REVERSIONARY CHARACTERS OF TRAUMATIC OAK
|
|
|
- Suzan Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVERSIONARY CHARACTERS OF TRAUMATIC OAK WOODSI IRVING W. BAILEY (WITH PLATES XI AND XII) In studying the phylogeny of plants there are certain principles or canons of comparative anatomy which have been formulated within recent years by morphologists and anatomists. Thus the application, to seedling plants, of HAECKEL'S law of recapitulation for stages in ontogenesis has been strikingly illustrated by STRAS- BURGER, GOEBEL, JEFFREY, EAMES, and others. Furthermore, the persistency of ancestral characters in certain regions of plants has been well established. In this connection the researches of SOLMS-LAUBACH, SCOTT, and JEFFREY have shown conclusively that the cone axis is often the seat of primitive characters. The importance of foliar organs in connection with ancestral characters has been shown by SCOTT, JEFFREY, and FAULL. JEFFREY has further pointed out in his memoir on Sequoia2 the importance of vigorous cone-bearing branches of Sequoia gigantea as the seat of recapitulation of ancestral conditions. The importance of hypertrophied or wounded areas as the seat of reversion to primitive characters is strongly appreciated by zoologists. This principle has also been applied to the traumatic areas of plants by JEFFREY, who has pointed out the traumatic reversionary origin of resin canals in the wood of the higher Abietineae,3 certain Sequoiineae,4 and the older Araucarineae,5 which normally possess none of these I Contributions from the Phanerogamic Laboratories of Harvard University, no The comparative anatomy and phylogeny of the Coniferales. I. The genus Sequoia. Mem. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 5:44I-459. pis. 68-7I. I The comparative anatomy and phylogeny of the Coniferales. II. The Abietineae. Mem. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 6:I-37. pls. I-7. I The comparative anatomy and phylogeny of the Coniferales. I. The genus Sequoia. Mem. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 5:44I-459. pis. 68-7I. I903. s The wound reactions of Brachyphyllum. Annals of Botany 20: pis. 27, 28. I906. Araucariopitys, a new genus of araucarians. BOT. GAZETTE 44: pis I907. Botanical Gazette, vol. 501 [374
2 I9IO1 BAILEY-TRA LIMATIC OAK WOODS 375 structures; and has demonstrated the presence of traumatic marginal tracheids in the wounded wood of Cunninghamia sinensis.6 An interesting parallel to the work of JEFFREY upon traumatic reversions in the Coniferales has been noted by the writer in the traumatic reversions of wounded oak wood. Owing to the controversy which exists as to the relative primitiveness of the Abietineae and Cupressineae this occurrence of traumatic reversions in a dicotyledonous genus is of particular interest in demonstrating the application of the principles of experimental morphology to plants. Before describing the reversionary characters of oaks, it will be well to have clearly in mind the normal structure of the wood of existing oaks, and also that of ancestral types. As is well known, the secondary xylem of living oaks consists of vessels, fibers, tracheids, and parenchyma. The last occurs vertically as wood parenchyma, and horizontally disposed in plates of tissue extending radially, the so-called primary and secondary medullary rays. The "primary rays" (fig. i) are the distinctive feature of oak wood, the "silver grain," and are broad, fusiform masses, many cells in width, which are supposed to originate as inclusions of fundamental tissue between the primary fibrovascular bundles. The "secondary rays" are thin sheets of tissue, and consist of a single row of cells when seen in tangential or transverse section (fig. i). These rays, unlike the primary rays, are supposed to originate only with secondary growth. In contrast to this type of structure occurring in the mature wood of extant oaks, EAMES has shown7 that certain miocene oaks do not possess large rays composed of homogeneous masses of ray parenchyma, but have in their place bands of aggregated smaller rays which are separated by fibers and wood parenchyma. These rays are homologous with the " false rays " of the Betulaceae, and lead to the conclusion that the so-called primary rays of extant oaks have been built up by an aggregation and fusion of numerous originally uniseriate rays. 6 Traumatic ray tracheids in Cunninghamia sinensis. Annals of Botany 22: pi. 3I. I On the origin of the broad ray in Quercus. BOT. GAZETTE 49: I6i-066. pis.. 8, 9. I9IO.
3 376 BOTANICAL GAZETTE [NOVEMBER The writer has shown,8 by a study of numerous species of Betulaceae and Fagaceae, that ample evidence of a compounding process exists in the rays of many living oaks, alders, birches, and hornbeams. Thus many American live oaks (fig. 5) possess bands of aggregated rays which are similar to the false rays of the Betulaceae. Among alders and birches species may be found with non-aggregated uniseriate rays, aggregated small rays, and large homogeneous rays like the so-called primary rays of oak. In fact, in the genus Alnus species may be found which form a perfect series of transitional steps between alders with non-aggregated uniseriate rays and Alnus rhombifolia Nutt., which often possesses large compound rays such as are found in the higher oaks. Further, EAMES has shown that in the development of seedling oaks a similar series of stages occur. Thus in seedlings of Quercus alba L. and Q. rubra L., which in the adult possess broad homogeneous rays, the first-formed wood resembles the adult wood of chestnut in possessing non-aggregated uniseriate rays. In the further growth of the young plant, aggregations of rays develop, which by subsequent fusion constitute the large rays of the mature wood. Thus three lines of evidence, afforded by the study of seedling stages, fossil ancestral forms, and the development of ray structures in living forms, show conclusively that the wood of primitive Fagaceae and Betulaceae was characterized by the entire absence of large medullary rays. With the development of unequal seasonal temperatures, a highly organized storage system for foods became advantageous to plants, and the large rays of modern oaks have been evolved by an aggregation and fusion of numerous uniseriate rays to meet this demand. With these preliminary statements on the normal and ancestral features of oak wood, we may now turn to a more detailed consideration of the abnormal structures which exist in traumatic oaks. It has been pointed out above that traumatic regions are often the seat of ancestral characters and show a series of stages similar 8 Relation of the leaf trace to the origin and development of compound rays in the dicotyledons. Annals of Botany. Ined.
4 I9IO] BAILEY-TRAUMATIC OAK WOODS 377 to embryonic or seedling stages. We should accordingly expect to find in wounded oak wood a reversion to primitive ray structure. That this reversion does occur has been shown conclusively by the examination of numerous areas of wounded oak wood. In fact, in all cases a complete series of transitional stages in the development of compound rays occurred, resembling the series of steps found by EAMES in the development of seedling plants. The wood formed immediately after wounding possesses characteristically only uniseriate rays. In following layers aggregations of the rays develop, with subsequent enlargement of the uniseriate rays, and their subsequent fusion into homogeneous masses or compound rays. During this compounding process, fibers and wood parenchyma included in the fusing mass are transformed into ray parenchyma. In all cases, in securing material, burls and distorted tissues were carefully avoided and straight-grained traumatic tissue selected. In fig. i may be seen a tangential section of the normal adult wood of Quercus nigra L. The so-called primary and secondary rays are characteristically developed; the former consists of a homogeneous mass of ray parenchyma. In contrast to this the traumatic wood of the same species may be seen in fig. 2. The large ray is seen to consist of a compounding mass of smaller rays. Figs. 3 and 4 illustrate the normal and traumatic condition in Quercus virginiana Mill., the important live oak of the southern United States. As may be seen, in this species the normal adult wood is characterized by an imperfectly compounded ray. Numerous included fibers and wood parenchyma cells, evidences of fusion, are usually present. Fig. 4 illustrates the reversion of the wood in the vicinity of the wound to the non-aggregated uniseriate condition. In figs. 5 and 6 are shown sections of the normal and the traumatic wood of Quercus densiflora Hook. and Arn., a live oak whose normal adult wood is characterized by large rays in which the process of compounding is clearly shown. The wounded wood of the species reverts to a more primitive type of compounding, as may be seen in fig. 6.
