Correlation between the Ship Grounding Accident and the Ship Traffic A Case Study Based on the Statistics of the Gulf of Finland
|
|
|
- Virgil Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 7 Number 1 March 2013 DOI: / Correlation between the Ship Grounding Accident and the Ship Traffic A Case Study Based on the Statistics of the Gulf of Finland A. Mazaheri, J. Montewka & P. Kujala Aalto University, Department of Applied Mechanics, Espoo, Finland ABSTRACT: Ship traffic is one of the factors that is presented in almost all of the existing grounding models, and is considered as one of the affecting factors on the likelihood of grounding accident. This effect in grounding accident is mostly accepted by the experts as a common sense or simply by just generalizing the ship ship collision cases to grounding accidents. There is no available research on the actual causal link between the ship traffic and grounding accident in the literature. In this paper, authors have utilized the statistical analysis on historical grounding accident data in the Gulf of Finland between the years 1989 and 2010 and the AIS data of the same area in year 2010, as the source of ship traffic data, to investigate the possible existence of any correlation between the ship traffic and the grounding accident. The results show that for the studied area (Gulf of Finland) there is no correlation between the traffic density and the grounding accident. However, the possibility of the existence of minor relation between the traffic distribution and grounding accident is shown by the result. This finding, however, needs further investigation for more clarification. 1 INTRODUCTION From among the many factors that scholars have considered as affecting factors on the likelihood of grounding accident when they have modeled this type of accident, traffic is one of the factors that are presented in almost all of the existing models related to grounding accident; see e.g. [1 6]. Similar to the correlation of the ship traffic and frequency of shipship collision that is merely noted in the literature [7], it seems that this effect in grounding accident is mostly accepted by the experts as a common sense or simply by just generalizing the ship ship collision cases to grounding accidents. There is no available study on the actual causal link between the traffic and grounding accident in the literature. It can be argued that one of the reasons behind the common belief of the existence of causal link between the traffic and grounding accident is that people assume when the traffic is more dense, the likelihood that the ships have to alter their courses to avoid collision and eventually ending up grounded is higher; however there is no statistical analysis on this common belief to either support or reject it. One of the problems that may rise when such doubtful beliefs become commonly accepted by the researchers is that the models that are developed to analyze a phenomenon will not be accurate enough and may not represent the reality; and if the model is used for risk management purposes it might result in ineffective or even wrong risk control options. In this paper, it has been tried to test this common belief by finding the possible correlation between the two variables, using the statistical data of the actual grounding accidents happened in the Gulf of Finland (GOF) within 22 years ( ). 119
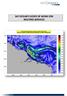
2 The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: The data that is used for the analysis is presented in the next Chapter. The research methodology and the implemented algorithms for data analysis are explained and presented in Chapter 3; the results of the data analysis are presented in Chapter 4; followed by the discussion of the results in Chapter 5. The paper is concluded in Chapter 6. paper, the location of these 112 grounding accidents are referred as grounding points. 2 DATA In order to analyze the possible correlation between the traffic of ships and the grounding accidents, two different sources of historical data are used as: 1 HELCOM (Helsinki Commission) database regarding the ship accidents happened in the Baltic Sea area within the years of 1989 and 2010; 2 HELCOM AIS (Automatic Identification System) data on marine traffic in the GOF in year HELCOM Accident Database The first dataset that is utilized in this paper is HELCOM database regarding the ship accidents previously occurred in the Baltic Sea area, including Gulf of Finland, between the years of 1989 and The data consist of inputs such as the date and time of the accident, geographical coordinate of the accident, type of the accident, flag states of the involved ships, name of the involved ships, whether the accident caused any pollution, and type and amount of the possible pollution. From among all the available fields in the database, the only input values that have been utilized in this research are the type and the location of the accident. Although the database was not flawless, especially regarding the ship and cargo properties and crew competences, when it comes to the data useful for the purpose of this study, the only problem that was needed to be addressed seems to be the wrong recorded location of the accident that in some cases were reported in land areas. The data were first filtered regarding the type of the accident, in which all the accidents that were recorded as grounding were chosen. Before utilizing the database, the database was filtered to limit the data to those accidents that have happened in the GOF, means limiting the coordination to o E and o E longitude, and to o N and o N latitude. There were in total 616 records of grounding accidents in HELCOM database for the years of , in which 123 of them were occurred in the Gulf of Finland based on the above geographical limitation. Next, the database was filtered to remove those accidents that have reported as occurred in land area. To do so, the accident points were visualized in GIS software over the map of the GOF and then those accident points that have located in the land area were spotted and manually removed from the database (Figure 1). From among 123 grounding accident records in the GOF, 11 were found as registered by wrong coordination. As the result, 112 grounding cases spotted as happened in the GOF between years 1989 and 2010, and have been used in the statistical data analysis for this paper. Here in this Figure 1. The location of the grounding accidents happened in the Gulf of Finland between HELCOM AIS Database The second source of historical data that is utilized in this study is the AIS data of the marine traffic in the GOF in The AIS data of the ship traffic has been used to extract the recent traffic properties of ships navigating in the GOF. The AIS data of the ships navigating in the Baltic Sea area were all reported and stored in the database of HELCOM. The database have input values such as IMO and MMSI numbers of the vessel, timestamp of the AIS record, geographical coordinate of the AIS record as latitude and longitude, main dimension of the vessel, speed over ground, course over ground, and rate of turn. However, the only input values that were utilized in this research were timestamps and geographical location of the ships. The AIS data received from HELCOM were filtered and sorted using the methodologies suggested in the literature [8,9]. 3 METHODOLOGY The methodology adopted in this paper is integrated into two main phases. The first phase is to define algorithms to detect the traffic definitions as Traffic Density and Traffic Distribution in the utilized AIS data; and the second phase was implementing statistical hypothesis testing in order to find whether there is any correlation between the traffic and the historical location of the grounding accident using the defined algorithms. 3.1 Algorithm Definitions In the literature, the traffic of the ships was utilized in two ways of definitions as Traffic Density and Traffic Distribution (lateral distribution of the ships along the path). Traffic density is defined as the number of ships per unit area of the waterway within a desired time window [10, 11]. Since we are dealing with the AIS data of year 2010, the time window for this study is defined as a year. The algorithms to estimate the traffic density from the AIS data based on the above definition is shown in Figure 2. In general, the Gulf of Finland is divided into grid cells of size one by one nautical mile. Thereafter, the annual traffic density in the cells that has at least a grounding point inside is estimated. The annual traffic density is counted as the 120
