r : Mg 2+, Ca 2+ 1(b)(ii) Soaps are biodegradable 1
|
|
|
- Ethelbert Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MARKING SCHEME CHEMISTRY PAPER SECTION A (454/) Question scheme Sub (a) A: Detergents B: Soap r : sodium salt magnesium ion // or calcium ion SKEMA SBP0 (b)(i) r : Mg +, Ca + (b)(ii) Soaps are biodegradable Total (c) (d)(i) (d)(ii) Analgesics Psychotherapeutic r: wrong spelling Sugar Aspartame To add / restore the colour of food // To enhance its visual appeal / appearance// more attractive TOTAL 9 Question (a)(i) Magnesium r:mg scheme (a)(ii) Has shell occupied with electrons (b). Proton number of chlorine is higher than magnesium // the number of proton of chlorine atom higher than magnesium atom // total positive charged in nucleus higher than magnesium. The attractive force between the nucleus and the electrons in chlorine atom stronger than magnesium atom // nuclei attraction towards electrons stronger. Sub Total (c) Light bulb // in welding process (d) Argon (e)(i) Cl (g) + Fe (s) FeCl (s) (e)(ii) Mass iron (III) chloride = 0.05 x 6 // 8.05 g
2 (e)(ii) Chlorine gas Gas klorin Heat Panaskan Hot iron wool Wul besi panas Total 9 Question scheme Sub (a)(i) 6 (a)(ii) To estimate the age of fossils and artifacts (a)(iii) C- // C- Total C 6 Or C 6 (a)(iv) 7 / 6 4 (b)(i) A: covalent r: covalent bond B: ionic r: ionic bond (b)(ii).8.8. (b)(iii) High melting point and boiling point // conduct electricity in molten or aqueous solution // soluble in water // insoluble in organic solvent. [Any one] (c)(iv) K + Cl KCl. Formula of reactants and products correct. Balance the chemical equation TOTAL 6 0 4
3 Question 4(a)(i) 4(a)(ii) 4(a)(iii) 4(b)(i) 4(b)(ii) scheme Pipette r: wrong spelling Phenolphthalein // methyl orange r: wrong spelling Phenolphthalein : pink to colourless // methyl orange : yellow to orange KOH + H SO 4 K SO 4 + H O Formula of reactants and products correct Balance the chemical equation. Mol of KOH = (.0)(5) / 000 = 0.05 mol. Molarity of H SO 4 = (0.05)(000) / 0 =.5 mol dm - // Molarity of H SO 4 = 0.05 /0.0 =.5 mol dm - Or M av M V b a b a ; Molarity of H SO 4 = b r: wrong unit or without unit (5) x 0 =.5 mol dm - Sub Total 4(c)(i) 4(c)(ii) Hydrogen ion r: H + (symbol ion). no water. contain of molecule // no hydrogen ion, H + TOTAL 0 5
4 Question scheme Sub Total 5(a) Chemical formula that shows the simplest whole number ratio of atom of each element in the compound. 5(b)(i) Mass of Mg =.4 g Mass of O =.6 g 5(b)(ii) Mole of Mg =.4 / 4 = 0. Mol of O =.6 / 6 = 0. Mg : O = : 5(b)(iii) MgO 5(b)(iv) to allow oxygen enter the crucible 5(b)(v) Repeat the process heating, cooling and weighing until a 6 constant mass is obtained. 5(c) crucible Magnesium ribbon Heat Apparatus set-up correct and functional Labeled : magnesium ribbon, heat 5(d)(i) Zinc oxide // aluminium oxide r: formula 5(d)(ii) Silver is less reactive / not reactive metal TOTAL 6
5 Question scheme Sub 6(a) Hydrogenation 6(b) C 4 H 8 + H C 4 H 0 6(c)(i) Mole of butene =.8 /56 = 0.05 mol Total 6(c)(ii) 6(d) 6(e)(i) 6(e)(ii) P. mol of butene burns in oxygen gas produce 4 mol of carbon dioxide. Therefore 0.05 mol of butene burns in oxygen gas produce 0. mol of carbon dioxide // C 4 H 8 : CO : : 0. P. volume of CO = 0. x 4 = 4.8 dm P: cm of but--ene and cm of butane gas are filled in two different test tubes. P : - drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution is added to both test tubes. P: But--ene decolourises purple acidified KMnO 4 Purple acidified KMnO 4 in butane remains unchange. Or P: cm of but--ene and cm of butane gas are filled in two different test tubes. P : - drops of bromine water is added to both test tubes. P: But--ene decolourises brown bromine water. Brown bromine water in butane remains unchange. A: unvulcanised rubber B: vulcanised rubber Rubber type B/ vulcanised rubber is more elastic than rubber type A/ unvulcanised rubber TOTAL Or 5 7
6 SECTION B Question scheme Σ 7 (a) (i) Ascending order : Cu, Y,X, W (ii) P : Positive terminal : Cu P : Potential difference :.V P: Copper is less electropositive // X is more electropositive correct value and unit 4 7 ( b) (i) Experiment I : Pb +, Cl - Experiment II: H +. OH -, Cl r: lead(ii) ion, chloride ion Hydrogen ion, hydroxide ion, chloride ion Experiment Experiment II Product at anode: Chlorine gas Products at cathode: Oxygen gas + Reason: Reason: P: Cl - is discharged P:OH - is selected to be discharged + 7(b)(ii) P: the only anion presence and discharged at anode P:the position of OH - is lower than Cl - in electrochemical series +.Half equation:. Half equation: Cl - Cl + e 4OH - H O + O + 4e P:Correct formula of reactant and product : P: Balance equation P: Correct formula of reactant and product P: Balance equation
