the compound
Type and Origin of Springs and Hotsprings at Surrounding Ridges of Bandung Basin, Related With its Potential Natural Contamination
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 6 ( 2013 ) 262 268 International Symposium on Earth Science and Technology, CINEST 2012 Type and Origin of Springs and Hotsprings
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 6 ( 2013 ) 262 268 International Symposium on Earth Science and Technology, CINEST 2012 Type and Origin of Springs and Hotsprings
Redox, ph, pe OUTLINE 9/12/17. Equilibrium? Finish last lecture Mineral stability Aquatic chemistry oxidation and reduction: redox
 Redox, ph, pe Equilibrium? OUTLINE Finish last lecture Mineral stability Aquatic chemistry oxidation and reduction: redox Reading: White p555-563 1 Question of the day? So what about the CO 2 system? CO
Redox, ph, pe Equilibrium? OUTLINE Finish last lecture Mineral stability Aquatic chemistry oxidation and reduction: redox Reading: White p555-563 1 Question of the day? So what about the CO 2 system? CO
Which other compounds react with acids to produce salts? Acids can also react with metals and carbonates to produce salts.
 Salts Textbook pages 234 243 Section 5.2 Summary Before You Read How many different uses for salts can you name? Write your answers on the lines below. What are salts? In chemistry, salts are a class of
Salts Textbook pages 234 243 Section 5.2 Summary Before You Read How many different uses for salts can you name? Write your answers on the lines below. What are salts? In chemistry, salts are a class of
Atoms and Ions Junior Science
 2018 Version Atoms and Ions Junior Science 1 http://msutoday.msu.edu Introduction Chemistry is the study of matter and energy and the interaction between them. The elements are the building blocks of all
2018 Version Atoms and Ions Junior Science 1 http://msutoday.msu.edu Introduction Chemistry is the study of matter and energy and the interaction between them. The elements are the building blocks of all
Evolution of the Earth
 Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
A. Correct. Sodium (on the far left) has the largest atomic radius, since the atomic radius decreases from left to right across the periodic table.
 MCAT General Chemistry - Problem Drill 12: Periodic Table - Properties Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which element has the largest atomic radius? Question #01 (A) Na (B) P (C) Cl (D) H A. Correct. Sodium (on
MCAT General Chemistry - Problem Drill 12: Periodic Table - Properties Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which element has the largest atomic radius? Question #01 (A) Na (B) P (C) Cl (D) H A. Correct. Sodium (on
insoluble partial very soluble (< 0.1 g/100ml) solubility (> 1 g/100ml) Factors Affecting Solubility in Water
 Aqueous Solutions Solubility is a relative term since all solutes will have some solubility in water. Insoluble substances simply have extremely low solubility. The solubility rules are a general set of
Aqueous Solutions Solubility is a relative term since all solutes will have some solubility in water. Insoluble substances simply have extremely low solubility. The solubility rules are a general set of
Fluid Geochemistry at the Nir Geothermal Field, Nw-Iran
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Fluid Geochemistry at the Nir Geothermal Field, Nw-Iran Mohammad Reza Rahmani Renewable Energy Organization of Iran (SUNA),
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Fluid Geochemistry at the Nir Geothermal Field, Nw-Iran Mohammad Reza Rahmani Renewable Energy Organization of Iran (SUNA),
Unit 3: Solubility. solubilitynotesbqv3.notebook. October 11, I) Ionic & Covalent Solutions What is a solution?
 Unit 3: Solubility I) Ionic & Covalent Solutions What is a solution? What are some examples of different types of solutions? solid solid: liquid solid: liquid liquid: liquid gas: gas gas: Jul 23 2:07 PM
Unit 3: Solubility I) Ionic & Covalent Solutions What is a solution? What are some examples of different types of solutions? solid solid: liquid solid: liquid liquid: liquid gas: gas gas: Jul 23 2:07 PM
Ocean Chemical Dynamics. EAS 2200 Lecture 21
 Ocean Chemical Dynamics EAS 2200 Lecture 21 Summary of Water s H-bonding accounts for high heat capacity, latent heats of fusion and evaporation. important for heat transport, transfer to atmosphere, and
Ocean Chemical Dynamics EAS 2200 Lecture 21 Summary of Water s H-bonding accounts for high heat capacity, latent heats of fusion and evaporation. important for heat transport, transfer to atmosphere, and
6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items S6E3c.
