Synthesis of Zeolite Monolith with Hierarchical Micro/Macropores by Ice-Templating and Steam-Assisted Crystallization
|
|
|
- Claire Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A publication of 259 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN ; ISSN The Italian Association of Chemical Engineering Online at: Synthesis of Zeolite Monolith with Hierarchical Micro/Macropores by Ice-Templating and Steam-Assisted Crystallization Hajime Tamon*, Takuya Akatsuka, Hiroki Mori, Noriaki Sano Department of Chemical Engineering, Kyoto University, Katsura, Kyoto , Japan Zeolite monolith was synthesized by ice-templating and steam-assisted crystallization (SAC) by using a structure-directing agent (SDA). The precursor silica gel was prepared by applying ice-templating to the hydrogels synthesized from colloidal silica. Sodium aluminate (NaAlO 2 ) was supported in the precursor by impregnation to prepare zeolite monolith. Silicalite monolith or zeolite monolith with three-dimensionally interconnected macropores was synthesized by SAC of the precursor by using tetrapropylammonium hydroxide as SDA. The monolith had the continuous macropores, and the surface of these macropores was densely covered with zeolite crystals. The crystals were identified as MFI-type by XRD and had a well ordered microporous structure. Since the macropores, which were formed by ice-templating, were directly connected to the micropores of the synthesized zeolite crystals, the synthesized zeolite monolith had the hierarchical structure of macropores and micropores. The macroporous structure of monolith could be controlled by the freezing conditions because the macropore size became large with the decrease in freezing rate of hydrogels. The BET surface area and the degree of crystallinity of zeolite monolith were increased up to 347 m 2 /g and 89 % by SAC. When the zeolite monolith was synthesized by changing the Si/Al ratio, the crystallization rate increased with the increase in Si/Al ratio, and the hydrophilic or hydrophobic property was also controlled by choosing the Si/Al ratio. 1. Introduction Zeolites are widely used as catalysts, adsorbents, and ion exchangers. The mass transfer is one of the most important factors affecting the performance of microporous materials. The short diffusion length is needed to decrease the resistance of mass transfer. Zeolite is usually synthesized in the form of particles. Although extremely fine particles of zeolite are useful for the short diffusion length, the pressure drop is extremely large in the case where the particles are used in the packed bed (Hartmann M., 24). Hence, the fabrication is important for the effective application of zeolite. Fiber or microhoneycomb morphology has recently attracted great attention from their low pressure drops and short diffusion lengths. However, it is extremely difficult to fabricate zeolite in honeycomb or fiber morphology without any binder. Recently, porous materials with a hierarchical pore system have attracted considerable attention from the enhanced accessibility to their functional sites, which are distributed on the surface of their micro/mesopores (Soler-Illia et al., 22). Such materials are usually prepared through sol gel synthesis using special templates, such as fine polymer particles and microemulsions. Hence, it is extremely important to propose a novel methodology for preparing porous materials with hieratical pore system. The authors have proposed a novel template synthesis (ice-templating) using a unidirectional freezing of sols or hydrogels to synthesize porous fibers or microhoneycombs (Mukai et al., 23). Ice-templating consists of so-gel polycondensation, unidirectional freezing of hydrosols or hydrogels, and pore-protecting drying method, such as freeze drying. Therefore, highly porous cryogels with ordered morphology can be obtained. The authors have previously reported that silica cryogel microhoneycombs (Mukai et al., 24a), titania cryogel fibers (Mukai et al., 24b), carbon cryogel microhoneycombs (CMHs) (Nishihara et al., 24), alumina-silica microhoneycombs (Nishihara et al., 26) and titania-silica microhoneycomb
