Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron
|
|
|
- Edwina Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron INTRODUCTION Many investigations of chemical species involve the interaction between light and matter. One class of these investigations, called absorbance spectrophotometry, involves the transfer of energy from a photon of light to an analyte to produce an excited state species. By accounting for the quantity of light absorbed, the amount of analyte can be determined. Common analytical applications of spectrophotometry take advantage of the Beer-Lambert Law (often simply called Beer s Law) that relates the concentration of an analyte to its absorbance of monochromatic radiation as shown below: A = -log T = bc Where A is absorbance, T is transmittance, is a constant called the molar absorptivity, b is the path length through the sample, c is analyte concentration. In practice, instruments monitor the transmittance of light by comparing the amount of light that leaves the light source, passes through the absorbing solution and strikes a detector (P) to the amount of light that strikes the detector when a non-absorbing solution is in the beam path (P 0 ). The ratio of these responses is the transmittance (or percent transmittance). P T or %T 100% x P P 0 P 0 This ratio assumes that the response at the detector in the absence of any light is zero, which if often not the case. Most detectors have a nonzero response, even if no light is striking the detector, called the dark current (P dark ), which must be compensated for in order for the transmittance (and absorbance) value to be meaningful. T P P dark P 0 P dark or %T 100% x P P dark P 0 P dark Therefore, to make a useful measurement, the instrument must know three things (1) the response when no light strikes the detector (P dark ), (2) the response when a blank is in the beam path (P 0 ), and (3) the response when the sample is in the beam path (P). Ideally, P dark and P 0 are constant for a particular instrument under a particular set of conditions. Therefore, by measuring P at a single wavelength for a series of analyte solutions of known concentration and using P 0 and P dark to calculate the absorbance (or transmittance) it is possible prepare a calibration curve for the analyte response. The Spectronic 20 is an example of a direct-reading, single-beam spectrophotometer. By virtue of being direct-reading, spectrophotometers feature fast operation, and because of their simple design they are relatively inexpensive and require a minimum of maintenance. They are particularly well suited for spectrophotometric determinations of a single component at a single wavelength where only moderate accuracy ( 1 to T) is required. The Spec-20 has only three controls (1) an On/Off/0%T knob used to set zero percent transmittance when the sample chamber is empty, (2) a 100% T knob used to set 100 percent transmittance when a blank is in the sample chamber, and (3) a wavelength control used to set the desired wavelength for the
2 measurement. Output on the Spec -20 is through an analog display that has both percent transmittance and absorbance scales. When recording data, it is wise to record both transmittance and absorbance values. The limitations of the single-beam instrument become apparent when an absorption spectrum over a wavelength range is required. The response of the phototube, the emissivity of the light source, and the intensity of the light diffracted by the grating are all a function of wavelength. Accordingly, in order to obtain the absorption spectrum of a compound, the instrument must be recalibrated each time the wavelength setting is changed. The reaction between ferrous ion and 1,10-phenanthroline to form a red complex serves as a sensitive method for determining iron. Fe phen Fe(phen) 3 N N 1,10 phenanthrolene (phen) The molar absorptivity of the complex, [(C 12 H 8 N 2 ) 3 Fe] 2+, is 11,100 at 508 nm. The intensity of the color is independent of ph in the range 2 to 9. The complex is very stable and the color intensity does not change appreciably over long periods of time. Beer's law is obeyed. The iron must be in the ferrous state, and hence a reducing agent is added before the color is developed. Hydroxylamine, as its hydrochloride, can be used to reduce any ferric ion that is present: 2 Fe NH 2 OH + 2 OH - 2 Fe 2+ + N H 2 O The ph is adjusted to a value between 6 and 9 by addition of ammonia or sodium acetate. An excellent discussion of interferences and of applications of this method is given by Sandell.1
3 HANDLING OF CUVETTES The handling of the cuvettes is extremely important. Often two cuvettes are used simultaneously, one for the "blank" solution and one for the samples to be measured. Yet any variation in the cuvette (such as a change in the cuvette width or curvature of the glass, stains, smudges, or scratches) will cause varying results. Thus, it is essential to follow several rules in dealing with cuvettes: 1. Do not handle the lower portion of a cuvette through which the light beam will pass. 2. Always rinse the cuvette with several portions of the solution before taking a measurement. 3. Wipe off any liquid drops or smudges on the lower half of the cuvette with a clean Kimwipe (or other lens paper) before placing the the cuvette in the instrument. Never wipe the cuvette with paper towels or handkerchiefs. Inspect the cuvette to ensure that nor bubbles are clinging to the inside walls. 4. When inserting a cuvette into the sample holder: a. To avoid any possible scratching of the cuvette in the optical path, insert the cuvette with the index line facing toward the front of the instrument. b. After the cuvette is seated, line up the index lines exactly. 5. When using two cuvettes simultaneously, use one of the cuvettes always for the blank solution and the other for the various samples being measured. Mark the cuvette ( on the upper portion) accordingly and do not interchange the cuvettes during the remainder of the experiment. 