Vibrational properties and phonon transport of amorphous solids
|
|
|
- Jonah Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 June 29th (Fri.), 2018 Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Japan Rheology of disordered particles suspensions, glassy and granular materials 10:15-11:05, 40mins. talk and 10mins. discussion Vibrational properties and phonon transport of amorphous solids Hideyuki Mizuno, Hayato Shiba, Atsushi Ikeda The University of Tokyo, Tohoku University
2 Background Vibrational properties of amorphous solids 2/27 Crystals (lattice structure) Amorphous solids (amorphous structure) Molecules vibrate around lattice structure Molecules vibrate around amorphous structure Tanguy et al., EPL 2010 Vibrational modes are phonons Some modes are localized -> These modes are non-phonons
3 Background Vibrational properties of amorphous solids 3/27 Crystals (lattice structure) Amorphous solids (amorphous structure) Vibrational density of states (one component Lennard-Jones system) Transverse Longitudinal
4 Background Excess low-ω vibrational modes in amorphous solids Excess over Debye-theory prediction (Boson peak) is observed in many glasses (amorphous solids) 4/27 DOS Crystal Crystal Yamamuro et al., JCP 1996 Buchenau et al., PRL 1984
5 Zeller and Pohl, PRB, 1971 Background Low-T thermal properties of amorphous solids Specific heat Thermal conductivity 5/27 SiO2 Crystal SiO2 Glass SiO2 Crystal SiO2 Glass
6 Background Extension of Debye theory: Elastic heterogeneities 6/27 Crystals Debye theory Amorphous solids: Extended Debye theory Ø Ø Ø Homogeneous elastic media Elastic mechanics predict phonons or acoustic waves as vibrational modes This explains heat capacity of crystals T cubed behavior Ø Ø Ø Heterogeneous elastic media Vibrational modes are deformed to nonphonon modes by elastic heterogeneities This predicts heat capacity larger than Debye prediction Thermal properties of amorphous solids (Boson peak) Heterogeneous modulus Schirmacher et al., EPL 2006, PRL 2007
7 Background Multi-scale structure of amorphous solids 7/27 Molecules Local elastic modulus Homogeneous media? Micro-scale Meso-scale Macro-scale At meso-scale, local elastic modulus fluctuates in the space. -> Elastic heterogeneities control thermal properties of amorphous solids Mizuno, Mossa, Barrat, EPL 2013, PNAS 2014, PRB 2016 At macro-scale (continuum limit), amorphous solids behave as homogeneous elastic media? Mizuno, Shiba, Ikeda, PNAS 2017
8 Zeller and Pohl, PRB, 1971 Background Low-T thermal properties of amorphous solids Specific heat Thermal conductivity 8/27 SiO2 Crystal SiO2 Glass SiO2 Crystal SiO2 Glass
9 Contents 9/27 Questions l What is nature of low-frequency vibrations of amorphous solids? l What laws do they obey? We perform molecular-dynamics simulations on a simple model amorphous solid ü Molecules interact through harmonic pair potential ü System size : up to 4,096,000 ü Periodic boundary condition in all the directions
10 Zeller and Pohl, PRB, 1971 Background Low-T specific heat of amorphous solids Specific heat Within the harmonic approximation 10/27 vdos Low-temperature thermal properties are controlled by low-frequency vibrations: SiO2 Crystal SiO2 Glass
11 Background Two level system / Soft potential model Two level system 11/27 Debye theory -> Phonons Additional, non-phonon modes exist in amorphous solids -> Two level system, presumably considered as localized motions of particles -> C T is explained Anderson, et al., Phil. Mag., 1972 Density of two level system with very low energy barriers
12 Vibrational modes analysis 12/27 Spring-mass model u = r r 0 ( ) ü Linearized equation of motion ( 2 ) Φ ü = u r r ü Diagonalize Hessian matrix : (3N 3N matrix) 0 ( e k 2 ) Φ r r 0 ( )) e k = ω k2 ü Vibrational modes (normal modes, eigen modes) Eigen frequencies: k =1, 2,...,3N Eigen vectors:
13 Vibrational modes in Lennard-Jones crystals 13/27 Crystals (lattice structure) Eigen vectors: Transverse phonon Vibrational density of states Transverse Longitudinal Longitudinal phonon
14 Vibrational modes in simple amorphous solid 14/27 Ø A, Debye-like regime : Elastic-wave-like modes Silbert, Liu, Nagel, PRE 2009 Ø B, Plateau regime : Disordered extended modes Ø C, High frequency regime : Highly localized modes Elastic-wave-like mode Disordered extended mode Highly localized mode
15 Vibrational density of states 15/27 Debye level ü We observe the boson peak around ω = 0.1. ü Reduced vdos goes towards the Debye level, but does not converge in our frequency regime.
