Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms
|
|
|
- Bethany Peters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Answers Questions 16.2 Molecular polarity 1. Write a dot diagram for the HCl molecule. Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms Difference in electronegativity = 1.06 Is the bond nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic? Polar covalent What is the percentage ionic character in the bond? 22% ionic character Which atom is slightly negative and which is slightly positive? Why? Chlorine is slightly negative because it has a higher attraction for the bond electrons than the hydrogen. About 22% of the time the electron bond pair is around the chlorine atom only. The element with the higher electronegativity will always be slightly negative. Hydrogen is slightly positive because the bond electrons are completely absent part of the time. 2. Why does increasing the number of pi bonds add to charge density? Sigma bonds are formed from hybridized orbitals and will have some s orbital and some p orbital character. Single bonds are always sigma bonds. Pi bonds are formed from an overlap of unhybridized p orbitals. The pi bonds will overlap the sigma bonds, creating a volume with a larger charge density because you have more electron bond pairs in the volume between the atoms bonded together. Single bond Sigma bond only
2 Double Bond 1 Sigma bond and 1 Pi bond The sigma bonds are arranged at 120 degrees in a plane. The pi bond has two parts, one above the plane and one below the plane. The pi bond overlaps the sigma to form the double bond.
3 Triple Bond 1 Sigma bond and 2 Pi bonds The triple bond is formed from one sigma bond and two pi bonds. The sigma bond forms a linear molecule (180 degrees) while the two pi bonds overlap the sigma to form a "pig in a blanket" tunnel of pi electrons.
4 3. Build models and draw sketches of CH 4, CH 3 Cl, CH 2 Cl 2, CHCl 3, and CCl 4 All models have 4 single bonds, sp3 hybridized, with a bond angle of degrees. No pi bonds are present. Is the carbon-hydrogen bond polar? The C-H bond in nonpolar (difference in electronegativity of 0.45) Is the carbon-chlorine bond polar? The C-Cl bond is polar (difference in electronegativity of 0.61) Which atom is negative and which is positive? Chlorine is slightly negative since it has the higher electronegativity Which of the CH 3 Cl, CH 2 Cl 2, CHCl 3, and CCl 4 molecules has the biggest distance between the center of positive and negative charges? CH 3 Cl has the largest distance between the center of positive and negative charges. The dipole moment is a vector from the center of positive charge to the center of negative charge of the molecule. The larger the dipole moment the more polar the molecule. Why is the center of negative and positive charges the same in CCl 4? Because the slightly negative chlorines are arranged symmetrically the centers of positive and negative charges are both in the center of the molecule.
5 4. Draw a sketch of BBr 3 Is the boron-bromine bond polar or nonpolar? Difference of electronegativity = 0.92 Polar covalent bond with bromine negative and boron positive. Locate the center of positive and negative charge in the BBr 3 molecule. Why is the molecule nonpolar? The slightly negative charges are distributed symmetrically on the molecule In general molecular polarity can be summed up as follows: Negative areas of a molecule are caused by more the electronegative atom of polar bonds, with the strength of the negative charge increasing with higher percentage ionic character. Lone pairs and pi bonds produce weaker areas of negative charge. If a molecule has no polar bonds, lone pairs, or pi bonds it cannot be polar. If a molecule has negative charges distributes symmetrically it is not polar. If polar bonds are on the opposite end of a molecule from nonpolar bonds the molecules will be polar because the centers of positive and negative charge will be far apart.
