Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 83 90
|
|
|
- Isabella McDowell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission Dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3 Prompt fission γ-ray spectra characteristics - a first summary S. Oberstedt a,, R. Billnert a,b, A. Gatera a, W. Geerts a, P. Halipré c, F.-J. Hambsch a, M. Lebois c, A. Oberstedt b,d, P. Marini e, M. Vidali a, J.N. Wilson c a European Commission, DG Joint Research Centre (IRMM), 2440 Geel, Belgium b Fundamental Fysik, Chalmers Tekniska Högskola, Göteborg, Sweden c Institut de Physique Nucléaire Orsay, Orsay, France d OSSOLUTIONS Consulting, Örebro, Sweden e Centre d Etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux Gradignan, Gradignan Cedex, France Abstract In this work we give an overview of our investigations of prompt γ-ray emission in nuclear fission. This work was conducted during the last five years in response to a high priority nuclear data request formulated by the OECD/NEA. The aim was to reveal data deficiencies responsible for a severe under-prediction of the prompt γ heating in nuclear reactor cores. We obtained new prompt fission γ-ray spectral (PFGS) data for 252 Cf(SF) as well as for thermal-neutron induced fission on 235 U(n th,f) and 241 Pu(n th,f). In addition, first PFGS measurements with a fast-neutron beam were accomplished, too. The impact of the new data and future data needs are discussed. c 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier by Elsevier B.V. B.V. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license ( Peer-review under responsibility of the European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute for Reference Materials and Peer-review Measurements. under responsibility of the European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements Keywords: Prompt fission γ-rays; total γ-ray energy; prompt γ-ray multiplicity; Generation IV; nuclear energy; lanthanum bromide; cerium bromide; scintillation detector; 252 Cf(SF); 235 U(n th,f); 241 Pu(n th,f); 1. Introduction In nuclear fission around 99.8% is binary fission, where a total energy of around 200 MeV is released. About 80% appears as kinetic energy of the two fission fragments. The fragments may be highly excited, the excitation energy of each fragment ranging between 0 and 40 MeV. About 40% of the excitation energy is released shortly after scission through the emission of neutrons and γ-rays, in average about 5 and 7 MeV, respectively. All energy release before the onset of β -decay is defined as prompt heat. The regime of prompt emission may, therefore, comprise several hundreds of ns and even extend into the 100 μs range. Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: stephan.oberstedt@ec.europa.eu The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license ( Peer-review under responsibility of the European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements doi: /j.phpro
2 84 S. Oberstedt et al. / Physics Procedia 64 ( 2015 ) In order to understand the share of excitation energy between the two fission fragments, prompt neutrons and γ-rays are excellent probes to investigate the re-organization of nuclear matter around scission and the subsequent de-excitation process. Whilst prompt-neutron emission is being studied along the last three decades (Boikov et al., 1991; Lemaire et al., 2005; Kornilov et al., 2010; Tudora et al., 2013), prompt γ-ray measurements date back to the early 1970s (Verbinski et al., 1973; Pleasonton et al., 1972; Peelle and Maienschein, 1971) and have been disregarded until in the very recent years. However, the latter probe may, however, help revealing in how far prompt neutron and γ emission is a competing process. Depending on the excitation energy and the angular momentum of a fragment with mass A and its decay product, with mass A-1, neutron emission is favored or suppressed. Those quantities are not directly experimentally assessable but may be deduced by comparing model calculations with neutron and γ-ray spectral data. 2. Prompt fission γ-ray emission - the why Regardless the fundamental aspects of prompt fission neutron and γ-ray emission, the driving force for a renaissance of prompt fission γ-ray measurements was the community of nuclear applications. Since four out of six impending Generation-IV reactors will be operated with a fast-neutron spectrum, modeling of innovative reactor cores is required to handle the excessive heat deposit during operation. Model calculations consistently under-predicted the prompt heat deposition by up to 28% (Rimpault et al., 2006, 2012; Rimpault, 2006b). Since the under-prediction was attributed to deficiencies in the prompt fission γ-ray spectral (PFGS) data from thermal-neutron induced fission on 235 U as well as on 239 Pu, the OECD/NEA published a high priority nuclear data request in 2006 (NEA, 2006). New data on the average prompt γ-ray energy per fission should be measured within an uncertainty of 7.5% for thermaland fast-neutron induced fission. In the following we summarize the subsequent activities and present, in the following, recent achievements in measuring PFGS data, average multiplicity (ν γ ), mean photon energy (ɛ γ ) and average total γ-ray energy (E γ,tot ) per fission. 3. Experiment technique - the how For the investigation of prompt fission γ-rays an efficient separation from prompt fission neutrons must be achieved. Those neutrons may interact with the fission chamber and surrounding materials as well as with the γ-detector through inelastic scattering, causing the detection of γ-rays to be confounded with prompt fission γ-rays. This separation is usually achieved by means of time-of-flight. This method requires an excellent timing resolution allowing to use a not too large distance between fission source and γ-detector. A crucial point is the, in general, not negligible amount of material around a fission source itself, e.g. material from a diamond detector mounted close to the sample or from a (twin) Frisch-grid ionization chamber (TFGIC), which requires sufficiently high energy resolution as well. Of the historically employed detectors that based e.g. on thallium-doped sodium-iodine crystals possesses of both characteristics to a certain extent. With the newly emerged cerium-doped lanthanum halide, e.g.labr 3 :Ce and LaCl 3 :Ce, and cerium-halide, e.g. CeBr 3, crystals the situation improved considerably. Before we started with PFGS measurements we investigated the characteristics of those detectors with respect to energy and timing resolution (Billnert et al., 2011, 2012; Oberstedt et al., 2013; Billnert et al., 2013), which we found superior by a factor of 2 and 5, respectively. Also the detection efficiency is higher by a factor of about 2. The reproducibility of spectral data measurements lies within a few percent as demonstrated with the spontaneous fission of 252 Cf, where PFGS data were measured with different lanthanide-halide detectors of different sizes (Oberstedt et al., 2014b). In the left part of Fig. 1 a typical setup for PFGS measurements is shown as it was used at the KFKI research reactor at Budapest (KFKI, 2014). As a fission trigger we used artificial diamond detectors, which provide an intrinsic timing resolution better than 110 ps (σ) (Oberstedt et al., 2013c) or a TFGIC, when fission-fragment characteristics were to be measured in correlation with prompt fission γ-rays. A coincidence timing resolution between γ-detector and fission trigger better than 2 ns (FWHM) may routinely be achieved when integrating over all γ-ray energies (Oberstedt et al.,
