CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION...1
|
|
|
- Bruno Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acknowledgement My most sincere thanks go to my advisor and mentor, Dr. Roe-Hoan Yoon. I thank him for introducing me to the wonders and frustrations of scientific research. I thank him for his guidance, encouragement and support during the development of this work. He has been teaching me all about self-discipline in laboratory work and in written scientific communication. I am indebted to my committee members: Dr. Gerald H. Luttrell, Dr. Rickey M. Davis, Dr. Demetri P. Telionis and Dr. Pavlos Vlachos. They have provided, with kindness, their insight and suggestions, which are precious to me. Especially, I thank Dr. Jan C. Eriksson for numerous helpful advices and inspiring discussions since his first visit to Virginia Tech in Dr. Eriksson has directly involved with many aspects of Chapter 6. I want to express sincere gratitude to Drs. Hans J. Müller and Rumen Krustev for the experimental training while I was a visiting student at the Max-Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces in Germany. I thank Ramanathan Muruganathan, Narayan C. Mishra and R. Emrich for their help, generosity, and friendship. I also thank Liqin Ge and Dr. Junbai Li for their kind help. Special thanks are due to Luis G. Cascão Pereira and Dr. Clayton J. Radke for kindly providing me the bike-wheel microcell and sharing information on related experimental details. Dr. William A. Ducker is gratefully acknowledged for allowing me to use the pendant drop apparatus in his laboratory. I also want to thank Tom Wertalik and Billy Slusser for their great technical support. I want to express my sincere gratitude to past and present members of the Center for Advanced Separation Technologies (CAST). Especially, I thank Jinming Zhang, Jinhong Zhang, Jialin Wang, Emilio Lobato, Baris Yazgan, Hubert Schimann, Chris Hull, and Carol Trutt for their support and friendship. I would like to express my eternal gratitude to my parents for their everlasting love and support. iii
2 Tables of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION MOTIVATION FOAM FILMS Charge of Air-Water Interface Foam Film Structure and Types DISJOINING PRESSURE Definition Thermodynamic definition Components of the disjoining pressure DISSERTATION OUTLINE REFERENCES...14 CHAPTER 2 HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN THE FOAM FILMS STABILIZED BY SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE: EFFECT OF ELECTROLYTE...18 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION COUNTERION BINDING MODEL EXPERIMENTAL SECTION Materials Experimental Method RESULTS DISCUSSION CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES...36 APPENDIX 2A...38 THIN FILM PRESSURE BALANCE TECHNIQUE A.1 Film Thickness Measurement A.2. Disjoining Pressure Measurement...41 APPENDIX 2B...42 THREE-DIMENSIONAL FOAM STABILITY MEASUREMENT...42 CHAPTER 3 ROLE OF HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN THE THINNING OF THE FOAM FILMS IN THE PRESENCE OF SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE...43 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION THEORETICAL METHODS Surface Potential at Air-Water Interface Determination of Hydrophobic Force Constant MATERIALS AND EXPERIMENTAL METHODS RESULTS AND DISCUSSION CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES...56 APPENDIX 3.A COMPARISON OF THE MAGNITUDE OF HYDROPHOBIC FORCE...58 APPENDIX 3.B THEORETICAL FITS OF FILM THINNING...59 CHAPTER 4 ROLE OF HYDROPHOBIC FORCE IN THE THINNING OF FOAM FILMS CONTAINING METHYL ISOBUTYL CARBINOL...61 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS RESULTS DISCUSSION CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES...75 iv
3 CHAPTER 5 STABILITY OF FOAMS AND FOAM FILMS CONTAINING METHYL ISOBUTYL CARBINOL...78 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS RESULTS AND DISCUSSION CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES...89 CHAPTER 6 EFFECT OF CHANGING PH AND THE IONIC STRENGTH ON THE SURFACE FORCES IN SURFACTANT-FREE THIN AQUEOUS FILMS...91 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL SECTION EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS THEORETICAL CONSIDERATIONS CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES...99 CHAPTER 7 EFFECTS OF SURFACE FORCES AND FILM ELASTICITY ON FROTH STABILITY ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION THEORETICAL MODEL MATERIALS AND EXPERIMENTAL METHODS Materials Foam Stability Measurement Film Thickness Measurement RESULTS AND DISCUSSION CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES VITA v
4 List of Tables Table 1.1 Chemical formulas of reagents..14 Table 2.1 The values of K 232 of Eq. [2.14] at different SDS and NaCl concentrations...29 Table 7.1 Various parameters for frothers vi
5 List of Figures Figure 1.1 Schematic of a thin foam film Figure 1.2. The counterion density and electrostatic potential with the aqueous region between two charged surfaces 5 Figure 2.1 Schematic presentation of the electrical double-layer at the air-water interface.20 Figure 2.2 Surface tensions of SDS solutions in presence and absence of NaCl...24 Figure 2.3 Adsorption isotherms for SDS..25 Figure 2.4 The Stern potential at the air-water interface as calculated using the counter ion binding model developed in the present work...25 Figure 2.5. Comparison of the surface potentials Figure 2.6 The surface excess ratio between the counterions (Na + ) and the surfactant ions (DS - ) as a function of SDS concentration in the presence and absence of NaCl..26 Figure 2.7 Equilibrium film thicknesses as a function of SDS concentration at 0, 0.4 and 1 mm NaCl; ph ; and 25±0.1 C.27 Figure 2.8 K 232 in Eq. [2.14] as a function of SDS concentration at 0, 0.4 and 1 mm NaCl.. 28 Figure 2.9 A disjoining pressure isotherm obtained at 0.1 mm SDS without NaCl..30 Figure 2.10 Disjoining pressure isotherms obtained in 10-4 SDS solutions at different NaCl additions..32 Figure 2.11 Surface area decay of SDS foams containing various concentrations of NaCl Figure 2.12 K 232 of Eq. [2.14] as a function of the fraction of the air/water interface covered by SDS Figure 2A.1 Schematic of Scheludko cell...38 Figure 2A.2 The intensity of light reflected from the two air/water interfaces of a foam film changes with time.. 40 Figure 2A.3 Equilibrium film thicknesses (H e ) versus SDS concentration.. 41 Figure 2A.4 Schematic of the experimental apparatus for measuring disjoining pressure isotherm.41 Figure 2B.1 Schematic drawing of pressure decay method..42 Figure 3.1 Surface tensions of SDS solutions in the presence and absence of NaCl.49 vii