6 Finding the shapes of molecules from the hybridization 5. For each molecule below sketch the molecule, tell if each bond is polar or nonpolar, put S- by each negative part of the molecule and S+ by each positive part of the molecule, and tell if the molecule is polar or nonpolar. Na 2 S Sulfur has 2 bond pair and 2 lone pair (sp3 hybridized) (distorted tetrahedral) Difference in electronegativity is Polar covalent bond with sulfur negative and sodium positive
7 AlF 3 Aluminum has 3 bond pair no lone pair (sp 2 hybridized) (Trigonal planar) Difference in electronegativity is Ionic Bond SiI 4 Silicon has 4 bond pair, no lone pair (sp 3 hybridized) (Tetrahedal) Difference in electronegativity is 0.76 Polar covalent bond Iodine is negative, Silicon is positive NH 3 Nitrogen has 3 bond pair, 1 lone pair. (sp 3 hybridized) (distorted tetrahedral) Difference in electronegativity = 0.94 Polar Covalent bond Nitrogen is slightly negative, Hydrogen is slightly positive
8 H 2 O Oxygen has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs (sp 3 hybridization) (distorted tetrahedral) Difference in electronegativity = 1.34 Polar covalent bond Oxygen is slightly negative, Hydrogen is slightly positive PCl 3 Phosphorus has 3 bond pair and 1 lone pair (sp 3 hybridized) (distorted tetrahedral) Difference in electronegativity is 0.97 Polar covalent bond Chlorine is slightly negative, phosphorus is slightly positive
9 AsBr 5 Arsenic must have 5 bond pairs and no lone pairs. (sp 3 d hybridized) (trigonal bipyramidal) Difference in electronegativity = 0.78 Polar covalent bond Bromine is slightly negative, Arsenic is slightly positive SCl 6 Sulfur has 6 bond pairs, no lone pairs (sp 3 d 2 hybridized) (octahedral) Difference in electronegativity = 0.58 Polar covalent bond Chlorine slightly negative, sulfur slightly positive
Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding
 Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding Chapter 16: 1 26; 28, 30, 31, 35-37, 40, 43-46, Extra Credit: 50-53, 55, 56, 58, 59, 62-67 Section 16.1 The Nature of Covalent Bonding Practice Problems
Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding Chapter 16: 1 26; 28, 30, 31, 35-37, 40, 43-46, Extra Credit: 50-53, 55, 56, 58, 59, 62-67 Section 16.1 The Nature of Covalent Bonding Practice Problems
SMK SULTAN ISMAIL JB, NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB
 SMK SULTAN ISMAIL JB, NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB POLAR AND NON POLAR BONDS BOND POLARITY 1. Atoms with different electronegative from polar bonds (difference in EN) 2. Depicted as polar arrow : 3. Example
SMK SULTAN ISMAIL JB, NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB POLAR AND NON POLAR BONDS BOND POLARITY 1. Atoms with different electronegative from polar bonds (difference in EN) 2. Depicted as polar arrow : 3. Example
Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017
 Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
electronegativity difference greater than or equal to Ionic Bonding occurs between a metal and a nonmetal when there is an
 Chemistry Unit 4 Review Packet Sweeeeeeeettt ANSWER KEY For the following compounds identify the bond types as one of the following: Ionic, Metallic, Polar Covalent, Non Polar Covalent, and Moderately
Chemistry Unit 4 Review Packet Sweeeeeeeettt ANSWER KEY For the following compounds identify the bond types as one of the following: Ionic, Metallic, Polar Covalent, Non Polar Covalent, and Moderately
Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam
 Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam 1. What is the correct electron configuration for bromine? b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 9 4s 2 4p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p
Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam 1. What is the correct electron configuration for bromine? b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 9 4s 2 4p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Valence Bond Theory - Description
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Hybridization of Orbitals
 Hybridization of Orbitals Structure & Properties of Matter 1 Atomic Orbitals and Bonding Previously: Electron configurations Lewis structures Bonding Shapes of molecules Now: How do atoms form covalent
Hybridization of Orbitals Structure & Properties of Matter 1 Atomic Orbitals and Bonding Previously: Electron configurations Lewis structures Bonding Shapes of molecules Now: How do atoms form covalent
* one of these choices is not used
 IONIC BONDING REVIEW WORKSHEET Part 1 - Complete each of the following sentences by filling in the appropriate word or phrase from the list below. negative noble gas octet anion positive electrons ions
IONIC BONDING REVIEW WORKSHEET Part 1 - Complete each of the following sentences by filling in the appropriate word or phrase from the list below. negative noble gas octet anion positive electrons ions
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Valence shell electron
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Valence shell electron
CHAPTER TEN MOLECULAR GEOMETRY MOLECULAR GEOMETRY V S E P R CHEMICAL BONDING II: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY AND HYBRIDIZATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS
 CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY
 Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Electron Geometry Hybrid Orbitals
 Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University, Fall 2014 Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important
Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University, Fall 2014 Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important
1) H2 2) O2 3) N2. 4) HCl 5) H2O CHEMISTRY LAB MODELING COVALENT MOLECULES BOND TYPE(S) LEWIS STRUCTURE POLARITY OF MOLECULE ELECTRONIC SHAPE
 CHEMISTRY LAB MODELING COVALENT S NAME: PER: FORMULA MOLECULAR 1) H2 hydrogen gas 2) O2 oxygen gas 3) N2 nitrogen gas 4) HCl hydrochloric acid 5) H2O dihydrogen oxide FORMULA MOLECULAR 6) CO2 carbon dioxide
CHEMISTRY LAB MODELING COVALENT S NAME: PER: FORMULA MOLECULAR 1) H2 hydrogen gas 2) O2 oxygen gas 3) N2 nitrogen gas 4) HCl hydrochloric acid 5) H2O dihydrogen oxide FORMULA MOLECULAR 6) CO2 carbon dioxide
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Downloaded from
 I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #4 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Chemical Bonding I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. The energy required to break a chemical bond to
I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #4 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Chemical Bonding I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. The energy required to break a chemical bond to
Chapter 4. Molecular Structure and Orbitals
 Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Electron Geometry Hybrid Orbitals
 Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam
 AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
 CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q.1. Select the correct statement. i. An ionic compound A + B - is most likely to be formed when ii. iii. a. the ionization energy of A is high and electron
CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q.1. Select the correct statement. i. An ionic compound A + B - is most likely to be formed when ii. iii. a. the ionization energy of A is high and electron
Class Period. 4. What distinguishes a polar covalent bond from a nonpolar covalent bond?
