Variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
|
|
|
- Todd Haynes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Rowan Sutton Director of Climate Research UK National Centre for Atmospheric Science (NCAS) Department of Meteorology University of Reading Thanks to: Ed Hawkins, Len Shaffrey, Jon Robson, Dan Hodson, Tom Delworth,
2 Outline Introduction to the AMOC and its importance for climate Variability of the AMOC: Observations and Mechanisms AMOC response to radiative forcing Rapid change of the AMOC Climate impacts of AMOC variability and change Summary Outstanding research issues
3 Contrasting properties of the Atmosphere and Ocean Density: At SLP ocean is ~ 1000x more dense than the atmosphere Heat capacity: Specific heat capacity is ~1200x atmosphere 2.5m of ocean has same heat capacity as whole atmosphere Velocities: Advective Atmos. ~10 m/s ~10 m/s Ocean ~1-10 cm/s ~1cm/s mid-latitude internal Rossby waves Ocean moves and adjusts ~1000x more slowly than the atmosphere a source of memory (& hence predictability) in the climate system
4 Ocean Circulation Driven by: Windstress, τ curl of windstress ( xτ) is a key forcing of vorticity in the ocean = > horizontal gyre circulation buoyancy fluxes heat and fresh water fluxes modify ocean temperature and salinity and hence density => resulting pressure gradients drive thermohaline or overturning circulation
5 Atlantic Ocean circulation Overturning Circulation Horizontal Gyre Circulation HadCM3 climate model (~1 o ocean resolution) Mass circulation in Sverdrups 1 Sverdrup = 10 6 m 3 /s NB: Gyre and overturning circulations are not independent
6 The Thermohaline Circulation (Courtesy: D.J. Webb) THC involves a deep overturning circulation driven by contrasts in density, and hence pressure, between different regions THC is responsible for a large fraction of the ~O(1PW) northward heat transport of the Atlantic Ocean
7 Maintenance of Overturning Circulation Forcing by buoyancy fluxes generates only a very weak & shallow circulation w T z = K 2 T 2 z Need downward mixing of heat to get a stronger deep circulation Mixing generated by flow over topography, tides, internal waves NB: Wind forcing & eddies in Southern Ocean also play a key role
8 Formation of deep waters Sinking of dense waters fundamental to MOC. Deep ocean tends to fill up with the densest waters formed at the surface Dense water formation is associated with regions of deep convection (>1km) and/or shallow marginal seas - very few such regions worldwide Water must become more dense by: Cooling Increasing salinity
9 The North Atlantic Transformation Pipeline McCartney et al, 1996
10 Overflows Shallow marginal seas favour production of dense waters Waters then overflow sills, mixing with ambient waters as they descend Cooling or evaporation sill
11 Climatic importance of MOC: Poleward Heat Transport Forcing of the climate system by solar insolation generates equator-pole temperature gradient. Heat transport by the atmosphere and ocean reduces this gradient Total: ~5PW Ocean: ~ 1.5-2PW (Trenberth & Caron 2001)
12 Oceanic Heat Transport Atlantic Ocean transports heat northwards in both hemispheres Peak Atlantic Heat transport: ~ 1PW Heat released to atmosphere helps maintain mean climate
13 Cunningham & Marsh 2010 Variability of the MOC Direct obs of the MOC very sparse in space & time, until recently Schematic by L.Bell & N. White / CSIRO UK/US RAPID array gives unprecedented time series since 2004 (but only at 26N) Other estimates of MOC variability from models
14 Variability of the MOC Cunningham & Marsh 2010 HadCM3 model 10 days 50 days Variability on a wide range of timescales Red spectra High frequency variability (<1 year) probably of little importance for climate Climate models typically show enhanced decadal variability, but dominant frequencies vary Dong & Sutton, 2005
15 Variability of the AMOC: estimates based on data assimilation Holger Pohlmann, Met Office Hadley Centre Relationship to North Atlantic Oscillation All time series are 3-year running means NAO + NAO -
16 Indirect observational evidence of decadal variability in the AMOC Folland et al, 84, 86 ; Schlesinger & Ramankutty 94; Kushnir 94; Enfield et al, 2001 etc. Extratropical North Atlantic 75W 7.5W, 30N 60N DJF SST anomalies ( )-( ) Tropical North Atlantic 75W 7.5W, 10N 25N Fig courtesy of Tom Delworth
17 Indirect observational evidence of decadal variability in the AMOC Spectra of paleoclimatic records from Puerto Rico corals (left) and Cariaco Basin (right). Both show distinct multidecadal variability. Kilbourne et al, 2008; Slide courtesy of Tom Delworth
18 Mechanisms of decadal variability in the AMOC: atmospheric forcing ECHO-G climate model. Ortega, Hawkins & Sutton, submitted
19 Mechanisms of decadal variability in the AMOC: feedbacks Quasi-stochastic forcing by the atmosphere (buoyancy fluxes and wind stress) an important driver of MOC variability Simplest case gives red noise MOC spectrum But oceanic response is complex: adjustment through wave and advective processes may give rise to feedbacks and preferred timescales of response (e.g. Delworth & Greatbach, 2000; Dong & Sutton, 2005) Coupled ocean-atmosphere feedbacks may also play a role (e.g. Timmerman et al, 98; Vellinga and Wu, 2004) NB: The relevant processes are imperfectly captured in current climate models, and are sensitive to resolution - must treat results with due caution.