6. Do not use a test tube brush to clean the cuvettes after the experiment is complete. REAGENTS 1,10-phenanthroline (0.1 g of 1,10-phenanthroline monohydrate in 100 ml of distilled water, warming to effect solution if necessary). Hydroxylamine hydrochloride (10 g in 100 ml of distilled water). Sodium acetate (10 g in 100 ml of distilled water). Ferrous ammonium sulfate hexahydrate. SAMPLE PREPARATION 1. Weigh accurately about 0.07 g of pure ferrous ammonium sulfate hexahydrate, dissolve it in water, and transfer the solution to a 1-liter volumetric flask. Add 2.5 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid and dilute the solution to the mark. Calculate the concentration of the solution in mg of iron per ml. (Remember, your solution was prepared using Fe(NH 4 ) 2 (SO 4 ) 2 6H 2 O). 2. Prepare the unknown sample as follows. Add about 0.12 g of the solid unknown and approximately 0.25 ml concentrated sulfuric acid into a 100 ml volumetric flask and dilute to the mark. Now transfer a 1 ml aliquot of this solution to another 100 ml volumetric flask
4 - do not dilute yet. This will be referred to as the "prepared unknown". 3. Into five 100 ml volumetric flasks, pipet (volumetrically) 1, 5, 10, 25, and 50 ml portions of the standard iron solution. Put 50 ml of distilled water into another flask to serve as the blank. To each flask, including the "prepared unknown", add 1 ml of the hydroxylamine solution, 10 ml of the 1,10 phenanthroline solution and 8 ml of the sodium acetate solution. Then dilute all the solutions to the 100 ml marks and allow them to stand for 10 minutes with occasional shaking of the flasks. PART A -- Determination of Spectral Response of a Single-Beam Spectrophotometer The purpose of this section is to familiarize you with the Spectronic 20 operation and to illustrate the inherent impact of the performance of the light source and detector on a measurement. The light source in the Spectronic 20 is a type S-4 (cesium-antimony) phototube. The relative response of the phototube to a beam of monochromatic light of constant intensity is greatest near 400 nm and decreases fairly rapidly above 475 nm. Its response at 625 nm is only 5% of that at its maximum near 400 nm. PROCEDURE The Spectronic 20 should be allowed to warm-up at least 10 minutes before use. 1. First, adjust the instrument, photocell dark (i.e. no cuvette in the sample holder), with the zero control. 2. Insert a cuvette filled with water into the sample holder. Rotate the 100% control until the meter needle reads near mid-scale. Now rotate the wavelength control in the range between 350 and 625 nm, adjusting the 100% control to allow the meter to stay on scale throughout the entire wavelength range. Note the wavelength where the transmittance is maximum (needle deflection is greatest). 3. Carefully balance the instrument at 100% transmittance at the wavelength of maximum transmittance. You should now be able to rotate the wavelength control between 350 and 625 nm without the meter going off scale. 4. Without changing either the dark current control or the 100%T control, vary the wavelength from 350 to 625 nm in 25 nm intervals and record the instrument response. 5. Plot the instrument response vs. wavelength. PART B -- Determination of Iron with 1,10-phenanthroline In this portion of the experiment, you will record the absorbance spectrum of the ironphenanthroline complex by measuring the absorbance as a function of wavelength, and use this data to select a wavelength at which to measure the rest of your standards and unknowns. Since you want your absorbance values to be meaningful, you will need to set zero transmittance to account for dark current and 100% transmittance with a blank each time you change wavelength. PROCEDURE 1. Using the blank as a reference and any one of the iron solutions prepared above, measure the absorbance at 20-nm intervals in the range from 400 to 600 nm. (Note that it is necessary to
5 re-adjust the 0% T and 100%T settings whenever the wavelength is changed). 2. Once you have reached 600 nm, return to the region where absorbance was maximum and collect absorbance readings at 5 nm intervals in this region. 3. Plot the absorbance vs. wavelength and connect the points to from a smooth curve. Select the proper wavelength to use for the determination of iron with 1,10-phenanthroline and calculate the molar absorption coefficient,, at the wavelength of maximum absorption ( max ) on the absorption curve (assume b = 1 cm). 4. Measure the absorbance of each of the standard solutions and the unknown at the selected wavelength. Plot the absorbance vs. the concentration of the standards. Note whether Beer's law is obeyed. Using the absorbance of the unknown solution calculate the % (w/w) iron in your original solid sample and its 95% confidence interval, remember to correct for dilutions. (1) E. B. Sandell, Colorimetric Determination of Traces of Metals, 3rd Ed. Interscience Publishers, Inc., New York, 1959.
Experiment 7: Adsorption Spectroscopy I, Determination of Iron with 1,10 Phenanthroline
 Procedure Experiment 7: Adsorption Spectroscopy I, Determination of Iron with 1,10 Phenanthroline John Smith CHE226.001 4/10/95 In this experiment, we aim to determine the Na concentration of an unknown
Procedure Experiment 7: Adsorption Spectroscopy I, Determination of Iron with 1,10 Phenanthroline John Smith CHE226.001 4/10/95 In this experiment, we aim to determine the Na concentration of an unknown
EXPERIMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study
 OBJECTVES: EXPERMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study To operate a Spectronic 20 To convert from percent transmission to absorbance units To plot absorbance versus wavelength and find max To plot absorbance versus
OBJECTVES: EXPERMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study To operate a Spectronic 20 To convert from percent transmission to absorbance units To plot absorbance versus wavelength and find max To plot absorbance versus
