Hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite into RUT zeolite. in TMAOH system
|
|
|
- Alvin Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite into RUT zeolite in TMAOH system Hery Jon, Shoutarou Takahashi, Hitoshi Sasaki, Yasunori Oumi and Tsuneji Sano * Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Hiroshima University, Higashi-Hiroshima , Japan; tsano@hiroshima-u.ac.jp Abstract The highly crystalline and pure RUT (RUB-10) zeolite could be obtained from the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite used as a crystalline Si/Al source in tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAOH) media. As compared to amorphous silica/al(oh) 3 and amorphous silica/γ-al 2 O 3 sources, the crystallization rate for the formation of RUT zeolite was clearly faster when FAU zeolite was employed as the Si/Al source. Moreover, it was found that the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite into RUT zeolite depended significantly upon the Si/Al ratio of the starting FAU zeolite. FAU zeolite could be hydrothermally converted into the highly crystalline and pure RUT zeolite under the following molar ratios: Si/Al = 17-28, TMAOH/SiO 2 = 0.2 and H 2 O/SiO 2 = 3-7. Keywords: FAU zeolite; RUT zeolite; Tetramethylammonium hydroxide; Hydrothermal conversion. 1
2 1. Introduction Before the framework type was assigned to be RUT zeolite by IZA [1] based on the work of Gies et al. [2], the zeolite had been known as Nu-1 (nomenclature- unknown-1) zeolite. The synthesis of aluminosilicate Nu-1 zeolite was reported in detail for the first time by Whittam et al. in 1977 [3]. It was claimed that Nu-1 zeolite has Si/Al ratio of 10 to 75 and that its H-form shows high activity and selectivity for xylenes isomerization. The hydrothermal synthesis was performed in the presence of tetramethylammonium (TMA) cations as organic structure-directing agent (OSDA). After this disclosure, the attempts to extend synthesis area yielded the remarkable achievement through the synthesis of boron isomorphous substituted Nu-1 zeolite (B-Nu-1) [4]. Moreover, in 1990 Bellussi et al. reported the possibility of synthesizing Nu-1 zeolite-like materials with boro-, gallo-, ferro- and aluminosilicate frameworks using TMAOH in the presence and absence of Na + cations [5]. In near-neutral fluoride containing media, Patarin et al. succeeded in the preparation of pure aluminosilicate Nu-1 zeolite even in a very narrow range of experimental conditions [6]. Almost two decades after Nu-1 zeolite was discovered, however, the crystal structure had remained unrevealed due to its microcrystallinity and poor crystallinity. In 1995 Gies et al. described the detailed ab initio analysis and the refinement of the crystal structure of RUB-10 (RUT) zeolite, a borosilicate Nu-1 zeolite, from low resolution powder X-ray diffraction data using Patterson search methods in combination with chemical analysis and physical characterization [2]. At the same year by the use of synchrotron powder diffraction data Broach et al. determined the structure of TMA silicate that has a chemical composition and XRD pattern similar to that of Nu-1 zeolite [7]. Furthermore, Ahedi et al. [8] and 2
3 Bhaumik et al. [9] described the synthesis of titanium substituted Nu-1 zeolite. Although the pure phase of all silica Nu-1 zeolite could not be obtained, Marler et al. [10] published the preparation of it by using pyrrolidine as OSDA instead of TMAOH (a well-known OSDA for RUT) in the presence of ammonium fluoride. From the above reports, moreover, it seems that in general the synthesis of RUT zeolite favors either the media containing Na + cations or high synthesis temperatures ( C). Despite such system, in order to obtain the highly crystalline and pure RUT zeolite the synthesis commonly requires prolonged crystallization time. Recently, the hydrothermal conversion of one zeolite into another, i.e. inter-zeolite conversion has drawn a lot of attention as an alternative synthesis strategy for zeolite synthesis [11-14]. Zones et al. reported that by the use of boron beta zeolite inter-zeolite conversion demonstrates enhanced nucleation, increased reaction rates and greater flexibility in choice of template and new possibilities for lattice substitution. Furthermore, it is believed that the crystalline starting material reduces supersaturation level and may have different surface reactivity for the generation of heterogeneous nucleation sites [11]. However, a detailed crystallization process (i.e. any evidence for an entity bringing about the above phenomena) during inter-zeolite conversion has not been clarified yet. We have also investigated the potential of the hydrothermal conversion method, and very recently have reported the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite into *BEA zeolite [15]. It was found that when the amount of tetraethylammonium hydroxide (TEAOH) added as OSDA is small, the crystallization rate toward *BEA zeolite from FAU zeolite is obviously faster than that from amorphous silica/γ-al 2 O 3. We supposed that the hydrothermal conversion route is of an alternative strategy for synthesizing 3
4 zeolite. In the present study, we investigated the possibility of zeolite synthesis with different zeolite frameworks using several OSDAs and succeeded in the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite into highly crystalline and pure RUT zeolite in TMAOH media. The influences of hydrothermal conversion parameters on RUT zeolite synthesis are discussed in detail. 2. Experimental 2.1. Hydrothermal conversion FAU zeolites with various Si/Al ratios used in this work were prepared from NH 4 -Y zeolite (Si/Al = 2.8, Tosoh Co., Japan) through dealumination treatment involving a combination of steaming at 700 C and H 2 SO 4 ( M) treatment at 75 C for 4 h. The particle size of dealuminated FAU zeolite was μm. The hydrothermal conversion was performed as follows. The dealuminated FAU zeolite was mixed well with aqueous TMAOH 20 wt% (Aldrich, USA) and then the mixture was placed into 30 cm 3 Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave. The hydrothermal conversion was conducted at 140 C for 6 h 18 days in the convection oven. The solid product was collected by centrifugation and washed thoroughly with deionized water until near neutral and then dried overnight at 70 C. For comparison, the starting gels from amorphous silica powder produced by wet process (SiO 2 = 88 wt%, Al 2 O 3 = 0.27 wt%, Nipsil, Nippon Silica Ind. Japan) and sodium aluminate (NaAlO 2, Na 2 O = wt%, Al 2 O 3 = wt%, Kanto Chemical Co., Inc. Japan), Al(OH) 3 (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. 4
