A NOTE ON THE MEASUREMENT OF STOMATAL APERTURE
|
|
|
- Francine French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New Phytol. (1969) 68, A NOTE ON THE MEASUREMENT OF STOMATAL APERTURE BY Y. LESHEM* AND R. THAINE The Grassland Research Institute, Hurley, Maidenhead, Berkshire {Received 18 March 1969) SUMMARY Cellulose acetate replicas were made from silicone rubber impressions of the abaxial surfaces of perennial ryegrass leaves. Apertures between i /x and 4 ju (mean 2 ju) were measured in replicas from leaves which had been exposed to conditions expected to close the stomata. This discrepancy is explained by observations of the ventral walis of guard cells in transverse sections of stomata, and by Araldite impressions of the cut ends of ryegrass leaves. These show that when a stoma is closed the ventral walls make contact below the paradermal walls of the guard cells and consequently a small depression is left between the cells. These depressions are similar in width to the apparent apertures in the cellulose replicas which may be wrongly interpreted as slightly open stomata. In some species the silicone impression method is incapable of giving an accurate measurement of stomatal aperture. Consequently, in attempts to relate such measurements to stomatal function or rate of transpiration it should be established that small apertures shown in cellulose acetate replicas are not the result of depressions between the external surfaces of guard cells in closed stomata. INTRODUCTION In studies of stomatal function and in attempts to relate stomatal aperture to rates of transpiration a direct measurement of stomatal aperture is often needed. Impressions of the leaf surfaces have been made with silicone rubber from which a cellulose acetate replica is taken (Sampson, 1961; Zelitch, 1961). In cotton leaves (Shimshi, 1964) it was found that, using a viseous flow porometer, measurements of the drop of pressure applied to one side of a leaf could be correlated over the whole range of apertures from closed to fully open stomatal apertures, measured with the silicone rubber method. In tobacco leaves (Zelitch, 1961; Walker and Zelitch, i963)and in maize leaves(shmueliandleshem, 1967), however, apparent stomatal apertures of about 2 pl were found in impressions where stomata were expected to be closed in leaves kept in the dark in air containing at least 10% CO2 or in leaves under water stress. When maize leaves, treated in these ways, were placed in a viscous flow porometer there was no drop in the pressure of air applied to one side of the leaves, showing that the stomata were in fact closed. A similar inconsistency was found during a study of water loss from isolated ryegrass leaves, in which the present authors are engaged. In an attempt to find an explanation for this inconsistency it was necessary to obtain a direct view of the ventral walls of guard cells to determine whether or not the pores observed in surface impressions represent stomatal apertures which penetrate to sub-stomatal cavities. * Present address: Department of Field Crops, Volcani Institute of Agriculture, Rehovot, Israel. E* 1047
2 1048 Y. LESHEM AND R. THAINE METHODS, Perennial ryegrass {Lolium perenne) plants were grown for 3 weeks in growth cabinets in which the light intensity was 1800 ft-candles at the level of the leaves, the length of day was 16 hours and the temperature 20 C day/10 C night. Leaves were removed at different times during the day and held in the dark in air containing at least 10% COj to close the stomata. Cellulose acetate replicas were taken from silicone rubber impressions of the abaxial surfaces of these leaves. To prepare replicas giving a cross-sectional view of a stomata, leaves were cut at right angles to the long axis and the cut end was embedded in fluid silicone rubber mixed with a catalyst. The rubber set in 2 or 3 minutes, the leaf was removed and when the mould was filled with the fluid monomer of Araldite it was placed in an oven at 60 C for 2 days to harden. When the rubber impressions were removed replicas of the cells exposed at the cut ends of the leaves remained in the moulded Araldite blocks. The moulded blocks were embedded in a small quantity of fluid Araldite coloured with Janus green B to distinguish it from the moulded blocks. When the mountingfluidhad hardened, the Araldite disc so formed was reduced by grinding on the reverse side with a medium grade emery cloth. Finally, the ground surface was polished on a glass plate in a pool of metal polish. The thin Araldite replicas were mounted in liquid paraffin between a miscroscope slide and a coverslip and observed and photographed in the light microscope with transmitted light. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The surface impression (Plate i. No. i) and the impressions of a cut end (Plate i, No. 2) gave different measurements of stomatal aperture. In eight replicas of the abaxial surface of perennial ryegrass leaves in which the stomata were expected to be closed, all the stomata appeared slightly open and their apparent apertures varied between i n and 4 p. in diameter (mean 2 ix). On the other hand, in three Araldite replicas of the cut ends of leaves all the stomata were closed. However, a surface depression in these replicas can be detected where the external surfaces of the two guard cells meet which, in Plate i. No. 2, is 3jU wide and within the range of the apparent apertures in surface replicas. When the surface impression was made this depression probably filled with fluid silicon rubber, so that in the cellulose acetate replica it looked like a small aperture. In stomata with large apertures, this artefact is not likely to occur for the fluid silicone easily penetrates the larger pores giving an accurate representation of the stomatal aperture in the cellulose acetate replica. A photomicrograph of the replica of a stoma with an aperture of 17 ^l diameter is shown in Plate i. No. 3. To relate the impressions of stomata from fresh leaves to the anatomy of guard cells and their subsidiary cells, transverse sections were made of leaves which were fixed in absolute ethanol stained azure blue and embedded in Araldite following treatments to close the stomata. Plate i. No. 4, shows a cross-section of a stoma in which the general appearance of the guard cells and the subsidiary cells can be related to the stomata seen in the Araldite impression of the cut end (Plate i. No. 2). The depression between the guard cells of the closed stoma can also be seen in this section. It is concluded that in some species including perennial ryegrass the surface impression method is incapable of giving an accurate measurement of stomatal aperture when the stomata are nearly or completely closed.
