POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
|
|
|
- Blake Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES NQF LEVEL: LEVEL 4 COURSE NAME: COURSE CODE: BASIC SCIENCE BSC410S DATE: JANUARY 2016 DURATION: 3 HOURS MARKS: ND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER EXAMINER(S): MODERATOR: Dr. Martha Uumati, Dr. Marius Mutorwa and Mr. Vaino Indongo Dr.Habauka Kwaambwa INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all the questions in the booklet provided 2. Show clearly all the steps used in the calculations 3. All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink and sketches must be done in pencils. 4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed. 5. Answers must be in SI units unless otherwise stated. PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS 1. Non-Programmable Calculator This paper consists of 13 pages including this cover and the Periodic Table Page 1 of 13
2 SECTION A: BIOLOGY QUESTION 1 [10] Question Type: Multiple Choices. Each answer equals 1 mark. 1.1 Who of the following scientists developed the 7 level classification scheme? (1) A. Aristotle B. Linnaeus C. Whittaker D. Darwin 1.2 Which of the following is a correct sequence of levels of classification? (1) A. Genus species family order class phylum kingdom B. Species genus family order class phylum kingdom C. Genus species order phylum family class kingdom D. Genus species order family class phylum kingdom 1.3 The science of describing, naming and classifying organisms is. (1) A. Hierarchal Naming System B. Classification C. Taxonomy D. Dewey Decimal 1.4 A garden pea plant forms flowers that undergo self or cross pollination to produce seeds. These seeds mature in two to three weeks. Which characteristics of living things are being described here? (1) A. Growth and reproduction B. Cellular organization and use of energy C. Reproduction and response to environment D. Use of energy and development 1.5 Pyramids of biomass show. (1) A. the relative amount of living organic matter at each trophic level B. the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level C. the relative number of individual organism at each trophic level in an ecosystem D. None of the above 1.6 Which of the following statements best describes the gymnosperms? (1) A. They are lower plants with seeds that are totally exposed and borne on the scales of cones. B. They are higher plants with seeds that are totally exposed and their seeds are enclosed in the ovary. C. They are basically vascular plants D. They can produce fruits from their flowers. Page 2 of 13
3 1.7 The three macronutrients are. (1) A. monosaccharide, polysaccharide, disaccharide B. fibre, vitamins, proteins C. lipids, carbohydrates, proteins D. carbohydrates, lipids, glycerol 1.8 What elements make up a lipid? (1) A. hydrogen, calcium, oxygen B. glycerol, fatty acids C. hydrogen, oxygen, carbon D. calcium, potassium, oxygen 1.9 Where is keratin proteins found in your body? (1) A. Insulin B. In blood plasma C. In connective tissue D. Hair 1.10 When sucrose is hydrolysed, it yields. (1) A. Glucose & glucose B. Glucose & fructose C. Glucose & galactose D. All of the above 1.11 What gives yoghurt a sour taste? (1) A. Sour milk B. Lactic acid C. Fermented fruits D. Complete fermentation 1.12 Viruses are exceptions to the cell theory, but they have some characteristics of living things. What is one of these characteristics? (1) A. They are made up of many specialized cells. B. They contain genetic material. C. They reproduce by mitosis. D. They contain chlorophyll Which of the following is the critical function of proteins? (1) A. repair of damaged cells B. manufacture of antibodies C. growth of new cells D. production of energy Page 3 of 13
4 1.14 Which of these food types is the main dietary cause of high cholesterol in the blood? (1) A. Protein B. Saturated fat C. Monounsaturated fat D. All of the above 1.15 A closely related family may be grouped together in a single. (1) A. Domain B. Phylum C. Species D. family 1.16 The proper term for "cold-blooded" animals is. (1) A. Mesotherms B. Exotherms C. Ectotherms D. Endotherms 1.17 All of the following statements about ecology are correct EXCEPT: (1) A. Ecology is the study of the interactions between biotic and abiotic aspects of the environment. B. Ecologists may study populations and communities of organisms. C. Ecology is a discipline that is independent from natural selection and evolutionary history. D. Ecology spans increasingly comprehensive levels of organization, from individuals to ecosystems About 50-60% of the human body weight consists of water. One of the following is NOT among the functions of water in the human body: (1) A. Acts as a solvent for nutrients B. Clots the blood C. Helps regulate the body temperature D. Participates in chemical reactions 1.19 Fibre cannot actually be digested. However, it is an important part of our diet for various reasons. One of the following reasons is false, identify which. (1) A. It causes constipation. B. As it remains undigested it passes through the entire gut from mouth to anus and thus keeps food moving smoothly through our system. C. High fibre diets are believed to reduce the risk of heart disease, bowel cancer and cholesterol in the body. D. The fibre absorbs poisonous waste from the digested food. Page 4 of 13
