TERTIARY AND QUATERNARY STRUCTURE FOR RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN L7 IN SOLUTION
|
|
|
- Ophelia Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume 82, number 1 FEBS LETTERS October 1977 TERTIARY AND QUATERNARY STRUCTURE FOR RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN L7 IN SOLUTION A. T. GUDKOV, J. BEHLKE*, N. N. VTIURIN and V. I. LIM Institute of Protein Research, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Poustchino, Moscow Region, USSR Received 20 July Introduction Protein L7 was the first ribosomal protein the primary structure of which was determined [ 11. The high a-helical content determined experimentally [2] was in good agreement with the results of the theoretical prediction of protein L7 secondary structure [3]. The protein L7 was found to exist in solution as a dimer [4]. Small-angle X-ray scattering studies evidenced of the highly elongated shape of the dimer; the data were interpreted in terms of the model of the model of a rod 130 A long with a diameter of 17 A [ 51 or a triaxial ellipsoid with semiaxes of 90 A, 16 A and 6 W [6]. The essential role of the N-terminal sequence of protein L7 for its dimerization has been shown by one of us [7]. This paper reports the result of the combined use of the recent stereochemical theory of the tertiary structure of globular proteins [&lo] and the set of experimental chemical and physical approaches [7,1 l] for the study of the protein L7. The tertiary and quaternary structure for the protein L7 dimer in solution is proposed. This structure can be presented as a dumb-bell where the two N-terminal helical regions interact with each other in the antiparallel manner thus forming a dimer, while the distal C-terminal parts of the subunits are globular. *Present address: Zentralinstitut ftir Molekularbiologie DDR, Berlin-Buch, Lindenberger Weg 70, GDR North-Holland Atblishing Company - Amsterdam 2. Materials and methods The results of sedimentation studies of protein L7, of its 27-l 20 fragment and of protein L7 with oxidized methionine residues in positions 14, 17 and 26 have been reported earlier [7]. The data on infrared, CD and NMR spectra, as well as on calorimetric measurements are given elsewhere [ 111. Synthetic polypeptides having amino acid sequence of the,l-26 N-terminal fragment of protein L7 [ 121 were also used in the experiments. 3. Results and discussion 3.I. Experimental A number of important structural features of protein L7 can be deduced from several groups of experimental data available. (i) In the native state, the protein L7 in solution is known to exist in the form of dimers [4,5,7]. At the same time, oxidation of the methionine residues in positions 14, 17 and 26 into sulphoxide, or the cleavage of the first 26 amino acids by cyanogen bromide leads to the loss of ability of the oxidized protein or the remaining fragment to dimerize (table 1). On the grounds of these data a conclusion is made on the essential role of the l-26 N-terminal sequence of protein L7 for its dimerization [7]. Moreover, the oxidized protein L7 cannot be a substitute for the intact protein in factor-dependent reactions on the ribosome [13]. At the same time, the fragment l-73 of protein L7 is capable of binding with the ribosome [14]. Thus, it can be presumed that 125
2 Table 1 Some characteristics of the protein L7, the oxidized protein L7 and the fragments (l-26) and (27-120) Sample L7 L7 oxidized Fragment (27-120) Fragment (l-26) S20,W D 20,W v MS,D M (equilibr.) f/f0 Helical AH content (%) kcal/mol kcal/mol (eff.) (calor.) 2 E! 1.57? t a ~ & 1.04? a f ? f f a 9500a 9970 f ?r a 2760a 2750 f a Calculated from the amino acid composition
3 Volume 82, number 1 FEBSLETTERS October 1911 the ability to dimerize and to bind with the ribosome is determined by a region of the sequence in the fragment l-73 [7]. (ii) The coincidence between the effective enthalpy of melting (calculated from the half-width of transition, see table 1) and the calorimetric enthalpy (calculated from the area under the curve) for the oxidized protein L7 and the fragment 27-l 20 evidences of such a structure in the C-terminal region of the protein which melts cooperatively [I 11. This suggests the globular conformation of the C-terminal part of the protein L7. (iii) The data on NMR spectra of the dimer of L7 protein, of its 27-l 20 fragment and of the oxidized protein indicate that the Phe54 residue must be in an internal hydrophobic environment within the C-terminal region structure. (The spectrum signal does not change depending on the monomeric or the dimeric state of the protein in the samples studied, while the PheW residue participates in dimerization of the protein; the signal depends on the monomeric or dimeric state of the protein in solution [ 111.) (iv) The high o-helical content (see table i) and the absence of &structures [ 1 l] are characteristic of the protein L7 and of its dimer. This permits the assumption that dimerization is stipulated by the contact of helical regions of the two protein subunits. (v) The high friction ratio (see table 1) and the data of X-ray diffuse scattering [S $1 evidence an elongated shape of the protein L7 dimer in solution Theory (i) The identity of the subunits in the protein L7 dimer and the high association constant (over 10 M-l) satisfy the principles of organization of subunit proteins [ 15,161. It can be assumed that the dimer has a symmetry axis of the second order with an antiparallel orientation of the subunits [ 15,161. (ii) There can be a helical region from residue 4-41 in the