ADAPTIVE CONTROL OF a ph PROCESS
|
|
|
- Georgia Goodwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ADAPTIVE CONTROL OF a ph PROCESS Dr.Karima M. Putrus* Zahra'a F. Zihwar** * Lecturer in Chemical Engineering Department/University of Technology Karima_cheng@yahoo.com ** Assistant Lecturer in Chemical Engineering Department/University of Technology ABSTRACT A control system of neutralization process in a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) has been developed in this work where the dynamic and control system based on basic mass balance has been carried out. A dynamic model for neutralization process is described by a first order with dead time; the approximate transfer function is; S 2.95 e G( s) = 270 s + The responses of ph electrode were analyzed to give the first order transfer function which is: G( s) = 0.32 s + The tuning of control parameters was determined by two different methods; frequency analysis method, and process reaction curve method to find the best values of proportional gain (K c ), integral time (τ I ) and derivative time (τ D ). The integral of time absolute error (ITAE) was used to compare between methods above. Adaptive control system was used as another strategy to compare with conventional control system, good improvement in controlling of the ph neutralization process is achieved when the adaptive control is used. MATLAB program was used as a tool of solution for all cases mentioned in this work. Key word: Neutralization Process, Adaptive Control, Conventional Control.
2 . INTRODUCTION Control of the ph neutralization process plays an important role in different chemical plants, such as chemical and biological reaction, waste water treatment, electrochemistry and () precipitation plants, production of pharmaceuticals, fermentation, food productionp P. However, it is difficult to control a ph process with adequate performance point due to its nonlinearities, time-varying properties and sensitivity to small disturbances when working (2) near the equivalence pointp P. For most industrial ph neutralization processes the influent stream is formed from the merging of effluents from many different plants each containing a variety of chemical species. The concentrations of the species in the resulting stream vary with time and hence the titration (3) curve changesp P. Continuous control systems are used when waste water is continuously being generated and generally one work day worth of flow is too large to be effectively captured in a batch system storage tank. As with batch control good mixing and safety precautions are very important, but also automatic reagent addition and continuous ph recording is required. The time required for influent flow to reach the probe is an important factor for properly setting the reagent feed control rate. By the time the added reagent reaches the sensor does not measure large variations in php (4) P. 2. CONTROL METHODS Conventional control theory deals predominantly with linear systems having constant parameters. This is often a good approximation for systems that are regulated at fixed operating points. With moderate disturbances and a good control system the deviations will be so small that the linear approximation is sufficiently good. However, the linear constant coefficient approximation will not always be satisfactory when the operating conditions change. However, an adaptive control for example can be designed to overcome the (5) limitations of conventional control systemsp P. The PID controller still does not satisfy the industrial demand for acceptable ph control in process streams in chemical plants or treatment of waste streams. The ph control process, therefore, demands the application of control theory taking into account the nonlinearity and the time varying titration curve.
3 The attention, therefore, has been focused on the application of more advanced control techniques like adaptive and self-tuning controllers. Adaptive control with linear feedback if we do not consider nonlinearity to be a major problem. Adaptive control with nonlinear feedback if we consider the richer model structure of a nonlinear model to have better prerequisites to adapt itself to the measured datap (6) P. 2. Adaptive Control Adaptive is called a control system, which can adjust its parameters automatically in such a way as to compensate for variations in the characteristics of the process it controls. The various types of adaptive control systems differ only in the way the parameters of the controller are adjusted. There are two main reasons for using adaptive control in chemical process:. Most chemical process is nonlinear. Therefore, the linearized models that are used to design linear controllers depend on the particular steady state. It 2. Most of the chemical process are non stationary (i.e. their characteristics change with time). The adaptive control needs an objective function that will guide the adaptation mechanism to the "best" adjustment of the controller parameters. Any of the performance criteria could be used as: One-quarter decay ratio. Integral of the square error (ISE). Gain or phase margins, etc. There are two different mechanisms for the adaptation of the controller parameters: a. Programmed or Scheduled Adaptive Control b. Self- Adaptive Control Model Reference Adaptive Systems (MRAS) are one popular adaptive control scheme currently used. These schemes rely on the creation of an exact mathematical model of the process for each application of the controller. It requires a detailed knowledge of the transfer function (plant order, time constants, dead time), usually determined experimentally. The proposed adaptive control in this work is based on the principle of model reference adaptive control.
4 The gain of the main control algorithm is altered by a superposed adaptive control loop so that, in the case of a control deviation, the ph value of the effluent approaches its setpoint by a prescribed trajectory. This is controlled by comparing the actual speed of the control deviation with the reference speed given by the reference trajectory. The reference speed is calculated depending on the control deviation. The adaptive control system is represented in Fig. (). A multi-model adaptive PID controller is developed and evaluated in a simulation study For a nonlinear ph neutralization process. The performance and robustness characteristics of the multi-model controller are compared to those for conventional PID controllers and an alternative multi-model interpolation controller P The use of a multi-model adaptive PID controller is developed and evaluated in an experimental study using a nonlinear ph neutralization process.. The performance and robustness characteristics of the multi-model controller are compared to those of a conventional PID controller, conventional self-tuning controller, and a multi-model adaptive PID controller using a prediction of error criterion P (7) P. (8) P. 3. REACTOR PROCESS The process can be considered as a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) to neutralize a strong acid with a strong base manipulated by a control valve. The process consists of an influent stream (HCl), reagent stream (NaOH) to regulate the ph of the effluent stream, and an effluent stream. A schematic diagram is shown in Fig. (2). The data of this reaction was taken from a previous experimental work by Syafiie et al., 2006 P (). (9) P, this data is shown in table 3. Model for Strong Acid-Strong Base System Consider a stirred tank into which hydrochloric acid of concentration [HCl] flows into the tank at a rate F a (influent stream) and is neutralized by sodium hydroxide of concentration [NaOH] flows at a rate F b (reagent). The volume of the reacting mixture in the tank is constant and equal to V. The chemical reaction of these two solutions occurring in the stirred tank reactor is NaOH HCl+ H 2O H 2O + Cl + Na + H + OH
5 Thus, the ionic concentrations of [Cl - ] and [Na + ] in the outflow from the tank would be related to the total flows F a, F b and to the feed concentrations of strong acid [HCl] and strong base [NaOH] entering the tank. Hence, the mass balances on this strong acid and strong base component are: d V [ Cl] = [ HCl ] F ( F + F )[ Cl] d V dt + [ Na] + = [ NaOHF ] ( F + F )[ Na] dt A B A A B B () (2) From charge balance: [Na + ] + [H + ] = [Cl - ] + [OH - ] (3) or [Cl - ] - [Na + ] = [H + ] - [OH - ] (4) Subtraction equation (3) from (4) to get: dg V = -(FA + FB )G + CA FA - CB FB (5) dt Where: G = the distance from neutrality and is given by G=[H + ]-[OH - ] V = the tank volume C A = the concentration of acid C = the concentration of base B F A = the flow rate of acid F B = the flow rate of base. The value of G is zero at neutral point, ph=7. The measurement equation is derived as follows: ph = - log 0 [ G +(G 2 + 4K w ) 0.5 ]+log 0 2 (6) where K w = 0-4 (mol/l) 2 is taken. The high nonlinearity is introduced by this output equation between the measurement ph value and state G (0).