5 1.20 A starter culture in the food industry is. (1) A. fungi that are used to make food rot so that we can eat the food B. a microorganism that is used to control the growth of other organisms C. a microorganism that can withstand high temperatures and can be used in fermentation industries D. bacteria that are used in the fermentation of food products QUESTION 2 [20] Question Type: Brief statement responses 2.1 List the six kingdoms of organisms. (3) 2.2 What are biotic and abiotic factors? Give at least two examples of each. (3) 2.3 What are the processes that autotrophs use to produce organic material from inorganic substances? (2) 2.4 Distinguish between detritivores and saprotrophs, and provide a suitable example of each. (2) 2.5 Define the term competition and use examples to illustrate the two types of competition. (3) 2.6 Carbohydrates are classified into simple and complex carbohydrates. what are the three types of carbohydrates? Give an example of each. (3) 2.7 How is sweet wine produced? (2) 2.8 Give two reasons why as a parent you would encourage the school canteens to sell unsweetened cereals rather than sweets. (2) SECTION B: CHEMISTRY QUESTION 3 [20] Question Type: Multiple Choices. Each answer equals 1 mark. 3.1 Carbon dioxide is an example of a sample of matter classified as a/n; (1) A. compound B. homogeneous mixture C. heterogeneous mixture D. element 3.2 A process which involves the input of energy or absorption of heat is called; (1) A. exothermic B. dissolving Page 5 of 13
6 C. endothermic D. thermodynamic 3.3 Sublimation is the transformation of a; (1) A. gas into a solid B. solid into gas C. gas into liquid D. liquid into gas 3.4 An appropriate physical method that can be used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid is; (1) A. Chromatography B. separating funnel C. fractional distillation D. filtration 3.5 Which of the following is a characteristic of a mixture; (1) A. no define composition B. consists of two or more substances C. retains original properties D. All of the above 3.6 How does the presence of an impurity affect the freezing point and boiling point of water? (1) A. raises the freezing point and lowers the boiling point B. lowers the freezing point and lowers the boiling point C. lowers the freezing point and raises the boiling point D. raises the freezing point and raises the boiling point 3.7 Which of the following samples of matter is NOT classified as a compound? (1) A. blood B. water C. salt D. glucose 3.8 The amount of space an object occupies is known as its. (1) A. density B. volume C. mass D. time 3.9 The ability of a measurement to be consistently reproduced is referred to as. (1) Page 6 of 13
7 A. accuracy B. qualitative C. quantitative D. precision 3.10 The amount of gravitational force on an object is known as its. (1) A. mass B. mole C. weight D. area 3.11 What is the density of a 61.8 g cube that is 2.3 cm wide, 4.0 cm tall, and 3.2 cm long? (1) A. 6.5 g/cm 3 B. 2.1 g/cm 3 C g/cm 3 D. None of the above 3.12 Which of the following measurements has the greatest number of significant figures? (1) A ml B ml C ml D x 10 9 ml 3.13 If the temperature of a freezer is equal to o F, what would the temperature of a freezer be in o C? (1) A o C B o C C o C D. None of the above 3.14 a cyclist travels a distance of 0.5 Km in a time of 0.5 hours. The speed of the cyclist in SI units is equal to. (1) A m/s B. 0.3 m/s 2 C. 1 Km/h D. None of the above 3.15 The identity of an element on the Periodic Table is determined by the; (1) A. Number of electrons in the shell B. Number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus C. Number of protons in the nucleus only D. Number of protons, neutrons and electrons Page 7 of 13
8 3.16 In terms of the periodic trend, the size of an atom as you go down a particular group or column on the Periodic Table. (1) A. Decreases B. Increases C. Remains the same D. It depends on which group 3.17 Elements with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are referred to as; (1) A. Ions B. Neutral C. Isotopes D. All of the above 3.18 In terms of bonding, elements found in group 5 tend to; (1) A. Lose five electrons B. Lose three electrons C. Gain three electrons D. Gain five electrons 3.19 are the most reactive metals on the Periodic Table. (1) A. Transition metals B. Alkali earth metals C. Lanthanide metals D. Alkali metals E. Actinide metals 3.20 The mixture of two or more metals is known as; (1) A. Ore B. Alloy C. Metalloid D. Mineral QUESTION 4 [10] Question Type: Brief statement responses 4.1 Define the following terms. (4) a. acid b. salt c. indicator d. base 4.2 List two physical properties of acids. (2) Page 8 of 13