20 Overturning circulation in HiGEM Atlantic meridional overturning at 40N Density ( m), correlated with boundary 40N Overturning black Density index red Dan Hodson
21 AMOC response to radiative forcing Natural (e.g. volcanic) and anthropogenic (e.g. GHG, aerosols) forcings can modify buoyancy fluxes, and influence AMOC Response to GHG forcing: slow down due to warming and freshening Source: IPCC Response to Volcanic forcing Stenchikov et al, 2009
22 AMOC response to radiative forcing Simulated North Atlantic AMOC Index 10 6 m 3 s 1 (Sverdrups) All forcings Aerosol only forcing Greenhouse gas only forcing Delworth and Dixon, 2006
23 Potential for Rapid change of the MOC (from TheGuardian)
24 Dansgaard-Oeschger Cycles Current interglacial period much more stable Oxygen isotope record from Greenland Ice Core Younger Dryas Records from Greenland show high frequency spikes in glacial periods Amplitudes imply a warming of the air temperature of 6-7 degrees C, half the glacial-interglacial range. Rapid (~decades) onset (warming), more gradual cooling Rapid change of the MOC a leading theory to explain D-O events
25 Multiple equilibria & rapid change Evidence that the MOC has multiple stable states Stationary states of the MOC (from a simple model): Overturning strength Small increase in freshwater forcing can trigger abrupt shutdown of overturning Freshwater forcing stronger overturning 3 stationary states (2 stable) Animation from:
26 AMOC hysteresis in a coupled GCM Ed Hawkins, R. Smith, J. Gregory, L. Allison, T. Woollings NCAS-Climate & University of Reading J. Rodriguez, R. Wood Met Office Hadley Centre FAMOUS a low res version of HadCM3: Atmos: 5.0 x 7.5, 11 levels Ocean: 2.5 x 3.75, 20 levels Atlantic overturning streamfunction Smith et al. (2009) Winter mixed-layer depths
27 Experimental design The following runs were performed with FAMOUS: CONTROL 4000 year run with no hosing HOSING add freshwater to North Atlantic between N TRANSIENT RAMP UP increase hosing from 0Sv to 1Sv over 2000 years TRANSIENT RAMP DOWN reduce hosing from 1Sv to 0Sv over 2000 yrs CONSTANT HOSING spun off at various points to check equilibrium state Important design aspects: COMPENSATION in all runs the total freshwater flux is zero Hosing compensated by a small evaporative flux over the rest of the ocean surface ( 0.3 psu/year for 1Sv hosing)
28 Transient ramp-up of hosing Atlantic MOC
29 Transient experiments
30 Transient and equilibrium experiments Relevance to current climate change?
31 Climate impacts of AMOC variability and change
32 Climate Impacts of AMOC variability Northward energy transport HadCM3: Max AMOC and northward heat transport (30s-70N); decadal correlation: 0.85 ~0.5 o C Atmospheric energy transport is anticorrelated on decadal timescales (Bjerknes compensation) Shaffrey and Sutton, 2006 Regression on North Atlantic OHT index T surface (K.PW -1 )
33 Climate Impacts of AMOC variability Surface temperature Observed DJF SST anomalies ( )-( ) Impact of THC shutdown Vellinga and Wood, 2002
34 Climate Impacts of AMOC variability High latitude changes observed trend in winter (Nov-Apr) (Johannessen et al, 2004) Regression of HadCM3 winter fields on index of decadal variability in Atlantic Ocean northward heat transport SAT ice fraction
35 Climate Impacts of AMOC variability Other N. Atlantic Impacts SLP precipitation Vertical Shear & Hurricane numbers DJF MAM JJA SON Goldenberg & Shapiro 2001 Knight et al, 2006
36 Climate Impacts of AMOC variability Other climate impacts: N. American precipitation / drought (Enfield et al, 2001; Sutton & Hodson, 2005) Wider tropical precipitation: Sahel, S. & E. Asian monsoons (Zhang & Delworth) ENSO variability (Dong & Sutton, 2007; Timmerman et al, 2007) Beyond climate: Sea level Ecosystems Greenland Ice Sheet?