N-terminal sequence of the protein L7 [3]. In the helical net of this helix it is easily seen that side groups of hydrophobic amino acid residues form a hydrophobic strip in the region from residue (fig.1). The contact of these two a-helices will ensure the formation of a dimer at the expense of massive and complementary hydrophobic interactions, the amino acid residues with large side groups (Val, Ile) being in contact with the smaller ones (Ala). In such Fig.1. Two-dimensional surface of the helical region (14-41) of protein L7. Circles indicate residues contacting with the other protein molecule. Dashed line shows direction of hydrophobic strip. an interaction, the helices are shifted relative to each other by a half-turn; their axes form a small angle (about 6 ) and are antiparallel (see scheme, tig.2). The side groups of Met26 and Phem slightly protrude away from the region of contact. Two different areas are formed in the bi-helical structure, one with a predominance of hydrophilic residues and the other with many hydrophobic side groups. It is possible that the hydrophobic area of the dimer can serve for binding with the ribosome and/or with protein LlO u71. (iii) A globular structure of the C-terminal part of the protein L7 molecule was constructed using the recent theory of spatial structure of proteins [8-lo]. This globule is formed by two adhering hydrophobic surfaces. One of these surfaces is formed by helices and 65-73, and the other by helices and 105-l 13. There is also a helical region and an elongated chain fragment The helix is located in the region of the N-termini of helices 65-73, and the C-termini of helices 5 l- 59 and 105-l 13. The elongated chain fragment is on the surface of the globule between helices and 105-l 13. There is a hydrophobic cavity on the surface N C Fig.2. Scheme of the bi-helical part of the protein L7 dimer. Hatching indicates contacting ammo acid side groups. Circles show Co -atoms (filled circles above the plane of the scheme and open circles below it). Hydrophilic amino acids predommate on the reverse side of the bi-helical part (see text). c N 127
4 Volume 82, number 1 FEBS LETTERS October 1977 i i J+J-Nl a i i b C - 40A * IOA -30A. b Fig.3;Scheme of the tertiary and quaternary structure formation of the protein L7 (monomer and dimer). (a) Distribution of o-helical regions in the molecule. The regions included in boxes form the globular parts of the monomers. (b) Tertiary structure of monomers. (c) Quaternary structure of the protein L7. Arrows indicate helical regions and elongated chain fragment At dimerization of monomers, the N-terminal helix 4-11 of one molecule, fits into the globular part of the other and vice versa. Helices of both monomers interact according to the scheme in fig.2. The three-dimensional model of the L7 dimer assembled from CPK atomic models has linear dimensions shown in the figure. 128
5 Volume 82. number 1 FEBS LETTERS October 1977 Fig.4. Photo of the atomic model of the protein L7 (monomer). Figures show helical regions. N and C indicate the corresponding helical ends. The oval between helices and indicates the cavity into which the helix 4-11 of another monomer fits at protein dimerization. of this globule between the helices and At dimerization of protein L7, the hydrophobic surface of the helix 4-l 1 of one molecule will fit into the hydrophobic cavity of the other molecule and vice versa. The scheme of the three-dimensional structure of the protein L7 monomer and dimer is seen in tig.3. A photo of the atomic model of the L7 protein in the monomeric form is given in fig.4. The linear dimension along the long axis of the dimer in the model proposed (120 A) is smaller than those claimed on the basis of small-angle X-ray diffuse scattering (130 A [.5] or 180 A [6]). However, the relatively large experimental values of the radius of gyration reported in these papers (38 A [5] and 41 A [6]) do not contradict the model. Acknowledgements The authors express their sincere thanks to Academician A. S. Spirin for initiating these studies, and to Professor 0. B. Ptitsyn, A. L. Mazanov and A. V. Etimov for helpful discussions. References [l] Terhorst, C., Moller, W., Laursen, R. and Wittmann- Liebold, B. (1972) FEBS Lett. 28, [2] Boublik, M., Brot, N. and Weissbach, H. (1973) Biopolymers 12, [3] Ptitsyn, 0. B., Denesyuk, A. I., Finkelstein, A. V. and Lim, V. I. (1973) FEBS Lett. 34, [4] Moller, W., Groene, A., Terhorst, C. and Amons, R. (1972) Eur. J. Biochem. 25, (51 Wong, K. P. and Paradies, H. H. (1974) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 61, [6] ijsterberg, R., Sjoberg, B., Liljas, A. and Pettersson, I. (1976) FEBS Lett. 66, [7] Gudkov, A. T. (1977) Molekul. Biol. in press. [8] Lim, V. I. (1975) Dokl. Akad. Nauk. 222, [ 91 Lim, V. I. and Efimov A. V. (1976) FEBS Lett. 69, [lo] Lim, V. I. and Mazanov A. L. (1977) FEBS Lett. submitted. [ll] Gudkov A. T., Khechinashvili N. N. and Bushuev V. N., in preparation. [12] Gudkov A. T. and Shekhvatova G. V. (1976) Bioorgan. Khim. 2, [ 131 Koteliansky V. E., Domogatsky S. P. and Gudkov A. T., in preparation. [ 141 Van Agthoven A. J., Maassen J. A., Schreier P. J. and Moller W. (1975) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 64, [15] Haschemeyer, R. H. and Haschemeyer, A. E. V. (1973) in: Proteins, p. 386, John Wiley New York, London, Sydney, Toronto. [ 161 Neurath H. and Hill R. L. (1975) in: The Proteins, 3rd edn, vol. 1, ch. 5, Academic Press, New York, London. [ 171 Gudkov A. T. (1976) Dokl. Akad. Nauk 230,
Peptides And Proteins
 Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