2 26 (Nishihara et al., 21) can be obtained through the ice-templating method. Recently, the authors have applied ice-templating to the synthesis of silicalite monolith (Mori et al., 211). In this work, the zeolite monolith is synthesized by ice-templating and steam-assisted crystallization (SAC) (Matsukata et al., 22) by using a structure-directing agent (SDA). The influence of freezing condition, SAC condition, and Si/Al ratio on morphology, crystallinity, nanostructure, and hydrophobicity of zeolite monolith is experimentally examined. 2. Experimental 2.1 Preparation of precursor monolith The silica gel monolith used as the precursor of zeolite monolith was prepared by applying the ice templating method to a silica hydrogel. The silica hydrogel was synthesized from commercially available colloidal dispersion of silicon (IV) oxide (5 wt% in H 2 O, Alfa Aesar) by using an ion-exchange resin (Amberlite IR12B H AG, Organo Co.). The colloidal silica hydrogel was unidirectionally frozen by immersing the sample into a liquid nitrogen bath at various rates. Here the freezing temperature T f was C, and the freezing rate v f was changed form 15 cm/h to 7 cm/h to control the macroporous structure of silica gel. After the colloidal silica hydrogel was completely frozen, the sample was dried at 25 C for 24 h, and then the silica gel monolith was obtained. 2.2 Preparation of zeolite monolith The precursor silica gel was subsequently heated at 8 C for 2 h in air atmosphere at a heating rate of 3 C/min in order to give an alkali-proof property to the sample. After calcination, the precursor was impregnated with sodium aluminate (NaAlO 2 ). Then the sample was soaked in the SDA solution and dried at 5 C for 24 h. The SDA solution was prepared by diluting tetrapropyl ammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) solution (1 mass%, Wako Pure Chemicals Co.) with water. The obtained dry silica gel containing SDA was crystallized by SAC in an autoclave. The SDA concentration was 3.3 g-sda/g-precursor. The crystallization temperature T SAC was 13 C, 15 C or 18 C, and the heating rate was 5 C/min. The crystallization time t SAC was varied from 3 to 24 h. The sample after crystallization was calcined at 6 C for 4 h in air atmosphere at a heating rate of 1 C/min. By the calcination, SDA was removed from crystallized samples, and finally the silicalite monolith or zeolite monolith was obtained. 2.3 Characterization The morphology of the samples prepared was observed by a field emission scanning electron microscope(fe-sem)(jeol Japan Inc.; JSM-67F), and the average size of silicalite-1 crystals was determined from the obtained SEM images. The crystal structure of silicalite monolith was investigated using a powder X-ray diffractometer (XRD) (Rigaku Co. Ltd.; RINT21). The crystallinity of the sample was determined from the obtained XRD pattern, and the degree of crystallinity, X c, is given by X c = I c / ( I c + I a ) 1 (%) (1) where I c is the integrated intensity of crystalline peaks, and I a is the integrated intensity of the amorphous halo. Zeolite synthesis was confirmed by a solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer (Varian Inc.; VNMRS-4). Porous properties of cryogels were analyzed from N 2 adsorption-desorption isotherms measured at -196 C using an adsorption apparatus (BEL Japan Inc.; BELSORP28). The BET surface area S BET was calculated through the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method, and mesopore size distribution and mesopore volume V mes were calculated through the Dollimore-Heal method (Dollimore and Heal, 1964). The microporosity was evaluated by the t-plot method (Lippens and de Boer, 1965), and the micropore volume V mic was calculated. 3. Results and discussion 3.1 Crystallization of precursor by SAC Crack-free monoliths of precursor silica gel and silicalite can be synthesized by ice-templating and SAC. Figure 1 shows SEM images of cross section of silicalite monoliths synthesized under different freezing rates. Here the synthesis conditions of monoliths are as follows; T f = -196 C, T SAC = 13 C and t SAC = 12 h. The freezing rate v f is changed as 15, 3, 5 and 7 cm/h. The continuous macroporous structure formed by ice-templating is observed in the crystallized samples as shown in Figure 1. It is experimentally confirmed that the channels run from one side to the opposite side of the sample by ink penetration tests, which were carried out using red ink dissolved in t-butanol, and that the monolith shows much lower pressure drop than that of the packed-bed of particles.