3 THE NEW PHYTOLOGIST, 68, 4 PLATE I Nos. I and 2. Impressions of ryegrass leaves {Lolitimperenne) which were kept in the dark in a high concentration of CO2 to close the stomata. No. i shows a surface replica obtained with the silicone rubber method. The stoma reveals an apparent aperture of 2 /; which is due to a depression formed by the external surfaces of the guard cells (G) while the stoma is actually closed. No. 2 is a photomicrograph of a cross-sectional Araldite replica of a stoma. A depression occurs between two ridges at the external surface of the epidermis and closure occurred by contact of the ventral cell walls (arrow). It is this depression which gives the appearance of a pore shown in No. i. No. 3. A cellulose acetate replica miade from a silicone rubber impression of a stoma with a large aperture (17 /;) fronn a ryegrass leaf kept in light and in air with the CO2 removed. No. 4. A cross-section of a stoma in leaves held in darkness and in air containing at least 10% CO2 to close the stomiata and then fixed in alcohol and embedded with Araldite. The subsidiary cells of the stomata are indicated by the letter S. lo/x Y. LESHEM AND R. MEASUREMENT OF STOMATAL APERTURE {facing page 1048)
4 Measurement of stomatal aperture 1049 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We are grateful to Dr H. Meidner for helpful comments and discussion and to G. E. Barton for his skilful preparation of the Araldite replicas. REFERENCES SAMPSON, J. A. (1961). A method of replicating dry or moist surfaces for examination by light microscopy. Nature, Lond., 191, 932. SHIMSHI, D. (1964). The use of a field porometer for the study of water stress in plants. Israel J. agric. Res., 14, 137. SHMUELI, E. & LESHEM, Y. (1967). The response of forage corn to four irrigation regimes. Volcani Inst. agric. Res. {Israel), Pamphlet No WALKER, D. A. & ZELITCH, I. (1963). Some effects of metabolic inhibitors, temperature and anaerobic conditions on stomatal movement. PI. PhysioL, Lancaster, 38, 390. ZELITCH, I. (1961). Biochemical control of stomatal opening in leaves. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 47, 1423-
5
THE EFFECT OF ABSCISIC ACID ON STOMATAL BEHAVIOUR IN FLACCA, A V\^ILTY MUTANT OF TOMATO, IN DARKNESS
 New Phytol (1972) 71, 81-84. THE EFFECT OF ABSCISIC ACID ON STOMATAL BEHAVIOUR IN FLACCA, A V\^ILTY MUTANT OF TOMATO, IN DARKNESS BY M. T A L AND D O R O T I M B E R Division of Life Sciences, Negev Institute
New Phytol (1972) 71, 81-84. THE EFFECT OF ABSCISIC ACID ON STOMATAL BEHAVIOUR IN FLACCA, A V\^ILTY MUTANT OF TOMATO, IN DARKNESS BY M. T A L AND D O R O T I M B E R Division of Life Sciences, Negev Institute
EFFECTS OF PHENYL-MERCURIC ACETATE ON, STOMATAL AND CUTICULAR RESISTANCE TO TRANSPIRATION
 New PhytoL (1975) 75,47-52.. :: i vi EFFECTS OF PHENYL-MERCURIC ACETATE ON, STOMATAL AND CUTICULAR RESISTANCE TO TRANSPIRATION BY S. MORESHET Agricultural Research Organization, The Volcani Centre, Bet
New PhytoL (1975) 75,47-52.. :: i vi EFFECTS OF PHENYL-MERCURIC ACETATE ON, STOMATAL AND CUTICULAR RESISTANCE TO TRANSPIRATION BY S. MORESHET Agricultural Research Organization, The Volcani Centre, Bet
(i) The respiratory openings found on stems of woody plants. (ii) An apparatus to compare the rate of transpiration in cut shoots.
 SN Kansagra School Assignment-Transpiration Grade10 TRANSPIRATION :ASSIGNMENT Question.1. Name the following : (i) The respiratory openings found on stems of woody plants. (ii) An apparatus to compare
SN Kansagra School Assignment-Transpiration Grade10 TRANSPIRATION :ASSIGNMENT Question.1. Name the following : (i) The respiratory openings found on stems of woody plants. (ii) An apparatus to compare
STOMATAL RESPONSES TO CHANGES IN CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION IN LEAVES TREATED WITH 3- (4-CHLOROPHENYL) -1,1 -DI METHYLUREA
 New Phytol. (1967) 66, 57 63. STOMATAL RESPONSES TO CHANGES IN CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION IN LEAVES TREATED WITH 3- (4-CHLOROPHENYL) -1,1 -DI METHYLUREA BY W. G. ALLAWAY AND T. A. MANSFIELD Department
New Phytol. (1967) 66, 57 63. STOMATAL RESPONSES TO CHANGES IN CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION IN LEAVES TREATED WITH 3- (4-CHLOROPHENYL) -1,1 -DI METHYLUREA BY W. G. ALLAWAY AND T. A. MANSFIELD Department
STOMATAL RESPONSES TO LIGHT AND CARBON DIOXIDE IN THE HART'S-TONGUE FERN, PHYLLITIS SCOLOPENDRIUM NEWM.
 New PhytoL (1969) 68, 63-66.. STOMATAL RESPONSES TO LIGHT AND CARBON DIOXIDE IN THE HART'S-TONGUE FERN, PHYLLITIS SCOLOPENDRIUM NEWM. BY T. A. MANSFIELD AND C. M. WILLMER Department of Biological Sciences,
New PhytoL (1969) 68, 63-66.. STOMATAL RESPONSES TO LIGHT AND CARBON DIOXIDE IN THE HART'S-TONGUE FERN, PHYLLITIS SCOLOPENDRIUM NEWM. BY T. A. MANSFIELD AND C. M. WILLMER Department of Biological Sciences,
Tissues and organs PART 2
 Tissues and organs PART 2 The structure and function of the mesophytic leaf (a plant organ) The mesopyhtic leaf (lives in a moderately moist environment) contains 7 layers of tissue: 1. Upper epidermis
Tissues and organs PART 2 The structure and function of the mesophytic leaf (a plant organ) The mesopyhtic leaf (lives in a moderately moist environment) contains 7 layers of tissue: 1. Upper epidermis
TRANSPIRATION. An important regulator of transpiration is the stomatal complex composed of the opening or
 BIOL 1134 1 TRANSPIRATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completing this exercise, students should be able to: Describe the process of and principles behind transpiration. Describe how stomata, guard cells,
BIOL 1134 1 TRANSPIRATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completing this exercise, students should be able to: Describe the process of and principles behind transpiration. Describe how stomata, guard cells,
Transport in Plants Question Paper 3
 Transport in Plants Question Paper 3 Level IGCSE Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Transport in Plants Paper Type (Extended) Theory Paper Booklet Question Paper 3 Time Allowed: 57 minutes Score: /47
Transport in Plants Question Paper 3 Level IGCSE Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Transport in Plants Paper Type (Extended) Theory Paper Booklet Question Paper 3 Time Allowed: 57 minutes Score: /47
Investigating Stomata
 Investigating Stomata Learning Objectives: To be able to identify stomata and compare stomata on leaves of a plant To understand the function of stomata and the role they play in a plant To understand
Investigating Stomata Learning Objectives: To be able to identify stomata and compare stomata on leaves of a plant To understand the function of stomata and the role they play in a plant To understand
Plants and animals both have a layer of tissue called the epidermal layer. This is the layer of cells on the outside of the organism.