7 7(c) P: Positive terminal: R P: Negative terminal:cu P: Suitable metal for R : Silver P4: Suitable solution for R : Silver nitate solution 4 Total 0 Question scheme Σ 8(a) P. Smaller size has larger total surface area. P. Absorb heat faster. P. Bigger size has smaller total surface area. P4. Absorb heat slower 4 (b)(i) Copper(II) sulphate (b)(ii) (b)(iii). Experiment I Rate of reaction = 40/ = 0 cm min -. Experiment II Rate of reaction = 60/ = 0 cm min - P. Rate of reaction in Experiment II is higher than Experiment I. P. Substance X used in Experiment II is a catalyst. P. Catalyst provided an alternative path with requires a lower activation energy. P4. More particles are able to achieve lower activation energy. P5. Frequency of effective collisions between zinc atoms and hydrogen ions are higher. 5 9
8 (b)(iv). Label of axes and unit. Correct curve and label Volume of gas / cm Exp II Exp I Time / min (v). Correct formula of reactants and product. Balanced equation Zn + H + Zn + + H (vi). Rate of reaction using sulphuric acid is higher.. Volume of hydrogen gas released is doubled.. Sulphuric acid is a diprotic acid. 4. Concentration of hydrogen ions in sulphuric acid is double than that in hydrochloric acid. 4 Total 0 0
9 Question scheme Σ 9(a) P: Magnesium atom undergoes oxidation P: oxidation number increases from 0 to + P: Copper (II) ion undergoes reduction P4: oxidation number decreases from + to 0 MAX P5: The reaction involving oxidation and reduction 4 (b) Experiment I L can reduce copper(ii) oxide// L can react with copper(ii) oxide L is more reactive than copper. Experiment II M can reduce copper(ii) oxide//m can react with copper(ii) oxide M is more reactive than copper. Experiment III M cannot reduce L oxide // M cannot react with L oxide. M is less reactive than L//L is more reactive than M. Max 6 5 The arrangement in order of increasing reactivity toward oxygen is Cu, M and L. (c) Procedure : P. Pour cm of potassium bromide solution into a test tube. P. Add cm of chlorine water to the test tube and shake the mixture. P. Add cm of,, trichloroethane to the test tube and shake the mixture. P4. Record the observation P5. Repeat steps -4 using another halogens and halide solution..
10 Result : Chlorine water Bromine water Iodine water Potassium chloride X X Potassium bromide X Potassium iodide Ionic equation:. Cl + Br - Cl - + Br. Cl + I - Cl - + I. Br + I - Br - + I 0 0
11 Question scheme Σ Precipitation / double decomposition reaction 0(a) Barium nitrate solution/barium chloride solution [Any sulphate solution] Example: sodium sulphate, potasium sulphate, sulphuric acid Reject : Lead(II) sulphate, calcium sulphate Ba + + SO 4 BaSO 4 4 0(b)(i) Cation : Iron(II) ion / Fe + Anion: Chloride ion / Cl Test for NO 0(b)(ii) P: Add cm of dilute sulphuric acid into the test tube follow by cm of iron(ii) sulphate solution. P: Add a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid P: carefully and slowly along the side of slanting test tube into the mixture. P: A brown ring is formed. 4 Procedure: 0(c) P. Add zinc nitrate solution to sodium carbonate solution in a beaker. P. Stir the mixture. P. Filter the white precipitate/solid zinc carbonate formed. P4. Add zinc carbonate to sulphuric acid in a beaker until some zinc carbonate solid no longer dissolve. P5. Filter the mixture. P6. Transfer the filtrate to a evaporating dish. P7. Heat the filtrate(zinc sulphate solution) until saturated// Heat the filtrate to about one-third (/) of its initial volume P8. Allow the saturated solution to cool at room temperature. P9. Filter the crystals formed. P0. Dry the crystals by pressing it between two sheets of filter papers. 0 Total 0
12 ing Scheme Chemistry Paper [KK050 Mengukur menggunakan nombor] SKEMA SBP0 (a) Able to measure the diameter of dents correctly and accurately Copper:.5,.60,.50 Bronze:.0,.00,.0 Able to measure the diameter of dents without decimal point Able to state 4 diameter of dents correctly [KK0506 Berkomunikasi] (b) Able to construct the table with correct label and unit Type of Diameter of dents(cm) Average diameter blocks I II III of dents (cm) Copper Bronze Able to construct the table without correct label or unit Able to construct the idea of table [KK050 Memerhati] (c) (i) Able to state the observation correctly and accurately The average diameter of dents on bronze block is. cm, the average diameter of dents on copper block is.48 cm.// The size / diameter of dents on bronze block is smaller than the size / diameter of dents on copper block// The size / diameter of dents on copper block is bigger than the size / diameter of dents on bronze block Able to state the incomplete observation Able to state the average diameter of one block only. The size / diameter of dents on bronze block is smaller// The size / diameter of dents on copper block is bigger. Able to state the idea of observation Sample answer : The size / diameter of dents on bronze block is small/ The size / diameter of dents on copper block is big.