6 4. RESULT AND DISCUSSION In this work, dynamic models have been developed to study the influence of manipulated variable (F B ) on controlled variable (ph) of the process. The results include two main parts:. The first part is to study the open loop system (without control) where the transfer functions were computed by using state space model as follows: a. Transfer function between the controlled variable and manipulated variables are: Transfer function between flow rate of base (F B ) and controlled variable (ph) 6 6 A= [ ] B=[ 0.005*0 ] C=[ ] Transfer function between concentration of base (C B ) and controlled variable (ph) 6 A= [ ] B=[ 0.008] C=[ ] b. Transfer functions between the controlled variable and disturbance variables are: Transfer function between flow rate of acid (F A ) and controlled variable (ph) 6 6 A= [ ] B=[ 0.005*0 ] C=[ ] Transfer function between concentration of acid (C A ) and controlled variable (ph) 6 A= [ ] B=[ 0.008] C=[ ] c. Then the step responses are plotted and the stability of the open loop system is determined by finding the roots of the characteristic equations. 2. The second part is to study the closed loop system which is the main aim of this work through applying different control strategies. 4. Stability Analysis of the Closed Loop After applying different methods to the control tuning, stability of the closed loop must be studied. The stability analysis of the closed loop system is implemented by using the computer program simulation. Table (3) gives the roots of characteristic equation of the (CSTR) reactor of ph neutralization process.
7 As shown in Table (3), this table shows that the system is stable in this work where all values for PI and PID controllers gave negative sign of the real part of the roots of the characteristic equations. 4.2 Adaptive Control In this section, the adaptive control is discussed. Adaptive controller was applied using PI and PID adaptive controller modes for the continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) of ph neutralization process, the minimum integral of the time-weighted absolute error (ITAE) values for PI and PID adaptive controllers are given in Table (2). From this table, it is clear that the PI adaptive controller is better than PID adaptive controller where the value of ITAE of the first controller is smaller than the second controller. Fig. (3) shows the comparison between transient response of PI and PID adaptive controllers while Fig. (4) shows the comparison between time absolute error versus time for this case. As shown in Figs. (3) and (4), it is clear that the two modes are used in adaptive control, the responses in the Fig. (3) show the good improvement in controlling of the ph process by shortening time to reach the ph set point and minimal overshoot. In those figures, it can seen that response PI adaptive is better than PID adaptive with lower settling and gives the smaller area under the curve. 4.3 Comparison between Feedback and Adaptive Controllers Fig. (5) shows the comparison between the transient response for PID controller and PID adaptive controller. Fig. (6) shows the comparison between the transient response for PID controller and PI adaptive controller. Fig. (7) shows the comparison between the transient response for PI controller and PID adaptive controller. Fig. (8) shows the comparison between the transient
8 the integral of the time-weighted absolute error (ITAE) values for Comparisons between feedback control and adaptive control are given in Table (4). As shown in Figs (3) to (8), it is clear that good improvement is achieved when the adaptive control is used compared to the feedback control, where (ITAE) value is the lowest and the responses reach the steady state in less time with minimal overshoot, so its more effective than using feedback control. 5. CONCLUSIONS The present work represents a simulation programs in MATLAB language used to study and develop a mathematical model of the dynamic behavior of neutralization process in a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR), and the process control implemented using different control strategies. The following conclusions can be drawn:. The dynamic response of the mixing tank is described by a first order differential equation whose time constant is the vessel residence time. The approximate transfer function is: G ( p) S ph 2.95 e = = F 270s + B 2. A first order response system is an adequate model for a glass membrane electrode. The approximate transfer function describing the ph electrode is: G ( S ) = 0.32 s +
9 REFERENCES - Riggs, J. B., Rhinehart, and Russel, R., (990), Method for ph Control, United State Patent No Fuente, J. M., Robles, C., Casado, O., Syafiie, S. and Tadeo, F., (2005), "Fuzzy control of a neutralization process", IEEE Trans. on Control System Technology 8, Doherty, S. K., (999), Control of ph in Chemical Processes Using Artificial Neural Network, Thesis Ph.D. from Liverpool John Moores University. 4- Shinskey, F. G., (973), ph and pion Control in Process and Waste Stream, John Wiley & Sons, New York. 5- Astrom, K. J. and Wittenmark, B., (999), Adaptive Control, Addision-Wesley. 6- Gustafsson, T., (999), ph Control, Internet, 7- Jari M. Böling, Dale E. Seborg and João P. Hespanha, (2007) Control Engineering Practice, Multi-model adaptive control of a simulated ph neutralization process, Volume 5, Issue 6, Pages J Böling, T K Gustafsson, K E Häggblom Output-Error Criteria in Multi-Model Adaptive Control with Experimental Application to ph Control, (2008) IEEE Multi-conference on Systems and Control, September 3-5, 2008, San Antonio, Texas, USA. 9- Syafiie.S, Tadeo.F, and Martinez.E, (2006),"Model-Free Intelligent Control of Neutralization Processes Using Reinforcement Learning" IFAC Workshop Congress, Prague, Czech. 0- Kwok D. P., Z. D, Deng, C. K. li, T. P. Leung, Z. Q. Sun and J. C. K. Wong, (2003), "Fuzzy neural control of systems with unknown dynamics using Q-learning strategies", Proceeding of The 2th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems,, Albert, W. and Kurz, H., (985) "Adaptive control of a waste water neutralization process control concept, implementation and practical experiences", Copyright IFAC Adaptive control of chemical process, Frankfurt am Main.
10 NOMENCLATURE Symbol Definition Units ITAE The integral of time weight absolute error K c Proportional gain [ml/s] τ I Integral time [sec] τ D Derivative time [sec] C A Concentration of acid [mole/ml] C B Concentration of base [mole/ml] F A Volumetric flow rate of acid [cm 3 /sec] F B Volumetric flow rate of base [cm 3 /sec] F A (s) Transfer function of acid [cm 3 /sec] F B (s) Transfer function of base [cm 3 /sec] G The distance from neutrality and is given by G=[H + ]-[OH - ] [ ] ph The negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration in aqueous solution [ ] Table () Operating parameters Strong acid flow Strong base flow Acid concentration Base concentration Tank volume Pressure Temperature F A F B C A C B V P T.8333 ml/sec.8333 ml/sec *0-6 mol/ml *0-6 mol/ml 000 ml Atm C
11 Table (2) ITAE values for PI and PID adaptive controllers. Controllers ITAE PI adaptive controller PID adaptive controller Table (3) The Roots of Characteristic equation of (CSTR) reactor of ph neutralization process. Control Tuning Methods Frequency Analysis Process Reaction Curve PI mode i i i i i i i i PID mode i i i i i i Table (4) Comparisons between feedback control and adaptive control Controllers ITAE PID PI PID adaptive PI adaptive
12 Integral gain CE CE ref _ Cal. of the ref. d Ref. trajector Adaptive control loop Differentiati on (2) Controlle r gain + ph ref _ ph + _ E(k) Controller with variable gain () M(k Neutralization process ph e Main control loop Fig. () Schematic representation of the adaptive control system (9). Fig. (2) ph Neutralization Process.