6 Figure 3.2 The ratio between the surface excesses for the Na + and DS - ions as a function of SDS concentration in the presence of 0.3 M NaCl and absence of NaCl..49 Figure 3.3 Kinetics of film thinning at 10-5 M SDS...50 Figure 3.4 Kinetics of film thinning at 10-4 M SDS and M NaCl Figure 3.5 Kinetics of film thinning at a) M SDS and 0.3 M NaCl; b) M SDS and 0.3 M NaCl Figure 3.6 Effect of SDS concentration on K 232 at 0.3 M NaCl Figure 3.7 Effect of SDS concentration on the film lifetime (τ) and the critical rupture thickness (H cr ) at 0.3 M NaCl...54 Figure 3.8 K 232 versus (Γ s +Γ c ) -1 as a function of SDS concentration in the absence and presence of 0.3 M NaCl...55 Figure 3A.1 Hydrophobic force in foam films containing 0.3M NaCl; ( ), 10-4 M SDS with P c =49.6 Pa; ( ) M SDS with P c =71.4 Pa. The solid line is the expected van der Waals attraction Figure 3B.1 Kinetics of film thinning at 5x10-7 M SDS and 0.3 M NaCl 59 Figure 4.1 Kinetics of film thinning at a) 10-5 M MIBC and 0.1 M NaCl; b) M MIBC and 0.1 M NaCl; c) M MIBC and 0.1 M NaCl.. 65 Figure 4.2 Effect of MIBC concentration on K 232 at 0.1 M NaCl..67 Figure 4.3 Effect of MIBC concentration at 0.1 M NaCl on the lifetimes of foam ( ) and film ( ) Figure 4.4 Effect of MIBC concentration on the critical rupture thickness (H cr )..69 Figure 4.5 Effect of film elasticity (E) on the film lifetime ( ) and the foam lifetime ( ) at various concentrations of MIBC at 0.1 M NaCl...71 Figure 4.6 The hydrophobic force constants, K 232, determined from the film thinning data, are plotted as a function of Γ -1 s.74 Figure 5.1 Static surface tension of MIBC solutions as a function of concentration...81 Figure 5.2 Surface excess of MIBC as a function of bulk concentration Figure 5.3 Equilibrium film thickness as a function of MIBC concentration in the presence of 5x10-5 M NaCl...83 Figure 5.4 Disjoining pressure isotherm of MIBC at varying concentrations in the presence of 5x10-5 M NaCl..84 Figure 5.5 The lifetime of three-dimensional foams measured using shake tests as a function of MIBC concentration in the present of 5x10-5 M NaCl. The error bar denotes the maximum data scattering range Figure 5.6 Effect of MIBC concentration on film elasticity (E) viii
7 Figure 5.7 The effects of MIBC concentration on the critical rupture pressure of single films (taken from Figure 5.4), lifetime of three-dimensional foams (taken from Figure 5.5), and film elasticity (E) (taken from Figure 5.6) Figure 5.8 Effects of MIBC concentration on the stability of foams measured by the shake tests: ( ), τ I, the time it took for the appearance of liquid surface for foams in the presence of 5x10-5 M NaCl; ( ), τ II, the time it took until only the isolated bubbles became visible for foams in the presence of 0.1 M NaCl Figure 6.1 Effect of the NaCl concentration on the lifetime of thin films formed in a Scheludko cell with inner radius of 1.0 mm. The dotted line is hypothesized on the basis of the observation that the lifetime of a thin film formed from pure water is less than 1 second Figure 6.2 The influence of ph-changes on the equilibrium film thickness (H e ). Thin aqueous films were formed using a Scheludko cell with the radius 1.0 mm. The error bars show the maximal measuring errors. 95 Figure 6.3 The estimated surface potential (ψ 0 ) shown as a function of ph. The filled circle represents the predicted surface potential (= mv) from the measured equilibrium film thickness at ph 6.2 (=133 nm) using Eq. [6.9]. The empty circle represents the measured ζ-potential (= mv) at ph Figure 6.4 The estimated hydrophobic force constant (K 232 ) in Eq. [6.9] as a function of ph at 10-5 M NaCl. 98 Figure 6.5 The area per (negative) surface charge plotted vs. ph..99 Figure 7.1 Surface tension as a function of frother concentration Figure 7.2 Film elasticity (E) calculated using Eq. [7.6] for various frothers: pentanol, MIBC, octanol, and PPG Figure 7.3 Foam stability (τ) as a function of frother concentration 108 Figure 7.4 Foam stability (τ) as a function of film elasticity (E).109 Figure 7.5 Disjoining pressure (Π) as a function of equilibrium film thickness (H e ) at ph ix
Hydrophobic Forces in the Foam Films Stabilized by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate: Effect of Electrolyte
 Langmuir 2004, 20, 11457-11464 11457 Hydrophobic Forces in the Foam Films Stabilized by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate: Effect of Electrolyte Liguang Wang and Roe-Hoan Yoon* Center for Advanced Separation Technologies,
Langmuir 2004, 20, 11457-11464 11457 Hydrophobic Forces in the Foam Films Stabilized by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate: Effect of Electrolyte Liguang Wang and Roe-Hoan Yoon* Center for Advanced Separation Technologies,
HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN FLOTATION. Rajesh Pazhianur ABSTRACT
 HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN FLOTATION Rajesh Pazhianur ABSTRACT An atomic force microscope (AFM) has been used to conduct force measurements to better understand the role of hydrophobic forces in flotation.
HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN FLOTATION Rajesh Pazhianur ABSTRACT An atomic force microscope (AFM) has been used to conduct force measurements to better understand the role of hydrophobic forces in flotation.
Contents. Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII. 1 Introduction 1
 V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces
 Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Module 4: "Surface Thermodynamics" Lecture 21: "" The Lecture Contains: Effect of surfactant on interfacial tension. Objectives_template
 The Lecture Contains: Effect of surfactant on interfacial tension file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture21/21_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:10:36 PM] Surface Thermodynamics: Roles of Surfactants and
The Lecture Contains: Effect of surfactant on interfacial tension file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture21/21_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:10:36 PM] Surface Thermodynamics: Roles of Surfactants and
Multimedia : Boundary Lubrication Podcast, Briscoe, et al. Nature , ( )
 3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
Effect of Non-Ionic Surfactants and Nano-Particles on the Stability of Foams
 Effect of Non-Ionic Surfactants and Nano-Particles on the Stability of Foams Ruijia Wang Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Effect of Non-Ionic Surfactants and Nano-Particles on the Stability of Foams Ruijia Wang Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Surface Tension and Adsorption Kinetics of Volatile Organic Amphiphiles in Aqueous Solution
 Surface Tension and Adsorption Kinetics of Volatile Organic Amphiphiles in Aqueous Solution by Abdolhamid Firooz A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfilment of the thesis requirement
Surface Tension and Adsorption Kinetics of Volatile Organic Amphiphiles in Aqueous Solution by Abdolhamid Firooz A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfilment of the thesis requirement
Critical Micellization Concentration Determination using Surface Tension Phenomenon
 Critical Micellization Concentration Determination using Phenomenon 1. Introduction Surface-active agents (surfactants) were already known in ancient times, when their properties were used in everyday
Critical Micellization Concentration Determination using Phenomenon 1. Introduction Surface-active agents (surfactants) were already known in ancient times, when their properties were used in everyday
DLVO Theory and Non-DLVO Forces
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 5 DLVO Theory and Non-DLVO Forces Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 5 DLVO Theory and Non-DLVO Forces Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039
Contents. Preface XIII
 V Contents Preface XIII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Fundamental Knowledge Required for Successful Dispersion of Powders into Liquids 1 1.1.1 Wetting of Powder into Liquid 1 1.1.2 Breaking of Aggregates
V Contents Preface XIII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Fundamental Knowledge Required for Successful Dispersion of Powders into Liquids 1 1.1.1 Wetting of Powder into Liquid 1 1.1.2 Breaking of Aggregates
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Determination of the critical micelle concentration of SDS Electrical conductivity and light scattering measurements were used to determine the CMC value of SDS. Since the mobility
Supporting Information Determination of the critical micelle concentration of SDS Electrical conductivity and light scattering measurements were used to determine the CMC value of SDS. Since the mobility
Stability of colloidal systems
 Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Surfactants role on the deformation of colliding small bubbles
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 156 (1999) 547 566 www.elsevier.nl/locate/colsurfa Surfactants role on the deformation of colliding small bubbles D.S. Valkovska, K.D. Danov
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 156 (1999) 547 566 www.elsevier.nl/locate/colsurfa Surfactants role on the deformation of colliding small bubbles D.S. Valkovska, K.D. Danov
Surface Potential of 1 Hexanol Solution: Comparison with Methyl Isobutyl Carbinol
 pubs.acs.org/jpcb Surface Potential of 1 Hexanol Solution: Comparison with Methyl Isobutyl Carbinol Cuong V. Nguyen, Chi M. Phan,*, Ha M. Ang, Hiromichi Nakahara, Osamu Shibata, and Yoshikiyo Moroi Department
pubs.acs.org/jpcb Surface Potential of 1 Hexanol Solution: Comparison with Methyl Isobutyl Carbinol Cuong V. Nguyen, Chi M. Phan,*, Ha M. Ang, Hiromichi Nakahara, Osamu Shibata, and Yoshikiyo Moroi Department
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 324 (2008) 35 40 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfa
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 324 (2008) 35 40 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfa
*blood and bones contain colloids. *milk is a good example of a colloidal dispersion.
 Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Gas Permeability of Foam Films Stabilized by an r-olefin Sulfonate Surfactant
 Langmuir 2009, 25, 2881-2886 2881 Gas Permeability of Foam Films Stabilized by an r-olefin Sulfonate Surfactant R. Farajzadeh, R. Krastev,*, and P. L. J. Zitha*, Department of Geotechnology, Delft UniVersity
Langmuir 2009, 25, 2881-2886 2881 Gas Permeability of Foam Films Stabilized by an r-olefin Sulfonate Surfactant R. Farajzadeh, R. Krastev,*, and P. L. J. Zitha*, Department of Geotechnology, Delft UniVersity
Single action pressing (from top)
 www.komage.de Single action pressing (from top) Double action pressing with fixed die Typical course of the pressure during pressing and ejection (Single action) Upper punch Pressure Lower punch Time Green
www.komage.de Single action pressing (from top) Double action pressing with fixed die Typical course of the pressure during pressing and ejection (Single action) Upper punch Pressure Lower punch Time Green
50%-50% Beam Splitters Using Transparent Substrates Coated by Single- or Double-Layer Quarter-Wave Thin Films
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 5-22-2006 50%-50% Beam Splitters Using Transparent Substrates Coated by Single- or
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 5-22-2006 50%-50% Beam Splitters Using Transparent Substrates Coated by Single- or
Detection of the Hydrophobic Surface Force in Foam Films by Measurements of the Critical Thickness of the Film Rupture
 Langmuir 2004, 20, 1799-1806 1799 Detection of the Hydrophobic Surface Force in Foam Films by Measurements of the Critical Thickness of the Film Rupture J. K. Angarska, B. S. Dimitrova, K. D. Danov, P.
Langmuir 2004, 20, 1799-1806 1799 Detection of the Hydrophobic Surface Force in Foam Films by Measurements of the Critical Thickness of the Film Rupture J. K. Angarska, B. S. Dimitrova, K. D. Danov, P.
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications
 Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Effects of Counterions and Co-ions on the Drainage and Stability of Liquid Films and Foams
 JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE 200, 31 45 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CS975334 Effects of Counterions and Co-ions on the Drainage and Stability of Liquid Films and Foams J. K. Angarska,*, K. D. Tachev,*,
JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE 200, 31 45 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CS975334 Effects of Counterions and Co-ions on the Drainage and Stability of Liquid Films and Foams J. K. Angarska,*, K. D. Tachev,*,
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 38: "" The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c )
 The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
CHEMISTRY PHYSICAL. of FOODS INTRODUCTION TO THE. CRC Press. Translated by Jonathan Rhoades. Taylor & Francis Croup
 Christos Ritzoulis Translated by Jonathan Rhoades INTRODUCTION TO THE PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY of FOODS CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis
Christos Ritzoulis Translated by Jonathan Rhoades INTRODUCTION TO THE PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY of FOODS CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Module 4: "Surface Thermodynamics" Lecture 22: "" The Lecture Contains: Examples on Effect of surfactant on interfacial tension. Objectives_template
 The Lecture Contains: Examples on Effect of surfactant on interfacial tension file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture22/22_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:10:07 PM] Example Consider liquid, its vapors and
The Lecture Contains: Examples on Effect of surfactant on interfacial tension file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture22/22_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:10:07 PM] Example Consider liquid, its vapors and
Effect of F-AOT surfactant on the interface between supercritical CO 2 and nickel plating solution
 Effect of F-AOT surfactant on the interface between supercritical CO 2 and nickel plating solution Ji-Young Park, Jong Sung Lim* Supercritical Research Laboratory, KIST * Department of Chemical Engineering,
Effect of F-AOT surfactant on the interface between supercritical CO 2 and nickel plating solution Ji-Young Park, Jong Sung Lim* Supercritical Research Laboratory, KIST * Department of Chemical Engineering,
Chemical Physics of Colloid Systems and Interfaces
 7 Chemical Physics of Colloid Systems and Interfaces Peter A. Kralchevsky, Krassimir D. Danov, and Nikolai D. Denkov CONTENTS 7.1 Introduction... 199 7.2 Surface Tension of Surfactant Solutions... 200
7 Chemical Physics of Colloid Systems and Interfaces Peter A. Kralchevsky, Krassimir D. Danov, and Nikolai D. Denkov CONTENTS 7.1 Introduction... 199 7.2 Surface Tension of Surfactant Solutions... 200
Monolayers. Factors affecting the adsorption from solution. Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support
 Monolayers Adsorption as process Adsorption of gases on solids Adsorption of solutions on solids Factors affecting the adsorption from solution Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support Adsorption
Monolayers Adsorption as process Adsorption of gases on solids Adsorption of solutions on solids Factors affecting the adsorption from solution Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support Adsorption
Supercritical Fluid Extraction Directly Coupled with Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Quantitative Analysis of Analytes in Complex Matrices
 Supercritical Fluid Extraction Directly Coupled with Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Quantitative Analysis of Analytes in Complex Matrices by Zhenyu Wang Dissertation submitted to the Graduate
Supercritical Fluid Extraction Directly Coupled with Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Quantitative Analysis of Analytes in Complex Matrices by Zhenyu Wang Dissertation submitted to the Graduate