5 Japan) or γ-al 2 O 3 (Catalysts & Chemicals Ind. Co., Ltd. Japan) as other Si and Al sources respectively were also prepared Characterization The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the solid products were collected by powder X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku, RINT 2000) with graphite monochromatized Cu K α radiation at 40 kv and 30 ma. The relative crystallinities of samples were calculated in relation to that of sample obtained after 6 days of heating. The crystallinity was based on the sum of intensities of peaks with reflection (-111), (111), (220), (022) and (-113). Si/Al ratios were determined by X-ray fluorescence (XRF, Philips spectrometer PW 2400). 0.5 g of sample was fused with 5 g of dilithium tetraborate (Li 2 BB4O 7 ) at 1100 C. The Si/Al ratio was calculated by using Si and Al concentrations determined by the corresponding calibration curves. This Si/Al ratio accuracy has been confirmed by inductively-coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES, Seiko SPS 7700). The crystal morphology was observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JEOL JSM-6320FS). Thermal analysis was carried out using TG/DTA (SSC/5200 Seiko Instruments). The sample about 7 mg was heated in a flow of air (50 ml/min) at 10 C/min from room temperature to 800 C. C CP/MAS NMR and Al MAS NMR spectra were recorded using a 7 mm diameter zirconia rotor on Bruker Avance DRX-400 at MHz and MHz, respectively. The rotor was spun at 4 khz for C CP/MAS NMR and 9 khz for Al MAS NMR. The spectra were accumulated with 6.0 μs pulses, 25 s recycle delay and 1000 scans for C CP/MAS NMR, and 2.3 μs, 1 s 27 and 4000 scans for Al MAS NMR. Glycine (H2NCH 2 COOH) and Al(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O 13 5
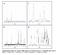
6 13 27 were used as chemical shift references for C CP/MAS NMR and Al MAS NMR, 27 respectively. Prior to Al MAS NMR measurement, the sample was moisture-equilibrated over a saturated solution of NH4Cl for 24 h. 3. Results and discussion At first, in order to study the influence of Si/Al ratio of the starting FAU zeolite on RUT zeolite synthesis, FAU zeolites with various Si/Al ratios were prepared by the dealumination treatment and subjected to the hydrothermal treatment. The hydrothermal conversion conditions are listed in detail in Table 1. Fig. 1 shows the XRD patterns of the starting FAU zeolites with various Si/Al ratios and the products obtained after the hydrothermal treatment for 6 days. From these results, it was found that although the hydrothermal conversion toward pure RUT zeolite strongly depended upon the Si/Al ratio of the starting FAU zeolite, which was similar to the crystallization of *BEA zeolite from FAU zeolite [15], the highly crystalline and pure RUT zeolite could be easily obtained without any impurity. As stated in the introduction section, the synthesis of RUT zeolite seems to be difficult because some zeolitic phases commonly coexist with RUT zeolite as impurities. However, by the present route even at moderate temperature (i.e. 140 C) and the absence of Na + cations, the highly crystalline and pure RUT zeolite could be obtained from FAU zeolites with Si/Al ratios of 17 28; while Si/Al ratios of 14 and 33 yielded RUT zeolite together with SOD (sodalite) zeolite (denoted by asterisk in Fig. 1(B)-a) and amorphous phase, respectively. Fig. 2 shows the SEM images of RUT zeolites obtained. After thorough observation, we could not find any crystals of the starting FAU zeolite. Only crystals of RUT zeolite with disk-like 6
7 morphology were observed. The disk-like morphology of RUT zeolite observed here agrees with the results reported by Hao et al. [16]. Taking into account the fact that the Si/Al ratio of RUT zeolite was almost consistent with that of the starting FAU zeolite (see below), these results strongly indicate that FAU zeolite was completely converted into RUT zeolite during hydrothermal treatment in TMAOH media. Moreover, from Table 1 it was observed that when the Si/Al ratios were 10 and 14, i.e. higher aluminum content, the formation of SOD zeolite considerably competed with RUT zeolite. It seems that high aluminum system favors the formation of SOD zeolite (see below). In the case of the synthesis of *BEA zeolite from FAU zeolite, as the starting material from FAU zeolite showed faster crystallization rate toward *BEA zeolite, compared to amorphous silica/γ-al 2 O 3, we supposed that local-ordered aluminosilicate species (zeolitic building units) originated by the decomposition and dissolution of FAU zeolite framework under alkaline media of TEAOH may be present. We put forward the hypothesis based on the following considerations. To start with, Davis et al. who also studied the inter-zeolite conversion suggested a possibility of an existence of such aluminosilicates species, whose structure and concentration were affected by the framework type and composition of the starting zeolite [14]. Furthermore, Matsukata et al. [17] and Pinnavaia et al. [18] also showed the presence of aluminosilicate species by analyzing the mesoporous materials prepared using the solution obtained from the dissolution of ZSM-5 zeolite. Thus, in order to further support the hypothesis, we studied the crystallization kinetics of RUT zeolite with various Si/Al sources. The crystallization curves are presented in Fig. 3. It became clear that the crystallization rate toward RUT zeolite from FAU zeolite was obviously faster than that from amorphous silica/al(oh) 3 and amorphous silica/γ-al 2 O 3 sources. To obtain highly crystalline RUT 7
