2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic Analysis
|
|
|
- Conrad Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 146 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 60, (3), (2017) [Regular Paper] 2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic Analysis Gaku WATANABE Yuta NAKASAKA and Takao MASUDA Research Gr. of Chemical Engineering, Div. of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University, N13 W8, Kita-ku, Sapporo , JAPAN (Received December 12, 2016) Aluminosilicate and ferrisilicate with the MTW-type zeolite structure were hydrothermally prepared and used to catalyze the methylation of 2-methylnaphthalene (2-MN) under supercritical conditions in a batch-type reactor. Dimethylnaphthalene (DMN) and 1-methylnaphthalene (1-MN) yields increased with decreasing Si/Al ratio of the zeolite. In contrast, ferrisilicate with the MTW-type zeolite structure (Si/Fe 100) exhibited higher DMN selectivity and the β,β-dmn fraction in total DMNs was higher than that over aluminosilicate with MTW structure (Si/ Al 100). Kinetic analysis of 2-MN methylation over MTW zeolites was conducted, to obtain the reaction rate constants and apparent activation energies. The activation energy for the methylation of 2-MN over aluminosilicate with MTW structure was 176 kj mol 1, which was almost the same as that for the ferrisilicate with MTW structure. This indicates that the mechanism for methylation is independent of hetero-atoms species in the MTW zeolite framework. The introduction of Fe atoms into the framework significantly decreased the rate constant for the isomerization of 2-MN compared with that for the methylation of 2-MN. Therefore, ferrisilicate with MTW structure is effective for 2-MN methylation due to the decrease of the isomerization rate. Keywords Kinetic analysis, Methylation, MTW-type zeolite catalyst, 2-Methylnaphthalene, Ferrisilicate 1. Introduction 2,6-Dimethylnaphthalene (2,6-DMN) is an important substance as an intermediate of in the production polyethylenenaphthalate (PEN), which possesses superior properties such as gas impermeability and heat resistance to those of polyethyleneterephthalate (PET). However, 2,6-DMN is commercially produced from o-xylene and butadiene in a multistep reaction process using an alkali metal catalyst and a large quantity of organic solvent 1). DMN has 10 different isomers; β,β- DMN (2,6-DMN, 2,7-DMN and 2,3-DMN), α,β- DMN (1,2-DMN, 1,3-DMN, 1,6-DMN and 1,7-DMN) and α,α-dmn (1,4-DMN, 1,5-DMN and 1,8-DMN). The boiling points of these DMN isomers are close to each other 2),3) ; therefore, separation of the isomers requires a large amount of energy. Furthermore, the separation of 2,6- and 2,7-DMN is difficult because the difference in their boiling points is only 0.3, and they form eutectic crystals when the 2,6-DMN/2,7- DMN ratio is 0.7 4). To decrease the number of reaction steps and energy consumption thus requires the DOI: doi.org/ /jpi To whom correspondence should be addressed. nakasaka@eng.hokudai.ac.jp development of an alternative process for the selective production of 2,6-DMN, and catalysis over zeolites has received much attention for the production of 2,6- DMN. Zeolite, a crystalline aluminosilicate, has strong acid sites, high surface area and micropores close in size to the molecular diameter of hydrocarbons, which can enable shape-selectivity for specific molecules. Various medium- and large-pore zeolites have been applied for 2,6-DMN synthesis by the methylation of naphthalene or 2-methylnaphthalene (2-MN) 5) 8). Although MFItype zeolite that possesses smaller pores than the molecular size of 2,6-DMN exhibits high β,β-dmn selectivity, conversion of the feedstock is low due to high diffusion resistance. In contrast, MTW-type zeolite possesses pores close in size to β,β-dmn molecules; therefore, MTW-type zeolite are considered to have an advantage for the production of β,β-dmn. In addition, during the methylation of 2-MN over zeolite in the vapor phase, coke formed on the zeolite crystal leads to fast deactivation of the zeolite due to pore blocking. MTW-type zeolite (Si/Al 100) with different crystal sizes was previously applied for 2-MN methylation under supercritical conditions, and deactivation by coke formation was successfully suppressed. Moreover, kinetic analysis of the methylation (DMN formation)
2 147 and isomerization (1-MN formation) of 2-MN have been achieved 9). Isomorphous substitution of Al in the zeolite framework by Fe to form a ferrisilicate can weaken the acidity of the zeolite 8),10) 12), and it has been reported that ferrisilicate with MFI-type zeolite structure enhances selectivity toward β,β-dmn as the product 8). The conversion and selectivity of 2-MN methylation is considered to be strongly affected by the relationship between the methylation and isomerization rates over the zeolite catalyst. Accordingly, the present study is focused on the effect of the amount of acid sites and isomorphous substitution of Al by Fe in the MTW-type structure on the 2-MN methylation and isomerization rates. To clarify these factors, nano-sized MTW-type zeolite with various Si/Al ratios (Si/Al 50, 100, 200, here after Al-MTW) and nano-sized ferrisilicate with MTW-type zeolite structure (Si/Fe 100, here after Fe- MTW) were hydrothermally prepared and applied for 2-MN methylation under supercritical conditions. 