5 378 BOTANICAL GAZETTE [NOVEMBER Figs. 7-IO illustrate the normal and traumatic wood of the well known Quercus alba, a deciduous oak with highly specialized ray structure. Figs. 8 and io, tangential and transverse sections respectively of the traumatic wood, show that this species also reverts to ancestral type of ray structures. This reversion to ancestral conditions has been found by the writer in woody tissues subsequent to severe injury. Slight injuries, on the other hand, particularly in oaks with highly specialized ray structure, often produce no morphological effect upon the wood. In a limited number of cases very slight wounds have produced a stimulation of the compounding tendency or acceleration of development rather than a reversion to ancestral structures. In fig. i i may be seen a cross-section of Alnus sp. The lower portion of the figure shows none of the so-called false rays, but in the upper half numerous rays have developed abruptly outside a zone indicating slight injury. Fig. I2 shows a similar phenomenon in the young stem of Quercus densiflora. In the lower half may be seen normal seedling wood in which only uniseriate rays occur. Starting from a zone of slight injury in the middle of the section, a compound ray has suddenly appeared in the upper portion of the figure. From this we see that very slight injuries produce an acceleration in the formation of compound rays. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS i. The phylogenetic importance of traumatic areas as the seat of reversion to primitive structures is well illustrated by the specimens of wounded oak wood which have been examined by the writer. 2. In traumatic wood progressive stages are found which are similar to the stages of recapitulation found in the seedling, and equivalents to the condition found in adult miocene oaks. 3. Woody tissues in the immediate vicinity of a severe wound show only non-aggregated- uniseriate or small rays. In subsequently formed tissues the gradual building up of the compound ray may be traced in a consecutive series of steps to the normal homogeneous large ray of the adult wood. 4. On the basis of traumatic and developmental as well as paleo-
6 19I0] BAILEY-TRAUMATIC OAK WOODS 379 botanical evidence, the large homogeneous masses of ray parenchyma, or the so-called primary rays of oaks with deciduous foliage, appear to have been built up by an aggregation and fusion of numerous uniseriate rays. 5. Traumatic reversions are confined to regions which have been severely injured. Occasionally areas where the traumatic effect has been slight show an acceleration of the compounding process instead of a reversion to ancestral stages. 6. The so-called primary ray is seen to have originated from an aggregation and fusion of secondary rays, and to be in no way related to inclusions of fundamental tissue between the primary fibrovascular bundles. From this phylogenetic relation of the two sorts of medullary rays it seems that the term primary is inadmissible entirely for the large rays of oak, and that the term compound might be advantageously substituted. In conclusion I wish to express my sincere thanks to Mr. G. B. SUDWORTH, dendrologist of the U.S. Forest Service, for material of Alnus rhombifolia. I am also much indebted to Professor E. C. JEFFREY for suggestions and advice, and to Mr. A. J. EAMES for material of several wounded oaks. HARVARD UNIVERSITY CAMBRIDGE, MASS. EXPLANATION OF PLATES XI AND XII PLATE XI FIG. I.-Quercus nigra: tangential section of the normal adult wood, showing the so-called primary and secondary rays; the former are seen to consist of large masses of homogeneous ray parenchyma; X 120. FIG. 2.-Quercus nigra: tangential section of the traumatic wood, showing compounding mass of small rays; X I 20. FIG. 3.-Quercus virginiana: tangential section of the normal adult wood, showing strong evidences of a compounding process; inclusions of fibers and wood parenchyma cells occur conspicuously; X 120. FIG. 4.-Quercus virginiana: tangential section of the traumatic wood, showing uniseriate non-aggregated rays in the immediate vicinity of a severe wound; X I20. FIG. 5.-Quercus densifiora: tangential section of the normal adult wood, showing aggregating and fusing mass of small rays; X 6o.
7 380 BOTANICAL GAZETTE [NOVEMBER FIG. 6.-Quercus densiflora: tangential section of the traumatic wood, showing aggregation of uniseriate and biseriate rays; X I20. PLATE FIG. 7.-Quercus alba: tangential section of the normal adult wood, showing highly organized broad homogeneous ray; X 120. FIG. 8.-Quercus alba: tangential section of the traumatic wood, showing the aggregation and fusion of triseriate and biseriate rays; these rays have been produced by the enlargement or growth in diameter of uniseriate rays; X I20. FIG. 9.-Quercus alba: transverse section of the normal adult wood, showing the highly organized type of ray; XI 20. FIG. io.-quercus alba: transverse section of the traumatic wood, showing aggregation of uniseriate, biseriate, and triseriate rays; X 120. FIG. ii.-alnus sp.: transverse section of very slightly injured wood; compounding rays are absent from the lower half of the section; starting abruptly from a line of slightly injured tissue which crosses the middle of the section, numerous rays extend outward to the exterior of the stem; X40. FIG. I2.-Quercus densiflora: transverse section of very slightly injured wood; the lower half of the section possesses only uniseriate rays, but starting from the middle of the section a compounding ray has originated from a slight injury to the wood; X6o. XII
8 BOTANICAL GAZETTE, L PLATE XI 3 4 c).
9 A~~~ BOTANICAL GAZETTE, L PLATE XII 10 c).
NOTES ON GINKGO BILOBA'
 NOTES ON GINKGO BILOBA' WALTER WV. TUPPER (WITH PLATE xx) Among the gymnosperms, one of the groups most interesting from a morphological standpoint is the Ginkgoales, the only living representative of
NOTES ON GINKGO BILOBA' WALTER WV. TUPPER (WITH PLATE xx) Among the gymnosperms, one of the groups most interesting from a morphological standpoint is the Ginkgoales, the only living representative of
SIGNIFICANCE OF RESINOUS TRACHEIDS
 SIGNIFICANCE OF RESINOUS TRACHEIDS SAMUEL J. RECORD (WITH FIVE FIGURES) The occurrence of resinous tracheids in gymnosperms has been noted by PENHALLOW' in the woods of certain species of Cordaites, A
SIGNIFICANCE OF RESINOUS TRACHEIDS SAMUEL J. RECORD (WITH FIVE FIGURES) The occurrence of resinous tracheids in gymnosperms has been noted by PENHALLOW' in the woods of certain species of Cordaites, A
GAZETTE BOTANICAL NOVEMBER, A FOSSIL SEQUOIA FROM THE SIERRA NEVADA.' VOLUME XXXVIII N IUMIBER 5 I90,/
 VOLUME XXXVIII N IUMIBER 5 BOTANICAL GAZETTE NOVEMBER, I90,/ A FOSSIL SEQUOIA FROM THE SIERRA NEVADA.' EDWARD C. JEFFREY. (WITH PLATES XVIII AND XIX) AMONG the material of fossil woods stored in the basement
VOLUME XXXVIII N IUMIBER 5 BOTANICAL GAZETTE NOVEMBER, I90,/ A FOSSIL SEQUOIA FROM THE SIERRA NEVADA.' EDWARD C. JEFFREY. (WITH PLATES XVIII AND XIX) AMONG the material of fossil woods stored in the basement
VARIATION IN THE SIZE OF RAY PITS OF CONIFERS.*
 VARIATION IN THE SIZE OF RAY PITS OF CONIFERS.* FOREST B. H. BROWN. Since Haeckel proposed the word Ecology in 88, there has been an ever growing interest in the influence which environmental factors may
VARIATION IN THE SIZE OF RAY PITS OF CONIFERS.* FOREST B. H. BROWN. Since Haeckel proposed the word Ecology in 88, there has been an ever growing interest in the influence which environmental factors may
A Branched Cone of Equisetum, 113
 A Branched Cone of Equisetum, 113 6. E. C. Jeffrey. " The Development, Structure and Affinities of the genus Equisetum." Memoirs of the Boston Society of Natural History, Vol. V., No. 5, 1899. 7. R. Kidston.