13 .4.2 PI adaptive PID adaptive 0.8 ph ph Time Fig. (3) The comparison between the transient response for PI adaptive and PID adaptive controllers 7 6 PI adaptive PID adaptive 5 Time*absolute error Time(sec) Fig. (4) Time absolute error versus time
14 .6.4 PID PID adaptive PID adaptive PID feedback.2 ph ph Time (sec) Fig. (5) The comparison between the transient response for PID feedback controller and PID adaptive controller.6.4 PI adaptive PID PID feedback PI adaptive.2 ph ph Time (sec) Fig. (6) The comparison between the transient response for PID feedback controller and PI adaptive controller
15 .6.4 PID adaptive PI PI feedback.2 ph ph Time (sec) Fig. (7) The comparison between the transient response for PI feedback controller and PID adaptive controller.6.4 PI adaptive PI adaptive PI PI feedback.2 ph ph Time (sec) Fig. (8) The comparison between the transient response for PI feedback controller and PI adaptive controller.
16 وτ السيطرة المتكيفة على عملية التعادل د. كريمة مروكي بطرس م.م. زه ارء فاضل زجوار قسم الهندسة الكيمياوية- الجامعة التكنولوجية الخلاصة فى هذا العمل تم تطويرنظام سيطره لعملية التعادل فى المفاعل ذي الخلط المستمر (CSTR) حيث ان السلوك الديناميكي و نظام السيطره قد اعنمدا على اساس موازنة الماده. الموديل الرياضي لعملية التعادل تم وصفه على انه نظام من الدرجه الاولى مع تاخر في الزمن دالة التحويل التقريبيه S 2.95 e G( s) = 270 s + هي: تم نحليل استجابة قطب الحامضيه ليعطي دالة تحويل من الدرجه الاولى: G( s) = 0.32 s + تم توصيف متغي ارت المسيطر بطريقتين مختلفتين هما Frequency curve method و Process Reaction (ITAE) و تم استخدام معيار التكامل.τD I K c لايجاد افضل قيم للمعاملات Curve و كاساس للمقارنة بين الطريقتين اعلاه. استخدم نظام السيطرة المتكيفة كست ارتيجية اخرى للمقارنة مع المسيطر التقليدي. وقد وجد با ن المسيطر المتكيف يعطي اداء سيطرة افضل بالمقارنة مع المسيطر التقليدي. تم استخدام ب ارمج MATLAB كاداة في الحل لجميع الحالات المستخدمة في هذا العمل. الكلمات الدالة: عملية التعادل السيطرة المتكيفة السيطرة التقليديه
Modified Mathematical Model For Neutralization System In Stirred Tank Reactor
 Available online at BCREC Website: http://bcrec.undip.ac.id Bulletin of Chemical Reaction Engineering & Catalysis, (), 0, - Research Article Modified Mathematical Model For Neutralization System In Stirred
Available online at BCREC Website: http://bcrec.undip.ac.id Bulletin of Chemical Reaction Engineering & Catalysis, (), 0, - Research Article Modified Mathematical Model For Neutralization System In Stirred
Mathematical model for neutralization system
 Mathematical model for neutralization system Ahmmed Saadi IBREHEM UCSI University Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Ahmadsaadi1@yahoo.com ABSTRACT A modified model for the neutralization process of Stirred Tank Reactors
Mathematical model for neutralization system Ahmmed Saadi IBREHEM UCSI University Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Ahmadsaadi1@yahoo.com ABSTRACT A modified model for the neutralization process of Stirred Tank Reactors
Nonlinear ph Control Using a Three Parameter Model
 130 ICASE: The Institute of Control, Automation and Systems Engineers, KOREA Vol. 2, No. 2, June, 2000 Nonlinear ph Control Using a Three Parameter Model Jietae Lee and Ho-Cheol Park Abstract: A two parameter
130 ICASE: The Institute of Control, Automation and Systems Engineers, KOREA Vol. 2, No. 2, June, 2000 Nonlinear ph Control Using a Three Parameter Model Jietae Lee and Ho-Cheol Park Abstract: A two parameter
DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR ph CONTROL
 DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR CONTROL Alex D. Kalafatis Liuping Wang William R. Cluett AspenTech, Toronto, Canada School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne,
DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR CONTROL Alex D. Kalafatis Liuping Wang William R. Cluett AspenTech, Toronto, Canada School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne,
Performance Analysis of ph Neutralization Process for Conventional PI Controller and IMC Based PI Controller
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 01 June 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Performance Analysis of ph Neutralization Process for Conventional PI Controller
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 01 June 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Performance Analysis of ph Neutralization Process for Conventional PI Controller
IMPROVING OF ph CONTROL FOR A WASTEWATER TREATMENT UNIT USING GENETIC ALGORITHM
 IMPROVING OF ph CONTROL FOR A WASTEWATER TREATMENT UNIT USING GENETIC ALGORITHM GHANIM M. ALWAN Assist. Prof. Dr. University of Technology, Chemical Engineering Department, Iraq ghnm_mag@yahoo.com FAROOQ
IMPROVING OF ph CONTROL FOR A WASTEWATER TREATMENT UNIT USING GENETIC ALGORITHM GHANIM M. ALWAN Assist. Prof. Dr. University of Technology, Chemical Engineering Department, Iraq ghnm_mag@yahoo.com FAROOQ
Inferential Control of a Wastewater Treatment Unit
 τrir were P Inferential Control of a Wastewater Treatment Unit Assis. Lec. Farooq A. Mehdi Chemical Eng. Department - University of Technology Abstract Inferential control of a wastewater treatment was
τrir were P Inferential Control of a Wastewater Treatment Unit Assis. Lec. Farooq A. Mehdi Chemical Eng. Department - University of Technology Abstract Inferential control of a wastewater treatment was
Control of Neutralization Process in Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
 Control of Neutralization Process in Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) Dr. Magan P. Ghatule Department of Computer Science, Sinhgad College of Science, Ambegaon (Bk), Pune-41. gmagan@rediffmail.com
Control of Neutralization Process in Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) Dr. Magan P. Ghatule Department of Computer Science, Sinhgad College of Science, Ambegaon (Bk), Pune-41. gmagan@rediffmail.com
ECE Introduction to Artificial Neural Network and Fuzzy Systems
 ECE 39 - Introduction to Artificial Neural Network and Fuzzy Systems Wavelet Neural Network control of two Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors in Series using MATLAB Tariq Ahamed Abstract. With the rapid
ECE 39 - Introduction to Artificial Neural Network and Fuzzy Systems Wavelet Neural Network control of two Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors in Series using MATLAB Tariq Ahamed Abstract. With the rapid
PROPORTIONAL-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers
 Multiple Model and Neural based Adaptive Multi-loop PID Controller for a CSTR Process R.Vinodha S. Abraham Lincoln and J. Prakash Abstract Multi-loop (De-centralized) Proportional-Integral- Derivative
Multiple Model and Neural based Adaptive Multi-loop PID Controller for a CSTR Process R.Vinodha S. Abraham Lincoln and J. Prakash Abstract Multi-loop (De-centralized) Proportional-Integral- Derivative
NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve
 D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
CONTROL OF MULTIVARIABLE PROCESSES
 Process plants ( or complex experiments) have many variables that must be controlled. The engineer must. Provide the needed sensors 2. Provide adequate manipulated variables 3. Decide how the CVs and MVs
Process plants ( or complex experiments) have many variables that must be controlled. The engineer must. Provide the needed sensors 2. Provide adequate manipulated variables 3. Decide how the CVs and MVs
Control Introduction. Gustaf Olsson IEA Lund University.