 Cut along dotted line. Name Assignment #1 Chemical Bonding (Predicting Bond Types) 1. What is a chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms form chemical bonds? 3. What distinguishes an ionic bond from a covalent bond?
Cut along dotted line. Name Assignment #1 Chemical Bonding (Predicting Bond Types) 1. What is a chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms form chemical bonds? 3. What distinguishes an ionic bond from a covalent bond?
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules
 Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
SL Score. HL Score ! /30 ! /48. Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding. Name
 Name Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding SL SL Score! /30 HL Score! /48 1. What is the correct Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, a compound containing chlorine, hydrogen and oxygen? A. B. C. D.
Name Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding SL SL Score! /30 HL Score! /48 1. What is the correct Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, a compound containing chlorine, hydrogen and oxygen? A. B. C. D.
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chapter 7. Ionic & Covalent Bonds
 Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces. Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2
 1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
Chapter 9 practice questions
 Class: Date: Chapter 9 practice questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following statements concerning valence bond (VB)
Class: Date: Chapter 9 practice questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following statements concerning valence bond (VB)
Chapter 6 PRETEST: Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6 PRETEST: Chemical In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.The charge on an ion is a. always positive.
Chapter 6 PRETEST: Chemical In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.The charge on an ion is a. always positive.
Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new substances.
 Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
1. What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium and nitrogen?
 IB Chem 1 Name Topic 4 Bonding - Sample Test Problems 1. What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium and nitrogen? A. CaN B. Ca 2 N C. Ca 2 N 3 D. Ca 3 N 2 2. Element X is in group 2, and element
IB Chem 1 Name Topic 4 Bonding - Sample Test Problems 1. What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium and nitrogen? A. CaN B. Ca 2 N C. Ca 2 N 3 D. Ca 3 N 2 2. Element X is in group 2, and element
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds
 Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
Lewis Dot Structures for Methane, CH 4 The central C atom is bonded by single bonds (-) to 4 individual H atoms
 Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
Name Date Class MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS. Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides
 8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model.
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry
 Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: Give one word/term for each of the following descriptions. 1. The distance between two adjacent atoms in a molecule. 2. A type of chemical bond that involves the sharing
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: Give one word/term for each of the following descriptions. 1. The distance between two adjacent atoms in a molecule. 2. A type of chemical bond that involves the sharing
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction
 Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY
 365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. Determine
365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. Determine
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions
 CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Chapter 9
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Molecular Structure and Bonding- 2. Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed Hassan Lecture 3
 Molecular Structure and Bonding- 2 Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed Hassan Lecture 3 Hybridization of atomic orbitals Orbital hybridization was proposed to explain the geometry of polyatomic molecules. Covalent
Molecular Structure and Bonding- 2 Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed Hassan Lecture 3 Hybridization of atomic orbitals Orbital hybridization was proposed to explain the geometry of polyatomic molecules. Covalent
B. (i), (iii), and (v) C. (iv) D. (i), (ii), (iii), and (v) E. (i), (iii), (iv), and (v) Answer: B. SO 3, and NO 3 - both have 24 VE and have Lewis
 SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
BONDING THEORIES Chapter , Carey
 BONDING THEORIES Chapter 10.6-10.7, Carey The Covalent Chemical Bond (9.2) FIG I Potential Energy Change to Form H2 What is a chemical bond? Why do chemical bonds occur? Descriptions of bonding: Valence
BONDING THEORIES Chapter 10.6-10.7, Carey The Covalent Chemical Bond (9.2) FIG I Potential Energy Change to Form H2 What is a chemical bond? Why do chemical bonds occur? Descriptions of bonding: Valence
Molecular Geometry. Dr. Williamson s Molecular Geometry Notes. VSEPR: Definition of Terms. Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version
 Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry. Dr. Williamson s Molecular Geometry Notes. VSEPR: Definition of Terms. VSEPR: Electronic Geometries VSEPR
 Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
Chemical Bonding II: and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding
 Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry
 Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry
 Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
Essential Organic Chemistry. Chapter 1
 Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 1 Electronic Structure and Covalent Bonding Periodic Table of the Elements 1.1 The Structure of an Atom Atoms have an internal structure consisting
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 1 Electronic Structure and Covalent Bonding Periodic Table of the Elements 1.1 The Structure of an Atom Atoms have an internal structure consisting
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures
 CHAPTERS 9 AND 10 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures Objectives You will be able to: 1. Write a description of the formation of the covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms to form a hydrogen molecule.