2. Experimental Synthesis of Al- and Fe-MTW Zeolites Al- and Fe-MTW were prepared by conventional hydrothermal synthesis. Colloidal silica (Sigma-Aldrich, Co., LLC.), sodium aluminates (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) or iron (III) nitrate monohydrate (Fe source, Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) and sodium hydroxide (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) were used as sources of Si, Al (for Al-MTW), Fe (for Fe-MTW) and alkali, respectively. Tetraethylammonium bromide (TEABr, Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was used as organic structure directing agent (OSDA) 13). The reaction gel composition was Na2O : OSDA : SiO2 : T2O3 : H2O 10 : 60 : 100 : x : 5555, where x 0.25 to 1.0 and T Al or Fe. The resulting solution was sonically agitated for 1 h, poured into a Teflon-sealed stainless steel bottle and then heated at 423 K for 6 days. The precipitates obtained were washed with alcohol, dried at 383 K for 12 h, and calcined at 823 K for 12 h in an air stream to remove OSDA molecules and other adsorbed hydrocarbons. The white powders obtained were treated with NH4 ions (10 % NH4NO3 aqueous solution) at 343 K for 9 h to exchange sodium ions on the acid sites for ammonium ions. The resultant powdered zeolites were pelletized, crushed and sieved to yield samples with particles diameters of ca. 0.4 mm. Details concerning the preparation of Al-MTW and Fe-MTW have been described previously 13) Characterization of Al- and Fe-MTW Zeolites The morphology and crystallinity of the obtained samples were analyzed using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM; JSM-6500F, JEOL Ltd.) and X-ray diffraction (XRD; Ultima IV, Rigaku Fig. 1 Experimental Setup of Batch-type Reactor Corp.), respectively. Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface areas, external surface areas and micropore volumes for the obtained samples were calculated using the BET and t-plot methods, respectively, based on nitrogen adsorption isotherms obtained (BELsorp mini, MicrotracBEL Corp.). The Si/T (T Al or Fe) ratios for the samples were measured using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF; supermini, Rigaku Corp.). The acidity and amount of acid sites the samples was evaluated from ac-nh3-temperature programmed desorption (TPD) profile measurements 14) Methylation of 2-MN over MTW-type Zeolites with Different Acid Properties The methylation of 2-MN over a zeolite catalyst was performed out using a batch-type reactor with a volume of m 3 under high-pressure as shown in Fig. 1. Prior to the reaction, the catalyst (NH4 form) was activated by calcination at 823 K under an air stream for 1 h. A mixture of 2-MN and methanol (2-MN : methanol molar ratio 0.1) with a volume of m 3 and 0.5 g of Al-MTW or 1.0 g of Fe-MTW were placed in the reactor. The reactions were conducted at reaction temperatures in the range of K and maintained for min after the reaction temperature was reached. The pressure in the reactor was 25 MPa, which was monitored with a pressure gauge. Details concerning the experimental procedure have been described previously reported 9). 3. Results and Discussion Characterization of Al- and Fe-MTW Zeolites Figure 2 shows XRD patterns for the samples obtained with various Si/T ratios. The patterns showed
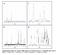
3 148 peaks corresponding to the MTW-type zeolite phase and no other phases were observed. The crystallite sizes of the MTW-type zeolite determined from the XRD peaks and the Scherrer equation were nm. Fig. 2 XRD Patterns for (a) Al-MTW (Si/Al 50), (b) Al-MTW (Si/ Al 100), (c) Al-MTW (Si/Al 200), and (d) Fe-MTW (Si/ Fe 100) Figure 3 shows FE-SEM images of the obtained samples. Secondary particle aggregates with sizes in the range of nm were formed from primary particles with sizes of approximately nm. Table 1 summarizes the BET surface area (SBET), external surface area (SEXT) and micropore volume (Vm) for the zeolites obtained from nitrogen desorption isotherms, and the Si/T ratio determined from XRF measurements. SBET, SEXT and Vm for all the zeolites were similar, and were equivalent to those previously reported 15),16). Si/ T ratios for the zeolites measured by XRF were almost the same as those calculated from the Si and T concentrations in the synthesis solutions. Figure 4 shows ac-nh3-tpd profiles for the Al- MTW and Fe-MTW. Peaks observed above 600 K for Al-MTW and above 550 K for Fe-MTW are associated with desorption of NH3 adsorbed on the strong acid sites, which indicates that Al and Fe are present in the MTW-type zeolite frameworks. In contrast, peaks observed below these temperatures were assigned to the desorption of NH3 weakly held adsorbed or physisorbed on the zeolite surfaces. It was confirmed that NH3 was desorbed from the strong acid sites of Fe-MTW at lower temperature than Al-MTW, which is consistent with our previous report 13). The amounts of strong acid sites estimated from the peak areas of the ac-nh3-tpd profiles are also listed in Table 1. The acid sites on Fig. 3 FE-SEM Micrographs of (a) Al-MTW (Si/Al 50), (b) Al- MTW (Si/Al 100), (c) Al-MTW (Si/Al 200), and (d) Fe- MTW (Si/Fe 100) Fig. 4 ac-nh 3 -TPD Profiles for Al-MTW (Si/Al 50, 100 and 200) and Fe-MTW (Si/Fe 100) Table 1 Micropore Volume, BET Surface Area, External Surface Area, Si/T Ratio, and Amount of Acid Sites for the Al-MTW and Fe-MTW Zeolites Sample V m [cm 3 g 1 ] S BET [m 2 g 1 ] S EXT [m 2 g 1 ] Si/T ratio [-] Amount of acid sites [mmol g 1 ] Al-MTW (50) Al-MTW (100) Al-MTW (200) Fe-MTW (100) V m : micropore volume by the t-plot method; S BET : BET surface area by the BET method; S EXT : external surface area by the t-plot method.