37 Slide courtesy Rong Zhang (or Atlantic Multidecadal Variability, AMV)
38 Role for AMOC in recent N. Atlantic change? Subpolar gyre 500m heat content June 1995 DePreSys observations Jon Robson Evidence of predictability suggests important role for oceanic memory in rapid warming
39 Summary AMOC exhibits variability on timescales from days to decades; red spectrum, possibly with decadal or longer timescale peaks Decadal/longer timescale variability of greatest importance for climate (including predictability). Mechanisms of natural variability involve quasistochastic forcing by the atmosphere + oceanic and/or coupled feedbacks. Large model uncertainty. AMOC is sensitive to natural & anthropogenic radiative forcing. Potential to trigger rapid change? Large model uncertainty. Evidence for important climate impacts globally
40 Outstanding research issues Mechanisms: Large model uncertainty concerning natural variability of the AMOC and the response to radiative forcings. Sensitivity to resolution (e.g. boundary currents; overflows) one important dimension. which are the dominant feedbacks and their associated timescales? Is AMOC variability quasi-periodic? What is the role of exchanges with the Arctic? What is the role of the Southern Ocean? Climate impacts: multiple coupled mechanisms, poorly understood attribution: separating AMOC influence from others Observations and synthesis: Improving analyses Relating observations at different latitudes
AMOC Impacts on Climate
 AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
Rapid Climate Change: Heinrich/Bolling- Allerod Events and the Thermohaline Circulation. By: Andy Lesage April 13, 2010 Atmos.
 Rapid Climate Change: Heinrich/Bolling- Allerod Events and the Thermohaline Circulation By: Andy Lesage April 13, 2010 Atmos. 6030 Outline Background Heinrich Event I/Bolling-Allerod Transition (Liu et
Rapid Climate Change: Heinrich/Bolling- Allerod Events and the Thermohaline Circulation By: Andy Lesage April 13, 2010 Atmos. 6030 Outline Background Heinrich Event I/Bolling-Allerod Transition (Liu et
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY
 NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation as seen in models, observations and paleo data
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation as seen in models, observations and paleo data Odd Helge Otterå, et al., oddho@nersc.no G.C. Rieber Climate Institute, NERSC, Bergen Bjerknes Centre
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation as seen in models, observations and paleo data Odd Helge Otterå, et al., oddho@nersc.no G.C. Rieber Climate Institute, NERSC, Bergen Bjerknes Centre
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Variability of Atlantic Ocean heat transport and its effects on the atmosphere
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N., February 3 Variability of Atlantic Ocean heat transport and its effects on the atmosphere Buwen Dong and Rowan T. Sutton Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N., February 3 Variability of Atlantic Ocean heat transport and its effects on the atmosphere Buwen Dong and Rowan T. Sutton Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate
 What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
Multi year predictability of the tropical Atlantic atmosphere driven by the high latitude North Atlantic Ocean
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047949, 2011 Multi year predictability of the tropical Atlantic atmosphere driven by the high latitude North Atlantic Ocean N. J. Dunstone, 1 D.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047949, 2011 Multi year predictability of the tropical Atlantic atmosphere driven by the high latitude North Atlantic Ocean N. J. Dunstone, 1 D.
Fast and Slow Response of Sea ice and the Southern Ocean to Ozone Depletion
 Fast and Slow Response of Sea ice and the Southern Ocean to Ozone Depletion Annual Minimum Sea ice extent 1979-2013 10 6 km 2 Arctic September Antarctic February Data from in passive microwave satellite
Fast and Slow Response of Sea ice and the Southern Ocean to Ozone Depletion Annual Minimum Sea ice extent 1979-2013 10 6 km 2 Arctic September Antarctic February Data from in passive microwave satellite
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components
 Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global warming?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042743, 2010 Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042743, 2010 Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
Atlantic overturning in decline?
 Atlantic overturning in decline? Article Accepted Version Robson, J., Hodson, D., Hawkins, E. and Sutton, R. (2014) Atlantic overturning in decline? Nature Geoscience, 7 (1). pp. 2 3. ISSN 1752 0894 doi:
Atlantic overturning in decline? Article Accepted Version Robson, J., Hodson, D., Hawkins, E. and Sutton, R. (2014) Atlantic overturning in decline? Nature Geoscience, 7 (1). pp. 2 3. ISSN 1752 0894 doi:
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change
 Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
Adjustment of the global climate to an abrupt slowdown of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation
 Adjustment of the global climate to an abrupt slowdown of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Wei Cheng 1, Cecilia M. Bitz 2, John C.H. Chiang 3 1 Joint Institute for the Study of the Atmosphere
Adjustment of the global climate to an abrupt slowdown of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Wei Cheng 1, Cecilia M. Bitz 2, John C.H. Chiang 3 1 Joint Institute for the Study of the Atmosphere
THE AMOC IN MILLENNIAL ECHO-G CLIMATE SIMULATIONS AND FUTURE CLIMATE CHANGE SCENARIOS
 THE AMOC IN MILLENNIAL ECHO-G CLIMATE SIMULATIONS AND FUTURE CLIMATE CHANGE SCENARIOS Pablo Ortega, Marisa Montoya and Fidel González-Rouco PALMA Research Group Dpto. Astrofísica y Ciencias de la Atmósfera
THE AMOC IN MILLENNIAL ECHO-G CLIMATE SIMULATIONS AND FUTURE CLIMATE CHANGE SCENARIOS Pablo Ortega, Marisa Montoya and Fidel González-Rouco PALMA Research Group Dpto. Astrofísica y Ciencias de la Atmósfera
Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections
 Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections Doug Smith Walter Orr Roberts memorial lecture, 9 th June 2015 Contents Motivation Practical issues
Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections Doug Smith Walter Orr Roberts memorial lecture, 9 th June 2015 Contents Motivation Practical issues
LETTERS. Tropical Stabilization of the Thermohaline Circulation in a Greenhouse Warming Simulation
 VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 1JUNE 2000 LETTERS Tropical Stabilization of the Thermohaline Circulation in a Greenhouse Warming Simulation M. LATIF, E.ROECKNER, U.MIKOLAJEWICZ, AND R. VOSS Max-Planck-Institut
VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 1JUNE 2000 LETTERS Tropical Stabilization of the Thermohaline Circulation in a Greenhouse Warming Simulation M. LATIF, E.ROECKNER, U.MIKOLAJEWICZ, AND R. VOSS Max-Planck-Institut
Presentation A simple model of multiple climate regimes
 A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
Forecast system development: what next?