 Name Date Period Lab Number Counting Stomata Lab Introduction Plants and animals both have a layer of tissue called the epidermal layer. This is the layer of cells on the outside of the organism. Plants
Name Date Period Lab Number Counting Stomata Lab Introduction Plants and animals both have a layer of tissue called the epidermal layer. This is the layer of cells on the outside of the organism. Plants
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *5818991458* BIOLOGY 9700/51 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation October/November 2016 1 hour 15
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *5818991458* BIOLOGY 9700/51 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation October/November 2016 1 hour 15
2.2 Page 3 Gas exchange S. Preston 1
 AS Unit BY2: Biodiversity and Physiology of Body Systems Name: Date: Topic 2.2 Adaptations for Gas Exchange Page 3 1. Read pages 2 and 3 Label the diagram showing the cross section of a leaf. Complete
AS Unit BY2: Biodiversity and Physiology of Body Systems Name: Date: Topic 2.2 Adaptations for Gas Exchange Page 3 1. Read pages 2 and 3 Label the diagram showing the cross section of a leaf. Complete
LEAF RESISTANCE IN A GLASSHOUSE TOMATO CROP IN RELATION TO LEAF POSITION AND SOLAR RADIATION
 New Phytol. (1969) 68, 265-273. LEAF RESISTANCE IN A GLASSHOUSE TOMATO CROP IN RELATION TO LEAF POSITION AND SOLAR RADIATION BY R. G. HURD Glasshouse Crops Research Institute, Littlehampton, Sussex {Received
New Phytol. (1969) 68, 265-273. LEAF RESISTANCE IN A GLASSHOUSE TOMATO CROP IN RELATION TO LEAF POSITION AND SOLAR RADIATION BY R. G. HURD Glasshouse Crops Research Institute, Littlehampton, Sussex {Received
of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does not cross the
 Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
Cells: 3 Star. Which row in the chart below best explains the movement of some molecules between the model cell and the solution in the beaker?
 ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *5839121393* BIOLOGY 9700/53 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation October/November 2016 1 hour 15
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *5839121393* BIOLOGY 9700/53 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation October/November 2016 1 hour 15
A CRITICAL EXAMINATION OF THE USE OF DETACHED EPIDERMIS IN STUDIES OF STOMATAL PHYSIOLOGY
 New Phytol. (1969) 68, 363-375. A CRITICAL EXAMINATION OF THE USE OF DETACHED EPIDERMIS IN STUDIES OF STOMATAL PHYSIOLOGY BY C. M. WILLMER AND T. A. MANSFIELD Department of Biological Sciences, University
New Phytol. (1969) 68, 363-375. A CRITICAL EXAMINATION OF THE USE OF DETACHED EPIDERMIS IN STUDIES OF STOMATAL PHYSIOLOGY BY C. M. WILLMER AND T. A. MANSFIELD Department of Biological Sciences, University
The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match the part of the plant (A, B, C or D) to its function by writing the letters in the table.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
INTERACTIONS OF CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION, LIGHT INTENSITY AND TEMPERATURE ON PLANT RESISTANCES TO WATER VAPOUR AND CARBON DIOXIDE DIFFUSION
 New Phytol. (1967) 66, 463-473. INTERACTIONS OF CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION, LIGHT INTENSITY AND TEMPERATURE ON PLANT RESISTANCES TO WATER VAPOUR AND CARBON DIOXIDE DIFFUSION BY P. C. W H I T E M A N*
New Phytol. (1967) 66, 463-473. INTERACTIONS OF CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION, LIGHT INTENSITY AND TEMPERATURE ON PLANT RESISTANCES TO WATER VAPOUR AND CARBON DIOXIDE DIFFUSION BY P. C. W H I T E M A N*
How drought stress and CO2 concentration influence stomatal conductance and photosynthesis? Abstract. Introduction
 How drought stress and CO2 concentration influence stomatal conductance and photosynthesis? Simon Keck 1, Julian Müller 1, Dominik Guttschick 1, Kaisa Pajusalu 2, Elodie Quer 3, Maria Majekova 4 1 University
How drought stress and CO2 concentration influence stomatal conductance and photosynthesis? Simon Keck 1, Julian Müller 1, Dominik Guttschick 1, Kaisa Pajusalu 2, Elodie Quer 3, Maria Majekova 4 1 University
CHAPTER Introduction
 27 CHAPTER 2 2.1 Introduction Pharmacognosy as a subject of pharmaceutical curriculum focused on those natural products employed in the allopathic system of medicine. Coincident with the increasing attractiveness
27 CHAPTER 2 2.1 Introduction Pharmacognosy as a subject of pharmaceutical curriculum focused on those natural products employed in the allopathic system of medicine. Coincident with the increasing attractiveness
An Introduction to Plant Vascular Systems
 Chapter 9 An Introduction to Plant Vascular Systems Laura K. Thompson Biology Department Furman University Greenville, SC 29717 864-294-2085 laura.thompson@furman.edu Laura received her B.S from James
Chapter 9 An Introduction to Plant Vascular Systems Laura K. Thompson Biology Department Furman University Greenville, SC 29717 864-294-2085 laura.thompson@furman.edu Laura received her B.S from James
Topic 10: Transpiration, transport and support in plants
 Topic 10: Transpiration, transport and support in plants 1. Transpiration is A. the loss of water vapour from the surfaces of plants due to evaporation B. the gain of water vapour from the surfaces of
Topic 10: Transpiration, transport and support in plants 1. Transpiration is A. the loss of water vapour from the surfaces of plants due to evaporation B. the gain of water vapour from the surfaces of
AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata
 AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata Living things must exchange matter with the environment to survive, Example: Gas Exchange in Plants photosynthesis cellular respiration 1. During which hours does a
AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata Living things must exchange matter with the environment to survive, Example: Gas Exchange in Plants photosynthesis cellular respiration 1. During which hours does a
Hole-y Moley Examining Stomates
 Examining Stomates As plants colonized the land, there was a selection pressure for plants to grow and increase in size. This required the development of supportive tissue. An increase in height also meant
Examining Stomates As plants colonized the land, there was a selection pressure for plants to grow and increase in size. This required the development of supportive tissue. An increase in height also meant
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Chapter 4-2. Transpiration diffusion of water vapor
 Chapter 4-2 Transpiration diffusion of water vapor Transpiration diffusion of water vapor Diffusion is primary means of any further movement of the water out of the leaf. That is water movement is controlled
Chapter 4-2 Transpiration diffusion of water vapor Transpiration diffusion of water vapor Diffusion is primary means of any further movement of the water out of the leaf. That is water movement is controlled
23 4 Leaves Slide 1 of 32
 23 4 Leaves 1 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. 2 of 32 Leaf Structure To collect sunlight, most leaves have thin, flattened
23 4 Leaves 1 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. 2 of 32 Leaf Structure To collect sunlight, most leaves have thin, flattened
Relationship between leaf and xylem water potentials in rice plants
 Plant & CcllPhysiol. 19(7): 1289-1294 (1978) Short communication Relationship between leaf and xylem water potentials in rice plants Kuni Ishihara and Tadashi Hirasawa Laboratory of Crop Science, Faculty
Plant & CcllPhysiol. 19(7): 1289-1294 (1978) Short communication Relationship between leaf and xylem water potentials in rice plants Kuni Ishihara and Tadashi Hirasawa Laboratory of Crop Science, Faculty
Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants
 Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Effect of 1-MCP on Water Relations Parameters of Well-Watered and Water-Stressed Cotton Plants
 Effect of 1-MCP on Water Relations Parameters of Well-Watered and Water-Stressed Cotton Plants Eduardo M. Kawakami, Derrick M. Oosterhuis, and John L. Snider 1 RESEARCH PROBLEM The cotton crop in the U.S.
