The Convective Boundary Layer
|
|
|
- Peregrine Barry Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Convective Boundary Layer and the PM Sounding In addition to the great service they offer to glider pilots, BLIPMAPS have given widespread currency to two key concepts in thermal soaring forecasts: The convective boundary layer, and the Forecast PM sounding. The two are interconnected. In the following discussion I will exemplify the defining properties of the convective boundary layer (BL), and argue that the use of forecast PM soundings, although seeming to elevate theory above practice in its reliance upon numerical models rather than balloon soundings, is often to be preferred over the traditional approach. I will also compare the PM sounding thermal forecast with the traditional AM balloon sounding forecast. This tutorial assumes a decent familiarity with thermodynamic diagrams ("SkewT's") and their use in predicting lift height and strength and cumulus cloudbase. In a separate tutorial I have presented more than enough material to allow anyone interested to develop the necessary familiarity. The Convective Boundary Layer The following sequence of soundings illustrates the evolution of the convective BL at the Allentown-Bethlehem-Easton airport on July 3, The sequence starts at 1000Z (6 AM local) and ends at 2100Z (5 PM local). The red lines are the forecast temperature, the blue the forecast dewpoint. The most of the figures reproduced with permission from the excellent and widely used FSL interactive site. 1
2 6:00am The 6:00 AM sounding shows a nocturnal inversion from the surface (~400 ft) to about 1,000 ft. Above this inversion, between about 2,000 ft and 4,000 ft lies a region with a dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) - this region is essentially unchanged from its state late in the previous day where it was created by that day's convection. The origin of the nocturnal inversion is night time radiative cooling of the earth's surface. A second inversion, of quite different origin is also apparent beginning at about 4,000 ft. This subsidence inversion will generally persist throughout the soaring day. 2
3 8:00am By 8 AM solar heating has begun to erode the nocturnal inversion and has forced the first 500 ft or so of the atmosphere to have a dry adiabatic lapse rate. 3
4 9:00am One hour later the nocturnal inversion has almost gone, and a super adiabatic layer exists at the surface. Soaring to about 2,000 ft would be possible, at least for soaring birds which can generally be seen a few hours after the sun begins to hit the ground slowly rising in the growing but still shallow convective BL. It is clear from the 8 AM sounding that the surface temperature will only need to rise to about 23 C at which point the nocturnal inversion will be completely gone and the lapse rate will be dry adiabatic in a convectively mixed BL about 4,000 feet thick. This particular temperature is what is, or should be, understood by "trigger temperature". I will have more to say about this when comparing the forecast PM sounding method with the traditional AM balloon sounding method. 4
5 11:00am The 11 AM sounding confirms that with a surface temperature of 20 C the soaring day should begin with lift to just less than 5,000 ft, the point at which the 23 C surface adiabat intersects the temperature lapse rate line. 5
6 2:00pm-5:00pm The 2 PM and 5 PM soundings show that as the surface temperature continues to increase the convective BL deepens eventually reaching a value of about 6,000 ft at 5 PM. Careful inspection of the superadiabatic layer at 2 PM and 5 PM reveals that by 5 PM the cycle is about to begin again: The shrinking superadiabatic layer will first disappear as insolation weakens to be followed shortly thereafter by radiative cooling and the establishment of another nocturnal inversion. Multi-Sounding Plots Superimposing the 6 AM, 8 AM, and 11 AM soundings in a single skewt diagram very clearly shows how, by 11 AM, (green line, 1500 UCT) the nocturnal inversion is eroded and trigger temperature is reached. Superimposition of the 11 AM, 2 PM and 5 PM soundings reveals something important which may not have been obvious from the individual soundings: Following trigger temperature the temperature lapse rate in the convective BL generally moves right as the day progresses. This of course is exactly what would be expected since warm air has been convectively transported aloft all day. Absent any other changes, this guarantees that the next day will need to be hotter to get the same kind of instability because the air aloft is already hotter before convection begins. Fortunately, it is often the case that a persistent flow of cooler and drier air sweeps away the warm air aloft allowing for another soarable day without too much in the way of higher surface temperatures. 6
7 7
8 The multi-sounding plots also reveal another basic attribute of the mixed BL: Surface moisture is transported aloft as the day progresses and accumulates at the base of the inversion. Inspection of the forecast soundings for this particular day suggests that it would have been blue, at least until late afternoon, but nonetheless, "dry" (i.e. blue) thermals would have transported moisture aloft. It can be seen that as soon as trigger temperature is reached the dewpoint aloft (green line) jumps to the right. Further convection increases the dewpoint aloft until, in the vicinity of the top of the BL, the temperature and the dewpoint start to converge. This is to be expected: The inversion traps the moisture can now only be removed by advection. Thermal Soaring Forecasting Using AM and PM Soundings AM Sounding Method I don't use this method, but many do. It is taught in all introductory texts and is the source of the Thermal Index (TI) concept. Understanding how AM soundings have been used in making thermal soaring forecasts is essential to understanding how and why the PM sounding method came to be used, and why that approach is now generally accepted to be superior. It should be noted that the distinction I am drawing is between AM and PM soundings - not RAOB (balloon) and model soundings. The AM sounding methodology 8