3 S. Oberstedt et al. / Physics Procedia 64 ( 2015 ) Fig. 1. (Color online) Left: Typical set-up for measuring prompt fission γ-rays at the cold-neutron beam at the KFKI research reactor in Budapest. The fissile actinide sample is mounted in a Frisch-grid ionization chamber covered here by (yellow) 6 Li-loaded sheets to minimize neutron scattering into the detectors; Right: Measured prompt fission γ-ray spectrum (black) from 252 Cf(SF) and the spectrum simulated with the PENELOPE Monte- Carlo code (PENELOPE, 2011). 2014). Data are collected with an acquisition system based on wave-form digitization. We store the entire signal trace released from each γ-ray or fission detector using M3i digitizer cards (400 Ms/s, 12bit) from Spectrum (Spectrum, 2011), 252 Cf(SF) and 235 U(n th,f), while during the measurement on 241 Pu digitizer boards from SPDevices with 400 Ms/s and 14 bit resolution (SPDevices, 2012) were used. The recorded traces were then treated off-line using a ROOTbased analysis program (ROOT, 2014) developed at the Joint Research Centre IRMM. The measured γ-ray spectrum was corrected for the detector response, which was simulated for each detector type and size by means of the PENELOPE Monte-Carlo code (PENELOPE, 2011). Up to 200 γ-ray energies were simulated between 50 kev and 12 MeV. The distance between each simulated energy corresponded to the energy resolution of the corresponding detector. Each simulated γ-ray energy was then fitted to the measured spectrum until minimization of χ 2 was achieved (see Fig. 1, right part). The sum of all fitted intensities for each γ-line represents the PFG emission spectrum, from which we calculate the characteristic parameters average multiplicity (ν γ ), mean photon energy (ɛ γ ) and average total γ-ray energy (E γ,tot ) per fission, viz (Oberstedt et al., 2014). 4. Prompt fission γ-ray data - the achievements During the last three years new PFGS for the spontaneous fission of 252 Cf (Billnert et al., 2013) and thermalneutron induced fission of 235 U (Oberstedt et al., 2013b) and 241 Pu (Oberstedt et al., 2014) were obtained. In Fig. 2 the low-energy part of the emission spectrum obtained from the spontaneous fission of 252 Cf is shown (red symbols and full line) and compared to the historical data from (Verbinski et al., 1973) (blue dashed line). We observe a similar structure in the spectrum, which is more complex thanks to the better energy resolution of lanthanide-halide detectors. The additional structure below about 0.2 MeV appears due to a lower pulse-height threshold achieved in our measurements. Figure 2 also includes the latest evaluated spectrum in (ENDF/B-VII.1, 2011) (dotted line) and a recent model calculation performed with the Monte-Carlo code FIFRELIN (Regnier et al., 2012; Regnier, 2013) shown as full black line. The model calculation is able to reproduce well the observed structure and rules out the structureless and, hence, unphysical evaluation. The PFGS characteristics for our investigated fissioning systems are summarized in Tab. 1. We compare the results with corresponding data from the (ENDF/B-VII.1, 2011) library and quantify the observed differences in the third line for each investigated system. In all systems studied up to this point we observe
4 86 S. Oberstedt et al. / Physics Procedia 64 ( 2015 ) Fig. 2. (Color online) Prompt fission γ-ray spectrum from the spontaneous fission from 252 Cf (Billnert et al., 2013) compared to the historical data of Verbinski et al. (Verbinski et al., 1973) and recent FIFRELIN model calculations (Regnier, 2013). The dotted line represents the evaluated data (ENDF/B-VII.1, 2011). Table 1. Summary of our results compared to present ENDF/B-VII.1 data. The relative difference is how the evaluated data needs to change to correspond to our measurement. Reaction Dataset Multiplicity γ-energy released /fission MeV/Fission 252 Cf(SF) Our measurement 8.29(6) 6.63(8) ENDF/B-VII Relative difference +5.6% +8.2% 235 U(n th,f) Our measurement 8.19(11) 6.92(9) ENDF/B-VII Relative difference +19.3% +5.2% 241 Pu(n th,f) Our measurement 8.21(9) 6.41(6) ENDF/B-VII Relative difference +1.3% +3.6% an excess in the released average total γ-ray energy per fission of a few percent. If we make a reasonable assumption that the excess in the reaction 239 Pu(n th, f) is not dramatically higher than the one in the studied reaction on 241 Pu, the observed excess cannot explain the under-predicted prompt γ heat in the cores of nuclear reactors as suggested in (Rimpault et al., 2006, 2012; Rimpault, 2006b). In consequence, other reactions should be considered as well, as e.g. fast-neutron induced fission on 235 U and 239 Pu, but certainly on 238 U, which represents the main component in the nuclear fuel. For the investigation of the above suggestion we are being developing a forward-directed fast-neutron beam based on the reaction H( 7 Li, n) 7 Be enabling the placement of a large number of γ-ray detectors in close geometry with the fissioning sample outside the fast-neutron beam (Lebois et al., 2014). This novel neutron source, called LICORNE (Lithium Inverse Cinematiques ORsay NEutron source), is installed at the tandem accelerator of the Institut de Physique Nucléaire in Orsay, France. Spectra from a first measurement on 235,238 U(n, f) at an average neutron energy E n = 1.5 MeV are shown in Fig. 3 for illustration. PFGS data were taken with two different sets of detectors, one consisting of two clusters of 7 BaF 2 detector with a size 10 cm 15 cm (diameter length) each (red lines) and another made from three individual LaBr 3 :Ce detectors of size 5 cm 5 cm (diameter length) and shown as green dashed lines. In the left part of Fig. 3 the spectrum measured at thermal neutron energy (blue line) is shown for
5 S. Oberstedt et al. / Physics Procedia 64 ( 2015 ) Fig. 3. (Color online) Left: Measured prompt γ-ray spectra for the neutron induced fission on 235 U; the red full and green dashed line depicts the spectrum obtained from fats-neutron induced fission at LICORNE taken with the BaF 2 detector clusters and the LaBr 3 :Ce as explained in the text. The blue dashed curve gives the corresponding spectrum obtained from thermal-neutron induced fission. (Oberstedt et al., 2013b). Right: Measured prompt γ-ray spectrum for fast-neutron induced fission on 238 U again for the two different detector systems. comparison. The spectral shape looks very good albeit the much smaller number of events in the spectrum and the higher pulse-height threshold. The right part of Fig. 3 depicts the corresponding PFGS for the reaction 238 U. Details on the LICORNE facility and the PFGS measurements are subject to another contribution in this issue of Physics Procedia (Wilson et al., 2014b). The low-energy structure observed in the PFGS from 252 Cf(sf) is also visible in the spectra from thermal-neutron induced fission on 235 U and 241 Pu with the individual peaks showing different intensities (Oberstedt et al., 2013b, 2014). This may be due to the different shape of the corresponding mass distributions. To study this intriguing feature of the PFGS in more detail we started measuring the spontaneous fission of 252 Cf with focus on correlations of PFGS with fission-fragment properties, in particular on the link between the (low-energy) structure and particular mass splits, and on whether the PFGS characteristics change significantly as a function of mass. In a first step we measured PFGS as a function of the heavy fragment mass, in Fig. 4 shown for mass cuts of 2 mass units. Apart form the strongly changing structure at γ-ray energies below 1 MeV, we may observe a distinct shape change at mass splits with a heavy mass around or smaller than A = 132. A harder γ-ray spectrum was already observed in the 1990s (Hotzel et al., 1996) in an experiment with a 4π NaI-detector array and attributed to nonstatistical γ-emission with E γ > 3.5 MeV from spherical fission fragments. Our data shows that the shape change starts already around 2.5 MeV. Of course, more data is necessary for a quantitative explanation in terms of fissionfragment mass and total kinetic energy. In a second step we started to look at isomeric γ-rays in fission fragments. In Figure 5 emission spectra for time cuts corresponding to 3-6 ns(red) and 7-10 ns(green) relative to the instant of fission are shown together with the prompt distribution for comparison (black line). Prompt and isomer spectra are corrected for the inelastic scattering of fission neutrons populating the first excited state in 56 Fe (E γ = MeV) present in the construction material of the fission chamber. Contributions from (n, n ) in bromine isotopes present in the LaBr 3 :Ce detectors at E γ 0.28 MeV can only be caused by fission neutrons with an energy of at least 8 MeV according to their time of flight. Their fraction is extremely small and does not affect the present spectra in a significant way. In Fig. 5 some transitions are indicated, which are visible in the first isomer spectrum but not in the second. Therefore, one may put a stringent condition on the half-life of the decaying level. Together with the γ-ray energy fragment identification seems possible, at least in a few cases. This work is still ongoing and with a further increased number of events later time cuts are possible to be investigated allowing spectroscopy of very neutron-rich isotopes very close to scission and, more applied, determining the contribution of isomeric γ-decay to the prompt γ heating.
