WAS LEPENSKI VIR AN ANCIENT SUN OR PLEIADES OBSERVATORY? Vladan Panković, Milan Mrdjen, Miodrag Krmar
|
|
|
- Francis Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WAS LEPENSKI VIR AN ANCIENT SUN OR PLEIADES OBSERVATORY? Vladan Panković, Milan Mrdjen, Miodrag Krmar Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, Novi Sad, Trg Dositeja Obradovića 4., Serbia, Abstract In this work we testify using simulation programs some old hypotheses according to which remarkable mesolithic village Lepenski Vir ( BC) at the right (nearly west) Danube riverside in the Iron gate in Serbia was an ancient (one of the oldest) Sun (proto) observatory. We use method recently suggested by A. C. Sparavigna, concretely we use at internet simply and freely available software or local Sun radiation direction simulation and calculation computer programs. In this way we obtain and discuss figures of the sunrise in the Lepenski Vir during winter and summer solstice and spring and autumnal equinox in relation to position of the mountains, especially Treskavac (Trescovat in Romanian) and Kukuvija at left (nearly east) Danube riverside (in Romania). While mountain Kukuvija represents really the natural marker for the Sun in date of the winter solstice, mountain Treskavac, in despite to usual opinions, does not represent any real marker for the Sun in date of the summer solstice. Sun rises exactly behind Treskavac, relatively exactly (in the domain of used methods) speaking, between 20. April and 1. May. It more or less corresponds to year period when heliacal rising of the Pleiades constellation occurs, which by many ancient cultures, e.g. Celts of northern Europe, denotes very beginning of the year. Really, in common with some other facts obtained using at internet simply and freely available stellarium software or sky objects position simulation programs, we demonstrate that for the Lepenski Vir observer heliacal rising of the Pleiades ends exactly at 20. April and this observationally accurately determined event can be used for very beginning of the year. All this opens a very probable possibility according to which Lepenski Vir was really an ancient (one of the oldest) Sun and Pleiades constellation (proto)observatory too with Treskavac as a (natural) marker. Key words: Lepenski Vir, ancient observatory, Sun, Pleiades
2 1. Introduction As it is well-known [1], [2], [3], [4] Lepenski Vir discovered by D. Srejović represents remarkable mesolithic village and culture (about BC) at the right (nearly west) Danube riverside in the Iron gate in Serbia at the border with Romania. In the Lepenski Vir originated first monumental sculptures in the Europe, on the one hand, and base of the houses in the Lepenski Vir have had original, specific nearly trapezoidal forms and their buildings have been realized using very sophisticated geometrical and architectonic procedures. Nevertheless form of the basis of the house is very similar to the trapezoidal form of the mountain Treskavac (Trescovat in Romanian) placed oppositely to the Lepenski Vir at left (nearly east) Danube riverside (in Romania). It does not represent a coincidence only. On the contrary it expresses a deep connection of the culture with religious elements of the Lepenski Vir with Treskavac. It causes some less or more accurate hypotheses according to which Lepenski Vir with Treskavac have had some astronomical characteristics [1]. [2], [5] even that it was an ancient (one of the oldest) Sun (proto)observatory. In this work we shall test such hypotheses using methods recently suggested by A. C. Sparavigna for some other ancient Sun observatories [6], [7], [8]. Concretely we shall use the following at internet simply and freely available software or different local Sun direction simulation and calculation computer programs: 1. recomanded. by Sparavigna [6], [7], [8], ,2/ /14:25, 3. Additionally, we shall use at internet simply and freely available stellarium software or sky objects position simulation program 4. All four mentioned and similar programs can be simply funded at internet by everyone which can check and affirm our results. Also, everyone can in the analogous way simply find additional data that go over basic intention of this work and that, for this reason or reason for simplicity, are here omitted. By first and second program we shall simply obtain figures of the satellite and ground map of the Lepenski Vir and its close environment. We start programs by insertion of two necessary words, Boljetin (village about 5km southern to Lepenski Vir), and, Serbia, after which naviation procedure leads simply toward Lepenski Vir with latitude and longitude Then we shall obtain and discuss figures of the sunrise in the Lepenski Vir during winter and summer solstice, spring and autumnal