Chemical Physics of Colloid Systems and Interfaces
 4 Chemical Physics of Colloid Systems and Interfaces Peter A. Kralchevsky and Krassimir D. Danov CONTENTS 4. Introduction...48 4. Surface Tension of Surfactant Solutions...49 4.. Static Surface Tension...49
4 Chemical Physics of Colloid Systems and Interfaces Peter A. Kralchevsky and Krassimir D. Danov CONTENTS 4. Introduction...48 4. Surface Tension of Surfactant Solutions...49 4.. Static Surface Tension...49
Electrical double layer
 Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena
 ? Pierre-Gilles de Gennes Frangoise Brochard-Wyart David Quere Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves Translated by Axel Reisinger With 177 Figures Springer Springer New York Berlin
? Pierre-Gilles de Gennes Frangoise Brochard-Wyart David Quere Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves Translated by Axel Reisinger With 177 Figures Springer Springer New York Berlin
 Studies on the Coalescence o f Liqu Title Influence of the Polarizing Potenti Phases in Aqueous Solutions (Commem to Professor Rempei Gotoh On the Oc Author(s) Matsumoto, Mutsuo Citation Bulletin of the
Studies on the Coalescence o f Liqu Title Influence of the Polarizing Potenti Phases in Aqueous Solutions (Commem to Professor Rempei Gotoh On the Oc Author(s) Matsumoto, Mutsuo Citation Bulletin of the
2 no mark for choice. allow a (very) good heat conductor. allow will not melt when heated on a stove / does not melt easily
 1 a C 2 no mark for choice high(est) heat conductivity (1) high melting point (1) b idea of (close packed) positive metal ions (1) idea electrons interspersed within the particles drawn / sea of electrons
1 a C 2 no mark for choice high(est) heat conductivity (1) high melting point (1) b idea of (close packed) positive metal ions (1) idea electrons interspersed within the particles drawn / sea of electrons
HONORS CHEMISTRY Putting It All Together II
 NAME: SECTION: HONORS CHEMISTRY Putting It All Together II Calculations in Chemistry It s time to pull out your calculators! In the first review sheet, you were able to write formulas of compounds when
NAME: SECTION: HONORS CHEMISTRY Putting It All Together II Calculations in Chemistry It s time to pull out your calculators! In the first review sheet, you were able to write formulas of compounds when
Foundations of. Colloid Science SECOND EDITION. Robert J. Hunter. School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Development of a Turbulent Flotation Model from First Principles. Hyunsun Do
 Development of a Turbulent Flotation Model from First Principles Hyunsun Do Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the
Development of a Turbulent Flotation Model from First Principles Hyunsun Do Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the
2-2 Properties of Water
 22 Properties of Water Polarity As for most molecules, the and charges in a water molecule are equal so that overall the molecule is neutral. However, note that the molecule is not linear. The water molecule
22 Properties of Water Polarity As for most molecules, the and charges in a water molecule are equal so that overall the molecule is neutral. However, note that the molecule is not linear. The water molecule
Lecture 3. Phenomena at Liquid-gas and Liquid-Liquid interfaces. I
 Lecture 3 Phenomena at Liquid-gas and Liquid-Liquid interfaces. I Adsorption at Gas-Liquid interface Measurements of equilibrium adsorption surface tension measurements (Wilhelmy plate) surface analysis
Lecture 3 Phenomena at Liquid-gas and Liquid-Liquid interfaces. I Adsorption at Gas-Liquid interface Measurements of equilibrium adsorption surface tension measurements (Wilhelmy plate) surface analysis
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS. Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France
 SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
Kinetics of Surfactant Adsorption at Fluid-Fluid Interfaces
 13732 J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 1, 13732-13742 Kinetics of Surfactant Adsorption at Fluid-Fluid Interfaces Haim Diamant and David Andelman* School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and BeVerly Sackler Faculty
13732 J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 1, 13732-13742 Kinetics of Surfactant Adsorption at Fluid-Fluid Interfaces Haim Diamant and David Andelman* School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and BeVerly Sackler Faculty
DEFOAMING THE SCIENCE Theory, Experiment and Applications. Peter R. Garrett. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business
 THE SCIENCE OF DEFOAMING Theory, Experiment and Applications Peter R. Garrett @Taylor & CRC Press Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa
THE SCIENCE OF DEFOAMING Theory, Experiment and Applications Peter R. Garrett @Taylor & CRC Press Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa
EMULSIFICATION AND EMULSION STABILITY OF SILICA-CHARGED SILICONE OILS
 EMULSIFICATION AND EMULSION STABILITY OF SILICA-CHARGED SILICONE OILS Authors Name Paper No 50 E-mail Institution Country sc@lcpe.uni-sofia.bg University of Sofia Bulgaria DENKOV Nikolai Sofia University
EMULSIFICATION AND EMULSION STABILITY OF SILICA-CHARGED SILICONE OILS Authors Name Paper No 50 E-mail Institution Country sc@lcpe.uni-sofia.bg University of Sofia Bulgaria DENKOV Nikolai Sofia University
Chemistry CP Putting It All Together II
 Chemistry CP Putting It All Together II Name: Date: Calculations in Chemistry It s time to pull out your calculators! In the first review sheet, you were able to write formulas of compounds when different
Chemistry CP Putting It All Together II Name: Date: Calculations in Chemistry It s time to pull out your calculators! In the first review sheet, you were able to write formulas of compounds when different