Physical principles of protein structure and protein folding
 Proc. Int. Symp. Biomol. Struct. Interactions, Suppl. J. Biosci., Vol. 8, Nos 1 & 2, August 1985, pp. 1 13. Printed in India. Physical principles of protein structure and protein folding O. B. PTITSYN
Proc. Int. Symp. Biomol. Struct. Interactions, Suppl. J. Biosci., Vol. 8, Nos 1 & 2, August 1985, pp. 1 13. Printed in India. Physical principles of protein structure and protein folding O. B. PTITSYN
Problem Set 1
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
Basics of protein structure
 Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Section Week 3. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section Week 3 Junaid Malek, M.D. Biological Polymers DA 4 monomers (building blocks), limited structure (double-helix) RA 4 monomers, greater flexibility, multiple structures Proteins 20 Amino Acids,
Section Week 3 Junaid Malek, M.D. Biological Polymers DA 4 monomers (building blocks), limited structure (double-helix) RA 4 monomers, greater flexibility, multiple structures Proteins 20 Amino Acids,
Guessing the upper bound free-energy difference between native-like structures. Jorge A. Vila
 1 Guessing the upper bound free-energy difference between native-like structures Jorge A. Vila IMASL-CONICET, Universidad Nacional de San Luis, Ejército de Los Andes 950, 5700- San Luis, Argentina Use
1 Guessing the upper bound free-energy difference between native-like structures Jorge A. Vila IMASL-CONICET, Universidad Nacional de San Luis, Ejército de Los Andes 950, 5700- San Luis, Argentina Use
Protein Structure. W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES
 Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Protein Synthetic Lipid Interactions
 Acta Biophysica Romana 2006 22-24 Febbraio Università di Roma - Tor Vergata Protein Synthetic Lipid Interactions Silvia Tardioli and Adalberto Bonincontro CNISM-Dipartimento di Fisica Camillo La Mesa Dipartimento
Acta Biophysica Romana 2006 22-24 Febbraio Università di Roma - Tor Vergata Protein Synthetic Lipid Interactions Silvia Tardioli and Adalberto Bonincontro CNISM-Dipartimento di Fisica Camillo La Mesa Dipartimento
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties
 1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
Principles of Physical Biochemistry
 Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Molecular dynamics simulations of anti-aggregation effect of ibuprofen. Wenling E. Chang, Takako Takeda, E. Prabhu Raman, and Dmitri Klimov
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 98 Supporting Material Molecular dynamics simulations of anti-aggregation effect of ibuprofen Wenling E. Chang, Takako Takeda, E. Prabhu Raman, and Dmitri Klimov Supplemental
Biophysical Journal, Volume 98 Supporting Material Molecular dynamics simulations of anti-aggregation effect of ibuprofen Wenling E. Chang, Takako Takeda, E. Prabhu Raman, and Dmitri Klimov Supplemental
12/6/12. Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay. Primary Structure. Secondary Structure. Tertiary Structure. Quaternary Structure.
 Dr. anjeeva rivastava Primary tructure econdary tructure Tertiary tructure Quaternary tructure Amino acid residues α Helix Polypeptide chain Assembled subunits 2 1 Amino acid sequence determines 3-D structure
Dr. anjeeva rivastava Primary tructure econdary tructure Tertiary tructure Quaternary tructure Amino acid residues α Helix Polypeptide chain Assembled subunits 2 1 Amino acid sequence determines 3-D structure
Crystal structure of a prokaryotic ribosomal protein
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 83, pp. 7251-7255, October 1986 Biochemistry Crystal structure of a prokaryotic ribosomal protein (x-ray crystallography/protein-protein interaction/rna binding site/common
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 83, pp. 7251-7255, October 1986 Biochemistry Crystal structure of a prokaryotic ribosomal protein (x-ray crystallography/protein-protein interaction/rna binding site/common
Central Dogma. modifications genome transcriptome proteome
 entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
What is the central dogma of biology?
 Bellringer What is the central dogma of biology? A. RNA DNA Protein B. DNA Protein Gene C. DNA Gene RNA D. DNA RNA Protein Review of DNA processes Replication (7.1) Transcription(7.2) Translation(7.3)
Bellringer What is the central dogma of biology? A. RNA DNA Protein B. DNA Protein Gene C. DNA Gene RNA D. DNA RNA Protein Review of DNA processes Replication (7.1) Transcription(7.2) Translation(7.3)
Protein Dynamics. The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron.
 Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
Introduction to" Protein Structure
 Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability
 Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions: Van der Waals Interactions
Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions: Van der Waals Interactions
From Amino Acids to Proteins - in 4 Easy Steps
 From Amino Acids to Proteins - in 4 Easy Steps Although protein structure appears to be overwhelmingly complex, you can provide your students with a basic understanding of how proteins fold by focusing
From Amino Acids to Proteins - in 4 Easy Steps Although protein structure appears to be overwhelmingly complex, you can provide your students with a basic understanding of how proteins fold by focusing
Objective: Students will be able identify peptide bonds in proteins and describe the overall reaction between amino acids that create peptide bonds.
