The Physics of UFOs Kevin Pitts University of Illinois
|
|
|
- James Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Physics of UFOs Kevin Pitts University of Illinois 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 1
2 Why UFOs? It all starts at Fermilab 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 2
3 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 3
4 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 4
5 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 5
6 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 6
7 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 7
8 Phys 192: Science & Pseudoscience What is good science? bad science? pseudoscience? Topics covered Alternative medicine, UFOs, ghosts, cold fusion, statistics, logical fallacies, lie detectors, climate change, creationism, Last semester we performed extrasensory perception experiments, all results negative! This semester, we re making videos! 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 8
9 Things aren t always as they seem
10 A Face On Mars Credit: The Viking Project, NASA APOD: 1998 April 6 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 10
11 The Face on Mars Credit: NASA,Viking Project, APOD: 1995 July 22 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 11
12 Mars Express Close-Up of the Face on Mars APOD: 2006 September 25 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 12
13 Polling Numbers Gallup In your opinion, are UFO s something real, or just people s imaginations? Real just people s imagination don t know 48.5% 31.0% 20.6% Gallup Do you think that UFO s have ever visited the earth in some form, or not? Yes no don t know 45.1% 40.0% 15.9% In this same poll, 71% of those surveyed believe that the government knows more about UFOs than it is telling. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 13
14 Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence Dr. Pitts, I noticed that you will be presenting a lecture entitled The Physics of UFOs. I am not attending the lecture, but would like to know if you have written an article on this topic and, if so, whether it is available for people to read. On the basis of what I have read, there seems to be a fair amount of evidence based on (a) reports from highly reliable witnesses (including former military people, police officers, and pilots) (b) physical trace findings, and (c) radar recordings, which support the hypothesis that at least some reported UFOs are highly technologically advanced craft that may have an extraterrestrial origin. The Extraterrestrial Hypothesis seems plausible for explaining at least some reported UFO sightings. No testimony is sufficient to establish a miracle, unless the testimony be of such a kind that its falsehood would be more miraculous than the fact which it endeavors to establish -David Hume s maxim 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 14
15 Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence -Carl Sagan
16 Basic question Questions about UFOs Is there life anywhere other than Earth? If yes: Is there intelligent life anywhere other than Earth? If yes: Could we communicate? Could they come and visit us? Could we visit them? Have we communicated? Have we visited? 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 16
17 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 17
18 Questions/Topics 1. Distances 2. Nature s speed limit 3. Acceleration 4. Radiation 5. Is there anybody out there? 6. How would they know we re here? 7. Making contact 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 18
19 Speed of light 186,000 miles/second = 299,792,458 m/s 7x around Earth in one second Sun to Earth in about 8 minutes Earth to Mars in 3 22 minutes 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 19
20 Distance Scales Measurement unit: 1 light-year = distance light travels in one year 1 ly = 5,843,190,000,000 miles 6 trillion miles It takes Earth about years to travel 1 ly around the Sun 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 20
21 Mars Rover Landing Landing called 7 Minutes of Terror 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 21
22 The Milky Way Galaxy 100,000 light years You are here (approximately) 2-Nov-12 from Atlasoftheuniverse.com World Science - UFOs 22
23 Distances Nearest star is Alpha Centari, 4.3 ly away. About 14,000 stars (3500 visible) within 100 ly Sun about 25,000 ly from center of milky way. To travel to planets orbiting other stars, aliens (or humans) need 1. to travel near the speed of light 2. to be able to handle long-duration flights even with these criteria, can probably only visit a few nearby stars. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 23
24 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 24
25 Nature s Speed Limit In 1905, Albert Einstein published the Special Theory of Relativity One consequence of the theory is the famous equation: E = mc 2 Important for this discussion is another constant: no information or object can travel faster than the speed of light. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 25
26 Testing the speed limit protons circulate around accelerator rings Speed=0.99c=184,500mi/sec Speed= c=185, mi/sec reminder: speed of light c = 186,000 mi/sec Fermilab, Batavia, IL 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 26
27 High Speed travel Fastest manned object: Apollo 10: speed 25,000 mph = c Fastest man made object Helios 2 space probe: 158,000 mph = c This speed was attained by orbiting the sun, not through rocket propulsion. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 27