CHAPTERS 9 AND 10 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures Objectives You will be able to: 1. Write a description of the formation of the covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms to form a hydrogen molecule.
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals. Copyright 2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents (9.1) (9.2) (9.3) (9.4) (9.5) (9.6) Hybridization and the localized electron model The molecular orbital model Bonding in homonuclear diatomic
Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents (9.1) (9.2) (9.3) (9.4) (9.5) (9.6) Hybridization and the localized electron model The molecular orbital model Bonding in homonuclear diatomic
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS CHEMICAL BONDS: LEWIS SYMBOLS: CHEMICAL BONDING. What are valence electrons?
 REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
HYBRIDIZATION THEORY
 HYBRIDIZATION THEORY According to carbon's orbital diagram, it should only be able to form two bonds... 1s 2s 2p But we know carbon forms 4 bonds, not 2!!! Dec 5 8:19 PM HYBRIDIZATION THEORY Scientists
HYBRIDIZATION THEORY According to carbon's orbital diagram, it should only be able to form two bonds... 1s 2s 2p But we know carbon forms 4 bonds, not 2!!! Dec 5 8:19 PM HYBRIDIZATION THEORY Scientists
16. NO 3, 5 + 3(6) + 1 = 24 e. 22. HCN, = 10 valence electrons
 Solution to Chapts 9 & 10 Problems: 16. N 3, 5 + 3(6) + 1 = 24 e 22. HCN, 1 + 4 + 5 = 10 valence electrons Assuming N is hybridized, both C and N atoms are sp hybridized. The C H bond is formed from overlap
Solution to Chapts 9 & 10 Problems: 16. N 3, 5 + 3(6) + 1 = 24 e 22. HCN, 1 + 4 + 5 = 10 valence electrons Assuming N is hybridized, both C and N atoms are sp hybridized. The C H bond is formed from overlap
Chemical Bonds, Orbital Shapes, and Orbital Hybridization
 Chemical Bonds, Orbital Shapes, and Orbital Hybridization PRELAB ASSIGNMENT Read the entire laboratory write up. Write an objective and answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook before
Chemical Bonds, Orbital Shapes, and Orbital Hybridization PRELAB ASSIGNMENT Read the entire laboratory write up. Write an objective and answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook before
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro
 Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
Unit 6: Molecular Geometry
 Unit 6: Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry [6-5] the polarity of each bond, along with the geometry of the molecule determines Molecular Polarity. To predict the geometries of more complicated molecules,
Unit 6: Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry [6-5] the polarity of each bond, along with the geometry of the molecule determines Molecular Polarity. To predict the geometries of more complicated molecules,
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING
 Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
Ex. 1) F F bond in F = 0 < % covalent, no transfer of electrons
 #60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
#60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
LESSON 10. Glossary: Molecular Geometry. a quantitative measure of the degree of charge separation in a molecule. Dipole moment
 LESSON 10 Glossary: Molecular Geometry Dipole moment Electronegativity Molecular geometry Pi bond Polar covalent bond Sigma bond Valence-shell electronpair repulsion (VSEPR) model a quantitative measure
LESSON 10 Glossary: Molecular Geometry Dipole moment Electronegativity Molecular geometry Pi bond Polar covalent bond Sigma bond Valence-shell electronpair repulsion (VSEPR) model a quantitative measure
Polar? * POLAR BONDS? YES. C=O should be polar. * GEOMETRY? LINEAR geometry, with the oxygens 180 degrees apart, so NONPOLAR.
