Chapter 8. Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Ch. 8-1
|
|
|
- Jeffrey O’Connor’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions h. 8-1
2 1. Addition Reactions of Alkenes E + E Nu Nu h. 8-2
3 1A. ow To Understand Additions to Alkenes This is an addition reaction: E Nu added across the double bond E + E Nu Nu π-bond σ-bond 2 σ-bonds Bonds broken Bonds formed h. 8-3
4 Since p bonds are formed from the overlapping of π orbitals, π electron clouds are above and below the plane of the double bond π electron clouds h. 8-4
5 Electrophilic electron seeking = and π bonds are particularly susceptible to electrophilic reagents (electrophiles) ommon electrophile +, X + (X = l,, I), g 2+, etc. h. 8-5
6 In an electrophilic addition, the π electrons seek an electrophile, breaking the π bond, forming a σ bond and leaving a positive charge on the vacant π orbital on the adjacent carbon. Addition of B to form a σ bond provides an addition product h. 8-6
7 δ + E δ Nu E + Nu Nu E h. 8-7
8 2. Electrophilic Addition of ydrogen alides to Alkenes: Mechanism and Markovnikov s Rule Mechanism δ + E δ Nu A Nu Nu E h. 8-8
9 Mechanism Sometimes do not go through a free carbocation, may go via E h. 8-9
10 Markovnikov s Rule For symmetrical substrates, no problem for regiochemistry E E E Nu same as Nu E Nu same as Nu E h. 8-10
11 Markovnikov s Rule But for unsymmetrical substrates, two regioisomers are possible 3 E Nu 3 E or 3 E Nu Nu 3 E Nu different from 3 Nu E h. 8-11
12 Markovnikov s Rule In the electrophilic addition of an unsymmetrical electrophile across a double bond of an alkene, the more highly substituted and more stabilized carbocation is formed as the intermediate in preference to the less highly substituted and less stable one h. 8-12
13 Markovnikov s Rule Thus δ + E δ Nu E Nu E NOT E Note: carbocation stability 3 o > 2 o > 1 o h. 8-13
14 Addition of ydrogen alides Addition of l, and I across a = bond + is the electrophile + δ + δ slow r.d.s fast NO h. 8-14
15 h. 8-15
16 2A. Theoretical Explanation of Markovnikov s Rule 3 δ + δ X 3 step 1 (slow r.d.s.) 2 o carbocation (more stable) or 3 1 o carbocation (more stable) One way to state Markovnikov s rule is to say that in the addition of X to an alkene, the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon atom of the double bond that already has the greater number of hydrogen atoms h. 8-16
17 (1 o cation) fast (minor) slow (r.d.s.) (2 o cation) fast (major) Step 1 Step 2 h. 8-17
18 h. 8-18
19 Examples (1) l l + l (95 : 5) (2) + (98 : 2) h. 8-19
20 2B. Modern Statement of Markovnikov s Rule In the ionic addition of an unsymmetrical reagent to a double bond, the positive portion of the added reagent attaches itself to a carbon atom of the double bond so as to yield the more stable carbocation as an intermediate h. 8-20
21 Examples O O l l (1) δ + l δ O more stable 3 o cation (major) l O l O less stable 1 o cation (minor) h. 8-21
22 Examples l I I (2) δ + I δ l more stable 3 o cation l (major) I less stable 1 o cation l l I (minor) h. 8-22
23 2. Regioselective Reactions When a reaction that can potentially yield two or more constitutional isomers actually produces only one (or a predominance of one), the reaction is said to be regioselective l l (major) + l (minor) Regioselectivity: regioisomers 95 : 5 h. 8-23
24 2D. An Exception to Markovnikov s Rule RO OR heat (anti-markovnikov's product) Via a radical mechanism (see hapter 10) This anti-markovnikov addition does not take place with I, l, and F, even when peroxides are present h. 8-24
25 3. Stereochemistry of the Ionic Bu Addition to an Alkene attack from top X Bu achiral trigonal planar carbocation X X 3 Bu (S)-2-alohexane (50%) 2 X attack from bottom Bu 3 X (R)-2-alohexane (50%) racemate h. 8-25
26 4. Addition of Sulfuric Acid to Alkenes O O S O δ O δ + conc. 2 SO 4 cold Addition of OSO 3 across a = bond more stable 3 o cation OSO 3 OSO 3 less stable 1 o cation h. 8-26
27 4A. Alcohols from Alkyl ydrogen Sulfates conc. 2 SO 4 OSO 3 2 O O cold heat The overall result of the addition of sulfuric acid to an alkene followed by hydrolysis is the Markovnikov addition of and O h. 8-27
28 5. Addition of Water to Alkenes: Acid-atalyzed ydration Overall process Addition of O across a = bond + is the electrophile Follow Markovnikov s rule 2 O dilute 3 O + (e.g. dilute 2 SO 4, 3 PO 4 ) O h. 8-28
29 5A. Mechanism O 2 O slow fast (step 1) more stable (step 2) O 3 o cation fast (step 3) 2 O O + O h. 8-29
30 5B. Rearrangements Rearrangement can occur with certain carbocations 2 O 2 SO 4 NOT O O 2 O 1,2-alkyl shift (major product) h. 8-30
31 6. Alcohols from Alkenes through Oxymercuration Demercuration: Markovnikov Addition Step 1: Oxymercuration g(oac) 2 TF- 2 O O goac Step 2: Demercuration O goac NaB 4 O O h. 8-31
32 6A. Regioselectivity of Oxymercuration Demercuration Oxymercuration demercuration is also highly regioselective and follows Markovnikov s rule g(oac) 2 TF- 2 O O goac NaB 4 O O h. 8-32