 Scott Seiple AP Biology Lesson Plan Lesson: Primary and Secondary Structure of Proteins Purpose:. To understand how amino acids can react to form peptides through peptide bonds.. Students will be able
Scott Seiple AP Biology Lesson Plan Lesson: Primary and Secondary Structure of Proteins Purpose:. To understand how amino acids can react to form peptides through peptide bonds.. Students will be able
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures?
 1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
Translation. A ribosome, mrna, and trna.
 Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.11 TRANSLATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENETIC CODE Nucleotides and amino acids are translated in a 1 to 1 method The triplet code states that three nucleotides codes for one amino acid - A codon is a term for
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENETIC CODE Nucleotides and amino acids are translated in a 1 to 1 method The triplet code states that three nucleotides codes for one amino acid - A codon is a term for
Outline. Levels of Protein Structure. Primary (1 ) Structure. Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins
 Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2004 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2004 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Prof. Jason Kahn Your Signature: Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances.
 1 Biochemistry 461 February 16, 1995 Exam #1 Prof. Jason Kahn Your Printed Name: Your SS#: Your Signature: You have 75 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded
1 Biochemistry 461 February 16, 1995 Exam #1 Prof. Jason Kahn Your Printed Name: Your SS#: Your Signature: You have 75 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded
BCH 4053 Spring 2003 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4053 Spring 2003 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes 1 CHAPTER 6 Proteins: Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary Structure 2 Levels of Protein Structure Primary (sequence) Secondary (ordered structure along peptide
BCH 4053 Spring 2003 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes 1 CHAPTER 6 Proteins: Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary Structure 2 Levels of Protein Structure Primary (sequence) Secondary (ordered structure along peptide
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes. From Alberts et al
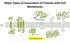 Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Making Proteins Using Directions From DNA
 RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Making Proteins Using Directions From DNA RNA & Protein Synthesis v Nitrogenous bases in DNA contain information that directs protein synthesis v DNA remains in nucleus v in order
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Making Proteins Using Directions From DNA RNA & Protein Synthesis v Nitrogenous bases in DNA contain information that directs protein synthesis v DNA remains in nucleus v in order
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Conformational change of L7/L12 stalk in the different functional states of 50S ribosomes
 J. Biosci., Vol. 11, Numbers 1 4, March 1987, pp. 561-569. Printed in India. Conformational change of L7/L12 stalk in the different functional states of 50S ribosomes DEBABRATA DASH, SUBODH MAHANTI and
J. Biosci., Vol. 11, Numbers 1 4, March 1987, pp. 561-569. Printed in India. Conformational change of L7/L12 stalk in the different functional states of 50S ribosomes DEBABRATA DASH, SUBODH MAHANTI and
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters
 Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Examples of Protein Modeling. Protein Modeling. Primary Structure. Protein Structure Description. Protein Sequence Sources. Importing Sequences to MOE
 Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Structural and mechanistic insight into the substrate. binding from the conformational dynamics in apo. and substrate-bound DapE enzyme
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 215 Structural and mechanistic insight into the substrate binding from the conformational
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 215 Structural and mechanistic insight into the substrate binding from the conformational
Model Mélange. Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins
 Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
BCH 4053 Exam I Review Spring 2017
 BCH 4053 SI - Spring 2017 Reed BCH 4053 Exam I Review Spring 2017 Chapter 1 1. Calculate G for the reaction A + A P + Q. Assume the following equilibrium concentrations: [A] = 20mM, [Q] = [P] = 40fM. Assume
BCH 4053 SI - Spring 2017 Reed BCH 4053 Exam I Review Spring 2017 Chapter 1 1. Calculate G for the reaction A + A P + Q. Assume the following equilibrium concentrations: [A] = 20mM, [Q] = [P] = 40fM. Assume
Protein Folding & Stability. Lecture 11: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a
 Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Any protein that can be labelled by both procedures must be a transmembrane protein.
 1. What kind of experimental evidence would indicate that a protein crosses from one side of the membrane to the other? Regions of polypeptide part exposed on the outside of the membrane can be probed
1. What kind of experimental evidence would indicate that a protein crosses from one side of the membrane to the other? Regions of polypeptide part exposed on the outside of the membrane can be probed
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London)
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
Videos. Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.
 Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
4. The Michaelis-Menten combined rate constant Km, is defined for the following kinetic mechanism as k 1 k 2 E + S ES E + P k -1
 Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
Outline. Levels of Protein Structure. Primary (1 ) Structure. Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins
 Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Introduction to Polymer Physics
 Introduction to Polymer Physics Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium February-May, 2016 Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium Introduction to Polymer Physics February-May, 2016 1 / 28 Polymers in Chemistry and
Introduction to Polymer Physics Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium February-May, 2016 Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium Introduction to Polymer Physics February-May, 2016 1 / 28 Polymers in Chemistry and
(6 pts) List three general characteristics shared by stable secondary structures.
 Biochemistry 461, Section I Your Name: March 19, 1998 Exam #2 Your SS#: Prof. Jason D. Kahn Your Signature: Please have photo ID available. You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or
Biochemistry 461, Section I Your Name: March 19, 1998 Exam #2 Your SS#: Prof. Jason D. Kahn Your Signature: Please have photo ID available. You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or
Introduction to the Ribosome Overview of protein synthesis on the ribosome Prof. Anders Liljas
 Introduction to the Ribosome Molecular Biophysics Lund University 1 A B C D E F G H I J Genome Protein aa1 aa2 aa3 aa4 aa5 aa6 aa7 aa10 aa9 aa8 aa11 aa12 aa13 a a 14 How is a polypeptide synthesized? 2
Introduction to the Ribosome Molecular Biophysics Lund University 1 A B C D E F G H I J Genome Protein aa1 aa2 aa3 aa4 aa5 aa6 aa7 aa10 aa9 aa8 aa11 aa12 aa13 a a 14 How is a polypeptide synthesized? 2
It s really this simple.