9 4.3 In agriculture, it is important to monitor the ph of the soil to ensure the growth of crops. Discuss how you would treat soil that is: (2) a. Too acidic b. Too basic 4.4 Fill in the products formed in the following reactions: (2) a. Mg + 2HNO 3 b. H 2 SO 4 + CaCO 3 SECTION C: PHYSICS QUESTION 5 [6] Question Type: Multiple Choices. Each answer equals 1 mark. 5.1 A police man sends out radar waves with a 3.4 cm wavelength from his police car with a speed of 3 x 10 8 m/s. What is their frequency? (1) A x 10 9 Hz B x 10 9 Hz C x 10 9 Hz D x 10 6 Hz 5.2 An apple of mass 23 g fall from a tree at 5 m height. What is the potential energy of an apple? (1) A. 3 Joules B. 2 joules C Joules D Joules Use the following table and graph to answer questions The height (in cm) for 30 students in a Physics class was determined as follows: Height in cm Frequency Page 9 of 13
10 5.3 The graph drawn is known as (1) A. Pie chart B. Line graph C. Bar graph D. Histogram 5.4 How many students have heights between ? (1) A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D How many students have heights more than 169.5? (1) A. 10 B. 8 C. 5 D What percentage of students have heights between ? (1) A. 17% B. 30% C. 22%12% 5.7 Nuclei having the same mass number but different atomic number are (1) A. isotopes B. isobars C. Isotones D. Isomers Page 10 of 13
11 5.8 The following nuclear equation shows a nuclide undergoing beta decay. What is the new nuclide formed indicated by the letter X: (1) A. Carbon B. Nitrogen C. helium atom D. Sulphur 14 6 C 14 7X + 0-1e 5.9 Which of the following statements is true? (1) A. the mass of a neutron and an beta particles are the same B. an electron is found in the nucleus of the atom C. a beta particle originate in the nucleus of the atom D. neutrons and x rays are basically the same in origin When a radionuclide undergo alpha decay, its mass number decreases by and atomic decreases by. (1) A. 2 and 4 B. 3 and 4 C. 4 and 2 D. 1 and 0 QUESTION 6 [8] Question Type: Brief statement responses. 6.1 If you were employed by the Directorate of Atomic Energy as a Radiation Scientist, list two advantages and one disadvantage you would offer with respect to the use of nuclear energy. (3) 6.2 Briefly explain how is produced from coal (4) 6.3 State the Law of Conservation of Energy state. (1) QUESTION 7 [4] Question Type: Brief statement responses 7.1 State Ohm s Law (2) 7.2 State the difference between conventional and direct current. (2) QUESTION 8 [5] Question Type: Brief statement responses. 8.1 Define the term inertia. (2) Page 11 of 13
12 8.2 List three effects that a force when applied can have on an object moving at a constant velocity. (3) QUESTION 9 [3] Question Type: Brief statement responses. 9.1 Define the following characteristics of a wave: (3) a. Wavelength b. Amplitude c. Trough THE END TOTAL: 100 MARKS Page 12 of 13
13 Page 13 of 13
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BASIC SCIENCE PARTTIME TEST 2
 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BASIC SCIENCE PARTTIME TEST 2 INITIALS: SURNAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MODE OF STUDY: QUALIFICATION: LECTURE
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BASIC SCIENCE PARTTIME TEST 2 INITIALS: SURNAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MODE OF STUDY: QUALIFICATION: LECTURE
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES NQF LEVEL: LEVEL 4 COURSE NAME: COURSE CODE: BASIC SCIENCE BSC410S DATE: NOVEMBER 2013 DURATION:
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES NQF LEVEL: LEVEL 4 COURSE NAME: COURSE CODE: BASIC SCIENCE BSC410S DATE: NOVEMBER 2013 DURATION:
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BASIC SCIENCE FULLTIME TEST 2
 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BASIC SCIENCE FULLTIME TEST 2 INITIALS: SURNAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MODE OF STUDY: QUALIFICATION: LECTURE
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BASIC SCIENCE FULLTIME TEST 2 INITIALS: SURNAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MODE OF STUDY: QUALIFICATION: LECTURE
FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BSC PROGRAMME NAME.. ST. #:. QUALIFICATION(S): CENTRE:.
 FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BSC PROGRAMME NAME.. ST. #:. QUALIFICATION(S): CENTRE:. MODE OF STUDY: FM PM DM CLASS VENUE: (FHAS Aud., or Mining Aud.)
FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BSC PROGRAMME NAME.. ST. #:. QUALIFICATION(S): CENTRE:. MODE OF STUDY: FM PM DM CLASS VENUE: (FHAS Aud., or Mining Aud.)
Chapter Two Test Chemistry. 1. If an atom contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons, its atomic number is A. 1 C. 12 B. 11 D. 23
 Name Chapter Two Test Chemistry 1. If an atom contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons, its atomic number is A. 1 C. 12 B. 11 D. 23 2. The nucleus is made up of all of the following: A. Electrons C. Protons
Name Chapter Two Test Chemistry 1. If an atom contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons, its atomic number is A. 1 C. 12 B. 11 D. 23 2. The nucleus is made up of all of the following: A. Electrons C. Protons
1. The atomic number is based on the number of. 2. A negatively charged particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom is called a(n).