16 Characterize each vibrational mode: Phonon order parameter 16/27 Phonons in isotropic medium under periodic boundary: : wave vector Expansion by phonon modes (Fourier expansion) of vibrational mode k: Phonon order parameter: : Phonon : Non-phonon
17 Characterize each vibrational mode: Participation ratio 17/27 Participation ratio of vibrational mode k: Mazzacurati, Ruocco, Sampoli, EPL Only one particle vibrates: 2. All the particles vibrate equivalently: Fraction P k of total particles participate in the vibrational mode k
18 Vibrational modes 18/27 At ω > ω* : Non-phonon, extended vibrational nature -> Disordered extended mode At ω ωbp < ω* : Hybrid character of phonon and disordered mode At ω < ωbp : Mixture of phonon mode and soft localized mode -> Consistent with the idea of two-level system
19 Close up to the low-frequency regime 19/27 N = 2,048,000, L = 114 Phonon mode Localized mode ü Non-phonon, localized modes sit between different phonon energy levels
20 Vibrational density of states 20/27
21 Vibrational density of states 21/27 Debye law Non-Debye law of localized modes
22 22/27 g(ω)/ω 2 ored the Vibrational low-frequencymodes vibrational properties in Lennard-Jones glass interacting via the LJ potential, We calculated d All modes figurations by the $!" # " # P > 10 σ 12 σ 6 nalize them to get < 10, φ(r) = 4ϵ P(1) r r ek = (ek1, ek2,, e A they are sorted in a ω vectors ω are normal lar dynamics simulations. When we use short0 eractions like the LJ potential, we usually 1trun ω otential at a fixed value rc [19]. Namely, we ω 0.6 ractions with particles at larger distances0.4than ω owever, when the potential is truncated, 0.2it has 0 nuity at r = rc and this discontinuity may lead 10 Given eigenfrequ 19]. Some methods are used to avoid such er10 λk, the vibration Firstly, we can truncate and shift the potential, 10 it vanishes at r = rc [19]. We call this 10type of 10 tential LJ0, Mixture of phonons and soft localized g(ω) = k 2 k BP 4 0 O k g(ω) Pk modes is observed in LJ glass % Shimada, Mizuno, Ikeda, PRE 2018 φ(r) φ(r c ) (r < rc ) ω 101
23 Conclusion 23/27 Questions l What is nature of low-frequency vibrations of amorphous solids? l What laws do they obey? ü Mixture of phonons and soft localized modes ü Phonons follow Debye law, while localized modes follow non-debye scaling law (ω4 law) ü This seems consistent with TLS/SPM picture ü In the continuum limit, glasses do NOT behave as homogeneous elastic media, but rather they behave as elastic media with ``defects Mizuno, Shiba, Ikeda, PNAS (2017)
24 Conclusion 24/27 Molecules Local elastic modulus Homogeneous media with defects Micro-scale Meso-scale Macro-scale At macro-scale (continuum limit), amorphous solids are essentially different from normal solids (elastic media). ü プレスリリース ( 東大 東北大 ) ガラスと通常の固体の本質的な違いを発見
25 Low-T specific heat Can we explain linear-t term by localized modes? Specific heat Continuum limit Phonon modes Localized modes 25/27 + SiO2 Glass SiO2 Crystal
26 Low-T specific heat Can we explain linear-t term by localized modes? Localized modes Two level system 26/27 l Do two-level tunneling transitions happen in the localized modes? l What is role of non-debye law? Anderson, et al., Phil. Mag., 1972
27 27/27 Localized mode is key to understand amorphous solids Local elastic modulus Homogeneous media with defects Meso-scale Macro-scale Disordered extended modes Phonon modes Localized modes + ω BP ω ex0, Continuum limit
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids
 Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids
 Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 12, 2014
 Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
Anomalous phonon scattering and elastic correlations in amorphous solids
 216MacmilanPublishersLimited,partofSpringerNature.Alrightsreserved.SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NMAT4736 Anomalous phonon scattering and elastic correlations in amorphous solids Simon Gelin 1,2,
216MacmilanPublishersLimited,partofSpringerNature.Alrightsreserved.SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NMAT4736 Anomalous phonon scattering and elastic correlations in amorphous solids Simon Gelin 1,2,
Jamming and the Anticrystal
 Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
Indiana University, January T. Witten, University of Chicago
 Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications
 6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 5: Specific Heat of Lattice Waves Outline Review Lecture 4 3-D Elastic Continuum 3-D Lattice Waves Lattice Density of Modes Specific Heat of Lattice Specific
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 5: Specific Heat of Lattice Waves Outline Review Lecture 4 3-D Elastic Continuum 3-D Lattice Waves Lattice Density of Modes Specific Heat of Lattice Specific
9.3. Total number of phonon modes, total energy and heat capacity
 Phys50.nb 6 E = n = n = exp - (9.9) 9... History of the Planck distribution or the Bose-Einstein distribution. his distribution was firstly discovered by Planck in the study of black-body radiation. here,
Phys50.nb 6 E = n = n = exp - (9.9) 9... History of the Planck distribution or the Bose-Einstein distribution. his distribution was firstly discovered by Planck in the study of black-body radiation. here,
Structural Signatures of Mobility in Jammed and Glassy Systems
 Lisa Manning Sam Schoenholz Ekin Dogus Cubuk Brad Malone Tim Kaxiras Joerg Rottler Rob Riggleman Jennifer Rieser Doug Durian Daniel Sussman Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel Structural Signatures of Mobility in
Lisa Manning Sam Schoenholz Ekin Dogus Cubuk Brad Malone Tim Kaxiras Joerg Rottler Rob Riggleman Jennifer Rieser Doug Durian Daniel Sussman Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel Structural Signatures of Mobility in
Lecture 11 - Phonons II - Thermal Prop. Continued
 Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Lecture 12 Debye Theory
 Lecture 12 Debye Theory 12.1 Background As an improvement over the Einstein model, we now account for interactions between particles they are really coupled together by springs. Consider the 3N normal
Lecture 12 Debye Theory 12.1 Background As an improvement over the Einstein model, we now account for interactions between particles they are really coupled together by springs. Consider the 3N normal
Inhomogeneous elastic response of silica glass
 Inhomogeneous elastic response of silica glass Fabien Leonforte, Anne Tanguy, Joachim Wittmer, Jean-Louis Barrat To cite this version: Inhomogeneous elastic re- Fabien Leonforte, Anne Tanguy, Joachim Wittmer,
Inhomogeneous elastic response of silica glass Fabien Leonforte, Anne Tanguy, Joachim Wittmer, Jean-Louis Barrat To cite this version: Inhomogeneous elastic re- Fabien Leonforte, Anne Tanguy, Joachim Wittmer,
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves
 Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
Rheological properties of polymer melt between rapidly oscillating plates: - an application of multiscale modeling -
 http://multiscale.jp Rheological properties of polymer melt between rapidly oscillating plates: - an application of multiscale modeling - Ryoichi Yamamoto and Shugo Yasuda Dept. Chemical Engineering, Kyoto
http://multiscale.jp Rheological properties of polymer melt between rapidly oscillating plates: - an application of multiscale modeling - Ryoichi Yamamoto and Shugo Yasuda Dept. Chemical Engineering, Kyoto
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis
 Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
Energy Density and Thermal Diffusivity of Ioffe-Regel Confined Vibrations
 (carolinesgorham.com) Energy Density and Thermal Diffusivity of Ioffe-Regel Confined Vibrations Caroline S. Gorham MRS Fall Meeting Symposium ii8: Phonons in Nano and Bulk Materials Session Chair(s): J.