 Control Introduction Gustaf Olsson IEA Lund University Gustaf.Olsson@iea.lth.se Lecture 3 Dec Nonlinear and linear systems Aeration, Growth rate, DO saturation Feedback control Cascade control Manipulated
Control Introduction Gustaf Olsson IEA Lund University Gustaf.Olsson@iea.lth.se Lecture 3 Dec Nonlinear and linear systems Aeration, Growth rate, DO saturation Feedback control Cascade control Manipulated
Simulation based Modeling and Implementation of Adaptive Control Technique for Non Linear Process Tank
 Simulation based Modeling and Implementation of Adaptive Control Technique for Non Linear Process Tank P.Aravind PG Scholar, Department of Control and Instrumentation Engineering, JJ College of Engineering
Simulation based Modeling and Implementation of Adaptive Control Technique for Non Linear Process Tank P.Aravind PG Scholar, Department of Control and Instrumentation Engineering, JJ College of Engineering
An Adaptive LQG Combined With the MRAS Based LFFC for Motion Control Systems
 Journal of Automation Control Engineering Vol 3 No 2 April 2015 An Adaptive LQG Combined With the MRAS Based LFFC for Motion Control Systems Nguyen Duy Cuong Nguyen Van Lanh Gia Thi Dinh Electronics Faculty
Journal of Automation Control Engineering Vol 3 No 2 April 2015 An Adaptive LQG Combined With the MRAS Based LFFC for Motion Control Systems Nguyen Duy Cuong Nguyen Van Lanh Gia Thi Dinh Electronics Faculty
Modeling and Control of Chemical Reactor Using Model Reference Adaptive Control
 Modeling and Control of Chemical Reactor Using Model Reference Adaptive Control Padmayoga.R, Shanthi.M 2, Yuvapriya.T 3 PG student, Dept. of Electronics and Instrumentation, Valliammai Engineering College,
Modeling and Control of Chemical Reactor Using Model Reference Adaptive Control Padmayoga.R, Shanthi.M 2, Yuvapriya.T 3 PG student, Dept. of Electronics and Instrumentation, Valliammai Engineering College,
University of Science and Technology, Sudan Department of Chemical Engineering.
 ISO 91:28 Certified Volume 3, Issue 6, November 214 Design and Decoupling of Control System for a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) Georgeous, N.B *1 and Gasmalseed, G.A, Abdalla, B.K (1-2) University
ISO 91:28 Certified Volume 3, Issue 6, November 214 Design and Decoupling of Control System for a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) Georgeous, N.B *1 and Gasmalseed, G.A, Abdalla, B.K (1-2) University
DESIGN OF AN ADAPTIVE FUZZY-BASED CONTROL SYSTEM USING GENETIC ALGORITHM OVER A ph TITRATION PROCESS
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue2/ijrras_17_2_05.pdf DESIGN OF AN ADAPTIVE FUZZY-BASED CONTROL SYSTEM USING GENETIC ALGORITHM OVER A ph TITRATION PROCESS Ibrahim Al-Adwan, Mohammad Al Khawaldah, Shebel
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue2/ijrras_17_2_05.pdf DESIGN OF AN ADAPTIVE FUZZY-BASED CONTROL SYSTEM USING GENETIC ALGORITHM OVER A ph TITRATION PROCESS Ibrahim Al-Adwan, Mohammad Al Khawaldah, Shebel
Model Predictive Control Design for Nonlinear Process Control Reactor Case Study: CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor)
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 7, Issue 1 (Jul. - Aug. 2013), PP 88-94 Model Predictive Control Design for Nonlinear Process
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 7, Issue 1 (Jul. - Aug. 2013), PP 88-94 Model Predictive Control Design for Nonlinear Process
Subject: Introduction to Process Control. Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring Content
 v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
Experimental Investigations on Fractional Order PI λ Controller in ph Neutralization System
 IJCTA, 8(3), 2015, pp. 867-875 International Science Press Experimental Investigations on Fractional Order PI λ Controller in ph Neutralization System B. Meenakshipriya, M. Prakash and C. Maheswari Abstract:
IJCTA, 8(3), 2015, pp. 867-875 International Science Press Experimental Investigations on Fractional Order PI λ Controller in ph Neutralization System B. Meenakshipriya, M. Prakash and C. Maheswari Abstract:
Hybrid Direct Neural Network Controller With Linear Feedback Compensator
 Hybrid Direct Neural Network Controller With Linear Feedback Compensator Dr.Sadhana K. Chidrawar 1, Dr. Balasaheb M. Patre 2 1 Dean, Matoshree Engineering, Nanded (MS) 431 602 E-mail: sadhana_kc@rediff.com
Hybrid Direct Neural Network Controller With Linear Feedback Compensator Dr.Sadhana K. Chidrawar 1, Dr. Balasaheb M. Patre 2 1 Dean, Matoshree Engineering, Nanded (MS) 431 602 E-mail: sadhana_kc@rediff.com
Design and Comparative Analysis of Controller for Non Linear Tank System
 Design and Comparative Analysis of for Non Linear Tank System Janaki.M 1, Soniya.V 2, Arunkumar.E 3 12 Assistant professor, Department of EIE, Karpagam College of Engineering, Coimbatore, India 3 Associate
Design and Comparative Analysis of for Non Linear Tank System Janaki.M 1, Soniya.V 2, Arunkumar.E 3 12 Assistant professor, Department of EIE, Karpagam College of Engineering, Coimbatore, India 3 Associate
Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil
![Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil](/thumbs/85/91730677.jpg) Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil Because of the strong interplay between process dynamics and control perfor mance, examples should begin with process equipment and operating conditions.
Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil Because of the strong interplay between process dynamics and control perfor mance, examples should begin with process equipment and operating conditions.
Cascade Control of a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
 Journal of Applied and Industrial Sciences, 213, 1 (4): 16-23, ISSN: 2328-4595 (PRINT), ISSN: 2328-469 (ONLINE) Research Article Cascade Control of a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) 16 A. O. Ahmed
Journal of Applied and Industrial Sciences, 213, 1 (4): 16-23, ISSN: 2328-4595 (PRINT), ISSN: 2328-469 (ONLINE) Research Article Cascade Control of a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) 16 A. O. Ahmed
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY CHEG 4137W/4139W. Reaction Kinetics Saponification of Isopropyl Acetate with Sodium Hydroxide
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY CHEG 4137W/4139W Reaction Kinetics Saponification of Isopropyl Acetate with Sodium Hydroxide Objective: The purpose of this experiment is to examine and determine the reaction
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY CHEG 4137W/4139W Reaction Kinetics Saponification of Isopropyl Acetate with Sodium Hydroxide Objective: The purpose of this experiment is to examine and determine the reaction
Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control
 Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control Third Edition Carlos A. Smith, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Florida Armando B. Corripio, Ph.D., P.E. Gordon A.
Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control Third Edition Carlos A. Smith, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Florida Armando B. Corripio, Ph.D., P.E. Gordon A.