Effect of 1-MCP on Water Relations Parameters of Well-Watered and Water-Stressed Cotton Plants Eduardo M. Kawakami, Derrick M. Oosterhuis, and John L. Snider 1 RESEARCH PROBLEM The cotton crop in the U.S.
stomata means mouth in Greek because they allow communication between the internal and
 Name: Date: Period: Photosynthesis Lab #1: Leaf Structure and Function Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to explore the structure of a leaf, specifically the stomata and guard cells. Once we have an
Name: Date: Period: Photosynthesis Lab #1: Leaf Structure and Function Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to explore the structure of a leaf, specifically the stomata and guard cells. Once we have an
LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: UNIT 2.1: Osmosis and Plant transport
 NAME 0 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 2.1.1-2.1.9 UNIT 2.1: Osmosis and Plant transport LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Pupils should be able to: Good Average Requires Attention 1 Carry out
NAME 0 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 2.1.1-2.1.9 UNIT 2.1: Osmosis and Plant transport LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Pupils should be able to: Good Average Requires Attention 1 Carry out
HORMONAL MODIFICATION OF PLANT RESPONSE TO WATER STRESS By Y. MIZRAHI* and A. E. RWHMOND* [Manuscript received 8 November 1971] Abstract
![HORMONAL MODIFICATION OF PLANT RESPONSE TO WATER STRESS By Y. MIZRAHI* and A. E. RWHMOND* [Manuscript received 8 November 1971] Abstract HORMONAL MODIFICATION OF PLANT RESPONSE TO WATER STRESS By Y. MIZRAHI* and A. E. RWHMOND* [Manuscript received 8 November 1971] Abstract](/thumbs/89/100126268.jpg) HORMONAL MODIFICATION OF PLANT RESPONSE TO WATER STRESS By Y. MIZRAHI* and A. E. RWHMOND* [Manuscript received 8 November 1971] Abstract Addition of either kinetin or abscisic acid (ABA) to the root medium
HORMONAL MODIFICATION OF PLANT RESPONSE TO WATER STRESS By Y. MIZRAHI* and A. E. RWHMOND* [Manuscript received 8 November 1971] Abstract Addition of either kinetin or abscisic acid (ABA) to the root medium
Importance. The Reaction of Life : The conversion of the sun s energy into a form man and other living creatures can use.
 PLANT PROCESSES Photosynthesis Importance The Reaction of Life : The conversion of the sun s energy into a form man and other living creatures can use. Photo light Synthesis to put together 3 Important
PLANT PROCESSES Photosynthesis Importance The Reaction of Life : The conversion of the sun s energy into a form man and other living creatures can use. Photo light Synthesis to put together 3 Important
ARIF ULLAH ITHS
 SUMMARY Feature of xylem and phloem and their role. Distribution of xylem and phloem (vascular bundles) in stem and root of dicotyledonous plants. Transport of water from the root to the atmosphere through
SUMMARY Feature of xylem and phloem and their role. Distribution of xylem and phloem (vascular bundles) in stem and root of dicotyledonous plants. Transport of water from the root to the atmosphere through
WATER RELATIONS OF WHEAT ALTERNATED BETWEEN TWO ROOT TEMPERATURES
 Nezo Phytol. (1979) 82, 89-96 89 WATER RELATIONS OF WHEAT ALTERNATED BETWEEN TWO ROOT TEMPERATURES BY M. B. KIRKHAM Department of Agrofiomy, Oklahoma State University^ StiHwater, Oklahoma 74074, U,S.A.
Nezo Phytol. (1979) 82, 89-96 89 WATER RELATIONS OF WHEAT ALTERNATED BETWEEN TWO ROOT TEMPERATURES BY M. B. KIRKHAM Department of Agrofiomy, Oklahoma State University^ StiHwater, Oklahoma 74074, U,S.A.