33 6B. Rearrangements Seldom Occur in Oxymercuration Demercuration Recall: acid-catalyzed hydration of some alkenes leads to rearrangement products e.g. 2 O 2 SO 4 O h. 8-33
34 2 O 2 SO 4 1,2-alkyl shift O 2 O 2 O O h. 8-34
35 Rearrangements of the carbon skeleton seldom occur in oxymercuration demercuration no rearrangement O 1. g(oac) 2, TF- 2 O 2. NaB 4 via O g(oac) h. 8-35
36 6. Mechanism of Oxymercuration Does not undergo a free carbocation δ + g δ OAc OAc AcO + δ + δ + goac 2 O goac goac O 2 O O h. 8-36
37 Stereochemistry Usually anti-addition 2 O g(oac) 2 δ + 3 TF- 2 O 3 δ + g(oac) O 3 g(oac) h. 8-37
38 Although attack by water on the bridged mercurinium ion leads to anti addition of the hydroxyl and mercury groups, the reaction that replaces mercury with hydrogen is not stereocontrolled (it likely involves radicals). This step scrambles the overall stereochemistry The net result of oxymercuration demercuration is a mixture of syn and anti addition of and O to the alkene h. 8-38
39 Solvomercuration-Demercuration g(o 2 F 3 ) 2 OR TF-RO g(o 2 F 3 ) NaB 4 O OR h. 8-39
40 7. Alcohols from Alkenes through ydroboration Oxidation: Anti-Markovnikov Syn ydration "B 3 " B 2 Addition of B 2 across a = bond h. 8-40
41 B 3 exists as dimer B 2 6 or complex with coordinative solvent B B Me B O B S Me (B 3 -TF) (B 3 -DMS) h. 8-41
42 syn addition 1. B 3 -TF O O 2, O 3 Anti-Markovnikov addition of & O h. 8-42
43 ompare with oxymercurationdemercuration O g(oac) 2 3 TF- 2 O 3 g(oac) anti addition NaB 4 O Markovnikov addition of & O 3 h. 8-43
44 8. ydroboration: Synthesis of Alkylboranes + B hydroboration B alkene boron hydride alkylborane h. 8-44
45 8A. Mechanism of ydroboration B B π complex B 3 syn addition of and B B four-atom concerted T.S. 3 δ + δ B h. 8-45
46 Other examples (1) B 2 -TF + B 2 2 B (99 : 1) (2) B 2 -TF + B 2 2 B (98 : 2) h. 8-46
47 8B. Stereochemistry of ydroboration Syn addition B 2 3 B 3 -TF 3 h. 8-47
48 9. Oxidation and ydrolysis of Alkylboranes δ + B δ B 2 B B always ends up on the least hindered carbon B B (trialkyl borane) h. 8-48
49 Oxidation B 2 O 2 O O B O h. 8-49
50 Via R 3 B O O R R B O O R R R B OR O O R RO B OR R R B O OR O O O R OR O O B OR OR RO B OR h. 8-50
51 ydrolysis O O B O NaO 2 O 3 O + Na 3 BO 3 h. 8-51
52 Overall synthetic process of hydroboration-oxidation-hydrolysis 1. B 3 -TF 2. 2 O 2 3. NaO, 2 O O Overall: anti-markovnikov addition of O across a = bond Opposite regioisomers as oxymercuration-demercuration h. 8-52
53 Example anti-markovnikov syn addition B 3 -TF B O 2 O 2 O 3 This oxidation step occurs with retention of configuration h. 8-53
54 10. Summary of Alkene ydration Methods Summary of Methods for onverting Alkene to Alcohol Reaction Regiochemistry Stereochemistry Acid-catalyzed hydration Markovnikov addition Not controlled Occurrence of Rearrangements Frequent Oxymercurationdemercuration Markovnikov addition Not controlled Seldom ydroborationoxidation Anti-Markovnikov addition Stereospecific: syn addition of and O Seldom h. 8-54
55 Examples via 1,2-hydride shift + 2 O O 1. g(oac) 2, TF- 2 O 2. NaB 4, O with rearrangement O Markovnikov addition of 2 O without rearrangement 1. B 3 -TF 2. 2 O 2, O O anti-markovnikov, syn addition of 2 O h. 8-55
56 11. Protonolysis of Alkylboranes 3 O 2 R B R + 3 O 2 B heat alkylborane alkane Protonolysis of an alkylborane takes place with retention of configuration; hydrogen replaces boron where it stands in the alkylborane Overall stereochemistry of hydroboration protonolysis: syn h. 8-56
57 e.g. 1. B 3 -TF O 2 D 3 D + enantiomer via 3 B 2 h. 8-57
58 12. Electrophilic Addition of omine and hlorine to Alkenes Addition of X X (X = l, ) across a = bond 2 l 4 (vicinal dibromide) h. 8-58
59 Examples (1) 2 5 o + (anti addition of 2 ) (racemate) l 2 (2) Ph Ph Ph 10 o (anti addition of l 2 ) 1 l l 2 Ph Ph Ph same as l l (rotation of 1-2 bond) h. 8-59
60 12A. Mechanism of alogen Addition + bond becomes polarized when close to alkene δ + δ (vincinal Dibromide) (bromonium) + h. 8-60
61 Stereochemistry Anti addition l 4 S N 2 reaction enantiomer + (anti) h. 8-61
62 13. Stereospecific Reactions A reaction is stereospecific when a particular stereoisomeric form of the starting material reacts by a mechanism that gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product h. 8-62
63 Reaction l trans-2-butene (2R,3S)-2,3-Dibromobutane (a meso compound) Reaction l cis-2-butene (2R,3R) (2S,3S) (a pair of enantiomers) h. 8-63
64 Addition of bromine to cis-2-butene 3 δ + δ 3 3 (a) bromonium ion (achiral) (a) 3 3 (b) (2R,3R)-2,3-Dibromobutane (chiral) 3 3 (b) 3 (2S,3S)-2,3-Dibromobutane (chiral) h. 8-64
65 Addition of bromine to trans-2-butene 3 δ + δ 3 3 (a) bromonium ion (achiral) 3 (a) 3 (b) (R,S)-2,3-Dibromobutane (meso) 3 3 (b) 3 (R,S)-2,3-Dibromobutane (meso) h. 8-65
66 14. alohydrin Formation X 2 2 O O X Addition of O and X (X = l, ) across a = bond X + is the electrophile Follow Markovnikov s rule h. 8-66