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems. Process Dynamics and Control
 Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department
 YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Date: Lab
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Date: Lab
CHAPTER 15: FEEDFORWARD CONTROL
 CHAPER 5: EEDORWARD CONROL When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Identify situations for which feedforward is a good control enhancement Design feedforward control using
CHAPER 5: EEDORWARD CONROL When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Identify situations for which feedforward is a good control enhancement Design feedforward control using
World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology WJERT
 wjert, 218, Vol. 4, Issue 1, 165-175. Original Article ISSN 2454-695X Pandimadevi et al. WJERT www.wjert.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.326 DESIGN OF PI CONTROLLER FOR A CONICAL TANK SYSTEM *G. Pandimadevi
wjert, 218, Vol. 4, Issue 1, 165-175. Original Article ISSN 2454-695X Pandimadevi et al. WJERT www.wjert.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.326 DESIGN OF PI CONTROLLER FOR A CONICAL TANK SYSTEM *G. Pandimadevi
H-Infinity Controller Design for a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 974-2174 Volume 7, Number 8 (214), pp. 767-772 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com H-Infinity Controller
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 974-2174 Volume 7, Number 8 (214), pp. 767-772 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com H-Infinity Controller
ANFIS Gain Scheduled Johnson s Algorithm based State Feedback Control of CSTR
 International Journal of Computer Applications (975 8887) ANFIS Gain Scheduled Johnsons Algorithm based State Feedback Control of CSTR U. Sabura Banu Professor, EIE Department BS Abdur Rahman University,
International Journal of Computer Applications (975 8887) ANFIS Gain Scheduled Johnsons Algorithm based State Feedback Control of CSTR U. Sabura Banu Professor, EIE Department BS Abdur Rahman University,
HYBRID FUZZY LOGIC AND PID CONTROLLER FOR PH NEUTRALIZATION PILOT PLANT
 HYBRID FUZZY LOGIC AND PID CONTROLLER FOR PH NEUTRALIZATION PILOT PLANT Oumair Naseer 1, Atif Ali Khan 2 1,2 School of Engineering, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, o.naseer@warwick.ac.uk atif.khan@warwick.ac.uk
HYBRID FUZZY LOGIC AND PID CONTROLLER FOR PH NEUTRALIZATION PILOT PLANT Oumair Naseer 1, Atif Ali Khan 2 1,2 School of Engineering, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, o.naseer@warwick.ac.uk atif.khan@warwick.ac.uk
DECENTRALIZED PI CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR NON LINEAR MULTIVARIABLE SYSTEMS BASED ON IDEAL DECOUPLER
 th June 4. Vol. 64 No. 5-4 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 DECENTRALIZED PI CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR NON LINEAR MULTIVARIABLE SYSTEMS BASED ON IDEAL DECOUPLER
th June 4. Vol. 64 No. 5-4 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 DECENTRALIZED PI CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR NON LINEAR MULTIVARIABLE SYSTEMS BASED ON IDEAL DECOUPLER
MULTILOOP PI CONTROLLER FOR ACHIEVING SIMULTANEOUS TIME AND FREQUENCY DOMAIN SPECIFICATIONS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 1, No. 8 (215) 113-1115 School of Engineering, Taylor s University MULTILOOP PI CONTROLLER FOR ACHIEVING SIMULTANEOUS TIME AND FREQUENCY DOMAIN SPECIFICATIONS
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 1, No. 8 (215) 113-1115 School of Engineering, Taylor s University MULTILOOP PI CONTROLLER FOR ACHIEVING SIMULTANEOUS TIME AND FREQUENCY DOMAIN SPECIFICATIONS
A Tuning of the Nonlinear PI Controller and Its Experimental Application
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(4), 451-455 (2001) A Tuning of the Nonlinear PI Controller and Its Experimental Application Doe Gyoon Koo*, Jietae Lee*, Dong Kwon Lee**, Chonghun Han**, Lyu Sung Gyu, Jae Hak
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(4), 451-455 (2001) A Tuning of the Nonlinear PI Controller and Its Experimental Application Doe Gyoon Koo*, Jietae Lee*, Dong Kwon Lee**, Chonghun Han**, Lyu Sung Gyu, Jae Hak
CM 3310 Process Control, Spring Lecture 21
 CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
Fuzzy logic Control of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor السيطرة عمى المفاعل ذو الخمط المستمر باستخدام منطق الدليل الغامض
 70 Fuzzy logic Control of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor Dr. Duraid Fadhil Ahmed Chemical Engineering Department Tikrit University Maha Nazar Esmaeel Abstract The mathematical modeling of continuous stirred
70 Fuzzy logic Control of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor Dr. Duraid Fadhil Ahmed Chemical Engineering Department Tikrit University Maha Nazar Esmaeel Abstract The mathematical modeling of continuous stirred
Temperature Control of CSTR Using Fuzzy Logic Control and IMC Control
 Vo1ume 1, No. 04, December 2014 936 Temperature Control of CSTR Using Fuzzy Logic Control and Control Aravind R Varma and Dr.V.O. Rejini Abstract--- Fuzzy logic controllers are useful in chemical processes
Vo1ume 1, No. 04, December 2014 936 Temperature Control of CSTR Using Fuzzy Logic Control and Control Aravind R Varma and Dr.V.O. Rejini Abstract--- Fuzzy logic controllers are useful in chemical processes
Solutions for Tutorial 10 Stability Analysis
 Solutions for Tutorial 1 Stability Analysis 1.1 In this question, you will analyze the series of three isothermal CSTR s show in Figure 1.1. The model for each reactor is the same at presented in Textbook
Solutions for Tutorial 1 Stability Analysis 1.1 In this question, you will analyze the series of three isothermal CSTR s show in Figure 1.1. The model for each reactor is the same at presented in Textbook
Control of MIMO processes. 1. Introduction. Control of MIMO processes. Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes
 Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
Index. INDEX_p /15/02 3:08 PM Page 765
 INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
An improved auto-tuning scheme for PI controllers
 ISA Transactions 47 (2008) 45 52 www.elsevier.com/locate/isatrans An improved auto-tuning scheme for PI controllers Rajani K. Mudi a,, Chanchal Dey b, Tsu-Tian Lee c a Department of Instrumentation and
ISA Transactions 47 (2008) 45 52 www.elsevier.com/locate/isatrans An improved auto-tuning scheme for PI controllers Rajani K. Mudi a,, Chanchal Dey b, Tsu-Tian Lee c a Department of Instrumentation and
Titration Curves. What is in the beaker at each stage of a titration? Beaker A Beaker B Beaker C Beaker D. 20 ml NaOH Added
 Why? Titration Curves What is in the beaker at each stage of a titration? Titration is a very useful technique for determining the properties of an unknown solution. The unknown is reacted with a known
Why? Titration Curves What is in the beaker at each stage of a titration? Titration is a very useful technique for determining the properties of an unknown solution. The unknown is reacted with a known
Anbar Journal of Engineering Science. Fuzzy Model Reference Adaptive Controller for DC Motor