3 number of the ship tracks that passed through such cells over a year. By this way of algorithm definition, the speeds of the vessels do not affect the results as the linear interpolation between the available AIS data points will remove the effect from the interval of the AIS points that are varied depends on the instant speed of the vessel. Another variable is defined in the algorithm to keep the numbers of grounding points that are located inside the grid cell that the traffic density is estimated. This variable has later been used to find the correlation between traffic density and number of groundings. a grounding point can be acceptably described by mean and variance of the distribution. Figure 2. Algorithm to extract the traffic density from the AIS data Lateral distribution of the ships or ship track distribution is the other way of defining the traffic of the ships when the probability of grounding is estimated in the literature; see e.g. [2 4, 12 16]. Nevertheless, there is no unique definition regarding where exactly along a path the distribution of the ships should be extracted. Obviously the extracted lateral distributions of the ships would be different depends on where they have been extracted; the closer to the shoal, the more corrected courses by the ships, thus the narrower or skewer distributions. In order to avoid confusion and also to simplify the algorithm for extracting the data, a definition of the ship distance from a grounding point is defined here. The utilized algorithm is shown in Figure 3. In general, the Gulf of Finland is divided into grid cells of size five by five nautical miles. The five nautical miles distance is estimated to be the distance that can be travelled by most of the merchant ships (excluding High Speed Light Crafts) in half an hour using the average speed of the ships navigating in the GOF. Thereafter, the distribution of the ship traffic in the cells that has at least a grounding point inside is estimated. The distribution is estimated in this way that when the track of a ship is passed through the defined grid cell, the distance of the ship on the border of the grid cell from the grounding point is calculated and stored in a variable. Another variable is also counting the number of grounding points inside the defined grid cell. Later on, the correlation between the distributions of the calculated distances and the number of the counted grounding points are analyzed based on the first and second moments of the obtained distributions. This means that it is assumed that a distance distribution of the ships from Figure 3. Algorithm to extract the traffic distribution from the AIS data 3.2 Statistical Analysis One of the methods to find the statistical dependencies between two random variables is to find if any correlation exists between the two variables. Knowing about the correlation between two variables is specifically useful as it indicates a predictive relationship between the two variables, which can be exploited in practice. Nevertheless, the existence of statistical dependencies as correlation between two variables does not necessarily imply causal relation between the two variables. For more information regarding the correlation and causal relation the readers are refer to [17]. There are several coefficients that represent correlation dependencies between two random variables, which in this paper two coefficients as Pearson and Spearman have been utilized. Pearson coefficient (r) of two variables is defined as the covariance of the variables divided by the product of their standard deviations. Pearson coefficient gives a value between 1 and 1, which the exact value of 1 and 1 means there is a perfect linear correlation between the variables. The value of zero means that there is no linear correlation between the two variables. Nevertheless, no linear correlation cannot be interpreted as absolutely no correlation between the two variables; and still some sort of correlation in the form of nonlinear correlation, might be existing between the two variables. Although, there is still no unique method or coefficient that can reveal absolute correlation between the two variables, 121
4 there are some coefficients like Spearman that can reveal some level of nonlinear correlation between two variables. Spearman coefficient (ρ) reveals if the relation of the two variables can be described using a monotonic function; thus it can grasp a degree of nonlinear correlation between the two variables. Spearman coefficient gives value between 1 and 1, which the exact value of 1 and 1 means that there are no repeated data values, and each variable is a perfect monotonic function of the other. Although Spearman and Pearson coefficients can somehow disclose the possible statistical dependencies between the two variables, one should be aware about their limitations and assumptions. For instance, Pearson coefficient is defined assuming the data are normally distributed, so in other cases it might be misleading; or Spearman coefficient is recommended when both variables are ordinal variables, or one is ordinal and the other is continues variable [17]. Therefore, since these assumptions are not perfectly matched with the limitation of our variables, some other methods like Mutual Information test should be used additionally. However, other tests like mutual information are not utilized in this paper and remained for the future research. 4 RESULTS After calculating r and ρ coefficients for each sets of variables, the statistical significance of the results are tested assuming the null hypothesis (H0) as nocorrelation against alternative hypothesis (H1) as non zero correlation by χ 2 test in significant levels of 95% (i.e. α = 0.05). The results are all shown in Table 1. As is seen in Table 1, H0 cannot be rejected for the traffic density and also for the mean value (mu) of the traffic distribution in 95% significant level. Therefore the validity of the null hypothesis is consistent with the resultant data. Thus, the existence of any correlation between the two variables as traffic density of the ships and the grounding accident is questionable. It should be noticed that the defined null hypothesis is a composite hypothesis; thus the trueness of the hypothesis cannot strictly verify that there is absolutely no correlation between the ship traffic and grounding accident; however it can strongly question its existence. Table 1. Correlation between the number of groundings and traffic as density and distribution with two coefficients as Pearson (r) and Spearman (ρ) Traffic Coefficient Correlation P value Accepted Property Value Hypothesis Traffic r H0 Density ρ H0 Distribution r H0 (mu) ρ H0 Distribution r H1 (std) ρ H1 One interesting point that can be seen from Table 1 is that the null hypothesis can be rejected for standard deviation (std) of the traffic distribution in 95% significant level. This might be the sign of slight correlation between the distributiveness of the ship traffic along the path and the grounding accidents. Although, the existence correlation is not very significant (less than 0.25), it has the potential for further investigation. 5 DISCUSSION The result of this study shows that there is no significant correlation between the density of ship traffic and the grounding accidents, while it shows slight correlation between the distributiveness of the traffic and grounding accident. Although this is an important and interesting result by its own as it is a counter claim for the currently existing common belief in the society, it should be used by caution and it needs further research for fully confirmation due to the available uncertainties. The three main sources of the uncertainties are the defined algorithms to extract the data regarding the traffic density and the ship traffic distribution, the issues regarding the utilized data, and the used statistical methods. The algorithms defined in this research to extract the data based on the utilized definition of the ship traffic in the literature have a main issue, which is the size of the used grid cells. For the traffic density, the grid size of 1 by 1 nautical mile and for the traffic distribution 5 by 5 nautical miles are utilized. Therefore, the number of the grounding points that will be caught by these grid sizes may be changed if the grid size is increased or decreased. Besides, the number of the ships in the area may also be changed if the size of the grid is changed. Thus, the effect of the grid size on the result should be investigated by choosing different grid sizes. The question is the factors that affect the grid size. One important factor is the average speed of the traffic in the area, which in this study is believed to be neutralized by the utilized algorithm. The other factor might be the traffic congestion in the area, which may be neutralized by affecting the width of the waterway. However, one may argue that by affecting the width of the waterway the result is biased to the location. The counter argument would be that the nature of such research is in fact biased to the location of the previous grounding accidents; and in fact the grounding accident, in contrary to the collision accident, is very location dependent as it only may happen in the shallow water areas. Nevertheless, the existence of any correlation between the grounding accident and the location (waterway) has a great potential for further investigation, especially since the slight correlation between the grounding accident and the distributiveness of the traffic can be seen as the effect of the width of the waterway on the traffic [18] and thus on the grounding accident. Furthermore, the size of the ships navigating in the area may also affect the results, as in some definition of traffic density the size of the ships is an affecting factor [11]. Therefore, the algorithm should be further 122
5 modified in order to take into account the size of the ship presented in the traffic. One another source of uncertainty is that the AIS data utilized for this research represent the recent ship traffic in the area (year 2010), while the historical accident data were from the years The current traffic does not necessarily represent the actual traffic density and distribution in the past. In fact, the ship traffic in the area has significantly increased during the past decades, due to the opening of the new ports in the area and also the economy growth of the neighboring nations [19]. Therefore, the result of this study needs to be verified using the AIS data of different years. Moreover, the AIS data used for this study covers the whole year of 2010; however, the studied area is normally covered with ice during the winter. The icy waterways may affect the traffic pattern in the area, which in this study is neglected. Thus, the effect of winter traffic on the result should also be investigated later. The other matter is related to the hypothesis testing, where the null hypothesis can never be proven and it can only be rejected or fail to reject. Failing to reject a null hypothesis does not mean that the null hypothesis is always true, rather is showing the null hypothesis is consistent with the resultant data; meaning that there is no enough evidence in the historical data to prove the opposite. Thus, although the existence of any possible correlation between the maritime traffic and the grounding accident is doubted by the result of this study, it certainly cannot be concluded as absolutely no correlation. Besides, the utilized coefficients as Pearson and Spearman may not fully detect the existence of nonlinear correlation between the two variables. Therefore, implementing other methods, like mutual information test, seems useful in order to decrease uncertainty of the results. The last but not the least matter is that whether non correlation can imply non causation. The opposite statement as correlation does not imply causation is widely accepted between the statisticians [20]; however, non correlation implies non causation is still being discussed within the statisticians and other scholars [21]. Distinguishing a true causal relationship is very difficult and cannot be directly resulted from a correlation test. Therefore, even if the results of this research can be accepted as the proof for non correlation between the density of ship traffic and grounding accident, still the causality link between these two should be investigated and discussed further. 