XVI. The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, BaTiSia09.
|
|
|
- Beverley Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 139 XV. The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, BaTiSia09. By w. H. Zachariasen (Oslo - Manchester). (With 2 figures.) 1. ntroduction. The mineral Benitoite from St. Benito in California has the composition BaTiSi309. From a crystallographical point of view this compound is especially interesting, being the only known member of the ditrigonalbipyramidal symmetry class. The axial ratio is given as: (Palachel), 0.73H (Louderback2), (Jezek3). The density is (Louderback). Some X-ray examinations of Benitoite have been made. Using the Laue-method F. Ri nne4) was able to prove the ditrigonal-bipyramidal symmetry of the crystals. B. Gossner and F. Mussgnug5) found the dimensions. of the unit cell to be: a = 6.59 A, c = 4.86 A,one molecule in the cell and space group DA. J. J. P. Valeton6) observed in rotation photographs weak layer lines incompatible with Gossn er and Mussgnug's dimensions. Valeton's investigation gave: a = 6.64 A, c = 9.71 A. Two molecules in the cell and space group Dlh or DA. He does not give any information about the atomic arrangement. n the following will give an account of a complete determination of the crystal structure of Benitoite. 2. Dimensions and Space Group. have worked with the Laue-, the oscillation- and the ionization methods. n agreement with Valeton's results found: a = A, c = A, cia = 2 X molecules in the cell. Calculated density No trace of odd order reflexions 0001 were observed, hence the space group is D32hor DA. As (h 0 h l) is absent if l is odd, the correct space croup is D3\' There are thus 2Ba, 2 Ti, 6 Si and 18 atoms in the unit cell. The positions of this space group are:.. 1) Z. Krist. 46, ) Z. Krist 46, ; 60, ) Z. Krist. 60, 6U ) C. Min ) C. Min. A 1927, ) C. Min. A 1927, 387; Z. Krist
2 140 W. H. Zachariascn 2a (000) (0 O.~) 2b (0 0t) (OOt) 2c (1'~'0) (lb-) 2d (H.t) (H -i) 2 e (H. 0) (H- i) 2f (~}l) (H--!) 49 (OOu) (OOu) (Oot-u) (OOu+-~) 4h(H-u)(-H-u)(l~t +-!) (1--1i - u) 4i (-~-lu) (} t u) (~-{-u + -~)(H- i - u) 6J (uuo) (2'uuO) (u2uo) (uu ) (2uu{-) (u2ut) 6k (uvt) (v-uu-}) (vu-vt) (uu-vt) (vut) (v-uvt) 12b (xyx) (y-xxx) (Yx-yx) (xx-yx) (Yxx) (y-xyx) (xy-~.-x (y-xx-~-x) (yx-yi-x) (xx-yx+-~) Ci)xx+-!). (y-xyx+t). 3. Observations. n the following tables have listed the most important observations. With regard to measurements of absolute intensities reference must be made to previous papers in this journal by Professor W. L. Bragg and his co-workers. Table 1. Absolute Measurements of the 0001 Reflexions. o sino l >< 106 =t F' =t' F corr. Fcalc ~ Table 2. Absolute Measurements of Reflexions ~Oh2h L~~J (!'><10~ ~ J' =!l Q = ( Ne2[F ) F' F corr. Fcalc \3 1 + cos220 2,u' mc2 2sin ~ N=--=--- V 370>< 10-24' -=2.816><10-13 mc fl = Po + gq, ', = >< 10-8, ' 9 = 1.85 >< 10-3.
3 The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, BaTiSi Table 3. Observations from Oscillation Photographs'). holt l sin () lnt. ohs. m s vs ~77 m vs m w w m vw vs w-m vs m vs w s s w vw w m. 60 F calc. holt l Table 4. F-Curves. sin (} Ba Ti Si sin () lnt. ohs. F calc. 4. Determination of the Structure. The 2Ba and the 2 Ti atoms must lie in twofold positions. n order to get a tetrahedral arrangement of 4 oxygens about each silicon, the 6 silicon atoms must be equivalent and lie either on the refjexion planes or halfway between. Of the 18 oxygen atoms in the cell 12 must be in general positions while the remaining 6 oxygens are equivalent and lie either on the refjexion planes or halfway between them. The silicon: oxygen ratio is 1 : 3, so the Si04-tetrahedra are not independent. From considerations of the symmetry of the space group we can take it as granted that every oxygen atom must belong to at least one Si04- tetrahedron. The 6 Si atoms and the 60 atoms must therefore lie either all on the refjexion planes or all halfway between. n every structure containing Ti and 0, Ti is found to be surrounded octahedrally by 6 oxygen atoms. f Ti in the present structure is lying in the twofold positions On the ref]exion planes, the 6 oxygens around Ti will form a trigonal prism. Such a configuration would not be stable as the oxygen - oxygen distance must be rather small in order to give the correct Ti - 0 distance 1.96 A, found in all other structures. t 1) s = strong, m = medium, w = weak.