 Background Light harvesting complexes exist to facilitate and maximize the absorption capacity of the reaction centers (RC) as well as PSI and PSII Purple bacteria utilize these functions by having an
Background Light harvesting complexes exist to facilitate and maximize the absorption capacity of the reaction centers (RC) as well as PSI and PSII Purple bacteria utilize these functions by having an
Spatial organization of catalase proteins
 Proc. Int. Symp. Biomol. Struct. Interactions, Suppl. J. Biosci., Vol. 8, Nos 1 & 2, August 1985, pp. 471 479. Printed in India. Spatial organization of catalase proteins B. K. VAINSHTEIN, W. R. MELIK-ADAMYAN,
Proc. Int. Symp. Biomol. Struct. Interactions, Suppl. J. Biosci., Vol. 8, Nos 1 & 2, August 1985, pp. 471 479. Printed in India. Spatial organization of catalase proteins B. K. VAINSHTEIN, W. R. MELIK-ADAMYAN,
First Problem Set, Due 30 Sep. (1st midterm is 7 Oct.) If you want it graded by 6 Oct, turn in on or before 30 Sep. at 5 pm.
 First Problem Set, Due 30 Sep. (1st midterm is 7 ct.) If you want it graded by 6 ct, turn in on or before 30 Sep. at 5 pm. Show your work calculations / steps!! Problems from Chapter 1 1 EM of a eukaryotic
First Problem Set, Due 30 Sep. (1st midterm is 7 ct.) If you want it graded by 6 ct, turn in on or before 30 Sep. at 5 pm. Show your work calculations / steps!! Problems from Chapter 1 1 EM of a eukaryotic
Exam I Answer Key: Summer 2006, Semester C
 1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints
 Vol. 49 No. 3/2002 683 692 QUARTERLY Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints Andrzej Sikorski 1, Andrzej Kolinski 1,2 and Jeffrey Skolnick 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Vol. 49 No. 3/2002 683 692 QUARTERLY Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints Andrzej Sikorski 1, Andrzej Kolinski 1,2 and Jeffrey Skolnick 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Physiochemical Properties of Residues
 Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. PAPER NO: 409 LOCATION: Fr. Kennedy Gold Gym PAGE NO: 1 of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM 4630 TIME: 3 HOURS
 PAPER NO: 409 LOCATION: Fr. Kennedy Gold Gym PAGE NO: 1 of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM 4630 TIME: 3 HOURS EXAMINATION: Biochemistry of Proteins EXAMINER: J. O'Neil Section 1: You must answer all of
PAPER NO: 409 LOCATION: Fr. Kennedy Gold Gym PAGE NO: 1 of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM 4630 TIME: 3 HOURS EXAMINATION: Biochemistry of Proteins EXAMINER: J. O'Neil Section 1: You must answer all of
Details of Protein Structure
 Details of Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Anne Mølgaard, Kemisk Institut, Københavns Universitet Learning Objectives
Details of Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Anne Mølgaard, Kemisk Institut, Københavns Universitet Learning Objectives
Protein Structure Basics
 Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
Supersecondary Structures (structural motifs)
 Supersecondary Structures (structural motifs) Various Sources Slide 1 Supersecondary Structures (Motifs) Supersecondary Structures (Motifs): : Combinations of secondary structures in specific geometric
Supersecondary Structures (structural motifs) Various Sources Slide 1 Supersecondary Structures (Motifs) Supersecondary Structures (Motifs): : Combinations of secondary structures in specific geometric
Lecture 10: Brownian Motion, Random Walk & Diffusion Side Chains of Amino Acids
 Lecture 10: Brownian Motion, Random Walk & Diffusion Side Chains of Amino Acids Lecturer: Prof. Brigita Urbanc (brigita@drexel.edu) PHYS 461 & 561, Fall 2009-2010 1 Stochastic Processes: Brownian Motion
Lecture 10: Brownian Motion, Random Walk & Diffusion Side Chains of Amino Acids Lecturer: Prof. Brigita Urbanc (brigita@drexel.edu) PHYS 461 & 561, Fall 2009-2010 1 Stochastic Processes: Brownian Motion
PROTEIN EVOLUTION AND PROTEIN FOLDING: NON-FUNCTIONAL CONSERVED RESIDUES AND THEIR PROBABLE ROLE
 PROTEIN EVOLUTION AND PROTEIN FOLDING: NON-FUNCTIONAL CONSERVED RESIDUES AND THEIR PROBABLE ROLE O.B. PTITSYN National Cancer Institute, NIH, Laboratory of Experimental & Computational Biology, Molecular
PROTEIN EVOLUTION AND PROTEIN FOLDING: NON-FUNCTIONAL CONSERVED RESIDUES AND THEIR PROBABLE ROLE O.B. PTITSYN National Cancer Institute, NIH, Laboratory of Experimental & Computational Biology, Molecular
Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase Cwc27
 Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Protein Structure Prediction
 Protein Structure Prediction Michael Feig MMTSB/CTBP 2006 Summer Workshop From Sequence to Structure SEALGDTIVKNA Ab initio Structure Prediction Protocol Amino Acid Sequence Conformational Sampling to
Protein Structure Prediction Michael Feig MMTSB/CTBP 2006 Summer Workshop From Sequence to Structure SEALGDTIVKNA Ab initio Structure Prediction Protocol Amino Acid Sequence Conformational Sampling to
BIOCHEMISTRY Unit 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #6 (Chapter 5) PROTEINS
 BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY Unit 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #6 (Chapter 5) NAME NAME PERIOD PROTEINS GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND IMPORTANCES: Polymers of amino acids Each has unique 3-D shape Vary in sequence of amino
BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY Unit 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #6 (Chapter 5) NAME NAME PERIOD PROTEINS GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND IMPORTANCES: Polymers of amino acids Each has unique 3-D shape Vary in sequence of amino
The protein folding problem consists of two parts:
 Energetics and kinetics of protein folding The protein folding problem consists of two parts: 1)Creating a stable, well-defined structure that is significantly more stable than all other possible structures.