6 88 S. Oberstedt et al. / Physics Procedia 64 ( 2015 ) Fig. 4. (Color online) Prompt fission γ-ray spectra as a function of the heavy pre-neutron fission-fragment mass, A pre, shown in logarithmic scale. Each mass cut contains also the contribution from the complementary light fragment, A comp. Indicated is the significant spectral shape change around E γ = 2.5 MeV for masses between A pre = 126 and A pre = 132 (including A comp = 126 and A comp = 120). Fig. 5. (Color online) Fission γ-ray spectra for time cuts corresponding to 3-6 ns(red) and 7-10 ns(green) relative to the instant of fission together with the prompt distribution shown for comparison (black line). The vertical dotted lines indicate presumable isomeric transitions in fission fragments with half-lives well below 3 ns (see text for details). 5. Further data needs - the future From the comparison of our new and precise prompt fission γ-ray data with the tabulated values in (ENDF/B-VII.1, 2011), cf. Tab. 1, we have to suspect that deficient data from other reactions contribute to the under-prediction of the prompt γ-heating in the core of a nuclear reactor. Although no new data from the reaction 239 Pu(n th, f) were measured yet, we have no reason to assume significant deficiencies in the historical data from (Verbinski et al., 1973; Pleasonton
7 S. Oberstedt et al. / Physics Procedia 64 ( 2015 ) et al., 1972). However, new measurements are scheduled for A measurable contribution may be expected to come from the fast-neutron induced fission. Here not only the fissile isotopes have to be investigated in the future but also the non-fissile isotope 238 U, representing the major constituent of the nuclear fuel. These measurements have been started already at the novel directional neutron source LICORNE for neutron energies up to 4 MeV and will be pursued in In addition, more isotopes should be investigated to reveal systematic trends as a function of incident neutron energy for the PFGS characteristics, average multiplicity (ν γ ), mean photon energy (ɛ γ ) and average total γ-ray energy (E γ,tot ) per fission, viz. In (Oberstedt et al., 2014c) this work has been started based on the approach of (Valentine, 2001). PFGS measurements on spontaneously fissioning isotopes 240,242 Pu and 246,248 Cm are under way or in preparation at the JRC-IRMM. The systematic investigation should be extended to photon-induced fission as well, which allows assessing different excitation regimes not (directly) accessible in neutron-induced fission. Moreover, fission induced from high-energy γ-rays from neutron capture in isotopes present in the construction materials close to the nuclear fuel is not even considered in present reactor calculations. It is tempting to estimate the possible contribution from this process to the total prompt heat production in the reactor. Acknowledgements Two of the authors (R. B. and A. G.) are indebted to the European Commission for providing a PhD fellowship at EC-JRC IRMM, during which part of this work was carried out. This work was also supported by the European Commission in the frame works of the FP7-ERINDA programme (agreement number ), which is hereby gratefully acknowledged. The authors are very grateful to the colleagues at the KFKI Budapest for their invaluable support during several measurement campaigns. References Billnert, R., Oberstedt, S., Andreotti, E., Hult, F.C., Marissens, G., Oberstedt, A., 2011, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 647, 94. Billnert, R., Andreotti, E., Hambsch, F.-J., Hult, M., Karlsson, J., Marissens, G., Oberstedt, A., Oberstedt, S., 2012, Phys. Procedia 3, 29. Billnert, R., Hambsch, F.-J., Oberstedt, A. and Oberstedt, S., 2013, Phys. Rev C87, Boikov, G.S., Dmitriev, V.D., Kudyaev, G.A., Ostapenko, Yu.B., Svirin, M.I., and Smirenkin, G.N., 1991, Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 53, 392. Chyzh, A., Wu, C. Y., Kwan, E., Henderson, R. A., Gostic, J. M., Bredeweg, T. A., Haight, R. C., Hayes-Sterbenz, A. C., Jandel, M., ODonnell, J. M., and Ullmann, J. L., 2012, Phys. Rev. C 85, ENDF/B-VII Evaluated Nuclear Data File ZA = 98251, MF = 15, MT = 18 (2011), Hotzel, A., Thirolf, P., Ender, Ch., Schwalm, D., Mutterer, M., Singer, P., Klemens, M., Theobald, J.P., Hesse., M., Gönnenwein, F., van den Ploeg, H., 1996, Z. Physik A - Hadrons and Nuclei 356, 299. KFKI Research Reactor, Budapest (HU), Kornilov, N., Hambsch, F.-J., Fabry, I., Oberstedt, S., Belgya, T., Kis, Z., Szentmiklosi, L., Simakov, S., 2010, Nucl. Sci. Engin. 165, 117. Lebois, M., Wilson, J.N., Halipré, P., Leniau, B., Matea, I., Oberstedt, A., Oberstedt, S., 2014, Nucl. Inst. Meth. A 735, 145. Lemaire, S., Talou, P., Kawano, T., Chadwick, M.B., and Madland, D.G., 2005, Phys. Rev. C 72, Lutter, G., Hult, M., Billnert, R., Oberstedt, A., Oberstedt, S., Andreotti, E., Marissens, G., Rosengard, U., Tzika, F., 2013, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 703, 158. Nuclear Data High Priority Request List of the NEA (Req. ID: H.3, H.4), and Oberstedt, A., Billnert, R., Oberstedt, S., 2013, Nucl. Instr. And Meth. A 708, 7. Oberstedt, A., Belgya, T., Billnert, R., Borcea, R., Bryś, T., Geerts, W., Göök, A., Hambsch, F.-J., Kis, Z., Martinez, T., Oberstedt, S., Szentmiklosi, L., Takacs, K. and Vidali, M., 2013, Phys. Rev. C87, (R). Oberstedt, A., Billnert, R., Hambsch, F.-J., Oberstedt, S., submitted for publication. Oberstedt, A., Billnert, R., Oberstedt, S., submitted for publication. Oberstedt, S., Borcea, R., Bryś, T., Gamboni, Th., Geerts, W., Hambsch, F.-J., Oberstedt, A., Vidali, M., 2013, Nucl. Inst. Meth. A 714, 31. Oberstedt, S., Billnert, R., Belgya, T., Bryś, T., Geerts, W., Guerrero, C., Hambsch, F.-J., Kis, Z., Moens, A., Oberstedt, A., Sibbens, G., Szentmiklosi, L., Vanleeuw, D. and Vidali, M., High precision prompt spectral γ-ray data from the reaction 241 Pu(n th, f), 2014, Phys. Rev. C90, Peelle, R.W. and Maienschein, F.C., 1971, Phys. Rev C3, 373.
8 90 S. Oberstedt et al. / Physics Procedia 64 ( 2015 ) PENELOPE 2011, Pleasonton, F., Ferguson, R.L. and Schmitt, H.W., 1972, Phys. Rev. C6, Regnier, D., Litaize, O. and Serot, O., 2012, Physics Procedia 31, 59. Regnier, D., 2013, private communication. Rimpault, G., Courcelle, A. and Blanchet, D., 2006, Comment to the HPRL: ID H.3 and H.4. Rimpault, G., Bernard, D., Blanchet, D., Vaglio-Gaudard, C., Ravaux, S., Santamaria, A., 2012, Phys. Procedia 31, 3. Rimpault, G., 2006, Proc. Workshop on Nuclear Data Needs for Generation IV, April 2005 (Editor: P. Rullhusen) Antwerp, Belgium, World Scientic, ISBN , 46. ROOT Data Analysis Framework, (2014). SP Devices, Spectrum GmbH, Tudora, A., Hambsch, F.-J., and Oberstedt, S., 2013, Nucl. Phys. A 917, 43. Valentine, T.E., 2001, Ann. Nucl. Energy 28, 191. Verbinski, V.V., Weber, H. and Sund, R.E., 1973, Phys. Rev C7, Wilson, J.N. et al., 2015, Physics Procedia, this issue.
Future research program on prompt γ-ray emission in nuclear fission
 Future research program on prompt γ-ray emission in nuclear fission Robert Billnert, Aleksandar Dragic, Angélique Gatera, Alf Göök, Pierre Halipré, Mattieu Lebois, Andreas Oberstedt, Stephan Oberstedt,
Future research program on prompt γ-ray emission in nuclear fission Robert Billnert, Aleksandar Dragic, Angélique Gatera, Alf Göök, Pierre Halipré, Mattieu Lebois, Andreas Oberstedt, Stephan Oberstedt,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 64 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 91 100 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3 Prompt
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 91 100 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3 Prompt
Characteristics of prompt fission γ-ray emission experimental results and predictions
 Characteristics of prompt fission γ-ray emission experimental results and predictions A. Oberstedt NEMEA-7/CIELO Workshop of the Collaborative International Evaluated Library Organization IRMM Geel, Belgium
Characteristics of prompt fission γ-ray emission experimental results and predictions A. Oberstedt NEMEA-7/CIELO Workshop of the Collaborative International Evaluated Library Organization IRMM Geel, Belgium
Preparatory experiments for cold-neutron induced fission studies at IKI
 Preparatory experiments for cold-neutron induced fission studies at IKI A. Oberstedt 1, S. Oberstedt 2, R. Billnert 1, J. Karlsson 1, X. Ledoux 3, J.-G. Marmouget 3 and F.-J. Hambsch 2 1 School of Science
Preparatory experiments for cold-neutron induced fission studies at IKI A. Oberstedt 1, S. Oberstedt 2, R. Billnert 1, J. Karlsson 1, X. Ledoux 3, J.-G. Marmouget 3 and F.-J. Hambsch 2 1 School of Science
Recent Developments in Neutron Measurements at the European Commission Joint Research Centre IRMM
 Recent Developments in Neutron Measurements at the European Commission Joint Research Centre IRMM CCRI(III) meeting of 04 to 06 March 2015 Stephan Oberstedt European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute
Recent Developments in Neutron Measurements at the European Commission Joint Research Centre IRMM CCRI(III) meeting of 04 to 06 March 2015 Stephan Oberstedt European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) Neutron-induced fission cross section of 240,242 Pu
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 177 182 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 177 182 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3
VERDI a double (v, E) fission-fragment fragment spectrometer
 EFNUDAT Slow and Resonance Neutrons, Budapest (HU), Sep. 23-25, 2009 1 VERDI a double (v, E) fission-fragment fragment spectrometer S. Oberstedt, R. Borcea,, Th. Gamboni,, W. Geerts, F.-J. Hambsch, A.
EFNUDAT Slow and Resonance Neutrons, Budapest (HU), Sep. 23-25, 2009 1 VERDI a double (v, E) fission-fragment fragment spectrometer S. Oberstedt, R. Borcea,, Th. Gamboni,, W. Geerts, F.-J. Hambsch, A.