4 142 W. H. Zachariasen is therefore far more plausible that the 2 Ti atoms are situated on the trigonal axes halfway between the ret1exion planes. n order to obtain almost regular tetrahedra around silicon we must further put the 6 silicon and the 6 oxygen atoms on the ret1exion planes. These assumptions can be most readily tested by means of the length of the c-axis. f we take the 0-0 distance in the tetrahedra as and the Ti-O distance equal to , and assume the octahedron about Ti to be regular, the length of the c-axis should be: ( Y3 ) 4 X = , the observed value is , so the agreement is real1y very good. Ba+Ti JSi+JO o Fig. 1. The distribution of electron density between planes n order to explain the very faint ret1exions 0002, 0006, , and we must put the 2Ba on the trigonal axes halfway between the ret1exion planes. The positions of the different atoms are thus: 2Ba in 2 e 2 Ti in 2 c 6 Si in 6 k with parameters Ul and Vt 6 Or in 6 k»» u2» V2 120u in 121»x, y and x. From the considerations given above we have got a rather accurate knowledge of the distribution of atoms in the c-direction. The only
5 The Crystal Struclure of Benitoite, BaTiSi parameter in this direction is the parameter x for oxygen in the general position. The probable value of x we can get from the 0-0 distance in the Si04-group. This knowledge enables us to tell the sign of the amplitude of all reflexions l. The accurate value of x can then be fixed by means of a Fourier sheet analysis. The distribution of electron density between planes 0001 is shown in Fig. 1. For the parameter x we get 4.2. n a later section the results of the Fourier analysis will be discussed more thoroughly. The remaining parameters represent the displacement of the atoms in horizontal directions. We know that the silicons are tetrahedrally surrounded by 4. oxygens. Considerations of the symmetry elements of the space group show that the SiOrtetrahedra must necessarily be linked up so as to form rings of composition Si309. From a large number of silicate structures we have gathered so much information about the Si04-group, that we with the greatest accuracy are able to predict the dimensions of these S~Oggroups. Trigonal rotation axes are passing through the centres of these rings. As a matter of fact, the problem of determining 6 parameters (2 for Si, 2 for Or and 2 for On) is now reduced to the determination of one parameter only, namely the angle of rotation of the Si309-group about the trigonal axis. This angle of rotation can be fixed in different ways. We can make use of 1) the distance Ti-O = 1.96 A, 2) theformation of a regular octahedron of 6 oxygens around Ti, 3) the distance Ba-O = 2.75 A, 4.) the requirement, which is accurately or approximately fullfilled in all silicate structures hitherto known, that an oxygen atom which is attached to three cations is lying in the plane formed by the three cations. An inspection now shows that if we rotate the Si309-group so as to make one of these 4. requirements fullfilled, the remaining three requirements will be simultaneously satisfied. The structure for Benitoite obtained in this way is the only one which is in accordance with. the empirical rules of silicate structures. However, in order to make a yet more thorough test of the structure, the intensities of reflexions must be considered. The tables 1, 2 and 3 show that the agreement between calculated and observed intensities is very good, so the correctness of the structure cannot he doubted. 2Ba in 2 Ti in 6 Si in 60r in 12 On in (-HO) (-1-~-0) Ui Vi t U2V2-1 xyx The parameter values are: Ui = 80 U2 = 800 x = 1250 Vi = - 20 Vi = 70 y = - 30
6 144 W. H. Zachariasen 5. Discussion of the Structure. Fig. 2 shows a projection of the structure on The silicon atoms are surrounded by 201 atoms at a distance 1.65 A and of 20u atoms at a dislance of 1.59 A. The 0-0 distances in the tetrahedra are: = A, O-OU = 2.69 A, ou-ou = 2.59 A 6 oxygen atoms forln an almost regular octahedron around Ti, the Ti-O distance being '1.965 A. Ba is surrounded by 6 oxygen atoms at a distance 2. HA, forming a distorted octahedron. 6 other oxygen atoms have a dislance of about Fig. 2. Projection of the structure on the plane A from Ba, but we cannot consider them as belonging to the first sphere of coordination around Ba. Paulings rule of the electrostatic valency bonds is satisfied: an O-ion is connected to two silicons only, while an Ou-ion is connected one barium. The Si04-tetrahedra share only corners wilh other polyhedra. The Ti06-octahedra share three edges with Ba06-polyhedra, and the reverse. The most interesting feature of the structure is the way in which the tetrahedra are linked together. Rings of composition Si309 are formed. to one silicon + one titanium +