6 CONCLUSION It is shown in this research that there is no correlation between the ship traffic density and the grounding accidents, while there is slight correlation between the grounding accident and the traffic distributiveness. The results are based on the historical grounding accidents that took place in the Gulf of Finland within the years and the ship traffic of the same area in Thus, it is worth to highlight again that the obtained results are only valid for the studied area, and they cannot be generalized over other locations without further investigation. There are some levels of uncertainty involved in the presented result, which are mostly related to the utilized algorithms to extract the required data from the databases. Some assumptions like the used grid cells should be tested against the different sizes in order to find the effect of the size of the grid cells in the final result. Besides, the effect of the winter traffic and size of the ships on the results, which are neglected in this study, have the potential of further investigation. More importantly, the non existence of any causal link between the ship traffic and the grounding accidents cannot be merely concluded from the result of this research, and it needs further research and discussion. AKNOWLEDGMENT This study was conducted as a part of Minimizing risks of maritime oil transport by holistic safety strategies (MIMIC) project. The MIMIC project is funded by the European Union and the financing comes from the European Regional Development Fund, The Central Baltic INTERREG IV A Programme ; the City of Kotka; Kotka Hamina Regional Development Company (Cursor Oy); Centre for Economic Development, and Transport and the Environment of Southwest Finland (VARELY). REFERENCES 1. Fujii, Y. and R. Shiobara, The Analysis of Traffic Accidents. The Journal of Navigation, (4): p Pedersen, P.T. Collision and Grounding Mechanics. in Proceedings of WEMT ʹ95ʹ Copenhagen, Denmark: The Danish Society of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering. 3. Simonsen, B.C., Mechanics of Ship Grounding, in Department of Naval Architecture and Offshore Engineering. 1997, Technical University of Denmark: Kongens Lyngby. 4. COWI, Risk Analysis for Sea Traffic in the Area around Bornholm. 2008, Danish Maritime Authority: Kongens, Lyngby. 5. Kristiansen, S., Traffic Based Models, in Maritime Transportation Safety Management and Risk Analysis Mazaheri A., et al., A Decision Support Tool for VTS Centers to Detect Grounding Candidates. TransNav International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation, Vol. 6, No. 3, pp , Judson, B., Collision risk circumstances and traffic routeing in the approaches to the strait of Juan de Fuca, in 7th International VTS Symposium. 1992: Vancouver, Canada. 8. Goerlandt, F. and P. Kujala, Traffic simulation based ship collision probability modeling. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, (1): p van Dorp, J.R. and J.R.W. Merrick, On a risk management analysis of oil spill risk using maritime transportation system simulation. Annals of Operations Research, 2009: p Fujii, Y., et al., Some Factors Affecting the Frequency of Accidents in Marine Traffic: I The Diameter of Evasion for Crossing Encounters, II The probability of 123
6 Stranding, III The Effect of Darkness of the Probability of Collision and Stranding. The Journal of Navigation, (2): p Mazaheri, A. and J. Ylitalo, Comments on geometrical modeling of ship grounding, in 5th International Conference on Collision and Grounding of Ships (ICCGS). 2010: Espoo, Finland. 12. Otto, S., et al., Elements of Risk Analysis for Collision and Grounding of a RoRo Passenger Ferry. Marine Structures, : p Karlsson, M., F.M. Rasmussen, and L. Frisk, Verification of ship collision frequency model, in Ship Collision Analysis. 1998: Balkema, Rotterdam. p Ramboll, Navigational safety in the Sound between Denmark and Sweden (Oresund). 2006, Ramboll Danmark A/S: Denmark. 15. Gucma, L. The method of navigational risk assessment on waterways based on generalised real time simulation data. in International conference on marine simulation and ship maneuverability Terschelling, Netherlands. 16. Kaneko, F. A method for estimation of grounding frequency by using trajectories of ships and geometry of seabed. in International Conference on Collision and Grounding of Ships (ICCGS) Espoo, Finland. 17. Lehman, A., JMP for Basic Univariate and Multivariate Statistics : A Step by step Guide. 2005, Cary, NC, USA: SAS Press. 18. Seong, Y. C., et al., The relation with width of fairway and marine traffic flow. TransNav International Journal of Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation (3): p Kujala, P., et al., Analysis of the Marine Traffic Safety in the Gulf of Finland. Reliability Engineering and System Safety (8): p Pearl, J., Causal inference in statistics: An overview, R 350, Editor. 2009, Computer Science Department, University of California: Los Angeles. p Neufeld, E. and S. Kristtorn, Does non correlation imply non causation. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, : p
The model of oil spills due to ships collisions in Southern Baltic area
 The model of oil spills due to ships collisions in Southern Baltic area L. Gucma, M. rzywarty Maritime University of Szczecin, oland ABSTRACT: The paper presents implementation of probabilistic ships collision
The model of oil spills due to ships collisions in Southern Baltic area L. Gucma, M. rzywarty Maritime University of Szczecin, oland ABSTRACT: The paper presents implementation of probabilistic ships collision
The Model of Oil Spills Due to Ships Collisions in Southern Baltic Area
 International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 4 December 28 The Model of Oil Spills Due to Ships Collisions in Southern Baltic Area L. Gucma & M. rzywarty
International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 4 December 28 The Model of Oil Spills Due to Ships Collisions in Southern Baltic Area L. Gucma & M. rzywarty
The model of oil spills due to ships collisions in Southern Baltic area
 The model of oil spills due to ships collisions in Southern Baltic area L. Gucma, M. rzywarty Maritime University of Szczecin, oland ABSTRACT: The paper presents implementation of probabilistic ships collision
The model of oil spills due to ships collisions in Southern Baltic area L. Gucma, M. rzywarty Maritime University of Szczecin, oland ABSTRACT: The paper presents implementation of probabilistic ships collision
Strategic and Operational Risk Management for Wintertime Maritime Transportation System
 Strategic and Operational Risk Management for Wintertime Maritime Transportation System PA SAFE Flagship Seminar Vantaa, Finland 25 November 2016 Floris Goerlandt Aalto University Research Group on Maritime
Strategic and Operational Risk Management for Wintertime Maritime Transportation System PA SAFE Flagship Seminar Vantaa, Finland 25 November 2016 Floris Goerlandt Aalto University Research Group on Maritime
COLLISION RISK ESTIMATION FOR MOTORWAYS OF THE SEA
 COLLISION RISK ESTIMATION FOR MOTORWAYS OF THE SEA A. Blokus-Roszkowska, L. Smolarek Gdynia Maritime University, Gdynia, Poland e-mail: ablokus@am.gdynia.pl ABSTRACT The Motorways of the Sea is rather
COLLISION RISK ESTIMATION FOR MOTORWAYS OF THE SEA A. Blokus-Roszkowska, L. Smolarek Gdynia Maritime University, Gdynia, Poland e-mail: ablokus@am.gdynia.pl ABSTRACT The Motorways of the Sea is rather
ANNEX 23 RESOLUTION MSC.231(82) ADOPTION OF AMENDMENTS TO THE EXISTING MANDATORY SHIP REPORTING SYSTEM IN THE GULF OF FINLAND
 RESOLUTION MSC.231(82) (adopted on 5 December 2006) ADOPTION OF AMENDMENTS TO THE EXISTING MANDATORY SHIP REPORTING SYSTEM IN THE GULF OF FINLAND THE MARITIME SAFETY COMMITTEE, RECALLING Article 28(b)
RESOLUTION MSC.231(82) (adopted on 5 December 2006) ADOPTION OF AMENDMENTS TO THE EXISTING MANDATORY SHIP REPORTING SYSTEM IN THE GULF OF FINLAND THE MARITIME SAFETY COMMITTEE, RECALLING Article 28(b)
Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission
 Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission Maritime Group Klaipeda, Lithuania, 23-25 November 2015 MARITIME 15-2015 Document title FAMOS Finalising Surveys for the Baltic Motorways of the Sea Code
Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission Maritime Group Klaipeda, Lithuania, 23-25 November 2015 MARITIME 15-2015 Document title FAMOS Finalising Surveys for the Baltic Motorways of the Sea Code
The HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan and Marine Spatial Planning
 The HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan and Marine Spatial Planning Anne Christine Brusendorff Executive Secretary HELCOM The Baltic Sea Our common responsibility. Workshop on Integrated Sea Use management Stockholm
The HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan and Marine Spatial Planning Anne Christine Brusendorff Executive Secretary HELCOM The Baltic Sea Our common responsibility. Workshop on Integrated Sea Use management Stockholm
