Full file at
|
|
|
- Erick Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPREHENSION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice Use the following informtion for questions 1 3. iploi somtic cell from rt hs totl of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). s in humns, sex chromosomes etermine sex: XX in femles n XY in mles. 1. Wht is the totl numer of telomeres in rt cell in G2? c *e Wht is the totl numer of chromosomes present in the cell uring metphse I of meiosis?. 21 *. 42 c e Wht is the totl numer of chromosomes in polr oy cell from rt? * c e iviing eukryotic cell is trete with rug tht inhiits the moleculr motors ssocite with kinetochores. t which cell cycle stge woul it stop?. G1. S c. G2 *. M (nphse) e. M (telophse) 5. The figure shows chromosoml seprtion tking plce. The letters stn for genes; cpitl n lowercse stn for ifferent lleles. The iploi chromosome numer in this orgnism is four. Wht process is shown?. nphse of mitosis
2 . telophse of meiosis I c. nphse of meiosis I. telophse of mitosis *e. nphse of meiosis II C C True/Flse 6. Errors in chromosome seprtion re rrely prolem for n orgnism. (F) 7. The prokryotes inclue oth the eucteri n the rche. (T) 8. rche re more closely relte to eukryotes thn they re to eucteri. (T) 9. Generlly, chromosomes of eukryotes re circulr. (F) 10. Cells with single set of chromosomes re clle iploi. (F) Fill in the lnk 11. In flowering plnt, the mle prt of the flower (the stmen) prouces hploi microspores tht ivie y mitosis to prouce sperm. pollen grin tht lns on stigm grows pollen tue to eliver 2 (how mny?) sperm to the ovry. Fusion of sperm with n egg prouces 2 n cell clle zygote. To provie
3 foo for the eveloping emryo, tissue clle enosperm is prouce through oule fertiliztion. Enosperm hs ploiy of 3 n. 12. In prokryotes, repliction usully egins t specific plce on the chromosome clle the origin of repliction. 13. The nucler mtrix is the highly orgnize internl scffoling of the nucleus. 14. The ttchment point on the chromosome for spinle microtuules is the centromere. 15. Cytokinesis refers to the splitting of the cytoplsm, seprting one cell into two. Multiple Choice 16. Prokryotic chromosomes o not hve telomeres ecuse:. they o not go through mitosis.. they o not go through N repliction. c. they re in the cytoplsm. *. they re circulr. e. they hve no centromeres. 17. In eukryotes, chromosomes o not contin: *. riosomes.. chromtin. c. proteins.. histones. e. N. 18. In orer to e functionl, eukryotic chromosome requires ll of the following except:. centromere.. origins of repliction. *c. nucleoi.. telomeres. 19. Wht process is unique to plnts?. meiosis *. oule fertiliztion c. crossing over. hploi gmetes e. spermtogenesis 20. Suppose tht iploi cell contins 8 chromosomes (2n = 8). How mny ifferent comintions in the gmetes re possile?
4 . 2.4 c. 8 *. 16 e. 64 Use the following choices for questions Meiosis I prophse. Meiosis I nphse c. Meiosis II prophse. Meiosis II nphse e. Mitosis prophse f. Mitosis nphse 21. Chromosomes re in unseprte, sister-chromti form, t the en of the phse(s),, c, e. 22. The first stge fter which iviing cell tht strte s iploi woul e hploi. 23. Sister chromtis seprte uring, f. 24. Chromosomes re rnomly prtitione uring, contriuting to genetic iversity. 25. Crossing over (genetic recomintion) occurs in. Use the following informtion for questions Pe plnts hve seven ifferent types of chromosomes. 26. True or Flse? iploi pe cell in G1 hs 14 centrioles. (F) 27. The nucleus of megspore in pe ovry woul contin how mny chromosomes? nucleus in the pe enosperm contins how mny chromosomes? chromosome with centromere t the very en is clle:. sumetcentric.. metcentric. c. crocentric.. centric. *e. telocentric.
5 Short nswer 30. uring prophse I of meiosis, crossing over is inicte y wht microscopiclly visile structure? Chismt (chism) or the synptoneml complex 31. List two ifferences n two similrities etween mitosis n meiosis. ifferences:. Mitosis occurs in somtic (nonsex) cells; meiosis occurs in sex cells to prouce gmetes.. Meiosis involves chromosome piring (of homologous chromosomes); mitosis oes not. c. Mitosis prouces nonsex cells; meiosis prouces gmetes.. Mitosis prouces cells of the sme ploiy; meiosis prouces hploi cells from iploi cells. e. Meiosis hs two consecutive ivisions; mitosis hs one. f. Mitosis prouces two ughter cells; meiosis prouces four ughter cells. g. Mitosis prouces ienticl ughter cells; meiosis prouces four ifferent ughter cells. Similrities:. oth involve the seprtion of replicte chromosomes uring cell ivision.. oth re processes to ensure tht ughter cells in cell ivision receive complete set of chromosomes. c. N repliction must occur first.. Cytokinesis usully occurs t the en of ech.