Measurement of prompt fission γ-ray spectra in fast neutroninduced
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 31 (2012 ) 13 20 GAMMA-1 Emission of Prompt Gamma-Rays in Fission and Related Topics Measurement of prompt fission γ-ray spectra in fast neutroninduced
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 31 (2012 ) 13 20 GAMMA-1 Emission of Prompt Gamma-Rays in Fission and Related Topics Measurement of prompt fission γ-ray spectra in fast neutroninduced
JRC Place on dd Month YYYY Event Name 1
 JRC Place on dd Month YYYY Event Name 1 A new measurement of the prompt fission neutron emission spectrum of 235 U(n,f) Correlation of prompt neutron emission with fission fragment properties F.-J. Hambsch
JRC Place on dd Month YYYY Event Name 1 A new measurement of the prompt fission neutron emission spectrum of 235 U(n,f) Correlation of prompt neutron emission with fission fragment properties F.-J. Hambsch
Correlated Prompt Fission Data
 Correlated Prompt Fission Data Patrick Talou 1, T. Kawano 1, I. Stetcu 1, D. Neudecker 2 1 Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA 2 XCP-5, Computational Physics Division, Los Alamos
Correlated Prompt Fission Data Patrick Talou 1, T. Kawano 1, I. Stetcu 1, D. Neudecker 2 1 Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA 2 XCP-5, Computational Physics Division, Los Alamos
Neutron capture and fission reactions on. sections, -ratios and prompt -ray emission from fission. 1 Introduction and Motivation
 EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01002 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Neutron capture and fission reactions on 235 U : cross sections, -ratios
EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01002 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Neutron capture and fission reactions on 235 U : cross sections, -ratios
A Monte Carlo Simulation of Prompt Gamma Emission from Fission Fragments
 A Monte Carlo Simulation of Prompt Gamma Emission from Fission Fragments D. Regnier, O. Litaize, O. Serot CEA Cadarache, DEN/DER/SPRC/LEPH WONDER, 27/09/2012 D. Regnier, O. Litaize, O. Serot - CEA Cadarache,
A Monte Carlo Simulation of Prompt Gamma Emission from Fission Fragments D. Regnier, O. Litaize, O. Serot CEA Cadarache, DEN/DER/SPRC/LEPH WONDER, 27/09/2012 D. Regnier, O. Litaize, O. Serot - CEA Cadarache,
Investigation of Prompt Fission Neutron and Gamma Spectra with their covariance matrices. Application to 239 Pu+n th, 238 U+n 1.
 Investigation of Prompt Fission Neutron and Gamma Spectra with their covariance matrices. Application to 239 Pu+n th, 238 U+n 1.8MeV, 235 U+n th O. Litaize, L. Berge, D. Regnier, O. Serot, Y. Peneliau,
Investigation of Prompt Fission Neutron and Gamma Spectra with their covariance matrices. Application to 239 Pu+n th, 238 U+n 1.8MeV, 235 U+n th O. Litaize, L. Berge, D. Regnier, O. Serot, Y. Peneliau,
Nuclear Cross-Section Measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center
 1 Nuclear Cross-Section Measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center M. Mocko 1, G. Muhrer 1, F. Tovesson 1, J. Ullmann 1 1 LANSCE, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos NM 87545,
1 Nuclear Cross-Section Measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center M. Mocko 1, G. Muhrer 1, F. Tovesson 1, J. Ullmann 1 1 LANSCE, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos NM 87545,
Author(s) Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki. Citation Physics Procedia (2015), 64:
 Title Fission Study of Actinide Nuclei Us Reactions Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Author(s) Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orland James; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Chiba, Sat Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki
Title Fission Study of Actinide Nuclei Us Reactions Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Author(s) Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orland James; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Chiba, Sat Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 48 54
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 48 54 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3 Evaluation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 48 54 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3 Evaluation
Fig. 1 Sketch of the experimental setup for PFN investigation.
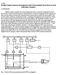 1) Title Prompt Fission Neutron Investigation with Frisch-gridded Twin Back-to-back Ionization Chamber. 2) Introduction Modern models consider the nuclear fission process as a result of competition between
1) Title Prompt Fission Neutron Investigation with Frisch-gridded Twin Back-to-back Ionization Chamber. 2) Introduction Modern models consider the nuclear fission process as a result of competition between
The 10 B(n,α 0. γ) 7 Li alpha-particle angular distributions, branching ratios and crosssections measurements for E n. < 3 MeV. ) 7 Li and 10 B(n,α l
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content The 10 B(n,α 0 ) 7 Li and 10 B(n,α l γ) 7 Li alpha-particle angular distributions, branching ratios and crosssections measurements for E n < 3 MeV
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content The 10 B(n,α 0 ) 7 Li and 10 B(n,α l γ) 7 Li alpha-particle angular distributions, branching ratios and crosssections measurements for E n < 3 MeV
Determination of neutron induced fission fragment spin distribution after neutron evaporation
 Determination of neutron induced fission fragment spin distribution after neutron evaporation A. Chebboubi, G. Kessedjian, C. Sage, O. Méplan LPSC, Université Grenoble-Alpes, CNRS/IN2P3, F-38026 Grenoble,
Determination of neutron induced fission fragment spin distribution after neutron evaporation A. Chebboubi, G. Kessedjian, C. Sage, O. Méplan LPSC, Université Grenoble-Alpes, CNRS/IN2P3, F-38026 Grenoble,
Needs for Nuclear Reactions on Actinides
 Needs for Nuclear Reactions on Actinides Mark Chadwick Los Alamos National Laboratory Talk at the Workshop on Nuclear Data Needs & Capabilities for Applications, May 27-29, 2015 Nuclear Data for National
Needs for Nuclear Reactions on Actinides Mark Chadwick Los Alamos National Laboratory Talk at the Workshop on Nuclear Data Needs & Capabilities for Applications, May 27-29, 2015 Nuclear Data for National
Investigation of the surrogate-reaction method via the simultaneous measurement of gamma-emission and fission probabilities
 Investigation of the surrogate-reaction method via the simultaneous measurement of gamma-emission and fission probabilities B. Jurado, P. Marini, M. Aiche, S. Czajkowski, D. Denis-Petit, L. Mathieu, R.
Investigation of the surrogate-reaction method via the simultaneous measurement of gamma-emission and fission probabilities B. Jurado, P. Marini, M. Aiche, S. Czajkowski, D. Denis-Petit, L. Mathieu, R.
Challenges in experiments and modelling of nuclear fission: prompt neutron and γ-ray emission
 Challenges in experiments and modelling of nuclear fission: prompt neutron and γ-ray emission F.-J. Hambsch IRMM, Belgium Content Introduction Neutron multiplicities and Neutron-fission fragment correlations
Challenges in experiments and modelling of nuclear fission: prompt neutron and γ-ray emission F.-J. Hambsch IRMM, Belgium Content Introduction Neutron multiplicities and Neutron-fission fragment correlations
Total kinetic energy and fragment mass distributions from fission of Th-232 and U-233
 Total kinetic energy and fragment mass distributions from fission of Th-232 and U-233 Daniel Higgins 1,2*, Uwe Greife 1, Shea Mosby 2, and Fredrik Tovesson 2 1 Colorado School of Mines, Physics Department,