Probability of Ship on Collision Courses Based on the New PAW Using MMG Model and AIS Data
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 1 March 215 DOI: 1.12716/11.9.1.5 robability of Ship on Collision Courses Based on
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 1 March 215 DOI: 1.12716/11.9.1.5 robability of Ship on Collision Courses Based on
Nonhomogenous Poisson process application to modelling accidents number at Baltic Sea waters and ports
 ORCID ID: 0000-0002-8274-3005 Naval University Gdynia Poland Nonhomogenous Poisson process application to modelling accidents number at Baltic Sea waters and ports Keywords Poisson process safety characteristics
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-8274-3005 Naval University Gdynia Poland Nonhomogenous Poisson process application to modelling accidents number at Baltic Sea waters and ports Keywords Poisson process safety characteristics
OILRISK Web: Advanced Tool. Decision-making
 2011 WMU IMO Conference on Oil Spill Risk Management 7 9 March, Malmö, Sweden OILRISK Web: Advanced Tool for Enhancing Spill Response Decision-making Aps 1, R., Ambjörn 2, C., Fetissov 1, M., Karjalainen
2011 WMU IMO Conference on Oil Spill Risk Management 7 9 March, Malmö, Sweden OILRISK Web: Advanced Tool for Enhancing Spill Response Decision-making Aps 1, R., Ambjörn 2, C., Fetissov 1, M., Karjalainen
IMO ROUTEING OF SHIPS, SHIP REPORTING AND RELATED MATTERS. Amendments to the existing mandatory ship reporting system In the Gulf of Finland
 INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION E IMO SUB-COMMITTEE ON SAFETY OF NAVIGATION 52nd session Agenda item 3 NAV 52/3/5 12 April 2006 Original: ENGLISH ROUTEING OF SHIPS, SHIP REPORTING AND RELATED MATTERS
INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION E IMO SUB-COMMITTEE ON SAFETY OF NAVIGATION 52nd session Agenda item 3 NAV 52/3/5 12 April 2006 Original: ENGLISH ROUTEING OF SHIPS, SHIP REPORTING AND RELATED MATTERS
Seatrack Web Developments
 Seatrack Web Seatrack Web Developments HELCOM RESPONSE 16/2012, 21 November 2012 Johan Mattsson, DCOO Seatrack Web Contents Short overview Recent developments Online demonstration (experimental) Questions
Seatrack Web Seatrack Web Developments HELCOM RESPONSE 16/2012, 21 November 2012 Johan Mattsson, DCOO Seatrack Web Contents Short overview Recent developments Online demonstration (experimental) Questions
Interaction of Ships while Opposing Navigation among Small Ice Floes
 ARCTIC OI RECOVERY EXERCISE 05 KEMI ARCTIC 05 Conference Interaction of Ships while Opposing Navigation among Small Ice Floes Vadim K. Goncharov Professor Department of Oceantechnics and Marine Technology
ARCTIC OI RECOVERY EXERCISE 05 KEMI ARCTIC 05 Conference Interaction of Ships while Opposing Navigation among Small Ice Floes Vadim K. Goncharov Professor Department of Oceantechnics and Marine Technology
VOYAGE (PASSAGE) PLANNING
 VOYAGE (PASSAGE) PLANNING Introduction O Passage planning or voyage planning is a procedure of developing a complete description of a vessel's voyage from start to finish. O Production of a passage plan
VOYAGE (PASSAGE) PLANNING Introduction O Passage planning or voyage planning is a procedure of developing a complete description of a vessel's voyage from start to finish. O Production of a passage plan
Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel
 RescOp - Development of rescue operations in the Gulf of Finland International Seminar: MARITIME SAFETY IN THE GULF OF FINLAND Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel Vadim K. Goncharov Department
RescOp - Development of rescue operations in the Gulf of Finland International Seminar: MARITIME SAFETY IN THE GULF OF FINLAND Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel Vadim K. Goncharov Department
Influence of compressive ice force in bow-to-aft ship collision
 Proceedings of the ICCGS 2016 15-18 June, 2016 University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea Influence of compressive ice force in bow-to-aft ship collision Kristjan Tabri 1), Floris Goerlandt 2), Pentti Kujala 2)
Proceedings of the ICCGS 2016 15-18 June, 2016 University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea Influence of compressive ice force in bow-to-aft ship collision Kristjan Tabri 1), Floris Goerlandt 2), Pentti Kujala 2)
Traffic accidents and the road network in SAS/GIS
 Traffic accidents and the road network in SAS/GIS Frank Poppe SWOV Institute for Road Safety Research, the Netherlands Introduction The first figure shows a screen snapshot of SAS/GIS with part of the
Traffic accidents and the road network in SAS/GIS Frank Poppe SWOV Institute for Road Safety Research, the Netherlands Introduction The first figure shows a screen snapshot of SAS/GIS with part of the
Proceedings of the ASME nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France
 Proceedings of the ASME 2013 32nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10316 PROBABILISTIC SELECTION OF SHIP-SHIP COLLISION
Proceedings of the ASME 2013 32nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10316 PROBABILISTIC SELECTION OF SHIP-SHIP COLLISION
Paul Bridge Meteorologist Vaisala/UKMO Work Groups/Committees: WMO/TRB/AMS
 Paul Bridge Meteorologist Vaisala/UKMO Work Groups/Committees: WMO/TRB/AMS Introduction (a) Identify and establish, if possible, inventories of transport networks in the ECE region which are vulnerable
Paul Bridge Meteorologist Vaisala/UKMO Work Groups/Committees: WMO/TRB/AMS Introduction (a) Identify and establish, if possible, inventories of transport networks in the ECE region which are vulnerable
Council conclusions on Arctic issues. 2985th FOREIGN AFFAIRS Council meeting Brussels, 8 December 2009
 COU CIL OF THE EUROPEA U IO EN Council conclusions on Arctic issues 2985th FOREIGN AFFAIRS Council meeting Brussels, 8 December 2009 The Council adopted the following conclusions: The Council recalls its
COU CIL OF THE EUROPEA U IO EN Council conclusions on Arctic issues 2985th FOREIGN AFFAIRS Council meeting Brussels, 8 December 2009 The Council adopted the following conclusions: The Council recalls its
An Overview of Maritime Waterway Quantitative Risk Assessment Models
 An Overview of Maritime Waterway Quantitative Risk Assessment Models Author Li, Suyi, Meng, Qiang, Qu, Xiaobo Published 2012 Journal Title Risk Analysis DOI https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2011.01697.x
An Overview of Maritime Waterway Quantitative Risk Assessment Models Author Li, Suyi, Meng, Qiang, Qu, Xiaobo Published 2012 Journal Title Risk Analysis DOI https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2011.01697.x
CANADIAN HYDROGRAPHIC SERVICE & OCEANOGRAPHIC SERVICES
 CANADIAN HYDROGRAPHIC SERVICE & OCEANOGRAPHIC SERVICES Presentation to Warming of the North Conference Ottawa, March 2 nd, 2015 Denis Hains, Director General & Hydrographer General of Canada TIP OF THE
CANADIAN HYDROGRAPHIC SERVICE & OCEANOGRAPHIC SERVICES Presentation to Warming of the North Conference Ottawa, March 2 nd, 2015 Denis Hains, Director General & Hydrographer General of Canada TIP OF THE
FINLAND, A COOL ARCTIC COUNTRY WITH SNOW-HOW
 FINLAND, A COOL ARCTIC COUNTRY WITH SNOW-HOW To succeed in a constantly changing world, you have to change as well. Finland has reinvented itself in just one short century and we re still at it. Our national
FINLAND, A COOL ARCTIC COUNTRY WITH SNOW-HOW To succeed in a constantly changing world, you have to change as well. Finland has reinvented itself in just one short century and we re still at it. Our national
USING MASSIVE AMOUNTS OF MARINE AIS DATA TO EVALUATE MARINE TRAFFIC
 ESRI UC 2014, CONFERENCE PRESENTATION USING MASSIVE AMOUNTS OF MARINE AIS DATA TO EVALUATE MARINE TRAFFIC AARON LICKER BC GIS LEAD - aaron_licker@golder.com BC REGION - GOLDER ASSOCIATES LTD. THE CHALLENGE
ESRI UC 2014, CONFERENCE PRESENTATION USING MASSIVE AMOUNTS OF MARINE AIS DATA TO EVALUATE MARINE TRAFFIC AARON LICKER BC GIS LEAD - aaron_licker@golder.com BC REGION - GOLDER ASSOCIATES LTD. THE CHALLENGE
Improved Maritime Statistics with Big Data
 Improved Maritime Statistics with Big Data Abboud Ado 1, Annica Isaksson de Groote 2, Ingegerd Jansson 3, Marcus Justesen 4, Jerker Moström 5, Fredrik Söderbaum 6 1 Transport Analysis, Stockholm, Sweden;
Improved Maritime Statistics with Big Data Abboud Ado 1, Annica Isaksson de Groote 2, Ingegerd Jansson 3, Marcus Justesen 4, Jerker Moström 5, Fredrik Söderbaum 6 1 Transport Analysis, Stockholm, Sweden;
Bivariate Relationships Between Variables
 Bivariate Relationships Between Variables BUS 735: Business Decision Making and Research 1 Goals Specific goals: Detect relationships between variables. Be able to prescribe appropriate statistical methods
Bivariate Relationships Between Variables BUS 735: Business Decision Making and Research 1 Goals Specific goals: Detect relationships between variables. Be able to prescribe appropriate statistical methods
E x a m p l e s o f t o o l s f o r s e a s i t u a t i o n a l a w a r e n e s s u s i n g C M E M S d a t a. Copernicus EU
 E x a m p l e s o f t o o l s f o r s e a s i t u a t i o n a l a w a r e n e s s u s i n g C M E M S d a t a Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu S e a S i t u a t i o n a l A w
E x a m p l e s o f t o o l s f o r s e a s i t u a t i o n a l a w a r e n e s s u s i n g C M E M S d a t a Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu S e a S i t u a t i o n a l A w
North Sea Ballast Water Exchange Area
 HELSINKI and OSPAR COMMISSIONS HELCOM/OSPAR TG BALLAST 8-2017 Joint HELCOM/OSPAR Task Group on Ballast Water Management Convention Exemptions Eighth Meeting Helsinki, Finland, 16-17 November 2017 Document
HELSINKI and OSPAR COMMISSIONS HELCOM/OSPAR TG BALLAST 8-2017 Joint HELCOM/OSPAR Task Group on Ballast Water Management Convention Exemptions Eighth Meeting Helsinki, Finland, 16-17 November 2017 Document
NEW TOOLS TO IMPROVE DESKTOP SURVEYS
 NEW TOOLS TO IMPROVE DESKTOP SURVEYS Pablo Vengoechea (Telemediciones S.A.), Jorge O. García (Telemediciones S.A.), Email: Telemediciones S.A. / Cra. 46 94-17 Bogotá D.C.
