Suggested solutions for Chapter 14
|
|
|
- Lindsay Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 s for Chapter PRBLEM 1 Are these molecules chiral? Draw diagrams to justify your answer. 2 C 2 C Reinforcement of the very important criterion for chirality. Make sure you understand the answer. nly one thing matters does the molecule have a plane of symmetry? We need to redraw some of them to see if they do. n no account look for chiral centres or carbon atoms with four different groups or anything else. Just look for a plane of symmetry. If the molecule has one, it isn t chiral. The first compound has been drawn with carboxylic acids represented in two different ways. The two C 2 groups are in fact the same and the molecule has a plane of symmetry (shown by the dashed lines). It isn t chiral. Me Me = 2 C 2 C C 2 2 C C 2
2 2 Solutions Manual to accompany rganic Chemistry 2e The second compound is chiral but if you got this wrong don t be dismayed. Making a model would help but there are only two plausible candidates planes of symmetry: the ring itself, in the plane of the page, and a plane at right angles to the ring. The molecule redrawn below with the tetrahedral centre displayed shows that the plane of the page isn t a plane of symmetry as the C 2 is on one side and the on the other, and neither is the plane perpendicular to the ring, as is on one side and on the other. No plane of symmetry: molecule is chiral. no plane of symmetry perpendicular to ring C 2 C 2 no plane of symmetry in plane of page C 2 The third compound is not chiral because of its high symmetry. All the C 2 groups are identical so the alcohol can be attached to any of them. The plane of symmetry (shown by the dotted lines) may be easier to see after redrawing, and will certainly be much easier to see if you make a model. = The fourth compound needs only the slightest redrawing to make it very clear that it is not chiral. The dashed line shows the plane of symmetry at right angles to the paper. Spiro compounds, which contain two rings joined at a single atom, are discussed on p. 653 of the textbook. The final acetal (which is a spiro compound) is drawn flat but the central carbon atom must in fact be tetrahedral so that the two rings are orthogonal. By drawing first one and then the other ring in the
3 Solutions for Chapter 14 Stereochemistry 3 plane of the page it is easy to see that neither ring is a plane of symmetry for the other because of the oxygen atoms. PRBLEM 2 If a solution of a compound has an optical rotation of +12, how could you tell if this was actually +12 or really 348 or +372? Revision of the meaning of optical rotation and what it depends on. Check the equation (p. 310 on the textbook) that states that rotation depends on three things: the rotating power of the molecule, the length of the cell used in the polarimeter, and the concentration of the solution. We can t change the first, we may be able to change the second, but the third is easiest to change. If we halve the concentration, the rotation will change to +6, 174, or That is not quite good enough as the last two figures are the same, but any other change of concentration will distinguish them. PRBLEM 3 Cinderella s glass slipper was undoubtedly a chiral object. But would it have rotated the plane of polarized light? Revision of cause of rotation and optical activity. No. The macroscopic shape of an object is irrelevant. nly the molecular structure matters as light interacts with electrons in the molecules. Glass is not chiral (it is usually made up of inorganic borosilicates). nly if the slipper had been made of single enantiomers of a transparent substance would it have rotated the plane of polarized light. The molecules of Cinderella s left foot are the same as those in her right foot, despite both feet being macroscopically enantiomeric.
4 4 Solutions Manual to accompany rganic Chemistry 2e PRBLEM 4 Discuss the stereochemistry of these compounds. int: this means saying how many diastereoisomers there are, drawing clear diagrams of each, and stating whether they are chiral or not. Making sure you can handle this important approach to the stereochemistry of molecules. Just follow the hint in the question! Diastereoisomers are different compounds so they must be distinguished first. Then it is easy to say if each diastereoisomer is chiral or not. The first two are simple: one compound no diastereoisomers plane of symmetry not chiral one compound no diastereoisomers no plane of symmetry: chiral The third structure could exist as two diastereoisomers. The one with the cis ring junction has a plane of symmetry and is not chiral. The one with the trans ring junction has no plane of symmetry and is chiral (it has C 2 symmetry). nly one enantiomer is shown here. not chiral chiral plane of symmetry no plane of symmetry C 2 axis of symmetry The last compound is most complicated as it has no symmetry at all. We can have two diastereoisomers and neither has a plane of symmetry. Both the cis compound and the trans compound can exist as two enantiomers.