2014 NJIT RET Program. MODULE TOPIC: Two Methods of Determining the Concentration of Soluble Compounds or Analytes..
 NJIT RET Summer program 2014 Lesson Module 2014 NJIT RET Program MODULE TOPIC: Two Methods of Determining the Concentration of Soluble Compounds or Analytes.. LESSON ONE TOPIC: Colorimetric Analysis of
NJIT RET Summer program 2014 Lesson Module 2014 NJIT RET Program MODULE TOPIC: Two Methods of Determining the Concentration of Soluble Compounds or Analytes.. LESSON ONE TOPIC: Colorimetric Analysis of
Experiment 18 - Absorption Spectroscopy and Beer s Law: Analysis of Cu 2+
 Experiment 18 - Absorption Spectroscopy and Beer s Law: Analysis of Cu 2+ Many substances absorb light. When light is absorbed, electrons in the ground state are excited to higher energy levels. Colored
Experiment 18 - Absorption Spectroscopy and Beer s Law: Analysis of Cu 2+ Many substances absorb light. When light is absorbed, electrons in the ground state are excited to higher energy levels. Colored
Rate law Determination of the Crystal Violet Reaction Using the Isolation Method
 Rate law Determination of the Crystal Violet Reaction Using the Isolation Method Introduction A common challenge in chemical kinetics is to determine the rate law for a reaction with multiple reactants.
Rate law Determination of the Crystal Violet Reaction Using the Isolation Method Introduction A common challenge in chemical kinetics is to determine the rate law for a reaction with multiple reactants.
Experiment 1 (Part A): Plotting the Absorption Spectrum of Iron (II) Complex with 1,10- Phenanthroline
 Experiment (Part A): Plotting the Absorption Spectrum of Iron (II) Complex with,0- Phenanthroline Background The first step of an analytical spectrophotometric procedure for quantitative determination
Experiment (Part A): Plotting the Absorption Spectrum of Iron (II) Complex with,0- Phenanthroline Background The first step of an analytical spectrophotometric procedure for quantitative determination
Expt 4: Determination of Iron by Absorption Spectrophotometry Calibration solutions: Iron(II)ammonium sulfate = ferrous ammonium sulfate
 Expt 4: Determination of Iron by Absorption Spectrophotometry Calibration solutions: Iron(II)ammonium sulfate = ferrous ammonium sulfate FeSO 4 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 6H 2 O, M.W. = 392.14 g Stock 1 0.210 g in
Expt 4: Determination of Iron by Absorption Spectrophotometry Calibration solutions: Iron(II)ammonium sulfate = ferrous ammonium sulfate FeSO 4 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 6H 2 O, M.W. = 392.14 g Stock 1 0.210 g in
Experiment#1 Beer s Law: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II)
 : Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant
 Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer
 Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Experiment 11 Beer s Law
 Experiment 11 Beer s Law OUTCOMES After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: determine the wavelength (color) of maximum absorbance for a solution. examine the relationship between
Experiment 11 Beer s Law OUTCOMES After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: determine the wavelength (color) of maximum absorbance for a solution. examine the relationship between
Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Experiment 11 Beer s Law
 Experiment 11 Beer s Law OUTCOMES After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: determine the wavelength (color) of maximum absorbance for a solution. examine the relationship between
Experiment 11 Beer s Law OUTCOMES After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: determine the wavelength (color) of maximum absorbance for a solution. examine the relationship between
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample
 Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer
 Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Experiment 13H THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1
 Experiment 13H 08/03/2017 AHRM THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1 PROBLEM: Determine the rate law for the chemical reaction between FD&C Red Dye #3 and sodium hypochlorite. LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
Experiment 13H 08/03/2017 AHRM THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1 PROBLEM: Determine the rate law for the chemical reaction between FD&C Red Dye #3 and sodium hypochlorite. LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
Exercise 6: Determination of Hardness of Water
 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, CHC014011L Exercise 6: Determination of Hardness of Water Introduction: Hardness in water is generally caused by the presence of dissolved calcium and magnesium carbonates
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, CHC014011L Exercise 6: Determination of Hardness of Water Introduction: Hardness in water is generally caused by the presence of dissolved calcium and magnesium carbonates
DETERMINATION OF K c FOR AN EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEM
 DETERMINATION OF K c FOR AN EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEM 1 Purpose: To determine the equilibrium constant K c for an equilibrium system using spectrophotometry to measure the concentration of a colored complex ion.
DETERMINATION OF K c FOR AN EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEM 1 Purpose: To determine the equilibrium constant K c for an equilibrium system using spectrophotometry to measure the concentration of a colored complex ion.