NEW TOOLS TO IMPROVE DESKTOP SURVEYS Pablo Vengoechea (Telemediciones S.A.), Jorge O. García (Telemediciones S.A.), Email: Telemediciones S.A. / Cra. 46 94-17 Bogotá D.C.
Education in Maritime Spatial Planning European Maritime Days May 22, 2012 Gothenburg
 Education in Maritime Spatial Planning European Maritime Days May 22, 2012 Gothenburg Paula Lindroos, director Baltic Centre for Sustainable Development Uppsala University BUP in Summary A regional university
Education in Maritime Spatial Planning European Maritime Days May 22, 2012 Gothenburg Paula Lindroos, director Baltic Centre for Sustainable Development Uppsala University BUP in Summary A regional university
Data Science Unit. Global DTM Support Team, HQ Geneva
 NET FLUX VISUALISATION FOR FLOW MONITORING DATA Data Science Unit Global DTM Support Team, HQ Geneva March 2018 Summary This annex seeks to explain the way in which Flow Monitoring data collected by the
NET FLUX VISUALISATION FOR FLOW MONITORING DATA Data Science Unit Global DTM Support Team, HQ Geneva March 2018 Summary This annex seeks to explain the way in which Flow Monitoring data collected by the
PSAM-0388 OIL SPILL RISK ASSESSMENT FOR LOVIISA POWER PLANT
 Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management May 14-18, 2006, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA OIL SPILL RISK ASSESSMENT FOR LOVIISA POWER PLANT PSAM-0388
Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management May 14-18, 2006, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA OIL SPILL RISK ASSESSMENT FOR LOVIISA POWER PLANT PSAM-0388
Paper: ST-161. Techniques for Evidence-Based Decision Making Using SAS Ian Stockwell, The Hilltop UMBC, Baltimore, MD
 Paper: ST-161 Techniques for Evidence-Based Decision Making Using SAS Ian Stockwell, The Hilltop Institute @ UMBC, Baltimore, MD ABSTRACT SAS has many tools that can be used for data analysis. From Freqs
Paper: ST-161 Techniques for Evidence-Based Decision Making Using SAS Ian Stockwell, The Hilltop Institute @ UMBC, Baltimore, MD ABSTRACT SAS has many tools that can be used for data analysis. From Freqs
Arctic Hydrographic Adequacy an Update
 Arctic Hydrographic Adequacy an Update Lt Cmd. Samuel F. Greenaway 1 and Amber Batts 1,2 1. NOAA Office of Coast Survey Development Lab, Hydrographic Systems & Technology Branch, Silver Spring, Maryland,
Arctic Hydrographic Adequacy an Update Lt Cmd. Samuel F. Greenaway 1 and Amber Batts 1,2 1. NOAA Office of Coast Survey Development Lab, Hydrographic Systems & Technology Branch, Silver Spring, Maryland,
Exploiting maritime Big Data, the Blue Hub
 Exploiting maritime Big Data, the Blue Hub Marlene Alvarez Alvarez, Michele Vespe, Harm Greidanus Marlene.alvarez@jrc.ec.europa.eu Joint Research Centre the European Commission's in-house science service
Exploiting maritime Big Data, the Blue Hub Marlene Alvarez Alvarez, Michele Vespe, Harm Greidanus Marlene.alvarez@jrc.ec.europa.eu Joint Research Centre the European Commission's in-house science service
D6.6 Crowd-sourcing of ice information
 D6.6 Crowd-sourcing of ice information Project no. 636329 Project acronym: EfficienSea2 EFFICIENSEA2 efficient, safe and sustainable traffic at sea Funding scheme: Innovation Action (IA) Start date of
D6.6 Crowd-sourcing of ice information Project no. 636329 Project acronym: EfficienSea2 EFFICIENSEA2 efficient, safe and sustainable traffic at sea Funding scheme: Innovation Action (IA) Start date of
Weather and ice information as a tool for arctic marine and offshore services
 Weather and ice information as a tool for arctic marine and offshore services World Meteorological Organization Executive Council Panel of Experts on Polar Observations, Research and Services President
Weather and ice information as a tool for arctic marine and offshore services World Meteorological Organization Executive Council Panel of Experts on Polar Observations, Research and Services President
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activityengage O CEAN AND SEA BO RDERS Who has the rights to valuable
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activityengage O CEAN AND SEA BO RDERS Who has the rights to valuable
Contribution of Norwegian partners (Aanderaa Data Instruments and NIVA) to Safeport project ( ). Final report
 Contribution of Norwegian partners (Aanderaa Data Instruments and NIVA) to Safeport project (2010-2012). Final report NFR-196866 Entry and Berthing Ship and Port Advising System as an Element of Port ITS.
Contribution of Norwegian partners (Aanderaa Data Instruments and NIVA) to Safeport project (2010-2012). Final report NFR-196866 Entry and Berthing Ship and Port Advising System as an Element of Port ITS.
Finnish Maritime Administration BULLETIN 5/
 Finnish Maritime Administration BULLETIN 5/23.5.2008 VOLUNTARY BALLAST WATER EXCHANGE IN THE NORTH-EAST ATLANTIC AND THE BALTIC SEA Invasive non-indigenous species, contained in ships ballast water, may
Finnish Maritime Administration BULLETIN 5/23.5.2008 VOLUNTARY BALLAST WATER EXCHANGE IN THE NORTH-EAST ATLANTIC AND THE BALTIC SEA Invasive non-indigenous species, contained in ships ballast water, may
An Attempt to Predict Manoeuvring Indices Using AIS Data for Automatic OD Data Acquisition
 An Attempt to Predict Manoeuvring Indices Using AIS Data for Automatic OD Data Acquisition Takeshige Nakano.* Kazuhiko Hasegawa.** *Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, Osaka Japan (Tel: +81-6-6877-5111,
An Attempt to Predict Manoeuvring Indices Using AIS Data for Automatic OD Data Acquisition Takeshige Nakano.* Kazuhiko Hasegawa.** *Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, Osaka Japan (Tel: +81-6-6877-5111,
NOAA Nautical Charts and Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning. Meredith Westington Chief Geographer NOAA/NOS/Office of Coast Survey
 NOAA Nautical Charts and Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning Meredith Westington Chief Geographer NOAA/NOS/Office of Coast Survey Ocean Policy Task Force What is CMSP? A comprehensive, adaptive, integrated,
NOAA Nautical Charts and Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning Meredith Westington Chief Geographer NOAA/NOS/Office of Coast Survey Ocean Policy Task Force What is CMSP? A comprehensive, adaptive, integrated,
HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission
 HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission HELCOM RECOMMENDATION 24/10 Adopted 25 June 2003, having regard to Article 20, Paragraph 1 b) of the 1992 Helsinki Convention IMPLEMENTATION
HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission HELCOM RECOMMENDATION 24/10 Adopted 25 June 2003, having regard to Article 20, Paragraph 1 b) of the 1992 Helsinki Convention IMPLEMENTATION
Baltic Sea Region cooperation in Maritime Spatial Planning - HELCOM/VASAB
 Baltic Sea Region cooperation in Maritime Spatial Planning - HELCOM/VASAB Sten Jerdenius Swedish Ministry of the Environment HELCOM/VASAB MSP Group Baltic Sea Region subregional workshop Espoo 31 March
Baltic Sea Region cooperation in Maritime Spatial Planning - HELCOM/VASAB Sten Jerdenius Swedish Ministry of the Environment HELCOM/VASAB MSP Group Baltic Sea Region subregional workshop Espoo 31 March
On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
 International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
I. LIBYA I.1. COUNTRY CHARACTERISTICS. Country reports
 Country reports I. LIBYA Disclaimer This document has not been adopted by the European Commission and should therefore not be relied upon as a statement of the European Commission. The purpose of this
Country reports I. LIBYA Disclaimer This document has not been adopted by the European Commission and should therefore not be relied upon as a statement of the European Commission. The purpose of this
New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data
 New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data Taizo Anan Hiroyuki Higuchi Naoki Hamada Fuel cost and CO 2 emissions
New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data Taizo Anan Hiroyuki Higuchi Naoki Hamada Fuel cost and CO 2 emissions
Texas A&M University
 Texas A&M University CVEN 658 Civil Engineering Applications of GIS Hotspot Analysis of Highway Accident Spatial Pattern Based on Network Spatial Weights Instructor: Dr. Francisco Olivera Author: Zachry