5 Solutions for Chapter 14 Stereochemistry 5 enantiomers of the cis compound enantiomers of the trans compound PRBLEM 5 In each case state, with explanations, whether the products of these reactions are chiral and/or enantiomericaly pure. C 2 C 2 Et biological reduction enzyme C 2 Et N 2 heat N 2 C C 2 S-(+)-glutamic acid C 2 LiAl 4 (±) aqueous work-up Combining mechanism and stereochemical analysis for the first time. We need a mechanism for each reaction, a stereochemical description for each starting material (achiral, chiral? enantiomerically enriched?) and an analysis of what happens to the stereochemistry in each reaction. Don t forget: you can t get single enantiomers out of nothing if everything that goes into a reaction is racemic or achiral, so is the product. In the first reaction the starting material is achiral as the two C 2 side chains are identical. The product is chiral as it has no plane of symmetry but it cannot be one enantiomer as that would require one of
6 6 Solutions Manual to accompany rganic Chemistry 2e Amides don t usually form well from amines and carboxylic acids (see p. 207 of the textbook). But in this case the reaction is intramolecular, and with a fair degree of heating (the product is known trivially as pyroglutamic acid ) the amide- forming reaction is all right. the C 2 side chains to cyclise rather than the other. It must be racemic. 2 The starting material for the second reaction is planar and achiral. If the reagent had been sodium borohydride, the product would be chiral but racemic. But an enzyme, because it is made up of enantiomerically pure compnents (amino acids), can deliver hydride to one side of the ketone only. We expect the product to be enantiomerically enriched. In the third reaction, the starting material is one enantiomer of a chiral compound. So we need to ask what happens to the chiral centre during the reaction. The answer is nothing as the reaction takes place between the amine and the carboxylic acid. The product is a single enantiomer too. N 2 C 2 N C 2 2 N C 2 N C 2 The final problem is a bit of a trick. The starting material is chiral, but racemic while the product is achiral as the two C 2C 2 side chains are identical so there can be a plane of symmetry between them. The mechanism doesn t really matter but we might as well draw it. (±) Al 3 Al x + PRBLEM 6 This compound racemizes in base. Why is that? To draw your attention to the dangers in working with nearly symmetrical molecules and revision of ester exchange (textbook p. 209).
7 Solutions for Chapter 14 Stereochemistry 7 Ester exchange in base goes in this case through a symmetrical (achiral) tetrahedral intermediate with a plane of symmetry. Loss of the right hand leaving group gives one enantiomer of the ester and loss of the left hand leaving group gives the other. B =
Suggested solutions for Chapter 16
 s for Chapter 16 16 PRBLEM 1 Identify the chair or boat rings in the following structures and say why this particular structure is adopted.. Exploration of simple examples of chair and boat forms. The
s for Chapter 16 16 PRBLEM 1 Identify the chair or boat rings in the following structures and say why this particular structure is adopted.. Exploration of simple examples of chair and boat forms. The
CH 3 C 2 H 5. Tetrahedral Stereochemistry
 Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated)
 7.8 FISCER PRJECTINS 237 (R)-RC 2 (S)-RC 2 Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated) Figure 7.5 RESLUTIN F A RACEMIC CARBYLIC ACID. (S)-RN 2 ne enantiomer of a chiral amine + (R)-RC
7.8 FISCER PRJECTINS 237 (R)-RC 2 (S)-RC 2 Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated) Figure 7.5 RESLUTIN F A RACEMIC CARBYLIC ACID. (S)-RN 2 ne enantiomer of a chiral amine + (R)-RC
Names. Chiral: A chiral object is not superimposable upon its mirror image. A chiral object contains the property of "handedness.
 CEM 241 IN-CLASS #3 MOLECULAR MODELS EXERCISE Names Stereoisomerism Construct a model containing a tetrahedral carbon (black ball) that is attached to four different atoms (use the green, orange, purple
CEM 241 IN-CLASS #3 MOLECULAR MODELS EXERCISE Names Stereoisomerism Construct a model containing a tetrahedral carbon (black ball) that is attached to four different atoms (use the green, orange, purple
Stereochemistry. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects.
 Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
Suggested solutions for Chapter 32
 s for Chapter 32 32 PBLEM 1 Explain how the stereo- and regio- chemistry of these reactions are controlled. Why is the epoxidation only moderately diastereoselective, and why does the amine attack where
s for Chapter 32 32 PBLEM 1 Explain how the stereo- and regio- chemistry of these reactions are controlled. Why is the epoxidation only moderately diastereoselective, and why does the amine attack where
CHEM J-10 June The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below.
 CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
Suggested solutions for Chapter 41
 s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
(1) Check to see if the two compounds are identical. (2) Recall the definitions of stereoisomers, conformational isomers, and constitutional isomers.
 MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 04: Stereochemistry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Determine the relationship of the molecules shown: O O Question #01 (A) Identical (B) Constitutional isomers (C)
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 04: Stereochemistry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Determine the relationship of the molecules shown: O O Question #01 (A) Identical (B) Constitutional isomers (C)
Suggested solutions for Chapter 6
 s for Chapter 6 6 PRBLEM 1 Draw mechanisms for these reactions: NaB 4 Et, 2 1. LiAl 4 C 2. 2 Rehearsal of a simple but important mechanism that works for all aldehydes and ketones. Draw out the B 4 and
s for Chapter 6 6 PRBLEM 1 Draw mechanisms for these reactions: NaB 4 Et, 2 1. LiAl 4 C 2. 2 Rehearsal of a simple but important mechanism that works for all aldehydes and ketones. Draw out the B 4 and
Loudon Chapter 24 Review: Carbohydrates Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 4/26/2018
 This chapter is about carbohydrates molecules with the general formula of C n( 2O) n, or in other words C n 2nO n. This is a very common formula for sugars and many other natural products. The structure
This chapter is about carbohydrates molecules with the general formula of C n( 2O) n, or in other words C n 2nO n. This is a very common formula for sugars and many other natural products. The structure
CHE Organic Chemistry Exam 4, May 4, 2004
 CE 232 - rganic Chemistry Exam 4, May 4, 2004 ame KEY Student ID o. Before you begin this exam: First: You are allowed to have a simple model set at your seat. Please put away all other materials. Second:
CE 232 - rganic Chemistry Exam 4, May 4, 2004 ame KEY Student ID o. Before you begin this exam: First: You are allowed to have a simple model set at your seat. Please put away all other materials. Second:
240 Chem. Stereochemistry. Chapter 5
 240 Chem Stereochemistry Chapter 5 1 Isomerism Isomers are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Constitutional isomers are isomers that differ because their atoms are connected in
240 Chem Stereochemistry Chapter 5 1 Isomerism Isomers are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Constitutional isomers are isomers that differ because their atoms are connected in
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry. Stereoisomers
 Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers Same bonding sequence Different arrangement in space Example: OOC-C=C-COO has two geometric (cis-trans) isomers: COO COO COO COO Stereochemistry Slide 5-2 1 Chirality
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers Same bonding sequence Different arrangement in space Example: OOC-C=C-COO has two geometric (cis-trans) isomers: COO COO COO COO Stereochemistry Slide 5-2 1 Chirality
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Suggested solutions for Chapter 31
 s for Chapter 31 31 PRBLEM 1 Predict the most favourable conformation for these insect pheromones. Practice drawing the conformations of cyclic acetals. There are many good ways to draw these conformations
s for Chapter 31 31 PRBLEM 1 Predict the most favourable conformation for these insect pheromones. Practice drawing the conformations of cyclic acetals. There are many good ways to draw these conformations
CHAPTER 5. Stereoisomers
 CHAPTER 5 Stereoisomers We have already covered two kinds of isomerism: Constitutional Isomers (structural isomers) Stereoisomers Examples of Constitutional Isomers: Examples of Stereoisomers: Another
CHAPTER 5 Stereoisomers We have already covered two kinds of isomerism: Constitutional Isomers (structural isomers) Stereoisomers Examples of Constitutional Isomers: Examples of Stereoisomers: Another
Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell
 Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 5-1 These two molecules, cyclopropylcyclopentane and cyclobutycyclobutane have the same number of carbon and hydrogen atoms and thus they are constitutional isomers. 5-2
Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 5-1 These two molecules, cyclopropylcyclopentane and cyclobutycyclobutane have the same number of carbon and hydrogen atoms and thus they are constitutional isomers. 5-2
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 9 Handouts 1
 Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 9 andouts 1 Ch. 9 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers have the same condensed formulas and basic bonding sequence, but have different 3-dimensional shape and cannot be interconverted 9.1,2
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 9 andouts 1 Ch. 9 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers have the same condensed formulas and basic bonding sequence, but have different 3-dimensional shape and cannot be interconverted 9.1,2
OH OH OH CH 2 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 2 (a) CH 3 CHCH 2 CHCH(CH 3 ) 2. (b)
 hem 226 Problem Set #8 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry, 4 th edition, John McMurry. hapter 8 1. Give IUPA names for the following alcohols. 2 2 ( 3 ) 2 3 2 ( 3 ) 2 Longest chain = 6 carbons:...hexanediol.
hem 226 Problem Set #8 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry, 4 th edition, John McMurry. hapter 8 1. Give IUPA names for the following alcohols. 2 2 ( 3 ) 2 3 2 ( 3 ) 2 Longest chain = 6 carbons:...hexanediol.
Organic Chemistry Chapter 5 Stereoisomers H. D. Roth
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 5 Stereoisomers. D. Roth 11. Chirality of conformationally mobile systems ring compounds Monosubstituted cycloalkanes cannot have an asymmetric carbon in the ring, because there
Organic Chemistry Chapter 5 Stereoisomers. D. Roth 11. Chirality of conformationally mobile systems ring compounds Monosubstituted cycloalkanes cannot have an asymmetric carbon in the ring, because there
Nitrogen Compounds - MS 1. (a) (i) is an amine and a carboxylic acid / contains both NH2 and COOH functional groups (1) AW 1
 itrogen ompounds - MS. (a) (i) is an amine and a carboxylic acid / contains both and functional groups () AW (c) R( ) () R Does not fit the formula because and are not attached to the same carbon () AW
itrogen ompounds - MS. (a) (i) is an amine and a carboxylic acid / contains both and functional groups () AW (c) R( ) () R Does not fit the formula because and are not attached to the same carbon () AW
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Stereochemistry CHAPTER SUMMARY
 2 7 2 7. Introduction APTER SUMMARY Isomers are compounds with identical molecular formulas but different structural formulas. Structural or constitutional isomers differ in the bonding arrangement of
2 7 2 7. Introduction APTER SUMMARY Isomers are compounds with identical molecular formulas but different structural formulas. Structural or constitutional isomers differ in the bonding arrangement of
STEREOCHEMISTRY A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
Form 0 CHE321 Exam 1 9/26/2006
 CE321 Exam 1 9/26/2006 Multiple Choice Questions. 60 points 1. Draw the two best contributing structures for methylimidate. To get you started a partial structure is given. C C C Choose the incorrect statement.
CE321 Exam 1 9/26/2006 Multiple Choice Questions. 60 points 1. Draw the two best contributing structures for methylimidate. To get you started a partial structure is given. C C C Choose the incorrect statement.
CHEM1902/ N-9 November 2014
 CEM1902/4 2014-N-9 November 2014 The elimination of 2 O from alcohol A can form the isomeric alkenes B and C. Elimination of Br from the alkyl halide D can generate the same two alkenes. 7 Assign the absolute
CEM1902/4 2014-N-9 November 2014 The elimination of 2 O from alcohol A can form the isomeric alkenes B and C. Elimination of Br from the alkyl halide D can generate the same two alkenes. 7 Assign the absolute
10/4/2010. Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration. Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration. 5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying.