13 [KK 0504 Membuat Inferens] (c)(ii) Able to state the inference correctly and accurately Bronze is harder than copper // Copper is less harder than bronze Able to state the incomplete inference correctly Sample answer : Bronze is harder // Copper is less harder Able to state the idea of inference Sample answer : Bronze is hard// Copper is soft [KK0508 Mentafsir data] (c)(iii) Able to explain the arrangement of particles in the materials correctly. The atomic size of tin is bigger than copper// The atomic size of tin and copper are different. The presence of tin atoms in bronze disrupts the orderly arrangement of copper atoms. Reduces/ Prevent the layers of atoms from sliding over each other/ easily. Able to state any points // points without the name of atoms correctly Able to state point point correctly [KK050 Mengawal pemboleh ubah] (d) Able to state all the variables Manipulated variable : Type of materials / blocks// Copper and bronze Responding variable : Size / diameter of dents Fixed variable : Size / diameter and mass of steel ball bearing // height of the weight // mass of the weight Able to state two variables correctly Able to state one variable correctly
14 [KK05 Membuat hipotesis] (e)(i) Able to state the hypothesis correctly Bronze is harder than copper // Copper is less harder than bronze Able to state the hypothesis less correctly Able to state idea of hypothesis [KK0509 Mendefinisikan secara operasi] (e)(ii) Able to state the operational definition correctly The smaller dent produced when a kg weight is dropped on the block. Able to state the operational definition less correctly The smaller dent produced when a weight is dropped on the block// When a weight is dropped on the block results smaller dent, thus the harder the block is. Able to state idea of operational definition The harder block has a smaller dent. [KK050 Mengelas] (e)(ii) Able to classify all substances correctly Alloy Pure metal Steel Iron Brass Chromium Pewter Tin Able to classify at least 4 substances less correctly Alloy Pure metal Steel Iron Brass Chromium Tin Pewter Able to state idea of classification (at least correct) Sample answer : Alloy Iron Chromium Pewter Pure metal Steel Brass Tin
15 [KK0505 Meramal] (a). Able to show an extrapolation on the graph. 500 Heat of combustion/ kj mol - Haba pembakaran/ kj mol Number of carbon atom per molecule of alcohols. Range of answer[ ]. Show the negative sign and correct unit, kjmol - Able to state any two correct answers Able to state any one correct answer [KK0507 Menggunakan perhubungan ruang dan masa] (b) Able to state the relationship between the number of carbon atom per molecule and the time taken for cooking correctly Sample answer The higher the number of carbon atom per molecule alcohol, the shorter the time taken for cooking Able to state the relationship between the number of carbon atom per molecule and the time taken for cooking less correctly Sample answer The higher the number of carbon atom, the shorter the time taken for cooking Able to give relevant idea 4
16 [KK05 Menyatakan masalah] (a) Able to give the problem statement correctly How does different type of metals in contact with iron affect rusting?// Does more electropositive metal in contact with iron inhibit the rusting of iron?// Does less electropositive metal in contact with iron speed up the rusting of iron? Able to give the problem statement less correctly To investigate the affect of other metals on the rusting of iron// How does a metal affect the rusting of iron? Able to state an idea of hypothesis More electropositive metal inhibit the rusting of iron// Less electropositive metal speed up the rusting of iron KK05 Menyatakan pemboleh ubah] Question Rubric s (b) Able to state all the three variables correctly Manipulated variable : Name of metal R and metal S// type of metals Responding variable : Rusting of iron//iron rust//formation of blue spot Constant variables: Iron nail//gelatine solution with potassium hexacyanoferrate(iii) and phenolpthtalein Able to state any two variables correctly Able to state any one variable correctly 5
17 [KK05 Menulis hipotesis] Question Rubric s (c) Able to state the relationship between the manipulated variable and the responding variable and state the direction. When a more electropositive metal is in contact with iron, the metal inhibits rusting. // When a less electropositive metal is in contact with iron, the metal speed up rusting Able to state the relationship between the manipulated variable and the responding variable less correctly A more electropositive metal will prevent iron from rusting. // A less electropositive metal will cause iron to rust. Able to state an idea of hypothesis Metal R and metal S affect rusting (of iron) [KK05 Menyenaraikan bahan dan radas] Question Rubric (d) Able to give complete list of substances and apparatus Answer: Substances Two Iron nails, Magnesium/zinc/aluminium strip Tin/copper/lead/silver strip Potassium hexacyanoferrate(iii) solution + phenolphthalein [Any suitable electrolyte]/[water] Apparatus Test tube/boiling tube Test tube rack Sand paper Able to list basic materials and apparatus Materials Magnesium/zinc/aluminium strip Tin/copper/lead/silver strip Iron nail Any suitable electrolyte 6
18 Apparatus: Any suitable container Able to give an idea of the materials and apparatus Materials Iron Any electrolyte Apparatus Any suitable container [KK05 Memilih teknik] Question Rubric s (e) Able to state all the steps correctly. Clean the iron nails and metals strip with sand paper.. Coil iron nails with magnesium ribbon and copper strip.. Put the coiled iron nail into different test tubes. 4. Pour the hot jelly solution containing potassium hexacyanoferrate(iii)solution and phenolphthalein into the test tube. 5. Leave the test tube in a test tube rack for a day. 6. Record the observation. Able to state the steps,4,and 6 correctly Able to state steps and 4 correctly [ and 4 ]//the idea combining iron and any metals and any substances 7
19 [KK05 Mempamerkan perancangan] Question Rubric s (f) Able to tabulate the data with the following aspects. Heading for the manipulated variables [pair of metals//test Tube]. Heading for responding variables Pair of metals Observation Mg/Fe Cu/Fe Able to give an idea on tabulation of data at least one information stated in the table. At least one heading Sample answer Set PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN TAMAT 8