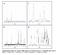
3 261 Figure 1: SEM images of cross section of silicalite monoliths synthesized under various freezing rates. The crystal structure of precursor or silicalite monolith has been examined using a powder X-ray diffractometer (XRD). XRD patterns of the precursor silica gel and the samples after crystallization are shown in Figure 2. The samples of Figure 2 are the same as those shown in Figure 1. Only the broad halo centered at around 2θ =23 is observed in the XRD pattern of the precursor silica gel, and no crystalline phase is detected as shown in Figure 2 (a). In the sample after crystallization, sharp peaks are observed at around 2θ = 8 and 23 as shown in Figure 2 (b). All of the observed diffraction peaks correspond to those of MFI-type zeolites. Since the synthesized samples contain no aluminum atom, the crystalline phase of the synthesized sample is identified as silicalite-1. (a) (b) Intensity [a.u.] Intensity [a.u.] θ [ deg. ] 2θ [ deg. ] Figure 2: XRD patterns of precursor silica gel (a) and silicalite monolith after crystallization (b). 3.2 Control of macroporous structure of silicalite monolith The authors have reported that the morphology of silica gel microhoneycombs depends on the unidirectional freezing conditions, and that the macropore size (channel size) and the wall thickness of SMHs can be controlled by the unidirectional freezing conditions and the silica concentration for synthesis of silica gels (Nishihara et al., 25). In the present work, the macropore size of silicalite is controlled by the unidirectional freezing rate. Figure 1 suggests that the average macropore size (channel size) d mac of monolith changes as 5.2, 7.7, 11 and 14 μm with the decrease in freezing rate v f. Hence, the macropore size can be controlled by the freezing rate. The influence of freezing rate on macroporous structure is the same as the case of silica gel microhoneycomb synthesized by unidirectional freezing (Nishihara et al., 25). 3.3 Influence of SAC conditions on crystallinity of silicalite monolith Figure 3 (a) shows the influence of SAC conditions on XRD patterns of silicalite monoliths synthesized for v f = 4 cm/h. It can be seen that the diffraction peaks become stronger with the increase in SAC temperature and SAC time. Figure 3 (b) shows the influence of SAC conditions on the degree of crystallinity of silicalite monolith. Here the degree of crystallinity is calculated from XRD patterns by using Equation (1). The degree of crystallinity increases with the increase in SAC temperature T SAC and the SAC
4 262 time t SAC, and reaches the values above 8 %. This result implies that the precursor silica gel is highly crystallized by the longer treatment than 12 h at high temperature. Hence, the XRD measurements of samples prepared suggest that silicalite monolith can be synthesized by ice-templationg and SAC. Degree of crystallinity [%] Figure 3: Influence of SAC temperature and SAC time on XRD patterns (a) and degree of crystallinity (b) of silicalite monoliths (b) 18 ºC 15 ºC 13 ºC SAC time [h] 3.4 Influence of SAC conditions on porous property of silicalite monolith Figure 4 shows the influence of SAC conditions on adsorption-desorption isotherms of nitrogen at -196 C on the precursor silica gel and the samples after crystallization. Here, p/p is relative pressure (p = saturated vapor pressure) and q is amount of N 2 adsorbed. The isotherm on the precursor silica gel is classified into type IV in IUPAC classification, and this result indicates that the precursor silica gel is mesoporous. After the crystallization for 24 h, the isotherm changes into type I. This is because most part of the mesopores originally existed in the precursor silica gel disappears, and the crystallized sample becomes microporous. The isotherms suggest that the BET surface area S BET and micropore volume V mic of the precursor silica gel are 118 m 2 /g and.1 cm 3 /g. On the other hand, S BET and V mic of zeolite monolith increases up to 347 m 2 /g and.17 cm 3 /g after t SAC = 24h. Since the macropores are formed by ice-templating, the zeolite monolith has the hierarchical structure of macropores and micropores. q [ml(stp)/g] 4 SDA ; TPAOH v Precursor f = 4 cm/h 3 T SAC =13 ºC, t SAC = h 2 T SAC =15 ºC, t SAC = 12 h 1 T SAC =15 ºC, t SAC = 24 h p/p [-] Figure 4: Influence of SAC conditions on adsorption-desorption isotherms of nitrogen at -196 C on zeolite monoliths (open symbols: adsorption, closed symbols: desorption). 3.5 Preparation of zeolite monolith by SAC Figure 5 (a) shows SEM images of cross section of zeolite monolith synthesized for Si/Al = 5, T f = -196 C, v f = 4 cm/h, T SAC = 15 C and t SAC = 12 h. From the SEM image, It is found that the zeolite monolith has three-dimensionally interconnected macropores as same as silicate monolith (Si/Al = ) shown in Figure 1. The existence of aluminium in zeolite can be identified by NMR. The 27 Al MAS NMR spectrum shown in Figure 5 (b) suggests that the sharp peak of 4-coordinated Al 3+ is observed at chemical shift of δ = 54 ppm. The result suggests that the sample has a framework structure composed of AlO 4 tetrahedra.