 TEST BANK FOR MEMMLER'S STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HUMAN BODY 10TH EDITION BY TAYLOR AND COHEN Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/memmlers-structure-and-functionof-the-human-body-10th-edition-by-taylor-and-cohen-test-bank/
TEST BANK FOR MEMMLER'S STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HUMAN BODY 10TH EDITION BY TAYLOR AND COHEN Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/memmlers-structure-and-functionof-the-human-body-10th-edition-by-taylor-and-cohen-test-bank/
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps
 Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Cells The Basic Unit of Life Unit 2: The Cell in Action Unit 3: Genes and DNA Unit 4: Heredity Unit 5: Evolution Unit 6: It s Alive! Or is it?! Unit 7: Bacteria
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Cells The Basic Unit of Life Unit 2: The Cell in Action Unit 3: Genes and DNA Unit 4: Heredity Unit 5: Evolution Unit 6: It s Alive! Or is it?! Unit 7: Bacteria
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life
 Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
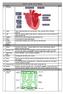 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Chapter: Cell Processes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 2
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 2 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 2 CHEMICAL BASIS OF
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 2 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 2 CHEMICAL BASIS OF
CHEMISTRY I - HONORS MIDTERM REVIEW* *Test may cover other topics not included on this review, yet have been covered throughout the semester.
 Name Period CHEMISTRY I - HONORS MIDTERM REVIEW* *Test may cover other topics not included on this review, yet have been covered throughout the semester. Chapter 2 Measurement & Calculations Describe the
Name Period CHEMISTRY I - HONORS MIDTERM REVIEW* *Test may cover other topics not included on this review, yet have been covered throughout the semester. Chapter 2 Measurement & Calculations Describe the
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry. And I mean BRIEF!
 A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
Ms. Levasseur Biology
 Ms. Levasseur Biology Atom: the actual basic unit - composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances pure Molecule: a substance made
Ms. Levasseur Biology Atom: the actual basic unit - composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances pure Molecule: a substance made
2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK
 2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK Term 1 1 Orientation 2 Introduction to Science Lab Safety 3 Physical Quantities and Units 1. All physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and a unit
2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK Term 1 1 Orientation 2 Introduction to Science Lab Safety 3 Physical Quantities and Units 1. All physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and a unit
8.L.5.1 Practice Questions
 Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
Chemistry of Life 10/1/2010. What makes up the chemistry of life?
 A. Students will be able to identify and define the parts of an atom. Chemistry of Life At the Completion of this Unit, Students will be able to: A. Identify and define the parts of an atom. B. Demonstrate
A. Students will be able to identify and define the parts of an atom. Chemistry of Life At the Completion of this Unit, Students will be able to: A. Identify and define the parts of an atom. B. Demonstrate
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Ch 2 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Ch 2 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of
- know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues can be massed together to form organs
 Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
BIOCHEMISTRY BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION ORGANIZATION? MATTER. elements into the order and appearance we now
 BIOCHEMISTRY MR. HULSE BVHS BIOLOGY MATTER Matter - anything that occupies space and has mass Lacked clarity and flow BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION Biochemistry study of chemical and physiological process
BIOCHEMISTRY MR. HULSE BVHS BIOLOGY MATTER Matter - anything that occupies space and has mass Lacked clarity and flow BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION Biochemistry study of chemical and physiological process
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 2
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 6 The Chemistry of Life
 Chapter 6 The Chemistry of Life Atoms: The Building Blocks of Life Both living and non-living things have atoms Everything, living and non, is made of Atoms. An elements is something you can break down
Chapter 6 The Chemistry of Life Atoms: The Building Blocks of Life Both living and non-living things have atoms Everything, living and non, is made of Atoms. An elements is something you can break down
BIOCHEMISTRY 10/9/17 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE. Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is
 BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 ch 2 chemical basis of life Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 1) When a change in matter
ch 2 chemical basis of life Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 1) When a change in matter
Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology
 Section 1: Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Section 2: Chemical Reactions Section 3: Water and Solutions Section 4: The Building Blocks of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and
Section 1: Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Section 2: Chemical Reactions Section 3: Water and Solutions Section 4: The Building Blocks of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and
Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry
 Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life I. Concept 2.1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules a. Atoms Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry i. Atom: _ ii. (They are SUPER small! It would take 3 million carbon
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life I. Concept 2.1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules a. Atoms Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry i. Atom: _ ii. (They are SUPER small! It would take 3 million carbon
Chemical Basis of Life
 Chemical Basis of Life Jan 30 11:42 AM In order to understand digestion and nutrition, we need some basic biochemistry Chemistry studies the composition of matter and its changes as well as the change
Chemical Basis of Life Jan 30 11:42 AM In order to understand digestion and nutrition, we need some basic biochemistry Chemistry studies the composition of matter and its changes as well as the change
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
 spqt csセbz MBASIC SCIENCE: quセstion@ PAPER- NOV_2_01_4 セ @"lo,j';;;;;t..jt.'"" POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES NQF LEVEL: LEVEL4
spqt csセbz MBASIC SCIENCE: quセstion@ PAPER- NOV_2_01_4 セ @"lo,j';;;;;t..jt.'"" POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES NQF LEVEL: LEVEL4
Chapter 2. Introduction: Chapter Chemical Basis of Life. Structure of Matter:
 Chapter 2.1-2.2 Read text 2.1 and describe why chemistry is important in understanding life. Read text 2.2 and discuss how atomic structure determines how atoms interact. Also describe the types of chemical
Chapter 2.1-2.2 Read text 2.1 and describe why chemistry is important in understanding life. Read text 2.2 and discuss how atomic structure determines how atoms interact. Also describe the types of chemical
LIFE OF CELL. Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1. BS Biology Graduate, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2
 LIFE OF CELL Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 BS Biology Graduate, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 MS Biology Student, Graduate School, Centro Escolar
LIFE OF CELL Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 BS Biology Graduate, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 MS Biology Student, Graduate School, Centro Escolar
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY. Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Covalent Bond: Hydrogen Bond:
 UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
8/24/2018. Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry. Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology Levels of biological organization Ecosystem (e.g. savanna) Community (e.g. the organisms
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology Levels of biological organization Ecosystem (e.g. savanna) Community (e.g. the organisms
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010
 CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
Review_Unit 2 Biochemistry
 Review_Unit 2 Biochemistry Basic Chemistry 1. What is an element? A substance that cannot be broken down into smaller particles. 2. What are atoms? The smallest part of an element that still maintains
Review_Unit 2 Biochemistry Basic Chemistry 1. What is an element? A substance that cannot be broken down into smaller particles. 2. What are atoms? The smallest part of an element that still maintains
Chapter 2. Chemical Basis of Life
 hapter 2 hemical Basis of Life opyright The McGrawill ompanies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: A. hemistry deals with the composition of matter and how it changes.