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Transport in plants
 Transport in plants Question Paper 1 Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board OCR Topic Exchange and transport Sub-Topic Transport in plants Booklet Question Paper 1 Time Allowed: 75 minutes Score: / 62
Transport in plants Question Paper 1 Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board OCR Topic Exchange and transport Sub-Topic Transport in plants Booklet Question Paper 1 Time Allowed: 75 minutes Score: / 62
Transportation in Plants
 Transportation in Plants Bell Ringer - 5 Min Why do you need transportation in living organisms? Explain your answer with a suitable example. Water movement through plants How does water move through a
Transportation in Plants Bell Ringer - 5 Min Why do you need transportation in living organisms? Explain your answer with a suitable example. Water movement through plants How does water move through a
5. Move several sections into the second well that contains a few drops of Toluidine Blue.
 HAIGLER PROTOCOL FOR VIEWING CROSS SECTIONS OF PLANTS Materials (per student team): Plants Double-edged razor blades (split into two as demonstrated by the teacher) Masking tape for razor blade handle
HAIGLER PROTOCOL FOR VIEWING CROSS SECTIONS OF PLANTS Materials (per student team): Plants Double-edged razor blades (split into two as demonstrated by the teacher) Masking tape for razor blade handle
LEAF STRUCTURE AND PLANT TISSUE LAB
 Name Period LEAF STRUCTURE AND PLANT TISSUE LAB Objectives: Use this lab handout and your textbook (Campbell, Chapter 35) to familiarize yourself with the different cell and tissue types found in plant
Name Period LEAF STRUCTURE AND PLANT TISSUE LAB Objectives: Use this lab handout and your textbook (Campbell, Chapter 35) to familiarize yourself with the different cell and tissue types found in plant
LEAF WATER POTENTIAL AND STOMATAL CONDUCTANCE OF RUBBER (Hevea brasiliensis) AS INFLUENCED BY SOIL MOISTURE AND LEAF AGE LALANI SAMARAPPULI ABSTRACT
 LEAF WATER POTENTIAL AND STOMATAL CONDUCTANCE OF RUBBER (Hevea brasiliensis) AS INFLUENCED BY SOIL MOISTURE AND LEAF AGE J BY LALANI SAMARAPPULI ABSTRACT Stomatal conductance and transpiration and leaf
LEAF WATER POTENTIAL AND STOMATAL CONDUCTANCE OF RUBBER (Hevea brasiliensis) AS INFLUENCED BY SOIL MOISTURE AND LEAF AGE J BY LALANI SAMARAPPULI ABSTRACT Stomatal conductance and transpiration and leaf
Plant Water Absorption and Transpiration
 Plant Water Absorption and Transpiration Studies in Plant Physiology Series No. 3 Plant Water Absorption and Transpiration S. S. Purohit R. Ranjan Agrobios (India) Dr. S. S. Purohit Laboratory of Plant
Plant Water Absorption and Transpiration Studies in Plant Physiology Series No. 3 Plant Water Absorption and Transpiration S. S. Purohit R. Ranjan Agrobios (India) Dr. S. S. Purohit Laboratory of Plant
BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN. SC.F The student knows that living things are different but share similar structures.
 activities 38&39 Stomata and Transpiration (Sessions I and II) BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 5 Quarter 4 Activities 38 & 39 SC.F.1.2.3 The student knows that living things are
activities 38&39 Stomata and Transpiration (Sessions I and II) BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 5 Quarter 4 Activities 38 & 39 SC.F.1.2.3 The student knows that living things are
Plant Gene and Trait, 2013, Vol.4, No.8,
 Research Report Open Access Effect of Water Stress on Leaf Temperature, Transpiration Rate, Stomatal Diffusive Resistance and Yield of Banana K. Krishna Surendar 1, D. Durga Devi 1, I. Ravi 2, P. Jeyakumar
Research Report Open Access Effect of Water Stress on Leaf Temperature, Transpiration Rate, Stomatal Diffusive Resistance and Yield of Banana K. Krishna Surendar 1, D. Durga Devi 1, I. Ravi 2, P. Jeyakumar
Name AP Biology - Lab 06
 LAB 06 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences in water potential. To test
LAB 06 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences in water potential. To test
Biology. Slide 1 of 32. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 32 23 4 Leaves 2 of 32 Leaf Structure Leaf Structure How does the structure of a leaf enable it to carry out photosynthesis? 3 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for
Biology 1 of 32 23 4 Leaves 2 of 32 Leaf Structure Leaf Structure How does the structure of a leaf enable it to carry out photosynthesis? 3 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for
Plants I - Water and Nutrient Management: Plant Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants I - Water and Nutrient Management: Plant Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features thatt distinguish plants from
Plants I - Water and Nutrient Management: Plant Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features thatt distinguish plants from
Nitroaromatic detection and infrared communication from wild-type plants using plant nanobionics
 Nitroaromatic detection and infrared communication from wild-type plants using plant nanobionics Min Hao Wong 1 *, Juan P. Giraldo 1,2 *, Seon-Yeong Kwak 1, Volodymyr B. Koman 1, Rosalie Sinclair 1, Tedrick
Nitroaromatic detection and infrared communication from wild-type plants using plant nanobionics Min Hao Wong 1 *, Juan P. Giraldo 1,2 *, Seon-Yeong Kwak 1, Volodymyr B. Koman 1, Rosalie Sinclair 1, Tedrick
Interactions between ozone and drought stress in plants: mechanisms and implications. Sally Wilkinson and William J. Davies, Lancaster University
 Interactions between ozone and drought stress in plants: mechanisms and implications Sally Wilkinson and William J. Davies, Lancaster University STOMATA: At the leaf surface water is lost to the atmosphere
Interactions between ozone and drought stress in plants: mechanisms and implications Sally Wilkinson and William J. Davies, Lancaster University STOMATA: At the leaf surface water is lost to the atmosphere
REVERSAL OF ABSCISIC ACID INDUCED STOMATAL CLOSURE BY BENZYL ADENINE
 (1976) 7 REVERSAL OF ABSCISIC ACID INDUCED STOMATAL CLOSURE BY BENZYL ADENINE BY V. S. R. DAS, I. M. RAO AND A. S. RAGHAVENDRA* Department of Botany, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati 51702, India
(1976) 7 REVERSAL OF ABSCISIC ACID INDUCED STOMATAL CLOSURE BY BENZYL ADENINE BY V. S. R. DAS, I. M. RAO AND A. S. RAGHAVENDRA* Department of Botany, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati 51702, India
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
! E EUKARYOTE CYTOLOGY INTERCELLULAR SPACE MIDDLE LAMELLA PEROXISOME PLASMODESMATA VACUOLE CYTOSOL CELL WALL GOLGI BODY MIDDLE LAMELLA NUCLEUS
 EUKARYOTE CYTOLOGY INTERCELLULAR SPACE! E PEROXISOME VACUOLE CELL WALL MIDDLE LAMELLA CHLOROPLAST CYTOPLASMIC STRAND CYTOSOL CELL MEMBRANE MIDDLE LAMELLA PLASMODESMATA CYTOSOL GOLGI BODY NUCLEUS MITOCHONDRION
EUKARYOTE CYTOLOGY INTERCELLULAR SPACE! E PEROXISOME VACUOLE CELL WALL MIDDLE LAMELLA CHLOROPLAST CYTOPLASMIC STRAND CYTOSOL CELL MEMBRANE MIDDLE LAMELLA PLASMODESMATA CYTOSOL GOLGI BODY NUCLEUS MITOCHONDRION
Investigation 11 Transpiration
 Introduction What factors, including environmental variables, affect the rate of transpiration in plants? Background Cells and organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce, and
Introduction What factors, including environmental variables, affect the rate of transpiration in plants? Background Cells and organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce, and
untitled 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both