equinox, and some other astronomically potentially interesting dates and intervals, in relation to position of the mountains, especially Treskavac and Kukuvija at left (nearly east) Danube riverside (in Romania). While, according to obtained figures, top of the mountain Kukuvija represents really the natural marker for the Sun in date of the winter solstice, mountain Treskavac, in despite to usual opinions, does not represent any real marker for the Sun in date of the summer solstice. Obtained figures clearly show that Sun rises behind Treskavac, relatively accurately (within our method) speaking, between 20. April and 1. May. It, roughly speaking, corresponds to year period when heliacal rising of the Pleiades constellation occurs, and
3 this event by many ancient cultures, e.g. Celts of northern Europe, denotes very beginning of the year [9], [10]. For reason of a relatively accurate analysis of the correlations between time interval of the sunrise immediately behind Treskavac and Pleiades constellation heliacal rising we shall use mentioned third and fourth programs Namely, according to the third program sunrise moment at Lepenski Vir at any day in the year, including days between 20. April and 1. May, can be exactly determined by calculations (al this can be doe by first and second program too). This moment will be introduced in the fourth program which will simulate figure of the sky horizon (with Pleiades constellation position) in this moment for days between 20. April and 1. May. All this will open a very probable possibility that Lepenski Vir was an ancient Sun and Pleiades constellation (proto)observatory with Treskavac as a (natural) marker. Fig. 1 Pleiades constellation Fig. 2 Bases of the houses in Lepenski Vir photography from [1], [2]
4 Fig. 3 Basis of the house in Lepenski Vir opposite to Treskavac photography from [1], [2] 2. Lepenski Vir an ancient Sun and Pleiades observatory consequence of the simulated figures We introduce two mentioned words, Boljetin, and, Serbia, in mentioned first or second program, 1. and ,2/ /14:25. After navigation, we obtain figure 4 of the satellite map of Lepenski Vir with close environment. More detailed analysis by the same programs, which here will not be given explicitly, points out that Lepenski Vir holds latitude and longitude At this figure 4 Lepenski Vir overlapped village area,with represents small white spot at the left hand of the figure or right Danube riverside opposite to white bare rock, i.e. mountain Treskavac. (The following here can be pointed out. After building of the hydropower Djerdap I, whole original plateau of the Lepenski Vir village has vertically lifted and covered for reason of the protection from atmospheric impacts. Nevertheles this lifting and overlap has no significant influence on the observations referring at Lepenski Vir ancient observatory hypotheses, since linear dimensions of the Lepenski Vir area are much smaller than distance between the Lepenski Vir and mentioned nearly mountains.)
5 Fig. 4 Then we decrease domain of the observation and focus our attention at the overlapped area of the Lepenski Vir village only. We chose a point on this overlapped white area and chose the date of the winter solstice (22. December) after which sunrise and other characteristic directions become created using programs (with an implicit notation of the latitude and longitude). All this is presented at figure 5. Fig. 5
6 Further we change previous satellite map by ground (street) map at which heights of the locations are relatively clearly denoted using isohypses (contours) method. Now overlapped Lepenski Vir village becomes immediately effectively unobservable but it becomes intermediately observable using endpoint of the sunrise line. Also we increase the domain of the observations and recognize unique hill Kukuvija (immediately beside Danube left riverside) behind of which Sun rises for Lepenski Vir observer at winter solstice (22. December). All this is presented at figures 6 and 7. Fig. 6
7 Fig. 7 By date change we can, using mentioned programs, do figures 8 and 9 at which we can recognize unique mountain or hill behind which Sun rises for Lepenski Vir observer at spring (21. March) and autumnal (23. September) equinox. Fig. 8
8 Fig. 9 Further, by date change, we can, using mentioned programs, do figures 10. and 11. which refer on the sunrise for Lepenski Vir observer at summer solstice (22. June). Quite obviously neither Treskavac nor any other mountain or hill top represents the place behind which sunrise occurs for Lepenski Vir observer at summer solstice. For the Lepenski Vir observer sunrise at summer solstice occurs behind a mountain ridge point roughly speaking northern in respect to Treskavac and with the same height as the Treskavac base.