8 zeolite, in the case of amorphous silica/al(oh) 3 and amorphous silica/γ-al 2 O 3 sources the crystallization time required 15 and 18 days (Table 1, Sample nos. 18 and 19; Fig. 3), respectively; while for FAU zeolite source it only required 6 days. These data also seem to strongly support our hypothesis that the local-ordered aluminosilicate species originated by the decomposition and dissolution of FAU zeolite framework may exist and be taking part in the construction of another zeolite framework in the presence of a specific OSDA. Although the hypothesis only indirectly describes the phenomena, in order to obtain the direct evidence the thorough investigation is now in progress. The use of zeolite as an alternative Si/Al source therefore provides several advantages in the enhancement of crystallization rate and the description of synthesis mechanism. Moreover, for comparison with the system prepared under the presence of Na + cations, we also performed the synthesis involving sodium aluminate as aluminum source together with sodium source consequently. The result that the crystallization rate from this system is faster than that from FAU zeolite was observed (Fig. 3). It should be noted that because in this system there are additional hydroxide ions from sodium aluminate that is bringing about the gel more soluble and more reactive and thus enhancing crystallization rate, it is almost impossible to compare this system to that from FAU zeolites directly. However, the information which can be achieved here is that the use of FAU zeolite considerably enhances the crystallization rate and the enhancement is comparable to that with sodium aluminate. Furthermore, other parameters involved in hydrothermal conversion such as temperature, H 2 O/SiO 2 ratio and TMAOH/SiO 2 ratio were also investigated thoroughly. In Table 1 when the starting FAU zeolite with Si/Al ratio of 22 was subjected to hydrothermal treatment at 170 C, the crystalline RUT zeolite could be obtained even 8
9 after 2 days of heating (Sample no. 8). This phenomenon can be easily explained as follows; since with the increase of synthesis temperature the decomposition and dissolution rate of the starting FAU zeolite also remarkably increases, the assembly rate (i.e. nucleation rate) and the crystal growth rate of RUT zeolite increase as well. Fig. 4 shows XRD patterns of solid products obtained from FAU zeolites with various H 2 O/SiO 2 ratios. It was found that in the range of H 2 O/SiO 2 ratios of 3-7, the highly crystalline RUT zeolites without any impurity could be achieved with this route (Fig. 4, Sample nos. 6, 7 and 9). On the other hand, while the H 2 O/SiO 2 ratio was 10, RUT zeolite along with amorphous phase was observed. This implies that more dilute system, namely less reactive, seems to be not favorable to the growth of RUT zeolite. Indeed, the more dilute system decreased the crystallization rate toward RUT zeolite. The SEM images of them are exhibited in Figs. 5 and 2(c). There was nearly no difference in the crystallites size and morphology even synthesized with different H 2 O/SiO 2 ratios (3-7). Moreover, Fig. 6 shows the XRD patterns of samples obtained from FAU zeolites prepared with various TMAOH/SiO 2 ratios. It was clear that only TMAOH/SiO 2 ratio of 0.2 could transform FAU zeolite into highly crystalline and pure RUT zeolite (Fig. 6(b)), while TMAOH/SiO 2 ratios of 0.1, 0.3 and 0.4 produced a small amount of undissolved FAU zeolite together with amorphous phase, RUT zeolite coexisted with a small amount of SOD zeolite and SOD zeolite with a small amount of RUT zeolite, respectively (Figs. 6(a), (c) and (d)). These results can be explained as follows. When the amount of TMAOH is small (TMAOH/SiO 2 = 0.1), the alkalinity of system required to decompose or dissolve FAU zeolite decreases and thus are not enough to break up FAU zeolite completely. On the other hand, with the increase of amount of TMAOH the alkalinity also increases consequently. In the case of the synthesis of *BEA zeolite in 9
10 TEAOH media, it has been already recognized that in extremely high alkalinity the aluminum-core is more favorable than the silicon one [19-21]. Therefore, in the case of TMAOH, the similar argument can be deduced. However, because TMA + cations are well-known as OSDA for the synthesis of SOD zeolite, an aluminous clathrasil [22-24], the favorable aluminum core leads to the preferential formation of SOD zeolite. Sample nos. 2 and 3 in Table 1 also supported this argument. Moreover, the subsequent analyses were conducted in order to get information concerning the characteristics of RUT zeolite obtained by the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite. The characteristics of organic molecules occluded in the pores were characterized by thermal analysis and 13 C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy. The TG/DTA curves corresponding to Sample no. 7 are presented in Fig. 7. From the DTA curve, we can categorize thermal profiles into five zones: (I) C, (II) C, (III) C, (IV) C and (V) C. The first zone with endothermic profile corresponds to the desorption of adsorbed water. Then the second zone with exothermic profile centered at 250 C is attributed to the decomposition and oxidation of either TMAOH occluded in pores [24] or TMA + cations interacting with silanol groups of crystal defects. Next, the third zone with exothermic profile centered at 450 C is assigned to the decomposition and oxidation of TMA + cations balancing the negative charge of framework generated by Al [25,26]. The forth zone with exothermic profile centered at 600 C corresponds to the decomposition and oxidation of either hydrocarbon residue produced on acid sites or pyrolysis products in the former steps. The fifth zone with a slightly endothermic profile indicates the dehydration through the condensation of silanol groups [27], which seems likely to imply the structure collapse. Based on the profiles described above, the weight losses between 200 and 700 C that 10