(carolinesgorham.com) Energy Density and Thermal Diffusivity of Ioffe-Regel Confined Vibrations Caroline S. Gorham MRS Fall Meeting Symposium ii8: Phonons in Nano and Bulk Materials Session Chair(s): J.
Heat conduction and phonon localization in disordered harmonic lattices
 Heat conduction and phonon localization in disordered harmonic lattices Anupam Kundu Abhishek Chaudhuri Dibyendu Roy Abhishek Dhar Joel Lebowitz Herbert Spohn Raman Research Institute NUS, Singapore February
Heat conduction and phonon localization in disordered harmonic lattices Anupam Kundu Abhishek Chaudhuri Dibyendu Roy Abhishek Dhar Joel Lebowitz Herbert Spohn Raman Research Institute NUS, Singapore February
Are the calorimetric and elastic Debye temperatures of glasses really different?
 Are the calorimetric and elastic Debye temperatures of glasses really different? M. A. Ramos Laboratorio de Bajas Temperaturas, Departamento de Física de la Materia Condensada, C-III, Instituto de Ciencia
Are the calorimetric and elastic Debye temperatures of glasses really different? M. A. Ramos Laboratorio de Bajas Temperaturas, Departamento de Física de la Materia Condensada, C-III, Instituto de Ciencia
Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016. Lecture 11, MLZ is a cooperation between:
 Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016 Lecture 11, 11.1.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Exam (after winter term) Registration: via TUM-Online between 16.11.2015 15.1.2015 Email: sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de
Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016 Lecture 11, 11.1.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Exam (after winter term) Registration: via TUM-Online between 16.11.2015 15.1.2015 Email: sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de
Theory of Disordered Condensed-Matter Systems
 Electronic hopping transport in disordered semiconductors Theory of Disordered Condensed-Matter Systems Walter Schirmacher University of Mainz, Germany Summer School on Soft Matters and Biophysics, SJTU
Electronic hopping transport in disordered semiconductors Theory of Disordered Condensed-Matter Systems Walter Schirmacher University of Mainz, Germany Summer School on Soft Matters and Biophysics, SJTU
Physics 541: Condensed Matter Physics
 Physics 541: Condensed Matter Physics In-class Midterm Exam Wednesday, October 26, 2011 / 14:00 15:20 / CCIS 4-285 Student s Name: Instructions There are 23 questions. You should attempt all of them. Mark
Physics 541: Condensed Matter Physics In-class Midterm Exam Wednesday, October 26, 2011 / 14:00 15:20 / CCIS 4-285 Student s Name: Instructions There are 23 questions. You should attempt all of them. Mark
Lecture 12: Phonon heat capacity
 Lecture 12: Phonon heat capacity Review o Phonon dispersion relations o Quantum nature of waves in solids Phonon heat capacity o Normal mode enumeration o Density of states o Debye model Review By considering
Lecture 12: Phonon heat capacity Review o Phonon dispersion relations o Quantum nature of waves in solids Phonon heat capacity o Normal mode enumeration o Density of states o Debye model Review By considering
Glasses display a set of universal low-temperature properties
 Breakdown of the Debye approximation for the acoustic modes with nanometric wavelengths in glasses Giulio Monaco 1 and Valentina M. Giordano European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, 6 rue Jules Horowitz,
Breakdown of the Debye approximation for the acoustic modes with nanometric wavelengths in glasses Giulio Monaco 1 and Valentina M. Giordano European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, 6 rue Jules Horowitz,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 23 Jan 1998
 Harmonic Vibrational Excitations in Disordered Solids and the Boson Peak Walter Schirmacher Physik Department E13, Technische Universität München, D 85747 Garching, Germany Gregor Diezemann Institut für
Harmonic Vibrational Excitations in Disordered Solids and the Boson Peak Walter Schirmacher Physik Department E13, Technische Universität München, D 85747 Garching, Germany Gregor Diezemann Institut für
Normal modes in model jammed systems in three dimensions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 79, 238 29 Normal modes in model jammed systems in three dimensions Leonardo E. Silbert, Andrea J. Liu, 2 and Sidney R. Nagel 3 Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 79, 238 29 Normal modes in model jammed systems in three dimensions Leonardo E. Silbert, Andrea J. Liu, 2 and Sidney R. Nagel 3 Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale,
4. Thermal properties of solids. Time to study: 4 hours. Lecture Oscillations of the crystal lattice
 4. Thermal properties of solids Time to study: 4 hours Objective After studying this chapter you will get acquainted with a description of oscillations of atoms learn how to express heat capacity for different
4. Thermal properties of solids Time to study: 4 hours Objective After studying this chapter you will get acquainted with a description of oscillations of atoms learn how to express heat capacity for different
Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses
 Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses A normal liquid will crystallize at a melting temperature T m as it is cooled via a first-order phase transition (see figure above).
Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses A normal liquid will crystallize at a melting temperature T m as it is cooled via a first-order phase transition (see figure above).