28 Rockets Rockets work by Newton s 3 rd Law Burn the fuel, it gets pushed out of the nozzle. The fuel pushes back on the rocket, accelerating it. Good news This works even in outer space Bad news Have to carry your fuel with you 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 28
29 Acceleration Something accelerating at 1g is speeding up at 10 m/s 2 At 1 second: speed 10 m/s At 2 seconds: speed 20 m/s At 3 seconds: speed 30 m/s F-16 pilots can withstand ~6g s for a few seconds. (link) People might be able to withstand 2-3g s for an extended period of time. Space Shuttle "Guidance also governs the main engine throttle command so that acceleration does not exceed 3 g's. The main engines are throttled down at approximately seven minutes 40 seconds into the mission to maintain 3 g's for physiological and structural constraints." 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 29
30 Acceleration Imagine we have a spaceship that can reach a speed of 0.75c This is 20,000 times faster than Apollo We start at rest on Earth (or near Earth) but we can only accelerate at 3g s or else we ll kill all of the passengers. How long does it take for our spaceship to reach a speed of 0.75c? Answer: 116 days We need enough fuel to accelerate at 3g s continuously for 4 months! Don t forget, we must decelerate at the same rate. So we need to fire our breaking rockets 4 months prior to when we want to stop. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 30
31 We need Anything prohibitive so far? Radically new technology to accelerate and decelerate our space ship The ability to undergo long duration space flight (decades to get to the nearest star) What about dangers during space flight? Radiation! 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 31
32 National Research Council, 2008 At the present time, given current knowledge, the level of radiation astronauts would encounter would not allow a human crew to undertake a Mars mission and might also seriously limit long-term Moon activity. International Space Station astronauts receive a radiation dose that is 27 times higher than we receive on Earth s surface. The ISS is still protected by Earth s magnetic field and upper atmosphere. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 32
33 Radiation Earth s atmosphere and magnetic field protect us from cosmic radiation. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 33
34 Radiation Radiation would be sufficient to kill humans in long duration space flight, unless an acceptable shielding method was developed. Perhaps other beings might be less susceptible to radiation effects. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 34
35 Questions/Topics 1. Distances 2. Nature s speed limit 3. Acceleration 4. Radiation 5. Is there anybody out there? 6. How would they know we re here? 7. Making contact 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 35
36 Galaxies Our sun is a small star toward the outside of the galaxy, the Milky Way (a spiral galaxy) containing approximately 200,000,000,000 stars (2 x ) A few others (e.g. Andromeda) visible to naked eye Telescopes reveal many galaxies, each ~ stars Andromeda Spiral Galaxy m100 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 36
37 The Milky Way Galaxy 100,000 light years You are here (approximately) 2-Nov-12 from Atlasoftheuniverse.com World Science - UFOs 37
38 Views from the Hubble Telescope Picture of an area of the sky (the size of a grain of sand held at arm s length) in which there are no stars visible to the naked eye! Shows visible stars in the Milky Way and distant fuzzy looking galaxies Estimate: ~10 11 =100 billion galaxies in the universe 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 38
39 Summary About stars per galaxy 2 to 4 x in the Milky Way About galaxies in the universe So we have about: x = = 100,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 stars in the universe. More stars in the universe than grains of sand on Earth Universe is dominated by light elements (H, He, Li) but there are plenty of heavy elements that have been produced by supernovae. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 39
40 Question: How many Earth-like planets: Requirements: Good Places for Life Single star system (not binary) Star should be sunlike (similar to our sun) Must have planets Must have Earth-like planet Estimates (arguable, but you can change them!) ~50% are single star systems (not binary) ~10% are sunlike (similar to our sun) ~10% have planets ~10% have an Earth-like planet These two estimates are pretty solid. These two estimates are low, reality possibly much higher. 4x10 11 x 0.5 x 0.1 x 0.1 x 0.1 = 2x10 8 =200,000,000 Earthlike planets in the Milky Way galaxy alone!!! [low estimate] 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 40
41 How Would We Make Contact? Einstein says we can t travel faster than the speed of light. Experiments say he s right. This immediately limits the possibilities for space travel between solar systems that are light years apart. Milky Way is about 100,000 light-years wide What can travel at the speed of light? Electromagnetic waves! Light, x-rays, radio-waves. First contact with an intelligent life form would most certainly be through electromagnetic waves! 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 41
42 Electromagnetic spectrum All EM radiation travels at speed of light! 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 42
43 SETI Search for Extra Terrestrial Intelligence Scanning the sky for all electromagnetic frequencies Looking for non-random patterns indicating a deterministic source. Note: Humans have been broadcasting to the galaxy since the early 20 th century. Our electromagnetic waves now reach out some 80 lightyears away from us. Anyone farther than 80 light-years would not yet be able to see our broadcasts! About 14,000 stars within 100 light-years of us (= % of the Milky Way) For signals originating elsewhere, our sensitivity depends upon location on time. To see a civilization on the other side of the Milky Way, they needed to begin broadcasting 30,000 years ago! 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 43