11 are corresponding to the total decomposition of organic moieties are about 15.2 wt% (ca. 5 TMA + /u.c.). Likewise, by 13 C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy the nature of organic moieties was studied. Fig. 8 depicts 13 C CP/MAS NMR spectrum of Sample no. 7. The spectrum revealed the presence of 2 resonances which centered at 57.1 and 45.3 ppm. Resonance at 57.1 ppm indicates methyl groups attached to N, namely CH 3 of N(CH 3 ) +, while resonances at 45.3 ppm is corresponding to methylene groups of N-CH 2 -CH 3 moieties [28], that are formed by the degradation of a small amount of TMAOH. It can be concluded that although there was a small amount of degraded TMA + species, almost all of TMA + species existed intact in zeolitic pores. Furthermore, the chemical state of aluminum in the RUT zeolite obtained was investigated by elemental analysis and 27 Al MAS NMR spectroscopy. The elemental analyses were performed by XRF. According to the results listed in Table 1, the bulk Si/Al ratios of the products were almost consistent with those of starting FAU zeolites, indicating that almost all of aluminum species have been converted from FAU zeolites into RUT zeolites. Then, to clarify the chemical state of aluminum in the zeolite, 27 Al MAS NMR spectra of as-synthesized and calcined Sample no. 7 were measured. Fig. 9(a) exhibits the spectrum of the as-synthesized sample. Only two resonances centered at 57.6 and 52.2 ppm were observed, while no resonance corresponding to octahedrally coordinated aluminum species, namely extraframework aluminum species, at chemical shift of around 0 ppm was observed. This means that all of aluminum species which are present in RUT zeolite obtained from hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite exist within the zeolite framework. Furthermore, the observation of two resonances indicates the presence of at least two groups of crystallographically distinct T-sites in RUT zeolite framework. According to the crystallographic data in literature [1,2], RUT 11
12 zeolite consists of five different T-sites. Abraham et al. by 27 Al MAS NMR and 27 Al 3Q MAS NMR measurements also found the similar results in *BEA zeolite [29]. Yet, in the 27 Al MAS NMR spectrum of RUT zeolite calcined at 500 C for 10 h (Fig. 9(b)), the considerable decrease in the intensity of resonance for framework aluminum was observed, indicating severe dealumination. 4. Conclucions The hydrothermal conversion parameters influencing the conversion of FAU zeolite into RUT zeolite in the presence of TMAOH were investigated in detail. As compared to amorphous silica/al(oh) 3 and amorphous silica/γ-al 2 O 3 sources, the crystallization rate toward the formation of RUT zeolite was clearly faster when FAU zeolite was employed as Si and Al sources. It seems that the decomposition and the dissolution of FAU zeolite in TMAOH media serve local-ordered aluminosilicate species which readily build up RUT zeolite framework. Moreover, it was found that the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite into RUT zeolite depended significantly upon the Si/Al ratio of the starting FAU zeolite. FAU zeolite could be hydrothermally converted into the highly crystalline and pure RUT zeolite under the following molar ratios: Si/Al = 17-28, TMAOH/SiO 2 = 0.2 and H 2 O/SiO 2 = 3-7. By TG/DTA analysis the weight loss corresponding to the degradation of TMA + species was about 15.2 wt%. As confirmed by 13 C CP MAS NMR spectrum, almost all of TMA + species existed intact in zeolitic pores. In addition, 27 Al MAS NMR spectrum of as-synthesized RUT zeolite showed that tetrahedrally coordinated aluminum species could be resolved into at least two crystallographically distinct T-sites. The absence of octahedrally coordinated aluminum 12
13 species implied that all of aluminum species are present within the zeolitic framework before calcination. 13
14 References [1] Ch. Baerlocher, W.M. Meier, D.H. Olson, Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types, 5 th Ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, Also in URL: databases/ [2] H. Gies, J. Rius, Z. Kristallogr. 210 (1995) 475. [3] T.V. Whittam, B. Youll, US Patent , Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd., London, [4] M. Taramasso, G. Perego, B. Notari, in L.V.C. Rees (Ed.), Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Zeolites, Naples, Heyden, London, 1980, pp. 40. [5] G. Bellussi, R. Millini, A. Carati, G. Maddinelli, A. Gervasini, Zeolites 10 (1990) 642. [6] J. Patarin, P. Caullet, B. Marler, A.C. Faust, J.L. Guth, Zeolites 14 (1994) 675. [7] R.W. Broach, N.K. McGuire, C.C. Chao, R.M. Kirchner, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 56 (1995) [8] R.K. Ahedi, S.S. Shevade, A.N. Kotasthane, Zeolites 18 (1997) 361. [9] A. Bhaumik, T. Tatsumi, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 34 (2000) 1. [10] B. Marler, U. Werthmann, H. Gies, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 43 (2001) 329. [11] C.S. Cundy, P.A. Cox, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 82 (2005) 1 and references therein. [12] S. Khodabandeh, M.E. Davis, Micropor. Mater. 9 (1997) 149. [13] S. Khodabandeh, G. Lee, M.E. Davis, Micropor. Mater. 11 (1997) 87. [14] S. Khodabandeh, M.E. Davis, Micropor. Mater. 12 (1997) 347. [15] H. Jon, K. Nakahata, B.-W. Lu, Y. Oumi, T. Sano, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 96 (2006)
15 [16] X. Hao, S. Liu, N. Guan, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 154 (2004) [17] S. Inagaki, M. Ogura, T. Inami, Y. Sasaki, E. Kikuchi, M. Matsukata, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 74 (2004) 163. [18] H. Wang, Y. Liu, T.J. Pinnavaia, J. Phys. Chem. B 110 (2006) [19]M.A. Camblor, A. Corma, A. Mifsud, J. Pérez-Pariente, S. Valencia, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 105 (1997) 341. [20] S. Mintova, V. Valtchev, T. Onfroy, C. Marichal, H. Knözinger, T. Bein, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 90 (2006) 237. [21] H. Jon, Y. Oumi, K. Itabashi, T. Sano, J. Cryst. Growth. 307 (2007) 177. [22] R.F. Lobo, S.I. Zones, M.E. Davis, J. Inclus. Phenom. Mol. 21 (1995) 47. [23] R.M. Barrer, Hydrothermal Chemistry of Zeolites, Academic Press, London, 1982, p [24] Ch. Baerlocher, W.M. Meier, Helv. Chim. Acta 52 (1969) [25] E. Bourgeat-Lami, F. Di Renzo, F. Fajula, P.H. Mutin, T.D. Courieres, J. Phys. Chem. 96 (1992) [26] M.A. Camblor, A. Corma, S. Valencia, J. Mater. Chem. 8 (1998) 2137.] [27] Y.X. Wang, H. Gies, J.H. Lin, Chem. Mater. 19 (2007) [28] C.J. Pouchert, J. Behnke, The Aldrich Library of 13 C and 1 H FT NMR Spectra, Aldrich Chemical Co. Inc., USA, [29] A. Abraham, S.-H. Lee, C.-H. Shin, S.B. Hong, R. Prins, J.A. van Bokhoven, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 6 (2004)