9 works just as well with model soundings. It works better when, as is generally the case, the nearest RAOB site is hundreds of miles away. The closest RAOB site to the center of my local soaring area (KABE) is KOKX (Brookhaven) about 100 miles East. Next closest is KIAD (Dulles), about 150 miles SW followed by KPIT ( Pittsburgh) 250 miles West. The distances and locations of these sites exemplify the first problem in relying upon RAOB data: It's generally not available from a site close enough to be useful on most days. This problem at least is rather easily fixed: Just use a 12Z forecast sounding from one of many numerical models. Because these models have so many grid points it is always possible to generate a sounding close to the home airport (or anywhere else for that matter, such as at task turnpoints). An interesting example of the use of a forecast AM sounding is Day 5 (Aug 8) of the M Nationals held at Uvalde. This was a day when the winner flew over 350 miles at about 86 mph - strong conditions clearly. The starting point for producing a thermal soaring forecast using the AM sounding method is of course the AM sounding. The next step is to estimate the surface temperature for the forecast time and to construct the surface adiabat for that temperature. The (almost) straight red line to the right of the temperature lapse rate line is the 35 C surface adiabat. The sounding, and the surface adiabat can now be used to make the forecast: At some point, about 8,500 feet in this case, the surface adiabat intersects the temperature lapse rate and (assuming no cloud flying) this intersection represents the maximum height for the day. The next step is to determine whether or not cumulus cloud will form, and if so at what height. That too is easily done by constructing the mixing 9
10 ratio line passing through the surface dewpoint. If that line intersects the 35 C surface adiabat then cumulus cloud will form at the altitude corresponding to the intersection. If there is no intersection there will be no cu. On this day cu are indicated at about 7,000 ft marked "CCL". The morning sounding also predicts a "trigger temperature" (blue line). This temperature cannot be defined without answering two questions - "for what height, and for what thermal index?" In the US at least the height is 3,000 ft agl and the TI is 3 F degrees. Underlying the choice of these values are the assumptions that for cross country soaring it's nice to be at 3,000 ft, and that to have sufficient instability to climb at all the air in a thermal needs to be 3 F degrees warmer than its surroundings. The (3,000 ft) trigger temperature is found by constructing an adiabat which at 3,000 ft agl is 3 F to the right of the environmental temperature lapse rate. That temperature is about 29.5 C. The term "trigger" implies a tipping point. Nothing about the AM sounding suggests such a point. On the other hand, inspection of the forecast sounding sequence for ABE on a typical soarable day does suggest an obvious tipping point: The completion of the erosion of the nocturnal inversion. When that happens there is a sharp discontinuity in the depth of the mixed layer. It remains only to determine the strength of the lift for an assumed surface temperature and this is where one of the limitations of the method becomes clear: Very large TI's are indicated for the lower levels, up to about 4,500 ft. A fundamental problem with 10
11 analyzing an AM sounding in this manner is that we know full well that the temperature lapse rate which will prevail at 2 PM is quite different. This means that the TI values, especially those in the first few thousand feet are meaningless. Lacking a PM lapse rate it simply is not possible to assign an average TI, or for that matter to pick a representative altitude. An additional problem, well illustrated in this example, is the sensitivity of the predicted lift height to changes in surface temperature. A one degree shift would change to BL depth by hundreds of feet. Anyone who has tried to even a few thermal soaring forecasts will appreciate that errors of 5 degrees (C!), let alone 1 degree, are all too common. Let's take a look at the 18z forecast sounding for the day. Now the TI values from the surface to the CCL have the meaning we want them to have: The difference, at a chosen height, between the environmental lapse rate and the surface adiabat. That difference averages to about 3 C (~5.5 F) from 1,000 ft to 7,000 ft. I seldom see those kind of numbers here in SE Pa, but then we seldom see Uvalde conditions. The forecast sounding based prediction of BL depth is much less sensitive to changes in the surface temperature: Were that temperature to be higher, the temperature profile of the mixed BL would shift right, lower, it would shift left. In neither case would there be a large change in the thickness of the mixed layer. Summary The convective boundary layer and the PM forecast sounding methodology are commutative. The PM sounding defines and quantifies the convectively mixed layer to 11
12 which thermal soaring is necessarily confined. The convective mixing creates the lapse rates which define the sounding. The forecast sounding presents the fullest and most accurate picture of the potential thermal soaring conditions. It forecasts the conditions expected to prevail at the time soaring will take place and it does so in a manner which makes its predictions less sensitive to errors in the forecast surface temperature. 12
Michael F. Stringfellow
 Michael F. Stringfellow Thermals Columns or bubbles of warm air that rise from the ground when it is heated by the sun Soaring Sustained engineless flight using natural sources of lift Boundary or mixing
Michael F. Stringfellow Thermals Columns or bubbles of warm air that rise from the ground when it is heated by the sun Soaring Sustained engineless flight using natural sources of lift Boundary or mixing
PRACTICAL INTERPRETATION OF RASP SOUNDINGS. Jean Oberson, February 2010.