Protein separation and characterization
 Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
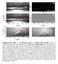 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Effect of counterions on surface and foaming properties of dodecyl sulfate
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 267 (2003) 160 166 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Effect of counterions on surface and foaming properties of dodecyl sulfate Samir Pandey, Rahul P. Bagwe, and Dinesh
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 267 (2003) 160 166 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Effect of counterions on surface and foaming properties of dodecyl sulfate Samir Pandey, Rahul P. Bagwe, and Dinesh
Fundamental Studies of Bitumen Aeration
 Fundamental Studies of Bitumen Aeration Juan Ma Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Fundamental Studies of Bitumen Aeration Juan Ma Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Interfacial Phenomena in Solvent Extraction and Its Influence on Process Performance
 TSINGHUA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSN 1007-0214 04/18 pp165-170 Volume 11, Number 2, April 2006 Interfacial Phenomena in Solvent Extraction and Its Influence on Process Performance Geoffrey W. Stevens **
TSINGHUA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSN 1007-0214 04/18 pp165-170 Volume 11, Number 2, April 2006 Interfacial Phenomena in Solvent Extraction and Its Influence on Process Performance Geoffrey W. Stevens **
Heat Capacity of Water A) heat capacity amount of heat required to change a substance s temperature by exactly 1 C
 CHEMISTRY Ch. 13 Notes: Water and Its Solutions NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. 13.1 Notes I. Water Molecule Characteristics POLAR molecule (a
CHEMISTRY Ch. 13 Notes: Water and Its Solutions NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. 13.1 Notes I. Water Molecule Characteristics POLAR molecule (a
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DISBONDED COATING AND CATHODIC DELAMINATION SYSTEMS KERRY N. ALLAHAR
 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DISBONDED COATING AND CATHODIC DELAMINATION SYSTEMS By KERRY N. ALLAHAR A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DISBONDED COATING AND CATHODIC DELAMINATION SYSTEMS By KERRY N. ALLAHAR A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE
EFFECT OF SEAWATER MAIN COMPONENTS ON FROTHABILITY IN THE FLOTATION OF Cu-Mo SULFIDE ORE
 Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 50(1), 2014, 17 29 www.minproc.pwr.wroc.pl/journal/ Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing ISSN 1643-1049 (print) ISSN 2084-4735 (online) Received May 8, 2013;
Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 50(1), 2014, 17 29 www.minproc.pwr.wroc.pl/journal/ Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing ISSN 1643-1049 (print) ISSN 2084-4735 (online) Received May 8, 2013;
Froth Flotation. Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati India
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 6: Lecture 6 Froth Flotation Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039 India Joint
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 6: Lecture 6 Froth Flotation Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039 India Joint
Particle-stabilized foams
 Particle-stabilized foams Brent S. Murray, Bernie P. Binks*, Eric Dickinson, Zhiping Du, Rammile Ettelaie & Thomas Kostakis Food Colloids Group Procter Department of Food Science, University of Leeds,
Particle-stabilized foams Brent S. Murray, Bernie P. Binks*, Eric Dickinson, Zhiping Du, Rammile Ettelaie & Thomas Kostakis Food Colloids Group Procter Department of Food Science, University of Leeds,
Next layer is called diffuse layer----ions not held tightly----thickness is > 1000 angstroms-- exact distance depends on ionic strength of soln
 What does double layer of IPE look like?-see Fig.1.2.3 Also called Electrified Inteface At no external E appl -- inner Stern layer or Inner Helmholz plane (IHP) contains mostly solvent solvent molecules
What does double layer of IPE look like?-see Fig.1.2.3 Also called Electrified Inteface At no external E appl -- inner Stern layer or Inner Helmholz plane (IHP) contains mostly solvent solvent molecules
Effect of Water Chemistry on Zeta Potential of Air Bubbles
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 8 (2013) 5828-5837 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Water Chemistry on Zeta Potential of Air Bubbles Weihong Jia, Sili Ren *,
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 8 (2013) 5828-5837 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Water Chemistry on Zeta Potential of Air Bubbles Weihong Jia, Sili Ren *,
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles. Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles
 Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Adsorption and structure of the adsorbed layer of ionic surfactants
 Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 13 16 (006) 189 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/cis Adsorption and structure of the adsorbed layer of ionic surfactants Ivan B. Ivanov a,, Kavssery P. Ananthapadmanabhan
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 13 16 (006) 189 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/cis Adsorption and structure of the adsorbed layer of ionic surfactants Ivan B. Ivanov a,, Kavssery P. Ananthapadmanabhan
ASSESSING AND EVALUATING RECREATION RESOURCE IMPACTS: SPATIAL ANALYTICAL APPROACHES. Yu-Fai Leung
 ASSESSING AND EVALUATING RECREATION RESOURCE IMPACTS: SPATIAL ANALYTICAL APPROACHES by Yu-Fai Leung Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial
ASSESSING AND EVALUATING RECREATION RESOURCE IMPACTS: SPATIAL ANALYTICAL APPROACHES by Yu-Fai Leung Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial
The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Dynamic Behavior of Self-Assembled Langmuir Films Composed of Soluble Surfactants and Insoluble Amphiphiles DISSERTATION
 Dynamic Behavior of Self-Assembled Langmuir Films Composed of Soluble Surfactants and Insoluble Amphiphiles DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy
Dynamic Behavior of Self-Assembled Langmuir Films Composed of Soluble Surfactants and Insoluble Amphiphiles DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy
INFLUENCE OF FROTHER TYPE AND DOSE ON COLLECTORLESS FLOTATION OF COPPER-BEARING SHALE IN A FLOTATION COLUMN
 Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 51(2), 215, 547 558 www.minproc.pwr.wroc.pl/journal/ Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing ISSN 1643-149 (print) ISSN 284-4735 (online) Received November 2,
Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 51(2), 215, 547 558 www.minproc.pwr.wroc.pl/journal/ Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing ISSN 1643-149 (print) ISSN 284-4735 (online) Received November 2,
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions
 Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
AN INVESTIGATION INTO BENEFICIATION OF JORDANIAN EL-LAJJUN OIL SHALE BY FROTH FLOATATION
 Oil Shale, 2008, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 247 253 ISSN 0208-189X doi: 10.3176/oil.2008.2.06 2008 Estonian Academy Publishers AN INVESTIGATION INTO BENEFICIATION OF JORDANIAN EL-LAJJUN OIL SHALE BY FROTH FLOATATION
Oil Shale, 2008, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 247 253 ISSN 0208-189X doi: 10.3176/oil.2008.2.06 2008 Estonian Academy Publishers AN INVESTIGATION INTO BENEFICIATION OF JORDANIAN EL-LAJJUN OIL SHALE BY FROTH FLOATATION
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview
 Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Chapter 2: Rigid Bar Supported by Two Buckled Struts under Axial, Harmonic, Displacement Excitation..14
 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Doctor of Philosophy
 STUDIES ON THE CORROSION INHIBITION BEHAVIOUR OF SOME AMINO ACID SURFACTANT ADDITIVES ABSTRACT SUBMITTED FOR THE AWARD OF THE DEGREE OF Doctor of Philosophy IN APPLIED CHEMISTRY By MOSARRAT PARVEEN UNDER
STUDIES ON THE CORROSION INHIBITION BEHAVIOUR OF SOME AMINO ACID SURFACTANT ADDITIVES ABSTRACT SUBMITTED FOR THE AWARD OF THE DEGREE OF Doctor of Philosophy IN APPLIED CHEMISTRY By MOSARRAT PARVEEN UNDER
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
Adsorption at Fluid Fluid Interfaces: Part II
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 4: Lecture 2 Adsorption at Fluid Fluid Interfaces: Part II Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati,
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 4: Lecture 2 Adsorption at Fluid Fluid Interfaces: Part II Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati,
Chapter 7. Pickering Stabilisation ABSTRACT
 Chapter 7 Pickering Stabilisation ABSTRACT In this chapter we investigate the interfacial properties of Pickering emulsions. Based upon findings that indicate these emulsions to be thermodynamically stable,
Chapter 7 Pickering Stabilisation ABSTRACT In this chapter we investigate the interfacial properties of Pickering emulsions. Based upon findings that indicate these emulsions to be thermodynamically stable,
Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges
 Supporting Information Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges Xiying Li 1, Yahui Xue 1, Mingchu Zou 2, Dongxiao Zhang 3, Anyuan Cao 2,* 1, 4,*, and Huiling Duan 1 State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges Xiying Li 1, Yahui Xue 1, Mingchu Zou 2, Dongxiao Zhang 3, Anyuan Cao 2,* 1, 4,*, and Huiling Duan 1 State Key Laboratory
7.1 Sampling Error The Need for Sampling Distributions
 7.1 Sampling Error The Need for Sampling Distributions Tom Lewis Fall Term 2009 Tom Lewis () 7.1 Sampling Error The Need for Sampling Distributions Fall Term 2009 1 / 5 Outline 1 Tom Lewis () 7.1 Sampling
7.1 Sampling Error The Need for Sampling Distributions Tom Lewis Fall Term 2009 Tom Lewis () 7.1 Sampling Error The Need for Sampling Distributions Fall Term 2009 1 / 5 Outline 1 Tom Lewis () 7.1 Sampling
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants
 Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
Wettability of polymeric solids by aqueous solution of surfactants
 A N N A L E S U N I V E R S I T A T I S M A R I A E C U R I E - S K Ł O D O W S K A L U B L I N P O L O N I A VOL. LX, 8 SECTIO AA 2005 Wettability of polymeric solids by aqueous solution of surfactants
A N N A L E S U N I V E R S I T A T I S M A R I A E C U R I E - S K Ł O D O W S K A L U B L I N P O L O N I A VOL. LX, 8 SECTIO AA 2005 Wettability of polymeric solids by aqueous solution of surfactants
PHYSICS. Course Structure. Unit Topics Marks. Physical World and Measurement. 1 Physical World. 2 Units and Measurements.
 PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
9.1 Water. Chapter 9 Solutions. Water. Water in Foods
 Chapter 9 s 9.1 Water 9.1 Properties of Water 9.2 s 9.3 Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes 9.6 Percent Concentration 9.7 Molarity Water is the most common solvent. The water molecule is polar. Hydrogen bonds
Chapter 9 s 9.1 Water 9.1 Properties of Water 9.2 s 9.3 Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes 9.6 Percent Concentration 9.7 Molarity Water is the most common solvent. The water molecule is polar. Hydrogen bonds
Chemistry Semester One Exam Review
 Chemistry Semester One Exam Review Name: 1. Compare physical and chemical changes in matter. 2. State the law on conservation of mass. 3. On which type of mixture(s) does the Tyndall Effect scatter light?
Chemistry Semester One Exam Review Name: 1. Compare physical and chemical changes in matter. 2. State the law on conservation of mass. 3. On which type of mixture(s) does the Tyndall Effect scatter light?