PAPER 1 PAPER 2 PAPER 3
 BAHAGIAN PENGURUSAN SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH DAN SEKOLAH KECEMERLANGAN KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA CHEMISTRY TRIAL-EXAM SPM 0 MARKING SCHEME PAPER PAPER PAPER 3 SKEMA KERTAS PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK
BAHAGIAN PENGURUSAN SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH DAN SEKOLAH KECEMERLANGAN KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA CHEMISTRY TRIAL-EXAM SPM 0 MARKING SCHEME PAPER PAPER PAPER 3 SKEMA KERTAS PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK
Jawapan. Chemistry. Chemistry Paper 1(4541/1) SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010 [4541/1] [4541/2] [4541/3]
![Jawapan. Chemistry. Chemistry Paper 1(4541/1) SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010 [4541/1] [4541/2] [4541/3] Jawapan. Chemistry. Chemistry Paper 1(4541/1) SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010 [4541/1] [4541/2] [4541/3]](/thumbs/77/76269749.jpg) SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 00 37 Jawapan Chemistry [454/] [454/] [454/3] Chemistry Paper (454/) A A 3 A 4 B 5 D 6 C 7 D 8 B 9 C 0 A B D 3 B 4 A 5 C 6 D 7 C 8 D 9 B 0 A A D 3 D 4 C 5 B 6 C 7 D 8 A 9 A 30 A 3
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 00 37 Jawapan Chemistry [454/] [454/] [454/3] Chemistry Paper (454/) A A 3 A 4 B 5 D 6 C 7 D 8 B 9 C 0 A B D 3 B 4 A 5 C 6 D 7 C 8 D 9 B 0 A A D 3 D 4 C 5 B 6 C 7 D 8 A 9 A 30 A 3
No Mark Scheme Sub Total. 1 (a) Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom 1 1
 SKEMA MRSM0 https://cikguadura.wordpress.com/ No Mark Scheme Sub Total mark (a) Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom (b) (i) P : 6 (c) 4 Q 6 (ii) R: (d) (i), 8, //. 8. (ii) / two (e) (i) P, Q (ii)
SKEMA MRSM0 https://cikguadura.wordpress.com/ No Mark Scheme Sub Total mark (a) Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom (b) (i) P : 6 (c) 4 Q 6 (ii) R: (d) (i), 8, //. 8. (ii) / two (e) (i) P, Q (ii)
Set 4 Marking Scheme: Acid Bases & Salts 2010
 Set 4 Marking Scheme: Acid Bases & Salts 00 ACID AND BASES PAPER : STRUCTURE (a) Neutralisation KOH + H SO 4 K SO 4 + H O Correct formulae of reactants and products Balanced equation i. H +, OH -, K +
Set 4 Marking Scheme: Acid Bases & Salts 00 ACID AND BASES PAPER : STRUCTURE (a) Neutralisation KOH + H SO 4 K SO 4 + H O Correct formulae of reactants and products Balanced equation i. H +, OH -, K +
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN CHEMISTRY 4541
 http://cikguadura.wordpress.com/ PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK SBP 04 SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN CHEMISTRY 454 SULIT 454 PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK SBP 04 SKEMA KERTAS CHEMISTRY
http://cikguadura.wordpress.com/ PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK SBP 04 SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN CHEMISTRY 454 SULIT 454 PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK SBP 04 SKEMA KERTAS CHEMISTRY
SULIT SKEMA SBP2010 MARKING SCHEME FOR CHEMISTRY PAPER 2. No Rubric Mark 1(a)(i) Gas 1
 SULIT 454 SKEMA SBP00 MARKING SEME FOR EMISTRY PAPER No Rubric Mark (a)(i) Gas (ii) (b)(i) The melting point and boiling point of substance X is lower than room temperature. - X and Y axes are labelled
SULIT 454 SKEMA SBP00 MARKING SEME FOR EMISTRY PAPER No Rubric Mark (a)(i) Gas (ii) (b)(i) The melting point and boiling point of substance X is lower than room temperature. - X and Y axes are labelled
Set 1 Structure of the atoms & Chemical Equation Perfect Score F Matter is anything that. and has.
 STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMS 1. Matter is anything that. and has. 2. The particle theory of matter state that matter is.. 3. Type of particle Example 4. Property Solid Liquid Gas Diagrammatic representation
STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMS 1. Matter is anything that. and has. 2. The particle theory of matter state that matter is.. 3. Type of particle Example 4. Property Solid Liquid Gas Diagrammatic representation
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CHEMISTRY 060/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 07 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CHEMISTRY 060/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 07 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This
SULIT 4541/1 dan /1 dan 2 Chemistry Mark Scheme Paper 1 and 2
 SULIT 454/ dan 454/ dan Chemistry Mark Scheme Paper and PERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUA SEKOLAH MENENGAH MALAYSIA (PKPSM) CAWANGAN MELAKA DENGAN KERJASAMA JABATAN PELAJARAN MELAKA PEPERIKSAAN
SULIT 454/ dan 454/ dan Chemistry Mark Scheme Paper and PERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUA SEKOLAH MENENGAH MALAYSIA (PKPSM) CAWANGAN MELAKA DENGAN KERJASAMA JABATAN PELAJARAN MELAKA PEPERIKSAAN
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date...
 IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
Year 10 Chemistry. Practice questions. Topics
 Year 10 Chemistry Practice questions Topics 1 Group 1 2 Group 7 3 Reactivity series 4 Air and Water 5 Rates of reaction 6 Electrolysis 7 Acids, Alkali and Salts Objective: Evaluate group 1 & 7 reactivity
Year 10 Chemistry Practice questions Topics 1 Group 1 2 Group 7 3 Reactivity series 4 Air and Water 5 Rates of reaction 6 Electrolysis 7 Acids, Alkali and Salts Objective: Evaluate group 1 & 7 reactivity
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
# Ans Workings / Remarks
 # Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
# Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
SKEMA JAWAPAN KERTAS 2 (4541/2) PERCUBAAN SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME OF PAPER 2 (4541/2) SPM TRIAL 2016
 SKEMA JAWAPAN KERTAS (454/) PERCUBAAN SPM 06 MARKING SCHEME OF PAPER (454/) SPM TRIAL 06 QUESTION RUBRIC MARKS (a) (i) W and X/X and Y/W and Y (any one answer) (ii) The elements have the same number of
SKEMA JAWAPAN KERTAS (454/) PERCUBAAN SPM 06 MARKING SCHEME OF PAPER (454/) SPM TRIAL 06 QUESTION RUBRIC MARKS (a) (i) W and X/X and Y/W and Y (any one answer) (ii) The elements have the same number of
ICSE Board. Class X Chemistry. Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.