Texas A&M University CVEN 658 Civil Engineering Applications of GIS Hotspot Analysis of Highway Accident Spatial Pattern Based on Network Spatial Weights Instructor: Dr. Francisco Olivera Author: Zachry
Spatial and Temporal Geovisualisation and Data Mining of Road Traffic Accidents in Christchurch, New Zealand
 166 Spatial and Temporal Geovisualisation and Data Mining of Road Traffic Accidents in Christchurch, New Zealand Clive E. SABEL and Phil BARTIE Abstract This paper outlines the development of a method
166 Spatial and Temporal Geovisualisation and Data Mining of Road Traffic Accidents in Christchurch, New Zealand Clive E. SABEL and Phil BARTIE Abstract This paper outlines the development of a method
1. Baltic SCOPE Towards coherence and cross-border solutions in Baltic Maritime Spatial Plans
 NSHC 32th Conference Explanatory Note Dublin, Ireland Item E.2 MSP 21-23 June 2016 Germany Cross border MSP for the EEZ, a case study from the Baltic Sea The Federal Maritime and Hydrographic Agency of
NSHC 32th Conference Explanatory Note Dublin, Ireland Item E.2 MSP 21-23 June 2016 Germany Cross border MSP for the EEZ, a case study from the Baltic Sea The Federal Maritime and Hydrographic Agency of
Figure 10. Travel time accessibility for heavy trucks
 Figure 10. Travel time accessibility for heavy trucks Heavy truck travel time from Rotterdam to each European cities respecting the prescribed speed in France on the different networks - Road, motorway
Figure 10. Travel time accessibility for heavy trucks Heavy truck travel time from Rotterdam to each European cities respecting the prescribed speed in France on the different networks - Road, motorway
The Changing Arctic: Strategic Opportunities and Challenges
 The Changing Arctic: Strategic Opportunities and Challenges Sherri Goodman Senior Vice President & General Counsel Executive Director, CNA Military Advisory Board 1 New Access to Resources Oil and Gas
The Changing Arctic: Strategic Opportunities and Challenges Sherri Goodman Senior Vice President & General Counsel Executive Director, CNA Military Advisory Board 1 New Access to Resources Oil and Gas
MR. George ALEXAKIS, parallel session 3. "Mediterranean Sea Region. laying the conditions. for sustainable growth and jobs"
 parallel session 3 "Mediterranean Sea Region laying the conditions for sustainable growth and jobs" MR. George ALEXAKIS, elected Regional Councillor of Crete, Greece and representative of Crete in CRPM.
parallel session 3 "Mediterranean Sea Region laying the conditions for sustainable growth and jobs" MR. George ALEXAKIS, elected Regional Councillor of Crete, Greece and representative of Crete in CRPM.
Oleksandr Neprokin,, Olga Bratchenko, Oleksandr Leposhkin
 19TH OSCE ECONOMIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL FORUM Promotion of common actions and co-operation in the OSCE area in the fields of development of sustainable energy and transport CONCLUDING MEETING Prague, 14-16
19TH OSCE ECONOMIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL FORUM Promotion of common actions and co-operation in the OSCE area in the fields of development of sustainable energy and transport CONCLUDING MEETING Prague, 14-16
The Danish Maritime Spatial Data Infrastructure (MSDI) Geodata of the Sea
 MSDI/MSP The Danish Maritime Spatial Data Infrastructure (MSDI) Geodata of the Sea Components of an infrastructure: DATA - metadata, datasets FUNCTIONALITY - spatial data services, web services and other
MSDI/MSP The Danish Maritime Spatial Data Infrastructure (MSDI) Geodata of the Sea Components of an infrastructure: DATA - metadata, datasets FUNCTIONALITY - spatial data services, web services and other
Probability and Statistics
 Probability and Statistics Kristel Van Steen, PhD 2 Montefiore Institute - Systems and Modeling GIGA - Bioinformatics ULg kristel.vansteen@ulg.ac.be CHAPTER 4: IT IS ALL ABOUT DATA 4a - 1 CHAPTER 4: IT
Probability and Statistics Kristel Van Steen, PhD 2 Montefiore Institute - Systems and Modeling GIGA - Bioinformatics ULg kristel.vansteen@ulg.ac.be CHAPTER 4: IT IS ALL ABOUT DATA 4a - 1 CHAPTER 4: IT
King Fahd University Of Petroleum and Minerals
 King Fahd University Of Petroleum and Minerals Construction Engineering & Management Department Construction Project Management CRP (514) Term (102) Term Paper Report Supervised by: Prof. Baqer M. Al-Ramadan
King Fahd University Of Petroleum and Minerals Construction Engineering & Management Department Construction Project Management CRP (514) Term (102) Term Paper Report Supervised by: Prof. Baqer M. Al-Ramadan
Effects of wind strength and wave height on ship incident risk: regional trends and seasonality
 Effects of wind strength and wave height on ship incident risk: regional trends and seasonality Christiaan Heij, Sabine Knapp Econometric Institute, Erasmus University Rotterdam Econometric Institute Report
Effects of wind strength and wave height on ship incident risk: regional trends and seasonality Christiaan Heij, Sabine Knapp Econometric Institute, Erasmus University Rotterdam Econometric Institute Report
ADOPTED ISOCHRONES METHOD IMPROVING SHIP SAFETY IN WEATHER ROUTING WITH EVOLUTIONARY APPROACH
 ADOPTED ISOCHRONES METHOD IMPROVING SHIP SAFETY Szłapczyńska Joanna, Śmierzchalski Roman Maritime University, Gdynia, Poland Keywords weather routing, isochrones method Abstract The paper is focused on
ADOPTED ISOCHRONES METHOD IMPROVING SHIP SAFETY Szłapczyńska Joanna, Śmierzchalski Roman Maritime University, Gdynia, Poland Keywords weather routing, isochrones method Abstract The paper is focused on
Confidence and prediction intervals for. generalised linear accident models
 Confidence and prediction intervals for generalised linear accident models G.R. Wood September 8, 2004 Department of Statistics, Macquarie University, NSW 2109, Australia E-mail address: gwood@efs.mq.edu.au
Confidence and prediction intervals for generalised linear accident models G.R. Wood September 8, 2004 Department of Statistics, Macquarie University, NSW 2109, Australia E-mail address: gwood@efs.mq.edu.au
BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS. Dr. Margarita Stancheva
 BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS Dr. Margarita Stancheva Name of presentation NEED FOR COHERENCE BETWEEN LAND AND SEA ACTIVITIES Name presenter Burgas is the fourth largest city in Bulgaria and
BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS Dr. Margarita Stancheva Name of presentation NEED FOR COHERENCE BETWEEN LAND AND SEA ACTIVITIES Name presenter Burgas is the fourth largest city in Bulgaria and
REPORT TO THE PLANNING, TRANSPORTATION AND PROTECTIVE SERVICES COMMITTEE MEETING OF JUNE 26, 2013
 PPS/PS 2013-07 REPORT TO THE PLANNING, TRANSPORTATION AND PROTECTIVE SERVICES COMMITTEE MEETING OF JUNE 26, 2013 SUBJECT UPDATES TO THE CAPITAL REGIONAL DISTRICT MODELLING OF POTENTIAL TSUNAMI INUNDATION
PPS/PS 2013-07 REPORT TO THE PLANNING, TRANSPORTATION AND PROTECTIVE SERVICES COMMITTEE MEETING OF JUNE 26, 2013 SUBJECT UPDATES TO THE CAPITAL REGIONAL DISTRICT MODELLING OF POTENTIAL TSUNAMI INUNDATION
Developing integrated remote sensing and GIS procedures for oil spill monitoring on the Libyan coast
 Coastal Processes III 125 Developing integrated remote sensing and GIS procedures for oil spill monitoring on the Libyan coast A. Eljabri & C. Gallagher Department of Civil Engineering and Built Environment,
Coastal Processes III 125 Developing integrated remote sensing and GIS procedures for oil spill monitoring on the Libyan coast A. Eljabri & C. Gallagher Department of Civil Engineering and Built Environment,
Spatial Variation in Local Road Pedestrian and Bicycle Crashes
 2015 Esri International User Conference July 20 24, 2015 San Diego, California Spatial Variation in Local Road Pedestrian and Bicycle Crashes Musinguzi, Abram, Graduate Research Assistant Chimba,Deo, PhD.,
2015 Esri International User Conference July 20 24, 2015 San Diego, California Spatial Variation in Local Road Pedestrian and Bicycle Crashes Musinguzi, Abram, Graduate Research Assistant Chimba,Deo, PhD.,
Territorial Cooperation within the Northern Periphery and the Arctic