5 Therefore, it can be concluded that not only silicalite monolith but also zeolite monolith can be synthesized by ice-templating and SAC. 263 Intensity [a.u.] (b) 4-coordinated Al 3+ (54 ppm) 6-coordinated Al δ [ppm] -5 Figure 5: SEM image of cross section (a) and 27 Al MAS NMR spectrum (b) of zeolite monolith synthesized for Si/Al = Influence of Si/Al ratio on crystallinity of zeolite monolith The influence of Si/Al ratio of zeolite monolith on the degree of crystallinity is shown in Figure 6. This figure shows the relation between the degree of crystallinity and the SAC time in the case where zeolite monolith is synthesized for T f = -196 C, v f = 4 cm/h and T SAC = 15 C. As Si/Al ration decreases, the crystallization rate becomes slow. One can see that the degree of crystallinity of zeolite monolith synthesized for Si/Al= 2 is below 6 % even at t SAC = 12 h. 1 Degree of crystallinity [%] Si/Al = Si/Al = 1 Si/Al = 5 Si/Al = SAC time [h] Figure 6: Influence of SAC time on degree of crystallinity of zeolite monoliths synthesized for various Si/Al ratios. 3.7 Influence of Si/Al ratio on hydrophilic property of zeolite monolith Figure 7 shows adsorption isotherms of water vapor at 25 C on zeolite monolith synthesized for Si/Al =, 5 and 2. These samples have almost the same degree of crystallinity of 84 %. The amount of water vapor adsorbed increases with the decrease in Si/Al ratio (the increase in aluminium content). This result suggests that zeolite becomes hydrophilic as the Si/Al ratio decreases. Hence, the hydrophilic or hydrophobic property can be controlled by choosing the Si/Al ratio. 4. Conclusion Zeolite monolith was synthesized from colloidal silica by ice-templating and steam-assisted crystallization (SAC) using a structure-directing agent (SDA). Since the macropores, which were formed by icetemplating, were directly connected to the micropores of the synthesized MFI-type crystals, the synthesized zeolite monolith had the hierarchical structure of macropores and micropores. The
6 264 macroporous structure of monolith can be controlled by the freezing conditions because the macropore size became large with the decrease in freezing rate of hydrogels. The BET surface area and the degree of crystallinity of zeolite monolith were increased up to 347 m 2 /g and 89 % by SAC. When the zeolite monolith was synthesized by changing Si/Al ratio, the crystallization rate decreased with the decrease in Si/Al ratio, and the hydrophilic or hydrophobic property was also controlled by choosing the Si/Al ratio. 3 6 q [ml (STP)/g] Si/Al = 2 2 Si/Al = 5 Si/Al = Si/Al = Si/Al = 5 Si/Al = p/p [-] Figure 7: Influence of Si/Al ratio on adsorption isotherms of water vapor at 25 C on zeolite monoliths. Acknowledgements This research was partially supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research (B) No ( ). References Dollimore D., Heal G. R., 1964, An improved method for the calculation of pore-size distribution from adsorption data, J. Appl. Chem. 14, Hartmann M., 24, Hierarchical zeolites: a proven strategy to combine shape selectivity with efficient mass transport, Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 43, Lippens B. C., de Boer J. H., 1965, Pore system in catalysts V: the t-method, J. Catal. 3, Matsukata M., Osaki T., Ogura M. Kikuchi E., 22, Crystallization behavior of zeolite beta during steamassisted crystallization of dry gel, Micropo. Mesopor. Mater. 56, 1-1. Mori H., Aotani K., Sano N., Tamon H., 211, Synthesis of hierarchically micro-macroporous structured zeolite monolith by ice-templating, J. Mater. Chem. 21, Mukai S. R., Nishihara H., Tamon H., 23, Porous properties of silica gels with controlled morphology synthesized by unidirectional freeze-gelation, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 63, Mukai S. R., Nishihara H., Tamon H., 24a, Formation of monolithic silica gel microhoneycombs (SMHs) using pseudosteady state growth of microstructural ice crystals, Chem. Commun., Mukai S. R., Nishihara H., Shichi S., Tamon H., 24b, Preparation of porous TiO 2 cryogel fibers through unidirectional freezing of hydrogel followed by freeze-drying, Chem. Mater. 16, Nishihara H., Mukai S. R., Tamon H., 24, Preparation of resorcinol-formaldehyde carbon cryogel microhoneycombs, Carbon 42, Nishihara H., Mukai S. R., Yamashita D., Tamon H., 25, Ordered macroporous silica by ice-templating, Chem. Mater. 17, Nishihara H., Mukai S. R., Fujii Y., Tago T., Masuda T., Tamon H., 26, Preparation of monolithic SiO 2 - Al 2 O 3 cryogels with inter-connected macropores through ice templating, J. Mater. Chem. 16, Nishihara H., Mukai S. R., Tamon H., 21, Preparation of titania silica cryogels with controlled shapes and photocatalysis through unidirectional freezing, Mater. Lett. 64, Soler-Illia G.J. de A.A., Sanchez C., Lebeau B., Patarin J., 22, Chemical strategies to design textured materials: From microporous and mesoporous oxides to nanonetworks and hierarchical structures, Chem. Rev. 12,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method
 Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres
 Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres Seong-Ick Kim, Takuji Yamamoto, Akira Endo, Takao Ohmori, and Masaru Nakaiwa
Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres Seong-Ick Kim, Takuji Yamamoto, Akira Endo, Takao Ohmori, and Masaru Nakaiwa
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS
 181 A publication of VOL. 42, 2014 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Neven Duić Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-33-4; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
181 A publication of VOL. 42, 2014 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Neven Duić Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-33-4; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Developing Carbon Tolerance Catalyst for Dry Methane Reforming
 745 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
745 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials
 Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NITROGEN-CONTAINING MICROPOROUS CARBON WITH A THREE-DIMENSIONAL NANO-ARRAY STRUCTURE
 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NITROGEN-CONTAINING MICROPOROUS CARBON WITH A THREE-DIMENSIONAL NANO-ARRAY STRUCTURE Peng-Xiang Hou 1, Takashi Kyotani 1, Koich Matsuoka 1, Akira Tomita 1, Norihiko Setoyama
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NITROGEN-CONTAINING MICROPOROUS CARBON WITH A THREE-DIMENSIONAL NANO-ARRAY STRUCTURE Peng-Xiang Hou 1, Takashi Kyotani 1, Koich Matsuoka 1, Akira Tomita 1, Norihiko Setoyama
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2014. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201404493 Micro/Macroporous System: MFI-Type Zeolite Crystals with Embedded
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2014. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201404493 Micro/Macroporous System: MFI-Type Zeolite Crystals with Embedded
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS
 CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core
 A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Report on Preparation of Nanotemplates for mab Crystallization
 Deliverable number D2.1 Due date 30/09/2017 Deliverable title Report on Preparation of Nanotemplates for mab Crystallization Issue date 21/09/2017 WP number WP2 Author(s) J. Heng, W. Chen, H. Yang Lead
Deliverable number D2.1 Due date 30/09/2017 Deliverable title Report on Preparation of Nanotemplates for mab Crystallization Issue date 21/09/2017 WP number WP2 Author(s) J. Heng, W. Chen, H. Yang Lead
Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction activity of nitrogen-doped carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
Supporting Information. From Metal-Organic Framework to Nanoporous Carbon: Toward a Very High Surface Area and Hydrogen Uptake
 Supporting Information From Metal-Organic Framework to Nanoporous Carbon: Toward a Very High Surface Area and Hydrogen Uptake Hai-Long Jiang, Bo Liu, Ya-Qian Lan, Kentaro Kuratani, Tomoki Akita, Hiroshi
Supporting Information From Metal-Organic Framework to Nanoporous Carbon: Toward a Very High Surface Area and Hydrogen Uptake Hai-Long Jiang, Bo Liu, Ya-Qian Lan, Kentaro Kuratani, Tomoki Akita, Hiroshi
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
CHAPTER 4. SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL
 93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
Adsorption Processes. Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Supplementary Information. Experimental Methods
 Extremely thin Pd-silica mixed-matrix membranes with nano-dispersion for improved hydrogen permeability Masakoto Kanezashi, Mitsunori Sano, Tomohisa Yoshioka, and Toshinori Tsuru Department of Chemical
Extremely thin Pd-silica mixed-matrix membranes with nano-dispersion for improved hydrogen permeability Masakoto Kanezashi, Mitsunori Sano, Tomohisa Yoshioka, and Toshinori Tsuru Department of Chemical
Experimental details. General
 Experimental details General TiO 2 P25 was purchased from Degussa; methyl methacrylate (MMA, 99%), 2,2 -azobis(2- methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (97%), titanium (IV) isopropoxide (97%), concentrated
Experimental details General TiO 2 P25 was purchased from Degussa; methyl methacrylate (MMA, 99%), 2,2 -azobis(2- methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (97%), titanium (IV) isopropoxide (97%), concentrated
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Grant agreement No ShaleXenvironmenT. Maximizing the EU shale gas potential by minimizing its environmental footprint
 Grant agreement No. 640979 ShaleXenvironmenT Maximizing the EU shale gas potential by minimizing its environmental footprint H2020-LCE-2014-1 Competitive low-carbon energy D7.2 Full experimental materials
Grant agreement No. 640979 ShaleXenvironmenT Maximizing the EU shale gas potential by minimizing its environmental footprint H2020-LCE-2014-1 Competitive low-carbon energy D7.2 Full experimental materials
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department. Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials
 Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Supplementary Information. Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Conception of hierarchical porous materials synthesized from single molecular precursors