6 32. The cells illustrte elow elong to species with iploi chromosome numer of four. Ech of the cells elow is in which stge of mitosis or meiosis?. meiosis I metphse. mitosis metphse c. mitosis nphse. meiosis I nphse e. meiosis II metphse For questions escrie the ifference etween: 33. centromere n kinetochore centromere is the physicl loction on chromosome where the kinetochore n spinle microtuules ttch. The kinetochore is compose of proteins tht ssemle on the centromere to provie site for the spinle microtuules to ttch. 34. G1 n G2 of the cell cycle
7 G1 occurs efore S phse n G2 occurs fter S phse. uring G1, cells grow in size, chromosomes re compose of single chromti. uring G1, cells pss criticl checkpoint (the G1/S checkpoint) fter which they re committe to unergoing cell ivision. uring G2, the chromosomes re compose of two chromtis. There is nother checkpoint uring G2 tht ensures cells re prepre for mitosis. Cells typiclly spen more time in G1 thn in G homologous chromosomes n sister chromtis Homologous chromosomes cn hve ifferent lleles. Sister chromtis re uplictes n (except for errors in repliction) re ienticl in sequence. 36. meiosis I n meiosis II Homologs pir n segregte in meiosis I. Sister chromtis re pire n segregte in meiosis II. Crossing over occurs in meiosis I, ut not in meiosis II. 37. sporophyte n gmetophyte The sporophyte is the iploi phse of plnt life cycle. The gmetophyte is the hploi stge. 38. Wht evience is there tht viruses evolve fter, not efore, cells? Viruses cn reprouce only within host cells. Thus, they must hve evolve fter cells. 39. Wht is one feture of meiosis tht prouces genetic vriility in gmetes? In two or three sentences, explin how this feture cuses genetic uniqueness. Inepenent ssortment. In meiosis I metphse n nphse nonhomologous chromosomes istriute rnomly. lignment n seprtion of one pir of homologous chromosomes is inepenent of how ifferent pir seprtes. ifferent gmetes hve ifferent comintions of the pternlly erive n mternlly erive chromosomes. These chromosomes cn hve ifferent lleles for the sme genes, so the gmetes normlly hve ifferent comintions of lleles. OR Crossing over. In meiosis I prophse portions of homologous chromosomes exchnge, chnging comintions of lleles of genes on single chromosome, so not
8 even sister chromtis re ienticl fter crossing over. Ech gmete hs only one copy of ech homolog, n ech homolog now hs unique comintion of lleles rw pir of telocentric homologous chromosomes s they woul pper in G2. Inicte centromeres with smll circle, n plce the lleles n on ech of the chromtis.. rw the sme chromosomes s they woul pper in G1. Plce the lleles n on ech of the chromtis. 41. Why is mitosis importnt within the cell cycle? single cell n ll its genetic informtion is uplicte. Ech cell contins full complement of chromosomes. 42. Explin why mitosis oes not prouce genetic vrition n how meiosis les to the prouction of tremenous genetic vrition. Mitosis prouces cells tht re geneticlly ienticl to the prent cell. Meiosis inclues two istinct processes tht contriute to the genertion of genetic vrition: crossing over shuffles lleles on the sme chromosome into new comintions, wheres the rnom istriution of mternl n pternl chromosomes shuffles lleles on ifferent chromosomes into new comintions. 43. Microscopy to look t cell's chromosomes is often one when the cell is in mitotic metphse. For exmple, kryotypes tht extrct chromosomes from
9 single cell n photogrph them to look for normlities re one on metphse, rther thn interphse, cells. Why? In metphse, chromosomes re conense n re more esily visulize. 44. Fin n escrie t lest four errors in the rwing elow of mitotic nphse. (1) Chromosomes tht re seprting re still uplicte. (2) Spinles re not coming from common spinle-pole oy. (3) Sister chromtis o not hve ienticl lleles for the gene. (4) Two lleles of the gene re on one chromosome. (5) No lleles of the gene re on the homologous chromosome. (6) Homologous chromosomes pper to hve pire n to e segregting
10 45. Wht events uring sexul reprouction re significnt in contriuting to genetic iversity? (1) Crossing over chnges llele comintions on chromosomes, so, fter meiosis I, even sister chromtis re not geneticlly ienticl. (2) Inepenent ssortment of non-homologous chromosomes ensures ech gmete hs ifferent comintion of lleles for genes on nonhomologs. (3) Two geneticlly unique gmetes from ech prent comine uring fertiliztion to form novel, geneticlly unique iniviul. 46. In tissue from the intestinl epithelium of frog, the following proportions of cells were foun t ech stge of the cell cycle: Stge Proportion of Cells Interphse 0.90 Prophse 0.04 Prometphse 0.02 Metphse 0.01 nphse 0.02 Telophse 0.01 If the entire cell cycle in frog epithelium cells requires 20 hours for completion, wht is the verge urtion of ech stge? = 18 hours, = 0.8 hours, =.4 hours, etc.
11 Use the following informtion for questions iploi, eukryotic cell in interphse hs these two pirs of homologous chromosomes with the inicte rrngement of lleles: 47. rw the chromosomes t the en of ) prophse of mitosis n ) prophse I (of meiosis I) with the most likely crossing over events. Inicte plcement of lleles on the chromosomes. )
12 ) 48. rw the chromosomes t the en of telophse of ) mitosis n ) meiosis II. Inicte plcement of lleles on the chromosomes. )
13 ) [One possiility] 49. Write ll possile genotypes of ech of the cells resulting from ) mitosis n ) meiosis, rwn in the previous question. Mitosis: / / / or / (iploi n heterozygous t ll three loci) Meiosis:,,, (hploi t ll three loci) 50.. Compre n contrst spermtogenesis n oogenesis in nimls. For ech process, e sure to inclue informtion out ivision of the nucleus, lloction of chromosomes to the vrious proucts, n ivision of the cytoplsm. ivision of the nucleus n lloction of the chromosomes to the proucts re essentilly the sme in oth processes. Strting with 2n germ cell, nucler ivision is y meiosis I n II, n ech prouct of meiosis contins one set of chromosomes (1n). The mjor ifference is tht ivision of the cytoplsm uring meiosis I n II is equl in spermtogenesis n unequl in oogenesis. uring oogenesis, meiosis I prouces lrge seconry oocyte with lots of cytoplsm n polr oy with very little cytoplsm. Meiosis II in the seconry oocyte prouces lrge ovum with lots of cytoplsm n smll secon polr oy.