Pre-yield non-affine fluctuations and a hidden critical point in strained crystals
 Supplementary Information for: Pre-yield non-affine fluctuations and a hidden critical point in strained crystals Tamoghna Das, a,b Saswati Ganguly, b Surajit Sengupta c and Madan Rao d a Collective Interactions
Supplementary Information for: Pre-yield non-affine fluctuations and a hidden critical point in strained crystals Tamoghna Das, a,b Saswati Ganguly, b Surajit Sengupta c and Madan Rao d a Collective Interactions
Crystals. Peter Košovan. Dept. of Physical and Macromolecular Chemistry
 Crystals Peter Košovan peter.kosovan@natur.cuni.cz Dept. of Physical and Macromolecular Chemistry Lecture 1, Statistical Thermodynamics, MC26P15, 5.1.216 If you find a mistake, kindly report it to the
Crystals Peter Košovan peter.kosovan@natur.cuni.cz Dept. of Physical and Macromolecular Chemistry Lecture 1, Statistical Thermodynamics, MC26P15, 5.1.216 If you find a mistake, kindly report it to the
7. Thermal Properties
 7. Thermal Properties 7.1 Definition and Methods Gibbs free energy G is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from an isothermal, isobaric thermodynamic
7. Thermal Properties 7.1 Definition and Methods Gibbs free energy G is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from an isothermal, isobaric thermodynamic
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
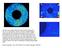 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Apr 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Apr 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Apr 2006](/thumbs/72/66886088.jpg) Universal Features of Terahertz Absorption in Disordered Materials S.N. Taraskin St. Catharine s College and Dept. of Chemistry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK arxiv:cond-mat/6425v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn]
Universal Features of Terahertz Absorption in Disordered Materials S.N. Taraskin St. Catharine s College and Dept. of Chemistry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK arxiv:cond-mat/6425v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn]
Inelastic X ray Scattering
 Inelastic X ray Scattering with mev energy resolution Tullio Scopigno University of Rome La Sapienza INFM - Center for Complex Dynamics in Structured Systems Theoretical background: the scattering cross
Inelastic X ray Scattering with mev energy resolution Tullio Scopigno University of Rome La Sapienza INFM - Center for Complex Dynamics in Structured Systems Theoretical background: the scattering cross
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011](/thumbs/91/104659018.jpg) arxiv:1006.2365v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 The jamming scenario an introduction and outlook Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
arxiv:1006.2365v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 The jamming scenario an introduction and outlook Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Classical Theory of Harmonic Crystals
 Classical Theory of Harmonic Crystals HARMONIC APPROXIMATION The Hamiltonian of the crystal is expressed in terms of the kinetic energies of atoms and the potential energy. In calculating the potential
Classical Theory of Harmonic Crystals HARMONIC APPROXIMATION The Hamiltonian of the crystal is expressed in terms of the kinetic energies of atoms and the potential energy. In calculating the potential
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials
 Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
Thermal properties of Engineering Materials
 Thermal properties of Engineering Materials Engineering materials are important in everyday life because of their versatile structural properties. Other than these properties, they do play an important
Thermal properties of Engineering Materials Engineering materials are important in everyday life because of their versatile structural properties. Other than these properties, they do play an important
ELECTRONS AND PHONONS IN SEMICONDUCTOR MULTILAYERS
 ELECTRONS AND PHONONS IN SEMICONDUCTOR MULTILAYERS В. К. RIDLEY University of Essex CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Introduction 1 Simple Models of the Electron-Phonon Interaction 1.1 General remarks
ELECTRONS AND PHONONS IN SEMICONDUCTOR MULTILAYERS В. К. RIDLEY University of Essex CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Introduction 1 Simple Models of the Electron-Phonon Interaction 1.1 General remarks
Normal Modes of Soft-Sphere Packings: from High to Physical Dimensions
 Normal Modes of Soft-Sphere Packings: from High to Physical Dimensions Alexis Poncet École Normale Supérieure - University of Oregon Why do amorphous solids exhibit an excess of low-energy excitations
Normal Modes of Soft-Sphere Packings: from High to Physical Dimensions Alexis Poncet École Normale Supérieure - University of Oregon Why do amorphous solids exhibit an excess of low-energy excitations
Xiaoming Mao. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania. Collaborators: Tom Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu
 Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
ENERGETICS AND DYNAMICS OF CAGED Zn 4 IN i-sczn
 ENERGETICS AND DYNAMICS OF CAGED Zn 4 IN i-sczn Marek Mihalkovič and Christopher L. Henley [Support: U.S. Dept. of Energy] ICQ11 Poster P02-3, June 14, 2010, Sapporo Japan 1 Introduction Recall: cluster
ENERGETICS AND DYNAMICS OF CAGED Zn 4 IN i-sczn Marek Mihalkovič and Christopher L. Henley [Support: U.S. Dept. of Energy] ICQ11 Poster P02-3, June 14, 2010, Sapporo Japan 1 Introduction Recall: cluster
Crystal Relaxation, Elasticity, and Lattice Dynamics
 http://exciting-code.org Crystal Relaxation, Elasticity, and Lattice Dynamics Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin http://exciting-code.org PART I: Structure Optimization Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität
http://exciting-code.org Crystal Relaxation, Elasticity, and Lattice Dynamics Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin http://exciting-code.org PART I: Structure Optimization Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität
PHONON HEAT CAPACITY
 Solid State Physics PHONON HEAT CAPACITY Lecture 11 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL 4.5 Experimental Specific Heats Element Z A C p Element Z A C p J K 1 mol 1 J K 1 mol 1 Lithium 3 6.94 24.77 Rhenium
Solid State Physics PHONON HEAT CAPACITY Lecture 11 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL 4.5 Experimental Specific Heats Element Z A C p Element Z A C p J K 1 mol 1 J K 1 mol 1 Lithium 3 6.94 24.77 Rhenium
Metamaterials with tunable dynamic properties
 Metamaterials with tunable dynamic properties Varvara Kouznetsova Marc Geers 6 October 2015 Mechanics of Materials Project aim development of new generation mechanical metamaterials with adaptive, tunable
Metamaterials with tunable dynamic properties Varvara Kouznetsova Marc Geers 6 October 2015 Mechanics of Materials Project aim development of new generation mechanical metamaterials with adaptive, tunable
Ultralow thermal conductivity and the thermal conductance of interfaces
 Ultralow thermal conductivity and the thermal conductance of interfaces David G. Cahill, C. Chiritescu, Y.-K. Koh, X. Zheng, W.-P. Hsieh Materials Research Lab and Department of Materials Science, U. of
Ultralow thermal conductivity and the thermal conductance of interfaces David G. Cahill, C. Chiritescu, Y.-K. Koh, X. Zheng, W.-P. Hsieh Materials Research Lab and Department of Materials Science, U. of
Raman scattering investigation of the boson peak in a sodium silicate glass
 Raman scattering investigation of the boson peak in a sodium silicate glass Giacomo Baldi, Aldo Fontana, F. Rossi, Giulio Monaco To cite this version: Giacomo Baldi, Aldo Fontana, F. Rossi, Giulio Monaco.