 Forecast system development: what next? Doug Smith, Adam Scaife, Nick Dunstone, Leon Hermanson, Rosie Eade, Vikki Thompson, Martin Andrews, Jeff Knight, Craig MacLachlan, and many others Improved models
Forecast system development: what next? Doug Smith, Adam Scaife, Nick Dunstone, Leon Hermanson, Rosie Eade, Vikki Thompson, Martin Andrews, Jeff Knight, Craig MacLachlan, and many others Improved models
Decadal to Centennial Variability of the Atlantic From Observations and Models
 GM01073_CH10.qxd 9/8/07 4:59 PM Page 131 Decadal to Centennial Variability of the Atlantic From Observations and Models Thomas L. Delworth and Rong Zhang Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory/NOAA, Princeton
GM01073_CH10.qxd 9/8/07 4:59 PM Page 131 Decadal to Centennial Variability of the Atlantic From Observations and Models Thomas L. Delworth and Rong Zhang Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory/NOAA, Princeton
Lecture 0 A very brief introduction
 Lecture 0 A very brief introduction Eli Tziperman Climate variability results from a very diverse set of physical phenomena and occurs on a very wide range of time scales. It is difficult to envision a
Lecture 0 A very brief introduction Eli Tziperman Climate variability results from a very diverse set of physical phenomena and occurs on a very wide range of time scales. It is difficult to envision a
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24701, doi:10.1029/2006gl027655, 2006 Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon Riyu Lu, 1,2 Buwen Dong, 3 and Hui Ding 2,4 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24701, doi:10.1029/2006gl027655, 2006 Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon Riyu Lu, 1,2 Buwen Dong, 3 and Hui Ding 2,4 Received
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Nandini Ramesh
 IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
Winds and Currents in the Oceans
 Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Ocean cycles and climate ENSO, PDO, AMO, AO
 Ocean cycles and climate ENSO, PDO, AMO, AO 3 2.5 2 enso-index 1.5 1 0.5 0-0.5-1 enso 3.4 -index - 1996 to 1999-1.5 1996 1997 1998 1999 Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale ENSO mechanisms animation http://esminfo.prenhall.com/science/geoanimations/animations/26_ninonina.html
Ocean cycles and climate ENSO, PDO, AMO, AO 3 2.5 2 enso-index 1.5 1 0.5 0-0.5-1 enso 3.4 -index - 1996 to 1999-1.5 1996 1997 1998 1999 Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale ENSO mechanisms animation http://esminfo.prenhall.com/science/geoanimations/animations/26_ninonina.html
The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system
 The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU), Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU), Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
Decadal-timescale changes of the Atlantic overturning circulation and climate in a coupled climate model with a hybrid-coordinate ocean component
 Clim Dyn (22) 39:2 42 DOI.7/s382-2-432-y Decadal-timescale changes of the Atlantic overturning circulation and climate in a coupled climate model with a hybrid-coordinate ocean component A. Persechino
Clim Dyn (22) 39:2 42 DOI.7/s382-2-432-y Decadal-timescale changes of the Atlantic overturning circulation and climate in a coupled climate model with a hybrid-coordinate ocean component A. Persechino
Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism
 Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism Yafang Zhong and Gifford Miller INSTAAR, University of Colorado at Boulder, USA Bette Otto-Bliesner, Caspar Ammann, Marika Holland,
Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism Yafang Zhong and Gifford Miller INSTAAR, University of Colorado at Boulder, USA Bette Otto-Bliesner, Caspar Ammann, Marika Holland,
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake
 Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Near-term climate prediction: new opportunities and challenges
 Near-term climate prediction: new opportunities and challenges Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani Atlantic multi-decadal variability
Near-term climate prediction: new opportunities and challenges Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani Atlantic multi-decadal variability
The Ice Age sequence in the Quaternary
 The Ice Age sequence in the Quaternary Subdivisions of the Quaternary Period System Series Stage Age (Ma) Holocene 0 0.0117 Tarantian (Upper) 0.0117 0.126 Quaternary Ionian (Middle) 0.126 0.781 Pleistocene