4 149 Reaction conditions: T 583 K, pressure 25 MPa, time min, catalyst weight 0.5 g (for Al- MTW) or 1.0 g (for Fe-MTW). Fig. 5 Effect of Amounts of Acid Sites and Isomorphous Substitution of Al by Fe in the MTW-type Zeolite Framework on (a) the Product Yield and (b) DMN Isomer Fraction, 2,6-DMN/2,7-DMN Ratio and 2,6-DMN/1,6-DMN Ratio; circles: 2,6-DMN/2,7-DMN ratio, triangles: 2,6-DMN/1,6- DMN ratio Al-MTW decreased with increasing Si/Al ratio. In addition, the amount of acid site amount for Al-MTW with a Si/Al ratio of 100 was almost the same as that for Fe-MTW with a Si/Fe ratio of 100. Moreover, the Si/T ratios estimated from the TPD profiles were close to those determined from XRF measurements Methylation of 2-MN over MTW Zeolites with Different Acid Properties To investigate the effect of the amount of acid sites on the product yield, the DMN isomer fractions and the amount of coke formed over the MTW-type zeolites, 2-MN methylation over nano-sized Al-MTW with various Si/Al ratios were conducted at a reaction temperature of 583 K. Figure 5(a) shows the product yields of DMN and 1-MN. Trimethylnaphthalene, which can be formed by the methylation of DMN, was not formed during the reaction. The yield of DMN formed by methylation of 2-MN and the yield of 1-MN formed by isomerization of 2-MN increased with the amount of acid sites on Al-MTW. Figure 5(b) shows the DMN isomer fractions in the product DMNs. β,β- and α,β- DMN were formed by the methylation of 2-MN, whereas α,α-dmn, which may form by the methylation of 1-MN and/or isomerization of other DMNs, was not formed, regardless of the Si/Al ratio in Al-MTW. The fraction of β,β-dmn in the product DMNs was 40 mol%, which was higher than that for thermo dynamic equilibrium (35-37 mol%) 4), regardless of the amount of acid sites. In contrast, the fraction of β,β-dmn in the product DMNs slightly decreased with increasing amount of acid sites. The isomerization of 2,6-DMN into 1,6-DMN can easily occur on acid sites because the isomerization of DMN proceeds predominantly between the β-position and α-position 12),17). Millini and Perego reported that the energy barrier for α,β-dmn formation within the pores of MTW-type zeolite and it was assumed that it is quite difficult for α,β-dmn to diffuse inside the pores 3). Therefore, it is considered that the β,β-dmn produced isomerizes into α,β-dmn on the outer surface of the zeolite because the 2,6-DMN/1,6-DMN ratio decreased over Al-MTW with higher a Si/Al ratio, as shown in Fig. 5(b). The methylation of 2-MN over Fe-MTW was also performed to investigate the effect of different heteroatoms in the zeolites framework. Fe-MTW had lower 2-MN conversion than Al-MTW (100) with the same catalyst loading in the reactor; therefore, twice the weight of Fe-MTW (100) was used for methylation to obtain almost the same 2-MN conversion with Al-MTW (100). Although the 2-MN conversions were similar, Fe-MTW (100) exhibited higher DMN selectivity than Al-MTW (100), which indicates 1-MN formation by isomerization of 2-MN could be suppressed and methylation of 2-MN became the preferred reaction. In addition, Fe-MTW (100) resulted in a higher β,β-dmn fraction ( 50 mol%) in the product DMNs than that over Al-MTW (100). It is known that isomerization activity over zeolite depends on the acid strength 4) 8),18). For this reason, it is considered that isomerizations of reactant/products on the outer surface are suppressed because isomerization activity over Fe-MTW is lower than that over Al-MTW. Therefore, it is considered that the isomerization of β,β-dmn into α,β-dmn over
5 150 Fe-MTW(100) is also suppressed as with Al-MTW(100). Furthermore, the 2,6-DMN/2,7-DMN ratio in the DMNs produced over Fe-MTW(100) was 2.0, which is higher than that obtained over Al-MTW. Komatsu et al. reported that the 2,6-DMN/2,7-DMN ratio in DMNs produced over Fe-MFI was also higher than that over Al-MFI 8). It is thus considered that isomorphous substitution of Al by Fe in the zeolite framework contributes to an increase in the 2,6-DMN/2,7-DMN ratio. The amount of coke loaded on the zeolite after the reaction was 1.5, 1.1, 0.6 and 0.9 wt% for Al-MTW (50), Al-MTW (100), Al-MTW (200) and Fe-MTW (100), respectively. These amounts were much lower than those reported under atmospheric reaction conditions ( wt%) 18). The amount of coke loaded on the zeolite increased due to an increase in the amount of acid sites on Al-MTW, which resulted in an increase in 2-MN conversion. In contrast, it seems that the effect of different heteroatoms on coke loading was small Kinetic Analysis of 2-MN Methylation over Al- and Fe-MTW Zeolites Because conversion of 1-MN methylation was quite lower than that of 2-MN methylation, it is considered that 2-MN methylation and the isomerization of 2-MN occurred as parallel reactions 9). Assuming that methylation and isomerization of 2-MN are first-order reactions with respect to the 2-MN concentration, the reaction rates can be expressed as follows: Rate of DMN formation r DMN = k 1 C 2 -MN (1) Rate of 1-MN formation r = k C -MN (2) 1-MN 2 2 where rdmn and r1-mn are the rates (mol kg 1 s 1 ) for methylation and isomerization of 2-MN, respectively. C2-MN is the concentration of 2-MN (mol m 3 ), and k1 and k2 are the apparent rate constants (m 3 kg 1 s 1 ) for the methylation and isomerization of 2-MN, respectively. From Eqs. (1) and (2), the consumption rate of 2-MN in the overall conversion is expected