 Territorial Cooperation within the Northern Periphery and the Arctic 12 March 2013 / By Silvia Curbelo Betancort North charr project, Landösjön lake, Sweden. Source: North Periphery Programme Today we
Territorial Cooperation within the Northern Periphery and the Arctic 12 March 2013 / By Silvia Curbelo Betancort North charr project, Landösjön lake, Sweden. Source: North Periphery Programme Today we
PLAN BOTHNIA MARE/2009/16
 PLAN BOTHNIA MARE/2009/16 Hermanni Backer Project Manager HELCOM Secretariat Partner Kick-Off Meeting Nordregio, Stockholm December 16 2010 Photo: Elena Bulycheva PLAN BOTHNIA MARE/2009/16 Co-financed
PLAN BOTHNIA MARE/2009/16 Hermanni Backer Project Manager HELCOM Secretariat Partner Kick-Off Meeting Nordregio, Stockholm December 16 2010 Photo: Elena Bulycheva PLAN BOTHNIA MARE/2009/16 Co-financed
INTERNATIONAL CONVENTION FOR THE CONTROL AND MANAGEMENT OF SHIPS' BALLAST WATER AND SEDIMENTS, 2004
 E 4 ALBERT EMBANKMENT LONDON SE1 7SR Telephone: +44 (0)20 7735 7611 Fax: +44 (0)20 7587 3210 BWM.2/Circ.56 13 July 2015 INTERNATIONAL CONVENTION FOR THE CONTROL AND MANAGEMENT OF SHIPS' BALLAST WATER AND
E 4 ALBERT EMBANKMENT LONDON SE1 7SR Telephone: +44 (0)20 7735 7611 Fax: +44 (0)20 7587 3210 BWM.2/Circ.56 13 July 2015 INTERNATIONAL CONVENTION FOR THE CONTROL AND MANAGEMENT OF SHIPS' BALLAST WATER AND
Correlation. What Is Correlation? Why Correlations Are Used
 Correlation 1 What Is Correlation? Correlation is a numerical value that describes and measures three characteristics of the relationship between two variables, X and Y The direction of the relationship
Correlation 1 What Is Correlation? Correlation is a numerical value that describes and measures three characteristics of the relationship between two variables, X and Y The direction of the relationship
Terje Pedersen Product Manager Software / Hydrography Hydroacoustics Division
 Terje Pedersen Product Manager Software / Hydrography Hydroacoustics Division WORLD CLASS through people, technology and dedication WORLD CLASS through people, technology and dedication 1 2 HYDROFEST 2005
Terje Pedersen Product Manager Software / Hydrography Hydroacoustics Division WORLD CLASS through people, technology and dedication WORLD CLASS through people, technology and dedication 1 2 HYDROFEST 2005
Marine Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region
 Marine Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region Towards coherence and cross-border solutions in Baltic Maritime Spatial Plans Coordinator & Project manager Dr Ingela Isaksson Swedish Agency for Marine
Marine Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region Towards coherence and cross-border solutions in Baltic Maritime Spatial Plans Coordinator & Project manager Dr Ingela Isaksson Swedish Agency for Marine
National Report of Finland
 National Report of 1. Finnish Hydrographic Office The Finnish Hydrographic Office (FHO) is responsible for nautical charting over the Finnish sea area and the most important inland water bodies. This covers
National Report of 1. Finnish Hydrographic Office The Finnish Hydrographic Office (FHO) is responsible for nautical charting over the Finnish sea area and the most important inland water bodies. This covers
Quotations from other works that I have written
 Quotations from other works that I have written (Including supporting documentation from other sources) The following five groups of quotations are in numerical order of what I consider to be of the greatest
Quotations from other works that I have written (Including supporting documentation from other sources) The following five groups of quotations are in numerical order of what I consider to be of the greatest
Using the Mercator ocean forecasting system to compute coastal maritime pollution risk indicators on the Atlantic European coasts
 Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 437 Using the Mercator ocean forecasting system to compute coastal maritime pollution risk indicators on the Atlantic European coasts S. Besnard 1, E. Dombrowsky
Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 437 Using the Mercator ocean forecasting system to compute coastal maritime pollution risk indicators on the Atlantic European coasts S. Besnard 1, E. Dombrowsky
Maritime Weather Information: Automatic Reporting, A New Paradigm
 Maritime Weather Information: Automatic Reporting, A New Paradigm Joe Sienkiewicz, NOAA/NWS Ocean Prediction Center Responsibilities under SOLAS Met Services Contracting governments Observations Limited
Maritime Weather Information: Automatic Reporting, A New Paradigm Joe Sienkiewicz, NOAA/NWS Ocean Prediction Center Responsibilities under SOLAS Met Services Contracting governments Observations Limited
Country Fiche Sweden.
 Country Fiche Sweden 1. General information the territorial sea (12- nm zone) 70,000 km2 the Exclusive Economic Zone 60,000 km2 the EEZ is limited to the central line between adjacent states because the
Country Fiche Sweden 1. General information the territorial sea (12- nm zone) 70,000 km2 the Exclusive Economic Zone 60,000 km2 the EEZ is limited to the central line between adjacent states because the
Cell-based Model For GIS Generalization
 Cell-based Model For GIS Generalization Bo Li, Graeme G. Wilkinson & Souheil Khaddaj School of Computing & Information Systems Kingston University Penrhyn Road, Kingston upon Thames Surrey, KT1 2EE UK
Cell-based Model For GIS Generalization Bo Li, Graeme G. Wilkinson & Souheil Khaddaj School of Computing & Information Systems Kingston University Penrhyn Road, Kingston upon Thames Surrey, KT1 2EE UK
A study on new customer satisfaction index model of smart grid
 2nd Annual International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Information Science (EEEIS 2016) A study on new index model of smart grid Ze-San Liu 1,a, Zhuo Yu 1,b and Ai-Qiang Dong 1,c
2nd Annual International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Information Science (EEEIS 2016) A study on new index model of smart grid Ze-San Liu 1,a, Zhuo Yu 1,b and Ai-Qiang Dong 1,c
Towards coherent maritime spatial planning in the Baltic Sea Region, transnational and project perspective Talis Linkaits Head of VASAB Secretariat
 3 June 2013 Riga PartiSEApate Workshop MSP as Tool for Underwater Cultural Heritage Management in the Baltic Sea Towards coherent maritime spatial planning in the Baltic Sea Region, transnational and project
3 June 2013 Riga PartiSEApate Workshop MSP as Tool for Underwater Cultural Heritage Management in the Baltic Sea Towards coherent maritime spatial planning in the Baltic Sea Region, transnational and project
Chapter 9. Correlation and Regression
 Chapter 9 Correlation and Regression Lesson 9-1/9-2, Part 1 Correlation Registered Florida Pleasure Crafts and Watercraft Related Manatee Deaths 100 80 60 40 20 0 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 Year Boats in
Chapter 9 Correlation and Regression Lesson 9-1/9-2, Part 1 Correlation Registered Florida Pleasure Crafts and Watercraft Related Manatee Deaths 100 80 60 40 20 0 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 Year Boats in
VIEWPOINTS. Slavica Jovetic* s comment on Correlation analysis of indicators of regional competitiveness: The case of the Republic of Serbia (2013)
 Economic Horizons, May - August 2014, Volume 16, Number 2, 161-167 Faculty of Economics, University of Kragujevac UDC: 33 eissn 2217-9232 www. ekfak.kg.ac.rs VIEWPOINTS Slavica Jovetic* s comment on analysis
Economic Horizons, May - August 2014, Volume 16, Number 2, 161-167 Faculty of Economics, University of Kragujevac UDC: 33 eissn 2217-9232 www. ekfak.kg.ac.rs VIEWPOINTS Slavica Jovetic* s comment on analysis
Dummy coding vs effects coding for categorical variables in choice models: clarifications and extensions
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 Dummy coding vs effects coding for categorical variables
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 Dummy coding vs effects coding for categorical variables
FORECAST ERRORS IN PRICES AND WAGES: THE EXPERIENCE WITH THREE PROGRAMME COUNTRIES
 Escola de Economia e Gestão Universidade do Minho e NIPE fjveiga@eeg.uminho.pt FORECAST ERRORS IN PRICES AND WAGES: THE EXPERIENCE WITH THREE PROGRAMME COUNTRIES ABSTRACT This paper evaluates the accuracy