Energetics and kinetics of protein folding The protein folding problem consists of two parts: 1)Creating a stable, well-defined structure that is significantly more stable than all other possible structures.
Dental Biochemistry Exam The total number of unique tripeptides that can be produced using all of the common 20 amino acids is
 Exam Questions for Dental Biochemistry Monday August 27, 2007 E.J. Miller 1. The compound shown below is CH 3 -CH 2 OH A. acetoacetate B. acetic acid C. acetaldehyde D. produced by reduction of acetaldehyde
Exam Questions for Dental Biochemistry Monday August 27, 2007 E.J. Miller 1. The compound shown below is CH 3 -CH 2 OH A. acetoacetate B. acetic acid C. acetaldehyde D. produced by reduction of acetaldehyde
Contents. xiii. Preface v
 Contents Preface Chapter 1 Biological Macromolecules 1.1 General PrincipIes 1.1.1 Macrornolecules 1.2 1.1.2 Configuration and Conformation Molecular lnteractions in Macromolecular Structures 1.2.1 Weak
Contents Preface Chapter 1 Biological Macromolecules 1.1 General PrincipIes 1.1.1 Macrornolecules 1.2 1.1.2 Configuration and Conformation Molecular lnteractions in Macromolecular Structures 1.2.1 Weak
THE TANGO ALGORITHM: SECONDARY STRUCTURE PROPENSITIES, STATISTICAL MECHANICS APPROXIMATION
 THE TANGO ALGORITHM: SECONDARY STRUCTURE PROPENSITIES, STATISTICAL MECHANICS APPROXIMATION AND CALIBRATION Calculation of turn and beta intrinsic propensities. A statistical analysis of a protein structure
THE TANGO ALGORITHM: SECONDARY STRUCTURE PROPENSITIES, STATISTICAL MECHANICS APPROXIMATION AND CALIBRATION Calculation of turn and beta intrinsic propensities. A statistical analysis of a protein structure
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding W. H. Freeman and Company
 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company CHAPTER 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding Learning goals: Structure and properties of the peptide bond Structural hierarchy
4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company CHAPTER 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding Learning goals: Structure and properties of the peptide bond Structural hierarchy
Lecture 10 (10/4/17) Lecture 10 (10/4/17)
 Lecture 10 (10/4/17) Reading: Ch4; 125, 138-141, 141-142 Problems: Ch4 (text); 7, 9, 11 Ch4 (study guide); 1, 2 NEXT Reading: Ch4; 125, 132-136 (structure determination) Ch4; 12-130 (Collagen) Problems:
Lecture 10 (10/4/17) Reading: Ch4; 125, 138-141, 141-142 Problems: Ch4 (text); 7, 9, 11 Ch4 (study guide); 1, 2 NEXT Reading: Ch4; 125, 132-136 (structure determination) Ch4; 12-130 (Collagen) Problems:
The Structure of Enzymes!
 The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
The Structure of Enzymes!