 Name: ate: 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both. are produced by nerve cells B. are highly specific in their actions. slow the rates of chemical reactions. are involved
Name: ate: 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both. are produced by nerve cells B. are highly specific in their actions. slow the rates of chemical reactions. are involved
Photonic multilayer structure of Begonia chloroplasts enhances photosynthetic efficiency
 Photonic multilayer structure of Begonia chloroplasts enhances photosynthetic efficiency Supplementary Figure. S1 Location and context of iridoplasts and chloroplasts in Begonia. a, TEM image of mesophyll
Photonic multilayer structure of Begonia chloroplasts enhances photosynthetic efficiency Supplementary Figure. S1 Location and context of iridoplasts and chloroplasts in Begonia. a, TEM image of mesophyll
Bio Factsheet. Transport in Plants. Number 342
 Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
 Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark the regions where active cell division and rapid division
Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark the regions where active cell division and rapid division
Topic 15. The Shoot System
 Topic 15. The Shoot System Introduction. This is the second of two lab topics that focus on the three plant organs (root, stem, leaf). In these labs we want you to recognize how tissues are organized in
Topic 15. The Shoot System Introduction. This is the second of two lab topics that focus on the three plant organs (root, stem, leaf). In these labs we want you to recognize how tissues are organized in
Stomata and water fluxes through plants
 Stomata and water fluxes through plants Bill Davies The Lancaster Environment Centre, UK Summary Stomata and responses to the environment Conductance, a function of frequency and aperture Measuring/estimating
Stomata and water fluxes through plants Bill Davies The Lancaster Environment Centre, UK Summary Stomata and responses to the environment Conductance, a function of frequency and aperture Measuring/estimating
H 2 O CO 2. A Fundamental Resource Tradeoff negotiated by Stomata. Outline. 1. Importance of stomata for water relations
 A Fundamental Resource Tradeoff negotiated by Stomata H 2 O Outline 1. Importance of stomata for water relations 2. Physical description of Stomata, and mechanical drivers for opening and closing CO 2
A Fundamental Resource Tradeoff negotiated by Stomata H 2 O Outline 1. Importance of stomata for water relations 2. Physical description of Stomata, and mechanical drivers for opening and closing CO 2
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
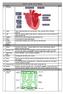 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
In vitro digestibility and neutral detergent fibre and lignin contents of plant parts of nine forage species
 Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1998), 131, 51 58. 1998 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 51 In vitro digestibility and neutral detergent fibre and lignin contents of
Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1998), 131, 51 58. 1998 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 51 In vitro digestibility and neutral detergent fibre and lignin contents of
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 Name: Date: Period: CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: Sunlight air (carbon dioxide) water minerals
Name: Date: Period: CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: Sunlight air (carbon dioxide) water minerals
Persistent Drought Monitoring Using a Microfluidic-Printed Electro-
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Persistent Drought Monitoring Using a Microfluidic-Printed Electro-
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Persistent Drought Monitoring Using a Microfluidic-Printed Electro-
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 3: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 3: PHOTOSYNTHESIS READING: Please read chapter 7 in your textbook prior to lab. INTRODUCTION: Photosynthesis is the process by which certain organisms use energy from sunlight and carbon
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 3: PHOTOSYNTHESIS READING: Please read chapter 7 in your textbook prior to lab. INTRODUCTION: Photosynthesis is the process by which certain organisms use energy from sunlight and carbon
fr>uafcji *> \E % jw r"'''f^,""'i;- ~^H^^
 NAME DATE Carolina Transpiration Kit for AP Biology Imagine that your family has received a bouquet of cut flowers as a gift. You place the flowers in a vase with a small volume of water, and return the
NAME DATE Carolina Transpiration Kit for AP Biology Imagine that your family has received a bouquet of cut flowers as a gift. You place the flowers in a vase with a small volume of water, and return the
Parenchyma Cell. Magnification 2375X
 Parenchyma Cell The large size of parenchyma cells is due in part to their relatively large vacuole (V) and in part also to the large number of chloroplasts (Cp) they contain. From a crimson clover, Trifolium
Parenchyma Cell The large size of parenchyma cells is due in part to their relatively large vacuole (V) and in part also to the large number of chloroplasts (Cp) they contain. From a crimson clover, Trifolium
Laboratory 9: Transpiration
 Laboratory 9: Transpiration YOU MUST KNOW The role of water potential and transpiration in the movement of water from roots to leaves. The effects of various environmental conditions on the rate of transpiration.
Laboratory 9: Transpiration YOU MUST KNOW The role of water potential and transpiration in the movement of water from roots to leaves. The effects of various environmental conditions on the rate of transpiration.
Photosynthesis. 1. What raw materials are used by producers for photosynthesis?
 Photosynthesis Recall that producers are found at the base of every food chain and are the foundation of ecosystems. This is due to their ability to capture light energy to produce their own food in the
Photosynthesis Recall that producers are found at the base of every food chain and are the foundation of ecosystems. This is due to their ability to capture light energy to produce their own food in the
LOOKING AT PLANT STEMS
 Activity 4.17 Student Sheet LOOKING AT PLANT STEMS Purpose To look at the structure of xylem vessels, phloem sieve tubes and sclerenchyma fibres. To locate the position of these tissues within the stem.
Activity 4.17 Student Sheet LOOKING AT PLANT STEMS Purpose To look at the structure of xylem vessels, phloem sieve tubes and sclerenchyma fibres. To locate the position of these tissues within the stem.
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring Water Relations, Osmosis and Transpiration
 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2008 Topic 07: Water Relations, Osmosis and Transpiration A. Water Relations Water plays a critical role in plants. Water is the universal solvent that allows biochemical
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2008 Topic 07: Water Relations, Osmosis and Transpiration A. Water Relations Water plays a critical role in plants. Water is the universal solvent that allows biochemical
Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology
 Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark
Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark
Investigations into biomass yield in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.)