67 Mechanism δ + 2 O 3 2 O 3 δ + O 3 3 h. 8-67
68 Other variation If 2 O is replaced by RO, RÖ will be the nucleophile e.g. 2 OMe MeO h. 8-68
69 15. Divalent arbon ompounds: arbenes 15A. Structure and Reactions of Methylene heat 2 N N 2 + N N or light Diazomethane Methylene (a carbene) Nitrogen h. 8-69
70 2 N N 2 N N 2 N N I II III + 2 Alkene Methylene yclopropane h. 8-70
71 15B. Reactions of Other arbenes: Dihalocarbenes :X 2 (e.g. :l 2 ) Generation by α-elimination of chloroform l l l O t Bu l 2 + t BuO + l h. 8-71
72 Usually a syn (cis) addition across a = bond t BuOK l 3 l l (a cyclopropane) h. 8-72
73 Stereospecific reactions l 2 l l l 2 l l h. 8-73
74 15. arbenoids: The Simmons-Smith yclopropane Synthesis 2 I 2 + Zn(u) (Zinc-copper couple) I ZnI 2 (a carbenoid) h. 8-74
75 A stereospecific syn (cis) addition across a = bond 2 I 2 (trans) Zn(u) (trans) 2 I 2 Zn(u) (cis) (cis) h. 8-75
76 16. Oxidation of Alkenes: Syn 1,2-Dihydroxylation Overall: addition of 2 O groups across a = bond O O Reagents: dilute KMnO 4 / O / 2 O / cold or OsO 4, pyridine then NaSO 3, 2 O h. 8-76
77 16A. Mechanism for Syn Dihydroxylation of Alkenes dil. KMnO 4 O, 2 O cold O O Mn O O O 2 O O O + MnO 2 OsO 4 pyridine O O Os O O NaSO 3 2 O O O + Os h. 8-77
78 Both reagents give syn dihydroxylation dil. KMnO 4 O, 2 O, cold or OsO 4, pyridine then NaSO 3 O O (cis-diol) h. 8-78
79 omparison of the two reagents KMnO 4 : usually lower yield and possibly side products due to overoxidation 1. KMnO 4, 2. + O + O O (oxidative cleavage of =) O OsO 4 : usually much higher yield but OsO 4 is extremely toxic h. 8-79
80 17. Oxidative leavage of Alkenes 17A. leavage with ot Basic Potassium Permanganate KMnO 4, O O a, 2 O b b 2 a a b or 3 O + O b a a b 2 b O a O h. 8-80
81 Other examples (1) 1. KMnO 4, O, 2 O, heat 2. 3 O + O + O O (2) 1. KMnO 4, O, 2 O, heat 2. 3 O + O O O h. 8-81
82 17B. leavage with Ozone R R" R R" R' 1. O 3 O + 2. Zn, AcO R' or Me 2 S O h. 8-82
83 Examples O (1) 1. O 3 2. Zn, AcO O (2) 1. O 3 2. Me 2 S + O O h. 8-83
84 Mechanism + O O O O O O initial ozonide O O O O O Zn(OAc) 2 + O O O O ozonide O + O h. 8-84
85 18. Electrophilic Addition of omine & hlorine to Alkynes R X 2 (excess) 2 l 2 (X = l,, I) R X X X X R X 2 X X2 R X X X X X (anti-addition) h. 8-85
86 19. Addition of ydrogen alides to Alkynes X (excess) R (X = l,, I) Regioselectivity Follow Markovnikov s rule X R X gem-dibromide h. 8-86
87 Mechanism h. 8-87
88 Anti-Markovnikov addition of hydrogen bromide to alkynes occurs when peroxides are present in the reaction mixture peroxides (E) and (Z) (74%) h. 8-88
89 20. Oxidative leavage of Alkynes 1. O 3 R R' RO 2 + R'O 2 2. OAc OR 1. KMnO 4, O R R' + R'O O + RO 2 Example 1. O 3 Ph 3 PhO O 2 2. AcO h. 8-89
90 21. ow to Plan a Synthesis: Some Approaches & Examples In planning a synthesis we often have to consider four interrelated aspects: 1. onstruction of the carbon skeleton 2. Functional group interconversions 3. ontrol of regiochemistry 4. ontrol of stereochemistry h. 8-90
91 21A. Retrosynthetic Analysis ow to synthesize? O Retrosynthetic analysis O (target molecule) (precursor) h. 8-91
92 Synthesis Markovnikov addition of 2 O + 2 O O or 1. g(oac) 2, TF- 2 O 2. NaB 4, O h. 8-92
93 ow to synthesize? Retrosynthetic analysis O O (target molecule) (precursor) Synthesis 1. B 3 -TF 2. 2 O 2, O anti-markovnikov addition of 2 O O h. 8-93
94 21B. Disconnections, Synthons, and Synthetic Equivalents One approach to retrosynthetic analysis is to consider a retrosynthetic step as a disconnection of one of the bonds In general, we call the fragments of a hypothetical retrosynthetic disconnection Synthons h. 8-94
95 Example Ph ow? Ph 3 Retrosynthetic analysis (i) Ph 3 Ph 3 (gem-dibromide came from addition of across a bond) h. 8-95
96 Retrosynthetic analysis synthons (ii) Ph 3 Ph + 3 disconnection 3 I + Ph Na synthetic equivalent h. 8-96
97 Synthesis Ph NaN 2 liq. N 3 Ph Na -30 o 3 I (via an S N 2 reaction) Ph 3 (excess) Ph 3 h. 8-97
98 21. Stereochemical onsiderations 3 3 ow? 3 3 h. 8-98
99 Retrosynthetic analysis 3 The precursor of a vicinal dibromide is usually an alkene omination of alkenes are anti addition 3 (rotate 180 o ) 3 3 (anti addition of 2 ) (anti addition of 2 ) 3 h. 8-99
100 Synthesis N 4 l 1. Li, liq. N (anti addition of 2 ) 3 3 same as 3 2 /l 4 3 (anti addition of 2 ) h
101 END OF APTER 8 h
1. Addition Reactions of Alkenes
 hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions reated by Professor William Tam & Dr. illis hang h. 8-1 About The Authors These PowerPoint Lecture Slides were created and prepared by Professor William
hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions reated by Professor William Tam & Dr. illis hang h. 8-1 About The Authors These PowerPoint Lecture Slides were created and prepared by Professor William
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions "
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Electrophilic Addition
 . Reactivity of = Electrons in pi bond are loosely held. Electrophiles are attracted to the pi electrons. arbocation intermediate forms. Nucleophile adds to the carbocation. Net result is addition to the
. Reactivity of = Electrons in pi bond are loosely held. Electrophiles are attracted to the pi electrons. arbocation intermediate forms. Nucleophile adds to the carbocation. Net result is addition to the
Chapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups
 hapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups Preparation of alkenes: two common elimination reactions 1. Dehydration of alcohols Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate
hapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups Preparation of alkenes: two common elimination reactions 1. Dehydration of alcohols Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate
Reactivity of C=C. Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes. Types of Additions. Electrophilic Addition. Addition of HX (1) Addition of HX (2)
 rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Jo Blackburn Richland ollege, allas, TX allas ounty ommunity ollege istrict 2003, Prentice all Reactivity of = Electrons in pi
rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Jo Blackburn Richland ollege, allas, TX allas ounty ommunity ollege istrict 2003, Prentice all Reactivity of = Electrons in pi
Chapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
 hapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis alcohol alkane halohydrin 1,2-diol 1,2-dihalide carbonyl halide halide Addition Y Y Elimination Electrophilic Addition Dehydrohalogenation: loss of from an alkyl
hapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis alcohol alkane halohydrin 1,2-diol 1,2-dihalide carbonyl halide halide Addition Y Y Elimination Electrophilic Addition Dehydrohalogenation: loss of from an alkyl
Chapter 8 Alkenes: Reactions
 Chamras Glendale Community College Organic Chemistry 105 Chapter 8 Alkenes: Reactions Name Type 1. alo-hydrogenation (Ionic & Radical) Electrophilic Addition 2. ydration (Acid-Catalyzed) Electrophilic
Chamras Glendale Community College Organic Chemistry 105 Chapter 8 Alkenes: Reactions Name Type 1. alo-hydrogenation (Ionic & Radical) Electrophilic Addition 2. ydration (Acid-Catalyzed) Electrophilic
Chapter 8 - Alkenes and Alkynes II Addition Reactions of Alkenes - Electrons in the π bond of alkenes react with electrophiles
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 8 - Alkenes and Alkynes II 8.1 - Addition Reactions of Alkenes - Electrons in the π bond of alkenes react with electrophiles 8.2 - Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes:
Andrew Rosen Chapter 8 - Alkenes and Alkynes II 8.1 - Addition Reactions of Alkenes - Electrons in the π bond of alkenes react with electrophiles 8.2 - Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes:
Chapter 8: Addition Reactions
 Chapter 8: Addition Reactions Addition Reactions to Alkenes (Section 8.1) Markovnikov s Rule (Section 8.2) Stereochemistry of Ionic Addition to Alkenes (Section 8.3) 2 S 4 Additions to Alkenes (Section
Chapter 8: Addition Reactions Addition Reactions to Alkenes (Section 8.1) Markovnikov s Rule (Section 8.2) Stereochemistry of Ionic Addition to Alkenes (Section 8.3) 2 S 4 Additions to Alkenes (Section
Double and Triple Bonds. The addition of an electrophile and a
 Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
6.10 Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes. Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes 6.10 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes O O reaction is acid catalyzed; typical hydration medium is 50% 2 SO 4-50% 2 O Follows Markovnikov's Rule Follows Markovnikov's
Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes 6.10 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes O O reaction is acid catalyzed; typical hydration medium is 50% 2 SO 4-50% 2 O Follows Markovnikov's Rule Follows Markovnikov's
Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
 Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis 1 Synthesis of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. loss of requires CH 2 CH 2 Cl Zaitsev s Rule: CH 2 C 2. Dehydration of
Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis 1 Synthesis of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. loss of requires CH 2 CH 2 Cl Zaitsev s Rule: CH 2 C 2. Dehydration of
Alkenes. Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula C n H 2n. Nomenclature
 Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Alcohol Synthesis. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes
 Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Electrophilic Additions o Regio vs stereoselectivity Regio where do the pieces add? Markovnikov s rule hydrogen will go to the side of the double bond with most hydrogens.
Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Electrophilic Additions o Regio vs stereoselectivity Regio where do the pieces add? Markovnikov s rule hydrogen will go to the side of the double bond with most hydrogens.
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #6 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkyne hemistry. Friday, March 26, 2002, 9 9:50 am Name: Answer Key Question 1. alogenation Reactions.
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #6 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkyne hemistry. Friday, March 26, 2002, 9 9:50 am Name: Answer Key Question 1. alogenation Reactions.
Chapter 8: Chemistry of Alkynes (C n H 2n-2 )
 hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem reaction what is added to the C=C what kind of molecule results addition of HX HX only
 I. Addition Reactions of Alkenes Introduction Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem 2310 An addition reaction always involves changing a double bond to a single bond and adding a new bond
I. Addition Reactions of Alkenes Introduction Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem 2310 An addition reaction always involves changing a double bond to a single bond and adding a new bond
Ether, NaOH. This is a two-step process, but is most commonly done as a one-pot procedure (upper right).
 CAPTE 8. ALKENES: EACTINS AND SYNTESIS ydration of Alkenes by xymercuration-eduction - concerted formation of three-membered ring intermediate - addition of water occurs through anti stereoselectivity
CAPTE 8. ALKENES: EACTINS AND SYNTESIS ydration of Alkenes by xymercuration-eduction - concerted formation of three-membered ring intermediate - addition of water occurs through anti stereoselectivity
alkene: versatile function group
 alkene: versatile function group X Alcohol Alkane alohydrin 1,2-Diol X X C C Carbonyl compound 1,2-Dihalide X C Cyclopropane alide Epoxide 7.1 Preparation of Alkenes: A Review of Elimination Reactions
alkene: versatile function group X Alcohol Alkane alohydrin 1,2-Diol X X C C Carbonyl compound 1,2-Dihalide X C Cyclopropane alide Epoxide 7.1 Preparation of Alkenes: A Review of Elimination Reactions
Option II: Chiral + Achiral = Optically Active Diastereomers
 Option II: Chiral + Achiral = Optically Active Diastereomers What about additions to chiral alkenes? The previous examples were reactions done on achiral alkenes. What is the difference when an alkene
Option II: Chiral + Achiral = Optically Active Diastereomers What about additions to chiral alkenes? The previous examples were reactions done on achiral alkenes. What is the difference when an alkene
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Synthesis and Retrosynthesis
 Synthesis and Retrosynthesis Putting Reactions Together A large part of ganic chemistry involves building me complex molecules from smaller ones using a designed sequence of reactions, i.e. chemical synthesis.
Synthesis and Retrosynthesis Putting Reactions Together A large part of ganic chemistry involves building me complex molecules from smaller ones using a designed sequence of reactions, i.e. chemical synthesis.
Alkenes are prepared by the reverse of the electrophilic reactions in the last chapter. That is, they are prepared by elimination reactions.
 Ch 8 Alkene Reactions and Syntheses Alkenes are prepared by the reverse of the electrophilic reactions in the last chapter. That is, they are prepared by elimination reactions. Dehydrohalogenation - Mechanism
Ch 8 Alkene Reactions and Syntheses Alkenes are prepared by the reverse of the electrophilic reactions in the last chapter. That is, they are prepared by elimination reactions. Dehydrohalogenation - Mechanism
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 Organic hemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #6 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkyne hemistry. Friday, March 26, 2002, 9 9:50 am Name: Question 1. alogenation Reactions.
hemistry 210 Organic hemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #6 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkyne hemistry. Friday, March 26, 2002, 9 9:50 am Name: Question 1. alogenation Reactions.