14 Therefore, only one lrge, functionl egg is prouce per primry oocyte, wheres four smll, functionl sperm re normlly prouce per primry spermtocyte.. Why is the ifference in cytoplsmic ivision etween spermtogenesis n oogenesis importnt to reprouction, consiering the ifferent roles of sperm n eggs in reprouction? The smll size n other fetures of sperm structure suit them well to elivery of the hploi nucleus to the egg. The lrge mount of cytoplsm in the egg suits it well to nourishing evelopment of the emryo fter fertiliztion escrie the chnging role of cohesin uring the mitotic cell cycle. Cohesin keeps sister chromtis together fter N repliction uring S phse through metphse of mitosis. The rekown of cohesin llows the sister chromtis to seprte from ech other uring nphse.. Explin the importnce of regultion of cohesin ctivity to norml cell ivision. Cohesin must e ctive eginning in S phse through metphse in orer to keep the sister chromtis together so tht they cn e properly ligne t the metphse plte to ensure equl ivision of the genetic informtion to the two ughter cells. Cohesin must e inctivte or roken own in orer to llow the sister chromtis to seprte uring nphse so tht ech ughter cell will get one copy of the genes on ech chromosome. 52. List n riefly escrie the three mjor cell cycle checkpoints. For ech checkpoint, preict the consequences if the checkpoint file to work properly. (1) The G1/S checkpoint hols the cell in G1 until the cell hs ll of the enzymes necessry for repliction of N. If the checkpoint file, the cell woul procee into S without the necessry enzymes, cusing the N not to e replicte properly or completely. This might cuse the cell cycle to hlt t the G2/M checkpoint. lterntively, the cell might ivie without the genetic mteril hving een replicte, cusing the ughter cells to receive incomplete genetic informtion. (oth preictions re resonle se on informtion in the chpter.) (2) The G2/M checkpoint is psse only if the cell s N is unmge. If it fils to work properly, ivision woul procee in the presence of mge N, possily leing to muttions in the ughter cells n/or eth of the ughter cells.
15 (3) The spinle-ssemly checkpoint is uring metphse, n it ensures tht ech chromosome is ligne t the metphse plte n ttche to spinle fiers from opposite poles. This checkpoint epens on tension t the kinetochores of ech chromosome. If the checkpoint fils, nphse will occur even when the chromosomes re not ligne properly, llowing ughter cells to e prouce with extr n/or missing chromosomes.
Mitosis vs meiosis: Lecture Outline 10/26/05. Independent Assortment
 Lectue Outline 10/26/05 Consequences of meiosis Gmetes e geneticlly vile Inepenent ssotment Cossing ove Lots of pctice polems Eos in meiosis Why epouce sexully? Mitosis vs meiosis: Mitosis ensues exct
Lectue Outline 10/26/05 Consequences of meiosis Gmetes e geneticlly vile Inepenent ssotment Cossing ove Lots of pctice polems Eos in meiosis Why epouce sexully? Mitosis vs meiosis: Mitosis ensues exct
Midterm#1 comments. Overview- chapter 6. Recombination. Recombination 1 st sense
 Midterm#1 comments So fr, ~ 10% of exms grded, wide rnge of results: 1 perfect score, 1 score < 100pts rtil credit is given if you get prt of the nswer right Tests will e returned next Thursdy Some of
Midterm#1 comments So fr, ~ 10% of exms grded, wide rnge of results: 1 perfect score, 1 score < 100pts rtil credit is given if you get prt of the nswer right Tests will e returned next Thursdy Some of
A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and XY in males.
 Multiple Choice Use the following information for questions 1-3. A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and
Multiple Choice Use the following information for questions 1-3. A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and
Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank
 Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism.
Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism.
2. Which of the following are NOT prokaryotes? A) eubacteria B) archaea C) viruses D) ancient bacteria
 1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism. B) Errors in chromosome separation can result in a miscarriage. C) Errors in chromosome
1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism. B) Errors in chromosome separation can result in a miscarriage. C) Errors in chromosome
CHAPTER 9 LECTURE NOTES: CHROMOSOME MUTATION II: CHANGES IN NUMBERS
 CHPTER 9 LECTURE NOTES: CHROMOSOME MUTTION II: CHNGES IN NUMBERS I. berrnt euploidy. Generl info. Euploidy refers to the sitution in which n orgnism hs one complete set of chromosomes or n integer multiple
CHPTER 9 LECTURE NOTES: CHROMOSOME MUTTION II: CHNGES IN NUMBERS I. berrnt euploidy. Generl info. Euploidy refers to the sitution in which n orgnism hs one complete set of chromosomes or n integer multiple
eiosis Section 1 Chromosomes and Chromosome Number Reading Preview Essential Questions
 Section 1 Reding Preview Essentil Questions I How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? I Wht re the stges of meiosis? I Wht is theimportnce of meiosis in providing genetic vrition?
Section 1 Reding Preview Essentil Questions I How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? I Wht re the stges of meiosis? I Wht is theimportnce of meiosis in providing genetic vrition?
MCB : Homologous Recombination
 MC 421-2006: Homologous Recomintion Prt I. Definitions Chnges in DN re clled muttions. Muttions cn e chnges in one se, in severl ses, in mny ses. Recomintion is lso chnge is DN. How is it different from
MC 421-2006: Homologous Recomintion Prt I. Definitions Chnges in DN re clled muttions. Muttions cn e chnges in one se, in severl ses, in mny ses. Recomintion is lso chnge is DN. How is it different from
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, November 14, 2018 Finite Automata II. Nickolas Rollick a b b. a b 4
 Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Course Information. Computational Genetics Lecture 1. Course Prerequisites. Course Goals
 Course Informtion. Computtionl Genetics Lecture 1 ckground Redings: Chpter 2&3 of n introduction to Genetics, Griffiths et l. 2000, Seventh Edition (CS/Fishch/Other lirries). This clss hs een edited from
Course Informtion. Computtionl Genetics Lecture 1 ckground Redings: Chpter 2&3 of n introduction to Genetics, Griffiths et l. 2000, Seventh Edition (CS/Fishch/Other lirries). This clss hs een edited from
APPENDIX. Precalculus Review D.1. Real Numbers and the Real Number Line
 APPENDIX D Preclculus Review APPENDIX D.1 Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Orer n Inequlities Asolute Vlue n Distnce Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel numers cn e represente