44 How Would We Make Contact? First contact with an intelligent life form would most certainly be through electromagnetic waves! Allen Telescope array, part of SETI = Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Project Scanning the sky for all electromagnetic frequencies Looking for non-random patterns indicating a deterministic source. You can participate in SETI at Home (link) 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 44
45 How Would They Know We re Here? Humans have been broadcasting to the galaxy since the early 20 th century. Our electromagnetic waves now reach out some 80 lightyears away from us. Anyone farther than 80 light-years would not yet be able to see our broadcasts! About 14,000 stars within 100 light-years of us (= % of the Milky Way) For signals originating elsewhere, our sensitivity depends upon location on time. To see a civilization near the center of the Milky Way, they needed to begin broadcasting 25,000 years ago! 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 45
46 The Milky Way Galaxy 100,000 light years Our electromagnetic footprint is smaller than this dot! The rest of the galaxy has no idea that we are here! 2-Nov-12 from Atlasoftheuniverse.com World Science - UFOs 46
47 Sound channels and Roswell
48 Ocean depth Sound channels Waves will channel where the wave speed is lowest. Speed of sound In ocean, channel is about ½ mile in depth Atmospheric sound channel about 30 miles up 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 48
49 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 49
50 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 50
51 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 51
52 Summary Is there life beyond Earth? We don t know. Has extraterrestrial life visited Earth? There is no credible evidence that it has. Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence. We have yet to see that evidence. If we make contact with another civilization, it will be by electromagnetic wave. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 52
53 How would they know we re here? We are looking for exoplanets Planets that orbit stars other than our own Any in the Goldilocks zone? 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 53
54 UFOs? Have we been visited? 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 54
55 UFOs Question: Why are they always seen by untrained observers? Professional astronomers and astrophysicists observe the sky daily with sophisticated equipment have never observed an extraterrestrial spaceship. Question: Why hasn t anyone observed the electromagnetic footprint (radio waves, gamma rays, light, etc.) of an alien? The electromagnetic footprint would be here before the aliens would. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 55
56 UFOs: Natural Explanation Some sources that might be misinterpreted: Approaching Aircraft (appear to hover) Unconventional Aircraft High Altitude Balloons Venus Artificial Satellites Reflections Off Clouds Optical Mirages Meteors Uncommon Atmospheric Phenomena (Aurora, Ball Lightning) Secret Military Objects Accidents 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 56
57 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 57
58 Material for Life Earth is teeming with elements: Nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, gold, iron, manganese, H uranium, silver, lithium Atomic # = # of protons The big bang (and it s aftermath) produced no element heavier than lithium (atomic number=3). Hydrogen, helium and lithium only.nothing heavier. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 58
59 Heavy Elements Heavy elements are crucial for life. Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, iron, potassium Where did the heavy elements come from? Normal stars (our sun) typically produce helium from hydrogen, but also produce some lithium and beryllium (Be, atomic #=4) Elements heavier than beryllium require a higher energy process to produce them a supernova. Supernovas occur at the end of a large star s life cycle. The stuff you are made of: carbon, oxygen, silicon, iron, etc. are supernova remnants! 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 59
60 Supernova Expels matter - all heavy elements in the universe (in you!) are formed in supernovae Remnant is a neutron star or black hole Radiates more energy than an entire galaxy for a brief period (months): Famous supernovae: 0 -- The Christmas Star?? in Crab Nebula, Recorded in China, in large Magellanic Cloud, seen by Kepler Pulsars (Neutron Stars) observed now as remnants of the 1054 and 1572 Supernovae! in Magellanic Cloud - remnants still observed 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 60
61 Does Life Develop? Experiments show that organic molecules form in conditions similar to the earliest stages of Earth s development. Carbon dioxide, water, nitrogen + energy (heat or lighting) Details of the mechanisms that bring single celled organisms (like amoeba) from the organic molecules are under study. Let s guess that there is only a 1% chance life will develop on an Earthlike planet. [This is probably a low estimate. The likelihood to develop life on an Earthlike planet is probably very high.] 2 x 10 8 Earthlike planets x 0.01 chance of developing life = 2 x 10 6 = 2,000,000 planets with life in the Milky Way. [this is still a low estimate] 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 61