Raman scattering investigation of the boson peak in a sodium silicate glass Giacomo Baldi, Aldo Fontana, F. Rossi, Giulio Monaco To cite this version: Giacomo Baldi, Aldo Fontana, F. Rossi, Giulio Monaco.
Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation
 Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation Katharina Vollmayr-Lee, Robin Bjorkquist, Landon M. Chambers Bucknell University & Göttingen 7 td tb r n (t) 6 R 5 4 3 2 ti t [ns] waiting
Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation Katharina Vollmayr-Lee, Robin Bjorkquist, Landon M. Chambers Bucknell University & Göttingen 7 td tb r n (t) 6 R 5 4 3 2 ti t [ns] waiting
Phononic Crystals. J.H. Page
 Phononic Crystals J.H. Page University of Manitoba with Suxia Yang and M.L. Cowan at U of M, Ping Sheng and C.T. Chan at HKUST, & Zhengyou Liu at Wuhan University. We study ultrasonic waves in complex
Phononic Crystals J.H. Page University of Manitoba with Suxia Yang and M.L. Cowan at U of M, Ping Sheng and C.T. Chan at HKUST, & Zhengyou Liu at Wuhan University. We study ultrasonic waves in complex
Motivation. Confined acoustics phonons. Modification of phonon lifetimes Antisymmetric Bulk. Symmetric. 10 nm
 Motivation Confined acoustics phonons Modification of phonon lifetimes 0 0 Symmetric Antisymmetric Bulk 0 nm A. Balandin et al, PRB 58(998) 544 Effect of native oxide on dispersion relation Heat transport
Motivation Confined acoustics phonons Modification of phonon lifetimes 0 0 Symmetric Antisymmetric Bulk 0 nm A. Balandin et al, PRB 58(998) 544 Effect of native oxide on dispersion relation Heat transport
Phonons Thermal energy Heat capacity Einstein model Density of states Debye model Anharmonic effects Thermal expansion Thermal conduction by phonons
 3b. Lattice Dynamics Phonons Thermal energy Heat capacity Einstein model Density of states Debye model Anharmonic effects Thermal expansion Thermal conduction by phonons Neutron scattering G. Bracco-Material
3b. Lattice Dynamics Phonons Thermal energy Heat capacity Einstein model Density of states Debye model Anharmonic effects Thermal expansion Thermal conduction by phonons Neutron scattering G. Bracco-Material
Dispersion relation for transverse waves in a linear chain of particles
 Dispersion relation for transverse waves in a linear chain of particles V. I. Repchenkov* It is difficult to overestimate the importance that have for the development of science the simplest physical and
Dispersion relation for transverse waves in a linear chain of particles V. I. Repchenkov* It is difficult to overestimate the importance that have for the development of science the simplest physical and
Ferroelectric Phenomena in Crystals
 В. А. Strukov А. Р. Levanyuk Ferroelectric Phenomena in Crystals Physical Foundations With 153 Figures and 14 Tables Springer Contents 1. General Characteristics of Structural Phase Transitions in Crystals
В. А. Strukov А. Р. Levanyuk Ferroelectric Phenomena in Crystals Physical Foundations With 153 Figures and 14 Tables Springer Contents 1. General Characteristics of Structural Phase Transitions in Crystals
Physics of disordered materials. Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University
 Physics of disordered materials Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University Course plan Familiarity with the basic description of disordered structures
Physics of disordered materials Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University Course plan Familiarity with the basic description of disordered structures
Phonon II Thermal Properties
 Phonon II Thermal Properties Physics, UCF OUTLINES Phonon heat capacity Planck distribution Normal mode enumeration Density of states in one dimension Density of states in three dimension Debye Model for
Phonon II Thermal Properties Physics, UCF OUTLINES Phonon heat capacity Planck distribution Normal mode enumeration Density of states in one dimension Density of states in three dimension Debye Model for
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 9 Apr 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 9 Apr 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 9 Apr 1998](/thumbs/74/70459142.jpg) Potential energy topology and relaxation processes in a model glass F. Demichelis 1 G. Viliani 1, G. Ruocco, 1 Universitá di Trento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica della Materia, I-38050, Povo, Trento,
Potential energy topology and relaxation processes in a model glass F. Demichelis 1 G. Viliani 1, G. Ruocco, 1 Universitá di Trento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica della Materia, I-38050, Povo, Trento,
Physics with Neutrons II, SS Lecture 1, MLZ is a cooperation between:
 Physics with Neutrons II, SS 2016 Lecture 1, 11.4.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Lecture: Monday 12:00 13:30, PH227 Sebastian Mühlbauer (MLZ/FRM II) Sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de Tel:089/289
Physics with Neutrons II, SS 2016 Lecture 1, 11.4.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Lecture: Monday 12:00 13:30, PH227 Sebastian Mühlbauer (MLZ/FRM II) Sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de Tel:089/289
Chapter 6. Heat capacity, enthalpy, & entropy
 Chapter 6 Heat capacity, enthalpy, & entropy 1 6.1 Introduction In this lecture, we examine the heat capacity as a function of temperature, compute the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy, as functions
Chapter 6 Heat capacity, enthalpy, & entropy 1 6.1 Introduction In this lecture, we examine the heat capacity as a function of temperature, compute the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy, as functions
Quantum and classical annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing. Anders W Sandvik, Boston University
 NATIONAL TAIWAN UNIVERSITY, COLLOQUIUM, MARCH 10, 2015 Quantum and classical annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Cheng-Wei Liu (BU) Anatoli Polkovnikov (BU)
NATIONAL TAIWAN UNIVERSITY, COLLOQUIUM, MARCH 10, 2015 Quantum and classical annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Cheng-Wei Liu (BU) Anatoli Polkovnikov (BU)