to be: ( ) r = k + k C 2-MN MN (3) By integrating Eq. (3), C2-MN, 0 W ln ( k1 k2) C = + V t (4) 2-MN where C 2-MN,0 is the initial 2-MN concentration (mol m 3 ), W is the catalyst weight (kg), and V is the volume of reactant (m 3 ). In addition, Eq. (5) was obtained from Eqs. (1) and (3). C C C C 2-MN, 0 2-MN DMN DMN, 0 k = + k k (5) The methylation of 2-MN over both Al-MTW and Fe-MTW was conducted in the temperature range from 523 to 583 K. Figure 6 shows the change in ln (C 2-MN,0/C2-MN) with the reaction time, t. Proportional relationships between ln (C2-MN,0/C2-MN) and reaction time were obtained for both catalysis. This indicates that the effect of coke formation on the kinetics was negligibly small under the reaction conditions. The slope in Fig. 6 indicates (k1 k2)w/v; therefore, the rate constant for methylation (k1) and isomerization (k2) could be calculated using the slope and Eq. (5). Figure 7 shows Arrhenius plots of the rate constants for methylation and isomerization of 2-MN over Al- MTW and Fe-MTW. The rate constants for both 2-MN isomerization and 2-MN methylation over Al- MTW zeolites increased with Al content in the zeolites. In contrast, the apparent activation energies for 2-MN methylation and 2-MN isomerization were 176 kj mol 1 and 26 kj mol 1, respectively, regardless of the Si/Al ratio in Al-MTW. The apparent activation energy generally becomes half that of the intrinsic activation energy when the reaction is conducted under diffusion-limiting condition 19), and it has found that 2-MN methylation over macro-sized Al-MTW has been reported to be approximately half of that over nano-sized Al-MTW due to the effect of diffusion 9). Although the rate constant for methylation is enhanced by a decrease in the Si/Al ratio, the apparent activation energy has the same value, regardless of the Si/Al ratio, which indicates that methylation proceeds under reaction-limiting condition, regardless of the Si/Al ratio in the zeolite. Conversely, the Si/Al ratio on the outer surface of the zeolite is considered to affect the rate constant for isomerization because isomerization mainly occurs on the outer surface of the zeolite 9). Although the activation energies for 2-MN methylation and 2-MN isomerization over Fe- MTW were also 176 kj mol 1 and 26 kj mol 1, respectively, the rate constant for methylation was the same while that for isomerization was lower value than over Al-MTW (100). This result indicates that the isomorphous substitution of Al by Fe in the MTW-type zeolite framework maintains the rate of methylation, while the rate of isomerization is decreased. Figure 8 shows the relationship between 2-MN conversion and the β,β-dmn yield over the Al-MTW and Fe-MTW zeolites. The linear relationship between the β,β-dmn yield and 2-MN conversion for Al-MTW indicated that the β,β-dmn yield is almost the same 2-MN conversions, regardless of the Si/Al ratio and reaction temperature. The β,β-dmn yield obtained by 2-MN methylation over Fe-MTW was higher than that over Al-MTW for each 2-MN conversion. The isomerization rate was selectively decreased by the isomorphous substitution of Al by Fe in the MTW-type zeolite framework; therefore, it is considered that the isomerization of β,β-dmn into α,β-dmn is also suppressed, which leads to a higher β,β-dmn yield than
6 151 Reaction conditions: T K, time min. Fig. 6 Relationship between ln (C 2-MN,0 /C 2-MN ) and Reaction Time t, in the Methylation of 2-MN over Al-MTW (Si/Al 50, 100 and 200) and Fe-MTW (Si/Fe 100) that with Al-MTW. 4. Conclusion Methylation of 2-MN with methanol over Al-MTW (Si/Al 50, 100 and 200) and Fe-MTW (Si/Fe 100) was performed at reaction temperatures in the range of 523 to 583 K under high-pressure reaction conditions. Kinetic analysis for 2-MN methylation over these MTW-type zeolites indicated the activation energies for the methylation and isomerization of 2-MN were almost the same for all the catalysis, regardless of the acid properties (Si/Al ratio and acid strength). The mechanism for the methylation and isomerization of 2-MN on acid sites was thus determined to be independent of the acid properties of the zeolites. Conversely, the rate constants for methylation and isomerization of 2-MN increased over Al-MTW with decreasing Si/Al ratio, which led to an increase in the yield of DMN and 1-MN. In contrast, the rate constant for methylation over Fe- MTW was the same value while that for isomerization was lower than that with Al-MTW (Si/Al 100), which indicates that the isomorphous substitution of Al by Fe in the MTW structure maintains the methylation rate and decreases the isomerization rate. For this reason, the DMN selectivity and β,β-dmn fraction in the DMNs produced with Fe-MTW (100) was higher than those with Al-MTW (100). Acknowledgment A part of work was supported by the Grant for Research of The Japan Petroleum Institute. A part of this work was conducted at Hokkaido University, supported by Nanotechnology Platform Program of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan. References 1) Lillwitz, L. D., Appl. Catal. A: General, 221, 337 (2001). 2) Bobuatong, K., Probst, M., Limtrakul, J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 114, (2010). 3) Milini, R., Perego, C., Top. Catal., 217, 298 (2003). 4) Fraenkel, D., Cherniavsky, M., Ittah, B., Levy, M., J. Catal., 101, 273 (1986). 5) Klein, H., Fuessa, H., Ernst, S., Weitkamp, J., Microporous Mater., 3, 291 (1994).