APPENDIX D Preclculus Review APPENDIX D.1 Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Orer n Inequlities Asolute Vlue n Distnce Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel numers cn e represente
( x) ( ) takes at the right end of each interval to approximate its value on that
 III. INTEGRATION Economists seem much more intereste in mrginl effects n ifferentition thn in integrtion. Integrtion is importnt for fining the expecte vlue n vrince of rnom vriles, which is use in econometrics
III. INTEGRATION Economists seem much more intereste in mrginl effects n ifferentition thn in integrtion. Integrtion is importnt for fining the expecte vlue n vrince of rnom vriles, which is use in econometrics
Today s Outline. Inheritance. Darwin & Mendel near miss. Gregor Johann Mendel. Terms Punnett-square. Modern Synthesis
 Tody s Outline Inheritne Gregor Mendel Theory of segregtion Theory of independent ssortment Soures of vrition in popultions hromosoml sis of inheritne Humn genetis & ethis Gregor Johnn Mendel Gregor Johnn
Tody s Outline Inheritne Gregor Mendel Theory of segregtion Theory of independent ssortment Soures of vrition in popultions hromosoml sis of inheritne Humn genetis & ethis Gregor Johnn Mendel Gregor Johnn
Things to Memorize: A Partial List. January 27, 2017
 Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
Lecture 3: Equivalence Relations
 Mthcmp Crsh Course Instructor: Pdric Brtlett Lecture 3: Equivlence Reltions Week 1 Mthcmp 2014 In our lst three tlks of this clss, we shift the focus of our tlks from proof techniques to proof concepts
Mthcmp Crsh Course Instructor: Pdric Brtlett Lecture 3: Equivlence Reltions Week 1 Mthcmp 2014 In our lst three tlks of this clss, we shift the focus of our tlks from proof techniques to proof concepts
Physics Lecture 14: MON 29 SEP
 Physics 2113 Physics 2113 Lecture 14: MON 29 SEP CH25: Cpcitnce Von Kleist ws le to store electricity in the jr. Unknowingly, he h ctully invente novel evice to store potentil ifference. The wter in the
Physics 2113 Physics 2113 Lecture 14: MON 29 SEP CH25: Cpcitnce Von Kleist ws le to store electricity in the jr. Unknowingly, he h ctully invente novel evice to store potentil ifference. The wter in the
A, Electromagnetic Fields Final Exam December 14, 2001 Solution
 304-351, Electrognetic Fiels Finl Ex Deceer 14, 2001 Solution 1. e9.8. In chpter9.proles.extr.two loops, e of thin wire crry equl n opposite currents s shown in the figure elow. The rius of ech loop is
304-351, Electrognetic Fiels Finl Ex Deceer 14, 2001 Solution 1. e9.8. In chpter9.proles.extr.two loops, e of thin wire crry equl n opposite currents s shown in the figure elow. The rius of ech loop is
2.4 Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation
 .4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
.4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
7.1 Integral as Net Change and 7.2 Areas in the Plane Calculus
 7.1 Integrl s Net Chnge nd 7. Ares in the Plne Clculus 7.1 INTEGRAL AS NET CHANGE Notecrds from 7.1: Displcement vs Totl Distnce, Integrl s Net Chnge We hve lredy seen how the position of n oject cn e
7.1 Integrl s Net Chnge nd 7. Ares in the Plne Clculus 7.1 INTEGRAL AS NET CHANGE Notecrds from 7.1: Displcement vs Totl Distnce, Integrl s Net Chnge We hve lredy seen how the position of n oject cn e
D. Harel, Statecharts: A visual formalism for complex systems, Science of Computer Programming 8, 1987, pp
 Sttechrts y Kenr ooper ontents Introuction Stte igrms epth (hierrchy) Orthogonlity (concurrency) rocst ommuniction Exmple Prolems Introuction Sttechrts were introuce y vi Hrel in 1987. Hrel, Sttechrts:
Sttechrts y Kenr ooper ontents Introuction Stte igrms epth (hierrchy) Orthogonlity (concurrency) rocst ommuniction Exmple Prolems Introuction Sttechrts were introuce y vi Hrel in 1987. Hrel, Sttechrts:
Reverse Engineering Gene Networks with Microarray Data
 Reverse Engineering Gene Networks with Microrry Dt Roert M Mllery Avisors: Dr Steve Cox n Dr Mrk Emree August 25, 2003 Astrct We consier the question of how to solve inverse prolems of the form e At x(0)
Reverse Engineering Gene Networks with Microrry Dt Roert M Mllery Avisors: Dr Steve Cox n Dr Mrk Emree August 25, 2003 Astrct We consier the question of how to solve inverse prolems of the form e At x(0)
Bridging the gap: GCSE AS Level
 Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Situation Calculus. Situation Calculus Building Blocks. Sheila McIlraith, CSC384, University of Toronto, Winter Situations Fluents Actions
 Plnning gent: single gent or multi-gent Stte: complete or Incomplete (logicl/probbilistic) stte of the worl n/or gent s stte of knowlege ctions: worl-ltering n/or knowlege-ltering (e.g. sensing) eterministic
Plnning gent: single gent or multi-gent Stte: complete or Incomplete (logicl/probbilistic) stte of the worl n/or gent s stte of knowlege ctions: worl-ltering n/or knowlege-ltering (e.g. sensing) eterministic
CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words)
 CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
4.5 THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS
 4.5 The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus Contemporry Clculus 4.5 THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS This section contins the most importnt n most use theorem of clculus, THE Funmentl Theorem of Clculus. Discovere
4.5 The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus Contemporry Clculus 4.5 THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS This section contins the most importnt n most use theorem of clculus, THE Funmentl Theorem of Clculus. Discovere
Farey Fractions. Rickard Fernström. U.U.D.M. Project Report 2017:24. Department of Mathematics Uppsala University
 U.U.D.M. Project Report 07:4 Frey Frctions Rickrd Fernström Exmensrete i mtemtik, 5 hp Hledre: Andres Strömergsson Exmintor: Jörgen Östensson Juni 07 Deprtment of Mthemtics Uppsl University Frey Frctions
U.U.D.M. Project Report 07:4 Frey Frctions Rickrd Fernström Exmensrete i mtemtik, 5 hp Hledre: Andres Strömergsson Exmintor: Jörgen Östensson Juni 07 Deprtment of Mthemtics Uppsl University Frey Frctions
Electric Potential. Electric Potential Video: Section 1 4. Electric Fields and WORK 9/3/2014. IB Physics SL (Year Two) Wednesday, September 3, 2014
 9/3/014 lectric Potentil IB Physics SL (Yer Two) Wenesy, Septemer 3, 014 lectric Potentil Vieo: Section 1 4 lectric Fiels n WORK In orer to rin two like chres ner ech other work must e one. In orer to
9/3/014 lectric Potentil IB Physics SL (Yer Two) Wenesy, Septemer 3, 014 lectric Potentil Vieo: Section 1 4 lectric Fiels n WORK In orer to rin two like chres ner ech other work must e one. In orer to