 Investigations into biomass yield in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) Ulrike Anhalt 1,2, Pat Heslop-Harrison 2, Céline Tomaszewski 1,2, Hans-Peter Piepho 3, Oliver Fiehn 4 and Susanne Barth 1 1 2
Investigations into biomass yield in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) Ulrike Anhalt 1,2, Pat Heslop-Harrison 2, Céline Tomaszewski 1,2, Hans-Peter Piepho 3, Oliver Fiehn 4 and Susanne Barth 1 1 2
" " " " " " " " " " " " " " " " " " " " " The Effect of Sunlight on the Rate of Photosynthesis in Trachelospermum Jasmenoides" Nika Vafadari "
 The Effect of Sunlight on the Rate of Photosynthesis in Trachelospermum Jasmenoides Nika Vafadari Biology Lab 111 Section 05 1 2 Introduction Different types of plant species, such as CAM plants, have
The Effect of Sunlight on the Rate of Photosynthesis in Trachelospermum Jasmenoides Nika Vafadari Biology Lab 111 Section 05 1 2 Introduction Different types of plant species, such as CAM plants, have
THE EFFECT OF PRE-EMERGENT TREATMENT OF PEAS WITH TRICHLORACETIC ACID ON THE SUB- MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF THE LEAF SURFACE
 THE EFFECT OF PRE-EMERGENT TREATMENT OF PEAS WITH TRICHLORACETIC ACID ON THE SUB- MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF THE LEAF SURFACE BY BARRIE E. JUNIPER Department of Botany, Oxford {Received 16 Jamiary 1957)
THE EFFECT OF PRE-EMERGENT TREATMENT OF PEAS WITH TRICHLORACETIC ACID ON THE SUB- MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF THE LEAF SURFACE BY BARRIE E. JUNIPER Department of Botany, Oxford {Received 16 Jamiary 1957)
FACTORS CONTROLLING VARIATIONS IN THE RATE OF TRANSPIRATION. HISTORICAL.
 FACTORS CONTROLLING VARIATIONS IN THE RATE OF TRANSPIRATION. J. D. SAYRE. While investigating the relation of hairy leaf coverings to the resistance of leaves to water loss,* a number of experiments were
FACTORS CONTROLLING VARIATIONS IN THE RATE OF TRANSPIRATION. J. D. SAYRE. While investigating the relation of hairy leaf coverings to the resistance of leaves to water loss,* a number of experiments were
Theme : PHOTOSYNTHESIS, FLUORESCENCE AND WATER REGIME. Experiment 1: Determination of the rate of photosynthesis under different conditions
 Theme : PHOTOSYNTHESIS, FLUORESCENCE AND WATER REGIME Experiment 1: Determination of the rate of photosynthesis under different conditions Exp.1a: Follow the changes in net photosynthesis rate depending
Theme : PHOTOSYNTHESIS, FLUORESCENCE AND WATER REGIME Experiment 1: Determination of the rate of photosynthesis under different conditions Exp.1a: Follow the changes in net photosynthesis rate depending
Stomatal Movement in Response to Root Zone Temperature in Purple Heart (Tradescantia pallida)
 Movement in Response to Root Zone Temperature in Purple Heart (Tradescantia pallida) Nabiyollah Ashrafi * and Abdolhossein Rezaei Nejad 2 Ph.D Student, Department of Horticultural Sciences, Faculty of
Movement in Response to Root Zone Temperature in Purple Heart (Tradescantia pallida) Nabiyollah Ashrafi * and Abdolhossein Rezaei Nejad 2 Ph.D Student, Department of Horticultural Sciences, Faculty of
Journal of Agricultural Science E-ISSN: Vol. 2, No. 2, June 2010
 ISSN: 1916-9752 Journal of Agricultural Science E-ISSN: 1916-9760 Vol. 2, No. 2, June 2010 Study of Behavior of Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) to Relative Turgidity, Diffusion Pressure Deficit and Transpiration
ISSN: 1916-9752 Journal of Agricultural Science E-ISSN: 1916-9760 Vol. 2, No. 2, June 2010 Study of Behavior of Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) to Relative Turgidity, Diffusion Pressure Deficit and Transpiration
Photosynthesis. Water is one of the raw materials needed for photosynthesis When water is in short supply the rate of photosynthesis is limited
 Photosynthesis Water is one of the raw materials needed for photosynthesis When water is in short supply the rate of photosynthesis is limited Support Water is needed to ensure plant cells remain turgid
Photosynthesis Water is one of the raw materials needed for photosynthesis When water is in short supply the rate of photosynthesis is limited Support Water is needed to ensure plant cells remain turgid
 Question 1: What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion? Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion of
Question 1: What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion? Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion of
* ' ION UPTAKE IN RELATION TO THE '''-'"u.n v DEVELOPMENT OF A ROOT HYPODERMIS
 New Phytol. (igj6) JJ, 11-14. '-^ ^^ ' '''-: ^i'i^ J i.. * ' ION UPTAKE IN RELATION TO THE '''-'"u.n v DEVELOPMENT OF A ROOT HYPODERMIS :?m::,^^ BY I. B. FERGUSON* AND D. T. CLARKSON '" ' 'I ARC Letcombe
New Phytol. (igj6) JJ, 11-14. '-^ ^^ ' '''-: ^i'i^ J i.. * ' ION UPTAKE IN RELATION TO THE '''-'"u.n v DEVELOPMENT OF A ROOT HYPODERMIS :?m::,^^ BY I. B. FERGUSON* AND D. T. CLARKSON '" ' 'I ARC Letcombe
3 Movement of substances in living organisms
 Mark schemes Movement of substances in living organisms Using and interpreting data a) (0 to 0 minutes) () decrease (in CO ) () carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis (0 to 0 minutes) () (steep) rise then
Mark schemes Movement of substances in living organisms Using and interpreting data a) (0 to 0 minutes) () decrease (in CO ) () carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis (0 to 0 minutes) () (steep) rise then
CHAPTER 6 ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS 27 27 CHAPTER 6 ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A transverse section of stem is stained first with safranin and then with fast green following the usual
ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS 27 27 CHAPTER 6 ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A transverse section of stem is stained first with safranin and then with fast green following the usual