A Branched Cone of Equisetum, 113 6. E. C. Jeffrey. " The Development, Structure and Affinities of the genus Equisetum." Memoirs of the Boston Society of Natural History, Vol. V., No. 5, 1899. 7. R. Kidston.
Secondary growth in stems
 Secondary growth in stems Secondary growth Some of the meristematic cells in plants with secondary growth keep their meristematic state and become cells of the cambium. The addition of secondary vascular
Secondary growth in stems Secondary growth Some of the meristematic cells in plants with secondary growth keep their meristematic state and become cells of the cambium. The addition of secondary vascular
AN OCCURRENCE OF PERFORATED TRACHEIDS IN THUJA OCCIDENTALIS L.
 AN OCCURRENCE OF PERFORATED TRACHEIDS IN THUJA OCCIDENTALIS L. BY M. W. B ANN AN Department of Botany, University of Toronto {Received 28 February 1957) (With Plate and i figure in the text) In a recent
AN OCCURRENCE OF PERFORATED TRACHEIDS IN THUJA OCCIDENTALIS L. BY M. W. B ANN AN Department of Botany, University of Toronto {Received 28 February 1957) (With Plate and i figure in the text) In a recent
The secondary meristem result in growth in a lateral direction, such as the increase in girth of a tree.
 Chapter 9b-Stems and Material Transport Woody plants produce wood tissue and bark through the activity of secondary meristems: The secondary meristem result in growth in a lateral direction, such as the
Chapter 9b-Stems and Material Transport Woody plants produce wood tissue and bark through the activity of secondary meristems: The secondary meristem result in growth in a lateral direction, such as the
Lecture 19. A Sieve Plate with large Sieve Pores. Secondary Phloem. Secondary phloem (cont d)
 Lecture 19 Secondary phloem (cont d) Secondary Phloem in Tilia americana (American Basswood) Secondary Phloem of Tilia Stained with Toluidine Blue & viewed with Crossed Polarizers. Secondary Phloem A Sieve
Lecture 19 Secondary phloem (cont d) Secondary Phloem in Tilia americana (American Basswood) Secondary Phloem of Tilia Stained with Toluidine Blue & viewed with Crossed Polarizers. Secondary Phloem A Sieve
Some Physical Features Associated with Pliability of Wood
 Some Physical Features Associated with Pliability of Wood J. E. Potzger and Florence Geisler, Butler University Many books and papers have been written on mechanical properties of wood, and elaborate equipment
Some Physical Features Associated with Pliability of Wood J. E. Potzger and Florence Geisler, Butler University Many books and papers have been written on mechanical properties of wood, and elaborate equipment
Angiosperms: Dicotyledons
 Angiosperms: Dicotyledons This section contains anatomical descriptions of stem and twig xylem, as well as the bark and pith regions of 244 dicotyledonous species belonging to 61 families. Angiosperms:
Angiosperms: Dicotyledons This section contains anatomical descriptions of stem and twig xylem, as well as the bark and pith regions of 244 dicotyledonous species belonging to 61 families. Angiosperms:
Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves
 Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues and cells Plants, like animals, have organs composed of different tissues, which are composed of cells. Tissue is
Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues and cells Plants, like animals, have organs composed of different tissues, which are composed of cells. Tissue is
(Photo Atlas: Figures , )
 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2009 Topic 05: Secondary Plant Body (Photo Atlas: Figures 9.35-9.55, 9.57-9.59) A. Introduction In many plants, development of the primary plant body and tissues is just
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2009 Topic 05: Secondary Plant Body (Photo Atlas: Figures 9.35-9.55, 9.57-9.59) A. Introduction In many plants, development of the primary plant body and tissues is just
Wood Anatomy Lab What is wood? The lateral meristems Cell types Vessels Tracheids
 Wood Anatomy Lab Objectives of the Lab: 1) Learn to recognize major cell types and features of wood including: tracheids vessels rays axial parenchyma pits tyloses resin canals 2) Look at wood in three
Wood Anatomy Lab Objectives of the Lab: 1) Learn to recognize major cell types and features of wood including: tracheids vessels rays axial parenchyma pits tyloses resin canals 2) Look at wood in three
Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves
 Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues and cells Plants, like animals, have organs composed of different tissues, which are composed of cells. Tissue is
Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues and cells Plants, like animals, have organs composed of different tissues, which are composed of cells. Tissue is
TEXT The name stele has been derived from Greek word meaning pillar or column. Sachs in 1875 proposed that the vascular system of the plant body is a
 TEXT The name stele has been derived from Greek word meaning pillar or column. Sachs in 1875 proposed that the vascular system of the plant body is a continuous system. For the first time, the stelar organisation
TEXT The name stele has been derived from Greek word meaning pillar or column. Sachs in 1875 proposed that the vascular system of the plant body is a continuous system. For the first time, the stelar organisation
Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology
 Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark
Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark
Topic 2: Plant Structure & Growth Ch. 35 Angiosperms are the most complex plants. They are composed of cells, tissues, organs and organ systems.