 The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections
 Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections Dean R. Appling Spencer J. Anthony-Cahill Christopher K. Mathews Chapter 6 The Three Dimensional Structure of Proteins Cartoon representation of myoglobin, showing
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections Dean R. Appling Spencer J. Anthony-Cahill Christopher K. Mathews Chapter 6 The Three Dimensional Structure of Proteins Cartoon representation of myoglobin, showing
Computer Simulations of De Novo Designed Helical Proteins
 92 Biophysical Journal Volume 75 July 1998 92 105 Computer Simulations of De Novo Designed Helical Proteins Andrzej Sikorski,* Andrzej Kolinski,* # and Jeffrey Skolnick # *Department of Chemistry, University
92 Biophysical Journal Volume 75 July 1998 92 105 Computer Simulations of De Novo Designed Helical Proteins Andrzej Sikorski,* Andrzej Kolinski,* # and Jeffrey Skolnick # *Department of Chemistry, University
Complex flexibility of the transforming growth factor
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 5406-5410, June 1995 Biophysics Complex flexibility of the transforming growth factor f3 superfamily (conformational analysis/protomer assembly) GANESH VENKATARAMAN*,
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 5406-5410, June 1995 Biophysics Complex flexibility of the transforming growth factor f3 superfamily (conformational analysis/protomer assembly) GANESH VENKATARAMAN*,
Chapter
 Chapter 17 17.4-17.6 Molecular Components of Translation A cell interprets a genetic message and builds a polypeptide The message is a series of codons on mrna The interpreter is called transfer (trna)
Chapter 17 17.4-17.6 Molecular Components of Translation A cell interprets a genetic message and builds a polypeptide The message is a series of codons on mrna The interpreter is called transfer (trna)
NMR Characterization of Partially Folded and Unfolded Conformational Ensembles of Proteins
 Elisar Barbar Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Ohio University, Athens, OH 45701 NMR Characterization of Partially Folded and Unfolded Conformational Ensembles of Proteins Abstract: Studies of
Elisar Barbar Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Ohio University, Athens, OH 45701 NMR Characterization of Partially Folded and Unfolded Conformational Ensembles of Proteins Abstract: Studies of
BCH Graduate Survey of Biochemistry
 BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Glen Graham Lecture 12 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Glen Graham Lecture 12 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
Final Morphology of Complex Materials
 120314 Final Morphology of Complex Materials 1) Proteins are the prototypical model for hierarchy. a) Give the generic chemical structure for an amino acid and a protein molecule (a tripeptide). b) Label
120314 Final Morphology of Complex Materials 1) Proteins are the prototypical model for hierarchy. a) Give the generic chemical structure for an amino acid and a protein molecule (a tripeptide). b) Label
Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV-1 protease dimerization?
 Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV- protease dimerization? Danzhi Huang and Amedeo Caflisch a Department of Biochemistry University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 9 CH-7 Zürich, Switzerland
Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV- protease dimerization? Danzhi Huang and Amedeo Caflisch a Department of Biochemistry University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 9 CH-7 Zürich, Switzerland
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules. Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 05: Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading BME42-620 Lecture 05, September 13, 2011 1 Outline Review:
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 05: Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading BME42-620 Lecture 05, September 13, 2011 1 Outline Review:
Author(s) Nishikawa, Ken; Oobatake, Motohisa; Citation University (1970), 48(2-3):
 TitleTertiary Structures Proteins : A Author(s) Nishikawa, Ken; Oobatake, Motohisa; Citation Bulletin nstitute for Chemi University (1970), 48(2-3): 102-110 ssue Date 1970-08-22 URL http://hdl.hle.net/2433/76330
TitleTertiary Structures Proteins : A Author(s) Nishikawa, Ken; Oobatake, Motohisa; Citation Bulletin nstitute for Chemi University (1970), 48(2-3): 102-110 ssue Date 1970-08-22 URL http://hdl.hle.net/2433/76330
Dental Biochemistry EXAM I
 Dental Biochemistry EXAM I August 29, 2005 In the reaction below: CH 3 -CH 2 OH -~ ethanol CH 3 -CHO acetaldehyde A. acetoacetate is being produced B. ethanol is being oxidized to acetaldehyde C. acetaldehyde
Dental Biochemistry EXAM I August 29, 2005 In the reaction below: CH 3 -CH 2 OH -~ ethanol CH 3 -CHO acetaldehyde A. acetoacetate is being produced B. ethanol is being oxidized to acetaldehyde C. acetaldehyde
Protein structure. Protein structure. Amino acid residue. Cell communication channel. Bioinformatics Methods
 Cell communication channel Bioinformatics Methods Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu SEQUENCE STRUCTURE DNA Sequence Protein Sequence Protein Structure Protein structure ATGAAATTTGGAAACTTCCTTCTCACTTATCAGCCACCT...
Cell communication channel Bioinformatics Methods Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu SEQUENCE STRUCTURE DNA Sequence Protein Sequence Protein Structure Protein structure ATGAAATTTGGAAACTTCCTTCTCACTTATCAGCCACCT...
Chemistry 224 Bioorganic Chemistry Friday, Sept. 29, This Exam is closed book and closed notes. Please show all your work!