 5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration Configuration The three-dimensional arrangement of substituents at a chirality center Sequence rules to specify the configuration of a chirality center:
5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration Configuration The three-dimensional arrangement of substituents at a chirality center Sequence rules to specify the configuration of a chirality center:
Loudon Chapter 24 Review: Carbohydrates CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 CEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about carbohydrates molecules with the general formula of C n ( 2 ) n, or in other words C n 2n n. This is a very common formula for sugars
CEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about carbohydrates molecules with the general formula of C n ( 2 ) n, or in other words C n 2n n. This is a very common formula for sugars
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Assign (R) or (S) configurations to the chiral carbons in the following molecules: enantiomers
 CAPTER 5: STERECEMISTRY (cont.) Assign (R) or (S) configurations to the chiral carbons in the following molecules: 3 C 3 C N 2 Molecules With Multiple Chiral Atoms. 1-chloro-2-methylcyclohexane has four
CAPTER 5: STERECEMISTRY (cont.) Assign (R) or (S) configurations to the chiral carbons in the following molecules: 3 C 3 C N 2 Molecules With Multiple Chiral Atoms. 1-chloro-2-methylcyclohexane has four
Suggested solutions for Chapter 27
 uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
STEREOCHEMISTRY. 2. Define the following, and tell whether or not a given compound or structure fits the description or possesses the feature.
 A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define each of the following terms, and give examples of
A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define each of the following terms, and give examples of
Lecture Topics: I. Stereochemistry Stereochemistry is the study of the three dimensional structure of molecules
 Stereochemistry eading: Wade chapter 5, sections 5-- 5-7 Study Problems: 5-26, 5-3, 5-32, 5-33, 5-34 Key oncepts and Skills: assify molecules as chiral or achiral, and identify planes of symmetry. Identify
Stereochemistry eading: Wade chapter 5, sections 5-- 5-7 Study Problems: 5-26, 5-3, 5-32, 5-33, 5-34 Key oncepts and Skills: assify molecules as chiral or achiral, and identify planes of symmetry. Identify
E30 ENANTIOMERS Chirality in organic chemistry
 E30 ENANTIMERS hirality in organic chemistry TE TASK To investigate the nature of chirality in organic chemistry. TE SKILLS By the end of the experiment you should be able to: use molecular modelling kits
E30 ENANTIMERS hirality in organic chemistry TE TASK To investigate the nature of chirality in organic chemistry. TE SKILLS By the end of the experiment you should be able to: use molecular modelling kits
Chemistry 3A. Midterm 2. Dr. Steven Pedersen November 9, Student name: ANSWERS Student signature:
 r. Steven Pedersen ovember 9, 2015 Chemistry 3A Midterm 2 Student name: ASWERS Student signature: Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 (18 pts) (30 pts) (32 pts) (18 pts)
r. Steven Pedersen ovember 9, 2015 Chemistry 3A Midterm 2 Student name: ASWERS Student signature: Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 (18 pts) (30 pts) (32 pts) (18 pts)
02/07/2017. Isomerism. Structural isomerism. 1. Structural isomerism different linkages of atoms. Same molecular formula Different structural formulae
 hain isomerism Position isomerism Metamerism Tautomerism Functional group isomerism Geometrical isomerism Optical isomerism 02/07/2017 Isomerism The presence of two or more compounds which has the same
hain isomerism Position isomerism Metamerism Tautomerism Functional group isomerism Geometrical isomerism Optical isomerism 02/07/2017 Isomerism The presence of two or more compounds which has the same
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry
 Chapter 5 Stereochemistry References: 1. Title: Organic Chemistry (fifth edition) Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice Publisher: Pearson International Edition 2. Title: Stereokimia Author: Poh Bo Long Publisher:
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry References: 1. Title: Organic Chemistry (fifth edition) Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice Publisher: Pearson International Edition 2. Title: Stereokimia Author: Poh Bo Long Publisher:
ANSWER KEY PAGE 1 of 11
 ANSWER KEY PAGE 1 of 11 UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY CHEM 3390 STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAMINATION Dr. Phil Hultin Tuesday December 13, 2011 9:00 am. NAME:
ANSWER KEY PAGE 1 of 11 UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY CHEM 3390 STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAMINATION Dr. Phil Hultin Tuesday December 13, 2011 9:00 am. NAME:
Experiment 8 Optical Isomers. In this experiment you will be given the opportunity to see the 3-dimensional aspects of
 Experiment 8 Optical Isomers In this experiment you will be given the opportunity to see the 3-dimensional aspects of stereochemistry and optical isomers. Previously in class you were exposed to the concept
Experiment 8 Optical Isomers In this experiment you will be given the opportunity to see the 3-dimensional aspects of stereochemistry and optical isomers. Previously in class you were exposed to the concept
Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry
 Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