 Composition 6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items Ocean water differs from freshwater in that it has. A. a lower temperature B. a higher temperature C. a higher concentration of silicon dioxide D.
Composition 6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items Ocean water differs from freshwater in that it has. A. a lower temperature B. a higher temperature C. a higher concentration of silicon dioxide D.
Learning Outcomes: At the end of this assignment, students will be able to:
 Chemical Equilibria & Sample Preparation Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to predict how solute concentrations are controlled by chemical equilibria, understand the chemistry involved with sample
Chemical Equilibria & Sample Preparation Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to predict how solute concentrations are controlled by chemical equilibria, understand the chemistry involved with sample
Salinity distribution in the Oceans
 Salinity distribution in the Oceans Average practical salinity of open ocean waters 34.72 http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c542/ 1/58 Salinity distribution in the Oceans Factors that control seawater salinity:
Salinity distribution in the Oceans Average practical salinity of open ocean waters 34.72 http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c542/ 1/58 Salinity distribution in the Oceans Factors that control seawater salinity:
Mid-Term #1 (125 points total)
 Ocean 520 Name: Chemical Oceanography 20 October 2009 Fall 2009 Points are in parentheses (show all your work) (use back if necessary) MidTerm #1 (125 points total) 1. Doney et al (2008) Ocean Acidification
Ocean 520 Name: Chemical Oceanography 20 October 2009 Fall 2009 Points are in parentheses (show all your work) (use back if necessary) MidTerm #1 (125 points total) 1. Doney et al (2008) Ocean Acidification
Solapur University, Solapur. Syllabus for B.Sc. II- Geochemistry - (IDS) Semester System - CGPA To be implemented from Academic Year
 Solapur University, Solapur Syllabus for B.Sc. II- Geochemistry - (IDS) Semester System - CGPA To be implemented from Academic Year- 2015-16 Course Structure Total Credit 16 - (Theory (4 x 3) = 12+Practical
Solapur University, Solapur Syllabus for B.Sc. II- Geochemistry - (IDS) Semester System - CGPA To be implemented from Academic Year- 2015-16 Course Structure Total Credit 16 - (Theory (4 x 3) = 12+Practical
Sci.tanta.edu.eg PALEOECOLOGY, GE 2218
 Sci.tanta.edu.eg PALEOECOLOGY, GE 2218 Lec. 4 1 Biosphere Lithosphere Community Hydrosphere Atmosphere 2 1 Temperature Temperature range in the ocean is approximately 2 to 40 º C. Coldest waters are found
Sci.tanta.edu.eg PALEOECOLOGY, GE 2218 Lec. 4 1 Biosphere Lithosphere Community Hydrosphere Atmosphere 2 1 Temperature Temperature range in the ocean is approximately 2 to 40 º C. Coldest waters are found
Supporting Information Appendix. Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for more than a century
 Supporting Information Appendix for article published in PNAS P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.1011915108 Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for
Supporting Information Appendix for article published in PNAS P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.1011915108 Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for
Lecture 6 - Determinants of Seawater Composition. Sets up electric dipole because O is more electronegative A o. Figure 3.