Experiment 13. Dilutions and Data Handling in a Spreadsheet rev 1/2013
 Absorbance Experiment 13 Dilutions and Data Handling in a Spreadsheet rev 1/2013 GOAL: This lab experiment will provide practice in making dilutions using pipets and introduce basic spreadsheet skills
Absorbance Experiment 13 Dilutions and Data Handling in a Spreadsheet rev 1/2013 GOAL: This lab experiment will provide practice in making dilutions using pipets and introduce basic spreadsheet skills
Colorimetric analysis of aspirin content in a commercial tablet
 Colorimetric analysis of aspirin content in a commercial tablet v010214 Objective In this lab, you will prepare standard solutions, and use Beer s Law to construct a calibration curve. You will determine
Colorimetric analysis of aspirin content in a commercial tablet v010214 Objective In this lab, you will prepare standard solutions, and use Beer s Law to construct a calibration curve. You will determine
Experiment 13I THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1
 Experiment 13I FV 1/11/16 THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1 PROBLEM: Determine the rate law for the chemical reaction between FD&C Red Dye #3 and sodium hypochlorite. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By
Experiment 13I FV 1/11/16 THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1 PROBLEM: Determine the rate law for the chemical reaction between FD&C Red Dye #3 and sodium hypochlorite. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By
MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION!
 Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
Determination of the Solubility-Product Constant for a Sparingly Soluble Salt
 Determination of the Solubility-Product Constant for a Sparingly Soluble Salt To become familiar with equilibria involving sparingly soluble substances by determining the value of the solubility-product
Determination of the Solubility-Product Constant for a Sparingly Soluble Salt To become familiar with equilibria involving sparingly soluble substances by determining the value of the solubility-product
Chemistry 213. A KINETIC STUDY: REACTION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET WITH NaOH LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Chemistry 213 A KINETIC STUDY: REACTION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET WITH NaOH The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES study the reaction rate of crystal violet with NaOH using a Spectronic
Chemistry 213 A KINETIC STUDY: REACTION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET WITH NaOH The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES study the reaction rate of crystal violet with NaOH using a Spectronic
Preparation of Standard Curves. Principle
 Preparation of Standard urves Principle Many laboratory tests require the measurement of concentration be evaluated or read in a photometer (colorimeter or spectrophotometer). Since these instruments are
Preparation of Standard urves Principle Many laboratory tests require the measurement of concentration be evaluated or read in a photometer (colorimeter or spectrophotometer). Since these instruments are
Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant v021214 Objective To determine the equilibrium constant (K c ) for the reaction of iron (III) ion with thiocyanate (SCN - ) to form the thiocyanatoiron(iii)
Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant v021214 Objective To determine the equilibrium constant (K c ) for the reaction of iron (III) ion with thiocyanate (SCN - ) to form the thiocyanatoiron(iii)
Exp 03 - Reaction Rate
 GENERAL CHEMISTRY II CAÑADA COLLEGE SUMMER 2018 Exp 03 - Reaction Rate How the speed at which quantities change during a chemical reaction can be measured, predicted and used to understand the mechanism
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II CAÑADA COLLEGE SUMMER 2018 Exp 03 - Reaction Rate How the speed at which quantities change during a chemical reaction can be measured, predicted and used to understand the mechanism
REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES
 Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
The Fluorometric Determination of Acetylsalicylic Acid in an Aspirin Tablet
 The Fluorometric Determination of Acetylsalicylic Acid in an Aspirin Tablet Introduction: Fluorescence is the emission of radiation from an atom or polyatomic species after the substance has been exposed
The Fluorometric Determination of Acetylsalicylic Acid in an Aspirin Tablet Introduction: Fluorescence is the emission of radiation from an atom or polyatomic species after the substance has been exposed
Aspirin Lab By Maya Parks Partner: Ben Seufert 6/5/15, 6/8/15
 Aspirin Lab By Maya Parks Partner: Ben Seufert 6/5/15, 6/8/15 Abstract: This lab was performed to synthesize acetyl salicylic acid or aspirin from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. We had learned in class
Aspirin Lab By Maya Parks Partner: Ben Seufert 6/5/15, 6/8/15 Abstract: This lab was performed to synthesize acetyl salicylic acid or aspirin from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. We had learned in class
Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS
 Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS FV 10/21/10 MATERIALS: Spectronic 20 spectrophotometers, 2 cuvettes, brass sample, 7 M HNO 3, 0.100 M CuSO 4, 2 M NH 3, two 50 ml beakers, 100 ml beaker, two 25 ml volumetric
Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS FV 10/21/10 MATERIALS: Spectronic 20 spectrophotometers, 2 cuvettes, brass sample, 7 M HNO 3, 0.100 M CuSO 4, 2 M NH 3, two 50 ml beakers, 100 ml beaker, two 25 ml volumetric
EXPERIMENT 5: PHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 EXPERIMENT 5: PHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to class. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas important
EXPERIMENT 5: PHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to class. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas important
Experiment 6: Determination of the Equilibrium Constant for Iron Thiocyanate Complex
 Experiment 6: Determination of the Equilibrium Constant for Iron Thiocyanate Complex The data for this lab will be taken as a class to get one data set for the entire class. I. Introduction A. The Spectrophotometer
Experiment 6: Determination of the Equilibrium Constant for Iron Thiocyanate Complex The data for this lab will be taken as a class to get one data set for the entire class. I. Introduction A. The Spectrophotometer