7 The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, BaTiSiaOg Fourier Sheet Analysis. The Fourier analysis of the distribution of electron density between planes 0001 was carried out in order to get the accurate value of the parameter x. n fig. 1 the results of the analysis are given. The dotted curve represents the distribution obtained when using only the observed amplitudes of table 1. The fully drawn curve is the distribution obtained when additional amplitudes were taken into consideration. calculated the amplitudes of the reflexions , and (introducing correction for the too high values of the F-curves at these glancing angles) and inserted the values in the Fourier series. t will be seen from Fig. 1 that the form of the curve depends considerably on the number of members of the series, which have been taken into consideration, although the value of the parameter does not seem to be so much affected. have tried to count up the number of electrons attached to the different ions. do not wish, however, to give any accurate figures here, as do not consider the results to be so unique, that we can draw any conclusions from them. found for Si about 11 electrons, for oxygen a little more than 9 and for Ba + Ti a little more than the number of electrons in the ionic state. A trial showed that it would not be impossible to draw the curves of the electron density so as to give the correct number of electrons in the ionic state. 7. Summary. Benitoite, Ba TiSia Og, crystallizes ditrigonal-bipyramidal. The unit -cell containing 2 molecules has the dimensions: a = A, c = A, cia = = '2 X The space group is DA. The calculated density is The Laue-, the oscilation- and the, ionization methods were used. The structure is given by the following information: '2Ba in positions 2e (-H- 0), 2 Ti in positions 2c (-H- 0) 6Si 6k (Ui Vi!) Ui = 80 Vi = -,:WO 60r in 6k (U2 V2 t) U2 = 80 V2 = 70 1'2On in 12l(xyx) x=125 y=-300 x=42. Si is surrounded by 2 Or + 2 On forming a nearly regular tetrahedron: Si-Or = 1.65 A, Si-On = 1.59 A. The silicon tetrahedra grouped three together form rings of composition SiaOg. Ti is surrounded by 6 On in an almost regular octahedron, the distance Ti-O being 1.96 A. Ba is also surrounded by six oxygens Zeitschr. f. Kristallographie. 74. Bd. 10
8 146 w. H. Zachariasen, The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, OaTiSi309. at a distance 2.74 A. The six oxygens around Ba form a distorted octahedron. The empirical rules of complex coordination structures are satisfied. Most of the experimental work was done in the Physical Laboratories of Victoria University, Manchester. wish to express my most sincere thanks to Professor W. L. Bragg, F. R. S. Manchester for the interest he always showed my work while stayed in his laboratories, and for his kind help and advice. Professor Ch. Palache of Harvard University supplied me with crystals of Benitoite. am very much indebted to him for his kindness. Received March 17th, Oslo, Mineralogical nstitute of the University, February 20th 1930.
Silicate Structures. Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and. Elemental Abundance in Crust. Elemental Abundance in Crust: Pauling s s Rules
 Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and Silicate Structures February 6, 2007 Elemental Abundance in Crust Fe Ion O 2- Si 4+ Al 3+, 3+ Ca Na + K + Mg mol % 2.6 1.4 mol% x charge 4.8 3.8 2.6 1.4 3.8 Sum
Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and Silicate Structures February 6, 2007 Elemental Abundance in Crust Fe Ion O 2- Si 4+ Al 3+, 3+ Ca Na + K + Mg mol % 2.6 1.4 mol% x charge 4.8 3.8 2.6 1.4 3.8 Sum
THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BORAX*
 MINERALOGICAL JOURNAL, VOL. 2, No. 1, pp. 1-18, DEC., 1956 THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BORAX* NOBUO MORIMOTO Mineralogical Institute, University of Tokyo ABSTRACT The crystal structure of borax, Na2B4O7 E10H2O,
MINERALOGICAL JOURNAL, VOL. 2, No. 1, pp. 1-18, DEC., 1956 THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BORAX* NOBUO MORIMOTO Mineralogical Institute, University of Tokyo ABSTRACT The crystal structure of borax, Na2B4O7 E10H2O,
Introduction to VSEPR Theory 1
 1 Class 8: Introduction to VSEPR Theory Sec 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes Two Electron Groups: Linear Geometry Three Electron Groups: Trigonal Planar Geometry Four Electron Groups: Tetrahedral
1 Class 8: Introduction to VSEPR Theory Sec 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes Two Electron Groups: Linear Geometry Three Electron Groups: Trigonal Planar Geometry Four Electron Groups: Tetrahedral
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
8.3 Bonding Theories > Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding. 8.3 Bonding Theories. 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
Geol /19/06 Labs 5 & 6 Crystal Chemistry Ionic Coordination and Mineral Structures
 Geol 2311 9/19/0 Labs 5 & Crystal Chemistry Ionic Coordination and Mineral Structures Handout Oral Mineral Tray Report Samples Ionic Coordination Exercise Investigating Mineral Structures using XtalDraw
Geol 2311 9/19/0 Labs 5 & Crystal Chemistry Ionic Coordination and Mineral Structures Handout Oral Mineral Tray Report Samples Ionic Coordination Exercise Investigating Mineral Structures using XtalDraw
Al2Mg5Si30O6(0H)8, lead to a monoclinic unit of structure with a = 5.2-
 578 CHEMISTR Y: L. PA ULING PRoc. N. A. S. THE STRUCTURE OF THE CHLORITES By LINus PAULING GATZS CHZMICAL LABORATORY, CALIFORNIA INSTITUTH OF TECHNOLOGY Communicated July 9, 1930 By the application of
578 CHEMISTR Y: L. PA ULING PRoc. N. A. S. THE STRUCTURE OF THE CHLORITES By LINus PAULING GATZS CHZMICAL LABORATORY, CALIFORNIA INSTITUTH OF TECHNOLOGY Communicated July 9, 1930 By the application of
Crystal Structure and Chemistry
 Crystal Structure and Chemistry Controls on Crystal Structure Metallic bonding closest packing Covalent bonding depends on orbital overlap and geometry Ionic bonding Pauling s Rules Coordination Principle
Crystal Structure and Chemistry Controls on Crystal Structure Metallic bonding closest packing Covalent bonding depends on orbital overlap and geometry Ionic bonding Pauling s Rules Coordination Principle
Lecture 05 Structure of Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000.
 MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 05 Structure of Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 05 Structure of Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
Chapter 13: Phenomena
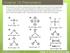
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
CHAPTER 4. Crystal Structure
 CHAPTER 4 Crystal Structure We can assume minerals to be made of orderly packing of atoms or rather ions or molecules. Many mineral properties like symmetry, density etc are dependent on how the atoms
CHAPTER 4 Crystal Structure We can assume minerals to be made of orderly packing of atoms or rather ions or molecules. Many mineral properties like symmetry, density etc are dependent on how the atoms
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)!
 Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)! 15 C 4+ 42 Si 4+ Size of atoms! Hefferan and O Brien, 2010; Earth Materials Force balance! Crystal structure (Chap. 4)!
Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)! 15 C 4+ 42 Si 4+ Size of atoms! Hefferan and O Brien, 2010; Earth Materials Force balance! Crystal structure (Chap. 4)!
XX VII. The Crystal Structure of Potassium Chlorate.
 501 XX VII. The Crystal Structure of Potassium Chlorate. By W. H. Zachariasen (Oslo, p. t. Manchester). (With 2 figures.) 1. Introduction. The chief purpose of the investigation described in the present
501 XX VII. The Crystal Structure of Potassium Chlorate. By W. H. Zachariasen (Oslo, p. t. Manchester). (With 2 figures.) 1. Introduction. The chief purpose of the investigation described in the present
8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook. September 10, 2015
 chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
Further refinement of the goyazite structure
 MNERALOGCAL JOURNAL, VOL. 13, NO.6, PP. 390-396, APRL 1987 Short Communication Further refinement of the goyazite structure Toshio KATO nstitute of Earth Sciences, Faculty of Liberal Arts, Yamaguchi University,
MNERALOGCAL JOURNAL, VOL. 13, NO.6, PP. 390-396, APRL 1987 Short Communication Further refinement of the goyazite structure Toshio KATO nstitute of Earth Sciences, Faculty of Liberal Arts, Yamaguchi University,
DETERMINATION OF THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LIROCONITE CU2A1[As04] (OH)4.4H20 R. V. Kolesova and E. G. Fesenko
![DETERMINATION OF THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LIROCONITE CU2A1[As04] (OH)4.4H20 R. V. Kolesova and E. G. Fesenko DETERMINATION OF THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LIROCONITE CU2A1[As04] (OH)4.4H20 R. V. Kolesova and E. G. Fesenko](/thumbs/94/118464751.jpg) SOVET PHYSCS - CRYSTALLOGRAPHY VOL. 13, NO.3 NOV.-DEC., 1968 DETERMNATON OF THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LROCONTE CU2A1[As04] (OH)4.4H20 R. V. Kolesova and E. G. Fesenko Rostov University Translated from Kristallografiya,
SOVET PHYSCS - CRYSTALLOGRAPHY VOL. 13, NO.3 NOV.-DEC., 1968 DETERMNATON OF THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LROCONTE CU2A1[As04] (OH)4.4H20 R. V. Kolesova and E. G. Fesenko Rostov University Translated from Kristallografiya,
Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures
 Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures Pauling s Rules A coordination polyhedron of anions forms around a cation Ionic distance determined by radii Coordination number determined by radius ratio. May
Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures Pauling s Rules A coordination polyhedron of anions forms around a cation Ionic distance determined by radii Coordination number determined by radius ratio. May
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Section 12: Lewis Structures
 Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory No. 1 of 10 1. Which shape would have sp 3 hybridization? (A) Linear (B) Bent (C) Tetrahedron (D) Trigonal planar (E) Octahedron C. Correct.
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory No. 1 of 10 1. Which shape would have sp 3 hybridization? (A) Linear (B) Bent (C) Tetrahedron (D) Trigonal planar (E) Octahedron C. Correct.