 12.742 - Marine Chemistry Fall 2004 Lecture 6 - Determinants of Seawater Composition Prof. Scott Doney What is seawater? Water Dissolved inorganic salts (major ions) Trace species, organics, colloids,
12.742 - Marine Chemistry Fall 2004 Lecture 6 - Determinants of Seawater Composition Prof. Scott Doney What is seawater? Water Dissolved inorganic salts (major ions) Trace species, organics, colloids,
Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces. & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry
 Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry 3. charge transfer (e.g., ligand/donor sorption): Sorption involves a number of related processes that all
Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry 3. charge transfer (e.g., ligand/donor sorption): Sorption involves a number of related processes that all
Lab 8 Dynamic Soil Systems I: Soil ph and Liming
 Lab 8 Dynamic Soil Systems I: Soil ph and Liming Objectives: To measure soil ph and observe conditions which change ph To distinguish between active acidity (soil solution ph) and exchangeable acidity
Lab 8 Dynamic Soil Systems I: Soil ph and Liming Objectives: To measure soil ph and observe conditions which change ph To distinguish between active acidity (soil solution ph) and exchangeable acidity
Name... Requirements for the task and Chemistry lessons
 Name... HAUTLIEU SCHOOL CHEMISTRY Pre AS and IB Diploma Task Expectations All sections of the task will be attempted please check you have answered all questions (even those on the back page) Answers should
Name... HAUTLIEU SCHOOL CHEMISTRY Pre AS and IB Diploma Task Expectations All sections of the task will be attempted please check you have answered all questions (even those on the back page) Answers should
GHGT-10. Investigation of the effect of brine composition and ph buffer on CO 2 -Brine. Sequestration
 Energy Energy Procedia Procedia 4 (2011) 00 (2010) 4503 4507 000 000 Energy Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia GHGT-10 Investigation of the effect of brine composition
Energy Energy Procedia Procedia 4 (2011) 00 (2010) 4503 4507 000 000 Energy Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia GHGT-10 Investigation of the effect of brine composition
Hydro-chemical Characters and Ions Source of Groundwater from Qidong Coal Mine, Northern Anhui Province, China
 An Interdisciplinary Response to Mine Water Challenges Sui, Sun & Wang (eds) 2014 China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou, ISBN 9787564624378 Hydrochemical Characters and Ions Source of
An Interdisciplinary Response to Mine Water Challenges Sui, Sun & Wang (eds) 2014 China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou, ISBN 9787564624378 Hydrochemical Characters and Ions Source of
Chemistry 12 Solubility Equilibrium I. Name: Date: Block: 1. Solutions Vocab & Calculations 2. Predicting Solubility 3.
 Chemistry 12 Solubility Equilibrium I Name: Date: Block: 1. Solutions Vocab & Calculations 2. Predicting Solubility 3. Writing Equations Solutions Vocab & Calculations What is a solution? A homogenous
Chemistry 12 Solubility Equilibrium I Name: Date: Block: 1. Solutions Vocab & Calculations 2. Predicting Solubility 3. Writing Equations Solutions Vocab & Calculations What is a solution? A homogenous
Solubility Rules and Net Ionic Equations
 Solubility Rules and Net Ionic Equations Why? Solubility of a salt depends upon the type of ions in the salt. Some salts are soluble in water and others are not. When two soluble salts are mixed together
Solubility Rules and Net Ionic Equations Why? Solubility of a salt depends upon the type of ions in the salt. Some salts are soluble in water and others are not. When two soluble salts are mixed together
Tailings and Mineral Carbonation: The Potential for Atmospheric CO 2 Sequestration
 Tailings and Mineral Carbonation: The Potential for Atmospheric CO 2 Sequestration H. Andrew Rollo Lorax Environmental Services Ltd. Heather. E. Jamieson Department of Geological Sciences and Geological
Tailings and Mineral Carbonation: The Potential for Atmospheric CO 2 Sequestration H. Andrew Rollo Lorax Environmental Services Ltd. Heather. E. Jamieson Department of Geological Sciences and Geological
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding
 Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU Where does table
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU Where does table
This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates
 Why are some minerals harder than others? Their atomic structure and chemical formula. This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates Part #1 - Silicates: Silicon and Oxygen make up 70%
Why are some minerals harder than others? Their atomic structure and chemical formula. This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates Part #1 - Silicates: Silicon and Oxygen make up 70%
Atoms, Molecules and Minerals
 Atoms, Molecules and Minerals Atoms Matter The smallest unit of an element that retain its properties Molecules - a small orderly group of atoms that possess specific properties - H 2 O Small nucleus surrounded
Atoms, Molecules and Minerals Atoms Matter The smallest unit of an element that retain its properties Molecules - a small orderly group of atoms that possess specific properties - H 2 O Small nucleus surrounded
Geochemical Modelling of Low-Temperature Geothermal Fields from Bihor County, Romania
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Geochemical Modelling of Low-Temperature Geothermal Fields from Bihor County, Romania Oana Stǎnǎşel, Iulian Stǎnǎşel University
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Geochemical Modelling of Low-Temperature Geothermal Fields from Bihor County, Romania Oana Stǎnǎşel, Iulian Stǎnǎşel University