Total kinetic energy and fragment mass distributions from fission of Th-232 and U-233 Daniel Higgins 1,2*, Uwe Greife 1, Shea Mosby 2, and Fredrik Tovesson 2 1 Colorado School of Mines, Physics Department,
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIGHT CHARGED PARTICLE EMISSION IN THE TERNARY FISSION OF 250 CF AND 252 CF AT DIFFERENT EXCITATION ENERGIES
 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIGHT CHARGED PARTICLE EMISSION IN THE TERNARY FISSION OF 25 CF AND 252 CF AT DIFFERENT EXCITATION ENERGIES S. VERMOTE AND C. WAGEMANS Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIGHT CHARGED PARTICLE EMISSION IN THE TERNARY FISSION OF 25 CF AND 252 CF AT DIFFERENT EXCITATION ENERGIES S. VERMOTE AND C. WAGEMANS Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Influence of primary fragment excitation energy and spin distributions on fission observables
 Influence of primary fragment excitation energy and spin distributions on fission observables Olivier Litaize 1,, Loïc hulliez 1,2, Olivier Serot 1, Abdelaziz Chebboubi 1, and Pierre amagno 1 1 CEA, DEN,
Influence of primary fragment excitation energy and spin distributions on fission observables Olivier Litaize 1,, Loïc hulliez 1,2, Olivier Serot 1, Abdelaziz Chebboubi 1, and Pierre amagno 1 1 CEA, DEN,
Cf-252 spontaneous fission prompt neutron and photon correlations
 Cf-252 spontaneous fission prompt neutron and photon correlations M. J. Marcath 1,*, P. Schuster 1, P. Talou 2, I. Stetcu 2, T. Kawano 2, M. Devlin 2, R. C. Haight 2, R. Vogt 3,4, J. Randrup 5, S. D. Clarke
Cf-252 spontaneous fission prompt neutron and photon correlations M. J. Marcath 1,*, P. Schuster 1, P. Talou 2, I. Stetcu 2, T. Kawano 2, M. Devlin 2, R. C. Haight 2, R. Vogt 3,4, J. Randrup 5, S. D. Clarke
High precision neutron inelastic cross section measurements
 High precision neutron inelastic cross section measurements A. Olacel, C. Borcea, M. Boromiza, A. Negret IFIN-HH, DFN Outline The experimental setup GELINA GAINS Data analysis algorithm. Monte Carlo simulations
High precision neutron inelastic cross section measurements A. Olacel, C. Borcea, M. Boromiza, A. Negret IFIN-HH, DFN Outline The experimental setup GELINA GAINS Data analysis algorithm. Monte Carlo simulations
Development and test of the high-precision -beam monitor at the ESFRI facility ELI-NP
 Development and test of the high-precision -beam monitor at the ESFRI facility ELI-NP Göök A., Oberstedt S., Geerts W., Hambsch F.-J. Public 2017 EUR 29002 EN This publication is a Technical report by
Development and test of the high-precision -beam monitor at the ESFRI facility ELI-NP Göök A., Oberstedt S., Geerts W., Hambsch F.-J. Public 2017 EUR 29002 EN This publication is a Technical report by
Measurement of (n, xn γ) reaction cross sections in W isotopes
 Measurement of (n, xn γ) reaction cross sections in isotopes Greg Henning IPHC/CNRS 1 Context: Nuclear data evaluations for applications 4 th generation nuclear reactors and new fuel cycles, currently
Measurement of (n, xn γ) reaction cross sections in isotopes Greg Henning IPHC/CNRS 1 Context: Nuclear data evaluations for applications 4 th generation nuclear reactors and new fuel cycles, currently
Alpha-Gamma discrimination by Pulse Shape in LaBr 3 :Ce and LaCl 3 :Ce
 Alpha-Gamma discrimination by Pulse Shape in LaBr 3 :Ce and LaCl 3 :Ce F.C.L. Crespi 1,2, F.Camera 1,2, N. Blasi 2, A.Bracco 1,2, S. Brambilla 2, B. Million 2, R. Nicolini 1,2, L.Pellegri 1, S. Riboldi
Alpha-Gamma discrimination by Pulse Shape in LaBr 3 :Ce and LaCl 3 :Ce F.C.L. Crespi 1,2, F.Camera 1,2, N. Blasi 2, A.Bracco 1,2, S. Brambilla 2, B. Million 2, R. Nicolini 1,2, L.Pellegri 1, S. Riboldi
Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu
 Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu Vorobyev AS, Shcherbakov OA, Gagarski AM, Val ski GV, Petrov GA National Research Center Kurchatov
Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu Vorobyev AS, Shcherbakov OA, Gagarski AM, Val ski GV, Petrov GA National Research Center Kurchatov
Correlations in Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays from Fission
 Correlations in Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays from Fission S. A. Pozzi 1, B. Wieger 1, M. J. Marcath 1, S. Ward 1, J. L. Dolan 1, T. H. Shin 1, S. D. Clarke 1, M. Flaska 1, E. W. Larsen 1, A. Enqvist
Correlations in Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays from Fission S. A. Pozzi 1, B. Wieger 1, M. J. Marcath 1, S. Ward 1, J. L. Dolan 1, T. H. Shin 1, S. D. Clarke 1, M. Flaska 1, E. W. Larsen 1, A. Enqvist
Review of nuclear data of major actinides and 56 Fe in JENDL-4.0
 Review of nuclear data of major actinides and 56 Fe in JENDL-4.0 Osamu Iwamoto, Nobuyuki Iwamoto Nuclear Data Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Directorate Japan Atomic Energy Agency Ibaraki, Japan
Review of nuclear data of major actinides and 56 Fe in JENDL-4.0 Osamu Iwamoto, Nobuyuki Iwamoto Nuclear Data Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Directorate Japan Atomic Energy Agency Ibaraki, Japan
Benchmark test: Description of prompt-neutron spectra with the GEF code
 Benchmark test: Description of prompt-neutron spectra with the GEF code Karl-Heinz Schmidt Beatriz Jurado January 2014 1 Introduction This work deals with the description of prompt-neutron spectra in neutroninduced
Benchmark test: Description of prompt-neutron spectra with the GEF code Karl-Heinz Schmidt Beatriz Jurado January 2014 1 Introduction This work deals with the description of prompt-neutron spectra in neutroninduced
The energy dependence of fissionfragment characteristics for neutron-induced fission on Pu-239
 The energy dependence of fissionfragment characteristics for neutron-induced fission on Pu-239 Göök, A Oberstedt, S. 2018 EUR 29472 EN This publication is a Technical report by the Joint Research Centre
The energy dependence of fissionfragment characteristics for neutron-induced fission on Pu-239 Göök, A Oberstedt, S. 2018 EUR 29472 EN This publication is a Technical report by the Joint Research Centre
A Photofission Delayed γ-ray Spectra Calculation Tool for the Conception of a Nuclear Material Characterization Facility
 A Photofission Delayed γ-ray Spectra Calculation Tool for the Conception of a Nuclear Material Characterization Facility D. BERNARD *, O. SEROT *, E. SIMON *, L. BOUCHER * and S. PLUMERI + Abstract The
A Photofission Delayed γ-ray Spectra Calculation Tool for the Conception of a Nuclear Material Characterization Facility D. BERNARD *, O. SEROT *, E. SIMON *, L. BOUCHER * and S. PLUMERI + Abstract The
High-spin studies and nuclear structure in three semi-magic regions of the nuclide chart High-seniority states in Sn isotopes
 High-spin studies and nuclear structure in three semi-magic regions of the nuclide chart High-seniority states in Sn isotopes Outline: Alain Astier, CSNSM Orsay, France Motivations Experimental conditions
High-spin studies and nuclear structure in three semi-magic regions of the nuclide chart High-seniority states in Sn isotopes Outline: Alain Astier, CSNSM Orsay, France Motivations Experimental conditions
Investigation of the surrogate-reaction method via the simultaneous measurement of gamma-emission and fission probabilities in 3 He Pu reactions
 Investigation of the surrogate-reaction method via the simultaneous measurement of gamma-emission and fission probabilities in 3 He + 240 Pu reactions M.Aiche, S.zajkowski, D. Denis-Petit, B. Jurado, L.
Investigation of the surrogate-reaction method via the simultaneous measurement of gamma-emission and fission probabilities in 3 He + 240 Pu reactions M.Aiche, S.zajkowski, D. Denis-Petit, B. Jurado, L.