The Ice Age sequence in the Quaternary Subdivisions of the Quaternary Period System Series Stage Age (Ma) Holocene 0 0.0117 Tarantian (Upper) 0.0117 0.126 Quaternary Ionian (Middle) 0.126 0.781 Pleistocene
Lecture 8. Lecture 1. Wind-driven gyres. Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk
 Lecture 8 Lecture 1 Wind-driven gyres Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk wek > 0 VEk wek < 0 VEk 1 8.1 Vorticity and circulation The vorticity of a parcel is a measure of its
Lecture 8 Lecture 1 Wind-driven gyres Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk wek > 0 VEk wek < 0 VEk 1 8.1 Vorticity and circulation The vorticity of a parcel is a measure of its
Multiple timescale coupled atmosphere-ocean data assimilation
 Multiple timescale coupled atmosphere-ocean data assimilation (for climate prediction & reanalysis) Robert Tardif Gregory J. Hakim H L H University of Washington w/ contributions from: Chris Snyder NCAR
Multiple timescale coupled atmosphere-ocean data assimilation (for climate prediction & reanalysis) Robert Tardif Gregory J. Hakim H L H University of Washington w/ contributions from: Chris Snyder NCAR
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
lecture 11 El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part II
 lecture 11 El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part II SYSTEM MEMORY: OCEANIC WAVE PROPAGATION ASYMMETRY BETWEEN THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEAN The atmosphere and ocean are not symmetrical in their responses
lecture 11 El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part II SYSTEM MEMORY: OCEANIC WAVE PROPAGATION ASYMMETRY BETWEEN THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEAN The atmosphere and ocean are not symmetrical in their responses
DATA REQUIREMENTS FOR DECADAL-TO-CENTENNIAL CLIMATE VARIABILITY STUDIES AND COUPLED MODELS. MPI, Hamburg, Germany 2. NASA/GSFC, Goddard Md USA
 DATA REQUIREMENTS FOR DECADAL-TO-CENTENNIAL CLIMATE VARIABILITY STUDIES AND COUPLED MODELS M. Latif 1, V. Mehta 2 and co-authors * 1 MPI, Hamburg, Germany 2 NASA/GSFC, Goddard Md USA 1 - INTRODUCTION The
DATA REQUIREMENTS FOR DECADAL-TO-CENTENNIAL CLIMATE VARIABILITY STUDIES AND COUPLED MODELS M. Latif 1, V. Mehta 2 and co-authors * 1 MPI, Hamburg, Germany 2 NASA/GSFC, Goddard Md USA 1 - INTRODUCTION The
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes
 Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming.
 Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Isotopic Evidence 16 O isotopes "light 18 O isotopes "heavy" Evaporation favors light Rain favors heavy Cloud above ice is
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Isotopic Evidence 16 O isotopes "light 18 O isotopes "heavy" Evaporation favors light Rain favors heavy Cloud above ice is
Coherent multidecadal variability in North Atlantic sea level
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L15604, doi:10.1029/2009gl039455, 2009 Coherent multidecadal variability in North Atlantic sea level L. M. Frankcombe 1 and H. A. Dijkstra
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L15604, doi:10.1029/2009gl039455, 2009 Coherent multidecadal variability in North Atlantic sea level L. M. Frankcombe 1 and H. A. Dijkstra
There is evidence of a widespread reduction in solar radiation at the earth s surface, often referred to as global dimming, lasted from the mid-1950s
 1 There is evidence of a widespread reduction in solar radiation at the earth s surface, often referred to as global dimming, lasted from the mid-1950s until the mid-1980s when a recovery, referred to
1 There is evidence of a widespread reduction in solar radiation at the earth s surface, often referred to as global dimming, lasted from the mid-1950s until the mid-1980s when a recovery, referred to
Projections of future climate change
 Projections of future climate change Matthew Collins 1,2 and Catherine A. Senior 2 1 Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre,
Projections of future climate change Matthew Collins 1,2 and Catherine A. Senior 2 1 Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
Impact of atmosphere and sub surface ocean data on decadal climate prediction
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041609, 2010 Impact of atmosphere and sub surface ocean data on decadal climate prediction N. J. Dunstone 1 and D.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041609, 2010 Impact of atmosphere and sub surface ocean data on decadal climate prediction N. J. Dunstone 1 and D.
NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE, SOUTHAMPTON. RESEARCH & CONSULTANCY REPORT No. 1
 NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE, SOUTHAMPTON RESEARCH & CONSULTANCY REPORT No. The impact of surface flux anomalies on the mid-high latitude Atlantic Ocean circulation in HadCM3 J P Grist, S A Josey & B Sinha
NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE, SOUTHAMPTON RESEARCH & CONSULTANCY REPORT No. The impact of surface flux anomalies on the mid-high latitude Atlantic Ocean circulation in HadCM3 J P Grist, S A Josey & B Sinha
Bering Strait, AMOC hysteresis, and abrupt climate change
 DOE/UCAR Cooperative Agreement Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Bering Strait, AMOC hysteresis, and abrupt climate change Aixue Hu Gerald A. Meehl, Weiqing Han, Axel Timmerman, Bette Otto-Bliester,
DOE/UCAR Cooperative Agreement Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Bering Strait, AMOC hysteresis, and abrupt climate change Aixue Hu Gerald A. Meehl, Weiqing Han, Axel Timmerman, Bette Otto-Bliester,
Continental Hydrology, Rapid Climate Change, and the Intensity of the Atlantic MOC: Insights from Paleoclimatology
 Continental Hydrology, Rapid Climate Change, and the Intensity of the Atlantic MOC: Insights from Paleoclimatology W.R. Peltier Department of Physics University of Toronto WOCE derived N-S salinity section
Continental Hydrology, Rapid Climate Change, and the Intensity of the Atlantic MOC: Insights from Paleoclimatology W.R. Peltier Department of Physics University of Toronto WOCE derived N-S salinity section
Sensitivity of the Younger Dryas climate to changes in freshwater, orbital, and greenhouse gas forcing in CESM1.
 OCE-1536630 EAR-0903071 Sensitivity of the Younger Dryas climate to changes in freshwater, orbital, and greenhouse gas forcing in CESM1. The 21 st Annual CESM Workshop Paleoclimate Working Group Taylor
OCE-1536630 EAR-0903071 Sensitivity of the Younger Dryas climate to changes in freshwater, orbital, and greenhouse gas forcing in CESM1. The 21 st Annual CESM Workshop Paleoclimate Working Group Taylor
LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR
 LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR 1. Arctic (surface air) temperatures are rising twice as fast as the temperatures in the rest of the world (Amplification). The Arctic
LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR 1. Arctic (surface air) temperatures are rising twice as fast as the temperatures in the rest of the world (Amplification). The Arctic
isopycnal outcrop w < 0 (downwelling), v < 0 L.I. V. P.
 Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Global Dynamics of Climate Variability and Change
 MOSAC and SRG Meetings 2014 5 th -7 th November 2014 MOSAC PAPER 19.10 Global Dynamics of Climate Variability and Change Adam Scaife 1. Introduction On regional scales it is often the dynamics of regional
MOSAC and SRG Meetings 2014 5 th -7 th November 2014 MOSAC PAPER 19.10 Global Dynamics of Climate Variability and Change Adam Scaife 1. Introduction On regional scales it is often the dynamics of regional
Chapter 4. Understanding the Weather. Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations
 Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model
 An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model Virginie Guemas, David Salas-Mélia Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques (CNRM)
An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model Virginie Guemas, David Salas-Mélia Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques (CNRM)
Speleothems and Climate Models
 Earth and Life Institute Georges Lemaître Centre for Earth and Climate Research Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium Speleothems and Climate Models Qiuzhen YIN Summer School on Speleothem Science,
Earth and Life Institute Georges Lemaître Centre for Earth and Climate Research Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium Speleothems and Climate Models Qiuzhen YIN Summer School on Speleothem Science,
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Deep Ocean Circulation & implications for Earth s climate
 Deep Ocean Circulation & implications for Earth s climate I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge
Deep Ocean Circulation & implications for Earth s climate I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview
 Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Stochastically-driven multidecadal variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation in CCSM3
 Clim Dyn (212) 38:859 876 DOI 1.17/s382-11-14-2 Stochastically-driven multidecadal variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation in CCSM3 Young-Oh Kwon Claude Frankignoul Received: 2 August
Clim Dyn (212) 38:859 876 DOI 1.17/s382-11-14-2 Stochastically-driven multidecadal variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation in CCSM3 Young-Oh Kwon Claude Frankignoul Received: 2 August
Vertical Coupling in Climate
 Vertical Coupling in Climate Thomas Reichler (U. of Utah) NAM Polar cap averaged geopotential height anomalies height time Observations Reichler et al. (2012) SSWs seem to cluster Low-frequency power Vortex
Vertical Coupling in Climate Thomas Reichler (U. of Utah) NAM Polar cap averaged geopotential height anomalies height time Observations Reichler et al. (2012) SSWs seem to cluster Low-frequency power Vortex
The ocean and abrupt climate change
 The ocean and abrupt climate change Marisa Montoya Dpto. Astrofísica y Ciencias de la Atmósfera UCM, Madrid UB, Barcelona 23/11/2005 Outline (1) Introduction to the ocean s large-scale circulation (2)
The ocean and abrupt climate change Marisa Montoya Dpto. Astrofísica y Ciencias de la Atmósfera UCM, Madrid UB, Barcelona 23/11/2005 Outline (1) Introduction to the ocean s large-scale circulation (2)