Gravitational Drainage of Foam Films
 pubs.acs.org/langmuir Gravitational Drainage of Foam Films S. Sett, S. Sinha-Ray, and A. L. Yarin* Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, 84 West Taylor
pubs.acs.org/langmuir Gravitational Drainage of Foam Films S. Sett, S. Sinha-Ray, and A. L. Yarin* Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, 84 West Taylor
SIMULATION OF DYNAMICS OF ADSORTION OF MIXED PROTEIN-SURFACTANT ON A BUBBLE SURFACE
 SIMULATION OF DYNAMICS OF ADSORTION OF MIXED PROTEIN-SURFACTANT ON A BUBBLE SURFACE Denny Vitasari 1*, Paul Grassia 2, Peter Martin 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta
SIMULATION OF DYNAMICS OF ADSORTION OF MIXED PROTEIN-SURFACTANT ON A BUBBLE SURFACE Denny Vitasari 1*, Paul Grassia 2, Peter Martin 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta
Contact, Adhesion and Rupture of Elastic Solids
 D. Maugis Contact, Adhesion and Rupture of Elastic Solids With 186 Figures Springer Contents г 1. Elements of Surface Physics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 3 1.2.1 The
D. Maugis Contact, Adhesion and Rupture of Elastic Solids With 186 Figures Springer Contents г 1. Elements of Surface Physics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 3 1.2.1 The
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer
 Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
Lecture 4 Flotation 1 CHAPTER 6 FLOTATION CHEMICALS
 Lecture 4 Flotation 1 CHAPTE 6 FLTATIN CHEMICALS Contents: Action of the different reagents. Collectors, frothers, activators, depressants, ph modifiers. Natural hydrophobicity. Collectors: Collectors
Lecture 4 Flotation 1 CHAPTE 6 FLTATIN CHEMICALS Contents: Action of the different reagents. Collectors, frothers, activators, depressants, ph modifiers. Natural hydrophobicity. Collectors: Collectors
Intermolecular Force of Attraction
 Note Packet # 11 Intermolecular Force of Attraction I Love Chemistry An intermolecular force of attraction is a force of attraction between molecules. Remember! Molecules are groups of atoms that are covalently
Note Packet # 11 Intermolecular Force of Attraction I Love Chemistry An intermolecular force of attraction is a force of attraction between molecules. Remember! Molecules are groups of atoms that are covalently
Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic
 Lecture Note #7 Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic phenomena Reading: Shaw, ch. 7 Origin of the charge at colloidal surfaces 1. Ionization Proteins acquire their charge by ionization of COOH and NH 2
Lecture Note #7 Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic phenomena Reading: Shaw, ch. 7 Origin of the charge at colloidal surfaces 1. Ionization Proteins acquire their charge by ionization of COOH and NH 2
Contents XVII. Preface
 V Preface XVII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Suspensions 1 1.2 Latexes 2 1.3 Emulsions 2 1.4 Suspoemulsions 3 1.5 Multiple Emulsions 3 1.6 Nanosuspensions 4 1.7 Nanoemulsions 4 1.8 Microemulsions 5 1.9
V Preface XVII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Suspensions 1 1.2 Latexes 2 1.3 Emulsions 2 1.4 Suspoemulsions 3 1.5 Multiple Emulsions 3 1.6 Nanosuspensions 4 1.7 Nanoemulsions 4 1.8 Microemulsions 5 1.9
THE MODIFIED YOUNG S EQUATION FOR THE CONTACT ANGLE OF A SMALL SESSILE DROP FROM AN INTERFACE DISPLACEMENT MODEL
 International Journal of Modern Physics B, Vol. 13, No. 7 (1999) 355 359 c World Scientific Publishing Company THE MODIFIED YOUNG S EQUATION FOR THE CONTACT ANGLE OF A SMALL SESSILE DROP FROM AN INTERFACE
International Journal of Modern Physics B, Vol. 13, No. 7 (1999) 355 359 c World Scientific Publishing Company THE MODIFIED YOUNG S EQUATION FOR THE CONTACT ANGLE OF A SMALL SESSILE DROP FROM AN INTERFACE
On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer
 1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit. Lecture 2 (9/11/17)
 16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
Efficient control of the bulk and surface rheological properties by using C8-C18 fatty acids as co-surfactants
 Efficient control of the bulk and surface rheological properties by using C8-C18 fatty acids as co-surfactants Zlatina Mitrinova, 1* Zhulieta Popova, 1 Slavka Tcholakova, 1 Nikolai Denkov, 1 Bivash R.
Efficient control of the bulk and surface rheological properties by using C8-C18 fatty acids as co-surfactants Zlatina Mitrinova, 1* Zhulieta Popova, 1 Slavka Tcholakova, 1 Nikolai Denkov, 1 Bivash R.
Molecular Driving Forces
 Molecular Driving Forces Statistical Thermodynamics in Chemistry and Biology SUBGfittingen 7 At 216 513 073 / / Ken A. Dill Sarina Bromberg With the assistance of Dirk Stigter on the Electrostatics chapters
Molecular Driving Forces Statistical Thermodynamics in Chemistry and Biology SUBGfittingen 7 At 216 513 073 / / Ken A. Dill Sarina Bromberg With the assistance of Dirk Stigter on the Electrostatics chapters
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science
 Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 168 (011) 50 70 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Advances in Colloid and Interface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cis The metastable
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 168 (011) 50 70 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Advances in Colloid and Interface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cis The metastable
Colloid Science Principles, methods and applications
 Colloid Science Principles, methods and applications Second Edition Edited by TERENCE COSGROVE School of Chemistry, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents
Colloid Science Principles, methods and applications Second Edition Edited by TERENCE COSGROVE School of Chemistry, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents
Colloid & Interface Science Case Study Model Answers
 Colloid & Interface Science Case Study Model Answers Distance Learning Course in Cosmetic Science Society of Cosmetic Scientists Common Features Formulations were examples of lyophobic colloidal systems
Colloid & Interface Science Case Study Model Answers Distance Learning Course in Cosmetic Science Society of Cosmetic Scientists Common Features Formulations were examples of lyophobic colloidal systems
Chemical Potential. Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties)
 Chemical Potential Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties) du = TdS pdv Hence For an open system, that is, one that can gain or lose mass, U will also
Chemical Potential Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties) du = TdS pdv Hence For an open system, that is, one that can gain or lose mass, U will also
Fundamentals of Interfacial Science Adsorption of surfactants
 Fundamentals of Interfacial Science This brief introduction into interfacial phenomena is thought to help users of interfacial measuring technique to better understand what instrument is most suitable
Fundamentals of Interfacial Science This brief introduction into interfacial phenomena is thought to help users of interfacial measuring technique to better understand what instrument is most suitable