 Topic 2: Plant Structure & Growth Ch. 35 Angiosperms are the most complex plants. They are composed of cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. Fig. 35.8 Plant Cells pp.798-802 Types of plant cells Include:
Topic 2: Plant Structure & Growth Ch. 35 Angiosperms are the most complex plants. They are composed of cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. Fig. 35.8 Plant Cells pp.798-802 Types of plant cells Include:
Microscopic structure of hardwoods
 Microscopic structure of hardwoods presentation 2 Wood microstructure Hardwoods Hardwoods differ from softwoods: 1) vessels occurrence 2) the lack of radial arrangement of the longitudinal cells (X section)
Microscopic structure of hardwoods presentation 2 Wood microstructure Hardwoods Hardwoods differ from softwoods: 1) vessels occurrence 2) the lack of radial arrangement of the longitudinal cells (X section)
 Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark the regions where active cell division and rapid division
Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark the regions where active cell division and rapid division
Lecture 4 Root Put line under your answer! There is only one correct answer in the multiple choice questions
 Lecture 4 Root Put line under your answer! There is only one correct answer in the multiple choice questions 1. The perception of gravity by a root is thought to take place in a) root hairs b) the region
Lecture 4 Root Put line under your answer! There is only one correct answer in the multiple choice questions 1. The perception of gravity by a root is thought to take place in a) root hairs b) the region
Plant Structure. Lab Exercise 24. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise Plant Structure Objectives - Be able to identify plant organs and give their functions. - Learn distinguishing characteristics between monocot and dicot plants. - Understand the anatomy of
Lab Exercise Plant Structure Objectives - Be able to identify plant organs and give their functions. - Learn distinguishing characteristics between monocot and dicot plants. - Understand the anatomy of
Anatomy of Flowering Plants. K C Meena PGT Biology
 Anatomy of Flowering Plants K C Meena PGT Biology Tissues A group of similar cells performing same function. Types of plant tissues - Meristematic tissues and permanent tissues. Meristematic tissues Have
Anatomy of Flowering Plants K C Meena PGT Biology Tissues A group of similar cells performing same function. Types of plant tissues - Meristematic tissues and permanent tissues. Meristematic tissues Have
Plants. Tissues, Organs, and Systems
 Plants Tissues, Organs, and Systems Meristematic cells Specialized cells that are responsible for producing specialized cells, they produce three types of tissue in the body of a plant. Meristematic Cells
Plants Tissues, Organs, and Systems Meristematic cells Specialized cells that are responsible for producing specialized cells, they produce three types of tissue in the body of a plant. Meristematic Cells
OF THE LEMNA FROND MORPHOLOGY
 MORPHOLOGY OF THE LEMNA FROND FREDERICK H. BLODGETT (WITH PLATE XIV AND ONE FIGURE) In the case of structure simplified by reduction, it is sometimes necessary to trace the development of the parts through
MORPHOLOGY OF THE LEMNA FROND FREDERICK H. BLODGETT (WITH PLATE XIV AND ONE FIGURE) In the case of structure simplified by reduction, it is sometimes necessary to trace the development of the parts through
ANATOMY OF PLANTS Introduction: The study of gross internal structure of plant organs by the technique of section cutting is called plant anatomy.
 ANATOMY OF PLANTS Introduction: The study of gross internal structure of plant organs by the technique of section cutting is called plant anatomy. (Pandey, 2002). Various plant organ viz. root, stem, leaves,
ANATOMY OF PLANTS Introduction: The study of gross internal structure of plant organs by the technique of section cutting is called plant anatomy. (Pandey, 2002). Various plant organ viz. root, stem, leaves,
Plant Tissues and Organs. Topic 13 Plant Science Subtopics , ,
 Plant Tissues and Organs Topic 13 Plant Science Subtopics 13.1.2, 13.1.3, 13.1.4 Objectives: List and describe the major plant organs their structure and function List and describe the major types of plant
Plant Tissues and Organs Topic 13 Plant Science Subtopics 13.1.2, 13.1.3, 13.1.4 Objectives: List and describe the major plant organs their structure and function List and describe the major types of plant
Plant Juvenility Text Pages: 15 18,
 45 Plant Juvenility Text Pages: 15 18, 613 619. Objectives: 1. Be able to describe and explain terms related to plant aging. 2. Be able to explain how a woody plant contains tissue of different ontogenetic
45 Plant Juvenility Text Pages: 15 18, 613 619. Objectives: 1. Be able to describe and explain terms related to plant aging. 2. Be able to explain how a woody plant contains tissue of different ontogenetic
Examine and draw the large, compressed leaf with the genus name Cordaites. Is it similar to the leaves of any living conifers?
 VASCULAR PLANT MORPHOLOGY LABORATORY 10 Cordaitales and Coniferales Cordaitales Cordaites are an important group of Carboniferous plants that are closely related to conifers. Rudolf Florin was able to
VASCULAR PLANT MORPHOLOGY LABORATORY 10 Cordaitales and Coniferales Cordaitales Cordaites are an important group of Carboniferous plants that are closely related to conifers. Rudolf Florin was able to
THE ROOTS OF WILD RICE. ZIZANIA AQUATICA L.
 THE ROOTS OF WILD RICE. ZIZANIA AQUATICA L. E. L. STOVER, Eastern Illinois State Teachers College. This grass grows from Maine to Minnesota in aquatic habitats (2 and 5). It is common in marsh lands all
THE ROOTS OF WILD RICE. ZIZANIA AQUATICA L. E. L. STOVER, Eastern Illinois State Teachers College. This grass grows from Maine to Minnesota in aquatic habitats (2 and 5). It is common in marsh lands all
THE ANATOMY OF SIX EPIPHYTIC SPECIES OF LYCOPODIUM
 THE ANATOMY OF SIX EPIPHYTIC SPECIES OF LYCOPODIUM CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY i8g J. BEN HILL (WITH TWENTY-EIGHT FIGURES) In this investigation, six epiphytic species of Lycopodium
THE ANATOMY OF SIX EPIPHYTIC SPECIES OF LYCOPODIUM CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY i8g J. BEN HILL (WITH TWENTY-EIGHT FIGURES) In this investigation, six epiphytic species of Lycopodium
1 Conducting Units: Tracheids and Vessels 1.1 Evolutionary Specialization
 1 Conducting Units: Tracheids and Vessels 1.1 Evolutionary Specialization The development of upright land plants depended on the development of a waterconducting system. Many of the earliest land plants,
1 Conducting Units: Tracheids and Vessels 1.1 Evolutionary Specialization The development of upright land plants depended on the development of a waterconducting system. Many of the earliest land plants,
THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE
 THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE VOL. XXIV JULY, 1924 No.. 4 THE VASCULAR ANATOMY OF CALAMOVILFA LONGIFOLIA.* ERNEST LINCOLN STOVER Eastern Illinois State Teachers' College The present study of the anatomy
THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE VOL. XXIV JULY, 1924 No.. 4 THE VASCULAR ANATOMY OF CALAMOVILFA LONGIFOLIA.* ERNEST LINCOLN STOVER Eastern Illinois State Teachers' College The present study of the anatomy
WOOD AND BARK ANATOMY OF. Rancho Santa Ana Botanic Garden and Department of Biology, Pomona College Claremont, California 91711
 ALISO 12(3), 1989, pp. 485-495 WOOD AND BARK ANATOMY OF DEGENERIA SHERWIN CARLQUIST Rancho Santa Ana Botanic Garden and Department of Biology, Pomona College Claremont, California 91711 ABSTRACT Wood anatomy
ALISO 12(3), 1989, pp. 485-495 WOOD AND BARK ANATOMY OF DEGENERIA SHERWIN CARLQUIST Rancho Santa Ana Botanic Garden and Department of Biology, Pomona College Claremont, California 91711 ABSTRACT Wood anatomy
Useful Propagation Terms. Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants.
 Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
Overview of Plant Tissues
 Plant Tissue Growth Key Concepts Overview of Plant Tissues Seed-bearing vascular plants have a shoot system with stems, leaves, and reproductive parts Most also have a root system These systems consist
Plant Tissue Growth Key Concepts Overview of Plant Tissues Seed-bearing vascular plants have a shoot system with stems, leaves, and reproductive parts Most also have a root system These systems consist
Effects of Sun-Blotch on the Anatomy of the Avocado Stem
 California Avocado Association 1935 Yearbook 20: 125-129 Effects of Sun-Blotch on the Anatomy of the Avocado Stem Charles A. Schroeder Because of the comparatively recent discovery of the avocado disease
California Avocado Association 1935 Yearbook 20: 125-129 Effects of Sun-Blotch on the Anatomy of the Avocado Stem Charles A. Schroeder Because of the comparatively recent discovery of the avocado disease
Acoustic Emission Technique for the Detection of Abnormal Cavitation in Pine Trees Infected with Pine Wilt Disease
 Acoustic Emission Technique for the Detection of Abnormal Cavitation in Pine Trees Infected with Pine Wilt Disease Keiko Kuroda (Kansai Research Center, Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute,
Acoustic Emission Technique for the Detection of Abnormal Cavitation in Pine Trees Infected with Pine Wilt Disease Keiko Kuroda (Kansai Research Center, Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute,
The Shoot System: Primary Stem Structure - 1
 The Shoot System: Primary Stem Structure - 1 Shoot System The shoot system comprises the leaves and stems of plants. Leaves are located at nodes on the stem; the distance along the stem between nodes is
The Shoot System: Primary Stem Structure - 1 Shoot System The shoot system comprises the leaves and stems of plants. Leaves are located at nodes on the stem; the distance along the stem between nodes is
Plant Structure and Function (Ch. 23)
 Plant Structure and Function (Ch. 23) Basic plant anatomy 1 root root tip root hairs Roots Roots anchor plant in soil, absorb minerals & water, & store food fibrous roots (1) mat of thin roots that spread
Plant Structure and Function (Ch. 23) Basic plant anatomy 1 root root tip root hairs Roots Roots anchor plant in soil, absorb minerals & water, & store food fibrous roots (1) mat of thin roots that spread
ARBORICULTURE JOURNAL OF WATER TRANSPORT AT STEM-BRANCH JUNCTURES IN WOODY ANGIOSPERMS. November 1991 Vol. 17, No. 11.
 28 JOURNAL OF ARBORICULTURE November 11 Vol. 17, No. WATER TRANSPORT AT STEM-BRANCH JUNCTURES IN WOODY ANGIOSPERMS by Dan Neely Abstract. A water soluble dye, methyl violet, was injected into the stems
28 JOURNAL OF ARBORICULTURE November 11 Vol. 17, No. WATER TRANSPORT AT STEM-BRANCH JUNCTURES IN WOODY ANGIOSPERMS by Dan Neely Abstract. A water soluble dye, methyl violet, was injected into the stems
POLYXYLIC STEM OF CYCAS MEDIA
 POLYXYLIC STEM OF CYCAS MEDIA CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY 252 WARD L. MILLER (WITH ELEVEN FIGURES) The question which lends particular interest to the polyxylic situation in 4 of the
POLYXYLIC STEM OF CYCAS MEDIA CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY 252 WARD L. MILLER (WITH ELEVEN FIGURES) The question which lends particular interest to the polyxylic situation in 4 of the
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION. Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology
 SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
Stems BI 103: Plant & Animal A & P. Learning Objectives
 Stems BI 103: Plant & Animal A & P Outline: 1. Stems: monocots vs dicots--handout 2. Woody plant growth 3. Discussion problems 4. Monocots & soutside Learning Objectives What are the differences between
Stems BI 103: Plant & Animal A & P Outline: 1. Stems: monocots vs dicots--handout 2. Woody plant growth 3. Discussion problems 4. Monocots & soutside Learning Objectives What are the differences between
BIOL 305L Laboratory One
 Please print Full name clearly: BIOL 305L Laboratory One General plant anatomy a great place to start! Introduction Botany is the science of plant life. Traditionally, the science included the study of
Please print Full name clearly: BIOL 305L Laboratory One General plant anatomy a great place to start! Introduction Botany is the science of plant life. Traditionally, the science included the study of
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 6. Anatomy of Flowering Plants Study of internal structure of plant is called anatomy. In plants cells are the basic unit. Cells organized into tissues and tissues organized into organs.
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 6. Anatomy of Flowering Plants Study of internal structure of plant is called anatomy. In plants cells are the basic unit. Cells organized into tissues and tissues organized into organs.
Cutting Propagation. Is the clonal multiplication of plants with propagules of stems, leaves or roots.
 Principles of Propagation by Cuttings Dr. Fred Davies Department of Horticultural Sciences Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Cutting Propagation Shoot Adventitious Buds & Shoots Bud Is the clonal
Principles of Propagation by Cuttings Dr. Fred Davies Department of Horticultural Sciences Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Cutting Propagation Shoot Adventitious Buds & Shoots Bud Is the clonal
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-6 ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
 Chapter-6 ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER Anatomy : Anatomy is the study of internal structure of organisms. Plant anatomy includes organisation and structure of tissues. Tissue : A group
Chapter-6 ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER Anatomy : Anatomy is the study of internal structure of organisms. Plant anatomy includes organisation and structure of tissues. Tissue : A group
Plants. Plant Form and Function. Tissue Systems 6/4/2012. Chapter 17. Herbaceous (nonwoody) Woody. Flowering plants can be divided into two groups:
 Monocots Dicots 6/4/2012 Plants Plant Form and Function Chapter 17 Herbaceous (nonwoody) In temperate climates, aerial parts die back Woody In temperate climates, aerial parts persist The Plant Body Functions
Monocots Dicots 6/4/2012 Plants Plant Form and Function Chapter 17 Herbaceous (nonwoody) In temperate climates, aerial parts die back Woody In temperate climates, aerial parts persist The Plant Body Functions
Primary Internal structure & Normal Secondary growth in Sunflower stem
 Primary Internal structure & Normal Secondary growth in Sunflower stem B. Sc. II - Botany Dr. (Miss) Kalpana R. Datar Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF BOTANY Willingdon College, Sangli. kalpana_datar@yahoo.com.
Primary Internal structure & Normal Secondary growth in Sunflower stem B. Sc. II - Botany Dr. (Miss) Kalpana R. Datar Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF BOTANY Willingdon College, Sangli. kalpana_datar@yahoo.com.