Escola de Economia e Gestão Universidade do Minho e NIPE fjveiga@eeg.uminho.pt FORECAST ERRORS IN PRICES AND WAGES: THE EXPERIENCE WITH THREE PROGRAMME COUNTRIES ABSTRACT This paper evaluates the accuracy
DELIVERING ECOSYSTEM- BASED MARINE SPATIAL PLANNING IN PRACTICE
 DELIVERING ECOSYSTEM- BASED MARINE SPATIAL PLANNING IN PRACTICE A first assessment for the UK and Ireland January 08 GLOBAL WARMING IMAGES / WWF ABOUT WWF WWF is the world s leading independent conservation
DELIVERING ECOSYSTEM- BASED MARINE SPATIAL PLANNING IN PRACTICE A first assessment for the UK and Ireland January 08 GLOBAL WARMING IMAGES / WWF ABOUT WWF WWF is the world s leading independent conservation
Distinguishing Causes from Effects using Nonlinear Acyclic Causal Models
 JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings 6:17 164 NIPS 28 workshop on causality Distinguishing Causes from Effects using Nonlinear Acyclic Causal Models Kun Zhang Dept of Computer Science and HIIT University
JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings 6:17 164 NIPS 28 workshop on causality Distinguishing Causes from Effects using Nonlinear Acyclic Causal Models Kun Zhang Dept of Computer Science and HIIT University
Geometric and probabilistic approaches towards Conflict Prediction
 Geometric and probabilistic approaches towards Conflict Prediction G.J. Bakker, H.J. Kremer and H.A.P. Blom Nationaal Lucht- en Ruimtevaartlaboratorium National Aerospace Laboratory NLR Geometric and probabilistic
Geometric and probabilistic approaches towards Conflict Prediction G.J. Bakker, H.J. Kremer and H.A.P. Blom Nationaal Lucht- en Ruimtevaartlaboratorium National Aerospace Laboratory NLR Geometric and probabilistic
Binary choice 3.3 Maximum likelihood estimation
 Binary choice 3.3 Maximum likelihood estimation Michel Bierlaire Output of the estimation We explain here the various outputs from the maximum likelihood estimation procedure. Solution of the maximum likelihood
Binary choice 3.3 Maximum likelihood estimation Michel Bierlaire Output of the estimation We explain here the various outputs from the maximum likelihood estimation procedure. Solution of the maximum likelihood
Environmental Risk from Ship traffic along the Norwegian Coast Odd Willy Brude, Det Norske Veritas, Veritasveien 1, 1322 Høvik, Norway
 Environmental Risk from Ship traffic along the Norwegian Coast 15.02.2012 Odd Willy Brude, Det Norske Veritas, Veritasveien 1, 1322 Høvik, Norway Marte Braathen, Det Norske Veritas, Veritasveien 1, 1322
Environmental Risk from Ship traffic along the Norwegian Coast 15.02.2012 Odd Willy Brude, Det Norske Veritas, Veritasveien 1, 1322 Høvik, Norway Marte Braathen, Det Norske Veritas, Veritasveien 1, 1322
Bayesian vs frequentist techniques for the analysis of binary outcome data
 1 Bayesian vs frequentist techniques for the analysis of binary outcome data By M. Stapleton Abstract We compare Bayesian and frequentist techniques for analysing binary outcome data. Such data are commonly
1 Bayesian vs frequentist techniques for the analysis of binary outcome data By M. Stapleton Abstract We compare Bayesian and frequentist techniques for analysing binary outcome data. Such data are commonly
Gulf of Finland Year 2014 An overview of activities and further visions
 Gulf of Finland Year 2014 An overview of activities and further visions The Gulf of Finland Maritime Assembly in Turku 6.-7.11.2014 Kai Myrberg Project Manager, Gulf of Finland Year 2014 Finnish Environment
Gulf of Finland Year 2014 An overview of activities and further visions The Gulf of Finland Maritime Assembly in Turku 6.-7.11.2014 Kai Myrberg Project Manager, Gulf of Finland Year 2014 Finnish Environment
HELCOM-VASAB Maritime Spatial Planning Working Group Twelfth Meeting Gdansk, Poland, February 2016
 HELCOM-VASAB Maritime Spatial Planning Working Group Twelfth Meeting Gdansk, Poland, 24-25 February 2016 Document title HELCOM database for the coastal and marine Baltic Sea protected areas (HELCOM MPAs).
HELCOM-VASAB Maritime Spatial Planning Working Group Twelfth Meeting Gdansk, Poland, 24-25 February 2016 Document title HELCOM database for the coastal and marine Baltic Sea protected areas (HELCOM MPAs).
Analysis of Satellite AIS Data to Derive Weather Judging Criteria for Voyage Route Selection
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 11 Number 2 June 2017 DOI: 10.12716/1001.11.02.09 Analysis of Satellite AIS Data to Derive
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 11 Number 2 June 2017 DOI: 10.12716/1001.11.02.09 Analysis of Satellite AIS Data to Derive
On the Use of Forecasts when Forcing Annual Totals on Seasonally Adjusted Data
 The 34 th International Symposium on Forecasting Rotterdam, The Netherlands, June 29 to July 2, 2014 On the Use of Forecasts when Forcing Annual Totals on Seasonally Adjusted Data Michel Ferland, Susie
The 34 th International Symposium on Forecasting Rotterdam, The Netherlands, June 29 to July 2, 2014 On the Use of Forecasts when Forcing Annual Totals on Seasonally Adjusted Data Michel Ferland, Susie
Central Baltic Programme
 Central Baltic Programme 2014-2020 About the Central Baltic Programme 2014-2020 Builds on the Central Baltic INTERREG IV A Programme 2007-2013 Cross-border cooperation projects in the central Baltic Sea
Central Baltic Programme 2014-2020 About the Central Baltic Programme 2014-2020 Builds on the Central Baltic INTERREG IV A Programme 2007-2013 Cross-border cooperation projects in the central Baltic Sea
1 Executive summary. 2 Principles of SAT-OCEAN service
 S SCOPE OF WORK FOR ROUTING SERVICES 1 Executive summary SAT-OCEAN has developed an innovative routing service enabling for significant time and energy savings. This solution is going beyond traditional
S SCOPE OF WORK FOR ROUTING SERVICES 1 Executive summary SAT-OCEAN has developed an innovative routing service enabling for significant time and energy savings. This solution is going beyond traditional
xxv PART I THE DIVIDED OCEANS: INTERNATIONAL LAW GOVERNING JURISDICTIONAL ZONES 1
 Contents Preface page xv List of Figures xvii List of Tables xviii List of Abbreviations xix Table of Cases xxi Table of Treaties and Instruments xxv PART I THE DIVIDED OCEANS: INTERNATIONAL LAW GOVERNING
Contents Preface page xv List of Figures xvii List of Tables xviii List of Abbreviations xix Table of Cases xxi Table of Treaties and Instruments xxv PART I THE DIVIDED OCEANS: INTERNATIONAL LAW GOVERNING
Doppler Weather Radars and Weather Decision Support for DP Vessels
 Author s Name Name of the Paper Session DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 14-15, 2014 RISK SESSION Doppler Weather Radars and By Michael D. Eilts and Mike Arellano Weather Decision Technologies, Inc.
Author s Name Name of the Paper Session DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 14-15, 2014 RISK SESSION Doppler Weather Radars and By Michael D. Eilts and Mike Arellano Weather Decision Technologies, Inc.
TOSCA RESULTS OVERVIEW
 TOSCA RESULTS OVERVIEW Almost 3 years after the project started, TOSCA has proved capable of improving oil spill tracking systems. TOSCA has brought updated knowledge on surface currents and noticeable
TOSCA RESULTS OVERVIEW Almost 3 years after the project started, TOSCA has proved capable of improving oil spill tracking systems. TOSCA has brought updated knowledge on surface currents and noticeable
Combatting nutrient spillage in the Archipelago Sea a model system for coastal management support
 Combatting nutrient spillage in the Archipelago Sea a model system for coastal management support H. Lauri% H. Ylinen*, J. Koponen*, H. Helminen* & P. Laihonen* ' Environmental Impact Assessment Centre
Combatting nutrient spillage in the Archipelago Sea a model system for coastal management support H. Lauri% H. Ylinen*, J. Koponen*, H. Helminen* & P. Laihonen* ' Environmental Impact Assessment Centre
SUBJECT: Non paper on the size, nature and dynamics of the blue economy, 15 September 2015, prepared by DG MARE
 SUBJECT: Non paper on the size, nature and dynamics of the blue economy, 15 September 2015, prepared by DG MARE Comments Directorate-General for Maritime Policy (DGPM) and Statistics Portugal (INE) 24
SUBJECT: Non paper on the size, nature and dynamics of the blue economy, 15 September 2015, prepared by DG MARE Comments Directorate-General for Maritime Policy (DGPM) and Statistics Portugal (INE) 24