16 Figure captions Fig. 1. XRD patterns of (A) the starting FAU zeolites with various Si/Al ratios and (B) the products obtained after hydrothermal treatment. Sample nos.: (a) 3, (b) 4, (c) 7, (d) 13 and (e) 14. The asterisk mark denotes the peak of SOD (sodalite) zeolite that is present as impurity. Fig. 2. SEM images of (a) the starting FAU zeolite with Si/Al ratio of 22 and the RUT zeolites obtained from FAU zeolites with various Si/Al ratios. Sample nos.: (b) 4, (c) 7 and (d) 13. Fig. 3. Crystallization curves of the RUT zeolites prepared from ( ) FAU zeolite, ( ) amorphous silica/naalo 2, ( ) amorphous silica/al(oh) 3 and ( ) amorphous silica/γ-al 2 O 3 under hydrothermal conditions: Si/Al = 22, TMAOH/SiO 2 = 0.2 and H 2 O/SiO 2 = 5 at 140 C. Fig. 4. XRD patterns of the RUT zeolites obtained from FAU zeolites with various H 2 O/SiO 2 ratios. Sample nos.: (a) 6, (b) 7, (c) 9 and (d) 10. Fig. 5. SEM images of the RUT zeolites obtained from FAU zeolites with various H 2 O/SiO 2 ratios. Sample nos.: (a) 6 and (b) 9. Fig. 6. XRD patterns of the RUT zeolites obtained from FAU zeolites with various TMAOH/SiO 2 ratios. Sample nos.: (a) 5, (b) 7, (c) 11 and (d) 12.
17 Fig. 7. TG/DTA curves of sample no. 7. Fig C CP MAS NMR spectrum of sample no. 7. Fig Al MAS NMR spectra of (a) as-synthesized and (b) calcined sample no. 7.
18 (A) (B) (e) (e) (d) (d) Intensity (c) (c) (b) (b) (a) * (a) theta / 2 theta / Figure 1
19 a b 500 nm 500 nm c d 500 nm 500 nm Figure 2
20 100 Relative crystallinity / % Crystallization time / days Figure 3
21 (d) (c) Intensity (b) (a) theta / Figure 4
22 a b 500 nm 500 nm Figure 5
23 (d) (c) Intensity (b) (a) theta / Figure 6
24 Weight loss / % DTA / μv Temperature / C Figure 7
25 Intensity Chemical shift / ppm Figure 8
26 Intensity (a) (b) Chemical shift / ppm Figure 9
27 Table 1 Hydrothermal conversion conditions and products obtained Synthesis conditions Product (by product) Si and Al Si/Al TMAOH/ H 2 O/ Temp. Time sources ratio SiO 2 SiO 2 / C / days Phase a 1 FAU FAU 2 FAU RUT (SOD) 3 FAU RUT (SOD) 4 FAU RUT 17 5 FAU AM (FAU) 6 FAU RUT 7 FAU RUT 20 8 FAU RUT 21 9 FAU RUT FAU RUT (AM) FAU RUT (SOD) 12 FAU SOD (RUT) 13 FAU RUT FAU AM 15 FAU AM 16 SiO 2 + Al(OH) AM 17 SiO 2 + γ-al 2 O AM 18 SiO 2 + Al(OH) RUT SiO 2 + γ-al 2 O RUT SiO 2 + NaAlO RUT 21 Sample no. a RUT = RUB-10, SOD = Sodalite, FAU = Faujasite, AM = Amorphous Bulk Si/Al ratio
Min Bum Park, Sang Hyun Ahn, Nak Ho Ahn and Suk Bong Hong*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supplementary Information. Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
広島大学学術情報リポジトリ Hiroshima University Institutional Repository
 広島大学学術情報リポジトリ Hiroshima University Institutional Repository Title Auther(s) Citation Issue Date DOI Synthesis of high-silica CHA type zeolite by interzeolite conversion of FAU type zeolite in the presence
広島大学学術情報リポジトリ Hiroshima University Institutional Repository Title Auther(s) Citation Issue Date DOI Synthesis of high-silica CHA type zeolite by interzeolite conversion of FAU type zeolite in the presence
Supplementary Information. for. Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High. Pressures
 S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins
 Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Supporting Information. for. Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under. Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via
 Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR
 University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution
 Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) for. Framework Stabilization of Si-Rich LTA Zeolite Prepared in Organic-Free Media
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information (ESI) for Framework Stabilization of Si-Rich LTA Zeolite Prepared
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information (ESI) for Framework Stabilization of Si-Rich LTA Zeolite Prepared
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials
 Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Supplementary Information. Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses
 Supplementary Information Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses of Extra-Large Pore Germanosilicate Zeolites Risheng Bai, Qiming Sun, Ning Wang, Yongcun Zou, Guanqi Guo, Sara Iborra, Avelino
Supplementary Information Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses of Extra-Large Pore Germanosilicate Zeolites Risheng Bai, Qiming Sun, Ning Wang, Yongcun Zou, Guanqi Guo, Sara Iborra, Avelino
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Synthesis of Zeolite Monolith with Hierarchical Micro/Macropores by Ice-Templating and Steam-Assisted Crystallization
 A publication of 259 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 259 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash
 BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
Supporting Information For
 Supporting Information For Heteroatom-Substituted Delaminated Zeolites as Solid Lewis-Acid Catalysts Xiaoying Ouyang 1, Son-Jong Hwang 2, Dan Xie 3, Thomas Rea 3, Stacey I. Zones*,1,3, Alexander Katz*,1
Supporting Information For Heteroatom-Substituted Delaminated Zeolites as Solid Lewis-Acid Catalysts Xiaoying Ouyang 1, Son-Jong Hwang 2, Dan Xie 3, Thomas Rea 3, Stacey I. Zones*,1,3, Alexander Katz*,1
Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41
 ESO 25(6) #7759 Energy Sources, 25:591 596, 2003 Copyright 2003 Taylor & Francis 0090-8312/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/00908310390195651 Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41 S.-H.