9 Fig. 10 Fig. 11
10 Now we can, according to all previous figures , practically uniquely determine such locations nearly Lepenski Vir that can be used for the markers for the sunrise in winter solstice, spring equinox, summer solstice and autumnal equinox. These locations are marked at figure 12. (implicitly) and 13 (explicitly). Fig. 12
11 Fig. 13 SS (summer solstice sunrise point), SE and AE (spring and autumnal equinox sunrise point), WS (winter solstice sunrise point) Even if Treskavac does not represent any of previously noted markers, it, according to unambiguous archeological facts [1], [2] represents probably most significant mountain for the Lepenski Vir people. For this reason we shall analyze using mentioned programs, figures and date changes, time period when sunrise occurs immediately behind Treskavac. It occurs, relatively accurately (within applied method) speaking, between 20. April and 1. May in the spring figures 14 and 15 or between 15. August and 27. August in the autumn figures 16 and 17.
12 Fig. 14 Fig. 15
13 Fig. 16 Fig. 17
14 So, with an admitable error characteristic for our method, it can be stated that sunrise beside Treskavac occurs in the Spring period between last third of the April and few first days of the May. Even if it does not represent any characteristic time interval for motion of the Sun itself, it would satisfactorily correspond to the remarkable period of the heliacal rising of the Pleiades constellation. Namely, during this time interval Pleiades constellation appear above the Eastern horizon very shortly before sunrise, after which, for intensive Sun shine, they become effectively non-visible. W. Kyselka states: For the Celts of northern Europe (fifth to first centuries BC), the Pleiades rising with the sun marked Beltane, or May Day. Since star cannot be seen rising with the sun, the timing of Beltane implies they had an accurate calendar. [9], Moreover, since it is well-known that Pleiades constellation nearly winter solstice becomes observable just after dark it is quite possible that mountain Kukuvija represented for Lepenski Vir people an implicit marker for the Pleiades constellation too. Finally, Pleiades constellation represents such sky object that over whole planet attracts human attention, admiration and respect from the oldest cultural epoch in the Europe, i.e. paleolithic age (Lascaux cave painting etc.) to the present [10]. For this reason, no doubt, Pleiades constellation has been excellently known to mesolithic Lepenski Vir peoples too. But before any final conclusion we must analyze positions of the Pleiades constellation by an Lepenski Vir observer during time interval between 20. April and 1. May. It will be done using mentioned third and fourth program, 3. and 4. Using third program we shall now determine for Lepenski Vir observer (characterized with mentioned latitude, longitude, and URS 1 time zone) exact moment of the sunrise for some days in the time interval between 20. April and 1. May. This moment and all other mentioned necessary characteristics, we shall further introduce in the fourth program according to which we shall obtain figure of the simulated position of the Pleiades constellation, i.e. M45 sky object by sunrise. Obtained results are presented at figures
15 Fig. 18
16 Fig. 19
17 Fig. 20
18 Fig. 21
19 Fig. 22 As it is not hard to see at figure 18, Pleiades constellation appears at horizon simultaneously with sunrise at 20. April, while at later dates, figures 19 22, it appears somewhat later than sunrise. It practically means that Pleiades constellation becomes effectively unobservable in the same day when Sun becomes to rise exactly behind Treskavac in the Spring. (Before this day heliacal rising of the Pleiades occurs for Lepenski Vir observer.) All this represents a certainly determined event which would be used for a primitive but accurate calendar constitution. All this opens a very probable possibility according to which Lepenski Vir was really an ancient Sun and Pleiades constellation (proto) observatory too with Treskavac as a (natural) marker. 3. Conclusion In conclusion we can only repeat and point out the following. In this work we testify using simulation programs some old hypotheses according to which remarkable mesolithic village Lepenski Vir ( BC) at the right (nearly west) Danube riverside in the Iron gate in Serbia was an ancient (one of the oldest) Sun (proto) observatory. We use method recently suggested by A. C. Sparavigna, concretely we use at internet simply and freely available software or local Sun radiation direction simulation