+ HBr!H = OH CH CH 2. HgOAc
 radical substitution Cl hv + Cl 2 + Cl! = Energy radical addition RR + electrophilic addition + C3 C3! = Energy Energy + 2 acetone water + 2 2 +! =! = Energy Energy acid catalyzed hydration + 2 +! = Energy
radical substitution Cl hv + Cl 2 + Cl! = Energy radical addition RR + electrophilic addition + C3 C3! = Energy Energy + 2 acetone water + 2 2 +! =! = Energy Energy acid catalyzed hydration + 2 +! = Energy
Chapter 7. dehydration
 hapter 7 7.1 ne problem with elimination reactions is that mixtures of products are often formed. For example, treatment of 2-bromo-2-methylbutane with K in ethanol yields a mixture of two alkene products.
hapter 7 7.1 ne problem with elimination reactions is that mixtures of products are often formed. For example, treatment of 2-bromo-2-methylbutane with K in ethanol yields a mixture of two alkene products.
sp 2 geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear ΔH C-C ΔH C-H % s character pk a 464 KJ/mol 33% 44
 hapter 10: Alkynes 10.1 Introduction to Alkynes ~ 111 ~ 122 1.06 Å 180 1.1 Å ~ 116 1.08 Å 1.54 Å 1.34 Å 1.20 Å hybridization of sp 3 sp 2 sp geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear 368 KJ/mol 632 KJ/mol
hapter 10: Alkynes 10.1 Introduction to Alkynes ~ 111 ~ 122 1.06 Å 180 1.1 Å ~ 116 1.08 Å 1.54 Å 1.34 Å 1.20 Å hybridization of sp 3 sp 2 sp geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear 368 KJ/mol 632 KJ/mol
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
1. Addition of HBr to alkenes
 eactions of Alkenes I eading: Wade chapter 8, sections 8-1- 8-8 tudy Problems: 8-47, 8-48, 8-55, 8-66, 8-67, 8-70 Key Concepts and kills: Predict the products of additions to alkenes, including regiochemistry
eactions of Alkenes I eading: Wade chapter 8, sections 8-1- 8-8 tudy Problems: 8-47, 8-48, 8-55, 8-66, 8-67, 8-70 Key Concepts and kills: Predict the products of additions to alkenes, including regiochemistry
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
10.1. Electrophilic Addition of to to give. Works with HCl HBr HI. Electrophilic Addition Mechanism. H Cl Cl. 3D picture of intermediate: Rxn Coord
 10.1 Electrophilic Addition of to to give Works with I F Electrophilic Addition Mechanism 3D picture of intermediate: E xn oord Thermodynamics: + Δ (kcal/mol) + + = Alkene ydration: Electrophilic Addition
10.1 Electrophilic Addition of to to give Works with I F Electrophilic Addition Mechanism 3D picture of intermediate: E xn oord Thermodynamics: + Δ (kcal/mol) + + = Alkene ydration: Electrophilic Addition
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes
 C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
CHEM 263 Oct 25, stronger base stronger acid weaker acid weaker base
 CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
Chapter 8 Addition Reactions to Alkenes
 . 8 hapter 8 Addition eactions to Alkenes In this chapter will we study the addition reactions of alkenes. We will see that the π electrons of the double bond are loosely held and that their maximum electron
. 8 hapter 8 Addition eactions to Alkenes In this chapter will we study the addition reactions of alkenes. We will see that the π electrons of the double bond are loosely held and that their maximum electron
Alkenes - Addition Reactions
 Alkenes - Addition Reactions Alkenes- reactions. Addition Ionic Free radical Reduction Oxidation Substitution Reactions, alkenes: 1. Addition of hydrogen (reduction). 2. Addition of halogens. 3. Addition
Alkenes - Addition Reactions Alkenes- reactions. Addition Ionic Free radical Reduction Oxidation Substitution Reactions, alkenes: 1. Addition of hydrogen (reduction). 2. Addition of halogens. 3. Addition
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
Organic Chemistry. Alkenes (2)
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkenes (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkenes (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
- NH2 or NH 3 H 2 O or CH 3 COO - BF 3 or F - I Br. or Br
 CEMSTRY 313-02 MDTERM # 3 answer key November 09, 2004 Statistics: Average: 71 pts (71%); ighest: 90 pts (90%); Lowest: 49 pts (49%) Number of students perfming at above average: 22 (51%) 1. (8 pts) Mark
CEMSTRY 313-02 MDTERM # 3 answer key November 09, 2004 Statistics: Average: 71 pts (71%); ighest: 90 pts (90%); Lowest: 49 pts (49%) Number of students perfming at above average: 22 (51%) 1. (8 pts) Mark
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 8 Notes 1
 hem 350 Jasperse h. 8 Notes 1 Summary of Alkene Reactions, h. 8. Memorize Reaction, rientation where Appropriate, Stereochemistry where Appropriate, and Mechanism where Appropriate. -all are drawn using
hem 350 Jasperse h. 8 Notes 1 Summary of Alkene Reactions, h. 8. Memorize Reaction, rientation where Appropriate, Stereochemistry where Appropriate, and Mechanism where Appropriate. -all are drawn using
p Bonds as Nucleophiles
 Chapter 8 p Bonds as Nucleophiles REACTIONS OF ALKENES, ALKYNES, DIENES, AND ENOLS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 8.2.1 Orbital structure of alkenes Geometry: Electrostatic potential: Electron-rich
Chapter 8 p Bonds as Nucleophiles REACTIONS OF ALKENES, ALKYNES, DIENES, AND ENOLS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 8.2.1 Orbital structure of alkenes Geometry: Electrostatic potential: Electron-rich
CHEMISTRY 231 GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FALL 2014 List of Topics / Examination Schedule
 Page 1 of 5 CHEMISTRY 231 FALL 2014 List of Topics / Examination Schedule Unit Starts Topic of Study 20 Aug 2014 STRUCTURE AND BONDING Suggested Reading: Chapter 1 29 Aug 2014 ALKANES & CYCLOALKANES Suggested