 FUNDP (CMI) Arnaud Lemaire Conception of hierarchical porous materials synthesized from single molecular precursors Summary of the presentation I. Introduction II. bjectives & Strategies III. Macro-mesoporous
FUNDP (CMI) Arnaud Lemaire Conception of hierarchical porous materials synthesized from single molecular precursors Summary of the presentation I. Introduction II. bjectives & Strategies III. Macro-mesoporous
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
A New Redox Strategy for Low-Temperature Formation of Strong Basicity on Mesoporous Silica
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information A New Redox Strategy for Low-Temperature Formation
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information A New Redox Strategy for Low-Temperature Formation
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Influence of Nickel Electroplating on Hydrogen Chloride Removal of Activated Carbon Fibers
 Carbon Science Vol. 5, No. 4 December 2004 pp. 186-190 Influence of Nickel Electroplating on Hydrogen Chloride Removal of Activated Carbon Fibers Soo-Jin Park, Sung-Yeol Jin and Seung-Kon Ryu 1 Advanced
Carbon Science Vol. 5, No. 4 December 2004 pp. 186-190 Influence of Nickel Electroplating on Hydrogen Chloride Removal of Activated Carbon Fibers Soo-Jin Park, Sung-Yeol Jin and Seung-Kon Ryu 1 Advanced
Design and Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Materials for CO 2 Capture and Investigation of CO 2 Sorption Kinetics
 Design and Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Materials for CO 2 Capture and Investigation of CO 2 Sorption Kinetics Investigators Jennifer Wilcox, Assistant Professor, Energy Resources Engineering;
Design and Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Materials for CO 2 Capture and Investigation of CO 2 Sorption Kinetics Investigators Jennifer Wilcox, Assistant Professor, Energy Resources Engineering;
Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Turning TS-1 zeolite into a highly active catalyst for olefin epoxidation with organic hydroperoxidesw
 COMMUNICATION www.rsc.org/chemcomm ChemComm Turning TS-1 zeolite into a highly active catalyst for olefin epoxidation with organic hydroperoxidesw David Serrano,* ab Raúl Sanz, a Patricia Pizarro a and
COMMUNICATION www.rsc.org/chemcomm ChemComm Turning TS-1 zeolite into a highly active catalyst for olefin epoxidation with organic hydroperoxidesw David Serrano,* ab Raúl Sanz, a Patricia Pizarro a and
Adsorption equilibrium and dynamics of toluene vapors onto three kinds of silica gels
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Adsorption equilibrium and dynamics of toluene vapors onto three kinds of silica gels To cite this article: K L Yan and Q Wang
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Adsorption equilibrium and dynamics of toluene vapors onto three kinds of silica gels To cite this article: K L Yan and Q Wang
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9
 Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Synthesis and Application of Hexagonal Perovskite BaNiO 3 with Quadrivalent
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Synthesis and Application of Hexagonal Perovskite BaNiO 3 with Quadrivalent
DOCTORAL THESIS. Structured Molecular Sieves. Valeri Naydenov. Department of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering Division of Chemical Technology
 2003:39 DOCTORAL THESIS Structured Molecular Sieves Synthesis, Modification and Characterization Valeri Naydenov Department of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering Division of Chemical Technology 2003:39
2003:39 DOCTORAL THESIS Structured Molecular Sieves Synthesis, Modification and Characterization Valeri Naydenov Department of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering Division of Chemical Technology 2003:39
Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity
 1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
Physical properties of porous membranes. Membranes D f S BET [m 2 /g] d peak [nm]
![Physical properties of porous membranes. Membranes D f S BET [m 2 /g] d peak [nm] Physical properties of porous membranes. Membranes D f S BET [m 2 /g] d peak [nm]](/thumbs/79/80072104.jpg) The Sol-Gel Preparation and Characterization of Nanoporous Silica Membrane with Controlled Pore Size T. Fujii, T. Izumi, Dept. of Food Sci., Niigata Univ. of Pharm. & Appl. Life Sci., Niitsu, Niigata 956-8603,
The Sol-Gel Preparation and Characterization of Nanoporous Silica Membrane with Controlled Pore Size T. Fujii, T. Izumi, Dept. of Food Sci., Niigata Univ. of Pharm. & Appl. Life Sci., Niitsu, Niigata 956-8603,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Supporting Information. for. Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under. Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via
 Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Electronic Supplementary Information. Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave Hexagon and Nanorod like Polyoxometalates
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave
Figure S1 XRD patterns of (a) Ti-MSE-A, (b) Ti-MSE-A-cal, (c) TS-1, (d) Ti-MWW, and (e) Ti-BEA.