20 and calculation computer programs. In this way we obtain and discuss figures of the sunrise in the Lepenski Vir during winter and summer solstice and spring and autumnal equinox in relation to position of the mountains, especially Treskavac (Trescovat in Romanian) and Kukuvija at left (nearly east) Danube riverside (in Romania). While mountain Kukuvija represents really the natural marker for the Sun in date of the winter solstice, mountain Treskavac, in despite to usual opinions, does not represent any real marker for the Sun in date of the summer solstice. Sun rises exactly behind Treskavac, relatively exactly (in the domain of used methods) speaking, between 20. April and 1. May. It more or less corresponds to year period when heliacal rising of the Pleiades constellation occurs, which by many ancient cultures, e.g. Celts of northern Europe, denotes very beginning of the year. Really, in common with some other facts obtained using at internet simply and freely available stellarium software or sky objects position simulation programs, we demonstrate that for the Lepenski Vir observer heliacal rising of the Pleiades ends exactly at 20. April and this observationally accurately determined event can be used for very beginning of the year. All this opens a very probable possibility according to which Lepenski Vir was really an ancient (one of the oldest) Sun and Pleiades constellation (proto)observatory too with Treskavac as a (natural) marker. References [1] D. Srejović, Lepenski Vir (nova praistorijska kultura u Podunavlju) (Srpska Književna Zadruga, Beograd, 1969) (in Serbian) [2] D. Srejović, Europe s first monumental sculpture: new discoveries at Lepenski Vir (New aspects of aniquity) (Stein and Day, New York, 1972) [3] D. Srejović, Lj. Babović, Umetnost Lepenskog Vira (Narodni Muzej, Beograd, 1983) (in Serbian) [4] D. Borić, The Lepenski Vir condurum: reinterpretation of the Mesolithic and Neolithic sequences in the Danube Georges, Antiquity 76 (2002) 1026 [5] Lj. Babović, Svetilišta Lepenskog Vira; mesto, položaj i funkcija (Narodni Muzej, Beograd, 2006) (in Serbian) [6] A. C. Sparavigna, The solar towers of Chankillo, arxiv: [physics.hist-ph] [7] A. C. Sparavigna, Stone circles on the harraat of Syrian desert, Archeoastronomy and ancient Technologies, 2 (2014), 1 ; arxiv: [physics.geo-ph] [8] A. C. Sparavigna, Arabia: from craters to stone circles, arxiv: [physics.geo-ph] [9] W. Kyselka, On the Rising of the Pleiades, The Hawaian Journal of History 27 (1993) 173 [10] A. Sparavigna, The celestial herd of ancient timekeepers, arxiv: [physics.hist-ph]
Stone circles on the harraat of Syrian desert
 Stone circles on the harraat of Syrian desert Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Department of Applied Science and Technology Politecnico di Torino, C.so Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, Italy Recently some stone
Stone circles on the harraat of Syrian desert Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Department of Applied Science and Technology Politecnico di Torino, C.so Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, Italy Recently some stone
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon. Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017
 Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Seasons. What causes the seasons?
 Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
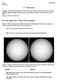
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Viewed from Earth's north pole, the rotation of Earth and its moon are counter-clockwise.!