ESO 25(6) #7759 Energy Sources, 25:591 596, 2003 Copyright 2003 Taylor & Francis 0090-8312/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/00908310390195651 Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41 S.-H.
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Flexibility of the aluminium coordination in alumino- silicates. Structure of dealuminated zeolites and feasibility of realumination Author(s):
 Research Collection Doctoral Thesis Flexibility of the aluminium coordination in aluminosilicates. Structure of dealuminated zeolites and feasibility of realumination Author(s): Omegna, Anna Publication
Research Collection Doctoral Thesis Flexibility of the aluminium coordination in aluminosilicates. Structure of dealuminated zeolites and feasibility of realumination Author(s): Omegna, Anna Publication
Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing. twin crystal growth during the secondary growth
 Supplementary Information Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing twin crystal growth during the secondary growth Xianming Li, a Yong Peng, a Zhengbao Wang,* a and Yushan Yan a,
Supplementary Information Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing twin crystal growth during the secondary growth Xianming Li, a Yong Peng, a Zhengbao Wang,* a and Yushan Yan a,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Facet-Selective Deposition of FeO x on α-moo 3 Nanobelts for Lithium Storage Yao Yao, 1 Nuo Xu, 2 Doudou Guan, 1 Jiantao Li, 1 Zechao Zhuang, 1 Liang Zhou,*,1 Changwei Shi 1, Xue
Supporting Information Facet-Selective Deposition of FeO x on α-moo 3 Nanobelts for Lithium Storage Yao Yao, 1 Nuo Xu, 2 Doudou Guan, 1 Jiantao Li, 1 Zechao Zhuang, 1 Liang Zhou,*,1 Changwei Shi 1, Xue
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Synthesis of zeolite crystallites for diffusion measurements
 Synthesis of zeolite crystallites for diffusion measurements Xiaobo Yang, Jürgen Caro Institut für Physikalische Chemie und Elektrochemie Leibniz Universität Hannover Main Activities in Previous Synthesis
Synthesis of zeolite crystallites for diffusion measurements Xiaobo Yang, Jürgen Caro Institut für Physikalische Chemie und Elektrochemie Leibniz Universität Hannover Main Activities in Previous Synthesis
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Supporting Information. Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Molecular Sieves Principles of Synthesis and Identification
 Molecular Sieves Principles of Synthesis and Identification Second Edition R. SZOSTAK Clark Atlanta University Atlanta, GA USA V D BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hail London Weinheim
Molecular Sieves Principles of Synthesis and Identification Second Edition R. SZOSTAK Clark Atlanta University Atlanta, GA USA V D BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hail London Weinheim
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Flowerlike Mesoporous Silica: A Bifunctionalized Catalyst for Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Aromatic Ketones in Aqueous Medium Fei Gao, Ronghua Jin,
Supporting Information for Flowerlike Mesoporous Silica: A Bifunctionalized Catalyst for Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Aromatic Ketones in Aqueous Medium Fei Gao, Ronghua Jin,
Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative Technology to Produce Commercial Zeolite material of High Cation Exchange Capacity
 Proceedings of NAWTEC16 16th Annual North American Waste-to-Energy Conference May 19-21, 2008, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA NAWTEC16-1919 Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative
Proceedings of NAWTEC16 16th Annual North American Waste-to-Energy Conference May 19-21, 2008, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA NAWTEC16-1919 Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment
 Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Figure S1 XRD patterns of (a) Ti-MSE-A, (b) Ti-MSE-A-cal, (c) TS-1, (d) Ti-MWW, and (e) Ti-BEA.