 Anbar Journal of Engineering Science ISSN:997-948 Fuzzy Model Reference Adaptive Controller for DC Motor Wesam Mohammed Jasim Lecturer College of Computer Science and Information Technology University
Anbar Journal of Engineering Science ISSN:997-948 Fuzzy Model Reference Adaptive Controller for DC Motor Wesam Mohammed Jasim Lecturer College of Computer Science and Information Technology University
FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL OF A NONLINEAR PH-NEUTRALISATION IN WASTE WATER TREATMENT PLANT
 197 FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL OF A NONLINEAR PH-NEUTRALISATION IN WASTE WATER TREATMENT PLANT S. B. Mohd Noor, W. C. Khor and M. E. Ya acob Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Universiti Putra
197 FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL OF A NONLINEAR PH-NEUTRALISATION IN WASTE WATER TREATMENT PLANT S. B. Mohd Noor, W. C. Khor and M. E. Ya acob Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Universiti Putra
Gain Scheduling Control with Multi-loop PID for 2-DOF Arm Robot Trajectory Control
 Gain Scheduling Control with Multi-loop PID for 2-DOF Arm Robot Trajectory Control Khaled M. Helal, 2 Mostafa R.A. Atia, 3 Mohamed I. Abu El-Sebah, 2 Mechanical Engineering Department ARAB ACADEMY FOR
Gain Scheduling Control with Multi-loop PID for 2-DOF Arm Robot Trajectory Control Khaled M. Helal, 2 Mostafa R.A. Atia, 3 Mohamed I. Abu El-Sebah, 2 Mechanical Engineering Department ARAB ACADEMY FOR
CHAPTER 2 PROCESS DESCRIPTION
 15 CHAPTER 2 PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION A process havin only one input variable used for controllin one output variable is known as SISO process. The problem of desinin controller for SISO systems
15 CHAPTER 2 PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION A process havin only one input variable used for controllin one output variable is known as SISO process. The problem of desinin controller for SISO systems
GAIN SCHEDULING CONTROL WITH MULTI-LOOP PID FOR 2- DOF ARM ROBOT TRAJECTORY CONTROL
 GAIN SCHEDULING CONTROL WITH MULTI-LOOP PID FOR 2- DOF ARM ROBOT TRAJECTORY CONTROL 1 KHALED M. HELAL, 2 MOSTAFA R.A. ATIA, 3 MOHAMED I. ABU EL-SEBAH 1, 2 Mechanical Engineering Department ARAB ACADEMY
GAIN SCHEDULING CONTROL WITH MULTI-LOOP PID FOR 2- DOF ARM ROBOT TRAJECTORY CONTROL 1 KHALED M. HELAL, 2 MOSTAFA R.A. ATIA, 3 MOHAMED I. ABU EL-SEBAH 1, 2 Mechanical Engineering Department ARAB ACADEMY
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16
 Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16 1. Cascade control 2. Time-delay compensation 3. Inferential control 4. Selective and override control 5. Nonlinear control 6. Adaptive control 1 Chapter
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16 1. Cascade control 2. Time-delay compensation 3. Inferential control 4. Selective and override control 5. Nonlinear control 6. Adaptive control 1 Chapter
Design and Implementation of Controllers for a CSTR Process
 Design and Implementation of Controllers for a CSTR Process Eng. Muyizere Darius, Dr. S. Sivagamasundari Dept. of M.Sc (EI), Annamalai University, Cuddalore. Abstract Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
Design and Implementation of Controllers for a CSTR Process Eng. Muyizere Darius, Dr. S. Sivagamasundari Dept. of M.Sc (EI), Annamalai University, Cuddalore. Abstract Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Control of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor
 dvance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 2 (2013), pp. 169-178 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Control of Continuous
dvance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 2 (2013), pp. 169-178 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Control of Continuous
BITS-Pilani Dubai, International Academic City, Dubai Second Semester. Academic Year
 BITS-Pilani Dubai, International Academic City, Dubai Second Semester. Academic Year 2007-2008 Evaluation Com anent: Com rehensive Examination Closed Book CHE UC441/11NSTR UC 45'1 PROCESS CONTROL Date:
BITS-Pilani Dubai, International Academic City, Dubai Second Semester. Academic Year 2007-2008 Evaluation Com anent: Com rehensive Examination Closed Book CHE UC441/11NSTR UC 45'1 PROCESS CONTROL Date:
CompensatorTuning for Didturbance Rejection Associated with Delayed Double Integrating Processes, Part II: Feedback Lag-lead First-order Compensator
 CompensatorTuning for Didturbance Rejection Associated with Delayed Double Integrating Processes, Part II: Feedback Lag-lead First-order Compensator Galal Ali Hassaan Department of Mechanical Design &
CompensatorTuning for Didturbance Rejection Associated with Delayed Double Integrating Processes, Part II: Feedback Lag-lead First-order Compensator Galal Ali Hassaan Department of Mechanical Design &
Titration of a strong acid with a strong base with Cobra4
 Titration of a strong acid with a strong base with Cobra4 TEC Related topics Strong and weak acids and bases, ph value, titration curves, equivalence point, potentiometry. Principle Hydrochloric acid is
Titration of a strong acid with a strong base with Cobra4 TEC Related topics Strong and weak acids and bases, ph value, titration curves, equivalence point, potentiometry. Principle Hydrochloric acid is
Chapter 8. Feedback Controllers. Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system.
 Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
-MASTER THESIS- ADVANCED ACTIVE POWER AND FREQUENCY CONTROL OF WIND POWER PLANTS
 -MASTER THESIS- ADVANCED ACTIVE POWER AND FREQUENCY CONTROL OF WIND POWER PLANTS C L AU D I U I O N I TA 1, 2, A L I N G EO R G E R A D U C U 1, F LO R I N I OV 2 1 V A T T E N F A L L W I N D P O W E
-MASTER THESIS- ADVANCED ACTIVE POWER AND FREQUENCY CONTROL OF WIND POWER PLANTS C L AU D I U I O N I TA 1, 2, A L I N G EO R G E R A D U C U 1, F LO R I N I OV 2 1 V A T T E N F A L L W I N D P O W E
Băieşu Alina, Cărbureanu Mădălina
 ECAI 206 - International Conference 8th Edition Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence 30 June -02 July, 206, Ploiesti, ROMÂNIA Internal Model Control for Wastewater ph Neutralization Process
ECAI 206 - International Conference 8th Edition Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence 30 June -02 July, 206, Ploiesti, ROMÂNIA Internal Model Control for Wastewater ph Neutralization Process
Decoupling Control of a FCC Unit Using Fuzzy Logic
 Decoupling Control of a FCC Unit Using Fuzzy Logic Prof. Dr. Safe A. AL-Niami, Assis. Lec. Farooq A. Mehdi Chemical Eng. Department - University of Technology Abstract A control system of a fluidized-bed
Decoupling Control of a FCC Unit Using Fuzzy Logic Prof. Dr. Safe A. AL-Niami, Assis. Lec. Farooq A. Mehdi Chemical Eng. Department - University of Technology Abstract A control system of a fluidized-bed
Design and analysis of the prototype of boiler for steam pressure control
 Design and analysis of the prototype of boiler for steam pressure control Akanksha Bhoursae, 2 Jalpa Shah, 3 Nishith Bhatt Institute of Technology, Nirma University, SG highway, Ahmedabad-38248,India 3
Design and analysis of the prototype of boiler for steam pressure control Akanksha Bhoursae, 2 Jalpa Shah, 3 Nishith Bhatt Institute of Technology, Nirma University, SG highway, Ahmedabad-38248,India 3