1B40 Practical Skills
 B40 Prcticl Skills Comining uncertinties from severl quntities error propgtion We usully encounter situtions where the result of n experiment is given in terms of two (or more) quntities. We then need
B40 Prcticl Skills Comining uncertinties from severl quntities error propgtion We usully encounter situtions where the result of n experiment is given in terms of two (or more) quntities. We then need
Parse trees, ambiguity, and Chomsky normal form
 Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
I1 = I2 I1 = I2 + I3 I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 I 3
 2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
Haplotype Frequencies and Linkage Disequilibrium. Biostatistics 666
 Hlotye Frequencies nd Linkge isequilirium iosttistics 666 Lst Lecture Genotye Frequencies llele Frequencies Phenotyes nd Penetrnces Hrdy-Weinerg Equilirium Simle demonstrtion Exercise: NO2 nd owel isese
Hlotye Frequencies nd Linkge isequilirium iosttistics 666 Lst Lecture Genotye Frequencies llele Frequencies Phenotyes nd Penetrnces Hrdy-Weinerg Equilirium Simle demonstrtion Exercise: NO2 nd owel isese
Designing finite automata II
 Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
x dx does exist, what does the answer look like? What does the answer to
 Review Guie or MAT Finl Em Prt II. Mony Decemer th 8:.m. 9:5.m. (or the 8:3.m. clss) :.m. :5.m. (or the :3.m. clss) Prt is worth 5% o your Finl Em gre. NO CALCULATORS re llowe on this portion o the Finl
Review Guie or MAT Finl Em Prt II. Mony Decemer th 8:.m. 9:5.m. (or the 8:3.m. clss) :.m. :5.m. (or the :3.m. clss) Prt is worth 5% o your Finl Em gre. NO CALCULATORS re llowe on this portion o the Finl
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.9 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Discrete Structures Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Discrete Structures Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Discrete Structures Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/96/126844436.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Discrete Structures Prelim Question Pper Solution 1. () (i) Disjoint set wo sets re si to be isjoint if they hve no elements in common. Exmple : A = {0, 4, 7, 9} n B = {3, 17, 15}
S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Discrete Structures Prelim Question Pper Solution 1. () (i) Disjoint set wo sets re si to be isjoint if they hve no elements in common. Exmple : A = {0, 4, 7, 9} n B = {3, 17, 15}
Stereoselective Synthesis
 Stereoselective Synthesis Dr Michel Perkins, Fliners University Reference Texts: Stereochemistry of orgnic compouns Ernest L. Eliel New York : Wiley & Sons, c1994. Chpter 12 on stereoselective synthesis
Stereoselective Synthesis Dr Michel Perkins, Fliners University Reference Texts: Stereochemistry of orgnic compouns Ernest L. Eliel New York : Wiley & Sons, c1994. Chpter 12 on stereoselective synthesis
List all of the possible rational roots of each equation. Then find all solutions (both real and imaginary) of the equation. 1.
 Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
Homework 3 Solutions
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
Lecture 6: Coding theory
 Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
VII. The Integral. 50. Area under a Graph. y = f(x)
 VII. The Integrl In this chpter we efine the integrl of function on some intervl [, b]. The most common interprettion of the integrl is in terms of the re uner the grph of the given function, so tht is
VII. The Integrl In this chpter we efine the integrl of function on some intervl [, b]. The most common interprettion of the integrl is in terms of the re uner the grph of the given function, so tht is
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE CONNECTION FORMULAE FOR THE SEMICLASSICAL APPROXIMATION
 Physics 8.06 Apr, 2008 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE CONNECTION FORMULAE FOR THE SEMICLASSICAL APPROXIMATION c R. L. Jffe 2002 The WKB connection formuls llow one to continue semiclssicl solutions from n
Physics 8.06 Apr, 2008 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE CONNECTION FORMULAE FOR THE SEMICLASSICAL APPROXIMATION c R. L. Jffe 2002 The WKB connection formuls llow one to continue semiclssicl solutions from n
u( t) + K 2 ( ) = 1 t > 0 Analyzing Damped Oscillations Problem (Meador, example 2-18, pp 44-48): Determine the equation of the following graph.
 nlyzing Dmped Oscilltions Prolem (Medor, exmple 2-18, pp 44-48): Determine the eqution of the following grph. The eqution is ssumed to e of the following form f ( t) = K 1 u( t) + K 2 e!"t sin (#t + $
nlyzing Dmped Oscilltions Prolem (Medor, exmple 2-18, pp 44-48): Determine the eqution of the following grph. The eqution is ssumed to e of the following form f ( t) = K 1 u( t) + K 2 e!"t sin (#t + $
Regular Language. Nonregular Languages The Pumping Lemma. The pumping lemma. Regular Language. The pumping lemma. Infinitely long words 3/17/15
 Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
Section 6: Area, Volume, and Average Value
 Chpter The Integrl Applied Clculus Section 6: Are, Volume, nd Averge Vlue Are We hve lredy used integrls to find the re etween the grph of function nd the horizontl xis. Integrls cn lso e used to find
Chpter The Integrl Applied Clculus Section 6: Are, Volume, nd Averge Vlue Are We hve lredy used integrls to find the re etween the grph of function nd the horizontl xis. Integrls cn lso e used to find
Conservation Law. Chapter Goal. 6.2 Theory
 Chpter 6 Conservtion Lw 6.1 Gol Our long term gol is to unerstn how mthemticl moels re erive. Here, we will stuy how certin quntity chnges with time in given region (sptil omin). We then first erive the
Chpter 6 Conservtion Lw 6.1 Gol Our long term gol is to unerstn how mthemticl moels re erive. Here, we will stuy how certin quntity chnges with time in given region (sptil omin). We then first erive the
GNFA GNFA GNFA GNFA GNFA
 DFA RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA Definition GNFA A generlize noneterministic finite utomton (GNFA) is grph whose eges re lele y regulr expressions, with unique strt stte with in-egree, n unique finl stte with
DFA RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA Definition GNFA A generlize noneterministic finite utomton (GNFA) is grph whose eges re lele y regulr expressions, with unique strt stte with in-egree, n unique finl stte with
378 Relations Solutions for Chapter 16. Section 16.1 Exercises. 3. Let A = {0,1,2,3,4,5}. Write out the relation R that expresses on A.