 1. (a) By referring to electrons, explain the meaning of the term oxidising agent.... For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.... (c) Complete the table
1. (a) By referring to electrons, explain the meaning of the term oxidising agent.... For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.... (c) Complete the table
SULIT 4541/1/2/ Chemistry Marking Scheme Mei 2007 BAHAGIAN SEKOLAH KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAHAN TAHUN 2007
 454//2/3 454 Chemistry Marking Scheme Mei 2007 BAAGIAN SEKOLA KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAAN TAUN 2007 FORM 5 CEMISTRY Marking Scheme for Papers, 2 and 3 Peraturan pemarkahan ini
454//2/3 454 Chemistry Marking Scheme Mei 2007 BAAGIAN SEKOLA KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAAN TAUN 2007 FORM 5 CEMISTRY Marking Scheme for Papers, 2 and 3 Peraturan pemarkahan ini
Electrolysis. Specification points. Year 11 Electrolysis
 Electrolysis Specification points Year Electrolysis The process of electrolysis When an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water, the ions are free to move about within the liquid or solution (the
Electrolysis Specification points Year Electrolysis The process of electrolysis When an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water, the ions are free to move about within the liquid or solution (the
Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases
 Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases The ph Scale Properties Acids Alkalis Physical. Substances that ionized in water to produce hydrogen ions.. Sour taste.. Turn blue litmus paper red. 4. Give a ph value
Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases The ph Scale Properties Acids Alkalis Physical. Substances that ionized in water to produce hydrogen ions.. Sour taste.. Turn blue litmus paper red. 4. Give a ph value
SKEMA JAWAPAN KERTAS 1 JUJ KIMIA SET D 11 C 21 A 31 D 41 C 2 C 12 B 22 D 32 C 42 A 3 C 13 B 23 C 33 A 43 B 4 C 14 B 24 D 34 A 44 B
 SKEMA JAWAPAN KERTAS JUJ KIMIA SET - 07 SKEMA PRAKTIS BESTARI JUJ KIMIA SET KERTAS, & D C A D 4 C C B D C 4 A C B C A 4 B 4 C 4 B 4 D 4 A 44 B 5 A 5 C 5 A 5 A 45 A 6 B 6 C 6 C 6 B 46 D 7 B 7 C 7 C 7 A
SKEMA JAWAPAN KERTAS JUJ KIMIA SET - 07 SKEMA PRAKTIS BESTARI JUJ KIMIA SET KERTAS, & D C A D 4 C C B D C 4 A C B C A 4 B 4 C 4 B 4 D 4 A 44 B 5 A 5 C 5 A 5 A 45 A 6 B 6 C 6 C 6 B 46 D 7 B 7 C 7 C 7 A
EXPERIMENTS. Testing products of combustion: Reducing Copper(III) Oxide to Copper. Page 4
 APPARATUS Page 2 APPARATUS Page 3 Reducing Copper(III) Oxide to Copper EXPERIMENTS Page 4 Testing products of combustion: EXPERIMENTS Showing that oxygen and water is needed for rusting iron Page 5 Showing
APPARATUS Page 2 APPARATUS Page 3 Reducing Copper(III) Oxide to Copper EXPERIMENTS Page 4 Testing products of combustion: EXPERIMENTS Showing that oxygen and water is needed for rusting iron Page 5 Showing
Chemistry Summer Holiday Homework Year Y9 & 10
 Chemistry Summer Holiday Homework Year Y9 & 10 1. An atom of aluminium has the symbol (a) Give the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in this atom of aluminium. Number of protons... Number of neutrons...
Chemistry Summer Holiday Homework Year Y9 & 10 1. An atom of aluminium has the symbol (a) Give the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in this atom of aluminium. Number of protons... Number of neutrons...
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min
 YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
2. Relative molecular mass, M r - The relative molecular mass of a molecule is the average mass of the one molecule when compared with
 Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations 1. Relative atomic mass, A r - The relative atomic mass of an element is the average mass of one atom of an element when compared with mass of an atom of carbon-12
Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations 1. Relative atomic mass, A r - The relative atomic mass of an element is the average mass of one atom of an element when compared with mass of an atom of carbon-12
MC 17 C - 6 SECTION - I
 SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
MARAKWET WEST DISTRICT 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 JULY/AUGUST 2015 TIME: 2 HOURS
 MARAKWET WEST DISTRICT 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 JULY/AUGUST 2015 TIME: 2 HOURS 1. State two reasons why we use the non- luminous flame for heating in the laboratory instead of using luminous flame. 2. The
MARAKWET WEST DISTRICT 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 JULY/AUGUST 2015 TIME: 2 HOURS 1. State two reasons why we use the non- luminous flame for heating in the laboratory instead of using luminous flame. 2. The
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
 Mark scheme Answers Marks (a) (i) 2.8.4 4 (b) (i) Decreases // Become smaller Proton number / Positive charges increases // Forces of attraction increases (c) Achieved octet electron arrangement // Has
Mark scheme Answers Marks (a) (i) 2.8.4 4 (b) (i) Decreases // Become smaller Proton number / Positive charges increases // Forces of attraction increases (c) Achieved octet electron arrangement // Has
flame test acidified silver nitrate solution added
 1 The results of two tests on solid X are shown. test aqueous sodium hydroxide added acidified silver nitrate added observation green precipitate formed yellow precipitate formed What is X? copper(ii)
1 The results of two tests on solid X are shown. test aqueous sodium hydroxide added acidified silver nitrate added observation green precipitate formed yellow precipitate formed What is X? copper(ii)
Chem!stry. Assignment on Redox
 Chem!stry Name: ( ) Class: Date: / / Assignment on Redox Question 1: Which one of the following elements is the most powerful reducing agent? A Aluminium B Copper C Lead D Potassium Question 2: Which of
Chem!stry Name: ( ) Class: Date: / / Assignment on Redox Question 1: Which one of the following elements is the most powerful reducing agent? A Aluminium B Copper C Lead D Potassium Question 2: Which of
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 4 3 3 5 2 H Paper Reference(s) 4335/2H London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry Paper 2H Higher Tier Wednesday 21 May 2008 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Surname Signature
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 4 3 3 5 2 H Paper Reference(s) 4335/2H London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry Paper 2H Higher Tier Wednesday 21 May 2008 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Surname Signature