5 th ASRC International Workshop, 14 th -16 th March 2012
 Fission Fragment Fragment Spectroscopy with Large Arrays and STEFF A.G. Smith, J. Dare, A. Pollitt, E. Murray The University of Manchester W. Urban, T. Soldner ILL Grenoble I. Tsekhanovich, J. Marrantz
Fission Fragment Fragment Spectroscopy with Large Arrays and STEFF A.G. Smith, J. Dare, A. Pollitt, E. Murray The University of Manchester W. Urban, T. Soldner ILL Grenoble I. Tsekhanovich, J. Marrantz
PROMPT FISSION NEUTRON MULTIPLICITY INVESTIGATION. Belgium
 PROMPT FISSION NEUTRON MULTIPLICITY INVESTIGATION Sh. Zeynalov a, O. Zeynalova a, F.-J. Hambsch b, S. Oberstedt b a) JINR-Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Moscow region, Russia b) EC JRC Institute
PROMPT FISSION NEUTRON MULTIPLICITY INVESTIGATION Sh. Zeynalov a, O. Zeynalova a, F.-J. Hambsch b, S. Oberstedt b a) JINR-Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Moscow region, Russia b) EC JRC Institute
An introduction to Neutron Resonance Densitometry (Short Summary)
 An introduction to Neutron Resonance Densitometry (Short Summary) H. Harada 1, M. Koizumi 1, H. Tsuchiya 1, F. Kitatani 1, M. Seya 1 B. Becker 2, J. Heyse 2, S. Kopecky 2, C. Paradela 2, P. Schillebeeckx
An introduction to Neutron Resonance Densitometry (Short Summary) H. Harada 1, M. Koizumi 1, H. Tsuchiya 1, F. Kitatani 1, M. Seya 1 B. Becker 2, J. Heyse 2, S. Kopecky 2, C. Paradela 2, P. Schillebeeckx
SURROGATE REACTIONS. An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL
 SURROGATE REACTIONS An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL Compound Nuclear Reaction cross sections Cross sections for compound-nuclear reactions are required input for astrophysical models and
SURROGATE REACTIONS An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL Compound Nuclear Reaction cross sections Cross sections for compound-nuclear reactions are required input for astrophysical models and
Correlations in Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays from Fission
 Correlations in Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays from Fission S. A. Pozzi 1, M. J. Marcath 1, T. H. Shin 1, Angela Di Fulvio 1, S. D. Clarke 1, E. W. Larsen 1, R. Vogt 2,3, J. Randrup 4, R. C. Haight 5,
Correlations in Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays from Fission S. A. Pozzi 1, M. J. Marcath 1, T. H. Shin 1, Angela Di Fulvio 1, S. D. Clarke 1, E. W. Larsen 1, R. Vogt 2,3, J. Randrup 4, R. C. Haight 5,
Current studies of neutron induced reactions regard essentially two mass regions, identified in the chart of nuclides: isotopes in the region from Fe
 The talk gives an overview of the current reseach activity with neutron beams for fundamental and applied Nuclear Physics. In particular, it presents the status and perspectives of neutron studies in the
The talk gives an overview of the current reseach activity with neutron beams for fundamental and applied Nuclear Physics. In particular, it presents the status and perspectives of neutron studies in the
DETECTORS. I. Charged Particle Detectors
 DETECTORS I. Charged Particle Detectors A. Scintillators B. Gas Detectors 1. Ionization Chambers 2. Proportional Counters 3. Avalanche detectors 4. Geiger-Muller counters 5. Spark detectors C. Solid State
DETECTORS I. Charged Particle Detectors A. Scintillators B. Gas Detectors 1. Ionization Chambers 2. Proportional Counters 3. Avalanche detectors 4. Geiger-Muller counters 5. Spark detectors C. Solid State
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 62 (29) 52 524 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 62 (29) 52 524 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
Modeling fission in FIFRELIN
 Excitation energy (MeV) Modeling fission in FIFRELIN 40 38 36 34 3 30 8 6 4 0 18 16 14 1 10 8 6 4 0 Heavy Primary 0 4 6 8 10 1 14 16 18 0 Total angular momentum 0 1E3 3E3 4E3 5E3 6E3 8E3 9E3 1E4 Olivier
Excitation energy (MeV) Modeling fission in FIFRELIN 40 38 36 34 3 30 8 6 4 0 18 16 14 1 10 8 6 4 0 Heavy Primary 0 4 6 8 10 1 14 16 18 0 Total angular momentum 0 1E3 3E3 4E3 5E3 6E3 8E3 9E3 1E4 Olivier
Subroutines to Simulate Fission Neutrons for Monte Carlo Transport Codes. J. P. Lestone Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, USA
 Subroutines to Simulate Fission Neutrons for Monte Carlo Transport Codes J. P. Lestone Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, USA Abstract Fortran subroutines have been written to simulate
Subroutines to Simulate Fission Neutrons for Monte Carlo Transport Codes J. P. Lestone Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, USA Abstract Fortran subroutines have been written to simulate
Hrant Gulkanyan and Amur Margaryan
 ALPHA-SPECTROSCOPY OF 252 Cf DECAYS: A NEW APPROACH TO SEARCHING FOR THE OCTONEUTRON YerPhI Preprint -1628 (2014) Hrant Gulkanyan and Amur Margaryan A.I. Alikhanyan National Science Laboratory (Yerevan
ALPHA-SPECTROSCOPY OF 252 Cf DECAYS: A NEW APPROACH TO SEARCHING FOR THE OCTONEUTRON YerPhI Preprint -1628 (2014) Hrant Gulkanyan and Amur Margaryan A.I. Alikhanyan National Science Laboratory (Yerevan
A new detector for neutron beam monitoring
 A new detector for neutron beam monitoring European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Geneva, Switzerland in collaboration with Commissariat à l Energie Atomique (CEA), Saclay, France, Instituto
A new detector for neutron beam monitoring European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Geneva, Switzerland in collaboration with Commissariat à l Energie Atomique (CEA), Saclay, France, Instituto
A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
RESPONSE FUNCTION STUDY FOR ENERGY TO LIGHT CONVERSION IN ORGANIC LIQUID SCINTILLATORS
 RESPONSE FUNCTION STUDY FOR ENERGY TO LIGHT CONVERSION IN ORGANIC LIQUID SCINTILLATORS S. Prasad *, A. Enqvist, S. D. Clarke, S. A. Pozzi, E. W. Larsen 1 Department of Nuclear Engineering and Radiological
RESPONSE FUNCTION STUDY FOR ENERGY TO LIGHT CONVERSION IN ORGANIC LIQUID SCINTILLATORS S. Prasad *, A. Enqvist, S. D. Clarke, S. A. Pozzi, E. W. Larsen 1 Department of Nuclear Engineering and Radiological
Fission Yield CEA-Cadarache
 Fission Yield Activities @ CEA-Cadarache Olivier SEROT CEA-Cadarache DEN/DER/SPRC/LEPh 13108 Saint Paul lez Durance France PAGE 1 Content Fission Yield Measurements on Lohengrin @ Institut Laue Langevin
Fission Yield Activities @ CEA-Cadarache Olivier SEROT CEA-Cadarache DEN/DER/SPRC/LEPh 13108 Saint Paul lez Durance France PAGE 1 Content Fission Yield Measurements on Lohengrin @ Institut Laue Langevin
VorobyevA.S., ShcherbakovO.A., GagarskiA.M., Val ski G.V., Petrov G.A.
 Investigation of the Prompt Neutron Emission Mechanism in Low Energy Fission of 233, 235 U(n th, f) and 252 Cf(sf) VorobyevA.S., ShcherbakovO.A., GagarskiA.M., Val ski G.V., Petrov G.A. Petersburg Nuclear
Investigation of the Prompt Neutron Emission Mechanism in Low Energy Fission of 233, 235 U(n th, f) and 252 Cf(sf) VorobyevA.S., ShcherbakovO.A., GagarskiA.M., Val ski G.V., Petrov G.A. Petersburg Nuclear
in Cross-Section Data
 Sensitivity of Photoneutron Production to Perturbations in Cross-Section Data S. D. Clarke Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana S. A. Pozzi University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan E. Padovani
Sensitivity of Photoneutron Production to Perturbations in Cross-Section Data S. D. Clarke Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana S. A. Pozzi University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan E. Padovani
Capture and Fission with DANCE and NEUANCE
 Capture and Fission with DANCE and NEUANCE Marian Jandel Nuclear and Radiochemistry Group P(ND)^2-2, Oct 14-17, 2014, Bruyeres-le-Chatel, France UNCLASSIFIED Nuclear data measurements at DANCE Neutron
Capture and Fission with DANCE and NEUANCE Marian Jandel Nuclear and Radiochemistry Group P(ND)^2-2, Oct 14-17, 2014, Bruyeres-le-Chatel, France UNCLASSIFIED Nuclear data measurements at DANCE Neutron
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 59 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 59 (24 ) 4 8 GAMMA-2 Scientific Workshop on the Emission of Prompt Gamma Rays in Fission and Related Topics Measurement of cross-sections
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 59 (24 ) 4 8 GAMMA-2 Scientific Workshop on the Emission of Prompt Gamma Rays in Fission and Related Topics Measurement of cross-sections
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 64 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 101 106 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 64 (2015 ) 101 106 Scientific Workshop on Nuclear Fission dynamics and the Emission of Prompt Neutrons and Gamma Rays, THEORY-3
B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec.
 2: Fission and Other Neutron Reactions B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents Concepts: Fission and other
2: Fission and Other Neutron Reactions B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents Concepts: Fission and other
Monte Carlo Simulation for Statistical Decay of Compound Nucleus
 5th ASRC International Workshop Perspectives in Nuclear Fission JAEA Mar. 4 6, 22 Monte Carlo Simulation for Statistical Decay of Compound Nucleus T. Kawano, P. Talou, M.B. Chadwick, I. Stetcu Los Alamos
5th ASRC International Workshop Perspectives in Nuclear Fission JAEA Mar. 4 6, 22 Monte Carlo Simulation for Statistical Decay of Compound Nucleus T. Kawano, P. Talou, M.B. Chadwick, I. Stetcu Los Alamos
FIFRELIN TRIPOLI-4 coupling for Monte Carlo simulations with a fission model. Application to shielding calculations
 FIFRELIN TRIPOLI-4 coupling for Monte Carlo simulations with a fission model. Application to shielding calculations Odile Petit 1,*, Cédric Jouanne 1, Olivier Litaize 2, Olivier Serot 2, Abdelhazize Chebboubi
FIFRELIN TRIPOLI-4 coupling for Monte Carlo simulations with a fission model. Application to shielding calculations Odile Petit 1,*, Cédric Jouanne 1, Olivier Litaize 2, Olivier Serot 2, Abdelhazize Chebboubi
Neutron inelastic scattering cross section measurements for 23 Na. C. Rouki, J. C. Drohé, A. Moens, N. Nankov, A. Plompen, M.