Understanding Cambial Behaviour. The key to wood quality
 Understanding Cambial Behaviour The key to wood quality A brief history Terminology Dormancy and reactivation Growth of derivatives and wall formation Pitting and plasmodesmata A brief history Nehemiah
Understanding Cambial Behaviour The key to wood quality A brief history Terminology Dormancy and reactivation Growth of derivatives and wall formation Pitting and plasmodesmata A brief history Nehemiah
SESSION 6: SUPPORT AND TRANSPORT SYSTEMS IN PLANTS PART 1
 SESSION 6: SUPPORT AND TRANSPORT SYSTEMS IN PLANTS PART 1 KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: - Anatomy of dicotyledonous plants Root and stem: distribution
SESSION 6: SUPPORT AND TRANSPORT SYSTEMS IN PLANTS PART 1 KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: - Anatomy of dicotyledonous plants Root and stem: distribution
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 21st, 2011 Outline Questions and answers 1 Questions and answers 2 Outline Questions and answers 1 Questions and answers
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 21st, 2011 Outline Questions and answers 1 Questions and answers 2 Outline Questions and answers 1 Questions and answers
-Each asexual organs. -Anchors the plant -Absorbs water and minerals -Stores sugars and starches
 Plants are made up of: -organs, tissues, and cells The three major plant organs are: -Roots, stems, and leaves -Each asexual organs Plants have a Root System beneath the ground that us a multicellular
Plants are made up of: -organs, tissues, and cells The three major plant organs are: -Roots, stems, and leaves -Each asexual organs Plants have a Root System beneath the ground that us a multicellular
with others and thus regenerate a functioning conductive system. Regeneration
 388 BOTANY: SINNOTT AND BLOCH PROC. N. A. S. VISIBLE EXPRESSION OF CYTOPLASMIC PA TTERN IN THE DIFFERENTIATION OF XYLEM STRANDS BY EDMUND W. SINOTT AND ROBERT BLOCH OsBORN BOTANCAL LABORATORY, YALE UNIVERSITY
388 BOTANY: SINNOTT AND BLOCH PROC. N. A. S. VISIBLE EXPRESSION OF CYTOPLASMIC PA TTERN IN THE DIFFERENTIATION OF XYLEM STRANDS BY EDMUND W. SINOTT AND ROBERT BLOCH OsBORN BOTANCAL LABORATORY, YALE UNIVERSITY
The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues, and cells. Plants, like multicellular animals:
 Chapter 28 The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues, and cells Plants, like multicellular animals: o Have organs composed of different tissues, which are in turn composed of cells 3 basic organs:
Chapter 28 The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues, and cells Plants, like multicellular animals: o Have organs composed of different tissues, which are in turn composed of cells 3 basic organs:
Chapter. Transport in. Structure of. 1- Epidermis: 2- Cortex: All plants 2- a specialized. In higher moving by. hydra and. with cuticles) 1-2-
 Chapter 2 Transport in living organisms The concept of transport and the need for it: All plants need CO 2, water and mineral salts to perform photosynthesis In primitive plants such as algae these materials
Chapter 2 Transport in living organisms The concept of transport and the need for it: All plants need CO 2, water and mineral salts to perform photosynthesis In primitive plants such as algae these materials
Chapter 29: Plant Tissues
 Chapter 29: Plant Tissues Shoots and Roots Shoots (Leaves and Stem) Produce food by photosynthesis Carry out reproductive functions Roots Anchor the plant Penetrate the soil and absorb water and dissolved
Chapter 29: Plant Tissues Shoots and Roots Shoots (Leaves and Stem) Produce food by photosynthesis Carry out reproductive functions Roots Anchor the plant Penetrate the soil and absorb water and dissolved
TARGET STUDY MATERIAL
 TARGET STUDY MATERIAL Plus-1 Botany VOL I TARGET EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION Target Educational institution is the one and only Entrance coaching and CBSE 10 th coaching centre at Mukkam with advanced technologies
TARGET STUDY MATERIAL Plus-1 Botany VOL I TARGET EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION Target Educational institution is the one and only Entrance coaching and CBSE 10 th coaching centre at Mukkam with advanced technologies
UNIT 6 - STRUCTURES OF FLOWERING PLANTS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
 6.1 Plant Tissues A tissue is a group of cells with common function, structures or both. In plants we can find 2 types of tissues: Meristem Permanent tissues Meristem is found in regions with continuous
6.1 Plant Tissues A tissue is a group of cells with common function, structures or both. In plants we can find 2 types of tissues: Meristem Permanent tissues Meristem is found in regions with continuous
GROWTH RINGS IN A MONOCOTYL
 GROWTH RINGS IN A MONOCOTYL CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY 285 CHARLES J. CHAMBERLAIN (WITH SIXTEEN FIGURES) The principal object of this paper is to announce the, discovery of growth
GROWTH RINGS IN A MONOCOTYL CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY 285 CHARLES J. CHAMBERLAIN (WITH SIXTEEN FIGURES) The principal object of this paper is to announce the, discovery of growth
Plant Form and Function I
 An overwiev of a flowering plant Main root Root Roots of most plants are covered with root hairs. Their function is to increase root surface area for more efficient absorption of water and nutrients from
An overwiev of a flowering plant Main root Root Roots of most plants are covered with root hairs. Their function is to increase root surface area for more efficient absorption of water and nutrients from
Plant Structure. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 3.2 Organisation and the Vascular Structures 3.2.1 Flowering plant structure and root structure Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 1. Label a diagram of the external
Name: 3.2 Organisation and the Vascular Structures 3.2.1 Flowering plant structure and root structure Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 1. Label a diagram of the external
DEPARTMENT OF LIFE AND CONSUMER SCIENCES. Plant Structure BOT1501. Semester I: Assignment no. 2 Memorandum
 University Examinations DEPARTMENT OF LIFE AND CONSUMER SCIENCES Plant Structure BOT1501 Semester I: Assignment no. 2 Memorandum 2018 QUESTION 1 1.1 Primary growth is the production of new primary tissues
University Examinations DEPARTMENT OF LIFE AND CONSUMER SCIENCES Plant Structure BOT1501 Semester I: Assignment no. 2 Memorandum 2018 QUESTION 1 1.1 Primary growth is the production of new primary tissues
Roots and leaves together are sufficient to take up all essential resources, so why make stems?
 STEMS Roots and leaves together are sufficient to take up all essential resources, so why make stems? Stem functions 1. Support leaves 2. Conductance (connect root and leaf vasculature) 3. Storage (some
STEMS Roots and leaves together are sufficient to take up all essential resources, so why make stems? Stem functions 1. Support leaves 2. Conductance (connect root and leaf vasculature) 3. Storage (some
Objectives. To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants.
 1 Objectives To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants. 2 Main Menu Plant Cell Biology Plant Structures Roots
1 Objectives To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants. 2 Main Menu Plant Cell Biology Plant Structures Roots
[279] A NOTE ON THE ORIGIN OF LATERAL ROOTS AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE ROOT-APEX OF LYGINOPTERIS OLDHAMIA
![[279] A NOTE ON THE ORIGIN OF LATERAL ROOTS AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE ROOT-APEX OF LYGINOPTERIS OLDHAMIA [279] A NOTE ON THE ORIGIN OF LATERAL ROOTS AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE ROOT-APEX OF LYGINOPTERIS OLDHAMIA](/thumbs/83/87080534.jpg) [279] A NOTE ON THE ORIGIN OF LATERAL ROOTS AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE ROOT-APEX OF LYGINOPTERIS OLDHAMIA BY A. C. HALKET (With Plate XI and i figure in the text) E 'GlNOPTERis oi.dh.imi.i, a plant of the
[279] A NOTE ON THE ORIGIN OF LATERAL ROOTS AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE ROOT-APEX OF LYGINOPTERIS OLDHAMIA BY A. C. HALKET (With Plate XI and i figure in the text) E 'GlNOPTERis oi.dh.imi.i, a plant of the
Chapter 35~ Plant Structure and Growth
 Chapter 35~ Plant Structure and Growth Plant Organization Plant morphology is based on plant s evolutionary history Need to draw in nutrients from the ground and the air Plant Organs Root system = roots
Chapter 35~ Plant Structure and Growth Plant Organization Plant morphology is based on plant s evolutionary history Need to draw in nutrients from the ground and the air Plant Organs Root system = roots
WHAT DO you think of when you
 Stem Anatomy WHAT DO you think of when you think of a stem? Do you think of a flower stalk, the trees in your area, or a soybean stalk? Most people probably visualize something like the flower or the bean
Stem Anatomy WHAT DO you think of when you think of a stem? Do you think of a flower stalk, the trees in your area, or a soybean stalk? Most people probably visualize something like the flower or the bean
Lab Exercise 4: Primary Growth and Tissues in Stems
 Lab Exercise 4: Primary Growth and Tissues in Stems Tissues of the plant body can be classified in a variety of ways: functionally (based on the tissue function, e.g. vascular tissue ), morphologically
Lab Exercise 4: Primary Growth and Tissues in Stems Tissues of the plant body can be classified in a variety of ways: functionally (based on the tissue function, e.g. vascular tissue ), morphologically
Plant Structure and Growth
 Plant Structure and Growth A. Flowering Plant Parts: The flowering plants or are the most diverse group of plants. They are divided into 2 classes and. Examples of monocots: Examples of dicots: The morphology
Plant Structure and Growth A. Flowering Plant Parts: The flowering plants or are the most diverse group of plants. They are divided into 2 classes and. Examples of monocots: Examples of dicots: The morphology
(Photo Atlas: Figures 9.147, 9.148, 9.150, 9.1, 9.2, )
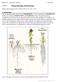 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Fall 2007 Topic 07: Primary Plant Body: The Root System (Photo Atlas: Figures 9.147, 9.148, 9.150, 9.1, 9.2, 9.5 9.23) A. Introduction The root has the primary functions of
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Fall 2007 Topic 07: Primary Plant Body: The Root System (Photo Atlas: Figures 9.147, 9.148, 9.150, 9.1, 9.2, 9.5 9.23) A. Introduction The root has the primary functions of
Stelar evolution. B. Sc. III Botany
 Stelar evolution B. Sc. III Botany Dr. (Miss) Kalpana R. Datar Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF BOTANY WILLINGDON COLLEGE, SANGLI. kalpana_datar@yahoo.com Stelar Evolution Stele is unit of vascular system.