LEAD (Colorimetric) 2. Muffle Furnace: Equipped with pyrometer and capable of operating at controlled temperatures up to 500 C
 LEADX.01-1 LEAD (Colorimetric) PRINCIPLE SCOPE Organic matter in the sample is destroyed by ignition in the presence of sulfuric acid. The residue is dissolved in dilute acid, and the lead is complexed
LEADX.01-1 LEAD (Colorimetric) PRINCIPLE SCOPE Organic matter in the sample is destroyed by ignition in the presence of sulfuric acid. The residue is dissolved in dilute acid, and the lead is complexed
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law
 Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown cobalt (II) chloride solution. You will use a Vernier SpectroVis
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown cobalt (II) chloride solution. You will use a Vernier SpectroVis
CHM 152 updated May 2011 Lab 6: Experimentally Determining an Equilibrium Constant using Spectrophotometry
 CHM 152 updated May 2011 Lab 6: Experimentally Determining an Equilibrium Constant using Spectrophotometry Introduction In this lab you will experimentally determine the equilibrium constant with respect
CHM 152 updated May 2011 Lab 6: Experimentally Determining an Equilibrium Constant using Spectrophotometry Introduction In this lab you will experimentally determine the equilibrium constant with respect
Experimental Procedure Lab 402
 Experimental Procedure Lab 402 Overview One set of solutions having known molar concentrations of FeNCS 2+ is prepared for a calibration curve, a plot of absorbance versus concentration. A second set of
Experimental Procedure Lab 402 Overview One set of solutions having known molar concentrations of FeNCS 2+ is prepared for a calibration curve, a plot of absorbance versus concentration. A second set of
CHEM Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy
 CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Absorbance Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious
Absorbance Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious
Experimental Procedure Overview
 Lab 4: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) Fe(SCN) 2+ (aq)
Lab 4: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) Fe(SCN) 2+ (aq)
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash
 Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES
 Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
The Synthesis and Analysis of Aspirin
 The Synthesis and Analysis of Aspirin Computer 22 Aspirin, the ubiquitous pain reliever, goes by the chemical name acetylsalicylic acid. One of the compounds used in the synthesis of aspirin is salicylic
The Synthesis and Analysis of Aspirin Computer 22 Aspirin, the ubiquitous pain reliever, goes by the chemical name acetylsalicylic acid. One of the compounds used in the synthesis of aspirin is salicylic
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious mining sites
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious mining sites
Spectrophotometry Materials
 Spectrophotometry Materials Item per Class per Bench Genesys 10UV Spectrophotometer 6 1 13 ml test tubes box 7 Test tube racks 6 1 1% Albumin solution 25 ml/one flask 2 ml 0.7% Albumin solution (unknown
Spectrophotometry Materials Item per Class per Bench Genesys 10UV Spectrophotometer 6 1 13 ml test tubes box 7 Test tube racks 6 1 1% Albumin solution 25 ml/one flask 2 ml 0.7% Albumin solution (unknown
Introduction. The amount of radiation absorbed may be measured in a number of ways: Transmittance, T = P / P 0 % Transmittance, %T = 100 T
 Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
METHOD 9200 NITRATE. 1.2 The applicable range of concentration is 0.1 to 2 mg NO -N per liter. 3 of sample.
 METHOD 9200 NITRATE 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 This method is applicable to the analysis of ground water, drinking, surface, and saline waters, and domestic and industrial wastes. Modification can be
METHOD 9200 NITRATE 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 This method is applicable to the analysis of ground water, drinking, surface, and saline waters, and domestic and industrial wastes. Modification can be
Determination of Orthophosphate Ion
 Determination of Orthophosphate Ion Introduction Phosphorous, in the form of phosphate, is one of several important elements in the growth of plants. Excessive algae growth in water is stimulated by the
Determination of Orthophosphate Ion Introduction Phosphorous, in the form of phosphate, is one of several important elements in the growth of plants. Excessive algae growth in water is stimulated by the
Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 7 Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Introduction When chemical substances react, the reaction typically does not go to completion. Rather, the system goes to some intermediate state in which the
7 Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Introduction When chemical substances react, the reaction typically does not go to completion. Rather, the system goes to some intermediate state in which the
Experiment 12H, Parts A and B
 Experiment 12H, Parts A and B AHRM 8/17 PRINCIPLES OF EQUILIBRIUM AND THERMODYNAMICS MATERIALS: PURPOSE: 0.0200 M Fe(NO 3 ) 3 in 1 M HNO 3, 0.000200 M KSCN, 2.0 M HNO 3, solid Fe(NO 3 ) 3. 9H 2 O with
Experiment 12H, Parts A and B AHRM 8/17 PRINCIPLES OF EQUILIBRIUM AND THERMODYNAMICS MATERIALS: PURPOSE: 0.0200 M Fe(NO 3 ) 3 in 1 M HNO 3, 0.000200 M KSCN, 2.0 M HNO 3, solid Fe(NO 3 ) 3. 9H 2 O with
'.. _~ - BAUSCH & LOMB {i) ANALYTICAL SYSTEMS DIVISION
 '.. _~ - BAUSCH & LOMB {i) ANALYTICAL SYSTEMS DIVISION ' '! TABLE OF CONTENTS Page Elements of Spectrophotometry ~ I Computation on Dilution Factors Fig. 1 - Spectral Transmission Curve Fig. 2- Spectral
'.. _~ - BAUSCH & LOMB {i) ANALYTICAL SYSTEMS DIVISION ' '! TABLE OF CONTENTS Page Elements of Spectrophotometry ~ I Computation on Dilution Factors Fig. 1 - Spectral Transmission Curve Fig. 2- Spectral
METHOD 7196A CHROMIUM, HEXAVALENT (COLORIMETRIC)
 METHOD 7196A CHROMIUM, HEXAVALENT (COLORIMETRIC) 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 7196 is used to determine the concentration of dissolved hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] in EP/TCLP characteristic extracts
METHOD 7196A CHROMIUM, HEXAVALENT (COLORIMETRIC) 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 7196 is used to determine the concentration of dissolved hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] in EP/TCLP characteristic extracts
Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye?
 Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye? USING SPECTROSCOPY TO DETERMINE SOLUTION CON- CENTRATION Guiding Question How could you make more of this dye? INTRODUCTION A solution is a homogeneous
Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye? USING SPECTROSCOPY TO DETERMINE SOLUTION CON- CENTRATION Guiding Question How could you make more of this dye? INTRODUCTION A solution is a homogeneous
ASCORBIC ACID METHOD FOR PHOSPHORUS DETERMINATION
 ASCORBIC ACID METHOD FOR PHOSPHORUS DETERMINATION Written by Pamela Doolittle, University of Wisconsin- Madison, pssemrad@wisc.edu 2014 In this experiment you will determine the phosphorus (P) concentration
ASCORBIC ACID METHOD FOR PHOSPHORUS DETERMINATION Written by Pamela Doolittle, University of Wisconsin- Madison, pssemrad@wisc.edu 2014 In this experiment you will determine the phosphorus (P) concentration
Determination of Orthophosphate Ion
 Determination of Orthophosphate Ion Introduction Phosphorous, in the form of phosphate, is one of several important elements in the growth of plants. Excessive algae growth in water is stimulated by the
Determination of Orthophosphate Ion Introduction Phosphorous, in the form of phosphate, is one of several important elements in the growth of plants. Excessive algae growth in water is stimulated by the
CHEM 334 Quantitative Analysis Laboratory
 The Methods of Calibration Curve and Standard Addition Introduction One of the principle activities in the Quantitative Analysis Laboratory is the measurement of the concentration or total quantity of
The Methods of Calibration Curve and Standard Addition Introduction One of the principle activities in the Quantitative Analysis Laboratory is the measurement of the concentration or total quantity of
Persulfate Digestion Method Method to 150 mg/l N (HR) Test N Tube Vials
 Nitrogen, Total DOC316.53.01085 Persulfate Digestion Method Method 10072 2 to 150 mg/l N (HR) Test N Tube Vials Scope and application: For water and wastewater. Test preparation Instrument-specific information
Nitrogen, Total DOC316.53.01085 Persulfate Digestion Method Method 10072 2 to 150 mg/l N (HR) Test N Tube Vials Scope and application: For water and wastewater. Test preparation Instrument-specific information
Persulfate Digestion Method Method to 25.0 mg/l N (LR) Test N Tube Vials
 Nitrogen, Total DOC316.53.01086 Persulfate Digestion Method Method 10071 0.5 to 25.0 mg/l N (LR) Test N Tube Vials Scope and application: For water and wastewater. Test preparation Instrument-specific
Nitrogen, Total DOC316.53.01086 Persulfate Digestion Method Method 10071 0.5 to 25.0 mg/l N (LR) Test N Tube Vials Scope and application: For water and wastewater. Test preparation Instrument-specific
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution 2.47 ml of solution 50.00 ml delivered delivered Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution 2.47 ml of solution 50.00 ml delivered delivered Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY
 INTRODUCTION SPECTROPHOTOMETRY OF Co 2+ (Revised: 1-24-93) In this experiment, the Beer-Lambert Law, A = åcl, will be applied to a series of aqueous solutions of CoCl 2. The pink color of the solutions
INTRODUCTION SPECTROPHOTOMETRY OF Co 2+ (Revised: 1-24-93) In this experiment, the Beer-Lambert Law, A = åcl, will be applied to a series of aqueous solutions of CoCl 2. The pink color of the solutions
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law.
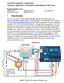 The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater
 4500-NO 2 NITROGEN (NITRITE)*#(1) 4500-NO 2 A. Introduction 1. Occurrence and Significance For a discussion of the chemical characteristics, sources, and effects of nitrite nitrogen, see Section 4500-N.
4500-NO 2 NITROGEN (NITRITE)*#(1) 4500-NO 2 A. Introduction 1. Occurrence and Significance For a discussion of the chemical characteristics, sources, and effects of nitrite nitrogen, see Section 4500-N.
For this lab, you will determine the purity of the aspirin by titration and by spectrophotometric analysis.
 Introduction: ommercially prepared aspirin tablets are not considered 100% pure acetylsalicylic acid. Most aspirin tablets contain a small amount of binder which helps prevent the tablets from crumbling.
Introduction: ommercially prepared aspirin tablets are not considered 100% pure acetylsalicylic acid. Most aspirin tablets contain a small amount of binder which helps prevent the tablets from crumbling.