Page 1 of 5 CHEMISTRY 231 FALL 2014 List of Topics / Examination Schedule Unit Starts Topic of Study 20 Aug 2014 STRUCTURE AND BONDING Suggested Reading: Chapter 1 29 Aug 2014 ALKANES & CYCLOALKANES Suggested
CHEMISTRY Topic #4: Electrophilic Addition Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 EMISTRY 2600 Topic #4: Electrophilic Addition Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay rganic Reactions (EM 2500 Review) Most reactions in organic chemistry fall into one (or more)
EMISTRY 2600 Topic #4: Electrophilic Addition Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay rganic Reactions (EM 2500 Review) Most reactions in organic chemistry fall into one (or more)
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
Lecture 20 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 20 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 18, 2010 1 Self-Test Question Capnellene (4) is a marine natural product that was isolated from coral
CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 20 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 18, 2010 1 Self-Test Question Capnellene (4) is a marine natural product that was isolated from coral
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles
 Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2018
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
Chemistry 234 (Organic I review) George A. O Doherty Please also refer to the Alkene Addition handout
 Chemistry 234 (Organic I review) George A. O Doherty Please also refer to the Alkene Addition handout So far we have built upon our understanding of the questions I and II, which deal with the number of
Chemistry 234 (Organic I review) George A. O Doherty Please also refer to the Alkene Addition handout So far we have built upon our understanding of the questions I and II, which deal with the number of
ELECTROPHILIC ADDITIONS OF ALKENES AS THE COUNTERPART OF ELIMINATIONS
 ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
Organic Halogen Compounds
 8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
Loudon Chapter 14 Review: Reactions of Alkynes Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/16/2018
 An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
Once familiar with chiral centers, models, drawings and mental images NOW: Final representation of chiral centers: Fischer Projections
 Once familiar with chiral centers, models, drawings and mental images NOW: Final representation of chiral centers: Fischer Projections Fischer Projections are 2-dimensional representations of 3-dimensional
Once familiar with chiral centers, models, drawings and mental images NOW: Final representation of chiral centers: Fischer Projections Fischer Projections are 2-dimensional representations of 3-dimensional
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
 An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
CH Organic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- Fall 2013
 C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition. Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i. Chapter 10 Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
Chapters Additions across C=C π Bonds.
 Grossman, CE 230 Chapters 9 10. Additions across C=C π Bonds. We ve learned a number of different substitution and elimination reactions of alkyl halides. We ve learned that compounds with lone pairs are
Grossman, CE 230 Chapters 9 10. Additions across C=C π Bonds. We ve learned a number of different substitution and elimination reactions of alkyl halides. We ve learned that compounds with lone pairs are
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ADDITION REACTIONS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENERAL MECHANISM Addition reactions are ones in which 1 bond is broken and 2 new bonds are formed. They are the inverse of reactions EXAMPLE: Provide the mechanism for the
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENERAL MECHANISM Addition reactions are ones in which 1 bond is broken and 2 new bonds are formed. They are the inverse of reactions EXAMPLE: Provide the mechanism for the
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
Chapter 4. Reactions of alkenes. Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions
 Chapter 4 Reactions of alkenes Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions Prob 47 p192. Give the reagents that would be required (including catalyst). Ch 4 #2 Electrophilic addition Ch 4
Chapter 4 Reactions of alkenes Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions Prob 47 p192. Give the reagents that would be required (including catalyst). Ch 4 #2 Electrophilic addition Ch 4
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALKENES AND REACTIONS OF ALKENES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
 Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview Andrew Rosen Editor: Raghav Malik January 13, 2013 Contents I Library of Synthetic Reactions 3 II Organic Trends and Essentials 4 1 The Basics: Bonding and Molecular
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview Andrew Rosen Editor: Raghav Malik January 13, 2013 Contents I Library of Synthetic Reactions 3 II Organic Trends and Essentials 4 1 The Basics: Bonding and Molecular
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I all Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser xamination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. riday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question 1.
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I all Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser xamination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. riday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question 1.