62 Does Intelligence Develop? Large uncertainty. See Hobson textbook for a discussion. Art Hobson, Physics Concepts and Connections The Drake Equation attempt to account for the likelihood of intelligent life to develop, as well as the lifetime time scale. See Origins web site. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 62
63 Details here 2009 Morristown Hoax The icing on the cake came when the popular History Channel show UFO Hunters featured the Morristown UFO as their main story one week. Bill Birnes, the lead investigator of the show and the publisher of UFO Magazine, declared definitively that the Morristown UFO could not have been flares or Chinese lanterns. 2-Nov-12 World of Science - UFOs 63
Are We Alone? 17-Oct-13 Phys 192 Lecture 6 1
 Are We Alone? 17-Oct-13 Phys 192 Lecture 6 1 UFO Detectives I saw a UFO about 3 years ago. Can you guess what I saw? 17-Oct-13 Phys 192 Lecture 6 2 Exercise Break into groups of 3 or 4 Nominate a scribe
Are We Alone? 17-Oct-13 Phys 192 Lecture 6 1 UFO Detectives I saw a UFO about 3 years ago. Can you guess what I saw? 17-Oct-13 Phys 192 Lecture 6 2 Exercise Break into groups of 3 or 4 Nominate a scribe
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it
 Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
The Moon s relationship with Earth The formation of the Moon The surface of the Moon Phases of the Moon Travelling to the Moon
 The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Light. Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation. Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays
 Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
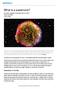 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Welcome Aboard!! CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS. Briefing Welcome to the Cosmic Tour: Some Guide Lines. Lecture 1 Our Place in the Universe
 CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS (Previous) Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 (New) Tuesdays 4:45 to 5:30 Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 YOURNAME 31AUG Welcome Aboard!! AUSTIN AST 301 YOURNAME 31AUG 2.5 MILLION
CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS (Previous) Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 (New) Tuesdays 4:45 to 5:30 Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 YOURNAME 31AUG Welcome Aboard!! AUSTIN AST 301 YOURNAME 31AUG 2.5 MILLION
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
9/5/16. Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM. Astronomy 1001 First Assignments: Chapter 1: A Modern View of the Universe
 9/5/16 Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM Syllabus: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/syllabi/ Lecture notes: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/ lecnotes/ Exams: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/
9/5/16 Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM Syllabus: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/syllabi/ Lecture notes: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/ lecnotes/ Exams: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/
The Universe and Galaxies
 The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
Universe Celestial Object Galaxy Solar System
 ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
Potentially useful formulas: F = G m 1m 2 r 2 F = k q 1q 2 F = ma Distance = Speed Time
 PHY100 May 4, 2010 Final Exam Name: Aran Garcia-Bellido Please read the problems carefully and answer them in the space provided. Write on the back of the page, if necessary. Show your work where requested
PHY100 May 4, 2010 Final Exam Name: Aran Garcia-Bellido Please read the problems carefully and answer them in the space provided. Write on the back of the page, if necessary. Show your work where requested
Space Explorer Glossary
 Space Explorer Glossary A. * Asteroid ~ a rocky object in space that can be a few feet wide to several hundred miles wide. Most asteroids in the Solar System orbit in a belt between Mars and Jupiter. *
Space Explorer Glossary A. * Asteroid ~ a rocky object in space that can be a few feet wide to several hundred miles wide. Most asteroids in the Solar System orbit in a belt between Mars and Jupiter. *
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life
 Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review of last class Introduction to Astronomy Contents of today s lecture Quiz time Review Review 1 n Science is a way of producing
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review of last class Introduction to Astronomy Contents of today s lecture Quiz time Review Review 1 n Science is a way of producing
2. The distance between the Sun and the next closest star, Proxima Centuari, is MOST accurately measured in
 Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Science Practice Astronomy (AstronomyJSuber)
 Name: Date: 1. The pull of gravity on Earth is a direct result of the A. mass of Earth. B. magnetic field of Earth. C. rotation of Earth on its axis. D. weight of Earth's atmosphere. This online assessment
Name: Date: 1. The pull of gravity on Earth is a direct result of the A. mass of Earth. B. magnetic field of Earth. C. rotation of Earth on its axis. D. weight of Earth's atmosphere. This online assessment
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Chapter 1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. A Modern View of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe Chapter Opener 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is
Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe Chapter Opener 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam
 Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
What is Earth Science?