7 152 Reaction conditions: T K, time min. Reaction conditions: T K, time min. Fig. 7 Arrhenius Plots of Rate Constants for the Methylation and Isomerization of 2-MN over Al-MTW (Si/Al 50, 100 and 200) and Fe-MTW (Si/Fe 100) 6) Park, N. J., Wang, J., Hong, I. S., Lee, W. C., Appl. Catal. A: General, 292, 68 (2005). 7) Weitkamp, J., Neuber, M., Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., 60, 291 (1991). 8) Komatsu, T., Araki, Y., Namba, S., Yashima, T., Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., 84, 1821 (1994). 9) Watanabe, G., Nakasaka, Y., Taniguchi, T., Yoshikawa, T., Tago, T., Masuda, T., Chem. Eng. J., 312, 288 (2017). 10) Kim, J. H., Namba, S., Yashima, T., Appl. Zeolites, 100, 27 (1991). 11) Kumar, R., Thangaraj, A., Bhaut, N. R., Ratnasamy, P., Zeolites, 10, 85 (1990). Fig. 8 Relationship between the β,β-dmn Yield and 2-MN Conversion for 2-MN Methylation over Al-MTW (Si/Al 50, 100 and 200) and Fe-MTW (Si/Fe 100) 12) Ahmed, S., J. Porous Mater., 19, 111 (2012). 13) Taniguchi, T., Nakasaka, Y., Yoneta, K., Tago, T., Masuda, T., Catal. Lett., 146, 666 (2016). 14) Masuda, T., Fujikata, Y., Mukai, R. S., Hashimoto, K., Appl. Catal. A: General, 165, 57 (1997). 15) Gil, B., Mokrzycki, L., Sulikowski, B., Olejniczak, Z., Walas, S., Catal. Today, 152, 24 (2010). 16) Wei, X., Panagiotis, P., Smirniotis, G., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 89, 170 (2006). 17) Suld, G., Stuart, P. A., J. Org. Chem., 29, 2939 (1964). 18) Pu, B. S., Inui, T., Appl. Catal. A: General, 146, 305 (1996). 19) Fogler, S. H., Element of Chemical Reaction Engineering, 4th ed., Prentice Hall, New Jersey (2013).
8 153 MTW MTW 2-2-MN 176 kj mol 1 26 kj mol 1 Si/Al Al Si/Al 100 Si/Fe 100 DMN β,β-dmn
Title. Author(s)Tago, Teruoki; Konno, Hiroki; Sakamoto, Mariko; Naka. CitationApplied Catalysis A: General, 403(1-2): Issue Date
 Title Selective synthesis for light olefins from acetone o Author(s)Tago, Teruoki; Konno, Hiroki; Sakamoto, Mariko; Naka CitationApplied Catalysis A: General, 403(1-2): 183-191 Issue Date 2011-08-22 Doc
Title Selective synthesis for light olefins from acetone o Author(s)Tago, Teruoki; Konno, Hiroki; Sakamoto, Mariko; Naka CitationApplied Catalysis A: General, 403(1-2): 183-191 Issue Date 2011-08-22 Doc
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method
 Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Synthesis of Zeolite Monolith with Hierarchical Micro/Macropores by Ice-Templating and Steam-Assisted Crystallization
 A publication of 259 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 259 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins
 Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Alkylation of Isobutane by 1-Butene over H-beta Zeolite in CSTR (Part 3) Effect of Property of H-beta Zeolite
 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 56, (5), 349-355 (2013) 349 [Technical Report] Alkylation of Isobutane by 1-Butene over H-beta Zeolite in CSTR (Part 3) Effect of Property of H-beta Zeolite Yuki
Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 56, (5), 349-355 (2013) 349 [Technical Report] Alkylation of Isobutane by 1-Butene over H-beta Zeolite in CSTR (Part 3) Effect of Property of H-beta Zeolite Yuki
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Accepted Manuscript. Kinetics of n-hexane Cracking over ZSM-5 Zeolites Effect of Crystal Size on Effectiveness Factor and Catalyst Lifetime-
 Accepted Manuscript Kinetics of n-hexane Cracking over ZSM- Zeolites Effect of Crystal Size on Effectiveness Factor and Catalyst Lifetime- Hiroki Konno, Takuya Okamura, Takahito Kawahara, Yuta Nakasaka,
Accepted Manuscript Kinetics of n-hexane Cracking over ZSM- Zeolites Effect of Crystal Size on Effectiveness Factor and Catalyst Lifetime- Hiroki Konno, Takuya Okamura, Takahito Kawahara, Yuta Nakasaka,
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Cyclic Molecule Aerogels: A Robust Cyclodextrin
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Cyclic Molecule Aerogels: A Robust Cyclodextrin
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts
 Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation
 S1 ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation Masato M. Maitani a *, Zhan Conghong a,b, Dai Mochizuki
S1 ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation Masato M. Maitani a *, Zhan Conghong a,b, Dai Mochizuki
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
RKCL4616. CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF HZSM-12 ZEOLITE IN n-heptane CATALYTIC CRACKING
 Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 84, No. 2, 287-293 and Springer, Dordrecht (2005) RKCL4616 CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF HZSM-12 ZEOLITE IN n-heptane CATALYTIC CRACKING
Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 84, No. 2, 287-293 and Springer, Dordrecht (2005) RKCL4616 CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF HZSM-12 ZEOLITE IN n-heptane CATALYTIC CRACKING
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Supplementary Information. Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS
 CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
Title. CitationCatalysis science & technology, 4(12): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information.