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO 3 Layered Double Hydroxide
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
Science & Technologies SYNTHESIS AND SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF ZEOLITE A TYPE AND X TYPE
 SYNTHESIS AND SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF ZEOLITE A TYPE AND X TYPE B. Bogdanov 1, D. Benev 2 and D.Georgiev 3 1 Department Technology of Water, Inorg. compounds and silicates, 2 Central Research Laboratory
SYNTHESIS AND SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF ZEOLITE A TYPE AND X TYPE B. Bogdanov 1, D. Benev 2 and D.Georgiev 3 1 Department Technology of Water, Inorg. compounds and silicates, 2 Central Research Laboratory
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic Analysis
 146 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 60, (3), 146-153 (2017) [Regular Paper] 2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic
146 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 60, (3), 146-153 (2017) [Regular Paper] 2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic
Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification
 Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
Control of Wall Thickness and Extraordinarily High Hydrothermal Stability of Nanoporous MCM-41 Silica
 Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2007, 54, 35-40 35 Control of Wall Thickness and Extraordinarily High Hydrothermal Stability of Nanoporous MCM-41 Silica Chi-Feng Cheng* ( ), Shu-Hsien Chou ( ),
Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2007, 54, 35-40 35 Control of Wall Thickness and Extraordinarily High Hydrothermal Stability of Nanoporous MCM-41 Silica Chi-Feng Cheng* ( ), Shu-Hsien Chou ( ),
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Stable aluminum metal-organic frameworks (Al-MOFs) for balanced CO 2 and water selectivity Haiwei Li, Xiao Feng, * Dou Ma, Mengxi Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Yi Liu, Jinwei Zhang,
Supplementary Information Stable aluminum metal-organic frameworks (Al-MOFs) for balanced CO 2 and water selectivity Haiwei Li, Xiao Feng, * Dou Ma, Mengxi Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Yi Liu, Jinwei Zhang,
Supporting Information An Interlaced Silver Vanadium Oxide-Graphene Hybrid with High Structural Stability for Use in Lithium Ion Batteries
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information An Interlaced Silver Vanadium Oxide-Graphene Hybrid with High Structural
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information An Interlaced Silver Vanadium Oxide-Graphene Hybrid with High Structural
A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite
 Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts
 A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
Supplementary Material for. Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive Nitrogen
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
PREPARATION OF NEW LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE, Co-V LDH
 Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Preparation of new layered 10 (2005) double 59-63hydroxide, Co-V LDH 59 PREPARATION OF NEW LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE, Co-V LDH O. Saber 1 and H. Tagaya 2 1 Egyptian Petroleum Research
Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Preparation of new layered 10 (2005) double 59-63hydroxide, Co-V LDH 59 PREPARATION OF NEW LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE, Co-V LDH O. Saber 1 and H. Tagaya 2 1 Egyptian Petroleum Research
Hydrogen desorption properties of Ca-N-H system
 Hydrogen desorption properties of Ca-N-H system Satoshi Hino, *Takayuki Ichikawa, Haiyan Leng and Hironobu Fujii Graduate School of Advanced Sciences of Matter, Hiroshima University, 1-3-1Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshima
Hydrogen desorption properties of Ca-N-H system Satoshi Hino, *Takayuki Ichikawa, Haiyan Leng and Hironobu Fujii Graduate School of Advanced Sciences of Matter, Hiroshima University, 1-3-1Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshima
Synthesis of borosilicate MFI type zeolite using different aging techniques
 Chem. Met. Alloys 3 (2010) 12-17 Ivan Franko National University of Lviv www.chemetal-journal.org Synthesis of borosilicate MFI type zeolite using different aging techniques Maryam ABRISHAMKAR 1, Seyed
Chem. Met. Alloys 3 (2010) 12-17 Ivan Franko National University of Lviv www.chemetal-journal.org Synthesis of borosilicate MFI type zeolite using different aging techniques Maryam ABRISHAMKAR 1, Seyed
One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor
 Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-, and MTMS-Modified Particles
 Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers
 Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Eco-Compatible Continuous Halogenation of Aromatics
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Eco-Compatible Continuous Halogenation of Aromatics P. Losch, a J. F. Kolb, a A. Astafan,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Eco-Compatible Continuous Halogenation of Aromatics P. Losch, a J. F. Kolb, a A. Astafan,
Supporting Information. Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-101(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid
 Supporting Information Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-11(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid Kunyue Leng a, Yinyong Sun a *, Xiaolin Li a, Shun Sun a, Wei Xu b a
Supporting Information Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-11(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid Kunyue Leng a, Yinyong Sun a *, Xiaolin Li a, Shun Sun a, Wei Xu b a
Supporting Information for:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
Synthesis of Zeolites via Interzeolite Transformations without Organic Structure-Directing Agents
 pubs.acs.org/cm Synthesis of Zeolites via Interzeolite Transformations without Organic Structure-Directing Agents Sarika Goel, Stacey I. Zones,*, and Enrique Iglesia* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
pubs.acs.org/cm Synthesis of Zeolites via Interzeolite Transformations without Organic Structure-Directing Agents Sarika Goel, Stacey I. Zones,*, and Enrique Iglesia* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Synthesis of zeolite beta in fluoride media under microwave irradiation
 Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 68 (2004) 77 82 www.elsevier.com/locate/micromeso Synthesis of zeolite beta in fluoride media under microwave irradiation Dae Sung Kim a, Jong-San Chang a, *, Jin-Soo
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 68 (2004) 77 82 www.elsevier.com/locate/micromeso Synthesis of zeolite beta in fluoride media under microwave irradiation Dae Sung Kim a, Jong-San Chang a, *, Jin-Soo
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) From metal-organic framework to hierarchical high surface-area hollow octahedral carbon cages
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) From metal-organic framework to hierarchical high surface-area
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) From metal-organic framework to hierarchical high surface-area
Supporting Information for. Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin
 Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