 [4541/1] [4541/2] [4541/3] Analysis Chemistry http://cikguadura.wordpress.com 99 Paper 1 Paper 2 Section A Section B Section C Paper3 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10
[4541/1] [4541/2] [4541/3] Analysis Chemistry http://cikguadura.wordpress.com 99 Paper 1 Paper 2 Section A Section B Section C Paper3 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10 11 12 08 09 10
Identification of ions and gases
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Identification Of ions nd Gases Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Identification Of ions nd Gases Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice. Section A Mulltiple Choice
 Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A Mulltiple Choice 1. An aqueous solution is obtained when: a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A Mulltiple Choice 1. An aqueous solution is obtained when: a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when
JABATAN PELAJARAN MELAKA
 SULIT 454/ Chemistry Paper Paper Oktober 009 Marking Scheme JABATAN PELAJARAN MELAKA PEPERIKSAAN SELARAS AKHIR TAHUN TINGKATAN 4 MATA PELAJARAN SAINS DAN MATEMATIK SEKOLAH-SEKOLAH MENENGAH NEGERI MELAKA
SULIT 454/ Chemistry Paper Paper Oktober 009 Marking Scheme JABATAN PELAJARAN MELAKA PEPERIKSAAN SELARAS AKHIR TAHUN TINGKATAN 4 MATA PELAJARAN SAINS DAN MATEMATIK SEKOLAH-SEKOLAH MENENGAH NEGERI MELAKA
ST EDWARD S OXFORD. Lower Sixth Entrance Assessment. November Chemistry. 1 Hour. Candidates name:... St Edward's School 1
 ST EDWARD S OXFORD Lower Sixth Entrance Assessment November 2013 Chemistry 1 Hour Candidates name:... St Edward's School 1 St Edward's School 2 1. Complete the table below. Element calcium Symbol Pb S
ST EDWARD S OXFORD Lower Sixth Entrance Assessment November 2013 Chemistry 1 Hour Candidates name:... St Edward's School 1 St Edward's School 2 1. Complete the table below. Element calcium Symbol Pb S
Electrodes are normally made out of inert (unreactive) materials. Graphite and platinum are common electrode materials.
 Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
ICSE Chemistry Board Paper 2016
 2015 Time: 2 hours; Max. Marks: 80 General Instructions: Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed 10 write during the first 15 minutes. This time
2015 Time: 2 hours; Max. Marks: 80 General Instructions: Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed 10 write during the first 15 minutes. This time
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
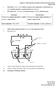 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Physical Science Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Physical Science Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Mendeleev arranged the known chemical elements in a table
Name: Class: Date: Physical Science Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Mendeleev arranged the known chemical elements in a table
Paper Reference. London Examinations IGCSE. Foundation Tier. Tuesday 10 November 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4335/1F London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry Paper 1F Foundation Tier Tuesday 10 November 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4335/1F London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry Paper 1F Foundation Tier Tuesday 10 November 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination
Electrolysis. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations. Score: /48. Percentage: /100
 Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
Identification of Ions and Gases
 Identification of Ions and Gases Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic cids, bases and salts Sub-Topic Identification of ions
Identification of Ions and Gases Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic cids, bases and salts Sub-Topic Identification of ions
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
ICSE-2010 Section 1(40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 [5]
![ICSE-2010 Section 1(40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 [5] ICSE-2010 Section 1(40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 [5]](/thumbs/88/117103030.jpg) MR D HR UV AS HE R ICSE BOA RD PAP ER 201 0 1 ICSE-2010 Section 1(40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 (a) From the list given below, select the word(s) required to correctly
MR D HR UV AS HE R ICSE BOA RD PAP ER 201 0 1 ICSE-2010 Section 1(40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 (a) From the list given below, select the word(s) required to correctly
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry
 Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry Duration: 2.30 Hours Index No:- Part -1 1) Select most suitable answers and underline them. 1) The diagram shows
Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry Duration: 2.30 Hours Index No:- Part -1 1) Select most suitable answers and underline them. 1) The diagram shows
Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr. When metals react with non-metals they form ionic compounds. ... [1] ... [1] ... [1] ...
![Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr. When metals react with non-metals they form ionic compounds. ... [1] ... [1] ... [1] ... Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr. When metals react with non-metals they form ionic compounds. ... [1] ... [1] ... [1] ...](/thumbs/77/75545958.jpg) High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 Look at the following section of the periodic table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 H He Li Na Be Mg B C N O F Ne Al Si P S Cl Ar K Use only the elements shown to answer the following
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 Look at the following section of the periodic table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 H He Li Na Be Mg B C N O F Ne Al Si P S Cl Ar K Use only the elements shown to answer the following
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.
 1 One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.) Standard temperature is 0 0 C or 273K and standard
1 One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.) Standard temperature is 0 0 C or 273K and standard
CHAPTER 8 SALTS. NaCl. A salt is an ionic substance produced when the hydrogen ion of the acid is replaced by metal ion or an ammonium ion.
 CHAPTER 8 SALTS A salt is an ionic substance produced when the hydrogen ion of the acid is replaced by metal ion or an ammonium ion. The salt consists of two parts, cation from base and anion from acid.
CHAPTER 8 SALTS A salt is an ionic substance produced when the hydrogen ion of the acid is replaced by metal ion or an ammonium ion. The salt consists of two parts, cation from base and anion from acid.