1 Earth s Oceans. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify What are the five main oceans?
 CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
Work hard. Be nice. Name: Period: Date: UNIT 3: Electrons Lesson 5: Atomic Radius and Ionic Radius
 UNIT 3: Electrons Lesson 5: Atomic Radius and Ionic Radius Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How the does the radius change when an atom becomes an ion? 1. How many protons, neutrons,
UNIT 3: Electrons Lesson 5: Atomic Radius and Ionic Radius Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How the does the radius change when an atom becomes an ion? 1. How many protons, neutrons,
1 st shell holds 2 electrons. 2 nd shell holds 8 electrons
 ATOM INDIVISIBLE ELEMENTS - Nucleus = protons (+ charge) & neutrons (no charge ) - Electrons (- charge) orbit the nucleus in shells of 2, 8, 8 electrons (inner orbit outward) - Atomic number = number of
ATOM INDIVISIBLE ELEMENTS - Nucleus = protons (+ charge) & neutrons (no charge ) - Electrons (- charge) orbit the nucleus in shells of 2, 8, 8 electrons (inner orbit outward) - Atomic number = number of
Origin and Evolution of Formation Waters in the West-Central Part of the Alberta Basin
 Page No. 004-1 Origin and Evolution of Formation Waters in the West-Central Part of the Alberta Basin Karsten Michael* University of Alberta, 1-26 ESB, Edmonton, AB T6G 2E3 karsten@ualberta.ca and Stefan
Page No. 004-1 Origin and Evolution of Formation Waters in the West-Central Part of the Alberta Basin Karsten Michael* University of Alberta, 1-26 ESB, Edmonton, AB T6G 2E3 karsten@ualberta.ca and Stefan
Elements in the Periodic Table show a periodic trend in atomic radius. In your answer you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly.
 1 The Periodic Table is arranged in periods and groups (a) Elements in the Periodic Table show a periodic trend in atomic radius State and explain the trend in atomic radius from Li to F In your answer
1 The Periodic Table is arranged in periods and groups (a) Elements in the Periodic Table show a periodic trend in atomic radius State and explain the trend in atomic radius from Li to F In your answer
Bell Work 6-Nov How many valence electrons does magnesium and oxygen have? Draw their Lewis dot structures.
 Bell Work 6-Nov-2012 How many valence electrons does magnesium and oxygen have? Draw their Lewis dot structures. Objective: You will UNDERSTAND how to write a basic chemical formula Ions Some compounds
Bell Work 6-Nov-2012 How many valence electrons does magnesium and oxygen have? Draw their Lewis dot structures. Objective: You will UNDERSTAND how to write a basic chemical formula Ions Some compounds
HYDROGEOCHEMI CAL ASPECTS IN COASTAL AQUIFERS - A CASE STUDY FROM CUDDALORE DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA. ABSTRACT
 HYDROGEOCHEMI CAL ASPECTS IN COASTAL AQUIFERS - A CASE STUDY FROM CUDDALORE DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA. SENTHILKUMAR G 1*, RAMANATHAN AL 1, NAINWAL HC 2 AND CHIDAMBARAM S 3 1 School of s, Jawaharlal Nehru University,
HYDROGEOCHEMI CAL ASPECTS IN COASTAL AQUIFERS - A CASE STUDY FROM CUDDALORE DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA. SENTHILKUMAR G 1*, RAMANATHAN AL 1, NAINWAL HC 2 AND CHIDAMBARAM S 3 1 School of s, Jawaharlal Nehru University,
UNIT III: SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIUM YEAR END REVIEW (Chemistry 12)
 I. Multiple Choice UNIT III: SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIUM YEAR END REVIEW (Chemistry 12) 1) Which one of the following would form an ionic solution when dissolved in water? A. I 2 C. Ca(NO 3 ) 2 B. CH 3 OH D.