Bonding and Packing: building crystalline solids
 Bonding and Packing: building crystalline solids The major forces of BONDING Gravitational forces: F = G m m 1 2 F = attractive forces between 2 bodies G = universal graviational constant (6.6767 * 10
Bonding and Packing: building crystalline solids The major forces of BONDING Gravitational forces: F = G m m 1 2 F = attractive forces between 2 bodies G = universal graviational constant (6.6767 * 10
Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m12594 1 Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory * John S. Hutchinson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1
OpenStax-CNX module: m12594 1 Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory * John S. Hutchinson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Now explore the Compare Two Structures link. Try changing the display to explore different combinations.
 Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Bonding. Bringing the atoms together
 Bonding Bringing the atoms together More than one atom Until now, we have been consumed with describing individual atoms of elements. However, isolating individual atoms in most elements is an arduous
Bonding Bringing the atoms together More than one atom Until now, we have been consumed with describing individual atoms of elements. However, isolating individual atoms in most elements is an arduous
Chemistry and the material world Lecture 3
 Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS
 CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
Earth Materials I Crystal Structures
 Earth Materials I Crystal Structures Isotopes same atomic number, different numbers of neutrons, different atomic mass. Ta ble 1-1. Su mmar y of quantu m num bers Name Symbol Values Principal n 1, 2,
Earth Materials I Crystal Structures Isotopes same atomic number, different numbers of neutrons, different atomic mass. Ta ble 1-1. Su mmar y of quantu m num bers Name Symbol Values Principal n 1, 2,
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Molecular Shapes. Molecular Shapes. Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms
 Answers Questions 16.2 Molecular polarity 1. Write a dot diagram for the HCl molecule. Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms Difference in electronegativity =
Answers Questions 16.2 Molecular polarity 1. Write a dot diagram for the HCl molecule. Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms Difference in electronegativity =
Earth and Planetary Materials
 Earth and Planetary Materials Spring 2013 Lecture 3 2013.01.14 14 1 Close Packed Anion Arrays Closest Packing Coordination number (C.N.) : number of anions bonded to a cation larger cation, higher C.N.
Earth and Planetary Materials Spring 2013 Lecture 3 2013.01.14 14 1 Close Packed Anion Arrays Closest Packing Coordination number (C.N.) : number of anions bonded to a cation larger cation, higher C.N.
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory
 Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Molecular Geometry. Valence Shell Electron Pair. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Localized Electron Model
 Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
CHEMICAL BONDS A CHEMICAL BOND IS A FORCE OF ATTRACTION HOLDING THE ATOMS OR IONS TOGETHER.
 CHEMICAL BONDS A CHEMICAL BOND IS A FORCE OF ATTRACTION HOLDING THE ATOMS OR IONS TOGETHER. q Elements tend to enter into chemical reaction to gain stability q This is satisfied by completing the octet
CHEMICAL BONDS A CHEMICAL BOND IS A FORCE OF ATTRACTION HOLDING THE ATOMS OR IONS TOGETHER. q Elements tend to enter into chemical reaction to gain stability q This is satisfied by completing the octet
Big Idea: Ionic Bonds: Ionic Bonds: Metals: Nonmetals: Covalent Bonds: Ionic Solids: What ions do atoms form? Electron Electron
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Review Chapter 10: Theories of Bonding & Structure. Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop
 Review Chapter 10: Theories of Bonding & Structure Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop Chapter 10 Concepts q VESPR theory q Predict molecular geometry
Review Chapter 10: Theories of Bonding & Structure Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop Chapter 10 Concepts q VESPR theory q Predict molecular geometry
3.012 Quiz Fall points total
 3.012 Quiz 1 3.012 09.23.04 Fall 2004 100 points total Structure (50 points total): 1.. (16 points). Let s consider an ionic compound of composition A 2 B 3 in which the coordination number C NA of every
3.012 Quiz 1 3.012 09.23.04 Fall 2004 100 points total Structure (50 points total): 1.. (16 points). Let s consider an ionic compound of composition A 2 B 3 in which the coordination number C NA of every
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 6 th Ed. Introductory Chemistry, 6 th Ed. Basic Chemistry, 6 th Ed.
 Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 6 th Ed. Introductory Chemistry, 6 th Ed. Basic Chemistry, 6 th Ed. by Steven S. Zumdahl & Donald J. DeCoste University of Illinois Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Structure
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 6 th Ed. Introductory Chemistry, 6 th Ed. Basic Chemistry, 6 th Ed. by Steven S. Zumdahl & Donald J. DeCoste University of Illinois Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Structure
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Learning Objective
 Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Topic 2. Structure and Bonding Models of Covalent Compounds of p-block Elements
 Topic 2 2-1 Structure and Bonding Models of Covalent Compounds of p-block Elements Bonding 2-2 Many different approaches to describe bonding: Ionic Bonding: Elements with large electronegativity differences;
Topic 2 2-1 Structure and Bonding Models of Covalent Compounds of p-block Elements Bonding 2-2 Many different approaches to describe bonding: Ionic Bonding: Elements with large electronegativity differences;
Experiment #2. Lewis Structures
 Experiment #2. Lewis Structures A Lewis structure shows how the valence electrons are arranged and indicates the bonding between atoms in a molecule. We represent the elements by their symbols. The shared
Experiment #2. Lewis Structures A Lewis structure shows how the valence electrons are arranged and indicates the bonding between atoms in a molecule. We represent the elements by their symbols. The shared
!"##$%&'()$*+,%'-./'
 !"##$%&()$*+,%-./ 0,1,%$234%5$1673896:2:567$2(),#6;+%& 6!#6+)! CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know! The difference between ionic and covalent bonds! Define cations and anions! Predict cation/anion
!"##$%&()$*+,%-./ 0,1,%$234%5$1673896:2:567$2(),#6;+%& 6!#6+)! CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know! The difference between ionic and covalent bonds! Define cations and anions! Predict cation/anion
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Lecture outline: Section 9. theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory. S. Ensign, Chem. 1210
 Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model
 1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
For more info visit Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule.
 Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models
 25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
Differentiaton: Redistribution of mass (elements) and energy by chemical & physical processes. Goal: Quantitative understanding of those processes.
 Differentiaton: Redistribution of mass (elements) and energy by chemical & physical processes. Goal: Quantitative understanding of those processes. 1 2 What controls the periodicity of behavior of the
Differentiaton: Redistribution of mass (elements) and energy by chemical & physical processes. Goal: Quantitative understanding of those processes. 1 2 What controls the periodicity of behavior of the
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
Lewis Dot Structures for Methane, CH 4 The central C atom is bonded by single bonds (-) to 4 individual H atoms
 Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
EXPERIMENT #13 Lewis Structures and Molecular Geometry
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING
 Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
Cation Exchange Capacity, CEC
 Cation Exchange Capacity, CEC The basic building blocks of clay minerals are: silicon atoms surrounded by four oxygen atoms (tetrahedra), and aluminium atoms surrounded by six hydroxide groups (dioctahedra),
Cation Exchange Capacity, CEC The basic building blocks of clay minerals are: silicon atoms surrounded by four oxygen atoms (tetrahedra), and aluminium atoms surrounded by six hydroxide groups (dioctahedra),
Chapter 13: Phenomena
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
A simple example of a polyhedral network or polynet, constructed from truncated octahedra and hexagonal prisms.
 Polyhedral Nets A simple example of a polyhedral network or polynet, constructed from truncated octahedra and hexagonal prisms. The building process indicated produces a labyrinth. The labyrinth graph
Polyhedral Nets A simple example of a polyhedral network or polynet, constructed from truncated octahedra and hexagonal prisms. The building process indicated produces a labyrinth. The labyrinth graph
Nanomaterial: Look at the Earth
 Nanomaterial: Look at the Earth Siddhartha S. Mukhopadhyay Electron Microscopy and Nanoscience Laboratory, Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana Why clay? The unit cell dimensions of clay minerals are
Nanomaterial: Look at the Earth Siddhartha S. Mukhopadhyay Electron Microscopy and Nanoscience Laboratory, Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana Why clay? The unit cell dimensions of clay minerals are
H O H C H H N H H. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity
 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity BJECTIVES Students will develop the ability to: 1. Predict the arrangement that valence e pairs assume around an atom (e pair geometry)
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity BJECTIVES Students will develop the ability to: 1. Predict the arrangement that valence e pairs assume around an atom (e pair geometry)
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures
 Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures 3.1.1. Fundamental concepts 3.1.2. Unit cells 3.1.3. Metallic crystal structures 3.1.4. Ceramic crystal structures 3.1.5. Silicate
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures 3.1.1. Fundamental concepts 3.1.2. Unit cells 3.1.3. Metallic crystal structures 3.1.4. Ceramic crystal structures 3.1.5. Silicate
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017
 Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to :
 At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
Pauli Principle. ! This requirement (which has no theoretical proof) does not change the overall state of the system.
 Pauli Principle! The complete wave function for a system of electrons in a multielectron atom depends upon orbital (spatial) and spin contributions; i.e., ψ = ψ orb ψ spin = ψ(n,l,m l )ψ(m s ).! All electrons
Pauli Principle! The complete wave function for a system of electrons in a multielectron atom depends upon orbital (spatial) and spin contributions; i.e., ψ = ψ orb ψ spin = ψ(n,l,m l )ψ(m s ).! All electrons
Chemical bonds. In some minerals, other (less important) bond types include:
 Chemical bonds Chemical bond: force of attraction between two or more atoms/ions Types of bonds in crystals: Ionic bond: electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. This type of bond
Chemical bonds Chemical bond: force of attraction between two or more atoms/ions Types of bonds in crystals: Ionic bond: electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. This type of bond
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS CHEMICAL BONDS: LEWIS SYMBOLS: CHEMICAL BONDING. What are valence electrons?
 REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6 Group 7 Group 8. Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
 CHM 111 Chapters 7 and 8 Worksheet and Study Guide Purpose: This is a guide for your as you work through the chapter. The major topics are provided so that you can write notes on each topic and work the
CHM 111 Chapters 7 and 8 Worksheet and Study Guide Purpose: This is a guide for your as you work through the chapter. The major topics are provided so that you can write notes on each topic and work the
Diamond. There are four types of solid: -Hard Structure - Tetrahedral atomic arrangement. What hybrid state do you think the carbon has?
 Bonding in Solids Bonding in Solids There are four types of solid: 1. Molecular (formed from molecules) - usually soft with low melting points and poor conductivity. 2. Covalent network - very hard with
Bonding in Solids Bonding in Solids There are four types of solid: 1. Molecular (formed from molecules) - usually soft with low melting points and poor conductivity. 2. Covalent network - very hard with
There are four types of solid:
 Bonding in Solids There are four types of solid: 1. Molecular (formed from molecules) - usually soft with low melting points and poor conductivity. 2. Covalent network - very hard with very high melting
Bonding in Solids There are four types of solid: 1. Molecular (formed from molecules) - usually soft with low melting points and poor conductivity. 2. Covalent network - very hard with very high melting
Memorize: Understand: Know how to:
 NAME: CLASS PERIOD: REVIEW FOR HONORS CHEMISTRY SEMESTER 1 EXAM Memorize: Understand: Know how to: 1 SI units for different measurements (length, volume, number, mass, temperature, density) Definition
NAME: CLASS PERIOD: REVIEW FOR HONORS CHEMISTRY SEMESTER 1 EXAM Memorize: Understand: Know how to: 1 SI units for different measurements (length, volume, number, mass, temperature, density) Definition
Lecture B2 VSEPR Theory
 Lecture B2 VSEPR Theory Covalent Bond Theories 1. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion model). A set of empirical rules for predicting a molecular geometry using, as input, a correct Lewis Dot
Lecture B2 VSEPR Theory Covalent Bond Theories 1. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion model). A set of empirical rules for predicting a molecular geometry using, as input, a correct Lewis Dot
Chapter 13: Phenomena
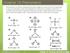 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc...
 Lewis Structure Lab For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc... I can t assume you have had all these, so
Lewis Structure Lab For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc... I can t assume you have had all these, so
Electron Geometry Hybrid Orbitals
 Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
VSEPR. Ch10. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions.
 Ch10 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions. version 1.5 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Valence Shell Electron
Ch10 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions. version 1.5 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Valence Shell Electron
Silicon-Oxygen Bond Lengths, Bridging Angles Si-O--Si and Synthetic Low Tridymite
 2615 Acta Cryst. (1977). B33, 2615-2619 Silicon-Oxygen Bond Lengths, Bridging Angles Si-O--Si and Synthetic Low Tridymite BY WERNER H. BAUR Department of Geological Sciences, University of Illinois, Chicago,
2615 Acta Cryst. (1977). B33, 2615-2619 Silicon-Oxygen Bond Lengths, Bridging Angles Si-O--Si and Synthetic Low Tridymite BY WERNER H. BAUR Department of Geological Sciences, University of Illinois, Chicago,
EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5
 EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5 Oxidation states of transition elements (many more in aqueous solutions than in the common rock-forming minerals) Notice that almost every transition metal has a +2 oxidation
EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5 Oxidation states of transition elements (many more in aqueous solutions than in the common rock-forming minerals) Notice that almost every transition metal has a +2 oxidation
CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF THE BASIC MANGANESE ARSENATES: III. The CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF EVEITE, Mn 2 (OH) (AsO 4 )
 THE AMERICAN MINERALOGIST, VOL. 53, NOVEMBER-DECEMBER, 1968 CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF THE BASIC MANGANESE ARSENATES: III. The CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF EVEITE, Mn 2 (OH) (AsO 4 ) PAUL B. MOORE and JOSEPH R. SMYTH,
THE AMERICAN MINERALOGIST, VOL. 53, NOVEMBER-DECEMBER, 1968 CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF THE BASIC MANGANESE ARSENATES: III. The CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF EVEITE, Mn 2 (OH) (AsO 4 ) PAUL B. MOORE and JOSEPH R. SMYTH,
PbFe3(PO4)2(OH,H20)6
 The crystal structure of kintoreite, PbFe3(PO4)2(OH,H20)6 KHARISUN*, M. R. TAYLOR, D. J. M. BEVAN Department of Chemistry, Hinders University, GPO Box 2100 Adelaide, South Australia 5000, Australia AND
The crystal structure of kintoreite, PbFe3(PO4)2(OH,H20)6 KHARISUN*, M. R. TAYLOR, D. J. M. BEVAN Department of Chemistry, Hinders University, GPO Box 2100 Adelaide, South Australia 5000, Australia AND
Coordination Compounds
 Coordination Compounds 1. What is a coordination compound composed of? a. Metal Ion b. Ligand c. Counter Ion 2. What is a complex ion? The metal ion and ligand combination. 3. What is a counter ion? An
Coordination Compounds 1. What is a coordination compound composed of? a. Metal Ion b. Ligand c. Counter Ion 2. What is a complex ion? The metal ion and ligand combination. 3. What is a counter ion? An
Wold of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding
![Wold of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Wold of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding](/thumbs/77/75442347.jpg) Wold of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding 1) The History of the Development of the Period Table (Not in the book!) Similarities between the chemical and physical
Wold of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding 1) The History of the Development of the Period Table (Not in the book!) Similarities between the chemical and physical
SL Score. HL Score ! /30 ! /48. Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding. Name
 Name Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding SL SL Score! /30 HL Score! /48 1. What is the correct Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, a compound containing chlorine, hydrogen and oxygen? A. B. C. D.