 378 Reltions 16.7 Solutions for Chpter 16 Section 16.1 Exercises 1. Let A = {0,1,2,3,4,5}. Write out the reltion R tht expresses > on A. Then illustrte it with digrm. 2 1 R = { (5,4),(5,3),(5,2),(5,1),(5,0),(4,3),(4,2),(4,1),
378 Reltions 16.7 Solutions for Chpter 16 Section 16.1 Exercises 1. Let A = {0,1,2,3,4,5}. Write out the reltion R tht expresses > on A. Then illustrte it with digrm. 2 1 R = { (5,4),(5,3),(5,2),(5,1),(5,0),(4,3),(4,2),(4,1),
Exploring parametric representation with the TI-84 Plus CE graphing calculator
 Exploring prmetric representtion with the TI-84 Plus CE grphing clcultor Richrd Prr Executive Director Rice University School Mthemtics Project rprr@rice.edu Alice Fisher Director of Director of Technology
Exploring prmetric representtion with the TI-84 Plus CE grphing clcultor Richrd Prr Executive Director Rice University School Mthemtics Project rprr@rice.edu Alice Fisher Director of Director of Technology
Quantitative Genetics and Twin Studies
 Count Count Count Count Quntittive Genetics nd Twin Studies n Introduction! co de Geus -Dept. Biologicl Psychology -Netherlnds Twin Register msterdm, the Netherlnds 600 N = 6602 M = 48,27 SD = 25,0 75
Count Count Count Count Quntittive Genetics nd Twin Studies n Introduction! co de Geus -Dept. Biologicl Psychology -Netherlnds Twin Register msterdm, the Netherlnds 600 N = 6602 M = 48,27 SD = 25,0 75
GEOMETRY OF THE CIRCLE TANGENTS & SECANTS
 Geometry Of The ircle Tngents & Secnts GEOMETRY OF THE IRLE TNGENTS & SENTS www.mthletics.com.u Tngents TNGENTS nd N Secnts SENTS Tngents nd secnts re lines tht strt outside circle. Tngent touches the
Geometry Of The ircle Tngents & Secnts GEOMETRY OF THE IRLE TNGENTS & SENTS www.mthletics.com.u Tngents TNGENTS nd N Secnts SENTS Tngents nd secnts re lines tht strt outside circle. Tngent touches the
1.2 What is a vector? (Section 2.2) Two properties (attributes) of a vector are and.
 Homework 1. Chpters 2. Bsis independent vectors nd their properties Show work except for fill-in-lnks-prolems (print.pdf from www.motiongenesis.com Textooks Resources). 1.1 Solving prolems wht engineers
Homework 1. Chpters 2. Bsis independent vectors nd their properties Show work except for fill-in-lnks-prolems (print.pdf from www.motiongenesis.com Textooks Resources). 1.1 Solving prolems wht engineers
Genetic Programming. Outline. Evolutionary Strategies. Evolutionary strategies Genetic programming Summary
 Outline Genetic Progrmming Evolutionry strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Bsed on the mteril provided y Professor Michel Negnevitsky Evolutionry Strtegies An pproch simulting nturl evolution ws proposed
Outline Genetic Progrmming Evolutionry strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Bsed on the mteril provided y Professor Michel Negnevitsky Evolutionry Strtegies An pproch simulting nturl evolution ws proposed
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory 2. Diffusion-Controlled Reaction
 Ch. 4 Moleculr Rection Dynmics 1. Collision Theory. Diffusion-Controlle Rection Lecture 17 3. The Mteril Blnce Eqution 4. Trnsition Stte Theory: The Eyring Eqution 5. Trnsition Stte Theory: Thermoynmic
Ch. 4 Moleculr Rection Dynmics 1. Collision Theory. Diffusion-Controlle Rection Lecture 17 3. The Mteril Blnce Eqution 4. Trnsition Stte Theory: The Eyring Eqution 5. Trnsition Stte Theory: Thermoynmic
2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
 Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Surface maps into free groups
 Surfce mps into free groups lden Wlker Novemer 10, 2014 Free groups wedge X of two circles: Set F = π 1 (X ) =,. We write cpitl letters for inverse, so = 1. e.g. () 1 = Commuttors Let x nd y e loops. The
Surfce mps into free groups lden Wlker Novemer 10, 2014 Free groups wedge X of two circles: Set F = π 1 (X ) =,. We write cpitl letters for inverse, so = 1. e.g. () 1 = Commuttors Let x nd y e loops. The
Table of contents: Lecture N Summary... 3 What does automata mean?... 3 Introduction to languages... 3 Alphabets... 3 Strings...