 PRACTICAL INTERPRETATION OF RASP SOUNDINGS Jean Oberson, www.soaringmeteo.ch, February 2010. Emagram (better referred to SkewT thermodynamic diagram) is actually a simple xy graph. The x axis represents
PRACTICAL INTERPRETATION OF RASP SOUNDINGS Jean Oberson, www.soaringmeteo.ch, February 2010. Emagram (better referred to SkewT thermodynamic diagram) is actually a simple xy graph. The x axis represents
A Case Study on Diurnal Boundary Layer Evolution
 UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA A Case Study on Diurnal Boundary Layer Evolution Meteorological Measurement Systems Fall 2010 Jason Godwin 12/9/2010 Lab partners: Sam Irons, Charles Kuster, Nathan New, and Stefan
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA A Case Study on Diurnal Boundary Layer Evolution Meteorological Measurement Systems Fall 2010 Jason Godwin 12/9/2010 Lab partners: Sam Irons, Charles Kuster, Nathan New, and Stefan
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
Chapter 5. Atmospheric Moisture
 Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
24: Monthly Report September Seeding Operations & Atmospheric Research (SOAR) Snapshot of Seeding Operations
 0.3.05 Monthly Report September 05 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker Snapshot of Seeding Operations Date Flight Time (hours) Number of Flares (total) September 0:04
0.3.05 Monthly Report September 05 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker Snapshot of Seeding Operations Date Flight Time (hours) Number of Flares (total) September 0:04
An on-line glider pilot self-briefing system
 Background An on-line glider pilot self-briefing system Edward (Ward) Hindman The City College of New York, New York NY USA hindman@sci.ccny.cuny.edu Presented at the Soaring Society of America Convention,
Background An on-line glider pilot self-briefing system Edward (Ward) Hindman The City College of New York, New York NY USA hindman@sci.ccny.cuny.edu Presented at the Soaring Society of America Convention,
Traffic and Weather. Soaring Safety Foundation. Tom Johnson CFIG
 Traffic and Weather Soaring Safety Foundation Tom Johnson CFIG Weather Contents Weather Gathering Sources Weather Acquisition Enroute Weather Analysis Weather Hazards Weather in the Landing Pattern Basic
Traffic and Weather Soaring Safety Foundation Tom Johnson CFIG Weather Contents Weather Gathering Sources Weather Acquisition Enroute Weather Analysis Weather Hazards Weather in the Landing Pattern Basic
Interpreting Skew-Ts (Part Three)
 Interpreting Skew-Ts (Part Three) Understanding Skew-Ts and some of the information previously presented now allows us to learn a few more things. Have you ever noticed that storms have a tendancy to favour
Interpreting Skew-Ts (Part Three) Understanding Skew-Ts and some of the information previously presented now allows us to learn a few more things. Have you ever noticed that storms have a tendancy to favour
Cloud Photography Flow Visualization
 Cloud Photography Flow Visualization Presented for: Professor Jean Hertzberg On: February 24, 2009 By: James Kostrzewa The purpose of this assignment is to display the behavior of clouds according to the
Cloud Photography Flow Visualization Presented for: Professor Jean Hertzberg On: February 24, 2009 By: James Kostrzewa The purpose of this assignment is to display the behavior of clouds according to the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997
 Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Air Mass. 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types
 Air Mass 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types A. Continental-relatively dry air masses that form over land. B. Maritime: relatively humid air masses
Air Mass 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types A. Continental-relatively dry air masses that form over land. B. Maritime: relatively humid air masses
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox
 Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
International Conference on Climate Change natural greenhouse effect radiative transfer model
 One of the points that Dr. Richard Lindzen made during his keynote speech at the 2nd International Conference on Climate Change, held in New York City March 8-10 this year, is that we global warming skeptics
One of the points that Dr. Richard Lindzen made during his keynote speech at the 2nd International Conference on Climate Change, held in New York City March 8-10 this year, is that we global warming skeptics
P1.26 A METEOROLOGICAL SYSTEM FOR PLANNING AND EVALUATING GLIDER FLIGHTS IN PENNSYLVANIA USA
 P1.26 A METEOROLOGICAL SYSTEM FOR PLANNING AND EVALUATING GLIDER FLIGHTS IN PENNSYLVANIA USA Edward Hindman* The City College of New York, New York City USA 10031 Stephen Saleeby Colorado State University,
P1.26 A METEOROLOGICAL SYSTEM FOR PLANNING AND EVALUATING GLIDER FLIGHTS IN PENNSYLVANIA USA Edward Hindman* The City College of New York, New York City USA 10031 Stephen Saleeby Colorado State University,
Meteorology Unit Study Guide
 Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
2.1 Temporal evolution
 15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
Your Task: Read each slide then use the underlined red or underlined information to fill in your organizer.
 Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
The Transfer of Heat
 The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
1. Static Stability. (ρ V ) d2 z (1) d 2 z. = g (2) = g (3) T T = g T (4)
 NCAR (National Center for Atmospheric Research) has an excellent resource for education called COMET-MetEd. There you can find some really great tutorials on SkewT-LogP plots: visit http://www.meted.ucar.edu/mesoprim/skewt/index.htm.
NCAR (National Center for Atmospheric Research) has an excellent resource for education called COMET-MetEd. There you can find some really great tutorials on SkewT-LogP plots: visit http://www.meted.ucar.edu/mesoprim/skewt/index.htm.
Numerical Example An air parcel with mass of 1 kg rises adiabatically from sea level to an altitude of 3 km. What is its temperature change?
 Numerical Example An air parcel with mass of 1 kg rises adiabatically from sea level to an altitude of 3 km. What is its temperature change? From the 1 st law, T = -g/c p z + Q/m air /c p Here, Q = 0,
Numerical Example An air parcel with mass of 1 kg rises adiabatically from sea level to an altitude of 3 km. What is its temperature change? From the 1 st law, T = -g/c p z + Q/m air /c p Here, Q = 0,
TFS WEATHER BRIEF. Monday, March 25
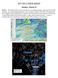 TFS WEATHER BRIEF Monday, March 25 Review: The leading edge of cooler and drier air was pushing through Central and East TX this morning. A few lingering thunderstorms were in progress south of I-20 in
TFS WEATHER BRIEF Monday, March 25 Review: The leading edge of cooler and drier air was pushing through Central and East TX this morning. A few lingering thunderstorms were in progress south of I-20 in
ANSWER KEY. Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map. Lab 12 Answer Key. Explorations in Meteorology 54
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points
 ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) 2. (5 points) Explain
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) 2. (5 points) Explain
Glider Flying Handbook FAA-H ADDENDUM December 1, 2003
 Glider Flying Handbook FAA-H-8083-13 ADDENDUM December 1, 2003 The Airman Testing Standards Branch (AFS-630) is responsible for the development and publication of the Glider Flying Handbook. We would like
Glider Flying Handbook FAA-H-8083-13 ADDENDUM December 1, 2003 The Airman Testing Standards Branch (AFS-630) is responsible for the development and publication of the Glider Flying Handbook. We would like
1st Annual Southwest Ohio Snow Conference April 8, 2010 Abner F. Johnson, Office of Maintenance - RWIS Coordinator
 1st Annual Southwest Ohio Snow Conference April 8, 2010 Abner F. Johnson, Office of Maintenance - RWIS Coordinator The Ohio Department of Transportation ODOT has approximately 5500 full-time employees
1st Annual Southwest Ohio Snow Conference April 8, 2010 Abner F. Johnson, Office of Maintenance - RWIS Coordinator The Ohio Department of Transportation ODOT has approximately 5500 full-time employees
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #1 Page 1 of 7
 1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
Water in the Atmosphere Understanding Weather and Climate
 Water in the Atmosphere Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 1 Cloud Development and Forms Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 2 Learning Objectives 1. The various atmospheric lifting mechanisms
Water in the Atmosphere Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 1 Cloud Development and Forms Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 2 Learning Objectives 1. The various atmospheric lifting mechanisms
6 Swimming with sharks. 9 Reading a Skew-T log(p) 14 Hold however you want. 21 Staying out of the wake
 Volume 24 Number 3 March 2008 The Magazine for the Accomplished Pilot 6 Swimming with sharks Sharpen your skills in the heart of the fastest-paced IFR around. Just be sure to bring a co-pilot and a checkbook.
Volume 24 Number 3 March 2008 The Magazine for the Accomplished Pilot 6 Swimming with sharks Sharpen your skills in the heart of the fastest-paced IFR around. Just be sure to bring a co-pilot and a checkbook.