Concepts, Techniques. Concepts, Techniques 9/11/2012. & Beer s Law. For a simple, transparent, COLORED material, e.g. ROYGBV
 9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
Chem 321 Name Answer Key D. Miller
 1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
Determination of the Equilibrium Constant. HIn - + H 2 O = H 3 O + + In 2-, [H 3 O + ][In 2- ] K ai = [HIn - ]
![Determination of the Equilibrium Constant. HIn - + H 2 O = H 3 O + + In 2-, [H 3 O + ][In 2- ] K ai = [HIn - ] Determination of the Equilibrium Constant. HIn - + H 2 O = H 3 O + + In 2-, [H 3 O + ][In 2- ] K ai = [HIn - ]](/thumbs/86/94897886.jpg) Determination of the Equilibrium Constant Introduction Indicators are substances whose solutions change color due to changes in ph. They are usually weak acids or bases, but their conjugate base and acid
Determination of the Equilibrium Constant Introduction Indicators are substances whose solutions change color due to changes in ph. They are usually weak acids or bases, but their conjugate base and acid
Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT INTRODUCTION The principle underlying a spectrophotometric method of analysis involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation
Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT INTRODUCTION The principle underlying a spectrophotometric method of analysis involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation
Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum.
 Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum. a. Is the spectrum above a band spectrum or a line spectrum? This is a band spectra, there are what
Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum. a. Is the spectrum above a band spectrum or a line spectrum? This is a band spectra, there are what
1. Preliminary qualitative analysis of unknown substances (liquid or solid).
 Name of Procedure: Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Suggested Uses: 1. Preliminary qualitative analysis of unknown substances (liquid or solid). 2. Quantitative analysis of known compounds. Apparatus Used to Perform
Name of Procedure: Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Suggested Uses: 1. Preliminary qualitative analysis of unknown substances (liquid or solid). 2. Quantitative analysis of known compounds. Apparatus Used to Perform
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Thousands of years ago, copper was abundant enough in quantity that it could be found on the Earth s surface. Prospecting for copper then was relatively
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Thousands of years ago, copper was abundant enough in quantity that it could be found on the Earth s surface. Prospecting for copper then was relatively
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests
 Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
NITROGEN, TOTAL, HR, Test N Tube
 Method 10072 NITROGEN, TOTAL, HR, Test N Tube 10 to 150 mg/l N TNT Persulfate Digestion Method For water and wastewater Digestion is required for determining total nitrogen. The digestion procedure is
Method 10072 NITROGEN, TOTAL, HR, Test N Tube 10 to 150 mg/l N TNT Persulfate Digestion Method For water and wastewater Digestion is required for determining total nitrogen. The digestion procedure is
Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kc
 Lab12 Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kc The purpose of this lab is to experimentally determine the equilibrium constant, K c, for the following chemical reaction: Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) FeSCN
Lab12 Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kc The purpose of this lab is to experimentally determine the equilibrium constant, K c, for the following chemical reaction: Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) FeSCN
Cadmium Reduction Method Method to 0.50 mg/l NO 3 N (LR) Powder Pillows
 Nitrate DOC316.53.01067 Cadmium Reduction Method Method 8192 0.01 to 0.50 mg/l NO 3 N (LR) Powder Pillows Scope and application: For water, wastewater and seawater. Test preparation Instrument-specific
Nitrate DOC316.53.01067 Cadmium Reduction Method Method 8192 0.01 to 0.50 mg/l NO 3 N (LR) Powder Pillows Scope and application: For water, wastewater and seawater. Test preparation Instrument-specific
A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal
 CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 1.2 A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal In this laboratory exercise, we will determine the amount of Calium in a serving of cereal. We
CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 1.2 A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal In this laboratory exercise, we will determine the amount of Calium in a serving of cereal. We
Spectrophotometry. Introduction
 Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
EXPERIMENT 7. Determination of Sodium by Flame Atomic-Emission Spectroscopy
 EXPERIMENT 7 Determination of Sodium by Flame Atomic-Emission Spectroscopy USE ONLY DEIONIZED WATER (NOT DISTILLED WATER!) THROUGHOUT THE ENTIRE EXPERIMENT Distilled water actually has too much sodium
EXPERIMENT 7 Determination of Sodium by Flame Atomic-Emission Spectroscopy USE ONLY DEIONIZED WATER (NOT DISTILLED WATER!) THROUGHOUT THE ENTIRE EXPERIMENT Distilled water actually has too much sodium
DR/4000 PROCEDURE NITRATE. Using Powder Pillows
 DR/4000 PROCEDURE Method 8171 Powder Pillows or AccuVac Ampuls Cadmium Reduction Method MR (0 to 5.0 mg/l NO 3 N) Scope and Application: For water, wastewater and seawater. The estimated detection limit
DR/4000 PROCEDURE Method 8171 Powder Pillows or AccuVac Ampuls Cadmium Reduction Method MR (0 to 5.0 mg/l NO 3 N) Scope and Application: For water, wastewater and seawater. The estimated detection limit
AP Chemistry Laboratory #15: Reaction Rate of Crystal Violet and Sodium Hydroxide. Lab days: Thursday and Friday, February 1-2, 2018
 AP Chemistry Laboratory #15: Reaction Rate of Crystal Violet and Sodium Hydroxide Lab days: Thursday and Friday, February 1-2, 2018 Lab due: TBD Goal (list in your lab book): The goal of this lab is to
AP Chemistry Laboratory #15: Reaction Rate of Crystal Violet and Sodium Hydroxide Lab days: Thursday and Friday, February 1-2, 2018 Lab due: TBD Goal (list in your lab book): The goal of this lab is to
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law. Evaluation copy. Figure 1
 Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law Computer 17 The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown copper (II) sulfate solution. You will use a
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law Computer 17 The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown copper (II) sulfate solution. You will use a