I. Multiple Choice UNIT III: SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIUM YEAR END REVIEW (Chemistry 12) 1) Which one of the following would form an ionic solution when dissolved in water? A. I 2 C. Ca(NO 3 ) 2 B. CH 3 OH D.
Lecture 3 questions Temperature, Salinity, Density and Circulation
 Lecture 3 questions Temperature, Salinity, Density and Circulation (1) These are profiles of mean ocean temperature with depth at various locations in the ocean which in the following (a, b, c) figures
Lecture 3 questions Temperature, Salinity, Density and Circulation (1) These are profiles of mean ocean temperature with depth at various locations in the ocean which in the following (a, b, c) figures
Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a nonmetal. Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. Metallic bonds occur between metal atoms only.
 Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a nonmetal. Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. Metallic bonds occur between metal atoms only. Using chemical equations to show ionization: Na Na +
Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a nonmetal. Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. Metallic bonds occur between metal atoms only. Using chemical equations to show ionization: Na Na +
Solubility and Complex-ion Equilibria
 Solubility and Complex-ion Equilibria Solubility Equilibria Many natural processes depend on the precipitation or dissolving of a slightly soluble salt. In the next section, we look at the equilibria of
Solubility and Complex-ion Equilibria Solubility Equilibria Many natural processes depend on the precipitation or dissolving of a slightly soluble salt. In the next section, we look at the equilibria of
****************************************************************************
 **************************************************************************** To quickly summarize: 1. The solubility of a compound is decreased when an ion which is the same as one of the ions in the compound
**************************************************************************** To quickly summarize: 1. The solubility of a compound is decreased when an ion which is the same as one of the ions in the compound
EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
The Lithosphere. Definition
 10/14/2014 www.komar.de The Lithosphere Ben Sullivan, Assistant Professor NRES 765, Biogeochemistry October 14th, 2014 Contact: bsullivan@cabnr.unr.edu Definition io9.com tedquarters.net Lithos = rocky;
10/14/2014 www.komar.de The Lithosphere Ben Sullivan, Assistant Professor NRES 765, Biogeochemistry October 14th, 2014 Contact: bsullivan@cabnr.unr.edu Definition io9.com tedquarters.net Lithos = rocky;
KRONDORF MINERAL WATER
 Water character Project Krondorf the restoration of traditional production of mineral water that preserves the source as well as the environment, utilising centuries-old procedures and focusing on water
Water character Project Krondorf the restoration of traditional production of mineral water that preserves the source as well as the environment, utilising centuries-old procedures and focusing on water
SEDIMENTATION IN CHRISTMAS ISLAND PONDS. Carol A. Yonamine. ~arine Option Program
 SEDIMENTATION IN CHRISTMAS ISLAND PONDS Carol A. Yonamine ~arine Option Program 1 May 1989 INTRODUCTION Christmas Island, with a surface area of approximately 350 square kilometers, is the largest atoll
SEDIMENTATION IN CHRISTMAS ISLAND PONDS Carol A. Yonamine ~arine Option Program 1 May 1989 INTRODUCTION Christmas Island, with a surface area of approximately 350 square kilometers, is the largest atoll
SeCtiOn 7 [STOCK AND CUSTOM] Ion Chromatography Single and Multi-Element Standards