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
MODULE 4.3A SHORT-RANGE FORECASTING OF WEATHER ELEMENTS. Temperature
 MODULE 4.3A SHORT-RANGE FORECASTING OF WEATHER ELEMENTS Temperature Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 1. INTRODUCTION 2 2. SITE/PROCESS APPROACH: 2 3. TRAJECTORY/PROCESS APPROACH: 2 4. PATTERN/PROCESS
MODULE 4.3A SHORT-RANGE FORECASTING OF WEATHER ELEMENTS Temperature Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 1. INTRODUCTION 2 2. SITE/PROCESS APPROACH: 2 3. TRAJECTORY/PROCESS APPROACH: 2 4. PATTERN/PROCESS
The enduring fog and low cloud episode of 5-10 December 2015: Big Bubble Fog Trouble
 1. Overview The enduring fog and low cloud episode of 5-10 December 2015: Big Bubble Fog Trouble By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA An enduring low cloud and fog episode affected
1. Overview The enduring fog and low cloud episode of 5-10 December 2015: Big Bubble Fog Trouble By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA An enduring low cloud and fog episode affected
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1
 Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
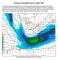 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology
 S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
Contents. Section 1: Climate Factors. Section 2: Climate Types. Section 3: Climate Effects
 Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
MET Lecture 34 Downbursts
 MET 4300 Lecture 34 Downbursts Downbursts A strong downdraft that originates within the lower part of a cumulus cloud or thunderstorms and spreads out at the surface Downbursts do not require strong thunderstorms
MET 4300 Lecture 34 Downbursts Downbursts A strong downdraft that originates within the lower part of a cumulus cloud or thunderstorms and spreads out at the surface Downbursts do not require strong thunderstorms
P1.16 ADIABATIC LAPSE RATES IN TORNADIC ENVIRONMENTS
 P1.16 ADIABATIC LAPSE RATES IN TORNADIC ENVIRONMENTS Matthew D. Parker Convective Storms Group, The Mesoscale Nexus in Atmospheric Sciences North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.16 ADIABATIC LAPSE RATES IN TORNADIC ENVIRONMENTS Matthew D. Parker Convective Storms Group, The Mesoscale Nexus in Atmospheric Sciences North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION
Hurricanes. Where's the Really Bad Weather 1. What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide
 Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Predicting Contrails Using an Appleman Chart [Student]
![Predicting Contrails Using an Appleman Chart [Student] Predicting Contrails Using an Appleman Chart [Student]](/thumbs/75/71655769.jpg) Page 1 of 13 Predicting Contrails Using an Appleman Chart [Student] Background: Military planners have been interested in condensation trail (contrail) forecasts since World War II. Contrails can make
Page 1 of 13 Predicting Contrails Using an Appleman Chart [Student] Background: Military planners have been interested in condensation trail (contrail) forecasts since World War II. Contrails can make
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points
 ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) The equation to
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) The equation to
Flight Report Sunday September 21, 2014 Summary
 Flight Report Sunday September 21, 2014 Summary 1 Flight Report: G1 Flight#10 & HALO AC14 1.1 Flight Strategy 2 1.2 Weather Conditions Before the Flight...3 1.3 Weather Conditions During the Flight...6
Flight Report Sunday September 21, 2014 Summary 1 Flight Report: G1 Flight#10 & HALO AC14 1.1 Flight Strategy 2 1.2 Weather Conditions Before the Flight...3 1.3 Weather Conditions During the Flight...6
1 in = ft (round answer to nearest integer)
 Hydrology LAB 1: DRAINAGE-BASIN PROPERTIES AND SIMPLE METEOROLOGIC CALCULATIONS OBJECTIVES: a. to develop your ability to extract basic drainage-basin data from topographic maps b. to learn how to make
Hydrology LAB 1: DRAINAGE-BASIN PROPERTIES AND SIMPLE METEOROLOGIC CALCULATIONS OBJECTIVES: a. to develop your ability to extract basic drainage-basin data from topographic maps b. to learn how to make
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy
 Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena
 The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
ESS55: EARTH S ATMOSPHERE / Homework #6 / (due 5/24/2018)
 ESS55: EARTH S ATMOSPHERE / Homework #6 / (due 5/24/2018) Name Student ID: 1) 21) 41) 2) 22) 42) 3) 23) 43) 4) 24) 44) 5) 25) 45) 6) 26) 46) 7) 27) 47) 8) 28) 48) 9) 29) 49) 10) 30) 50) 11) 31) 51) 12)
ESS55: EARTH S ATMOSPHERE / Homework #6 / (due 5/24/2018) Name Student ID: 1) 21) 41) 2) 22) 42) 3) 23) 43) 4) 24) 44) 5) 25) 45) 6) 26) 46) 7) 27) 47) 8) 28) 48) 9) 29) 49) 10) 30) 50) 11) 31) 51) 12)
P2.11 THE LAKE SHADOW EFFECT OF LAKE BREEZE CIRCULATIONS AND RECENT EXAMPLES FROM GOES VISIBLE SATELLITE IMAGERY. Frank S. Dempsey
 P2.11 THE LAKE SHADOW EFFECT OF LAKE BREEZE CIRCULATIONS AND RECENT EXAMPLES FROM GOES VISIBLE SATELLITE IMAGERY Frank S. Dempsey 1. ABSTRACT The lake shadow effect is a component of the lake breeze circulation
P2.11 THE LAKE SHADOW EFFECT OF LAKE BREEZE CIRCULATIONS AND RECENT EXAMPLES FROM GOES VISIBLE SATELLITE IMAGERY Frank S. Dempsey 1. ABSTRACT The lake shadow effect is a component of the lake breeze circulation
Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams
 Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams Have a think about a few things I m going to throw to you it will hopefully make you think a little outside the square! - LIs of -15 can give you clear skies - LIs of 0
Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams Have a think about a few things I m going to throw to you it will hopefully make you think a little outside the square! - LIs of -15 can give you clear skies - LIs of 0
WO2 ROZSA-HRABINSKI METEOROLOGY 1
 WO2 ROZSA-HRABINSKI METEOROLOGY 1 INTRODUCTION What are we covering today? The Atmosphere Clouds Atmospheric Stability Temperature and Humidity THE ATMOSPHERE THE ATMOSPHERE The atmosphere is composed
WO2 ROZSA-HRABINSKI METEOROLOGY 1 INTRODUCTION What are we covering today? The Atmosphere Clouds Atmospheric Stability Temperature and Humidity THE ATMOSPHERE THE ATMOSPHERE The atmosphere is composed
Climate vs. Weather. Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Climate: The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
 Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
Weather Systems Study Guide:
 Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties
 Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties For Further Reading Most information contained within these lecture notes is drawn from Chapters 1, 2, 4, and 6 of The Use of the Skew
Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties For Further Reading Most information contained within these lecture notes is drawn from Chapters 1, 2, 4, and 6 of The Use of the Skew
Thundersnow. flightops. Difficult to forecast and rare, but a real threat to landing or low-altitude aircraft. By Ed Brotak
 Thundersnow Difficult to forecast and rare, but a real threat to landing or low-altitude aircraft. By Ed Brotak 18 flight safety foundation AeroSafetyWorld October 2010 flightops Mike Tigas/Flickr It was
Thundersnow Difficult to forecast and rare, but a real threat to landing or low-altitude aircraft. By Ed Brotak 18 flight safety foundation AeroSafetyWorld October 2010 flightops Mike Tigas/Flickr It was
Lecture 12. The diurnal cycle and the nocturnal BL
 Lecture 12. The diurnal cycle and the nocturnal BL Over flat land, under clear skies and with weak thermal advection, the atmospheric boundary layer undergoes a pronounced diurnal cycle. A schematic and
Lecture 12. The diurnal cycle and the nocturnal BL Over flat land, under clear skies and with weak thermal advection, the atmospheric boundary layer undergoes a pronounced diurnal cycle. A schematic and
Fronts in November 1998 Storm
 Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
The Ice Crystal Weather Threat to Engines
 Jeanne Mason Boeing Commercial Airplanes The Ice Crystal Weather Threat to Engines BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Filename.ppt 1 Agenda Introduction Recognition of engine power-loss
Jeanne Mason Boeing Commercial Airplanes The Ice Crystal Weather Threat to Engines BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Filename.ppt 1 Agenda Introduction Recognition of engine power-loss
Water in the Atmosphere The Role of Water in Earth s Surface Processes. Hurricane Warning
 Hurricane Warning 1 Earth, the lue Planet. What makes Earth blue? It has to do with all of the water on Earth. There is water in more places than the vast oceans. Water is also in the atmosphere. High
Hurricane Warning 1 Earth, the lue Planet. What makes Earth blue? It has to do with all of the water on Earth. There is water in more places than the vast oceans. Water is also in the atmosphere. High
Lecture 3: Light and Temperature
 Lecture 3: Light and Temperature terrestrial radiative cooling Solar radiative warming (Light) Global Temperature atmosphere ocean land Light Temperature Different forms of energy Energy conservation energy,
Lecture 3: Light and Temperature terrestrial radiative cooling Solar radiative warming (Light) Global Temperature atmosphere ocean land Light Temperature Different forms of energy Energy conservation energy,
Elements of the National Weather Service Fire Weather Forecast By Casey Sullivan, National Weather Service, Chicago
 Elements of the National Weather Service Fire Weather Forecast By Casey Sullivan, National Weather Service, Chicago Today s Presentation Begins at 12 pm CST, 1 pm EST Please Take Our One Question Survey
Elements of the National Weather Service Fire Weather Forecast By Casey Sullivan, National Weather Service, Chicago Today s Presentation Begins at 12 pm CST, 1 pm EST Please Take Our One Question Survey
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection
 Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Empirical thunderstorm forecasting techniques Contents Necessary conditions for convection: Instability Low-level moisture Trigger mechanism Forecasting
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Empirical thunderstorm forecasting techniques Contents Necessary conditions for convection: Instability Low-level moisture Trigger mechanism Forecasting
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts
 Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR TEST NUMBER IS THE 5-DIGIT NUMBER AT THE TOP OF EACH PAGE.
 Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 Name (print, last rst): 1st Midterm Exam Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR TEST
Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 Name (print, last rst): 1st Midterm Exam Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR TEST
AMDAR Forecast Applications. Richard Mamrosh NWS Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA
 AMDAR Forecast Applications Richard Mamrosh NWS Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA AMDAR has many applications Aviation Low level wind shear Ceilings and visibilities Icing and turbulence Winter Storms Precipitation
AMDAR Forecast Applications Richard Mamrosh NWS Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA AMDAR has many applications Aviation Low level wind shear Ceilings and visibilities Icing and turbulence Winter Storms Precipitation
Understanding Inversions and Weather Conditions
 Understanding Inversions and Weather Conditions Inversion & Drift Mitigation Workshop April 10, 2018 Aaron Wilson OSU Extension Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center State Climate Office of Ohio OSU Extension
Understanding Inversions and Weather Conditions Inversion & Drift Mitigation Workshop April 10, 2018 Aaron Wilson OSU Extension Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center State Climate Office of Ohio OSU Extension
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Road Weather: Pavement Forecasting
 Road Weather: Pavement Forecasting By Jon Tarleton Marketing Development Manager Meteorologist Surface Systems, Inc. (SSI ) QTT Quixote Transportation Technologies 314-872-0509 jdt@surface.com 2006 APWA
Road Weather: Pavement Forecasting By Jon Tarleton Marketing Development Manager Meteorologist Surface Systems, Inc. (SSI ) QTT Quixote Transportation Technologies 314-872-0509 jdt@surface.com 2006 APWA
Practical Atmospheric Analysis
 Chapter 12 Practical Atmospheric Analysis With the ready availability of computer forecast models and statistical forecast data, it is very easy to prepare a forecast without ever looking at actual observations,
Chapter 12 Practical Atmospheric Analysis With the ready availability of computer forecast models and statistical forecast data, it is very easy to prepare a forecast without ever looking at actual observations,
Name: Section/TA Name: Atmospheric Science 101, Spring 2003 Midterm 2 Thursday 22 May 2003 Version A
 Name: Section/TA Name: Atmospheric Science 101, Spring 2003 Midterm 2 Thursday 22 May 2003 Version A Multiple Choice (2 points each) Choose the best answer and mark it on a Scantron sheet. 1. Choose the
Name: Section/TA Name: Atmospheric Science 101, Spring 2003 Midterm 2 Thursday 22 May 2003 Version A Multiple Choice (2 points each) Choose the best answer and mark it on a Scantron sheet. 1. Choose the
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES
 HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology. Lecture 8: September 16, AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2)
 MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
Monteverdi Metr 201 Quiz #4 100 pts.
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES Name San Francisco State University April 27, 2012 Monteverdi Metr 201 Quiz #4 100 pts. A. Definitions. (5 points each for a total of 25 points in this section). (a) Convective
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES Name San Francisco State University April 27, 2012 Monteverdi Metr 201 Quiz #4 100 pts. A. Definitions. (5 points each for a total of 25 points in this section). (a) Convective
Advanced Spotter Training Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms
 Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms From Last Time We discussed the different ways to make air rise. We discussed convection, convergence, and the different kinds of fronts.
Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms From Last Time We discussed the different ways to make air rise. We discussed convection, convergence, and the different kinds of fronts.
XC Meteorology. And other bullshit
 XC Meteorology And other bullshit (c) Jim White 2014 Why do Met? Choose whether to turn up Choose best task for day Choose glider configuration Choose pilot configuration! Avoid being in wrong place Achieve
XC Meteorology And other bullshit (c) Jim White 2014 Why do Met? Choose whether to turn up Choose best task for day Choose glider configuration Choose pilot configuration! Avoid being in wrong place Achieve
DRYLINE MAGIC by Tim Marshall (published in Weatherwise Magazine in 1992)
 DRYLINE MAGIC by Tim Marshall (published in Weatherwise Magazine in 1992) Every spring, veteran storm chasers head to West Texas to catch a weather show they call "dryline magic". The dryline is a boundary
DRYLINE MAGIC by Tim Marshall (published in Weatherwise Magazine in 1992) Every spring, veteran storm chasers head to West Texas to catch a weather show they call "dryline magic". The dryline is a boundary
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Week: Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules)
 NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules) Certain physical laws of motion and conservation of energy (for example, Newton's Second Law of Motion and the First Law of Thermodynamics) govern
NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules) Certain physical laws of motion and conservation of energy (for example, Newton's Second Law of Motion and the First Law of Thermodynamics) govern
Warming Earth and its Atmosphere The Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles
 Warming Earth and its Atmosphere The Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles Or, what happens to the energy received from the sun? First We Need to Understand The Ways in Which Heat Can be Transferred in the Atmosphere
Warming Earth and its Atmosphere The Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles Or, what happens to the energy received from the sun? First We Need to Understand The Ways in Which Heat Can be Transferred in the Atmosphere
Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017
 Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A cluster of thunderstorms developed in eastern Ohio around 1800 UTC on 19
Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A cluster of thunderstorms developed in eastern Ohio around 1800 UTC on 19
The Causes of Weather
 Meteorology The Causes of Weather Where does the weather in our country come from? * Which air masses determine the weather in our country? * Weather or Climate? *The current state of the atmosphere *
Meteorology The Causes of Weather Where does the weather in our country come from? * Which air masses determine the weather in our country? * Weather or Climate? *The current state of the atmosphere *
07/16/02. Obs: Two strong cells near Miami Anvils blowing toward western ground site Will try E-W legs as far east as we can get FC:
 07/16/02 Obs: Report: Two strong cells near Miami Anvils blowing toward western ground site Will try E-W legs as far east as we can get FC: Summary: Aircraft: Convection should develop mid-afternoon along
07/16/02 Obs: Report: Two strong cells near Miami Anvils blowing toward western ground site Will try E-W legs as far east as we can get FC: Summary: Aircraft: Convection should develop mid-afternoon along
Introduction to Forecasting Severe Thunderstorms
 Introduction to Forecasting Severe Thunderstorms Ok, we've baked our cake (made a thunderstorm) using some instability and a trigger. Not only that, we know what some of the ingredients actually mean.