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests
 Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS
 2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
Experiment #7. Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 Experiment #7. Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Introduction It is frequently assumed that reactions go to completion, that all of the reactants are converted into products. Most chemical reactions
Experiment #7. Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Introduction It is frequently assumed that reactions go to completion, that all of the reactants are converted into products. Most chemical reactions
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law
 Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law Vernier Spectrometer 1 The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown copper (II) sulfate solution. You
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law Vernier Spectrometer 1 The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown copper (II) sulfate solution. You
Lab #16: Determination of the Equilibrium Name: Constant of FeSCN 2+ Lab Exercise. 10 points USE BLUE/BLACK INK!!!! Date: Hour:
 Lab #16: Determination of the Equilibrium Name: Constant of FeSCN 2+ Lab Exercise Chemistry II Partner: 10 points USE BLUE/BLACK INK!!!! Date: Hour: Goal: The goal of this lab is to determine the equilibrium
Lab #16: Determination of the Equilibrium Name: Constant of FeSCN 2+ Lab Exercise Chemistry II Partner: 10 points USE BLUE/BLACK INK!!!! Date: Hour: Goal: The goal of this lab is to determine the equilibrium
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry
 1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
Spectroscopy. Page 1 of 8 L.Pillay (2012)
 Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Cadmium Reduction Method Method to 30.0 mg/l NO 3 N (HR) Powder Pillows or AccuVac Ampuls
 Nitrate DOC316.53.01066 Cadmium Reduction Method Method 8039 0.3 to 30.0 mg/l NO 3 N (HR) Powder Pillows or AccuVac Ampuls Scope and application: For water, wastewater and seawater. Test preparation Instrument-specific
Nitrate DOC316.53.01066 Cadmium Reduction Method Method 8039 0.3 to 30.0 mg/l NO 3 N (HR) Powder Pillows or AccuVac Ampuls Scope and application: For water, wastewater and seawater. Test preparation Instrument-specific
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution delivered 2.47 ml of solution delivered 50.00 ml Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution delivered 2.47 ml of solution delivered 50.00 ml Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy A. Evaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Objective The single feature that contributes most to making atomic
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy A. Evaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Objective The single feature that contributes most to making atomic
NITROGEN, TOTAL, Test N Tube * Method 10071
 NITROGEN, TOTAL, Test N Tube * Method 10071 TNT Persulfate Digestion Method (0 to 25.0 mg/l N) Scope and Application: For water and wastewater; digestion is required for determining total nitrogen. The
NITROGEN, TOTAL, Test N Tube * Method 10071 TNT Persulfate Digestion Method (0 to 25.0 mg/l N) Scope and Application: For water and wastewater; digestion is required for determining total nitrogen. The
Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kc
 Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kc Experiment 20 The purpose of this lab is to experimentally determine the equilibrium constant, K c, for the following chemical reaction: Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN -
Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kc Experiment 20 The purpose of this lab is to experimentally determine the equilibrium constant, K c, for the following chemical reaction: Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN -
Investigating Food Dyes in Sports Beverages. Sample
 Investigating Food Dyes in Sports Beverages Investigation 1 There are many different brands of beverages that fall under the general category of sports drinks. Most of these beverages contain an FD&C food
Investigating Food Dyes in Sports Beverages Investigation 1 There are many different brands of beverages that fall under the general category of sports drinks. Most of these beverages contain an FD&C food
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests
 Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
AP Biology Lab 4 PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 4 PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. separate plant pigments using chromatography, and 2. measure the rate of
AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 4 PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. separate plant pigments using chromatography, and 2. measure the rate of
Available online Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(4):1069-1073 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Development of extractive spectrophotometric method
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(4):1069-1073 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Development of extractive spectrophotometric method
A Study of Beer s Law Prelab
 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? A Study of Beer s Law Prelab 2. Using the absorbance versus wavelength curve given in Figure I, determine the approximate value of max of the dye used to construct
1. What is the purpose of this experiment? A Study of Beer s Law Prelab 2. Using the absorbance versus wavelength curve given in Figure I, determine the approximate value of max of the dye used to construct
For simplicity, we ll represent BTB s ionization in a solution by the equilibrium: HBTB = H + + BTB -
 Chemistry 160 Please have the following pages ready before class on Wednesday, April 11. An abstract (see the end of this handout) is needed for this write-up. The abstract and photocopied pages of the
Chemistry 160 Please have the following pages ready before class on Wednesday, April 11. An abstract (see the end of this handout) is needed for this write-up. The abstract and photocopied pages of the
LAB 05 Enzyme Action
 LAB 05 Enzyme Action Objectives: Name the substrate and products of the peroxidase-catalyzed reaction. To understand the terms: enzyme, activation energy, active site, ph, and denaturation. Distinguish
LAB 05 Enzyme Action Objectives: Name the substrate and products of the peroxidase-catalyzed reaction. To understand the terms: enzyme, activation energy, active site, ph, and denaturation. Distinguish