 Title Kinetics of the catalytic cracking of naphtha over Z naphthenes Author(s)Konno, Hiroki; Ohnaka, Ryota; Nishimura, Jun-ichi; T CitationCatalysis science & technology, 4(12): 4265-4273 Issue Date 2014-12-01
Title Kinetics of the catalytic cracking of naphtha over Z naphthenes Author(s)Konno, Hiroki; Ohnaka, Ryota; Nishimura, Jun-ichi; T CitationCatalysis science & technology, 4(12): 4265-4273 Issue Date 2014-12-01
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment
 Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres
 Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres Seong-Ick Kim, Takuji Yamamoto, Akira Endo, Takao Ohmori, and Masaru Nakaiwa
Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres Seong-Ick Kim, Takuji Yamamoto, Akira Endo, Takao Ohmori, and Masaru Nakaiwa
Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
to Increase Amount of Dimethylnaphthalenes using
 Methylation of Coal Tar Naphthalene Oil Fractions to Increase Amount of Dimethylnaphthalenes using Au-Beta Zeolite Catalysts Fatih Güleç, Aysun Özen, Ali Karaduman Ankara University, Engineering Faculty,
Methylation of Coal Tar Naphthalene Oil Fractions to Increase Amount of Dimethylnaphthalenes using Au-Beta Zeolite Catalysts Fatih Güleç, Aysun Özen, Ali Karaduman Ankara University, Engineering Faculty,
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Synthesis and Application of Hexagonal Perovskite BaNiO 3 with Quadrivalent
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Synthesis and Application of Hexagonal Perovskite BaNiO 3 with Quadrivalent
Catalytic activity of the beta zeolite with enhanced textural properties in the Friedel-Crafts acylation of aromatic compounds
 Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance
 Supporting Information Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance Javier García-Martínez,* Marvin Johnson, Julia Valla, Kunhao Li, and Jackie Y. Ying*
Supporting Information Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance Javier García-Martínez,* Marvin Johnson, Julia Valla, Kunhao Li, and Jackie Y. Ying*
Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of Benzene and Toluene with Hydrogen Peroxide in a Bubble Reactor
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Framework and Extraframework Tin Sites in Zeolite Beta React Glucose Differently
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Framework and Extraframework Tin Sites in Zeolite Beta React Glucose Differently Ricardo Bermejo-Deval, Rajamani Gounder and Mark E. Davis* Chemical Engineering, California Institute
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Framework and Extraframework Tin Sites in Zeolite Beta React Glucose Differently Ricardo Bermejo-Deval, Rajamani Gounder and Mark E. Davis* Chemical Engineering, California Institute
Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials
 Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION. Keywords: Ethylene oxide, Partial oxidation, Ethane epoxidation, Second metal.
 DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite
 Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Supporting Information. for. Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under. Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via
 Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Supporting Information. High-Performance Supercapacitor
 Supporting Information Mesoporous CoO Nanocubes @ Continuous 3D Porous Carbon Skeleton of Rose Based Electrode for High-Performance Supercapacitor Danni Lan, Yangyang Chen, Pan Chen, Xuanying Chen, Xu
Supporting Information Mesoporous CoO Nanocubes @ Continuous 3D Porous Carbon Skeleton of Rose Based Electrode for High-Performance Supercapacitor Danni Lan, Yangyang Chen, Pan Chen, Xuanying Chen, Xu
Catalytic Oxidation of Benzene with Ozone Over Nanoporous Mn/MCM-48 Catalyst
 Copyright 12 American Scientific Publishers All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Vol. 12, 5942 5946, 12 Catalytic Oxidation of Benzene with
Copyright 12 American Scientific Publishers All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Vol. 12, 5942 5946, 12 Catalytic Oxidation of Benzene with
Methanol Usage in Toluene Methylation over Pt Modified ZSM-5 Catalyst: Effect of. Total Pressure and Carrier Gas. Supporting Information
 Methanol Usage in Toluene Methylation over Pt Modified ZSM-5 Catalyst: Effect of Total Pressure and Carrier Gas Supporting Information Yiren Wang, a Min Liu, a Anfeng Zhang, a Yi Zuo, a Fanshu Ding, a
Methanol Usage in Toluene Methylation over Pt Modified ZSM-5 Catalyst: Effect of Total Pressure and Carrier Gas Supporting Information Yiren Wang, a Min Liu, a Anfeng Zhang, a Yi Zuo, a Fanshu Ding, a
Supporting Information for. Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin
 Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
INVESTIGATING DOPED MESOPROUS ZSM-5 FOR CASCADE CATALYSIS
 INVESTIGATING DOPED MESOPROUS ZSM-5 FOR CASCADE CATALYSIS Introduction With the recent innovations and progress in the nanotechnology industry, a family of microporous catalysts and adsorbents known as
INVESTIGATING DOPED MESOPROUS ZSM-5 FOR CASCADE CATALYSIS Introduction With the recent innovations and progress in the nanotechnology industry, a family of microporous catalysts and adsorbents known as
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Propylene: key building block for the production of important petrochemicals
 Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Facile synthesis of nanostructured CuCo 2 O 4 as a novel electrode material for high-rate supercapacitors
 Facile synthesis of nanostructured CuCo 2 O 4 as a novel electrode material for high-rate supercapacitors Afshin Pendashteh, a Mohammad S. Rahmanifar, b Richard B. Kaner, c and Mir F. Mousavi* a,c a Department
Facile synthesis of nanostructured CuCo 2 O 4 as a novel electrode material for high-rate supercapacitors Afshin Pendashteh, a Mohammad S. Rahmanifar, b Richard B. Kaner, c and Mir F. Mousavi* a,c a Department
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals
 Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
1. Materials All chemicals and solvents were purchased from Sigma Aldrich or SAMCHUN and used without further purification.