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure
 Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure Xiao-Feng Guo, Yong-Suk Kim, and Geon-Joong Kim Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha UniVersity,
Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure Xiao-Feng Guo, Yong-Suk Kim, and Geon-Joong Kim Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha UniVersity,
Research Article Synthesis and Electrochemical Characterization of Mesoporous MnO 2
 Chemistry Volume 2015, Article ID 768023, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/768023 Research Article Synthesis and Electrochemical Characterization of Mesoporous MnO 2 Jia Chang Zhao, Jun Wang, and
Chemistry Volume 2015, Article ID 768023, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/768023 Research Article Synthesis and Electrochemical Characterization of Mesoporous MnO 2 Jia Chang Zhao, Jun Wang, and
Supporting Information. Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of. Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment
 Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15 To cite this article: Norhasyimi Rahmat et al 2016 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15 To cite this article: Norhasyimi Rahmat et al 2016 IOP
CHAPTER 4 CHEMICAL MODIFICATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON CLOTH FOR POTENTIAL USE AS ELECTRODES IN CAPACITIVE DEIONIZATION PROCESS
 CHAPTER 4 CHEMICAL MODIFICATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON CLOTH FOR POTENTIAL USE AS ELECTRODES IN CAPACITIVE DEIONIZATION PROCESS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Capacitive deionization (CDI) is one of the promising energy
CHAPTER 4 CHEMICAL MODIFICATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON CLOTH FOR POTENTIAL USE AS ELECTRODES IN CAPACITIVE DEIONIZATION PROCESS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Capacitive deionization (CDI) is one of the promising energy
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION. Keywords: Ethylene oxide, Partial oxidation, Ethane epoxidation, Second metal.
 DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Aqueous, screen-printable paste for fabrication of mesoporous composite anatase-rutile TiO 2 nanoparticle thin films for (photo)electrochemical devices Amrita Yasin, Fuqiang Guo,
Supporting Information Aqueous, screen-printable paste for fabrication of mesoporous composite anatase-rutile TiO 2 nanoparticle thin films for (photo)electrochemical devices Amrita Yasin, Fuqiang Guo,
Preparation of Controlled Porosity Resorcinol Formaldehyde Xerogels for Adsorption Applications
 A publication of 1651 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 1651 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Min Bum Park, Sang Hyun Ahn, Nak Ho Ahn and Suk Bong Hong*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
 (Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
(Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer Drug Delivery
 Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins
 Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Manganese oxide based aerogels
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 112 (2018) 217-225 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Manganese oxide based aerogels ABSTRACT Małgorzata Rudnicka *, Joanna Łata, Piotr Kupracz Faculty
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 112 (2018) 217-225 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Manganese oxide based aerogels ABSTRACT Małgorzata Rudnicka *, Joanna Łata, Piotr Kupracz Faculty
Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chitosan Aerogels: Transparent, Flexible Thermal Insulators Satoru Takeshita* and Satoshi Yoda Detailed experimental procedure Materials: Chitosan (deacetylation rate: > 80%, viscosity:
Supporting Information Chitosan Aerogels: Transparent, Flexible Thermal Insulators Satoru Takeshita* and Satoshi Yoda Detailed experimental procedure Materials: Chitosan (deacetylation rate: > 80%, viscosity:
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation
 Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Synthesis of zeolite crystallites for diffusion measurements
 Synthesis of zeolite crystallites for diffusion measurements Xiaobo Yang, Jürgen Caro Institut für Physikalische Chemie und Elektrochemie Leibniz Universität Hannover Main Activities in Previous Synthesis
Synthesis of zeolite crystallites for diffusion measurements Xiaobo Yang, Jürgen Caro Institut für Physikalische Chemie und Elektrochemie Leibniz Universität Hannover Main Activities in Previous Synthesis
PROGRESS REPORT FOR AINGRA09119
 Date electronic copy received at AINSE: 14 September 2009 PROGRESS REPORT FOR AINGRA09119 PROJECT TITLE TEM characterisation of novel supported silver and gold nanoparticle catalysts INVESTIGATOR(S) Institution
Date electronic copy received at AINSE: 14 September 2009 PROGRESS REPORT FOR AINGRA09119 PROJECT TITLE TEM characterisation of novel supported silver and gold nanoparticle catalysts INVESTIGATOR(S) Institution
DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 8 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
 DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 8 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Charles Kappenstein, Professor Emeritus, University of Poitiers, France Preparation of catalysts
DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 8 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Charles Kappenstein, Professor Emeritus, University of Poitiers, France Preparation of catalysts
2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic Analysis
 146 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 60, (3), 146-153 (2017) [Regular Paper] 2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic
146 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 60, (3), 146-153 (2017) [Regular Paper] 2-Methylnaphthalene Methylation over Aluminosilicate and Ferrisilicate with MTW-type Zeolite Structure and Their Kinetic
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information The directing effect of linking unit on building microporous architecture in tetraphenyladmantane-based poly(schiffbase) networks Guiyang Li, Biao Zhang, Jun Yan and
Electronic Supplementary Information The directing effect of linking unit on building microporous architecture in tetraphenyladmantane-based poly(schiffbase) networks Guiyang Li, Biao Zhang, Jun Yan and
photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation
 Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification
 Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
Thermal Conductivity of Covalent Organic Frameworks as a Function of Their Pore Size
 Thermal Conductivity of Covalent Organic Frameworks as a Function of Their Pore Size Sunny K. S. Freitas a ; Raquel S. Borges b ; Claudia Merlini c, Guilherme M. O. Barra d, Pierre M. Esteves a, * a. Instituto
Thermal Conductivity of Covalent Organic Frameworks as a Function of Their Pore Size Sunny K. S. Freitas a ; Raquel S. Borges b ; Claudia Merlini c, Guilherme M. O. Barra d, Pierre M. Esteves a, * a. Instituto
Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of Benzene and Toluene with Hydrogen Peroxide in a Bubble Reactor
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
Synthesis of Size Distribution Controllable Zeolite Nanocrystals via a Novel Confined Space Strategy. Abstract
 Synthesis of Size Distribution Controllable Zeolite Nanocrystals via a Novel Confined Space Strategy Yi Huang, Monash University, Melbourne, VIC, Australia Dr. Anita J. Hill, Commonwealth Scientific and
Synthesis of Size Distribution Controllable Zeolite Nanocrystals via a Novel Confined Space Strategy Yi Huang, Monash University, Melbourne, VIC, Australia Dr. Anita J. Hill, Commonwealth Scientific and
Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
Effect of methanol content in commercial formaldehyde solutions on the porosity. of RF carbon xerogels
 Effect of methanol content in commercial formaldehyde solutions on the porosity of RF carbon xerogels Isabel D. Alonso-Buenaposada, Natalia Rey-Raap, Esther G. Calvo, J. Angel Menéndez, Ana Arenillas*
Effect of methanol content in commercial formaldehyde solutions on the porosity of RF carbon xerogels Isabel D. Alonso-Buenaposada, Natalia Rey-Raap, Esther G. Calvo, J. Angel Menéndez, Ana Arenillas*
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Catalytic activity of the beta zeolite with enhanced textural properties in the Friedel-Crafts acylation of aromatic compounds
 Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Electrophoretic Deposition. - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode
 Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by
 Supporting Information for: High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by Engineering Graphene Assemblies Min Zhou,, Xianglong Li, *, Bin Wang, Yunbo Zhang, Jing Ning, Zhichang Xiao, Xinghao Zhang,
Supporting Information for: High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by Engineering Graphene Assemblies Min Zhou,, Xianglong Li, *, Bin Wang, Yunbo Zhang, Jing Ning, Zhichang Xiao, Xinghao Zhang,
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts
 Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution
 Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
MOHAMED R. BERBER Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta 31527, Egypt.
 Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP211) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (212) 133-137 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.1142/S21194512366 CONTROL
Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP211) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (212) 133-137 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.1142/S21194512366 CONTROL
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Cyclic Molecule Aerogels: A Robust Cyclodextrin
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Cyclic Molecule Aerogels: A Robust Cyclodextrin
Structural Study of CHCl 3 Molecular Assemblies in Micropores Using X-ray Techniques
 Structural Study of CHCl 3 Molecular Assemblies in Micropores Using X-ray Techniques TAKU IIYAMA 1, YOSHIE KOBAYASHI 1, ATSUSHI MATSUMOTO 2, YOSHITAKA NAKAHIGASHI 2 AND SUMIO OZEKI 1 1 Department of Chemistry,
Structural Study of CHCl 3 Molecular Assemblies in Micropores Using X-ray Techniques TAKU IIYAMA 1, YOSHIE KOBAYASHI 1, ATSUSHI MATSUMOTO 2, YOSHITAKA NAKAHIGASHI 2 AND SUMIO OZEKI 1 1 Department of Chemistry,
Prediction of Viscosity of Slurry Suspended Fine Particles Using Coupled DEM-DNS Simulation
 A publication of 2089 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 2089 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