Name Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding SL SL Score! /30 HL Score! /48 1. What is the correct Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, a compound containing chlorine, hydrogen and oxygen? A. B. C. D.
X-ray determination of centrosymmetry in three felspars. 1
 759 X-ray determination of centrosymmetry in three felspars. 1 By S. W. BAILEY, R. B. FERUUSO~, and W. It. TAYLOR. Crystallographic Laboratory, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge. [Read May 16, 1951.] T Introduction.
759 X-ray determination of centrosymmetry in three felspars. 1 By S. W. BAILEY, R. B. FERUUSO~, and W. It. TAYLOR. Crystallographic Laboratory, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge. [Read May 16, 1951.] T Introduction.
11/14/2014. Chemical Bonding. Richard Philips Feynman, Nobel Laureate in Physics ( )
 Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Chapter 1 Bonding and Isomerism
 Chapter 1 Bonding and Isomerism Ionic Compounds: e-are transferred; Cation (+) & anion (-). Opposite charge creates bond. Occurs when compound is made of a metal & a nonmetal. Electron dot structures for:
Chapter 1 Bonding and Isomerism Ionic Compounds: e-are transferred; Cation (+) & anion (-). Opposite charge creates bond. Occurs when compound is made of a metal & a nonmetal. Electron dot structures for:
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
 VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
Forming Chemical Bonds
 Forming Chemical Bonds Why do atoms form chemical bonds? so that the system can achieve the lowest possible potential energy Example covalent bonding in H 2 H H Potential energy 0 Distance of separation
Forming Chemical Bonds Why do atoms form chemical bonds? so that the system can achieve the lowest possible potential energy Example covalent bonding in H 2 H H Potential energy 0 Distance of separation
TOPIC 4 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 IONIC BONDING
 TOPIC 4 ANSWERS & MARK SCEMES QUESTIONSEET 1 IONIC BONDING a) A bond formed by the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to form ions of opposite charge which attract each
TOPIC 4 ANSWERS & MARK SCEMES QUESTIONSEET 1 IONIC BONDING a) A bond formed by the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to form ions of opposite charge which attract each
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 1 - VSEPR
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 1 - VSEPR Objectives: 1. Understand and become proficient at using VSEPR to predict the geometries of simple molecules and ions. 2. Become proficient at predicting
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 1 - VSEPR Objectives: 1. Understand and become proficient at using VSEPR to predict the geometries of simple molecules and ions. 2. Become proficient at predicting
Origin of optical pleochroism in orthopyroxenes
 715 Origin of optical pleochroism in orthopyroxenes By ROGER G. BURNS Department of Mineralogy and Petrology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge [Read 4 November 1965] Summary. The necessary conditions
715 Origin of optical pleochroism in orthopyroxenes By ROGER G. BURNS Department of Mineralogy and Petrology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge [Read 4 November 1965] Summary. The necessary conditions
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTERS 5 & 6 Problem Set #4. (Questions 1-13) Choose the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement.
 NAME: AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTERS 5 & 6 Problem Set #4 (Questions 1-13) Choose the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement. (Questions 1-2) Consider atoms of the following elements.
NAME: AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTERS 5 & 6 Problem Set #4 (Questions 1-13) Choose the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement. (Questions 1-2) Consider atoms of the following elements.
Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond
 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the and electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Ionic Bond o that results from the attraction between large
Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the and electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Ionic Bond o that results from the attraction between large
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Lecture 6. Physical Properties. Solid Phase. Particle Composition
 Lecture 6 Physical Properties Solid Phase Particle Composition 1 Questions What are tetrahedrons and octahedrons? How do silica tetrahedra bonds affect mineral weathering? Difference between primary and
Lecture 6 Physical Properties Solid Phase Particle Composition 1 Questions What are tetrahedrons and octahedrons? How do silica tetrahedra bonds affect mineral weathering? Difference between primary and
Molecular Geometry & Polarity
 Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8
 Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