Stelar evolution B. Sc. III Botany Dr. (Miss) Kalpana R. Datar Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF BOTANY WILLINGDON COLLEGE, SANGLI. kalpana_datar@yahoo.com Stelar Evolution Stele is unit of vascular system.
13.2 The Vascular Plant Body (textbook p )
 13.2 The Vascular Plant Body (textbook p544 550) Learning Goal: Label and explain the anatomy of the Vascular Plant and it's Tissue Types Plants are classified into two main groups: and. Vascular plants
13.2 The Vascular Plant Body (textbook p544 550) Learning Goal: Label and explain the anatomy of the Vascular Plant and it's Tissue Types Plants are classified into two main groups: and. Vascular plants
The Anatomy of Arborescent Plant Life Through Time Mike Viney
 The Anatomy of Arborescent Plant Life Through Time Mike Viney Collectors of petrified wood focus on permineralized plant material related to arborescent (tree-like) plant life. Evidence for the first fossil
The Anatomy of Arborescent Plant Life Through Time Mike Viney Collectors of petrified wood focus on permineralized plant material related to arborescent (tree-like) plant life. Evidence for the first fossil
Learning objectives: Gross morphology - terms you will be required to know and be able to use. shoot petiole compound leaf.
 Topic 1. Introduction to Plants Introduction: Because of its history, several unrelated taxa have been grouped together with plants into the discipline of botany. Given this context, in this first lab
Topic 1. Introduction to Plants Introduction: Because of its history, several unrelated taxa have been grouped together with plants into the discipline of botany. Given this context, in this first lab
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 25
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 25 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University November 2, 2015 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 25 November 2, 2015 1 / 33 Outline 1 Questions and answers 2 Stem
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 25 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University November 2, 2015 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 25 November 2, 2015 1 / 33 Outline 1 Questions and answers 2 Stem
Plant Anatomy and Tissue Structures
 Plant Anatomy and Tissue Structures The Two Major Plant Systems Reproductive shoot (flower) Terminal bud Node Internode Angiosperm plants have threse major organs: Roots Stems Leaves & Flowers Terminal
Plant Anatomy and Tissue Structures The Two Major Plant Systems Reproductive shoot (flower) Terminal bud Node Internode Angiosperm plants have threse major organs: Roots Stems Leaves & Flowers Terminal
Chapter 28 Active Reading Guide Plant Structure and Growth
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 28 Active Reading Guide Plant Structure and Growth In this unit on plants, the challenge for students will be to learn the new vocabulary. As we work through this unit,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 28 Active Reading Guide Plant Structure and Growth In this unit on plants, the challenge for students will be to learn the new vocabulary. As we work through this unit,
Plant Structure and Organization - 1
 Plant Structure and Organization - 1 In our first unit of Biology 203 we will focus on the structure and function of the higher plants, in particular the angiosperms, or flowering plants. We will look
Plant Structure and Organization - 1 In our first unit of Biology 203 we will focus on the structure and function of the higher plants, in particular the angiosperms, or flowering plants. We will look
Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley
 Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley B.D. Mishler Feb. 7, 2012. Morphological data IV -- ontogeny & structure of plants The last frontier
Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley B.D. Mishler Feb. 7, 2012. Morphological data IV -- ontogeny & structure of plants The last frontier
Plant Anatomy AP Biology
 Plant Anatomy 2006-2007 Basic plant anatomy 1 root root tip root hairs Roots 1 Roots anchor plant in soil, absorb minerals & water, & store food fibrous roots (1) mat of thin roots that spread out monocots
Plant Anatomy 2006-2007 Basic plant anatomy 1 root root tip root hairs Roots 1 Roots anchor plant in soil, absorb minerals & water, & store food fibrous roots (1) mat of thin roots that spread out monocots
Today: Plant Structure Exam II is on F March 31
 Next few lectures are on plant form and function Today: Plant Structure Exam II is on F March 31 Outline Plant structure I. Plant Cells structure & different types II. Types of meristems Apical meristems:
Next few lectures are on plant form and function Today: Plant Structure Exam II is on F March 31 Outline Plant structure I. Plant Cells structure & different types II. Types of meristems Apical meristems:
On Descriptions of Vascular Structures 107
 On Descriptions of Vascular Structures 107 fluids xylol is found to be rather too volatile to be easy of use, a mixture of equal parts of xylol and cedar-wood oil works, perhaps, most easily. If cedar-wood
On Descriptions of Vascular Structures 107 fluids xylol is found to be rather too volatile to be easy of use, a mixture of equal parts of xylol and cedar-wood oil works, perhaps, most easily. If cedar-wood
^' 5. Adamson. NOTE ON THE ROOTS OF TERMINALIA BY R. S. ADAMSON. [TEXT-FIGS. 3-7.]
![^' 5. Adamson. NOTE ON THE ROOTS OF TERMINALIA BY R. S. ADAMSON. [TEXT-FIGS. 3-7.] ^' 5. Adamson. NOTE ON THE ROOTS OF TERMINALIA BY R. S. ADAMSON. [TEXT-FIGS. 3-7.]](/thumbs/89/99838551.jpg) ^' 5. Adamson. NOTE ON THE ROOTS OF TERMINALIA ARJUNA, BEDD. BY R. S. ADAMSON. [TEXT-FIGS. 3-7.] The material examined was collected by Mr. I. H. Burkill, near Sembadow, in the Satpura Hills of Central
^' 5. Adamson. NOTE ON THE ROOTS OF TERMINALIA ARJUNA, BEDD. BY R. S. ADAMSON. [TEXT-FIGS. 3-7.] The material examined was collected by Mr. I. H. Burkill, near Sembadow, in the Satpura Hills of Central
This exam is the property of CR Hardy. It may not be sold or distributed in any manner.