hapter 2 hemical Basis of Life opyright The McGrawill ompanies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: A. hemistry deals with the composition of matter and how it changes.
Figure ) Letter E represents a nucleic acid building block known as a. Answer: nucleotide Diff: 3 Page Ref: 54
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry 2.1 Short Answer Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) Which letter represents a carbohydrate polymer?
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry 2.1 Short Answer Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) Which letter represents a carbohydrate polymer?
Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology. 6.1 Atoms, Elements & Compounds 6.2 Chemical Reactions 6.3 Water and Solutions 6.4 The Building Blocks of Life
 Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology 6.1 Atoms, Elements & Compounds 6.2 Chemical Reactions 6.3 Water and Solutions 6.4 The Building Blocks of Life 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Main idea: Matter is composed
Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology 6.1 Atoms, Elements & Compounds 6.2 Chemical Reactions 6.3 Water and Solutions 6.4 The Building Blocks of Life 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Main idea: Matter is composed
Science 9-1 Grades Guidance
 U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life
 Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. The smallest unit of matter is the A. molecule. B. atom. C. compound. D. isotope. HAPS Objective: C.01.03 Compare and contrast the terms atoms,
Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. The smallest unit of matter is the A. molecule. B. atom. C. compound. D. isotope. HAPS Objective: C.01.03 Compare and contrast the terms atoms,
Elements, Compounds Mixtures Physical and Chemical Changes
 Elements, Compounds Mixtures Physical and Chemical Changes Fundamentals of Chemistry 1 Classification of Matter Matter is any substance having distinct physical characteristics and chemical properties.
Elements, Compounds Mixtures Physical and Chemical Changes Fundamentals of Chemistry 1 Classification of Matter Matter is any substance having distinct physical characteristics and chemical properties.
Atoms. Atoms 9/9/2015
 The Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter, Water,Carbon Compounds, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes The Nature of Matter B.1.9 Both living and nonliving things are composed of compounds, which are themselves
The Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter, Water,Carbon Compounds, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes The Nature of Matter B.1.9 Both living and nonliving things are composed of compounds, which are themselves
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review Please review the following topics and pages in your text. Be sure to review any worksheets that I have provided, old tests and quizzes, as well as notes taken in class. INTRODUCTION
Honors Biology Midterm Review Please review the following topics and pages in your text. Be sure to review any worksheets that I have provided, old tests and quizzes, as well as notes taken in class. INTRODUCTION
Mr. Carpenter s Biology Biochemistry. Name Pd
 Mr. Carpenter s Biology Biochemistry Name Pd Chapter 2 Vocabulary Atom Element Compound Molecule Ion Cohesion Adhesion Solution Acid Base Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Lipid Protein Amino acid Nucleic acid
Mr. Carpenter s Biology Biochemistry Name Pd Chapter 2 Vocabulary Atom Element Compound Molecule Ion Cohesion Adhesion Solution Acid Base Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Lipid Protein Amino acid Nucleic acid
Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review
 Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review Complete the following short answer questions. 1. Define microbiology. The study of microorganisms. 2. What are the six major groups of organisms
Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review Complete the following short answer questions. 1. Define microbiology. The study of microorganisms. 2. What are the six major groups of organisms
Biochemistry. Basic Chemistry Review, ph, Water, Organic Molecules
 Biochemistry Basic Chemistry Review, ph, Water, Organic Molecules Basic Chemistry Review Basic Atomic Structure H T T P : / / W W W. Y O U T U B E. C O M / W A T C H? V = L P 5 7 G E W C I S Y Atomic Structure
Biochemistry Basic Chemistry Review, ph, Water, Organic Molecules Basic Chemistry Review Basic Atomic Structure H T T P : / / W W W. Y O U T U B E. C O M / W A T C H? V = L P 5 7 G E W C I S Y Atomic Structure
BIOLOGY II ORGANIC CHEMISTRY UNIT
 BIOLOGY II ORGANIC CHEMISTRY UNIT ELEMENTS AND ATOMS Matter Anything that takes up space. Three classes of matter: Elements contain only 1 type of atom Compounds 2 or more elements combined in a chemical
BIOLOGY II ORGANIC CHEMISTRY UNIT ELEMENTS AND ATOMS Matter Anything that takes up space. Three classes of matter: Elements contain only 1 type of atom Compounds 2 or more elements combined in a chemical
Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology
 Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. Atomic B. Living C. Matter D. Energy E. Space 2. The electrons of an atom are A.
Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. Atomic B. Living C. Matter D. Energy E. Space 2. The electrons of an atom are A.
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry
 Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
0653 COMBINED SCIENCE
 9*CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw
9*CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw
WANGANUI HIGH SCHOOL
 Year 9 Science Examination 2007 Summary of Topics covered. Skills in Science What lab equipment is used for. Safety rules of the lab Interpreting diagrams, graphs, text etc Parts of a Bunsen burner, how
Year 9 Science Examination 2007 Summary of Topics covered. Skills in Science What lab equipment is used for. Safety rules of the lab Interpreting diagrams, graphs, text etc Parts of a Bunsen burner, how
Welcome to Biology 160! Welcome to Biology 160! Welcome to Biology 160! The Molecules of Life. Draw Biology. We re Made of Atoms?!
 Welcome to Biology 160! Today s Agenda: 1. Introductions 2. Syllabus and Course Website 3. Getting to Know You! 4. Group Discussions 5. Chemistry for Biologists? Welcome to Biology 160! Syllabus and Course
Welcome to Biology 160! Today s Agenda: 1. Introductions 2. Syllabus and Course Website 3. Getting to Know You! 4. Group Discussions 5. Chemistry for Biologists? Welcome to Biology 160! Syllabus and Course
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport
 Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Chemistry in Biology Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
 Name Chemistry in Biology Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Date Main Idea Details Scan the headings and boldfaced words in Section 1 of the chapter. Predict two things that you think might be discussed.
Name Chemistry in Biology Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Date Main Idea Details Scan the headings and boldfaced words in Section 1 of the chapter. Predict two things that you think might be discussed.
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. Honors Biology I
 NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-2, Biochemistry Honors Biology I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: Period: Seat #: Date: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE Honors Biology I Unit
NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-2, Biochemistry Honors Biology I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: Period: Seat #: Date: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE Honors Biology I Unit
Elements and Isotopes
 Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
Section Objectives: Section Objectives: Distinguish mixtures and solutions. Define acids and bases and relate their importance to biological systems.
 Section Objectives: Relate the structure of an atom to the identity of elements. Relate the formation of covalent and ionic chemical bonds to the stability of atoms. Section Objectives: Distinguish mixtures
Section Objectives: Relate the structure of an atom to the identity of elements. Relate the formation of covalent and ionic chemical bonds to the stability of atoms. Section Objectives: Distinguish mixtures
Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process?
 1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life I. Introduction A. The study of chemistry is essential for the study of physiology because
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life I. Introduction A. The study of chemistry is essential for the
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life I. Introduction A. The study of chemistry is essential for the
Lymm High School- KS3 Life after levels - Science Y9
 Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
FEEDBACK TUTORIAL LETTER
 FEEDBACK TUTORIAL LETTER 1 st SEMESTER 2017 ASSIGNMENT 1 BASIC SCIENCE BSC410S 1 Dear Student Assignment One has been marked and this serves as feedback on the assignment. Individual feedback is already
FEEDBACK TUTORIAL LETTER 1 st SEMESTER 2017 ASSIGNMENT 1 BASIC SCIENCE BSC410S 1 Dear Student Assignment One has been marked and this serves as feedback on the assignment. Individual feedback is already
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY. Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Covalent Bond: Hydrogen Bond:
 UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY. 3. Define physical changes. A change in any physical property of a substance, not in the substance itself.
 Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY Unit 2: Matter & Its Properties, Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Properties & Changes 1. Define physical properties. The characteristics of a substance that can be observed
Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY Unit 2: Matter & Its Properties, Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Properties & Changes 1. Define physical properties. The characteristics of a substance that can be observed
Part I: Short answer (25 points)
 Part I: Short answer (25 points) Part II: / 75 1. Recently, researchers published a five-year study involving 2,687 subjects with a disorder called sleep apnea. The subjects were between the ages of 45
Part I: Short answer (25 points) Part II: / 75 1. Recently, researchers published a five-year study involving 2,687 subjects with a disorder called sleep apnea. The subjects were between the ages of 45
Basic Chemistry. Chemistry Review. Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology
 Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
The study of life. All organisms share certain properties. All organisms do these things at some point during their life.