 The Earth rotates around once in 24 hours The time it takes for the Earth to rotate completely around once is what we call a day. It's Earth's rotation that gives us night and day. Viewed from Earth's
The Earth rotates around once in 24 hours The time it takes for the Earth to rotate completely around once is what we call a day. It's Earth's rotation that gives us night and day. Viewed from Earth's
Introduction to the sky
 Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
The Celestial Sphere. Chapter 1. Constellations. Models and Science. Constellations. Diurnal vs. Annular Motion 9/16/2010
 The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018
 Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
FOR DISCUSSION TODAY: THE ANNUAL MOTION OF THE SUN
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #1 due today at end of class. HW #2 due next Thursday. Homework #1 question #1 and Homework #2 meridian slice questions will be discussed in the course of the lecture today. Observing
ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #1 due today at end of class. HW #2 due next Thursday. Homework #1 question #1 and Homework #2 meridian slice questions will be discussed in the course of the lecture today. Observing
A Warm Up Exercise. The Motion of the Sun. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise
 A Warm Up Exercise The Motion of the Sun Which of the following is NOT true of a circumpolar star? a) It rises and sets from my latitude b) Its direction can be far North c) Its direction can be far South
A Warm Up Exercise The Motion of the Sun Which of the following is NOT true of a circumpolar star? a) It rises and sets from my latitude b) Its direction can be far North c) Its direction can be far South
Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
1/3/12. Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System. Ancient Measurements. Earth s Size and Shape. Ancient Measurements. Ancient Measurements
 // Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
// Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why?
 (1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS
 UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
Objectives. Duration: one week
 Objectives At the conclusion of the lesson, students will be able to: 1. Analyze data to describe the motion of the sun including equinox and solstice paths in the sky for an Ancient Culture 2. Use alt-azimuth
Objectives At the conclusion of the lesson, students will be able to: 1. Analyze data to describe the motion of the sun including equinox and solstice paths in the sky for an Ancient Culture 2. Use alt-azimuth
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere
 AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere Name: Student number (SUID): Lab section: Group Members: 1 Introduction Following the prelab, you should be now acquainted
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere Name: Student number (SUID): Lab section: Group Members: 1 Introduction Following the prelab, you should be now acquainted
Today. Tropics & Arctics Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses. Ancient Astronomy. Lunar, Solar FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME
 Today Tropics & Arctics Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME Tropic: Latitude where the sun [just] reaches the zenith at noon on the summer
Today Tropics & Arctics Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME Tropic: Latitude where the sun [just] reaches the zenith at noon on the summer
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Reminder: Seasonal Motion
 Seasonal Motion Reminder: Seasonal Motion If you observe the sky at the same time, say midnight, but on a different date, you find that the celestial sphere has turned: different constellations are high
Seasonal Motion Reminder: Seasonal Motion If you observe the sky at the same time, say midnight, but on a different date, you find that the celestial sphere has turned: different constellations are high
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Today. Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses. Ancient Astronomy. Lunar, Solar FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME
 Today Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME Tropic: Latitude where the sun [just] reaches the zenith at noon on the summer
Today Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME Tropic: Latitude where the sun [just] reaches the zenith at noon on the summer
For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern
 632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
CELESTIAL COORDINATES
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
Today FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME. Phases of the Moon. Eclipses. Lunar, Solar. Ancient Astronomy
 Today FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy Tropic: Latitude where the sun [just] reaches the zenith at noon on the summer solstice Arctic/Antarctic Circle:
Today FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy Tropic: Latitude where the sun [just] reaches the zenith at noon on the summer solstice Arctic/Antarctic Circle:
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
Chapter 1 Image Slides. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 1 Image Slides Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH. 1: CYCLES OF THE SKY CO a 1.1 The Celestial Sphere CO b The nearest star to us is about
Chapter 1 Image Slides Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH. 1: CYCLES OF THE SKY CO a 1.1 The Celestial Sphere CO b The nearest star to us is about
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation. How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?
 Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Lecture #03. January 20, 2010, Wednesday
 Lecture #03 January 20, 2010, Wednesday Causes of Earth s Seasons Earth-Sun geometry Day length Solar angle (beam spread) Atmospheric beam depletion Shape and Size of the Earth North Pole E Geoid: not
Lecture #03 January 20, 2010, Wednesday Causes of Earth s Seasons Earth-Sun geometry Day length Solar angle (beam spread) Atmospheric beam depletion Shape and Size of the Earth North Pole E Geoid: not
Reasons for the seasons - Rebecca Kaplan
 Reasons for the seasons - Rebecca Kaplan https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dd_8jm5ptlk https://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/sunearth.html https://www.time.gov/ https://www.space.com/33790-harvest-moon-guide.html
Reasons for the seasons - Rebecca Kaplan https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dd_8jm5ptlk https://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/sunearth.html https://www.time.gov/ https://www.space.com/33790-harvest-moon-guide.html
2. Knowing the Heavens
 2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
Astronomy#2 - Notebook
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#2 - Notebook Planet Earth LEARNING TARGETS I can describe a sphere and give evidence used to prove Earth is spherical. I can explain the difference between rotation and revolution.
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#2 - Notebook Planet Earth LEARNING TARGETS I can describe a sphere and give evidence used to prove Earth is spherical. I can explain the difference between rotation and revolution.
Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4)
 Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Discovering the Night Sky
 Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky
 Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Constellations and Asterisms
 Constellations and Asterisms Constellations When ancient people looked at the sky they saw patterns and gave names to apparent groups of stars. Constellation patterns have been found on tablets over 4000
Constellations and Asterisms Constellations When ancient people looked at the sky they saw patterns and gave names to apparent groups of stars. Constellation patterns have been found on tablets over 4000
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008
 Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
12.1 Earth, Moon and Sun Interactions
 12.1 Earth, Moon and Sun Interactions Humans have been aware of the relationships between the Earth, Sun and Moon for thousands of years, but only recently have we began to better understand the true nature
12.1 Earth, Moon and Sun Interactions Humans have been aware of the relationships between the Earth, Sun and Moon for thousands of years, but only recently have we began to better understand the true nature
The following terms are some of the vocabulary that students should be familiar with in order to fully master this lesson.
 Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
STONEHENGE AS A SOLSTICE INDICATOR
 STONEHENGE AS A SOLSTICE INDICATOR One of the most impressive megalithic structures in the world is Stonehenge just north of Salisbury, England. I first visited the monument during my post-doctorate year
STONEHENGE AS A SOLSTICE INDICATOR One of the most impressive megalithic structures in the world is Stonehenge just north of Salisbury, England. I first visited the monument during my post-doctorate year
Phys Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations
 Phys 10293 Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations Introduction Astronomers use a coordinate system that is fixed to Earth s latitude and longitude. This way, the coordinates of a star or planet are the
Phys 10293 Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations Introduction Astronomers use a coordinate system that is fixed to Earth s latitude and longitude. This way, the coordinates of a star or planet are the
Motions of the Earth
 Motions of the Earth Our goals for learning: What are the main motions of the Earth in space? How do we see these motions on the ground? How does it affect our lives? How does the orientation of Earth's
Motions of the Earth Our goals for learning: What are the main motions of the Earth in space? How do we see these motions on the ground? How does it affect our lives? How does the orientation of Earth's
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy
 Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
Astronomy 11. No, this course isn t all about Star Wars
 Astronomy 11 No, this course isn t all about Star Wars Earth s Rotation How fast are people on the equator moving? s=d/t =circumference/24 hours =(40,000 km)/24 hours =1670 km/h That s Mach 1.4! What
Astronomy 11 No, this course isn t all about Star Wars Earth s Rotation How fast are people on the equator moving? s=d/t =circumference/24 hours =(40,000 km)/24 hours =1670 km/h That s Mach 1.4! What
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson
 Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010
 Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World
 Days & Nights 1 Name Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World Purpose: To investigate the number of hours of daylight received by countries at different latitudes. Materials: Daylight data sheet
Days & Nights 1 Name Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World Purpose: To investigate the number of hours of daylight received by countries at different latitudes. Materials: Daylight data sheet
Chapter 26 Section 1 pages Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe
 Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
Daily Motions. Daily Motions. Solar and Sidereal Days. Annual Motions of the Sun. Coordinate system on Earth. Annual Motion of the Stars.
 Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
Knowing the Heavens. Chapter Two. Guiding Questions. Naked-eye (unaided-eye) astronomy had an important place in ancient civilizations
 Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
A2 Principi di Astrofisica. Coordinate Celesti
 A2 Principi di Astrofisica Coordinate Celesti ESO La Silla Tel. 3.6m Celestial Sphere Our lack of depth perception when we look into space creates the illusion that Earth is surrounded by a celestial sphere.
A2 Principi di Astrofisica Coordinate Celesti ESO La Silla Tel. 3.6m Celestial Sphere Our lack of depth perception when we look into space creates the illusion that Earth is surrounded by a celestial sphere.
Chapter 3 The Science of Astronomy
 Chapter 3 The Science of Astronomy 3.1 The Ancient Roots of Science Our goals for learning: In what ways do all humans employ scientific thinking? How did astronomical observations benefit ancient societies?
Chapter 3 The Science of Astronomy 3.1 The Ancient Roots of Science Our goals for learning: In what ways do all humans employ scientific thinking? How did astronomical observations benefit ancient societies?
4.6 Stars. Star Patterns
 4.6 Stars Star Patterns If you have ever looked up at the night sky in winter, you probably would recognize the pattern of stars below. The Ancient Greeks named this pattern of stars Orion, after the giant
4.6 Stars Star Patterns If you have ever looked up at the night sky in winter, you probably would recognize the pattern of stars below. The Ancient Greeks named this pattern of stars Orion, after the giant
Earth-Sun Relationships. The Reasons for the Seasons
 Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Ancient astronomical observatories
 FUTURE OF THE PAST: ICTS Mini Workshop, Mangalore, 22-26, 2011 Ancient astronomical observatories Srikumar M. Menon Manipal University, Manipal Stonehenge Nilaskal The Fascinating Heavens the sky as a
FUTURE OF THE PAST: ICTS Mini Workshop, Mangalore, 22-26, 2011 Ancient astronomical observatories Srikumar M. Menon Manipal University, Manipal Stonehenge Nilaskal The Fascinating Heavens the sky as a
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
November 20, NOTES ES Rotation, Rev, Tilt.notebook. vertically. night. night. counterclockwise. counterclockwise. East. Foucault.
 NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME. a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system.
 UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
What causes the seasons? 2/11/09
 2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017
 Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Fundamentals of Satellite technology
 Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky
 Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Astronomy is the oldest science! Eclipses. In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Bad Omens? Comets
 Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Seasons Page 520. A. What Causes Seasons?
 Seasons Page 520 A. What Causes Seasons? 1. Seasons are caused by the tilt of the earth s axis as it moves around the sun. 2. Seasons happen because the Earth is tilted on its axis at a 23.5 angle. 3.
Seasons Page 520 A. What Causes Seasons? 1. Seasons are caused by the tilt of the earth s axis as it moves around the sun. 2. Seasons happen because the Earth is tilted on its axis at a 23.5 angle. 3.
Section 2. Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate.
 Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Chapter 2 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Discovering the Universe for Yourself Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Alien Skies. Todd Timberlake
 Alien Skies Todd Timberlake Have you ever wanted to send your students to another planet? What would they see while looking up at the skies from their new home? Would they be able to interpret what they
Alien Skies Todd Timberlake Have you ever wanted to send your students to another planet? What would they see while looking up at the skies from their new home? Would they be able to interpret what they
b. So at 12:00 p.m., are the shadows pointing in the direction you predicted? If they are not, you must explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
2.2 The Reason for Seasons
 2.2 The Reason for Seasons Our goals for learning: What causes the seasons? How does the orientation of Earth's axis change with time? Thought Question TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer
2.2 The Reason for Seasons Our goals for learning: What causes the seasons? How does the orientation of Earth's axis change with time? Thought Question TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Chapter S1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107
 Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107 planetariums around the world. Figure 4.4 Foucault s Pendulum. As Earth turns, the plane of oscillation of the Foucault pendulum shifts gradually so that over the course
Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107 planetariums around the world. Figure 4.4 Foucault s Pendulum. As Earth turns, the plane of oscillation of the Foucault pendulum shifts gradually so that over the course
Earth s Orbit. Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology
 1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
Coordinates on the Sphere
 Survey Observations Coordinates on the Sphere Any position on the surface of a sphere (such as the Earth or the night sky) can be expressed in terms of the angular coordinates latitude and longitude Latitude
Survey Observations Coordinates on the Sphere Any position on the surface of a sphere (such as the Earth or the night sky) can be expressed in terms of the angular coordinates latitude and longitude Latitude
THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM
 Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018
 Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
Observing the Universe for Yourself
 Observing the Universe for Yourself Figure 6-20 Solar-System Formation What does the universe look like from Earth? With the naked eye, we can see more than 2,000 stars as well as the Milky Way. A constellation
Observing the Universe for Yourself Figure 6-20 Solar-System Formation What does the universe look like from Earth? With the naked eye, we can see more than 2,000 stars as well as the Milky Way. A constellation
Astronomy Unit Notes Name:
 Astronomy Unit Notes Name: (DO NOT LOSE!) To help with the planets order 1 My = M 2 V = Venus 3 Eager = E 4 M = Mars 5 Just = J 6 Served = Saturn 7 Us = Uranus 8 N = N 1 Orbit: The path (usually elliptical)
Astronomy Unit Notes Name: (DO NOT LOSE!) To help with the planets order 1 My = M 2 V = Venus 3 Eager = E 4 M = Mars 5 Just = J 6 Served = Saturn 7 Us = Uranus 8 N = N 1 Orbit: The path (usually elliptical)
Unit 2. Cycles of the Sky
 Unit 2 Cycles of the Sky The Celestial Sphere Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Unit 2 Cycles of the Sky The Celestial Sphere Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 Name The Sun-Earth-Moon System Section 28.3 The Sun-Earth-Moon System Date Main Idea Details Read the title of Section 3. List three things that might be discussed in this section. 1. 2. 3. Review Vocabulary
Name The Sun-Earth-Moon System Section 28.3 The Sun-Earth-Moon System Date Main Idea Details Read the title of Section 3. List three things that might be discussed in this section. 1. 2. 3. Review Vocabulary
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY
 CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
C) wavelength C) eastern horizon B) the angle of insolation is high B) increases, only D) thermosphere D) receive low-angle insolation
 1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 1: Spring 2018 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 598
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Spring 2018 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 598 Examination date: 12 May 2018 Time limit: 50 min Time of
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Spring 2018 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 598 Examination date: 12 May 2018 Time limit: 50 min Time of
Downloaded from
 I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 chapter 311 section 1 Earth The Sun-Earth-Moon System Before You Read What do you already know about Earth s shape, its size, and how it moves? Write what you know on the lines below. What You ll Learn
chapter 311 section 1 Earth The Sun-Earth-Moon System Before You Read What do you already know about Earth s shape, its size, and how it moves? Write what you know on the lines below. What You ll Learn
Astronomy 291. Professor Bradley M. Peterson
 Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 4 EARTH, MOON, AND SKY PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 4 EARTH, MOON, AND SKY PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 4.1 Southern Summer. As captured with a fish-eye lens aboard the Atlantis Space Shuttle on December 9, 1993, Earth hangs above
ASTRONOMY Chapter 4 EARTH, MOON, AND SKY PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 4.1 Southern Summer. As captured with a fish-eye lens aboard the Atlantis Space Shuttle on December 9, 1993, Earth hangs above
3 - Celestial Sphere
 3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations
 LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
Contrast the old definition of constellation with the. State why we see different constellations during. Summarize what is meant by the Celestial
 Contrast the old definition of constellation with the astronomers definition of constellation State why we see different constellations during different times of the year. Summarize what is meant by the
Contrast the old definition of constellation with the astronomers definition of constellation State why we see different constellations during different times of the year. Summarize what is meant by the