 16 Examples: Polar? * POLAR BONDS? YES. Large electronegativity difference beween C and F. * GEOMETRY? Tetrahedral. All these bonds are arranged symmetrically around the carbon, so electrons can't be pulled
16 Examples: Polar? * POLAR BONDS? YES. Large electronegativity difference beween C and F. * GEOMETRY? Tetrahedral. All these bonds are arranged symmetrically around the carbon, so electrons can't be pulled
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
NAME: DATE: CLASS: Chapter Metallic Bonding
 Chapter 7 7.3 Metallic Bonding Ionic & Metallic Bonding 1. LESSON REVIEW Use the diagram of metallic bonding to answer the following questions. 1. What is the name of the model of metallic bonding that
Chapter 7 7.3 Metallic Bonding Ionic & Metallic Bonding 1. LESSON REVIEW Use the diagram of metallic bonding to answer the following questions. 1. What is the name of the model of metallic bonding that
Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE
 Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten
 Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING
 CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING 6.1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different
CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING 6.1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different
Chapter 10. Geometry
 Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 9. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review
 Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Unit-3 Chemical Bonding Practice Exam
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Unit-3 Chemical Bonding Practice Exam Multiple Choice - NO CALCULATORS, show your work and justify your answers. 1. The concentration of a red colored solution of cobalt ions needs
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Unit-3 Chemical Bonding Practice Exam Multiple Choice - NO CALCULATORS, show your work and justify your answers. 1. The concentration of a red colored solution of cobalt ions needs
Chapter 13: Phenomena
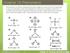 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Name Date Class MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS. Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides
 8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
 VSEPR Theory, Valence Bond Theory, Characteristic of Covalent Compounds 1. Which of the following is not correct? 1. A sigma bond is weaker than pi bond. 2. A sigma bond is stronger than pi bond.. A double
VSEPR Theory, Valence Bond Theory, Characteristic of Covalent Compounds 1. Which of the following is not correct? 1. A sigma bond is weaker than pi bond. 2. A sigma bond is stronger than pi bond.. A double
Molecular Structure. Valence Bond Theory Overlap of atomic orbitals is a covalent bond that joins atoms together to form a molecule
 Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Valence Bond
Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Valence Bond
Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity. Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity. Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity
 Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity When there is a difference in electronegativity between two atoms, then the bond between them is polar. It is possible for a molecule to contain polar bonds, but
Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity When there is a difference in electronegativity between two atoms, then the bond between them is polar. It is possible for a molecule to contain polar bonds, but
Chapter 1: Structure and Bonding
 1. What is the ground-state electronic configuration of a carbon atom? A) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 5 B) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 2 C) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 6 D) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 4 2. What is the ground-state electronic configuration
1. What is the ground-state electronic configuration of a carbon atom? A) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 5 B) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 2 C) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 6 D) 1s 2, 2s 2, 2p 4 2. What is the ground-state electronic configuration
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS
 CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
Activity Hybrid Atomic Orbitals
 Activity 201 8 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals Directions: This Guided Learning Activity (GLA) discusses Hybrid Atomic Orbitals, which are the basis for Valence Bond Theory. Part A introduces σ- and π-bonds. Part
Activity 201 8 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals Directions: This Guided Learning Activity (GLA) discusses Hybrid Atomic Orbitals, which are the basis for Valence Bond Theory. Part A introduces σ- and π-bonds. Part
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Localized electron model A bond is made when a half-filled orbital of one atom overlaps with a half-filled orbital of another.! Bond: orbitals overlap straight on p
Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Localized electron model A bond is made when a half-filled orbital of one atom overlaps with a half-filled orbital of another.! Bond: orbitals overlap straight on p
C PM RESURRECTION
 Announcements Final Exam TIME: October 8, 7:30-9:30AM VENUE: CTC 105 65-Multiple Choice Questions 3 Questions Each Chapter 2-5 7 Questions Each Chapter 6-8 30 Questions From Chapter 9-11 Saturday Review
Announcements Final Exam TIME: October 8, 7:30-9:30AM VENUE: CTC 105 65-Multiple Choice Questions 3 Questions Each Chapter 2-5 7 Questions Each Chapter 6-8 30 Questions From Chapter 9-11 Saturday Review
Name Unit Three March 7, 2017 Lab #3: Three-Dimensional Models of Covalent Molecules
 Unit 3: Types of Bonding & Geometry Chem. II Name Unit Three March 7, 2017 Lab #3: Three-Dimensional Models of Covalent Molecules A single covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons.
Unit 3: Types of Bonding & Geometry Chem. II Name Unit Three March 7, 2017 Lab #3: Three-Dimensional Models of Covalent Molecules A single covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons.