REAL-TIME MODELLING AND SIMULATION APPLIED TO THE TREATMENT OF ELECTROPLATING WASTEWATER. Cécile NARCE, Konrad SZAFNICKI, Jacques BOURGOIS
 Copyright 00 IFAC 15th Triennial World Congress, Barcelona, Spain REAL-TIME MODELLING AND SIMULATION APPLIED TO THE TREATMENT OF ELECTROPLATING WASTEWATER Cécile NARCE, Konrad SZAFNICKI, Jacques BOURGOIS
Copyright 00 IFAC 15th Triennial World Congress, Barcelona, Spain REAL-TIME MODELLING AND SIMULATION APPLIED TO THE TREATMENT OF ELECTROPLATING WASTEWATER Cécile NARCE, Konrad SZAFNICKI, Jacques BOURGOIS
Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process
 Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process D.Angeline Vijula #, Dr.N.Devarajan * # Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Sri Ramakrishna
Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process D.Angeline Vijula #, Dr.N.Devarajan * # Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Sri Ramakrishna
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF SELF TUNING CONTROLLER FOR DC SERVO MOTOR
 Diyala Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 999-876 Printed in Iraq Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 7-9, December 23 DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF SELF TUNING CONTROLLER FOR DC SERVO MOTOR Mustafa A. Khamis Assistant Lecturer,
Diyala Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 999-876 Printed in Iraq Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 7-9, December 23 DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF SELF TUNING CONTROLLER FOR DC SERVO MOTOR Mustafa A. Khamis Assistant Lecturer,
CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING. Professor Dae Ryook Yang
 CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 11-1 Road Map of the Lecture XI Controller Design and PID
CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 11-1 Road Map of the Lecture XI Controller Design and PID
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department
 YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Report
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Report
No. 6. Reaction Rate Constant in CSTR Reaction. 1. Introduction
 No. 6. Reaction Rate Constant in CSTR Reaction 1. Introduction In the majority of industrial chemical processes, the reactor vessel in which the process takes place is the key item of equipment. The design
No. 6. Reaction Rate Constant in CSTR Reaction 1. Introduction In the majority of industrial chemical processes, the reactor vessel in which the process takes place is the key item of equipment. The design
Process Control Hardware Fundamentals
 Unit-1: Process Control Process Control Hardware Fundamentals In order to analyse a control system, the individual components that make up the system must be understood. Only with this understanding can
Unit-1: Process Control Process Control Hardware Fundamentals In order to analyse a control system, the individual components that make up the system must be understood. Only with this understanding can
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF TWO-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM CONTROLLER AND MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROLLER FOR THREE TANK INTERACTING SYSTEM
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF TWO-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM CONTROLLER AND MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROLLER FOR THREE TANK INTERACTING SYSTEM K.Senthilkumar 1, Dr. D.Angeline Vijula 2, P.Venkadesan 3 1 PG Scholar, Department
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF TWO-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM CONTROLLER AND MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROLLER FOR THREE TANK INTERACTING SYSTEM K.Senthilkumar 1, Dr. D.Angeline Vijula 2, P.Venkadesan 3 1 PG Scholar, Department
Multiobjective optimization for automatic tuning of robust Model Based Predictive Controllers
 Proceedings of the 7th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Multiobjective optimization for automatic tuning of robust Model Based Predictive Controllers P.Vega*, M. Francisco*
Proceedings of the 7th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Multiobjective optimization for automatic tuning of robust Model Based Predictive Controllers P.Vega*, M. Francisco*
Improved Identification and Control of 2-by-2 MIMO System using Relay Feedback
 CEAI, Vol.17, No.4 pp. 23-32, 2015 Printed in Romania Improved Identification and Control of 2-by-2 MIMO System using Relay Feedback D.Kalpana, T.Thyagarajan, R.Thenral Department of Instrumentation Engineering,
CEAI, Vol.17, No.4 pp. 23-32, 2015 Printed in Romania Improved Identification and Control of 2-by-2 MIMO System using Relay Feedback D.Kalpana, T.Thyagarajan, R.Thenral Department of Instrumentation Engineering,
Study on Control of First Order Plus Delay Using Smith Predictor
 Journal of Al-Nahrain University Vol.18 (2), June, 2015, pp.10-17 Science Study on Control of First Order Plus Delay Using Smith Predictor Saad A. Ahmed Department of Chemistry, College of Education-Ibn
Journal of Al-Nahrain University Vol.18 (2), June, 2015, pp.10-17 Science Study on Control of First Order Plus Delay Using Smith Predictor Saad A. Ahmed Department of Chemistry, College of Education-Ibn
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control
 Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control 1 Cascade Control A disadvantage of conventional feedback
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control 1 Cascade Control A disadvantage of conventional feedback
2. Conductometry. Introduction This is a method of analysis based on measuring electrolytic conductance
 2. Conductometry Introduction This is a method of analysis based on measuring electrolytic conductance Conductance: is the ability of the medium to carry the electric current. Electric current passes through
2. Conductometry Introduction This is a method of analysis based on measuring electrolytic conductance Conductance: is the ability of the medium to carry the electric current. Electric current passes through
Design of de-coupler for an interacting tanks system
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 78-1676,p-ISSN: 3-3331, Volume 7, Issue 4 (Sep. - Oct. 13), PP 48-53 Design of de-coupler for an interacting tanks system Parag
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 78-1676,p-ISSN: 3-3331, Volume 7, Issue 4 (Sep. - Oct. 13), PP 48-53 Design of de-coupler for an interacting tanks system Parag
Autotuning of Gain-Scheduled ph Control: An Experimental Study
 Subscriber access provided by NATONAL TAWAN UNV Autotuning of Gain-Scheduled ph Control: An Experimental Study Hsiao-Chung Chan, and Cheng-Ching Yu nd. Eng. Chem. Res., 1995, 34 (5), 1718-1729 DO: 10.1021/ie00044a023
Subscriber access provided by NATONAL TAWAN UNV Autotuning of Gain-Scheduled ph Control: An Experimental Study Hsiao-Chung Chan, and Cheng-Ching Yu nd. Eng. Chem. Res., 1995, 34 (5), 1718-1729 DO: 10.1021/ie00044a023
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
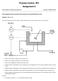 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Lecture (9) Reactor Sizing. Figure (1). Information needed to predict what a reactor can do.