Plant Structure and Function. Roots, Stems, and Leaves
 Plant Structure and Function Roots, Stems, and Leaves What is a Plant? Plants are living things that have: roots, stems, and leaves (some have flowers) Plants are made of cells that have cell walls, a
Plant Structure and Function Roots, Stems, and Leaves What is a Plant? Plants are living things that have: roots, stems, and leaves (some have flowers) Plants are made of cells that have cell walls, a
Maintaining a balance
 Gill Sans Bold Biology HSC Course Stage 6 Maintaining a balance Part 4: Transport in plants IncorporatingOctober2002 AMENDMENTS Gill Sans Bold Contents Introduction...2 Movement of materials in plants...3
Gill Sans Bold Biology HSC Course Stage 6 Maintaining a balance Part 4: Transport in plants IncorporatingOctober2002 AMENDMENTS Gill Sans Bold Contents Introduction...2 Movement of materials in plants...3
AP Biology Chapter 36
 Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/51 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/51 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:
STUDIES IN THE PHYSIOLOGY OF LICHENS
 STUDIES IN THE PHYSIOLOGY OF LICHENS V. TRANSLOCATION FROM THE ALGAL LAYER TO THE MEDULLA IN PELTIGERA POLYDACTYLA BY D. C. SMITH AND E. A. DREW Department of Agriculture, University of Oxford {Received
STUDIES IN THE PHYSIOLOGY OF LICHENS V. TRANSLOCATION FROM THE ALGAL LAYER TO THE MEDULLA IN PELTIGERA POLYDACTYLA BY D. C. SMITH AND E. A. DREW Department of Agriculture, University of Oxford {Received
STOMAT AL RESPONSE TO WIND ON ABAXIAL AND ADAXIAL SURFACES OF CUCUMBER LEAF UNDER DIFFERENT HUMIDITY CONDITIONS
 BIOTRONICS 30, 103-114, 2001 STOMAT AL RESPONSE TO WIND ON ABAXIAL AND ADAXIAL SURFACES OF CUCUMBER LEAF UNDER DIFFERENT HUMIDITY CONDITIONS D. YASUTAKE 1, M. KITAN0 2, T. ARAKI 3, K. NAGASUGA 1, T. KAWAN0
BIOTRONICS 30, 103-114, 2001 STOMAT AL RESPONSE TO WIND ON ABAXIAL AND ADAXIAL SURFACES OF CUCUMBER LEAF UNDER DIFFERENT HUMIDITY CONDITIONS D. YASUTAKE 1, M. KITAN0 2, T. ARAKI 3, K. NAGASUGA 1, T. KAWAN0
Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue
 PLANT TISSUES Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue Undifferentiated plant cells that are continually dividing by mitosis Large thin walled cells No vacuole Dense cytoplasm Large nucleus Found at
PLANT TISSUES Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue Undifferentiated plant cells that are continually dividing by mitosis Large thin walled cells No vacuole Dense cytoplasm Large nucleus Found at
Stomata Density of Orchids and Cloud Forest Humidity
 3.1 (2012) ISSN: 2160-617X (online) http://journals.oregondigital.org/ourj/ DOI: 10.5399/uo/ourj.3.1.2386 Stomata Density of Orchids and Cloud Forest Humidity *, Environmental Studies Program ABSTRACT
3.1 (2012) ISSN: 2160-617X (online) http://journals.oregondigital.org/ourj/ DOI: 10.5399/uo/ourj.3.1.2386 Stomata Density of Orchids and Cloud Forest Humidity *, Environmental Studies Program ABSTRACT
Cell Review. 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things.
 Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
TIME COURSE OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC RHYTHMS IN PHASEOLUS VULGARIS L. AS RELATED TO CHANGES IN DEGREE OF STOMATAL OPENING 12
 37S JOSEF N. KNULL Vol. 64 TIME COURSE OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC RHYTHMS IN PHASEOLUS VULGARIS L. AS RELATED TO CHANGES IN DEGREE OF STOMATAL OPENING 12 GEORGE F. HOWE 3 Department of Botany and Plant Pathology,
37S JOSEF N. KNULL Vol. 64 TIME COURSE OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC RHYTHMS IN PHASEOLUS VULGARIS L. AS RELATED TO CHANGES IN DEGREE OF STOMATAL OPENING 12 GEORGE F. HOWE 3 Department of Botany and Plant Pathology,
Transport in Vascular Plants
 Chapter 36 Transport in Vascular Plants PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Vascular tissue Transports nutrients throughout a plant; such
Chapter 36 Transport in Vascular Plants PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Vascular tissue Transports nutrients throughout a plant; such
EFFECTS OF SEED SIZE AND EMERGENCE TIME ON SUBSEQUENT GROWTH OF PERENNIAL RYEGRASS
 Phytol (980) 84, 33-38 EFFECTS OF SEED SIZE AND EMERGENCE TIME ON SUBSEQUENT GROWTH OF PERENNIAL RYEGRASS BY ROBERT E. L. NAYLOR School of Agriculture, The University, Aberdeen {Accepted 2 January 979)
Phytol (980) 84, 33-38 EFFECTS OF SEED SIZE AND EMERGENCE TIME ON SUBSEQUENT GROWTH OF PERENNIAL RYEGRASS BY ROBERT E. L. NAYLOR School of Agriculture, The University, Aberdeen {Accepted 2 January 979)
Plant Structure and Function Extension
 Plant Structure and Function Extension NGSSS: SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. (AA) Part 1A: Leaves The leaf of a plant serves
Plant Structure and Function Extension NGSSS: SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. (AA) Part 1A: Leaves The leaf of a plant serves
Validation of a leaf reflectance and transmittance model for three agricultural crop species
 Validation of a leaf reflectance and transmittance model for three agricultural crop species Application Note Author G. J. Newnham* and T. Burt** *Remote Sensing and Satellite Research Group, Curtin University
Validation of a leaf reflectance and transmittance model for three agricultural crop species Application Note Author G. J. Newnham* and T. Burt** *Remote Sensing and Satellite Research Group, Curtin University
Chapter 3 Materials and methods
 Chapter 3 3. MATERIALS AND METHODS 3.1 M aterials The experimental plant species of the present investigation belong to the family Asclepiadaceae and are available in the North Eastern regions of India.
Chapter 3 3. MATERIALS AND METHODS 3.1 M aterials The experimental plant species of the present investigation belong to the family Asclepiadaceae and are available in the North Eastern regions of India.