![SeCtiOn 7 [STOCK AND CUSTOM] Ion Chromatography Single and Multi-Element Standards SeCtiOn 7 [STOCK AND CUSTOM] Ion Chromatography Single and Multi-Element Standards](/thumbs/86/93303672.jpg) SeCtiOn 7 [STOCK AND CUSTOM] Ion Chromatography Single and Multi-Element Standards Your Science is Our Passion. Ion Chromatography Standards As with SPEX CertiPrep s Assurance Standards, every IC Standard
SeCtiOn 7 [STOCK AND CUSTOM] Ion Chromatography Single and Multi-Element Standards Your Science is Our Passion. Ion Chromatography Standards As with SPEX CertiPrep s Assurance Standards, every IC Standard
Ionic and Metallic Bonding
 Unit 5: Ionic and Metallic Bonding H 2 O Valence Electrons are? The electrons responsible for the chemical properties of atoms, and are those in the outer energy level. Valence electrons - The s and p
Unit 5: Ionic and Metallic Bonding H 2 O Valence Electrons are? The electrons responsible for the chemical properties of atoms, and are those in the outer energy level. Valence electrons - The s and p
it must be it must be it must have been formed by it must have it must have
 6. Minerals II (p. 78-87) What is a mineral? The five characteristics required in order for a compound to be a mineral are: it must be it must be it must have been formed by it must have it must have Characteristics
6. Minerals II (p. 78-87) What is a mineral? The five characteristics required in order for a compound to be a mineral are: it must be it must be it must have been formed by it must have it must have Characteristics
Tectonically conditioned brine leakage into usable freshwater aquifers implications for the quality of groundwater exploited in central Poland
 Tectonically conditioned brine leakage into usable freshwater aquifers implications for the quality of groundwater exploited in central Poland Dorota Kaczor-Kurzawa 1 1 Polish Geological Institute National
Tectonically conditioned brine leakage into usable freshwater aquifers implications for the quality of groundwater exploited in central Poland Dorota Kaczor-Kurzawa 1 1 Polish Geological Institute National
There are many different kinds of salt, but for simplicity sake, sodium chloride (NaCl) in particular will be the topic of discussion.
 There are many different kinds of salt, but for simplicity sake, sodium chloride (NaCl) in particular will be the topic of discussion. NaCl comes from both natural and anthropogenic sources. Naturally
There are many different kinds of salt, but for simplicity sake, sodium chloride (NaCl) in particular will be the topic of discussion. NaCl comes from both natural and anthropogenic sources. Naturally
31. GEOCHEMISTRY OF INTERSTITIAL WATERS INTERSTITIAL WATER STUDIES ON SMALL CORE SAMPLES FROM THE MEDITERRANEAN SEA 1
 31. GEOCHEMISTRY OF INTERSTITIAL WATERS 31.1. INTERSTITIAL WATER STUDIES ON SMALL CORE SAMPLES FROM THE MEDITERRANEAN SEA 1 F. L. Sayles and L. S. Waterman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods
31. GEOCHEMISTRY OF INTERSTITIAL WATERS 31.1. INTERSTITIAL WATER STUDIES ON SMALL CORE SAMPLES FROM THE MEDITERRANEAN SEA 1 F. L. Sayles and L. S. Waterman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods
Water Quality Evaluation and Limits
 Cooling Tower Institute Annual Conference February 7-10, 2010 Houston, TX, USA Water Quality Evaluation and Limits Robert J. Ferguson French Creek Software, Inc. Kimberton, PA 19442 Part 1: Evaluation
Cooling Tower Institute Annual Conference February 7-10, 2010 Houston, TX, USA Water Quality Evaluation and Limits Robert J. Ferguson French Creek Software, Inc. Kimberton, PA 19442 Part 1: Evaluation
elemental state. There are two different possibilities: DESCRIPTION 1. One cation (+ ion) replaces another. 2. One anion (- ion) replaces another.
 CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
AP Chemistry Table of Contents: Ksp & Solubility Products Click on the topic to go to that section
 Slide 1 / 91 Slide 2 / 91 AP Chemistry Aqueous Equilibria II: Ksp & Solubility Products Table of Contents: K sp & Solubility Products Slide 3 / 91 Click on the topic to go to that section Introduction
Slide 1 / 91 Slide 2 / 91 AP Chemistry Aqueous Equilibria II: Ksp & Solubility Products Table of Contents: K sp & Solubility Products Slide 3 / 91 Click on the topic to go to that section Introduction
Hydrogeochemistry of the Mid-levels Area, Hong Kong
 Hydrological Processes in Urban Areas 8 Hydrogeochemistry of the Mid-levels Area, Hong Kong Chiman Leung, Jiu Jimmy Jiao, John Malpas, Wing Tat Chan 2 Department of Earth Sciences, The University of Hong
Hydrological Processes in Urban Areas 8 Hydrogeochemistry of the Mid-levels Area, Hong Kong Chiman Leung, Jiu Jimmy Jiao, John Malpas, Wing Tat Chan 2 Department of Earth Sciences, The University of Hong
Weathering Cycle Teacher Notes
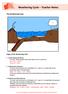 The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
Seawater and Ocean Chemistry
 Seawater and Ocean Chemistry Seawater Chemistry Water Seawater Salts in seawater Water Composition Properties Water is a chemical compound (H 2 O) comprising two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen,
Seawater and Ocean Chemistry Seawater Chemistry Water Seawater Salts in seawater Water Composition Properties Water is a chemical compound (H 2 O) comprising two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen,
Determination of the inorganic ion composition of standing surface water
 2. Experiment Determination of the inorganic ion composition of standing surface water Objectives All the biologically important inorganic chemical parameters of standing surface water are called halobity.
2. Experiment Determination of the inorganic ion composition of standing surface water Objectives All the biologically important inorganic chemical parameters of standing surface water are called halobity.
Physical Oceanography
 Physical Oceanography SECTION 15.1 The Oceans In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. Column A 1. German research
Physical Oceanography SECTION 15.1 The Oceans In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. Column A 1. German research
OCN 201. Chemistry & Physics of the Ocean. (but no need to panic) foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m. Length. Area m 2 square feet ~0.09m2
 Chemistry & Physics of the Ocean OCN 201 (but no need to panic) Length m foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m Area m 2 square feet ~0.09m2 Volume m 3 US pint ~ 0.47 L, L (liters) fl. oz. ~0.02 L Speed m/s mph Acceleration
Chemistry & Physics of the Ocean OCN 201 (but no need to panic) Length m foot = 0.305m yard = 0.91m Area m 2 square feet ~0.09m2 Volume m 3 US pint ~ 0.47 L, L (liters) fl. oz. ~0.02 L Speed m/s mph Acceleration
CHEMICAL BONDING. Dear Reader
 CHEMICAL BONDING Dear Reader As you have already studied that the substances exist as discrete units called molecules. These molecules are formed by the combination of atoms. When these atoms combine,
CHEMICAL BONDING Dear Reader As you have already studied that the substances exist as discrete units called molecules. These molecules are formed by the combination of atoms. When these atoms combine,
Unit 2. Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
 Unit 2 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions Memorize the list of elements You will have a quiz on this list. All of the elements will be on the quiz! Elements in the Earth System (% mass in
Unit 2 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions Memorize the list of elements You will have a quiz on this list. All of the elements will be on the quiz! Elements in the Earth System (% mass in
Lecture 16 Guest Lecturer this week. Prof. Greg Ravizza
 Lecture 16 Guest Lecturer this week. Prof. Greg Ravizza General Concepts for Natural Controls on Fresh Water Composition 1. Generalizations about freshwater compositions 2. Conservative/nonconservative
Lecture 16 Guest Lecturer this week. Prof. Greg Ravizza General Concepts for Natural Controls on Fresh Water Composition 1. Generalizations about freshwater compositions 2. Conservative/nonconservative