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials
 Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
T. Egami. Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP)
 Introduction to Metallic Glasses: How they are different/similar to other glasses T. Egami Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP) Hard Sphere vs. Soft Sphere Glass transition Universal behavior History:
Introduction to Metallic Glasses: How they are different/similar to other glasses T. Egami Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP) Hard Sphere vs. Soft Sphere Glass transition Universal behavior History:
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature. Nikolai V. Priezjev
 The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming
 Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons
 Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons D. B. Go Slide 1 The Crystal Lattice The crystal lattice is the organization of atoms and/or molecules in a solid simple cubic body-centered cubic hexagonal a NaCl
Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons D. B. Go Slide 1 The Crystal Lattice The crystal lattice is the organization of atoms and/or molecules in a solid simple cubic body-centered cubic hexagonal a NaCl
Phononic Crystals: Towards the Full Control of Elastic Waves propagation OUTLINE
 Phononic Crystals: Towards the Full Control of Elastic Waves propagation José Sánchez-Dehesa Wave Phenomena Group, Department of Electronic Engineering, Polytechnic University of Valencia, SPAIN. OUTLINE
Phononic Crystals: Towards the Full Control of Elastic Waves propagation José Sánchez-Dehesa Wave Phenomena Group, Department of Electronic Engineering, Polytechnic University of Valencia, SPAIN. OUTLINE
MatSci 331 Homework 4 Molecular Dynamics and Monte Carlo: Stress, heat capacity, quantum nuclear effects, and simulated annealing
 MatSci 331 Homework 4 Molecular Dynamics and Monte Carlo: Stress, heat capacity, quantum nuclear effects, and simulated annealing Due Thursday Feb. 21 at 5pm in Durand 110. Evan Reed In this homework,
MatSci 331 Homework 4 Molecular Dynamics and Monte Carlo: Stress, heat capacity, quantum nuclear effects, and simulated annealing Due Thursday Feb. 21 at 5pm in Durand 110. Evan Reed In this homework,
Composite materials: mechanical properties
 Composite materials: mechanical properties A computational lattice model describing scale effects @ nano-scale Luciano Colombo In collaboration with: Pier Luca Palla and Stefano Giordano Department of
Composite materials: mechanical properties A computational lattice model describing scale effects @ nano-scale Luciano Colombo In collaboration with: Pier Luca Palla and Stefano Giordano Department of
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry. Lecture Notes No. 5a ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SOLIDS
 3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5a ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SOLIDS 1. INTRODUCTION Crystals are held together by interatomic or intermolecular bonds. The bonds can be covalent,
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5a ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SOLIDS 1. INTRODUCTION Crystals are held together by interatomic or intermolecular bonds. The bonds can be covalent,
An Atomistic-based Cohesive Zone Model for Quasi-continua
 An Atomistic-based Cohesive Zone Model for Quasi-continua By Xiaowei Zeng and Shaofan Li Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA94720, USA Extended Abstract
An Atomistic-based Cohesive Zone Model for Quasi-continua By Xiaowei Zeng and Shaofan Li Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA94720, USA Extended Abstract
Introduction to Strain Gage (SG) Technology
 IDMIL - Input Devices and Music Interaction Laboratory McGill University Introduction to Strain Gage (SG) Technology Carolina Brum Medeiros March 14, 2011 About this talk objective: present the essential
IDMIL - Input Devices and Music Interaction Laboratory McGill University Introduction to Strain Gage (SG) Technology Carolina Brum Medeiros March 14, 2011 About this talk objective: present the essential
PHYS 101 Lecture 34 - Physical properties of matter 34-1
 PHYS 101 Lecture 34 - Physical properties of matter 34-1 Lecture 34 - Physical properties of matter What s important: thermal expansion elastic moduli Demonstrations: heated wire; ball and ring; rulers
PHYS 101 Lecture 34 - Physical properties of matter 34-1 Lecture 34 - Physical properties of matter What s important: thermal expansion elastic moduli Demonstrations: heated wire; ball and ring; rulers
New from Ulf in Berzerkeley
 New from Ulf in Berzerkeley from crystallization to statistics of density fluctuations Ulf Rørbæk Pedersen Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, USA Roskilde, December 16th, 21 Ulf
New from Ulf in Berzerkeley from crystallization to statistics of density fluctuations Ulf Rørbæk Pedersen Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, USA Roskilde, December 16th, 21 Ulf
Spin correlations in conducting and superconducting materials Collin Broholm Johns Hopkins University
 Spin correlations in conducting and superconducting materials Collin Broholm Johns Hopkins University Supported by U.S. DoE Basic Energy Sciences, Materials Sciences & Engineering DE-FG02-08ER46544 Overview
Spin correlations in conducting and superconducting materials Collin Broholm Johns Hopkins University Supported by U.S. DoE Basic Energy Sciences, Materials Sciences & Engineering DE-FG02-08ER46544 Overview
Introduction to solid state physics
 PHYS 342/555 Introduction to solid state physics Instructor: Dr. Pengcheng Dai Professor of Physics The University of Tennessee (Room 407A, Nielsen, 974-1509) Chapter 5: Thermal properties Lecture in pdf
PHYS 342/555 Introduction to solid state physics Instructor: Dr. Pengcheng Dai Professor of Physics The University of Tennessee (Room 407A, Nielsen, 974-1509) Chapter 5: Thermal properties Lecture in pdf
Peter Hertel. University of Osnabrück, Germany. Lecture presented at APS, Nankai University, China.