 Tle of contents: Lecture N0.... 3 ummry... 3 Wht does utomt men?... 3 Introduction to lnguges... 3 Alphets... 3 trings... 3 Defining Lnguges... 4 Lecture N0. 2... 7 ummry... 7 Kleene tr Closure... 7 Recursive
Tle of contents: Lecture N0.... 3 ummry... 3 Wht does utomt men?... 3 Introduction to lnguges... 3 Alphets... 3 trings... 3 Defining Lnguges... 4 Lecture N0. 2... 7 ummry... 7 Kleene tr Closure... 7 Recursive
Special Numbers, Factors and Multiples
 Specil s, nd Student Book - Series H- + 3 + 5 = 9 = 3 Mthletics Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series H Contents Topics Topic - Odd, even, prime nd composite numers Topic - Divisiility tests
Specil s, nd Student Book - Series H- + 3 + 5 = 9 = 3 Mthletics Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series H Contents Topics Topic - Odd, even, prime nd composite numers Topic - Divisiility tests
ELETROSTATICS Part II: BASICS
 GROWING WITH ONPTS: Physics LTROSTTIS Prt II: SIS Presence of chrge on ny oject cretes n electrosttic fiel roun it n in turn n electricl potentil is experience roun the oject. This phenomenon hs foun ppliction
GROWING WITH ONPTS: Physics LTROSTTIS Prt II: SIS Presence of chrge on ny oject cretes n electrosttic fiel roun it n in turn n electricl potentil is experience roun the oject. This phenomenon hs foun ppliction
Fault Modeling. EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald
 Fult Modeling EE5375 ADD II Prof. McDonld Stuck At Fult Models l Modeling of physicl defects (fults) simplify to logicl fult l stuck high or low represents mny physicl defects esy to simulte technology
Fult Modeling EE5375 ADD II Prof. McDonld Stuck At Fult Models l Modeling of physicl defects (fults) simplify to logicl fult l stuck high or low represents mny physicl defects esy to simulte technology
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER LANGUAGES AND COMPUTATION ANSWERS
 The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
Necessary and sufficient conditions for some two variable orthogonal designs in order 44
 University of Wollongong Reserch Online Fculty of Informtics - Ppers (Archive) Fculty of Engineering n Informtion Sciences 1998 Necessry n sufficient conitions for some two vrile orthogonl esigns in orer
University of Wollongong Reserch Online Fculty of Informtics - Ppers (Archive) Fculty of Engineering n Informtion Sciences 1998 Necessry n sufficient conitions for some two vrile orthogonl esigns in orer
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter Final Exam (solutions) SOLUTIONS
 CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Thoery of Automata CS402
 Thoery of Automt C402 Theory of Automt Tle of contents: Lecture N0. 1... 4 ummry... 4 Wht does utomt men?... 4 Introduction to lnguges... 4 Alphets... 4 trings... 4 Defining Lnguges... 5 Lecture N0. 2...
Thoery of Automt C402 Theory of Automt Tle of contents: Lecture N0. 1... 4 ummry... 4 Wht does utomt men?... 4 Introduction to lnguges... 4 Alphets... 4 trings... 4 Defining Lnguges... 5 Lecture N0. 2...
Hamiltonian Cycle in Complete Multipartite Graphs
 Annls of Pure nd Applied Mthemtics Vol 13, No 2, 2017, 223-228 ISSN: 2279-087X (P), 2279-0888(online) Pulished on 18 April 2017 wwwreserchmthsciorg DOI: http://dxdoiorg/1022457/pmv13n28 Annls of Hmiltonin
Annls of Pure nd Applied Mthemtics Vol 13, No 2, 2017, 223-228 ISSN: 2279-087X (P), 2279-0888(online) Pulished on 18 April 2017 wwwreserchmthsciorg DOI: http://dxdoiorg/1022457/pmv13n28 Annls of Hmiltonin
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
10. AREAS BETWEEN CURVES
 . AREAS BETWEEN CURVES.. Ares etween curves So res ove the x-xis re positive nd res elow re negtive, right? Wrong! We lied! Well, when you first lern out integrtion it s convenient fiction tht s true in
. AREAS BETWEEN CURVES.. Ares etween curves So res ove the x-xis re positive nd res elow re negtive, right? Wrong! We lied! Well, when you first lern out integrtion it s convenient fiction tht s true in
Controllable Microfluidic Production of Multicomponent Multiple Emulsions
 Supplementry Mteril (ESI) or L on Chip This journl is The Royl Society o Chemistry 0 Controllle Microluiic Prouction o Multicomponent Multiple Emulsions Supplementry Mteril Wei Wng, Rui Xie *, Xio-Jie
Supplementry Mteril (ESI) or L on Chip This journl is The Royl Society o Chemistry 0 Controllle Microluiic Prouction o Multicomponent Multiple Emulsions Supplementry Mteril Wei Wng, Rui Xie *, Xio-Jie
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter 11
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction. What is Cellular Reproduction?
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Counting Paths Between Vertices. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs
 Isomorphism of Grphs Definition The simple grphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) n G = (V, E ) re isomorphi if there is ijetion (n oneto-one n onto funtion) f from V 1 to V with the property tht n re jent in G 1 if
Isomorphism of Grphs Definition The simple grphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) n G = (V, E ) re isomorphi if there is ijetion (n oneto-one n onto funtion) f from V 1 to V with the property tht n re jent in G 1 if
1 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA and GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE
 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Convert the NFA into DFA
 Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
CSE 332. Sorting. Data Abstractions. CSE 332: Data Abstractions. QuickSort Cutoff 1. Where We Are 2. Bounding The MAXIMUM Problem 4
 Am Blnk Leture 13 Winter 2016 CSE 332 CSE 332: Dt Astrtions Sorting Dt Astrtions QuikSort Cutoff 1 Where We Are 2 For smll n, the reursion is wste. The onstnts on quik/merge sort re higher thn the ones
Am Blnk Leture 13 Winter 2016 CSE 332 CSE 332: Dt Astrtions Sorting Dt Astrtions QuikSort Cutoff 1 Where We Are 2 For smll n, the reursion is wste. The onstnts on quik/merge sort re higher thn the ones
Minnesota State University, Mankato 44 th Annual High School Mathematics Contest April 12, 2017
 Minnesot Stte University, Mnkto 44 th Annul High School Mthemtics Contest April, 07. A 5 ft. ldder is plced ginst verticl wll of uilding. The foot of the ldder rests on the floor nd is 7 ft. from the wll.
Minnesot Stte University, Mnkto 44 th Annul High School Mthemtics Contest April, 07. A 5 ft. ldder is plced ginst verticl wll of uilding. The foot of the ldder rests on the floor nd is 7 ft. from the wll.
p-adic Egyptian Fractions
 p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
How do we solve these things, especially when they get complicated? How do we know when a system has a solution, and when is it unique?
 XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
x = a To determine the volume of the solid, we use a definite integral to sum the volumes of the slices as we let!x " 0 :
 Clculus II MAT 146 Integrtion Applictions: Volumes of 3D Solids Our gol is to determine volumes of vrious shpes. Some of the shpes re the result of rotting curve out n xis nd other shpes re simply given
Clculus II MAT 146 Integrtion Applictions: Volumes of 3D Solids Our gol is to determine volumes of vrious shpes. Some of the shpes re the result of rotting curve out n xis nd other shpes re simply given
Physics 9 Fall 2011 Homework 2 - Solutions Friday September 2, 2011
 Physics 9 Fll 0 Homework - s Fridy September, 0 Mke sure your nme is on your homework, nd plese box your finl nswer. Becuse we will be giving prtil credit, be sure to ttempt ll the problems, even if you
Physics 9 Fll 0 Homework - s Fridy September, 0 Mke sure your nme is on your homework, nd plese box your finl nswer. Becuse we will be giving prtil credit, be sure to ttempt ll the problems, even if you
5.1 How do we Measure Distance Traveled given Velocity? Student Notes
 . How do we Mesure Distnce Trveled given Velocity? Student Notes EX ) The tle contins velocities of moving cr in ft/sec for time t in seconds: time (sec) 3 velocity (ft/sec) 3 A) Lel the x-xis & y-xis
. How do we Mesure Distnce Trveled given Velocity? Student Notes EX ) The tle contins velocities of moving cr in ft/sec for time t in seconds: time (sec) 3 velocity (ft/sec) 3 A) Lel the x-xis & y-xis
Basic Derivative Properties
 Bsic Derivtive Properties Let s strt this section by remining ourselves tht the erivtive is the slope of function Wht is the slope of constnt function? c FACT 2 Let f () =c, where c is constnt Then f 0
Bsic Derivtive Properties Let s strt this section by remining ourselves tht the erivtive is the slope of function Wht is the slope of constnt function? c FACT 2 Let f () =c, where c is constnt Then f 0
First Midterm Examination
 Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
State space systems analysis (continued) Stability. A. Definitions A system is said to be Asymptotically Stable (AS) when it satisfies
 Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
CELL REPRODUCTION. Unit 20 LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 Unit 20 CELL REPRODUCTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to distinguish the differences between mitotic and meiotic cell division. 2. Learn the role that both mitotic and meiotic types of cell division
Unit 20 CELL REPRODUCTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to distinguish the differences between mitotic and meiotic cell division. 2. Learn the role that both mitotic and meiotic types of cell division
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping
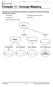 Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
CM10196 Topic 4: Functions and Relations
 CM096 Topic 4: Functions nd Reltions Guy McCusker W. Functions nd reltions Perhps the most widely used notion in ll of mthemtics is tht of function. Informlly, function is n opertion which tkes n input
CM096 Topic 4: Functions nd Reltions Guy McCusker W. Functions nd reltions Perhps the most widely used notion in ll of mthemtics is tht of function. Informlly, function is n opertion which tkes n input
Angel International School - Manipay
 Gre 6 Angel Interntionl Shool - Mnipy 2 n Term Exmintion Mrh, 2017 Siene Durtion: 02 Hours Inex No:- Prt 1 (1) Unerline the orret nswer. 1) Wht is the isese tht spre y unlen wter? ) Dengue ) Mlri ) Choler
Gre 6 Angel Interntionl Shool - Mnipy 2 n Term Exmintion Mrh, 2017 Siene Durtion: 02 Hours Inex No:- Prt 1 (1) Unerline the orret nswer. 1) Wht is the isese tht spre y unlen wter? ) Dengue ) Mlri ) Choler
School of Business. Blank Page
 Integrl Clculus This unit is esigne to introuce the lerners to the sic concepts ssocite with Integrl Clculus. Integrl clculus cn e clssifie n iscusse into two thres. One is Inefinite Integrl n the other
Integrl Clculus This unit is esigne to introuce the lerners to the sic concepts ssocite with Integrl Clculus. Integrl clculus cn e clssifie n iscusse into two thres. One is Inefinite Integrl n the other
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
Bases for Vector Spaces
 Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Meiosis. The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced.
 MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
Extension of the Villarceau-Section to Surfaces of Revolution with a Generating Conic
 Journl for Geometry n Grphics Volume 6 (2002), No. 2, 121 132. Extension of the Villrceu-Section to Surfces of Revolution with Generting Conic Anton Hirsch Fchereich uingenieurwesen, FG Sthlu, Drstellungstechnik
Journl for Geometry n Grphics Volume 6 (2002), No. 2, 121 132. Extension of the Villrceu-Section to Surfces of Revolution with Generting Conic Anton Hirsch Fchereich uingenieurwesen, FG Sthlu, Drstellungstechnik
Chapter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automata. Formal Language, chapter 5, slide 1
 Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Matrix Algebra. Matrix Addition, Scalar Multiplication and Transposition. Linear Algebra I 24
 Mtrix lger Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition Mtrix lger Section.. Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition rectngulr rry of numers is clled mtrix ( the plurl is mtrices ) nd the
Mtrix lger Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition Mtrix lger Section.. Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition rectngulr rry of numers is clled mtrix ( the plurl is mtrices ) nd the
Section 6.3 The Fundamental Theorem, Part I
 Section 6.3 The Funmentl Theorem, Prt I (3//8) Overview: The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus shows tht ifferentition n integrtion re, in sense, inverse opertions. It is presente in two prts. We previewe Prt
Section 6.3 The Funmentl Theorem, Prt I (3//8) Overview: The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus shows tht ifferentition n integrtion re, in sense, inverse opertions. It is presente in two prts. We previewe Prt
Last Time emphasis on E-field. Potential of spherical conductor. Quick quiz. Connected spheres. Varying E-fields on conductor.
 Lst Time emphsis on Efiel Electric flux through surfce Guss lw: Totl electric flux through close surfce proportionl to chrge enclose Q " E = E = 4$k e Q % o Chrge istribution on conuctors Chrge ccumultes
Lst Time emphsis on Efiel Electric flux through surfce Guss lw: Totl electric flux through close surfce proportionl to chrge enclose Q " E = E = 4$k e Q % o Chrge istribution on conuctors Chrge ccumultes