 Neutron inelastic scattering cross section measurements for 23 Na C. Rouki, J. C. Drohé, A. Moens, N. Nankov, A. Plompen, M. Stanoiu EUR 24871 EN - 2011 The mission of the JRC-IRMM is to promote a common
Neutron inelastic scattering cross section measurements for 23 Na C. Rouki, J. C. Drohé, A. Moens, N. Nankov, A. Plompen, M. Stanoiu EUR 24871 EN - 2011 The mission of the JRC-IRMM is to promote a common
Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
Neutronic studies on a pulsed thermal neutron source based on the Be(p,n) reaction by using a compact proton accelerator
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 26 (2012 ) 88 96 Union of Compact Accelerator-Driven Neutron Sources I & II Neutronic studies on a pulsed thermal neutron source based on the
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 26 (2012 ) 88 96 Union of Compact Accelerator-Driven Neutron Sources I & II Neutronic studies on a pulsed thermal neutron source based on the
Fission cross section measured at n_tof with PPACs
 Fission cross section measured at n_tof with PPACs L. Audoin1, I. Duran2, E. Leal2, LS. Leong1, C. Paradela2*, D. Tarrío2**, L. Tassan-Got1 on behalf of the n_tof Collaboration 1. Institut de Physique
Fission cross section measured at n_tof with PPACs L. Audoin1, I. Duran2, E. Leal2, LS. Leong1, C. Paradela2*, D. Tarrío2**, L. Tassan-Got1 on behalf of the n_tof Collaboration 1. Institut de Physique
Study of prompt neutron emission spectra in fast neutron induced fission of 238 U and 232 Th and 30 kev neutron induced fission on 235 U
 Study of prompt neutron emission spectra in fast neutron induced fission of 238 U and 232 Th and 30 kev neutron induced fission on 235 U S. Appannababu 1, J. Praena 2, P.F. Mastinu 1, T. Marchi 1, V.V.
Study of prompt neutron emission spectra in fast neutron induced fission of 238 U and 232 Th and 30 kev neutron induced fission on 235 U S. Appannababu 1, J. Praena 2, P.F. Mastinu 1, T. Marchi 1, V.V.
Nuclear cross-section measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center. Michal Mocko
 Nuclear cross-section measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center Michal Mocko G. Muhrer, F. Tovesson, J. Ullmann International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Research Applications and Utilization
Nuclear cross-section measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center Michal Mocko G. Muhrer, F. Tovesson, J. Ullmann International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Research Applications and Utilization
Lecture 5 Nuclear Reactions
 Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall understand the concept of kinetic energy from the perspective of particle physics. We shall conclude that for all practical purposes, mass
Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall understand the concept of kinetic energy from the perspective of particle physics. We shall conclude that for all practical purposes, mass
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission
 Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
Scintillation efficiency measurement of Na recoils in NaI(Tl) below the DAMA/LIBRA energy threshold
 Scintillation efficiency measurement of Na recoils in NaI(Tl) below the DAMA/LIBRA energy threshold Jingke Xu, Princeton (now @LLNL) Sept 24, 2015 2015 LowECal Workshop, Chicago, IL Outline 1. Overview
Scintillation efficiency measurement of Na recoils in NaI(Tl) below the DAMA/LIBRA energy threshold Jingke Xu, Princeton (now @LLNL) Sept 24, 2015 2015 LowECal Workshop, Chicago, IL Outline 1. Overview
Gamma production cross section measurements for 76Ge via (n,n'γγ) at GELINA
 Gamma production cross section measurements for 76Ge via (n,n'γγ) at GELINA C. Rouki, A. R. Domula*, J. C. Drohé, M. Hult, N. Nankov, A. Plompen, M. Stanoiu, K. Zuber* * Institute for Nuclear and Particle
Gamma production cross section measurements for 76Ge via (n,n'γγ) at GELINA C. Rouki, A. R. Domula*, J. C. Drohé, M. Hult, N. Nankov, A. Plompen, M. Stanoiu, K. Zuber* * Institute for Nuclear and Particle
Fission Fragment characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS
 EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Fission characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS D. Doré 1, F. Farget 2,
EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Fission characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS D. Doré 1, F. Farget 2,
CHEM 312 Lecture 7: Fission
 CHEM 312 Lecture 7: Fission Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 11; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 3 General Overview of Fission Energetics The Probability of Fission Fission Product Distributions
CHEM 312 Lecture 7: Fission Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 11; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 3 General Overview of Fission Energetics The Probability of Fission Fission Product Distributions
Digital simulation of neutron and gamma measurement devices
 3Security of radioactive materials and transport 3 2 Digital simulation of neutron and gamma measurement devices A.-L. WEBER (IRSN) 1 - Maximum activity that a radioactive element can present without being
3Security of radioactive materials and transport 3 2 Digital simulation of neutron and gamma measurement devices A.-L. WEBER (IRSN) 1 - Maximum activity that a radioactive element can present without being
Latest experimental results on (n,xnγ) on 235U and 238U
 Latest experimental results on (n,xnγ) on 235 and 238 CNRS-IPHC Strasbourg A. Bacquias, Ph. Dessagne, G. Henning, H. Karam, M. Kerveno, G. Rudolf, J.C. Thiry JRC-IRMM Geel J.C. Drohé, N. Nankov, M. Nyman,
Latest experimental results on (n,xnγ) on 235 and 238 CNRS-IPHC Strasbourg A. Bacquias, Ph. Dessagne, G. Henning, H. Karam, M. Kerveno, G. Rudolf, J.C. Thiry JRC-IRMM Geel J.C. Drohé, N. Nankov, M. Nyman,
A comparison between two evaluations of neutron multiplicity distributions
 Abstract A comparison between two evaluations of neutron multiplicity distributions J. P. February 22 nd 200 Applied Physics Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 7545, USA Within MCNP6,
Abstract A comparison between two evaluations of neutron multiplicity distributions J. P. February 22 nd 200 Applied Physics Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 7545, USA Within MCNP6,
Photoneutron reactions studies at ELI-NP using a direct neutron multiplicity sorting method Dan Filipescu
 EUROPEAN UNION GOVERNMENT OF ROMANIA Sectoral Operational Programme Increase of Economic Competitiveness Investments for Your Future Structural Instruments 2007-2013 Extreme Light Infrastructure Nuclear
EUROPEAN UNION GOVERNMENT OF ROMANIA Sectoral Operational Programme Increase of Economic Competitiveness Investments for Your Future Structural Instruments 2007-2013 Extreme Light Infrastructure Nuclear
CENBG, Bordeaux, France 2. CEA/DAM-DIF, Arpajon,France 3. CEA/DEN, Saint Paul Lez Durance, France 4. IPN Orsay, Orsay France 5
 D. Denis-Petit 1, B. Jurado 1, P. Marini 2, R. Pérez-Sanchez 1, M. Aiche 1, S. Czajkowski 1, L. Mathieu 1, I. Tsekhanovich 1,V. Méot 2,O. Roig 2,B. Morillon 2, P. Romain 2, O. Bouland 3, L. Audouin 4,
D. Denis-Petit 1, B. Jurado 1, P. Marini 2, R. Pérez-Sanchez 1, M. Aiche 1, S. Czajkowski 1, L. Mathieu 1, I. Tsekhanovich 1,V. Méot 2,O. Roig 2,B. Morillon 2, P. Romain 2, O. Bouland 3, L. Audouin 4,
DELAYED COINCIDENCE METHOD FOR PICOSECOND LIFETIME MEASUREMENTS
 306 DELAYED COINCIDENCE METHOD FOR PICOSECOND LIFETIME MEASUREMENTS ZHANG WEIJIE China Institute of Atomic Energy E-mail: zhangreatest@163.com The advanced time delay (ATD) technique, based by delayed
306 DELAYED COINCIDENCE METHOD FOR PICOSECOND LIFETIME MEASUREMENTS ZHANG WEIJIE China Institute of Atomic Energy E-mail: zhangreatest@163.com The advanced time delay (ATD) technique, based by delayed
High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR.