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award)
 EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation Question Explanation Marks
 Set Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 200 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMS PAPER 2 : STRUCTURE Question Explanation Marks (a)(i) Diffusion Molecules - Made of tiny / discrete particles/
Set Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 200 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMS PAPER 2 : STRUCTURE Question Explanation Marks (a)(i) Diffusion Molecules - Made of tiny / discrete particles/
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level CHEMISTRY 5070/4 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical 017 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 60 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level CHEMISTRY 5070/4 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical 017 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 60 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid
CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGE In our daily life many processes occur around us. Some of them do not lead to formation of any new substance, while others may lead to formation
CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGE In our daily life many processes occur around us. Some of them do not lead to formation of any new substance, while others may lead to formation
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/03
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/03 Paper 3 Practical Test Candidates answer on the Question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/03 Paper 3 Practical Test Candidates answer on the Question
Atomic Structure. Same atomic number Different mass number
 Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition Chemistry. Date : 26 April, 2015 Total no. of pages : 15
 Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition 2015 Chemistry Date : 26 April, 2015 Total no. of pages : 15 Time allowed : 12:00-1:15 pm (1 hour 15 minutes) Total marks : 60 1. Write your Candidate
Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition 2015 Chemistry Date : 26 April, 2015 Total no. of pages : 15 Time allowed : 12:00-1:15 pm (1 hour 15 minutes) Total marks : 60 1. Write your Candidate
Describe the structure and bonding in a metallic element. You should include a labelled diagram in your answer. ... [3] ...
![Describe the structure and bonding in a metallic element. You should include a labelled diagram in your answer. ... [3] ... Describe the structure and bonding in a metallic element. You should include a labelled diagram in your answer. ... [3] ...](/thumbs/78/76733031.jpg) 3 Gallium is a metallic element in Group III. It has similar properties to aluminium. (a) (i) Describe the structure and bonding in a metallic element. You should include a labelled diagram in your answer.
3 Gallium is a metallic element in Group III. It has similar properties to aluminium. (a) (i) Describe the structure and bonding in a metallic element. You should include a labelled diagram in your answer.
Chemistry Final Exam Sample Items
 Chemistry Final Exam Sample Items 1. Which best describes the current atomic theory? a. Atoms consist of electrons circling in definite orbits around a positive nucleus. b. Atoms are composed of electrons
Chemistry Final Exam Sample Items 1. Which best describes the current atomic theory? a. Atoms consist of electrons circling in definite orbits around a positive nucleus. b. Atoms are composed of electrons
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice. Section A Multiple Choice
 Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A Multiple Choice 1 An aqueous solution is obtained when: a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when a
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A Multiple Choice 1 An aqueous solution is obtained when: a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when a
MC 17 C SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section.
 Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
KIRINYAGA COUNTY MOCK JULY-AUGUST 2017
 NAME SCHOOL ------------------------------- 233/1 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 TIME: 2 HOURS ADM NO ----------------------------- SIGNATURE -------------------------- DATE ----------------------------------
NAME SCHOOL ------------------------------- 233/1 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 TIME: 2 HOURS ADM NO ----------------------------- SIGNATURE -------------------------- DATE ----------------------------------
GraspIT AQA GCSE Chemical and Energy Changes
 A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
Describe in full the colour change at the end-point of this titration. ... (1)
 Q1. (a) A solution of barium hydroxide is often used for the titration of organic acids. A suitable indicator for the titration is thymol blue. Thymol blue is yellow in acid and blue in alkali. In a titration
Q1. (a) A solution of barium hydroxide is often used for the titration of organic acids. A suitable indicator for the titration is thymol blue. Thymol blue is yellow in acid and blue in alkali. In a titration
0620 CHEMISTRY. 0620/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0620 CHEMISTRY 0620/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0620 CHEMISTRY 0620/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *6377602299* CHEMISTRY 5070/42 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2015 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *6377602299* CHEMISTRY 5070/42 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2015 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Separate Award Paper 1. Chemistry
 5 th Year Separate Award Paper 1 Chemistry Practice Paper 1 Instructions: Attempt ALL the questions. Make your answers in the spaces provided on the question paper. Mark allocations are given in brackets.
5 th Year Separate Award Paper 1 Chemistry Practice Paper 1 Instructions: Attempt ALL the questions. Make your answers in the spaces provided on the question paper. Mark allocations are given in brackets.
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4437/5H London Examinations IGCSE Science (Double Award) Chemistry Paper 5H Higher Tier Tuesday 16 November 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4437/5H London Examinations IGCSE Science (Double Award) Chemistry Paper 5H Higher Tier Tuesday 16 November 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
London Examinations GCE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 7081/02 London Examinations GCE Chemistry Ordinary Level Paper 2 Monday 17 January 2011 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 7081/02 London Examinations GCE Chemistry Ordinary Level Paper 2 Monday 17 January 2011 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
CHEMISTRY A N S W E R S. Paper 1
 CHEMISTRY A N S W E R S Paper 1 1. B 2. D 3. A 4. B 5. C 6. A 7. C 8. B 9. B 10. A 11. B 12. A 13. D 14. D 15. D 16. A 17. C 18. B 19. A 20. D 21. A 22. B 23. A 24. A 25. C 26. B 27. B 28. B 29. A 30.
CHEMISTRY A N S W E R S Paper 1 1. B 2. D 3. A 4. B 5. C 6. A 7. C 8. B 9. B 10. A 11. B 12. A 13. D 14. D 15. D 16. A 17. C 18. B 19. A 20. D 21. A 22. B 23. A 24. A 25. C 26. B 27. B 28. B 29. A 30.