 What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
5. What force holds the different astronomical systems described in this section together? What other forces exist in nature?
 SUMMARY The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is one of about a hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way, two other similar size galaxies, and dozens
SUMMARY The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is one of about a hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way, two other similar size galaxies, and dozens
Astrobiology: The Semester in Review
 A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
Earth Space Systems. Semester 1 Exam. Astronomy Vocabulary
 Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
MODERN ASTROPHYSICS PCES 4.55
 MODERN ASTROPHYSICS PCES 4.55 The 20 th century brought an appreciation of the colossal scale of the universe, and an explanation of how it all worked. The understanding of the stars came from nuclear
MODERN ASTROPHYSICS PCES 4.55 The 20 th century brought an appreciation of the colossal scale of the universe, and an explanation of how it all worked. The understanding of the stars came from nuclear
Space Physics Questions CfE
 Space Physics Questions CfE 1) Write down the definitions of the following: a) Moon b) Planet c) Sun d) Star e) Solar System f) Exoplanet g) Galaxy h) Universe. 2) What is cosmology the study of? 3) a)
Space Physics Questions CfE 1) Write down the definitions of the following: a) Moon b) Planet c) Sun d) Star e) Solar System f) Exoplanet g) Galaxy h) Universe. 2) What is cosmology the study of? 3) a)
Wallace Hall Academy
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Universe Notes Name 1 Newton and Gravity Newton s Thought Experiment Satellite s orbit as an Application of Projectiles Isaac Newton, as well as giving
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Universe Notes Name 1 Newton and Gravity Newton s Thought Experiment Satellite s orbit as an Application of Projectiles Isaac Newton, as well as giving
Supernovae Through the Ages
 Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
THE SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE
 1 THE SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE 1. Scientific notation review Write the following in proper scientific notation, giving the proper number of significant figures. 1.a Thirty-one million, seven hundred
1 THE SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE 1. Scientific notation review Write the following in proper scientific notation, giving the proper number of significant figures. 1.a Thirty-one million, seven hundred
Outline: Cosmological Origins. The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space
 Outline: Cosmological Origins The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space Reminder: HW #1 due in one week Homework is on class webpage
Outline: Cosmological Origins The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space Reminder: HW #1 due in one week Homework is on class webpage
Beyond the Solar System 2006 Oct 17 Page 1 of 5
 I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System
 Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System The Andromeda Galaxy One of hundreds of billions of galaxies, each with hundreds of billions of stars A warped spiral galaxy, 150 MLY away and 100,000
Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System The Andromeda Galaxy One of hundreds of billions of galaxies, each with hundreds of billions of stars A warped spiral galaxy, 150 MLY away and 100,000
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in
History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet
 Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target Question Example Date Target was Taught in Class The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe formed The
Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target Question Example Date Target was Taught in Class The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe formed The
Physics HW Set 3 Spring 2015
 1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos
 An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos What is Astronomy? 50 years ago, astronomy was the study of everything outside Earth s atmosphere: the planets, the Sun, stars, galaxies, the
An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos What is Astronomy? 50 years ago, astronomy was the study of everything outside Earth s atmosphere: the planets, the Sun, stars, galaxies, the
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Stars. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe. What Objects Do We Find in The Universe? 8/12/2010. Our goals for learning:
 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the past? Can we see the entire universe?
1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the past? Can we see the entire universe?
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe
 Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes
 Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how much bigger in radius is the Sun than the Earth? The ratio of the Sun's radius to the Earth's radius is 1,392,000/12756 = 109.1 How big is an astronomical
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how much bigger in radius is the Sun than the Earth? The ratio of the Sun's radius to the Earth's radius is 1,392,000/12756 = 109.1 How big is an astronomical
Space Booklet #3. The consists of a and all the other that orbit around that star. A is made up of several,, and that are held together by.
 Space Booklet #3 Explaining the Early Universe The consists of a and all the other that orbit around that star. A is made up of several,, and that are held together by. Three Types of Galaxies 1. 2. 3.
Space Booklet #3 Explaining the Early Universe The consists of a and all the other that orbit around that star. A is made up of several,, and that are held together by. Three Types of Galaxies 1. 2. 3.