A. Provide reagents for the following transformations. T 6. Cl OH
 rganic Chemistry I est 3 Extra Synthesis Practice Problems Page 1: Synthesis Design Practice. Page 2+3: Predict the Product Practice (including some that involve stereochemistry). Page 4: Cis/trans Stereospecific
rganic Chemistry I est 3 Extra Synthesis Practice Problems Page 1: Synthesis Design Practice. Page 2+3: Predict the Product Practice (including some that involve stereochemistry). Page 4: Cis/trans Stereospecific
Stereochemistry. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition
 Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
9. Stereochemistry. Stereochemistry
 9. Stereochemistry Stereochemistry Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry) A right-hand glove is different than a left-hand glove (See Figure
9. Stereochemistry Stereochemistry Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry) A right-hand glove is different than a left-hand glove (See Figure
Homework - Review of Chem 2310
 omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Course Information. Instructor Information
 Jordan University of Science and Technology Department of Chemistry Course Syllabus Fall 2018/2019 Course Information Course Number: CHEM 108 Course Name: General and Organic Chemistry Credit Hours: 4
Jordan University of Science and Technology Department of Chemistry Course Syllabus Fall 2018/2019 Course Information Course Number: CHEM 108 Course Name: General and Organic Chemistry Credit Hours: 4
Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional)
 Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional) Stereoisomers... have the same connectivity but a different
Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional) Stereoisomers... have the same connectivity but a different
NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Page 1 of 7
 NAME: STUDENT NUME: Page 1 of 7 CEM 3390 Midterm Test Monday ctober 26 and Tuesday ctober 27, 2008 This test is graded out of 40 Marks. You must complete all work within TW US. Put all answers in the spaces
NAME: STUDENT NUME: Page 1 of 7 CEM 3390 Midterm Test Monday ctober 26 and Tuesday ctober 27, 2008 This test is graded out of 40 Marks. You must complete all work within TW US. Put all answers in the spaces
Partial Periodic Table
 Easily Legible Printed Name: CHEM 3351 (100), Fall 2016 Professor Walba Second Hour Exam October 18, 2016 CU Honor Code Pledge: On my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder Student, I have neither
Easily Legible Printed Name: CHEM 3351 (100), Fall 2016 Professor Walba Second Hour Exam October 18, 2016 CU Honor Code Pledge: On my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder Student, I have neither
CHEM J-8 June Complete the following table. Make sure you give the name of the starting material where indicated. REAGENTS/ CONDITIONS
 CEM1102 2014-J-8 June 2014 Complete the following table. Make sure you give the name of the starting material where indicated. STARTIG MATERIAL REAGETS/ CDITIS STRUCTURAL FRMULA(S) F MAJR RGAIC PRDUCT(S)
CEM1102 2014-J-8 June 2014 Complete the following table. Make sure you give the name of the starting material where indicated. STARTIG MATERIAL REAGETS/ CDITIS STRUCTURAL FRMULA(S) F MAJR RGAIC PRDUCT(S)
Stereochemistry. 3-dimensional Aspects of Tetrahedral Atoms
 Stereochemistry 3-dimensional Aspects of Tetrahedral Atoms Chiral Entire molecules or simply atoms that do not possess a plane of symmetry are called chiral. Conversely, the term achiral is applied to
Stereochemistry 3-dimensional Aspects of Tetrahedral Atoms Chiral Entire molecules or simply atoms that do not possess a plane of symmetry are called chiral. Conversely, the term achiral is applied to
Loudon Chapter 20 & 21 Review: Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 20 & 21 eview: Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 These two chapters cover compounds which are all at the three bonds to more electronegative
Loudon Chapter 20 & 21 eview: Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 These two chapters cover compounds which are all at the three bonds to more electronegative
Partial Periodic Table
 CEM 3311, Fall 2011 Professor Walba Third our Exam November 17, 2011 scores: 1) 20 2) 20 3) 20 4) 20 5) 20 100 CU onor Code Pledge: n my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder tudent, I have neither
CEM 3311, Fall 2011 Professor Walba Third our Exam November 17, 2011 scores: 1) 20 2) 20 3) 20 4) 20 5) 20 100 CU onor Code Pledge: n my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder tudent, I have neither
(2/94)(6,7,9/95)(8,9/97)(12/99)(1/00) Neuman Chapter 4
 4: Stereochemistry Tetrahedral Carbon Configurations Stereoisomers and R,S Assignments The Number and Types of Stereoisomers Drawing Structures of Stereoisomers Cyclic Molecules Optical Activity Preview
4: Stereochemistry Tetrahedral Carbon Configurations Stereoisomers and R,S Assignments The Number and Types of Stereoisomers Drawing Structures of Stereoisomers Cyclic Molecules Optical Activity Preview
If Compound 2 (below) was used in the above reaction, how might things change? Name Page 1. I. (23 points)
 I. (2 points) ame Page itrogen atoms in amines can undergo substitution reactions repeatedly under mildly basic conditions. Provide the structure of the starting amine and supply the missing reagent(s).
I. (2 points) ame Page itrogen atoms in amines can undergo substitution reactions repeatedly under mildly basic conditions. Provide the structure of the starting amine and supply the missing reagent(s).