Part A Unit-based exercise
 Topic 2 Microscopic World I / Microscopic World (Combined Science) Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 5 Atomic structure Fill in the blanks 1 atoms 2 solids; liquids; gases 3 metals; metalloids; non-metals
Topic 2 Microscopic World I / Microscopic World (Combined Science) Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 5 Atomic structure Fill in the blanks 1 atoms 2 solids; liquids; gases 3 metals; metalloids; non-metals
PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK SBP 2015 SKEMA KERTAS 2 CHEMISTRY 4541/2. Hydroxyl group 1 Butan-1-ol 1. Hydration 1
 454/ PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK SBP 05 SKEMA KERTAS CHEMISTRY 454/ QUESTION NO. (a) MARK SCHEME General Formula Formula Am : CnHn Homologous series Siri Homolog : Alkene MARK TOTAL (b) (i) (ii) (c
454/ PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK SBP 05 SKEMA KERTAS CHEMISTRY 454/ QUESTION NO. (a) MARK SCHEME General Formula Formula Am : CnHn Homologous series Siri Homolog : Alkene MARK TOTAL (b) (i) (ii) (c
Exam practice mark scheme C2: Discovering chemistry
 Exam practice mark scheme C: Discovering chemistry Foundation Tier (a)(i) Photo chlorine Any one correct for one mark Photo iodine Photo bromine Allow only one line from each photo and to each name Group
Exam practice mark scheme C: Discovering chemistry Foundation Tier (a)(i) Photo chlorine Any one correct for one mark Photo iodine Photo bromine Allow only one line from each photo and to each name Group
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level * 5803539249 * CHEMISTRY 9701/35 Paper 31 Advanced Practical Skills May/June
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level * 5803539249 * CHEMISTRY 9701/35 Paper 31 Advanced Practical Skills May/June
Redox. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations Chemical Reactions. Score: /43. Percentage: /100
 Redox Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations hemical Reactions Redox Question Paper Time llowed: 52 minutes Score: /43 Percentage:
Redox Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations hemical Reactions Redox Question Paper Time llowed: 52 minutes Score: /43 Percentage:
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Draw one line from each solution to the ph value of the solution. Solution ph value of the solution
 1 The ph scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. (a) Draw one line from each solution to the ph value of the solution. Solution ph value of the solution 5 Acid 7 9 Neutral 11 13
1 The ph scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. (a) Draw one line from each solution to the ph value of the solution. Solution ph value of the solution 5 Acid 7 9 Neutral 11 13
Strontium is extracted from strontium oxide (SrO) by heating a mixture of powdered strontium oxide and powdered aluminium.
 Q1.Group 2 metals and their compounds are used commercially in a variety of processes. (a) Strontium is extracted from strontium oxide (SrO) by heating a mixture of powdered strontium oxide and powdered
Q1.Group 2 metals and their compounds are used commercially in a variety of processes. (a) Strontium is extracted from strontium oxide (SrO) by heating a mixture of powdered strontium oxide and powdered
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Chemical Bonds In elements and compounds, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds.
 Chemical Bonds In elements and compounds, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds. Forming a bond makes an atom more stable, so atoms form as many bonds are they are able to. Bonds are made using
Chemical Bonds In elements and compounds, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds. Forming a bond makes an atom more stable, so atoms form as many bonds are they are able to. Bonds are made using
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level * 8 2 6337145 4* CHEMISTRY 9701/33 Paper 31 Advanced Practical Skills May/June
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level * 8 2 6337145 4* CHEMISTRY 9701/33 Paper 31 Advanced Practical Skills May/June
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES
 5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES LEARNING OUTCOMES a) Be able to write formulae of simple compounds b) Be able to write
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES LEARNING OUTCOMES a) Be able to write formulae of simple compounds b) Be able to write
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
GCE O' LEVEL PURE CHEMISTRY (5073/02) Suggested Answers for 2016 O Level Pure Chemistry Paper 2
 Section A (50 M) Aa) trend The number of electron shell increases The number of valence electrons increases Proton number increases There is a change in character from metallic to non-metallic Only true
Section A (50 M) Aa) trend The number of electron shell increases The number of valence electrons increases Proton number increases There is a change in character from metallic to non-metallic Only true
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *1863307025* CHEMISTRY 9701/34 Advanced Practical Skills October/November
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *1863307025* CHEMISTRY 9701/34 Advanced Practical Skills October/November
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *4827396477* CHEMISTRY 9701/35 Advanced Practical Skills October/November
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *4827396477* CHEMISTRY 9701/35 Advanced Practical Skills October/November
Additional Science. Chemistry CH2FP. (Jun15CH2FP01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2015.
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Additional Science Unit Chemistry C2 Chemistry Unit Chemistry C2 Thursday 14
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Additional Science Unit Chemistry C2 Chemistry Unit Chemistry C2 Thursday 14
Comparison between NEW and OLD syllabuses
 Comparison between NEW and OLD syllabuses In the NEW Chemistry syllabus, some topics are newly added and some are removed or deleted. Moreover, the syllabus is divided into two parts: core and extension.
Comparison between NEW and OLD syllabuses In the NEW Chemistry syllabus, some topics are newly added and some are removed or deleted. Moreover, the syllabus is divided into two parts: core and extension.
Answers for UNIT ONE NAT 5 Flash Cards
 Answers for UNIT ONE NAT 5 Flash Cards 1. (a) rate increases (b) rate increases (c) rate increases (d) rate increases 2. Average rate = change in property / change in time Where property = concentration,
Answers for UNIT ONE NAT 5 Flash Cards 1. (a) rate increases (b) rate increases (c) rate increases (d) rate increases 2. Average rate = change in property / change in time Where property = concentration,
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/31 Paper 3 Advanced Practical Skills 1 May/June 2014 2 hours Candidates answer on the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/31 Paper 3 Advanced Practical Skills 1 May/June 2014 2 hours Candidates answer on the
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions)
 Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. covalent ionic non-metallic
 1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *4147278659* CHEMISTRY 9701/34 Paper 3 Advanced Practical Skills 2 May/June 2015 2 hours Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *4147278659* CHEMISTRY 9701/34 Paper 3 Advanced Practical Skills 2 May/June 2015 2 hours Candidates answer