 Lecture (9) Reactor Sizing 1.Introduction Chemical kinetics is the study of chemical reaction rates and reaction mechanisms. The study of chemical reaction engineering (CRE) combines the study of chemical
Lecture (9) Reactor Sizing 1.Introduction Chemical kinetics is the study of chemical reaction rates and reaction mechanisms. The study of chemical reaction engineering (CRE) combines the study of chemical
Behavior of the Discharge Coefficient for the Overflow Characteristics of Oblique Circular Weirs
 Tikrit Journal of Engineering Sciences/Vol.19/No.4/December 2012, (55-64) 55 Behavior of the Discharge Coefficient for the Overflow Characteristics of Oblique Circular Weirs Emad Abdul Gabbar Al Babely
Tikrit Journal of Engineering Sciences/Vol.19/No.4/December 2012, (55-64) 55 Behavior of the Discharge Coefficient for the Overflow Characteristics of Oblique Circular Weirs Emad Abdul Gabbar Al Babely
AN INTELLIGENT HYBRID FUZZY PID CONTROLLER
 AN INTELLIGENT CONTROLLER Isin Erenoglu Ibrahim Eksin Engin Yesil Mujde Guzelkaya Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Control Engineering Department, Maslak,
AN INTELLIGENT CONTROLLER Isin Erenoglu Ibrahim Eksin Engin Yesil Mujde Guzelkaya Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Control Engineering Department, Maslak,
CSTR CONTROL USING MULTIPLE MODELS
 CSTR CONTROL USING MULTIPLE MODELS J. Novák, V. Bobál Univerzita Tomáše Bati, Fakulta aplikované informatiky Mostní 39, Zlín INTRODUCTION Almost every real process exhibits nonlinear behavior in a full
CSTR CONTROL USING MULTIPLE MODELS J. Novák, V. Bobál Univerzita Tomáše Bati, Fakulta aplikované informatiky Mostní 39, Zlín INTRODUCTION Almost every real process exhibits nonlinear behavior in a full
Modeling and Simulation of a Multivariable
 IEEE ISIE 2006, July 9-12, 2006, Montreal, Quebec, Canada Modeling and Simulation of a Multivariable Process Control E. Cornieles1, M. Saad1, G. Gauthier2, Hamadou Saliah-Hassane3 The remainder of this
IEEE ISIE 2006, July 9-12, 2006, Montreal, Quebec, Canada Modeling and Simulation of a Multivariable Process Control E. Cornieles1, M. Saad1, G. Gauthier2, Hamadou Saliah-Hassane3 The remainder of this
Chemistry with Mr. Faucher. Acid-Base Titration
 Chemistry with Mr. Faucher Name Date Acid-Base Titration 24 A titration is a process used to determine the volume of a solution needed to react with a given amount of another substance. In this experiment,
Chemistry with Mr. Faucher Name Date Acid-Base Titration 24 A titration is a process used to determine the volume of a solution needed to react with a given amount of another substance. In this experiment,
CHAPTER 7 MODELING AND CONTROL OF SPHERICAL TANK LEVEL PROCESS 7.1 INTRODUCTION
 141 CHAPTER 7 MODELING AND CONTROL OF SPHERICAL TANK LEVEL PROCESS 7.1 INTRODUCTION In most of the industrial processes like a water treatment plant, paper making industries, petrochemical industries,
141 CHAPTER 7 MODELING AND CONTROL OF SPHERICAL TANK LEVEL PROCESS 7.1 INTRODUCTION In most of the industrial processes like a water treatment plant, paper making industries, petrochemical industries,
CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION
 11 CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the process description and analysis of CSTR. The process inputs, states and outputs are identified
11 CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the process description and analysis of CSTR. The process inputs, states and outputs are identified
EECE Adaptive Control
 EECE 574 - Adaptive Control Overview Guy Dumont Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia Lectures: Thursday 09h00-12h00 Location: PPC 101 Guy Dumont (UBC) EECE 574
EECE 574 - Adaptive Control Overview Guy Dumont Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia Lectures: Thursday 09h00-12h00 Location: PPC 101 Guy Dumont (UBC) EECE 574
CHAPTER 13: FEEDBACK PERFORMANCE
 When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
Soft Computing Technique and Conventional Controller for Conical Tank Level Control
 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 4, No. 1, March 016, pp. 65~73 ISSN: 089-37, DOI: 10.11591/ijeei.v4i1.196 65 Soft Computing Technique and Conventional Controller
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 4, No. 1, March 016, pp. 65~73 ISSN: 089-37, DOI: 10.11591/ijeei.v4i1.196 65 Soft Computing Technique and Conventional Controller
Outline. Classical Control. Lecture 1
 Outline Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 Prerequisites Block diagram for system modeling Modeling Mechanical Electrical Outline Introduction Background Basic Systems Models/Transfers functions 1 Introduction
Outline Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 Prerequisites Block diagram for system modeling Modeling Mechanical Electrical Outline Introduction Background Basic Systems Models/Transfers functions 1 Introduction
ADAPTIVE TEMPERATURE CONTROL IN CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology (IJEET), ISSN 0976 6545(Print), ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology (IJEET), ISSN 0976 6545(Print), ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online)
Design and Implementation of PI and PIFL Controllers for Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor System
 International Journal of omputer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJSEE olume, Issue (4 ISSN 3 48 (Online Design and Implementation of PI and PIFL ontrollers for ontinuous Stirred Tank Reactor System
International Journal of omputer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJSEE olume, Issue (4 ISSN 3 48 (Online Design and Implementation of PI and PIFL ontrollers for ontinuous Stirred Tank Reactor System
6 Acid Base Titration
 E x p e r i m e n t Acid Base Titration Experiment : http://genchemlab.wordpress.com/-titration/ objectives To understand the concept of titration. To explain the difference between the analyte and standard
E x p e r i m e n t Acid Base Titration Experiment : http://genchemlab.wordpress.com/-titration/ objectives To understand the concept of titration. To explain the difference between the analyte and standard
Experiment 7 Buffer Capacity & Buffer Preparation
 Chem 1B Dr. White 57 Experiment 7 Buffer Capacity & Buffer Preparation Objectives To learn how to choose a suitable conjugate acid- base pair for making a buffer of a given ph To gain experience in using
Chem 1B Dr. White 57 Experiment 7 Buffer Capacity & Buffer Preparation Objectives To learn how to choose a suitable conjugate acid- base pair for making a buffer of a given ph To gain experience in using
Be prepared to discuss the quantitative comparison method in the oral exam.
 Subject: Ring Experiment III 8 Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Control The shell and Tube Heat Exchanger has two control valves: one on the process fluid flowing to the tubes and one on the cooling water
Subject: Ring Experiment III 8 Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Control The shell and Tube Heat Exchanger has two control valves: one on the process fluid flowing to the tubes and one on the cooling water
Multiple Model Based Adaptive Control for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Process
 Multiple Model Based Adaptive Control for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Process R. Manikandan Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, Annamalai University, Annamalai
Multiple Model Based Adaptive Control for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Process R. Manikandan Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, Annamalai University, Annamalai
Overview of Control System Design
 Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems
 Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems This content has been downloaded from IOPscience.
Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems This content has been downloaded from IOPscience.
6.1 Sketch the z-domain root locus and find the critical gain for the following systems K., the closed-loop characteristic equation is K + z 0.
 6. Sketch the z-domain root locus and find the critical gain for the following systems K (i) Gz () z 4. (ii) Gz K () ( z+ 9. )( z 9. ) (iii) Gz () Kz ( z. )( z ) (iv) Gz () Kz ( + 9. ) ( z. )( z 8. ) (i)
6. Sketch the z-domain root locus and find the critical gain for the following systems K (i) Gz () z 4. (ii) Gz K () ( z+ 9. )( z 9. ) (iii) Gz () Kz ( z. )( z ) (iv) Gz () Kz ( + 9. ) ( z. )( z 8. ) (i)
Fuzzy Control of a Multivariable Nonlinear Process
 Fuzzy Control of a Multivariable Nonlinear Process A. Iriarte Lanas 1, G. L.A. Mota 1, R. Tanscheit 1, M.M. Vellasco 1, J.M.Barreto 2 1 DEE-PUC-Rio, CP 38.063, 22452-970 Rio de Janeiro - RJ, Brazil e-mail:
Fuzzy Control of a Multivariable Nonlinear Process A. Iriarte Lanas 1, G. L.A. Mota 1, R. Tanscheit 1, M.M. Vellasco 1, J.M.Barreto 2 1 DEE-PUC-Rio, CP 38.063, 22452-970 Rio de Janeiro - RJ, Brazil e-mail:
ANALYTICAL TASK EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
 ANALYTICAL TASK EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE Complexometric determination of zinc after separation from cadmium by ion chromatography It is almost impossible to correctly determine the content of zinc(ii) ions
ANALYTICAL TASK EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE Complexometric determination of zinc after separation from cadmium by ion chromatography It is almost impossible to correctly determine the content of zinc(ii) ions