 page 1 of 6 hemistry 224 ame Bioorganic hemistry Friday, ept. 29, 2000 Exam 1 100 points This Exam is closed book and closed notes Please show all your work! tereochemistry counts as indicated! eatness
page 1 of 6 hemistry 224 ame Bioorganic hemistry Friday, ept. 29, 2000 Exam 1 100 points This Exam is closed book and closed notes Please show all your work! tereochemistry counts as indicated! eatness
Protein Structure. Hierarchy of Protein Structure. Tertiary structure. independently stable structural unit. includes disulfide bonds
 Protein Structure Hierarchy of Protein Structure 2 3 Structural element Primary structure Secondary structure Super-secondary structure Domain Tertiary structure Quaternary structure Description amino
Protein Structure Hierarchy of Protein Structure 2 3 Structural element Primary structure Secondary structure Super-secondary structure Domain Tertiary structure Quaternary structure Description amino
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability
 Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents the lowest energy state for a
Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents the lowest energy state for a
Protein Folding & Stability. Lecture 11: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Protein Folding: What we know. Protein Folding
 Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents
ion mobility spectrometry IR spectroscopy
 Debasmita Gho 29.10.2016 Introducti on Owing to its accuracy, sensitivity, and speed, mass spectrometry (MS) coupled to fragmentation techniques is the method of choice for determining the primary structure
Debasmita Gho 29.10.2016 Introducti on Owing to its accuracy, sensitivity, and speed, mass spectrometry (MS) coupled to fragmentation techniques is the method of choice for determining the primary structure
Organic Chemistry Option II: Chemical Biology
 Organic Chemistry Option II: Chemical Biology Recommended books: Dr Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry Research Laboratory, University of Oxford email: stuart.conway@chem.ox.ac.uk Teaching
Organic Chemistry Option II: Chemical Biology Recommended books: Dr Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry Research Laboratory, University of Oxford email: stuart.conway@chem.ox.ac.uk Teaching
Advanced Topics in RNA and DNA. DNA Microarrays Aptamers
 Quiz 1 Advanced Topics in RNA and DNA DNA Microarrays Aptamers 2 Quantifying mrna levels to asses protein expression 3 The DNA Microarray Experiment 4 Application of DNA Microarrays 5 Some applications
Quiz 1 Advanced Topics in RNA and DNA DNA Microarrays Aptamers 2 Quantifying mrna levels to asses protein expression 3 The DNA Microarray Experiment 4 Application of DNA Microarrays 5 Some applications
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2009
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2009 Helical Hairpin Structure of a potent Antimicrobial Peptide MSI-594 in Lipopolysaccharide Micelles by NMR Anirban
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2009 Helical Hairpin Structure of a potent Antimicrobial Peptide MSI-594 in Lipopolysaccharide Micelles by NMR Anirban
Protein Structure Marianne Øksnes Dalheim, PhD candidate Biopolymers, TBT4135, Autumn 2013
 Protein Structure Marianne Øksnes Dalheim, PhD candidate Biopolymers, TBT4135, Autumn 2013 The presentation is based on the presentation by Professor Alexander Dikiy, which is given in the course compedium:
Protein Structure Marianne Øksnes Dalheim, PhD candidate Biopolymers, TBT4135, Autumn 2013 The presentation is based on the presentation by Professor Alexander Dikiy, which is given in the course compedium:
THE SOLUTION CONFORMATION OF NOVEL ANTIBODY FRAGMENTS STUDIED USING THE PROTEOMELAB XL-A ANALYTICAL ULTRACENTRIFUGE
 APPLICATION INFORMATION Peter J. Morgan, Olwyn D. Byron, Stephen E. Harding Department of Applied Biochemistry and Food Science University of Nottingham Sutton Bonington, U. K. Introduction One of the
APPLICATION INFORMATION Peter J. Morgan, Olwyn D. Byron, Stephen E. Harding Department of Applied Biochemistry and Food Science University of Nottingham Sutton Bonington, U. K. Introduction One of the
Energetics and Thermodynamics
 DNA/Protein structure function analysis and prediction Protein Folding and energetics: Introduction to folding Folding and flexibility (Ch. 6) Energetics and Thermodynamics 1 Active protein conformation
DNA/Protein structure function analysis and prediction Protein Folding and energetics: Introduction to folding Folding and flexibility (Ch. 6) Energetics and Thermodynamics 1 Active protein conformation
Mobile Domains in Ribosomes Revealed by Proton Nuclear Magnetic
 THE JOURNL OF BIOLOGICL CHEMISTRY e 1984 by The merican Society of Biological Chemists, lnc. Vol. 259, No. 24, Issue of December 25, pp. 15257--15263, 1984 Prlnted in U.S. Mobile Domains in Ribosomes Revealed
THE JOURNL OF BIOLOGICL CHEMISTRY e 1984 by The merican Society of Biological Chemists, lnc. Vol. 259, No. 24, Issue of December 25, pp. 15257--15263, 1984 Prlnted in U.S. Mobile Domains in Ribosomes Revealed
Aggregation of the Amyloid-β Protein: Monte Carlo Optimization Study
 John von Neumann Institute for Computing Aggregation of the Amyloid-β Protein: Monte Carlo Optimization Study S. M. Gopal, K. V. Klenin, W. Wenzel published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems
John von Neumann Institute for Computing Aggregation of the Amyloid-β Protein: Monte Carlo Optimization Study S. M. Gopal, K. V. Klenin, W. Wenzel published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems
A Single Outer Sphere Mutation Stabilizes apo- Mn Superoxide Dismutase by 35 C and. Disfavors Mn Binding.
 Supporting information for A Single Outer Sphere Mutation Stabilizes apo- Mn Superoxide Dismutase by 35 C and Disfavors Mn Binding. Anne-Frances Miller* and Ting Wang Department of Chemistry, University
Supporting information for A Single Outer Sphere Mutation Stabilizes apo- Mn Superoxide Dismutase by 35 C and Disfavors Mn Binding. Anne-Frances Miller* and Ting Wang Department of Chemistry, University
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I. 1. Of the 20 standard amino acids, only is not optically active. The reason is that its side chain.
 Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Structure, mechanism and ensemble formation of the Alkylhydroperoxide Reductase subunits. AhpC and AhpF from Escherichia coli
 Structure, mechanism and ensemble formation of the Alkylhydroperoxide Reductase subunits AhpC and AhpF from Escherichia coli Phat Vinh Dip 1,#, Neelagandan Kamariah 2,#, Malathy Sony Subramanian Manimekalai
Structure, mechanism and ensemble formation of the Alkylhydroperoxide Reductase subunits AhpC and AhpF from Escherichia coli Phat Vinh Dip 1,#, Neelagandan Kamariah 2,#, Malathy Sony Subramanian Manimekalai