Heat Uptake and the Thermohaline Circulation in the Community Climate System Model, Version 2
 4058 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Heat Uptake and the Thermohaline Circulation in the Community Climate System Model, Version 2 PETER R. GENT AND GOKHAN DANABASOGLU National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
4058 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Heat Uptake and the Thermohaline Circulation in the Community Climate System Model, Version 2 PETER R. GENT AND GOKHAN DANABASOGLU National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating
 Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
The Earth s Oceans/Climate What We Don t Know. February 20, 2016 Bernie McCune
 The Earth s Oceans/Climate What We Don t Know February 20, 2016 Bernie McCune What we Know There are generally large uncertainties with regard to our knowledge of the oceans Looking only at global effects
The Earth s Oceans/Climate What We Don t Know February 20, 2016 Bernie McCune What we Know There are generally large uncertainties with regard to our knowledge of the oceans Looking only at global effects
Ocean Model Uncertainty
 Ocean Model Uncertainty Chris Brierley University of Reading, UK Alan Thorpe Natural Environment Research Council, UK Mat Collins Hadley Centre, Met. Office, UK Malcolm MacVean European Centre for Medium-range
Ocean Model Uncertainty Chris Brierley University of Reading, UK Alan Thorpe Natural Environment Research Council, UK Mat Collins Hadley Centre, Met. Office, UK Malcolm MacVean European Centre for Medium-range
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
Gulf Stream Temperature, Salinity, and Transport during the Last Millennium
 Gulf Stream Temperature, Salinity, and Transport during the Last Millennium David Lund - University of Michigan Part I - Geostrophic estimation of Gulf Stream flow - Gulf Stream strength varied by ~10%
Gulf Stream Temperature, Salinity, and Transport during the Last Millennium David Lund - University of Michigan Part I - Geostrophic estimation of Gulf Stream flow - Gulf Stream strength varied by ~10%
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall?
 Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
A Rossby Wave Bridge from the Tropical Atlantic to West Antarctica
 A Rossby Wave Bridge from the Tropical Atlantic to West Antarctica A Physical Explanation of the Antarctic Paradox and the Rapid Peninsula Warming Xichen Li; David Holland; Edwin Gerber; Changhyun Yoo
A Rossby Wave Bridge from the Tropical Atlantic to West Antarctica A Physical Explanation of the Antarctic Paradox and the Rapid Peninsula Warming Xichen Li; David Holland; Edwin Gerber; Changhyun Yoo
How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading
 How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading Extratropical storms Extratropical storms Strong winds, extreme waves, storm
How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading Extratropical storms Extratropical storms Strong winds, extreme waves, storm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
Variability and Predictability of the Ocean Thermohaline Circulation
 Variability and Predictability of the Ocean Thermohaline Circulation Jochem Marotzke Max Planck Institute for Meteorology (MPI-M) Centre for Marine and Atmospheric Sciences (ZMAW) Bundesstrasse 53, 20146
Variability and Predictability of the Ocean Thermohaline Circulation Jochem Marotzke Max Planck Institute for Meteorology (MPI-M) Centre for Marine and Atmospheric Sciences (ZMAW) Bundesstrasse 53, 20146
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation
 Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
climate system and its subcomponents: the atmosphere, ocean, land surface, Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A A general description of the Earth
 Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
A Multimodel Study of Sea Surface Temperature and Subsurface Density Fingerprints of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
 15 NOVEMBER 2013 R O B E R T S E T A L. 9155 A Multimodel Study of Sea Surface Temperature and Subsurface Density Fingerprints of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation CHRISTOPHER D. ROBERTS
15 NOVEMBER 2013 R O B E R T S E T A L. 9155 A Multimodel Study of Sea Surface Temperature and Subsurface Density Fingerprints of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation CHRISTOPHER D. ROBERTS
Basic Ocean Current Systems. Basic Ocean Structures. The State of Oceans. Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate. Temperature.
 Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation
 1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
A reversal of climatic trends in the North Atlantic since 2005
 A reversal of climatic trends in the North Atlantic since 25 Article Accepted Version Robson, J., Ortega, P. and Sutton, R. (216) A reversal of climatic trends in the North Atlantic since 25. Nature Geoscience,
A reversal of climatic trends in the North Atlantic since 25 Article Accepted Version Robson, J., Ortega, P. and Sutton, R. (216) A reversal of climatic trends in the North Atlantic since 25. Nature Geoscience,
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Abstract Mechanisms of the internally generated decadal-to-multidecadal. variability of SST in the Atlantic Ocean in a coupled GCM
 Clim Dyn DOI 10.1007/s00382-015-2660-8 Mechanisms of internally generated decadal to multidecadal variability of SST in the Atlantic Ocean in a coupled GCM Hua Chen 1 Edwin K. Schneider 2,3 Zhiwei Wu 1
Clim Dyn DOI 10.1007/s00382-015-2660-8 Mechanisms of internally generated decadal to multidecadal variability of SST in the Atlantic Ocean in a coupled GCM Hua Chen 1 Edwin K. Schneider 2,3 Zhiwei Wu 1
The Future of Predictability: Can Decadal Prediction Be Informative?