Introduction to Forecasting Severe Thunderstorms Ok, we've baked our cake (made a thunderstorm) using some instability and a trigger. Not only that, we know what some of the ingredients actually mean.
ATMOSPHERIC ENERGY and GLOBAL TEMPERATURES. Physical Geography (Geog. 300) Prof. Hugh Howard American River College
 ATMOSPHERIC ENERGY and GLOBAL TEMPERATURES Physical Geography (Geog. 300) Prof. Hugh Howard American River College RADIATION FROM the SUN SOLAR RADIATION Primarily shortwave (UV-SIR) Insolation Incoming
ATMOSPHERIC ENERGY and GLOBAL TEMPERATURES Physical Geography (Geog. 300) Prof. Hugh Howard American River College RADIATION FROM the SUN SOLAR RADIATION Primarily shortwave (UV-SIR) Insolation Incoming
Wildfire Operations Research
 Wildfire Operations Research 2016 Environmental Lapse Rate Project Findings Greg Baxter, Jim Thomasson March 2016 Objective of Winter Work The objective of the work this winter was to determine if data
Wildfire Operations Research 2016 Environmental Lapse Rate Project Findings Greg Baxter, Jim Thomasson March 2016 Objective of Winter Work The objective of the work this winter was to determine if data
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
PREDICTING THE WEATHER
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) PREDICTING THE WEATHER How well does your local weatherman do in predicting the weather? Is he or she more accurate for the next day or for a week in the future? Why do you think that
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) PREDICTING THE WEATHER How well does your local weatherman do in predicting the weather? Is he or she more accurate for the next day or for a week in the future? Why do you think that
SENSOR PLACEMENT FOR SNOW & ICE MELT APPLICATIONS
 networketi.com SENSOR PLACEMENT FOR SNOW & ICE MELT APPLICATIONS By: Dave Mays A great number of service calls come in with the common problem of the heaters not coming on even though it is snowing outside
networketi.com SENSOR PLACEMENT FOR SNOW & ICE MELT APPLICATIONS By: Dave Mays A great number of service calls come in with the common problem of the heaters not coming on even though it is snowing outside
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology. Thunderstorms
 1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
THE type of sounding that is characteristic
 VOL. 39, No. 4, APRIL, 1958 195 Tornado Proximity Soundings ROBERT G. BEEBE U. S. Weather Bureau, Kansas City, Missouri (Manuscript received 12 March 1957) ABSTRACT Soundings near the time and site of
VOL. 39, No. 4, APRIL, 1958 195 Tornado Proximity Soundings ROBERT G. BEEBE U. S. Weather Bureau, Kansas City, Missouri (Manuscript received 12 March 1957) ABSTRACT Soundings near the time and site of
Using Temperature and Dew Point to Aid Forecasting Springtime Radiational Frost and/or Freezing Temperatures in the NWS La Crosse Service Area
 Using Temperature and Dew Point to Aid Forecasting Springtime Radiational Frost and/or Freezing Temperatures in the NWS La Crosse Service Area WFO La Crosse Climatology Series #21 The formation of radiational
Using Temperature and Dew Point to Aid Forecasting Springtime Radiational Frost and/or Freezing Temperatures in the NWS La Crosse Service Area WFO La Crosse Climatology Series #21 The formation of radiational
Chapter 9 Atmosphere Study Guide
 Science Chapter 9 Atmosphere Study Guide Name Due 1. What is the definition for: a. Conduction: The transfer of thermal energy by collisions between particles in matter. (Heats air close to Earth s surface)
Science Chapter 9 Atmosphere Study Guide Name Due 1. What is the definition for: a. Conduction: The transfer of thermal energy by collisions between particles in matter. (Heats air close to Earth s surface)
Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses
 Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Rainfall at Hilo, Hawaii1. By Tsutomu Takahashi
 February 1977 T. Takahashi 121 Rainfall at Hilo, Hawaii1 By Tsutomu Takahashi Cloud Physics Observatory, Department of Meteorology, University of Hawaii Hilo, Hawaii 96720 (Manuscript received 4 September
February 1977 T. Takahashi 121 Rainfall at Hilo, Hawaii1 By Tsutomu Takahashi Cloud Physics Observatory, Department of Meteorology, University of Hawaii Hilo, Hawaii 96720 (Manuscript received 4 September