 Relevant Sample Questions for Exam 1 from an old exam. Bio 221 Concepts of Botany Dr. Hardy Relevant bits from Exam 1 (Spring 2013) Name: Instructions: -Please do not turn this page over until Prof. Hardy
Relevant Sample Questions for Exam 1 from an old exam. Bio 221 Concepts of Botany Dr. Hardy Relevant bits from Exam 1 (Spring 2013) Name: Instructions: -Please do not turn this page over until Prof. Hardy
II. SIMPLE TISSUES Bot 404--Fall A. Introduction to Tissues (DIAGRAM allow a full page)
 II. SIMPLE TISSUES Bot 404--Fall 2004 A. Introduction to Tissues (DIAGRAM allow a full page) B. Definitions Adaxial = facing the axil; upper surface of leaf Abaxial = facing away from the axil; lower surface
II. SIMPLE TISSUES Bot 404--Fall 2004 A. Introduction to Tissues (DIAGRAM allow a full page) B. Definitions Adaxial = facing the axil; upper surface of leaf Abaxial = facing away from the axil; lower surface
Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution.
 Section 2: Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How do fossils provide evidence of evolution? How does
Section 2: Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How do fossils provide evidence of evolution? How does
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Monocots & dicots Angiosperm are divide into 2 classes dicots (eudicot) 2 cotyledons (seed leaves) leaves with network of veins woody plants, trees, shrubs, beans monocots 1 cotyledon leaves with parallel
Monocots & dicots Angiosperm are divide into 2 classes dicots (eudicot) 2 cotyledons (seed leaves) leaves with network of veins woody plants, trees, shrubs, beans monocots 1 cotyledon leaves with parallel
Chapter #35~ Plant Structure and Growth
 Chapter #35~ Plant Structure and Growth What part of a plant is represented by each of these: Carrot Celery Red Pepper Tomato Lettuce Garbanzo Bean Angiosperm structure Three basic organs: Roots (root
Chapter #35~ Plant Structure and Growth What part of a plant is represented by each of these: Carrot Celery Red Pepper Tomato Lettuce Garbanzo Bean Angiosperm structure Three basic organs: Roots (root
MAGNOLIA botany. evergreen ; spicy odor of blooms; chambered pith; hairy leaves(lower epidermis) & petioles
 MAGNOLIA botany Angiosperm: primitive, ancestral (Not Eudicot, Not Monocot): order Ranales: family Magnoliaceae: Magnolia grandiflora (southern magnolia) evergreen ; spicy odor of blooms; chambered pith;
MAGNOLIA botany Angiosperm: primitive, ancestral (Not Eudicot, Not Monocot): order Ranales: family Magnoliaceae: Magnolia grandiflora (southern magnolia) evergreen ; spicy odor of blooms; chambered pith;
Exercise 12. Procedure. Aim: To study anatomy of stem and root of monocots and dicots.
 Aim: To study anatomy of stem and root of monocots and dicots. Principle: The study of internal morphology, i.e., cells of various tissues in an organ of a living body is called Anatomy. Tissue, which
Aim: To study anatomy of stem and root of monocots and dicots. Principle: The study of internal morphology, i.e., cells of various tissues in an organ of a living body is called Anatomy. Tissue, which
Chapter 6. Biology of Flowering Plants. Anatomy Seedlings, Meristems, Stems, and Roots
 BOT 3015L (Outlaw/Sherdan/Aghoram); Page 1 of 6 Chapter 6 Biology of Flowering Plants Anatomy Seedlings, Meristems, Stems, and Roots Objectives Seedling germination and anatomy. Understand meristem structure
BOT 3015L (Outlaw/Sherdan/Aghoram); Page 1 of 6 Chapter 6 Biology of Flowering Plants Anatomy Seedlings, Meristems, Stems, and Roots Objectives Seedling germination and anatomy. Understand meristem structure
STEMS Anytime you use something made of wood, you re using something made from the stem of a plant. Stems are linear structures with attached leaves
 STEMS OUTLINE External Form of a Woody Twig Stem Origin and Development Stem Tissue Patterns Herbaceous Dicotyledonous Stems Woody Dicotyledonous Stems Monocotyledonous Stems Specialized Stems Wood and
STEMS OUTLINE External Form of a Woody Twig Stem Origin and Development Stem Tissue Patterns Herbaceous Dicotyledonous Stems Woody Dicotyledonous Stems Monocotyledonous Stems Specialized Stems Wood and
Fig (1):Layers of seconday cell wall
 Dr. Alaa J. Taha, Dr. Rana Alroomi and Dr. Hadeel Al-Newani :Secondary cell wall Although the secondary wall commonly is thought of as being deposited after the increase in surface area of the primary
Dr. Alaa J. Taha, Dr. Rana Alroomi and Dr. Hadeel Al-Newani :Secondary cell wall Although the secondary wall commonly is thought of as being deposited after the increase in surface area of the primary
Topic 23. The Ferns and Their Relatives
 Topic 23. The Ferns and Their Relatives Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Ferns Leptosporangiate Ferns Psilophytes Genus: Psilotum Horsetails Genus: Equisetum In this treatment we lump the Psilophytes and
Topic 23. The Ferns and Their Relatives Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Ferns Leptosporangiate Ferns Psilophytes Genus: Psilotum Horsetails Genus: Equisetum In this treatment we lump the Psilophytes and
(A) Buds (B) Lateral meristem (C) Apical meristem (D) Stem (E) Trichomes
 AP Biology - Problem Drill 17: Plant Structure Question No. 1 of 10 1. What are hair-like outgrowths that protect and absorb nutrients? Question #01 (A) Buds (B) Lateral meristem (C) Apical meristem (D)
AP Biology - Problem Drill 17: Plant Structure Question No. 1 of 10 1. What are hair-like outgrowths that protect and absorb nutrients? Question #01 (A) Buds (B) Lateral meristem (C) Apical meristem (D)
GALLS AND INSECTS PRODUCING THEM.
 140 The Ohio Naturalist. [Vol. IV, No. 6, APPENDIX I. GALLS AND INSECTS PRODUCING THEM. MEivViUvE THURSTON COOK. PART I. MORPHOLOGY OF L,EAF GALLS. I. GALLS OF THE APHIDIDAE. The gall of Pemphigus vagabundus
140 The Ohio Naturalist. [Vol. IV, No. 6, APPENDIX I. GALLS AND INSECTS PRODUCING THEM. MEivViUvE THURSTON COOK. PART I. MORPHOLOGY OF L,EAF GALLS. I. GALLS OF THE APHIDIDAE. The gall of Pemphigus vagabundus
Do we understand how pinewood nematode kills trees? Some hypotheses
 Do we understand how pinewood nematode kills trees? Some hypotheses Hugh Evans, Sam Evans & Makihiko Ikegami Forest Research, the research agency of the Forestry Commission, UK Adults emerge carrying nematodes
Do we understand how pinewood nematode kills trees? Some hypotheses Hugh Evans, Sam Evans & Makihiko Ikegami Forest Research, the research agency of the Forestry Commission, UK Adults emerge carrying nematodes
CAMBIUM, meristem, heartwood, and lenticel are
 Examining the Structures of a Tree CAMBIUM, meristem, heartwood, and lenticel are some terms that may be new to you. These terms are used to describe various tree structures. Not surprisingly, many terms
Examining the Structures of a Tree CAMBIUM, meristem, heartwood, and lenticel are some terms that may be new to you. These terms are used to describe various tree structures. Not surprisingly, many terms