 University of Osnabrück, Germany Lecture presented at APS, Nankai University, China http://www.home.uni-osnabrueck.de/phertel Spring 2012 are metamaterials with strange optical properties structures with
University of Osnabrück, Germany Lecture presented at APS, Nankai University, China http://www.home.uni-osnabrueck.de/phertel Spring 2012 are metamaterials with strange optical properties structures with
Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates. A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System
 Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System Dapeng Bi Sumantra Sarkar Kabir Ramola Jetin Thomas Bob Behringer, Jie Ren Dong Wang Jeff Morris
Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System Dapeng Bi Sumantra Sarkar Kabir Ramola Jetin Thomas Bob Behringer, Jie Ren Dong Wang Jeff Morris
Origin of the negative thermal expansion in ZrW 2 O 8 and ZrV 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 8 (1996) 10973 10982. Printed in the UK Origin of the negative thermal expansion in ZrW 2 O 8 and ZrV 2 O 7 Alexandra K A Pryde, Kenton D Hammonds, Martin T Dove, Volker Heine,
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 8 (1996) 10973 10982. Printed in the UK Origin of the negative thermal expansion in ZrW 2 O 8 and ZrV 2 O 7 Alexandra K A Pryde, Kenton D Hammonds, Martin T Dove, Volker Heine,
HWK#7solution sets Chem 544, fall 2014/12/4
 HWK#7solution sets Chem 544, fall 04//4 Problem # Show that the following relations for state functions hold: a. In analogy to ( lnz/ ) N,V =U and ( lnz/ ) N,V = U proved in class, what are ( ln / ) N,V
HWK#7solution sets Chem 544, fall 04//4 Problem # Show that the following relations for state functions hold: a. In analogy to ( lnz/ ) N,V =U and ( lnz/ ) N,V = U proved in class, what are ( ln / ) N,V
5.62 Physical Chemistry II Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.62 Physical Chemistry II Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.62 Spring 2008 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.62 Physical Chemistry II Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.62 Spring 2008 Lecture
Theory of Disordered Condensed-Matter Systems
 Vibrational anomalies in glasses Theory of Disordered Condensed-Matter Systems Walter Schirmacher University of Mainz, Germany Summer School on Soft Matters and Biophysics, SJTU Shanghai July 3-6, 2017
Vibrational anomalies in glasses Theory of Disordered Condensed-Matter Systems Walter Schirmacher University of Mainz, Germany Summer School on Soft Matters and Biophysics, SJTU Shanghai July 3-6, 2017
 Ph 136: Solution for Chapter 2 3.6 Observations of Cosmic Microwave Radiation from a Moving Earth [by Alexander Putilin] (a) let x = hν/kt, I ν = h4 ν 3 c 2 N N = g s h 3 η = 2 η (for photons) h3 = I ν
Ph 136: Solution for Chapter 2 3.6 Observations of Cosmic Microwave Radiation from a Moving Earth [by Alexander Putilin] (a) let x = hν/kt, I ν = h4 ν 3 c 2 N N = g s h 3 η = 2 η (for photons) h3 = I ν
Phonons I - Crystal Vibrations (Kittel Ch. 4)
 Phonons I - Crystal Vibrations (Kittel Ch. 4) Displacements of Atoms Positions of atoms in their perfect lattice positions are given by: R 0 (n 1, n 2, n 3 ) = n 10 x + n 20 y + n 30 z For simplicity here
Phonons I - Crystal Vibrations (Kittel Ch. 4) Displacements of Atoms Positions of atoms in their perfect lattice positions are given by: R 0 (n 1, n 2, n 3 ) = n 10 x + n 20 y + n 30 z For simplicity here
Phonon Dispersion, Interatomic Force Constants Thermodynamic Quantities
 Phonon Dispersion, Interatomic Force Constants Thermodynamic Quantities Umesh V. Waghmare Theoretical Sciences Unit J N C A S R Bangalore ICMR OUTLINE Vibrations and interatomic force constants (IFC) Extended
Phonon Dispersion, Interatomic Force Constants Thermodynamic Quantities Umesh V. Waghmare Theoretical Sciences Unit J N C A S R Bangalore ICMR OUTLINE Vibrations and interatomic force constants (IFC) Extended
Acoustooptic Bragg Diffraction in 2-Dimensional Photonic Crystals
 Acoustooptic Bragg Diffraction in 2-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Z.A. Pyatakova M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Physics Department zoya.pyatakova@gmail.com Abstract. The paper shows that silicon-based
Acoustooptic Bragg Diffraction in 2-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Z.A. Pyatakova M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Physics Department zoya.pyatakova@gmail.com Abstract. The paper shows that silicon-based
Electronic Properties of Materials An Introduction for Engineers
 Rolf E. Hummel Electronic Properties of Materials An Introduction for Engineers With 219 Illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo Contents PARTI Fundamentals of Electron Theory CHAPTER
Rolf E. Hummel Electronic Properties of Materials An Introduction for Engineers With 219 Illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo Contents PARTI Fundamentals of Electron Theory CHAPTER
Thermal characterization of Au-Si multilayer using 3- omega method
 Thermal characterization of Au-Si multilayer using 3- omega method Sunmi Shin Materials Science and Engineering Program Abstract As thermal management becomes a serious issue in applications of thermoelectrics,
Thermal characterization of Au-Si multilayer using 3- omega method Sunmi Shin Materials Science and Engineering Program Abstract As thermal management becomes a serious issue in applications of thermoelectrics,