C 4 H 10 O. butanol. diethyl ether. different carbon skeleton different functional group different position of FG
 hapter 5: Stereoisomerism- three-dimensional arrangement of atoms (groups) in space 5. verview of Isomerism Isomers: different chemical compounds with the same formula onstitutional isomers: same formula,
hapter 5: Stereoisomerism- three-dimensional arrangement of atoms (groups) in space 5. verview of Isomerism Isomers: different chemical compounds with the same formula onstitutional isomers: same formula,
Option II: Chiral + Achiral = Optically Active Diastereomers
 Option II: Chiral + Achiral = Optically Active Diastereomers What about additions to chiral alkenes? The previous examples were reactions done on achiral alkenes. What is the difference when an alkene
Option II: Chiral + Achiral = Optically Active Diastereomers What about additions to chiral alkenes? The previous examples were reactions done on achiral alkenes. What is the difference when an alkene
STEREOCHEMISTRY A STUDENT WHO HAS MASTERED THE MATERIAL IN THIS SECTION SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 STEREOEMISTRY A STUDENT WO AS MASTERED TE MATERIAL IN TIS SETION SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define each of
STEREOEMISTRY A STUDENT WO AS MASTERED TE MATERIAL IN TIS SETION SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define each of
Loudon Chapter 7 Review: Cyclic Compounds Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 8/24/2017
 Compounds with a single ring are monocyclic. For example: Assuming they have no double or triple bonds, they each have one degree of unsaturation. This means that their formulas follow the pattern C nh
Compounds with a single ring are monocyclic. For example: Assuming they have no double or triple bonds, they each have one degree of unsaturation. This means that their formulas follow the pattern C nh
Lesson 4. Molecular Geometry and Isomers II. Lesson 4 CH 3 HO H OH
 Lesson 4 Molecular Geometry and Isomers II 4 Lesson 4 3 O O 3 Organic Edge A. Structural Isomers (onstitutional Isomers) 1. Structural isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ
Lesson 4 Molecular Geometry and Isomers II 4 Lesson 4 3 O O 3 Organic Edge A. Structural Isomers (onstitutional Isomers) 1. Structural isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ
Amides, Amino acids and Chirality
 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Amides, Amino acids and hirality aming of Amides The amide functional group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to the nitrogen of an amine. Like amines,
R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Amides, Amino acids and hirality aming of Amides The amide functional group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to the nitrogen of an amine. Like amines,
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
8-3 This exercise is worked out on page 293 as "Working with Concepts".
 Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 8-1 This exercise combines your knowledge of basic nomenclature rules and concepts of stereochemistry introduced in Chapters 4 and 5. 8-2 Keep in mind that faculty at UCSD
Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 8-1 This exercise combines your knowledge of basic nomenclature rules and concepts of stereochemistry introduced in Chapters 4 and 5. 8-2 Keep in mind that faculty at UCSD
5. Stereochemical Analysis. 7. Dipole Moments and Inductive versus Resonance Effects. 8. Types of isomers from a given formula. 9. Physical Properties
 hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 2. Lewis Structures, Resonance, Formal harge 3. yclohexane onformations, 2 substituents, ewman
hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 2. Lewis Structures, Resonance, Formal harge 3. yclohexane onformations, 2 substituents, ewman
Do now: Brainstorm how you would draw the Lewis diagram for: H 2 O CO 2
 Do now: Brainstorm how you would draw the Lewis diagram for: 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules C 4 N 3 2 O C 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules Shapes of molecules are determined by the number of bonding and non-bonding
Do now: Brainstorm how you would draw the Lewis diagram for: 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules C 4 N 3 2 O C 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules Shapes of molecules are determined by the number of bonding and non-bonding
Suggested solutions for Chapter 34
 s for Chapter 34 34 PRBLEM 1 Predict the structure of the product of this Diels- Alder reaction. C 2 +? 3 Si Can you deal with a moderately complicated Diels- Alder? The diene is electron- rich and will
s for Chapter 34 34 PRBLEM 1 Predict the structure of the product of this Diels- Alder reaction. C 2 +? 3 Si Can you deal with a moderately complicated Diels- Alder? The diene is electron- rich and will
CH Organic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- Fall 2013
 C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
4Types of Isomers. 1. Structural Isomers/(Constitutional) 2. Geometric Isomers/(Cis/Trans) 3. Optical Isomers A. Enantiomers B.