 DESIR workshop, May 2010 High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR. Yuri Penionzhkevich Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Beta Decay of Exotic Nuclei: Goal to study Neutron emission
DESIR workshop, May 2010 High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR. Yuri Penionzhkevich Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Beta Decay of Exotic Nuclei: Goal to study Neutron emission
The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator
 The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator Svirikhin A.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Manipal University,
The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator Svirikhin A.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Manipal University,
Statistical Model Calculations for Neutron Radiative Capture Process
 Statistical Nuclear Physics and its Applications in Astrophysics, Jul. 8-, 2008 Statistical Model Calculations for Neutron Radiative Capture Process T. Kawano T-6 Nuclear Physics Los Alamos National Laboratory
Statistical Nuclear Physics and its Applications in Astrophysics, Jul. 8-, 2008 Statistical Model Calculations for Neutron Radiative Capture Process T. Kawano T-6 Nuclear Physics Los Alamos National Laboratory
Nuclear Fission Fission discovered by Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassman, Lisa Meitner in 1938
 Fission Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 11; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 3 General Overview of Fission Energetics The Probability of Fission Fission Product Distributions Total Kinetic
Fission Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 11; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 3 General Overview of Fission Energetics The Probability of Fission Fission Product Distributions Total Kinetic
Neutron capture cross section on Lu isotopes at DANCE
 Neutron capture cross section on Lu isotopes at DANCE Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, New-Mexico 8755, USA and CEA, DAM, DIF F-9197 Arpajon, France E-mail: olivier.roig@cea.fr A. Couture 1 Los
Neutron capture cross section on Lu isotopes at DANCE Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, New-Mexico 8755, USA and CEA, DAM, DIF F-9197 Arpajon, France E-mail: olivier.roig@cea.fr A. Couture 1 Los
THE USE OF GE DETECTORS FOR (N,XN) CROSS-SECTION MEASUREMENTS AT INTENSE AND LOW FREQUENCY PULSED NEUTRON BEAMS. Abstract
 THE USE OF GE DETECTORS FOR (N,XN) CROSS-SECTION MEASUREMENTS AT INTENSE AND LOW FREQUENCY PULSED NEUTRON BEAMS Strahinja Lukic, 1 Paule Baumann, 1 Catalin Borcea, 2 Erwin Jericha, 3 Stevan Jokic, 4 Aleksandra
THE USE OF GE DETECTORS FOR (N,XN) CROSS-SECTION MEASUREMENTS AT INTENSE AND LOW FREQUENCY PULSED NEUTRON BEAMS Strahinja Lukic, 1 Paule Baumann, 1 Catalin Borcea, 2 Erwin Jericha, 3 Stevan Jokic, 4 Aleksandra
Correlations of neutron multiplicity and gamma multiplicity with. fragment mass and total kinetic energy in spontaneous fission of 252 Cf
 Correlations of neutron multiplicity and gamma multiplicity with fragment mass and total kinetic energy in spontaneous fission of 252 Cf Taofeng Wang 1,2, Guangwu Li 3, Wenhui Zhang 3, Liping Zhu 3, Qinghua
Correlations of neutron multiplicity and gamma multiplicity with fragment mass and total kinetic energy in spontaneous fission of 252 Cf Taofeng Wang 1,2, Guangwu Li 3, Wenhui Zhang 3, Liping Zhu 3, Qinghua
7. Fission Products and Yields, ϒ
 7. Fission Products and Yields, ϒ 7.1 Nuclear Fission Among the processes of nuclear decay, fission is certainly the most complicated. Spontaneous fission (SF) was discovered by Flerov and Petrzhak in1940,
7. Fission Products and Yields, ϒ 7.1 Nuclear Fission Among the processes of nuclear decay, fission is certainly the most complicated. Spontaneous fission (SF) was discovered by Flerov and Petrzhak in1940,
Measurements of the Prompt Fission Neutron Spectrum at LANSCE: The Chi-Nu Experiment
 Measurements of the Prompt Fission Neutron Spectrum at LANSCE: The Chi-Nu Experiment 6 th Workshop on Nuclear Fission and Spectroscopy of Neutron-Rich Nuclei K.J. Kelly M. Devlin, J.A. Gomez, R.C. Haight,
Measurements of the Prompt Fission Neutron Spectrum at LANSCE: The Chi-Nu Experiment 6 th Workshop on Nuclear Fission and Spectroscopy of Neutron-Rich Nuclei K.J. Kelly M. Devlin, J.A. Gomez, R.C. Haight,
A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 364 371 TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 364 371 TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
Surrogate-reaction studies by the CENBG collaboration: status and perspectives
 Surrogate-reaction studies by the CENBG collaboration: status and perspectives Beatriz Jurado, Centre d Etudes Nucleaires de Bordeaux-Gradignan (CENBG), France The CENBG collaboration M.Aiche, G. Barreau,
Surrogate-reaction studies by the CENBG collaboration: status and perspectives Beatriz Jurado, Centre d Etudes Nucleaires de Bordeaux-Gradignan (CENBG), France The CENBG collaboration M.Aiche, G. Barreau,
Correlation in Spontaneous Fission of Cf252
 Correlation in Spontaneous Fission of Cf252 Stefano Marin 1, Matthew J. Marcath 1, Patricia F. Schuster 1, Shaun D. Clarke 1, and Sara A. Pozzi 1 1. Department of Nuclear Engineering and Radiological Sciences,
Correlation in Spontaneous Fission of Cf252 Stefano Marin 1, Matthew J. Marcath 1, Patricia F. Schuster 1, Shaun D. Clarke 1, and Sara A. Pozzi 1 1. Department of Nuclear Engineering and Radiological Sciences,
Karlsruhe Nuclide Chart
 Karlsruhe uclide Chart The ew Edition in 2015 s. Sóti 1, J. Magill 2 1 European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Transuranium Elements, Postfach 2340, 76125 Karlsruhe, Germany https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/
Karlsruhe uclide Chart The ew Edition in 2015 s. Sóti 1, J. Magill 2 1 European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Transuranium Elements, Postfach 2340, 76125 Karlsruhe, Germany https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ MeV, 4 T 8 MeV
 Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Error Budget in π + e + ν Experiment
 Error Budget in π + e + ν Experiment April 4, 2006 1 π + e + ν Lineshape 1.1 Simulation of the Photonuclear and Electronuclear Reactions: the current PIBETA simulation The current PIBETA detector Monte
Error Budget in π + e + ν Experiment April 4, 2006 1 π + e + ν Lineshape 1.1 Simulation of the Photonuclear and Electronuclear Reactions: the current PIBETA simulation The current PIBETA detector Monte
Neutrons For Science (NFS) at SPIRAL-2
 Neutrons For Science (NFS) at SPIRAL-2 X. Ledoux 1), M. Aïche 2), G. Ban 3), G. Barreau 2), P. Baumann 4), P. Bem 5), V. Blideanu 6), J. Blomgren 7), S. Czajkowski 2), P. Dessagne 4), E. Dupont 6), T.
Neutrons For Science (NFS) at SPIRAL-2 X. Ledoux 1), M. Aïche 2), G. Ban 3), G. Barreau 2), P. Baumann 4), P. Bem 5), V. Blideanu 6), J. Blomgren 7), S. Czajkowski 2), P. Dessagne 4), E. Dupont 6), T.
Addendum to the ISOLDE and Neutron Time-of-Flight Committee
 ` EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Addendum to the ISOLDE and Neutron Time-of-Flight Committee IS530: Properties of low-lying intruder states in 34 Al and 34 Si sequentially populated in beta-decay
` EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Addendum to the ISOLDE and Neutron Time-of-Flight Committee IS530: Properties of low-lying intruder states in 34 Al and 34 Si sequentially populated in beta-decay
Michael Dunn Nuclear Data Group Leader Nuclear Science & Technology Division Medical Physics Working Group Meeting October 26, 2005
 Nuclear Data Michael Dunn Nuclear Data Group Leader Nuclear Science & Technology Division Medical Physics Working Group Meeting October 26, 2005 ORELA LANSCE 0.1 00 Data Analyses ORELA data 0.0 75 Basic
Nuclear Data Michael Dunn Nuclear Data Group Leader Nuclear Science & Technology Division Medical Physics Working Group Meeting October 26, 2005 ORELA LANSCE 0.1 00 Data Analyses ORELA data 0.0 75 Basic
IFIN-HH participation at the n_tof CERN COLLABORATION (I)
 IFIN-HH participation at the n_tof CERN COLLABORATION (I) THE n_tof FACILITY CERN ENERGY DISTRIBUTION OF NEUTRONS Objectives of the activity at n_tof Experimental Set-Up -Pb Target Detection systems:
IFIN-HH participation at the n_tof CERN COLLABORATION (I) THE n_tof FACILITY CERN ENERGY DISTRIBUTION OF NEUTRONS Objectives of the activity at n_tof Experimental Set-Up -Pb Target Detection systems:
IRMM - Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements
 REACTION CROSS SECTIONS, FISSION YIELDS AND PROMPT-NEUTRON EMISSION FROM ACTINIDE TARGETS F.-J. Hambsch, S. Oberstedt, A. Al-Adili, Adili, P. Schillebeeckx, S. Kopecky, C. Sage, C. Lampoudis, IRMM - Institute
REACTION CROSS SECTIONS, FISSION YIELDS AND PROMPT-NEUTRON EMISSION FROM ACTINIDE TARGETS F.-J. Hambsch, S. Oberstedt, A. Al-Adili, Adili, P. Schillebeeckx, S. Kopecky, C. Sage, C. Lampoudis, IRMM - Institute
A new scintillator detector for nuclear physics experiments: the CLYC scintillator
 A new scintillator detector for nuclear physics experiments: the CLYC scintillator Franco Camera 1 and Agnese Giaz 2 1 Università di Milano and INFN sezione di Milano 2 INFN sezione di Milano (current
A new scintillator detector for nuclear physics experiments: the CLYC scintillator Franco Camera 1 and Agnese Giaz 2 1 Università di Milano and INFN sezione di Milano 2 INFN sezione di Milano (current