Physics 211B : Problem Set #0
 Physics 211B : Problem Set #0 These problems provide a cross section of the sort of exercises I would have assigned had I taught 211A. Please take a look at all the problems, and turn in problems 1, 4,
Physics 211B : Problem Set #0 These problems provide a cross section of the sort of exercises I would have assigned had I taught 211A. Please take a look at all the problems, and turn in problems 1, 4,
Neutron scattering from quantum materials
 Neutron scattering from quantum materials Bernhard Keimer Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research Max Planck UBC UTokyo Center for Quantum Materials Detection of bosonic elementary excitations in
Neutron scattering from quantum materials Bernhard Keimer Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research Max Planck UBC UTokyo Center for Quantum Materials Detection of bosonic elementary excitations in
Atomic Tunneling Systems in Solids
 Atomic Tunneling Systems in Solids real crystals Christian Enss Kirchhoff-Institut of Physics Heidelberg University glasses Tunneling of Atoms in Solids KCl:Li Specific Heat specific heat roughly a factor
Atomic Tunneling Systems in Solids real crystals Christian Enss Kirchhoff-Institut of Physics Heidelberg University glasses Tunneling of Atoms in Solids KCl:Li Specific Heat specific heat roughly a factor
Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure
 Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Introduction: heavy-ion fusion reactions 2. Fusion and Quasi-elastic
Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Introduction: heavy-ion fusion reactions 2. Fusion and Quasi-elastic
The Oxford Solid State Basics
 The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
Atomic Motion via Inelastic X-Ray Scattering
 Atomic Motion via Inelastic X-Ray Scattering Cheiron School Beamline Practical - Monday ONLY at BL35 Alfred Q.R. Baron & Satoshi Tsutsui We will introduce students to the use of inelastic x-ray scattering,
Atomic Motion via Inelastic X-Ray Scattering Cheiron School Beamline Practical - Monday ONLY at BL35 Alfred Q.R. Baron & Satoshi Tsutsui We will introduce students to the use of inelastic x-ray scattering,
Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University
 PY502, Computational Physics, December 12, 2017 Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Advancing Research in Basic Science and Mathematics Example:
PY502, Computational Physics, December 12, 2017 Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Advancing Research in Basic Science and Mathematics Example:
Weight and contact forces: Young's modulus, Hooke's law and material properties
 Weight and contact forces: Young's modulus, Hooke's law and material properties Many objects deform according to Hooke's law; many materials behave elastically and have a Young's modulus. In this section,
Weight and contact forces: Young's modulus, Hooke's law and material properties Many objects deform according to Hooke's law; many materials behave elastically and have a Young's modulus. In this section,
Acoustic study of nano-crystal embedded PbO P 2 O 5 glass
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 9, No. 4, August 6, pp. 357 363. Indian Academy of Sciences. Acoustic study of nano-crystal embedded PbO P O 5 glass SUDIP K BATABYAL, A PAUL, P ROYCHOUDHURY and C BASU* Department
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 9, No. 4, August 6, pp. 357 363. Indian Academy of Sciences. Acoustic study of nano-crystal embedded PbO P O 5 glass SUDIP K BATABYAL, A PAUL, P ROYCHOUDHURY and C BASU* Department
Phonons (Classical theory)
 Phonons (Classical theory) (Read Kittel ch. 4) Classical theory. Consider propagation of elastic waves in cubic crystal, along [00], [0], or [] directions. Entire plane vibrates in phase in these directions
Phonons (Classical theory) (Read Kittel ch. 4) Classical theory. Consider propagation of elastic waves in cubic crystal, along [00], [0], or [] directions. Entire plane vibrates in phase in these directions
Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids
 Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids Chandan Dasgupta Centre for Condensed Matter Theory Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science With Smarajit Karmakar
Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids Chandan Dasgupta Centre for Condensed Matter Theory Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science With Smarajit Karmakar
Topic 5-1: Introduction to Phonons Kittel pages: 91, 92
 Topic 5-1: Introduction to Phonons Kittel pages: 91, 92 Summary: In this video we introduce the concept that atoms are not rigid, fixed points within the lattice. Instead we treat them as quantum harmonic
Topic 5-1: Introduction to Phonons Kittel pages: 91, 92 Summary: In this video we introduce the concept that atoms are not rigid, fixed points within the lattice. Instead we treat them as quantum harmonic
Band gaps in a phononic crystal constituted by cylindrical dots on a homogeneous plate
 Band gaps in a phononic crystal constituted by cylindrical dots on a homogeneous plate B. Djafari-Rouhani, Y. Pennec, H. Larabi, J. Vasseur and A.-C. Hladky IEN, UR CNRS 852, avenue Poincaré, BP 669, 59652
Band gaps in a phononic crystal constituted by cylindrical dots on a homogeneous plate B. Djafari-Rouhani, Y. Pennec, H. Larabi, J. Vasseur and A.-C. Hladky IEN, UR CNRS 852, avenue Poincaré, BP 669, 59652