 4Types of Isomers 1. Structural Isomers/(Constitutional) 2. Geometric Isomers/(Cis/Trans) 3. Optical Isomers A. Enantiomers B. Diastereomers 4Types of Isomers C 4 10 C 4 10 O O O O O O O O O O O O C 3
4Types of Isomers 1. Structural Isomers/(Constitutional) 2. Geometric Isomers/(Cis/Trans) 3. Optical Isomers A. Enantiomers B. Diastereomers 4Types of Isomers C 4 10 C 4 10 O O O O O O O O O O O O C 3
Suggested solutions for Chapter 19
 s for Chapter 19 19 PRBLEM 1 Predict the orientation of addition to these alkenes. Simple examples of addition with regioselectivity. The first and last alkenes have different numbers of substituents at
s for Chapter 19 19 PRBLEM 1 Predict the orientation of addition to these alkenes. Simple examples of addition with regioselectivity. The first and last alkenes have different numbers of substituents at
CHEM1102 Worksheet 4 Answers to Critical Thinking Questions Model 1: Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
 CEM1102 Worksheet 4 Answers to Critical Thinking Questions Model 1: Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy 1. See below. Model 2: UV-Visible Spectroscopy 1. See below. 2. All of the above. 3. Restricted to the identification
CEM1102 Worksheet 4 Answers to Critical Thinking Questions Model 1: Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy 1. See below. Model 2: UV-Visible Spectroscopy 1. See below. 2. All of the above. 3. Restricted to the identification
Dr. Steven Pedersen July 28, Chemistry 3A. Midterm 2
 Dr. Steven Pedersen July 28, 2015 hemistry A Midterm 2 Student name: ANSWER KEY Student signature: Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Total Points (16 pts) (4 pts) (2 pts)
Dr. Steven Pedersen July 28, 2015 hemistry A Midterm 2 Student name: ANSWER KEY Student signature: Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Total Points (16 pts) (4 pts) (2 pts)
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
STEREOCHEMISTRY AND STEREOELECTRONICS NOTES
 - 1 - STEREOCHEMISTRY AND STEREOELECTRONICS NOTES Stereochemistry in Organic Molecules Conventions used in drawing molecules Also, Fischer projections can sometimes be useful for acyclic molecules with
- 1 - STEREOCHEMISTRY AND STEREOELECTRONICS NOTES Stereochemistry in Organic Molecules Conventions used in drawing molecules Also, Fischer projections can sometimes be useful for acyclic molecules with
Lecture 13A 05/11/12. Amines. [Sn2; Hofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis]
![Lecture 13A 05/11/12. Amines. [Sn2; Hofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis] Lecture 13A 05/11/12. Amines. [Sn2; Hofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis]](/thumbs/86/93838793.jpg) Lecture 13A 05/11/12 Amines [Sn2; ofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis] Curtius and ofmann rearrangements Both of these, in principle,
Lecture 13A 05/11/12 Amines [Sn2; ofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis] Curtius and ofmann rearrangements Both of these, in principle,
How to add your reactions to generate a Chemistry Space in KNIME
 How to add your reactions to generate a Chemistry Space in KNIME Introduction to CoLibri This tutorial is supposed to show how normal drawings of reactions can be easily edited to yield precise reaction
How to add your reactions to generate a Chemistry Space in KNIME Introduction to CoLibri This tutorial is supposed to show how normal drawings of reactions can be easily edited to yield precise reaction
a. Does the model have a plane of symmetry? Yes No The central carbon is said to be a stereocenter, stereogenic center, or chiral carbon.
 Name: TA Name Lab Section: Day Time OPTICAL ISOMERISM 1. Construct a model that has a central carbon atom with 4 different colored spheres attached to it, representing four different atoms or groups. Draw
Name: TA Name Lab Section: Day Time OPTICAL ISOMERISM 1. Construct a model that has a central carbon atom with 4 different colored spheres attached to it, representing four different atoms or groups. Draw
Problem Points Credit. 1. Nomenclature (one structure) 30
 alifornia State Polytechnic University, Pomona 1 hem 2010 Midterm #2 Fall, 2018 Beauchamp ame KY (int your name legibly) oblem Points redit 1. omenclature (one structure) 30 2. xplain relative stabilities
alifornia State Polytechnic University, Pomona 1 hem 2010 Midterm #2 Fall, 2018 Beauchamp ame KY (int your name legibly) oblem Points redit 1. omenclature (one structure) 30 2. xplain relative stabilities
STEREOGENIC CENTER (Chiral Center,Asymmetric Center)
 STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
Topics in the June 2009 Exam Paper for CHEM1102
 June 009 Topics in the June 009 Exam Paper for CEM110 ick on the links for resources on each topic. 009-J-: 009-J-3: 009-J-4: 009-J-5: 009-J-6: 009-J-7: 009-J-8: 009-J-9: 009-J-10: 009-J-1: 009-J-13: Periodic
June 009 Topics in the June 009 Exam Paper for CEM110 ick on the links for resources on each topic. 009-J-: 009-J-3: 009-J-4: 009-J-5: 009-J-6: 009-J-7: 009-J-8: 009-J-9: 009-J-10: 009-J-1: 009-J-13: Periodic
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
-SQA- SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION
 -SQA- SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Unit Number- 3481996 -Superclass- -Title- RD CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -------------------------------
-SQA- SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Unit Number- 3481996 -Superclass- -Title- RD CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -------------------------------
CHEM 261 Feb. 2, Stereochemistry and Chirality
 70 EM 261 eb. 2, 2017 Stereochemistry and hirality hiral object or molecule: has a non-superimposable mirror image Achiral object: not chiral, has a superimposable mirror image 1848 - Louis Pasteur separated
70 EM 261 eb. 2, 2017 Stereochemistry and hirality hiral object or molecule: has a non-superimposable mirror image Achiral object: not chiral, has a superimposable mirror image 1848 - Louis Pasteur separated
Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry
 hapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
hapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 6. Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry Some objects
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 6. Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry Some objects