REACTION STUDY SHEET. NAME OF REACTION: Antarafacial (anti) Addition of an Electrophile (:E Nu:) to an Alkene
 REACTONSTUDYSEET NAMEOFREACTON: Antarafacial(anti)AdditionofanElectrophile(:E Nu:)toan Alkene mportantfeatureofthisreaction:theelectrophilicatomcarriesanon bondingpairofelectrons. Generalformofthereaction:
REACTONSTUDYSEET NAMEOFREACTON: Antarafacial(anti)AdditionofanElectrophile(:E Nu:)toan Alkene mportantfeatureofthisreaction:theelectrophilicatomcarriesanon bondingpairofelectrons. Generalformofthereaction:
Chapter 6. Polar addition and Elimination Reaction. RCH-CH2Br R C CH 2 H. open carbocation. Br -
 hapter 6 Polar addition and Elimination eaction = 2 2 2 - -2 open carbocation - syn and anti products + + 17 kcal/mol Initial Protonation of the central carbon twisted structure and no allylic conjugation
hapter 6 Polar addition and Elimination eaction = 2 2 2 - -2 open carbocation - syn and anti products + + 17 kcal/mol Initial Protonation of the central carbon twisted structure and no allylic conjugation
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Question 1. Alkenes
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Question 1. Alkenes
When H and OH add to the alkyne, an enol is formed, which rearranges to form a carbonyl (C=O) group:
 Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors
 1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors I, Cl, N 3, 3 P 4 pka 10 to 5 Super strong acids 3 + pka 1.7 RC 2 pka ~ 5 acids Ph pka ~ 10 get 2, R pka ~ 16 weaker RCC (alkynes) pka ~ 26 RN 2 pka
1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors I, Cl, N 3, 3 P 4 pka 10 to 5 Super strong acids 3 + pka 1.7 RC 2 pka ~ 5 acids Ph pka ~ 10 get 2, R pka ~ 16 weaker RCC (alkynes) pka ~ 26 RN 2 pka
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320M/328M Due Friday, November 30
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0M/8M Due Friday, November 0 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0M/8M Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework November 9, 08 Please print the first three letters of your last name in
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0M/8M Due Friday, November 0 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0M/8M Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework November 9, 08 Please print the first three letters of your last name in
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised Date: January 2008 by Ryan H. Groeneman Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised Date: January 2008 by Ryan H. Groeneman Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217
 Part 2 Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes كيمياء عضوية ك 217 د. حسين المغيض Dr. Hussein Al-Mughaid Direct hydration: Addition of H 2 O (Acid-catalyzed hydration)
Part 2 Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes كيمياء عضوية ك 217 د. حسين المغيض Dr. Hussein Al-Mughaid Direct hydration: Addition of H 2 O (Acid-catalyzed hydration)
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
Name. Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry I. Examination #3 - November 11, 2002 ANSWERS
 Name INSTRUTINS Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 221 - rganic hemistry I Examination #3 - November 11, 2002 ANSWERS This examination has two parts. The first part is in multiple choice format; the
Name INSTRUTINS Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 221 - rganic hemistry I Examination #3 - November 11, 2002 ANSWERS This examination has two parts. The first part is in multiple choice format; the
2/26/18. Practice Questions. Practice Questions B F. How many steps are there in this reaction?
 Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
HONORS ORGANIC CHEM. HAHS MRS. RICHARDS
 NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols
 Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols [ Chapter 9 Sections: 9.10; Chapter 13 Sections: 13.1-13.3, 13.9-13.10] 1. Nomenclature of Alcohols simple alcohols C3 C3C2 Eddie Sachs 1927-1964 larger alcohols find the
Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols [ Chapter 9 Sections: 9.10; Chapter 13 Sections: 13.1-13.3, 13.9-13.10] 1. Nomenclature of Alcohols simple alcohols C3 C3C2 Eddie Sachs 1927-1964 larger alcohols find the
Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1 11.1 - Structure and Nomenclature - The common naming calls alcohols as alkyl alcohols (eg: methyl alcohol) - The common names of ethers have the groups
Andrew Rosen Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1 11.1 - Structure and Nomenclature - The common naming calls alcohols as alkyl alcohols (eg: methyl alcohol) - The common names of ethers have the groups
What is the major product of the following reaction?
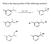 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
Week 11 Problem Set (Solutions) 4/24, 4/25, 4/26
 Week 11 Problem Set (Solutions) 4/24, 4/25, 4/26 Concepts Covered Alkynes Oxidation Alcohols Reactions/Reagents Deprotonation of Alcohols/Alkynes Jones Oxidation (Cr 2 O 7 ) Dess-Martin Periodinane (DMP)
Week 11 Problem Set (Solutions) 4/24, 4/25, 4/26 Concepts Covered Alkynes Oxidation Alcohols Reactions/Reagents Deprotonation of Alcohols/Alkynes Jones Oxidation (Cr 2 O 7 ) Dess-Martin Periodinane (DMP)
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Organic Chemistry. Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry by Nurlin Abu Samah, Dr. Md. Shaheen & Dr. Nadeem Akhtar Faculty of Industrial Sciences & Technology nurlin@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims The students should understand the fundamental
Organic Chemistry by Nurlin Abu Samah, Dr. Md. Shaheen & Dr. Nadeem Akhtar Faculty of Industrial Sciences & Technology nurlin@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims The students should understand the fundamental
CHEM J-10 June The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below.
 CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
Alkenes. sp 2 C 120 o. Electrophilic addition to alkenes. Nucleophilic addition to alkenes (chapt. 23) Radical react. (Polymerization etc, Chapt 7.
 Alkenes Double bond: π and σ sp 2 120 o Electrophilic addition to alkenes E- E Alkene Funktionalized "alkane" Nucleophilic addition to alkenes (chapt. 23) EWG Nu- EWG Nu adical react. (Polymerization etc,
Alkenes Double bond: π and σ sp 2 120 o Electrophilic addition to alkenes E- E Alkene Funktionalized "alkane" Nucleophilic addition to alkenes (chapt. 23) EWG Nu- EWG Nu adical react. (Polymerization etc,
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
7. Haloalkanes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