 Biochemistry The study of life All organisms share certain properties. Cellular organization Homeostasis Metabolism Responsiveness Reproduction Heredity Growth All organisms do these things at some point
Biochemistry The study of life All organisms share certain properties. Cellular organization Homeostasis Metabolism Responsiveness Reproduction Heredity Growth All organisms do these things at some point
Reinforcement Worksheet Organic Compounds
 1 Name Date Page 1- Day 1 Reinforcement Worksheet Organic Compounds KEY CONCEPT: Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Carbon atoms are the basis of most molecules that make up living things.
1 Name Date Page 1- Day 1 Reinforcement Worksheet Organic Compounds KEY CONCEPT: Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Carbon atoms are the basis of most molecules that make up living things.
1.Matter and Organic Compounds Matter =
 The Chemistry of Life Notes Unit 2 1.Matter and Organic Compounds Matter = All things are made of matter Name Matter is made up of substances Chemical substance = definite composition throughout Either
The Chemistry of Life Notes Unit 2 1.Matter and Organic Compounds Matter = All things are made of matter Name Matter is made up of substances Chemical substance = definite composition throughout Either
Basic Chemistry. Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos
 Basic Chemistry Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Chapter 2 Objectives Following this chapter, you should be able to describe: - Atoms, molecules, and ions - Composition and properties - Types of
Basic Chemistry Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Chapter 2 Objectives Following this chapter, you should be able to describe: - Atoms, molecules, and ions - Composition and properties - Types of
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life I. Water Liquid Naturally occurring It expands liquid to solid Covers more than 75% of our surface Most abundant in living organisms most important inorganic compound for
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life I. Water Liquid Naturally occurring It expands liquid to solid Covers more than 75% of our surface Most abundant in living organisms most important inorganic compound for
Chapter 2. The Chemistry of Life
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Introduction Cells, tissues and organs composed of chemicals Chemical reactions important for function Chemistry is the study of elements, compounds, chemical reactions,
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Introduction Cells, tissues and organs composed of chemicals Chemical reactions important for function Chemistry is the study of elements, compounds, chemical reactions,
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Lipid. 2) Functional protein. 3) Nucleotide.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Lipid. 2) Functional protein. 3) Nucleotide.
Chemistry of Life. Chapter Two
 Chemistry of Life Chapter Two 1 Biology and Chemistry Biology = study of life Chemistry = study of matter and the changes it undergoes Matter anything that takes up space and has mass Life is made up of
Chemistry of Life Chapter Two 1 Biology and Chemistry Biology = study of life Chemistry = study of matter and the changes it undergoes Matter anything that takes up space and has mass Life is made up of
Life Science Strand Grades K-8
 Life Science Strand Grades K-8 KINDERGARTEN K.L.1: Compare characteristics of animals that make them alike and different from other animals and nonliving things. K.L.1.1: Compare different types of the
Life Science Strand Grades K-8 KINDERGARTEN K.L.1: Compare characteristics of animals that make them alike and different from other animals and nonliving things. K.L.1.1: Compare different types of the
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy
 Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells 1. Define elements and compounds 2. Explain how water is important to the function of cells 3. Identify
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells 1. Define elements and compounds 2. Explain how water is important to the function of cells 3. Identify
7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet
 7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet Ms. Shirreffs Name: Introduction and Characteristics of Life 1. This year we studied life science, another word for life science is 2. Which term describes an organism
7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet Ms. Shirreffs Name: Introduction and Characteristics of Life 1. This year we studied life science, another word for life science is 2. Which term describes an organism
ATom,ion, molwcul in the dily live
 ATom,ion, molwcul in the dily live Chemistry of Life All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. There are 109 types of atoms. A substance made up of one kind of atom is called an element. An
ATom,ion, molwcul in the dily live Chemistry of Life All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. There are 109 types of atoms. A substance made up of one kind of atom is called an element. An
Botany The Nature of Life
 Botany The Nature of Life I. Attributes of Living Organisms A. It would seem a simple thing to define life, but it actually isn t. Many of the characteristics of life can be found in nonliving things.
Botany The Nature of Life I. Attributes of Living Organisms A. It would seem a simple thing to define life, but it actually isn t. Many of the characteristics of life can be found in nonliving things.
Teacher Instructions
 Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
Unit 2: Part 1 Matter & Energy in Ecosystems What elements am I made of?
 Unit 2: Part 1 Matter & Energy in Ecosystems What elements am I made of? I. Introduction: Matter in Ecosystems A. Organisms are composed of matter (anything that takes up space and has mass) B. Organisms
Unit 2: Part 1 Matter & Energy in Ecosystems What elements am I made of? I. Introduction: Matter in Ecosystems A. Organisms are composed of matter (anything that takes up space and has mass) B. Organisms
Chapter 2 Concepts of Chemistry
 Anatomy Physiology and Disease for the Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/anatomy-physiology-and-disease-for-the-health-professions-3rd-edition-booth-te
Anatomy Physiology and Disease for the Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/anatomy-physiology-and-disease-for-the-health-professions-3rd-edition-booth-te
The Chemistry of Biology
 The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
Name: 8 th Grade Science STAAR. Review Booklet. My STAAR Goal: The Science Duo
 Name: 8 th Grade Science STAAR Review Booklet My STAAR Goal: Table of Contents: Matter and Energy Matter and Energy Vocabulary Page 3-5 Atomic Structure Page 6 Arrangement of the Periodic Table Page 7
Name: 8 th Grade Science STAAR Review Booklet My STAAR Goal: Table of Contents: Matter and Energy Matter and Energy Vocabulary Page 3-5 Atomic Structure Page 6 Arrangement of the Periodic Table Page 7
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 (10021002) 11 March (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used.