C H C H 3. aspirin CHEMISTRY Topic #4: Organic Chemistry Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises in Topic 12
 = = 3 EMISTY 2000 aspirin Topic #4: rganic hemistry Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises in Topic 12 rganic Acids (arboxylic Acids) When you hear the term organic acid, it s generally referring to
= = 3 EMISTY 2000 aspirin Topic #4: rganic hemistry Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises in Topic 12 rganic Acids (arboxylic Acids) When you hear the term organic acid, it s generally referring to
Topics in the November 2007 Exam Paper for CHEM1904
 November 2007 Topics in the November 2007 Exam Paper for CEM1904 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2007-N-2: 2007-N-3: 2007-N-4: 2007-N-5: 2007-N-6: 2007-N-7: Solubility Equilibrium Intermolecular
November 2007 Topics in the November 2007 Exam Paper for CEM1904 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2007-N-2: 2007-N-3: 2007-N-4: 2007-N-5: 2007-N-6: 2007-N-7: Solubility Equilibrium Intermolecular
3.7 Organic naming and Isomerism continued
 3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism continued See chapter 3.1 for basic naming of organic molecules. This chapter extends the naming for functional groups met in next few chapters homologous series functional
3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism continued See chapter 3.1 for basic naming of organic molecules. This chapter extends the naming for functional groups met in next few chapters homologous series functional
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
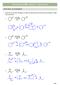 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
Luckily this intermediate has three saturated carbons between the carbonyls, which again points to a Michael reaction:
 Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
Conformational Analysis
 Conformational Analysis C01 3 C C 3 is the most stable by 0.9 kcal/mole C02 K eq = K 1-1 * K 2 = 0.45-1 * 0.048 = 0.11 C04 The intermediate in the reaction of 2 has an unfavorable syn-pentane interaction,
Conformational Analysis C01 3 C C 3 is the most stable by 0.9 kcal/mole C02 K eq = K 1-1 * K 2 = 0.45-1 * 0.048 = 0.11 C04 The intermediate in the reaction of 2 has an unfavorable syn-pentane interaction,
Chemistry 201. MW 12:00pm 1:15pm Examination #2 August 15 th Bronco ID. Question Score Possible Points. 1 (12pts) 2 (24pts) 3 (25pts)
 Chemistry 201 MW 12:00pm 1:15pm Examination #2 August 15 th 2016 Name Bronco ID. Question Score Possible Points 1 (12pts) 2 (24pts) 3 (25pts) 4... (12pts) 5 (27pts). Total (100pts) 1. Read each question
Chemistry 201 MW 12:00pm 1:15pm Examination #2 August 15 th 2016 Name Bronco ID. Question Score Possible Points 1 (12pts) 2 (24pts) 3 (25pts) 4... (12pts) 5 (27pts). Total (100pts) 1. Read each question
Mock Test 3 (Organic Chemistry) +2
 Mock Test (rganic hemistry) +2 Section (Single nswer) 1. Benzene is allowed to react with succinic anhydride in the presence of anhydrous ll and subsequently treated with dilute l. The product formed is
Mock Test (rganic hemistry) +2 Section (Single nswer) 1. Benzene is allowed to react with succinic anhydride in the presence of anhydrous ll and subsequently treated with dilute l. The product formed is
Importance of Carbohydrates
 Chapter 25 Importance of Carbohydrates Distributed widely in nature Key intermediates of metabolism (sugars) Structural components of plants (cellulose) Central to materials of industrial products: paper,
Chapter 25 Importance of Carbohydrates Distributed widely in nature Key intermediates of metabolism (sugars) Structural components of plants (cellulose) Central to materials of industrial products: paper,
Chem 342 Organic Chemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009
 hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
geometric isomers (diastereomers)
 Symmetry Monarch butterfly: bilateral symmetry= mirror symmetry Whenever winds blow butterflies find a new place on the willow tree -Basho (~6-69) 5 hapter 7: Stereochemistry - three-dimensional arrangement
Symmetry Monarch butterfly: bilateral symmetry= mirror symmetry Whenever winds blow butterflies find a new place on the willow tree -Basho (~6-69) 5 hapter 7: Stereochemistry - three-dimensional arrangement
Once familiar with chiral centers, models, drawings and mental images NOW: Final representation of chiral centers: Fischer Projections
 Once familiar with chiral centers, models, drawings and mental images NOW: Final representation of chiral centers: Fischer Projections Fischer Projections are 2-dimensional representations of 3-dimensional
Once familiar with chiral centers, models, drawings and mental images NOW: Final representation of chiral centers: Fischer Projections Fischer Projections are 2-dimensional representations of 3-dimensional
For more info visit
 Bond Fission: a) Homolytic fission: Each atom separates with one electron, leading to the formation of highly reactive entities called radicals, owing their reactivity to their unpaired electron. b) Heterolytic
Bond Fission: a) Homolytic fission: Each atom separates with one electron, leading to the formation of highly reactive entities called radicals, owing their reactivity to their unpaired electron. b) Heterolytic
Chem 201 Midterm Winter, 2013 Beauchamp
 hem 0 Midterm Winter, 0 Beauchamp Name Problems Points redit. Functional Group Nomenclature. Degrees of Unsaturation & Functional Groups or Various Nomenclature Terms. D structure, Functional Groups 0.
hem 0 Midterm Winter, 0 Beauchamp Name Problems Points redit. Functional Group Nomenclature. Degrees of Unsaturation & Functional Groups or Various Nomenclature Terms. D structure, Functional Groups 0.
Stereochemistry. Conformers: Compounds that differ by orientation of atoms in space. They are interconvertible via rotation about single bonds.
 Stereochemistry Terms onformers: ompounds that differ by orientation of atoms in space. They are interconvertible via rotation about single bonds. onstitutional isomers (also called structural isomers):
Stereochemistry Terms onformers: ompounds that differ by orientation of atoms in space. They are interconvertible via rotation about single bonds. onstitutional isomers (also called structural isomers):