 1. Materials All chemicals and solvents were purchased from Sigma Aldrich or SAMCHUN and used without further purification. 2. Experimental procedures Benzo[1,2-c:3,4-c':5,6-c'']trifuran, 1: The synthesis
1. Materials All chemicals and solvents were purchased from Sigma Aldrich or SAMCHUN and used without further purification. 2. Experimental procedures Benzo[1,2-c:3,4-c':5,6-c'']trifuran, 1: The synthesis
Supplementary Information. ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni(0) Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane
 Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information German Edition: DOI: High Catalytic Activity of Heteropolynuclear Cyanide Complexes Containing Cobalt and Platinum Ions: Visible-Light Driven Water Oxidation** Yusuke Yamada,* Kohei
Supporting Information German Edition: DOI: High Catalytic Activity of Heteropolynuclear Cyanide Complexes Containing Cobalt and Platinum Ions: Visible-Light Driven Water Oxidation** Yusuke Yamada,* Kohei
Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
 (Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
(Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Authors: Jeong-Chul Kim, Tae-Wan Kim, Youngjin Kim, Ryong Ryoo, Soon-Yong Jeong, Chul-Ung Kim. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental
 Accepted Manuscript Title: Mesoporous MFI Zeolites as High Performance catalysts for Diels-Alder Cycloaddition of Bio-derived Dimethylfuran and Ethylene to Renewable p-xylene Authors: Jeong-Chul Kim, Tae-Wan
Accepted Manuscript Title: Mesoporous MFI Zeolites as High Performance catalysts for Diels-Alder Cycloaddition of Bio-derived Dimethylfuran and Ethylene to Renewable p-xylene Authors: Jeong-Chul Kim, Tae-Wan
CHAPTER 7. for two different Diels-Alder-dehydration reactions catalyzed by the Lewis acid
 131 CHAPTER 7 MEASUREMENT OF ACTIVATION ENERGIES FOR ETHYLENE DIELS-ALDER-DEHYDRATION REACTIONS This chapter provides a summary and discussion of kinetic data obtained for two different Diels-Alder-dehydration
131 CHAPTER 7 MEASUREMENT OF ACTIVATION ENERGIES FOR ETHYLENE DIELS-ALDER-DEHYDRATION REACTIONS This chapter provides a summary and discussion of kinetic data obtained for two different Diels-Alder-dehydration
Supporting Information. From Metal-Organic Framework to Nanoporous Carbon: Toward a Very High Surface Area and Hydrogen Uptake
 Supporting Information From Metal-Organic Framework to Nanoporous Carbon: Toward a Very High Surface Area and Hydrogen Uptake Hai-Long Jiang, Bo Liu, Ya-Qian Lan, Kentaro Kuratani, Tomoki Akita, Hiroshi
Supporting Information From Metal-Organic Framework to Nanoporous Carbon: Toward a Very High Surface Area and Hydrogen Uptake Hai-Long Jiang, Bo Liu, Ya-Qian Lan, Kentaro Kuratani, Tomoki Akita, Hiroshi
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supporting Information. Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of. Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction activity of nitrogen-doped carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Effect of Transition Metal Mixing on Reactivities of Magnesium Oxide for Chemical Heat Pump
 Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, Vol. 40, No. 13, pp. 1281 1286, 2007 Research Paper Effect of Transition Metal Mixing on Reactivities of Magnesium Oxide for Chemical Heat Pump Junichi RYU, Rui
Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, Vol. 40, No. 13, pp. 1281 1286, 2007 Research Paper Effect of Transition Metal Mixing on Reactivities of Magnesium Oxide for Chemical Heat Pump Junichi RYU, Rui
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS
 EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Microporous Organic Network Hollow Spheres: Useful Templates for Nanoparticulate Co 3 O 4 Hollow Oxidation Catalysts Narae Kang, Ji Hoon Park, Mingshi Jin, Nojin Park, Sang Moon
Supporting Information for Microporous Organic Network Hollow Spheres: Useful Templates for Nanoparticulate Co 3 O 4 Hollow Oxidation Catalysts Narae Kang, Ji Hoon Park, Mingshi Jin, Nojin Park, Sang Moon
CHANGES IN SURFACE PROPERTIES OF KAOLIN MINERAL IN DEALUMINATION PROCESS BY SULFURIC ACID TREATMENT
 Clay Science 5, 163-169 (1978) 163 CHANGES IN SURFACE PROPERTIES OF KAOLIN MINERAL IN DEALUMINATION PROCESS BY SULFURIC ACID TREATMENT MIN CHE CHON Chon Engineering Co., Ltd., Seoul Korea AND TATSURO TSURU
Clay Science 5, 163-169 (1978) 163 CHANGES IN SURFACE PROPERTIES OF KAOLIN MINERAL IN DEALUMINATION PROCESS BY SULFURIC ACID TREATMENT MIN CHE CHON Chon Engineering Co., Ltd., Seoul Korea AND TATSURO TSURU
Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash
 BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation
 Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information TiO 2 interpenetrating networks decorated with SnO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information TiO 2 interpenetrating networks decorated with SnO
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Self-rearrangement of silicon nanoparticles. high-energy and long-life lithium-ion batteries
 Supporting Information Self-rearrangement of silicon nanoparticles embedded in micron carbon sphere framework for high-energy and long-life lithium-ion batteries Min-Gi Jeong,, Hoang Long Du, Mobinul Islam,,
Supporting Information Self-rearrangement of silicon nanoparticles embedded in micron carbon sphere framework for high-energy and long-life lithium-ion batteries Min-Gi Jeong,, Hoang Long Du, Mobinul Islam,,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. especially in last 50 years. Industries, especially power industry, are the large anthropogenic
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The concentration of CO 2 in atmosphere has increased considerably in last 100 years, especially in last 50 years. Industries, especially power industry, are the large anthropogenic
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The concentration of CO 2 in atmosphere has increased considerably in last 100 years, especially in last 50 years. Industries, especially power industry, are the large anthropogenic
Supplementary Information. for. Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High. Pressures
 S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate
 1 Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate ME Zeynali Petrochemical Synthesis Group, Petrochemical Faculty, Iran Polymer and Petrochemical Institute (IPPI), P.O.
1 Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate ME Zeynali Petrochemical Synthesis Group, Petrochemical Faculty, Iran Polymer and Petrochemical Institute (IPPI), P.O.
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core
 A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
Australian Institute of Innovative Materials, University of Wollongong, Australia.
 Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange by CeO 2 and Fe-doped CeO 2 Films under Visible Light Irradiation D. Channei a, B. Inceesungvorn a, N. Wetchakun b, S. Ukritnukun c, A. Nattestad d, J. Chen
Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange by CeO 2 and Fe-doped CeO 2 Films under Visible Light Irradiation D. Channei a, B. Inceesungvorn a, N. Wetchakun b, S. Ukritnukun c, A. Nattestad d, J. Chen
EFFECT OF MORPHOLOGY OF NANOSTRUCTURED CERIA-BASED CATALYSTS OVER CO, SOOT AND NO OXIDATIONS
 EFFECT OF MORPHOLOGY OF NANOSTRUCTURED CERIA-BASED CATALYSTS OVER CO, SOOT AND NO OXIDATIONS Melodj Dosa, Marco Piumetti, Samir Bensaid, Tahrizi Andana, Debora Fino, Nunzio Russo* melodj.dosa@polito.it
EFFECT OF MORPHOLOGY OF NANOSTRUCTURED CERIA-BASED CATALYSTS OVER CO, SOOT AND NO OXIDATIONS Melodj Dosa, Marco Piumetti, Samir Bensaid, Tahrizi Andana, Debora Fino, Nunzio Russo* melodj.dosa@polito.it
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid
 Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron double oxide catalyst
 Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Direct Synthesis of H 2 O 2 on AgPt Octahedra: The Importance of Ag-Pt Coordination for High H 2 O 2 Selectivity
 Supporting Information Direct Synthesis of H 2 O 2 on AgPt Octahedra: The Importance of Ag-Pt Coordination for High H 2 O 2 Selectivity Neil M. Wilson, 1 Yung-Tin Pan, 1 Yu-Tsun Shao, 2 Jian-Min Zuo, 2
Supporting Information Direct Synthesis of H 2 O 2 on AgPt Octahedra: The Importance of Ag-Pt Coordination for High H 2 O 2 Selectivity Neil M. Wilson, 1 Yung-Tin Pan, 1 Yu-Tsun Shao, 2 Jian-Min Zuo, 2
Supporting Information. Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic Compound Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF Fe-ZSM-5 CATALYSTS
 PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF Fe-ZSM-5 CATALYSTS D. Szalay*, G. Horváth**, J. Halász** and I. Kiricsi** Department of Environmental Engineering, Széchenyi
PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF Fe-ZSM-5 CATALYSTS D. Szalay*, G. Horváth**, J. Halász** and I. Kiricsi** Department of Environmental Engineering, Széchenyi
Core-shell 2 mesoporous nanocarriers for metal-enhanced fluorescence
 Core-shell Ag@SiO 2 @msio 2 mesoporous nanocarriers for metal-enhanced fluorescence Jianping Yang a, Fan Zhang a *, Yiran Chen a, Sheng Qian a, Pan Hu a, Wei Li a, Yonghui Deng a, Yin Fang a, Lu Han a,
Core-shell Ag@SiO 2 @msio 2 mesoporous nanocarriers for metal-enhanced fluorescence Jianping Yang a, Fan Zhang a *, Yiran Chen a, Sheng Qian a, Pan Hu a, Wei Li a, Yonghui Deng a, Yin Fang a, Lu Han a,
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction
 Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