 NESL / The Future of Predictability: Can Decadal Prediction Be Informative? Joe Tribbia NCAR Climate and Global Dynamics Division ECMWF Seminar 2010 Disclaimer Most of what we know about decadal climate
NESL / The Future of Predictability: Can Decadal Prediction Be Informative? Joe Tribbia NCAR Climate and Global Dynamics Division ECMWF Seminar 2010 Disclaimer Most of what we know about decadal climate
Decadal to multidecadal variability and the climate change background
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007jd008411, 2007 Decadal to multidecadal variability and the climate change background David Parker, 1 Chris Folland,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007jd008411, 2007 Decadal to multidecadal variability and the climate change background David Parker, 1 Chris Folland,
Assessing how North Atlantic ocean overturning has varied over the last 50 years
 Assessing how North Atlantic ocean overturning has varied over the last 50 years Vassil Roussenov 1, Ric Williams 1, M. Susan Lozier 2 and Doug Smith 3 1. School of Environmental Sciences, University of
Assessing how North Atlantic ocean overturning has varied over the last 50 years Vassil Roussenov 1, Ric Williams 1, M. Susan Lozier 2 and Doug Smith 3 1. School of Environmental Sciences, University of
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Influence of the Multidecadal Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation Variability on European Climate
 6062 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E S P E C I A L S E C T I O N VOLUME 19 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Influence of the Multidecadal Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation Variability on European Climate
6062 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E S P E C I A L S E C T I O N VOLUME 19 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Influence of the Multidecadal Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation Variability on European Climate
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Oceanography Quiz 2. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Oceanography Quiz 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The highest and lowest tides are known as the spring tides. When do these occur? a.
Oceanography Quiz 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The highest and lowest tides are known as the spring tides. When do these occur? a.
Ruddiman CHAPTER 13. Earth during the LGM ca. 20 ka BP
 Ruddiman CHAPTER 13 Earth during the LGM ca. 20 ka BP The Last Glacial Maximum When? How much more ice than today? How much colder was it than today (global average)? How much lower were snowlines? Did
Ruddiman CHAPTER 13 Earth during the LGM ca. 20 ka BP The Last Glacial Maximum When? How much more ice than today? How much colder was it than today (global average)? How much lower were snowlines? Did
LETTERS. Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic sector
 Vol 453 1 May 2008 doi:10.1038/nature06921 Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic sector N. S. Keenlyside 1, M. Latif 1, J. Jungclaus 2, L. Kornblueh 2 & E. Roeckner 2 The climate
Vol 453 1 May 2008 doi:10.1038/nature06921 Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic sector N. S. Keenlyside 1, M. Latif 1, J. Jungclaus 2, L. Kornblueh 2 & E. Roeckner 2 The climate
Global Warming, the AMO, and North Atlantic Tropical Cyclones
 Global Warming, the AMO, and North Atlantic Tropical Cyclones revised for Eos 5/17/06 BY M.E. MANN AND K.A. EMANUEL Increases in key measures of Atlantic hurricane activity over recent decades are believed
Global Warming, the AMO, and North Atlantic Tropical Cyclones revised for Eos 5/17/06 BY M.E. MANN AND K.A. EMANUEL Increases in key measures of Atlantic hurricane activity over recent decades are believed
Name Spin-up runs Flux Ocean Atmosphere adjustments CON-DEF O-DEF A-DEF O-DEF/A-DEF CON-SHF O-SHF A-SHF O-SHF/A-SHF CON-EFF O-EFF A-EFF O-EFF/A-EFF
 Chapter 5 Control runs 5.1 Introduction Three coupled model control runs are presented in this chapter; these are summarised in Table 5.1. They differ from each another only in the initial states of the
Chapter 5 Control runs 5.1 Introduction Three coupled model control runs are presented in this chapter; these are summarised in Table 5.1. They differ from each another only in the initial states of the
Atmosphere-ocean interactions and dynamic response of the Southern Ocean to climate variability and trends. Mike Meredith BAS, Cambridge, UK
 Atmosphere-ocean interactions and dynamic response of the Southern Ocean to climate variability and trends. Mike Meredith BAS, Cambridge, UK Structure Preliminary random thoughts Brief examples demonstrating
Atmosphere-ocean interactions and dynamic response of the Southern Ocean to climate variability and trends. Mike Meredith BAS, Cambridge, UK Structure Preliminary random thoughts Brief examples demonstrating
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models
 An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
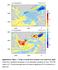 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models
 Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models Robert Marsh, Beverly de Cuevas, Andrew Coward & Simon Josey (+ contributions by
Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models Robert Marsh, Beverly de Cuevas, Andrew Coward & Simon Josey (+ contributions by
Decadal to multidecadal variability and the climate change background
 Decadal to multidecadal variability and the climate change background Article Published Version Parker, D., Folland, C., Scaife, A., Knight, J., Colman, A., Baines, P. and Dong, B. (2007) Decadal to multidecadal
Decadal to multidecadal variability and the climate change background Article Published Version Parker, D., Folland, C., Scaife, A., Knight, J., Colman, A., Baines, P. and Dong, B. (2007) Decadal to multidecadal