Electronic Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supporting Information Thermo-responsive white-light emission based on tetraphenylethylene-
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supporting Information Thermo-responsive white-light emission based on tetraphenylethylene-
One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation
 S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
CIT-9: a fault-free, gmelinite zeolite Supporting Information
 CIT-9: a fault-free, gmelinite zeolite Supporting Information 1. Synthesis and treatments 2. Characterization 3. Supporting Data and Figures 4. References 1. Synthesis and treatments 1.1 Synthesis and
CIT-9: a fault-free, gmelinite zeolite Supporting Information 1. Synthesis and treatments 2. Characterization 3. Supporting Data and Figures 4. References 1. Synthesis and treatments 1.1 Synthesis and
Supporting Information. For. Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver
 Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
Cu 2 graphene oxide composite for removal of contaminants from water and supercapacitor
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Cu 2 O@reduced graphene oxide composite for removal of contaminants from water and supercapacitor Baojun Li, a Huaqiang Cao,* a Gui Yin, b Yuexiang Lu, a
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Cu 2 O@reduced graphene oxide composite for removal of contaminants from water and supercapacitor Baojun Li, a Huaqiang Cao,* a Gui Yin, b Yuexiang Lu, a
Shape Assisted Fabrication of Fluorescent Cages of Squarate based Metal-Organic Coordination Frameworks
 Supporting Information Shape Assisted Fabrication of Fluorescent Cages of Squarate based Metal-Organic Coordination Frameworks Kolleboyina Jayaramulu, a Katla Sai Krishna, a Subi J. George, b Muthuswamy
Supporting Information Shape Assisted Fabrication of Fluorescent Cages of Squarate based Metal-Organic Coordination Frameworks Kolleboyina Jayaramulu, a Katla Sai Krishna, a Subi J. George, b Muthuswamy
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Supporting Information. for. Synthesis and Catalytic Behavior of Ferrierite Zeolite Nanoneedles
 Supporting Information for Synthesis and Catalytic Behavior of Ferrierite Zeolite Nanoneedles Yoorim Lee, Min Bum Park, Pyung Soon Kim, Aurélie Vicente, Christian Fernandez, In-Sik Nam, and Suk Bong Hong,*
Supporting Information for Synthesis and Catalytic Behavior of Ferrierite Zeolite Nanoneedles Yoorim Lee, Min Bum Park, Pyung Soon Kim, Aurélie Vicente, Christian Fernandez, In-Sik Nam, and Suk Bong Hong,*
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information AgPd@Pd/TiO 2 nanocatalyst synthesis by microwave
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information AgPd@Pd/TiO 2 nanocatalyst synthesis by microwave
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals
 Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
Controlling the Isolation and Pairing of Aluminum in Chabazite Zeolites Using Mixtures of Organic and Inorganic Structure-Directing Agents
 Controlling the Isolation and Pairing of Aluminum in Chabazite Zeolites Using Mixtures of Organic and Inorganic Structure-Directing Agents John R. Di Iorio, Rajamani Gounder * SUPPORTING INFORMATION Section
Controlling the Isolation and Pairing of Aluminum in Chabazite Zeolites Using Mixtures of Organic and Inorganic Structure-Directing Agents John R. Di Iorio, Rajamani Gounder * SUPPORTING INFORMATION Section
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
Synthesis of Highly Concentrated Ag Nanoparticles in a Heterogeneous Solid-Liquid System under Ultrasonic Irradiation
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 10 (2010) pp. 1764 to 1768 Special Issue on Lead-Free and Advanced Interconnection Materials for Electronics #2010 The Japan Institute of Metals Synthesis of Highly
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 10 (2010) pp. 1764 to 1768 Special Issue on Lead-Free and Advanced Interconnection Materials for Electronics #2010 The Japan Institute of Metals Synthesis of Highly
MCM-41 Ordered Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Synthesis and Characterization
 Materials Research, Vol. 2, No. 3, 173-179, 1999. 1999 MCM-41 Ordered Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Synthesis and Characterization Rogério A.A. Melo a, Marcus V. Giotto a, João Rocha b, Ernesto A. Urquieta-González
Materials Research, Vol. 2, No. 3, 173-179, 1999. 1999 MCM-41 Ordered Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Synthesis and Characterization Rogério A.A. Melo a, Marcus V. Giotto a, João Rocha b, Ernesto A. Urquieta-González
Plasma driven ammonia decomposition on Fe-catalyst: eliminating surface nitrogen poisoning
 Supporting Information for Plasma driven ammonia decomposition on Fe-catalyst: eliminating surface nitrogen poisoning Contents: 1. Scheme of the DBD plasma-driven catalysis reactor, Scheme S1. 2. XRF analysis
Supporting Information for Plasma driven ammonia decomposition on Fe-catalyst: eliminating surface nitrogen poisoning Contents: 1. Scheme of the DBD plasma-driven catalysis reactor, Scheme S1. 2. XRF analysis
MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS
 Inorganic Syntheses, Volume 30 Edited by Donald W. Murphy, Leonard V. Interrante Copyright 1995 by Inorganic Syntheses, Inc. Chapter Six MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS 43. ZEOLITE MOLECULAR SIEVES
Inorganic Syntheses, Volume 30 Edited by Donald W. Murphy, Leonard V. Interrante Copyright 1995 by Inorganic Syntheses, Inc. Chapter Six MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS 43. ZEOLITE MOLECULAR SIEVES
Synthesis of Zeolite A Membrane from Rice Husk Ash
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.79-83, 2009 Chayakorn BHAVORNTHANAYOD and Pesak RUNGROJCHAIPON * Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.79-83, 2009 Chayakorn BHAVORNTHANAYOD and Pesak RUNGROJCHAIPON * Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment
 Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Hydrophobic fluorinated TiO2 ZrO2 as catalyst in epoxidation of 1-octene with aqueous hydrogen peroxide
 University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur August, 2006 Hydrophobic fluorinated TiO2 ZrO2 as catalyst in epoxidation of 1-octene with aqueous hydrogen peroxide Hadi Nur, Universiti
University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur August, 2006 Hydrophobic fluorinated TiO2 ZrO2 as catalyst in epoxidation of 1-octene with aqueous hydrogen peroxide Hadi Nur, Universiti
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Insights into CO 2 and CH 4 Adsorption by Pristine and Aromatic Amine- Modified Periodic Mesoporous Phenylene-Silicas Mirtha A. O. Lourenço, a Christophe Siquet, b,* João Santos,
Supporting Information Insights into CO 2 and CH 4 Adsorption by Pristine and Aromatic Amine- Modified Periodic Mesoporous Phenylene-Silicas Mirtha A. O. Lourenço, a Christophe Siquet, b,* João Santos,
Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation
 Supporting Information for Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min, Wei Zhu, Hao-Shuai Wu, Ya-Wen Zhang* and Chun-Hua
Supporting Information for Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min, Wei Zhu, Hao-Shuai Wu, Ya-Wen Zhang* and Chun-Hua