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 (10021002) 11 March (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used.
Chapter 3.1 Chemistry of Life
 Life Science Chapter 3: Cell Processes 1. Chemistry of Life 2. Moving Cellular Materials 3. Energy for Life http://www.connecticutvalleybiological.com/cell processes vhs p 14026.html Chapter 3.1 Chemistry
Life Science Chapter 3: Cell Processes 1. Chemistry of Life 2. Moving Cellular Materials 3. Energy for Life http://www.connecticutvalleybiological.com/cell processes vhs p 14026.html Chapter 3.1 Chemistry
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
 All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. ydrogen
All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. ydrogen
Characteristics of Life
 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Chapter 2 Section 1: Classifying Matter. Classification of Matter. Classification of Matter 9/5/15
 Chapter 2 Section 1: Classifying Matter Classification of Matter Now that we have defined chemical and physical properties of matter, we can use that to help us classify it. One way chemists classify matter
Chapter 2 Section 1: Classifying Matter Classification of Matter Now that we have defined chemical and physical properties of matter, we can use that to help us classify it. One way chemists classify matter
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
 Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chemistry is the scientific study of the composition of matter and how composition changes. In order to understand human physiological processes, it is important to understand
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chemistry is the scientific study of the composition of matter and how composition changes. In order to understand human physiological processes, it is important to understand
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life
 Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/maders-understanding-human-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-longenbaker
Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/maders-understanding-human-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-longenbaker
SEKHUKHUNE DISTRICT. PHYSICAL SCIENCES PRE JUNE PAPER 2 GRADE 10 DATE 2016 MARKS 150 DURATION: 2Hrs
 SEKHUKHUNE DISTRICT PHYSICAL SCIENCES PRE JUNE PAPER 2 GRADE 10 DATE 2016 MARKS 150 DURATION: 2Hrs QUESTION 1 (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)Four possible options are provided as answers to the following questions.
SEKHUKHUNE DISTRICT PHYSICAL SCIENCES PRE JUNE PAPER 2 GRADE 10 DATE 2016 MARKS 150 DURATION: 2Hrs QUESTION 1 (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)Four possible options are provided as answers to the following questions.
CHAPTER 2. Environmental Systems
 CHAPTER 2 Environmental Systems A Lake of Salt Water, Dust Storms and Endangered Species Mono Lake CA Terminal lake water flows into it, no flow out High mineral/salt concentrations = no fish can survive
CHAPTER 2 Environmental Systems A Lake of Salt Water, Dust Storms and Endangered Species Mono Lake CA Terminal lake water flows into it, no flow out High mineral/salt concentrations = no fish can survive
Name Biology Chapter 2 Note-taking worksheet
 Name Biology Chapter 2 Note-taking worksheet The Nature of Matter 1. Life depends on Atoms 1. The study of chemistry starts with the basic unit of matter, the. 2. The atom was first used by the Greek philosopher
Name Biology Chapter 2 Note-taking worksheet The Nature of Matter 1. Life depends on Atoms 1. The study of chemistry starts with the basic unit of matter, the. 2. The atom was first used by the Greek philosopher
Behavioral and Structural Adaptations PPT Guided Notes
 A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
Chemistry. Animal Health Technology Student Development Program
 Chemistry Animal Health Technology Student Development Program Chemistry Chemistry is a fundamental component in all of us. Chemical reactions are happening in our bodies constantly. In the Animal Health
Chemistry Animal Health Technology Student Development Program Chemistry Chemistry is a fundamental component in all of us. Chemical reactions are happening in our bodies constantly. In the Animal Health
**Refer to your pre-lecture notes for all the sections we will be covering to help you keep an eye on the big picture
 Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life **Refer to your pre-lecture notes for all the sections we will be covering to help you keep an eye on the big picture Biology Bio = life ology =
Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life **Refer to your pre-lecture notes for all the sections we will be covering to help you keep an eye on the big picture Biology Bio = life ology =
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
 NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: QUALIFICATION CODE: LEVEL: 4 COURSE CODE: BSC410S SESSION:
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: QUALIFICATION CODE: LEVEL: 4 COURSE CODE: BSC410S SESSION:
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BSC PROGRAMME
 SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BSC PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): Bachelor of Science (Major and Minor in Natural Sciences) QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC NQF
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES BSC PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): Bachelor of Science (Major and Minor in Natural Sciences) QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC NQF