Planets, Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Mon. & Weds. 3:35-4:50. Prof. Todd Adams. Welcome! Department of Physics Florida State University
 Planets, Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Mon. & Weds. 3:35-4:50 Prof. Todd Adams Welcome! Department of Physics Florida State University Astronomy is the study of objects beyond the Earth s atmosphere and
Planets, Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Mon. & Weds. 3:35-4:50 Prof. Todd Adams Welcome! Department of Physics Florida State University Astronomy is the study of objects beyond the Earth s atmosphere and
Coriolis Effect - the apparent curved paths of projectiles, winds, and ocean currents
 Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Zoink Questions: Tools of Astronomy
 1. Optical telescopes are designed to do what? Gather and focus visible light to see distant objects more clearly 2. Visible light can be separated into various colors to form a(n). Spectrum 3. The full
1. Optical telescopes are designed to do what? Gather and focus visible light to see distant objects more clearly 2. Visible light can be separated into various colors to form a(n). Spectrum 3. The full
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2 Bennett/Shostak) Overview of Chapter 2. Overview of Chapter 2. Example Question
 The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2 Bennett/Shostak) 26 January 2010 - Lecture 3 HNRS 228 - Astrobiology Prof. Geller Overview of Chapter 2 Ancient Debate about Life Beyond Earth (2.1) Greeks and
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2 Bennett/Shostak) 26 January 2010 - Lecture 3 HNRS 228 - Astrobiology Prof. Geller Overview of Chapter 2 Ancient Debate about Life Beyond Earth (2.1) Greeks and
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
The Big Bang Theory (page 854)
 Name Class Date Space Homework Packet Homework #1 Hubble s Law (pages 852 853) 1. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? 2. The shift in the light of a galaxy toward the red wavelengths is called
Name Class Date Space Homework Packet Homework #1 Hubble s Law (pages 852 853) 1. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? 2. The shift in the light of a galaxy toward the red wavelengths is called
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars
 Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department. Space. Pupil Notes Name:
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Space Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state what the value is for acceleration due to gravity during freefall Be able to explain
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Space Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state what the value is for acceleration due to gravity during freefall Be able to explain
Today. life the university & everything. Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations
 life the university & everything Phys 2130 Day 41: Questions? The Universe Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations Today Today: - how big is the universe?
life the university & everything Phys 2130 Day 41: Questions? The Universe Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations Today Today: - how big is the universe?
A1199 Are We Alone? " The Search for Life in the Universe
 ! A1199 Are We Alone? " The Search for Life in the Universe Instructor: Shami Chatterjee! Summer 2018 Web Page: http://www.astro.cornell.edu/academics/courses/astro1199/! HW2 now posted...! So far: Cosmology,
! A1199 Are We Alone? " The Search for Life in the Universe Instructor: Shami Chatterjee! Summer 2018 Web Page: http://www.astro.cornell.edu/academics/courses/astro1199/! HW2 now posted...! So far: Cosmology,
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy
 CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
Galaxies and the Universe
 Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 28. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
SU230R Grades 4-8. Hayes FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
 Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes
 Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Directed Reading A. Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS THE LIFE CYCLE OF SUNLIKE STARS A TOOL FOR STUDYING STARS.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
of stars constellations. Perhaps you have seen The Big Dipper, Taurus the bull, Orion the hunter, or other well-known star groups.
 Discovering Space For all of history, people have gazed up at the night sky and wondered what was up there. Long before telescopes and space shuttles, ancient people saw stars in the sky. They made up
Discovering Space For all of history, people have gazed up at the night sky and wondered what was up there. Long before telescopes and space shuttles, ancient people saw stars in the sky. They made up
chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies
 chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies Day 1:Technology and the Big Bang Studying the Stars A. Telescopes - Electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars and other objects include light, radio, and X-ray Space telescopes
chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies Day 1:Technology and the Big Bang Studying the Stars A. Telescopes - Electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars and other objects include light, radio, and X-ray Space telescopes
Chapter 1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. A Modern View of the Universe
 Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe?
Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe?
Searching for Life: Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds. Life in the Universe. Earliest Fossils. Laboratory Experiments.
 Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Space Notes 3B. Covers objectives 5, 10, and 11
 Space Notes 3B Covers objectives 5, 10, and 11 Technologies Designed To Explore Space Space Shuttle History Rocket Propulsion 1. Rockets transport astronauts and materials into space. 2. Animals such as
Space Notes 3B Covers objectives 5, 10, and 11 Technologies Designed To Explore Space Space Shuttle History Rocket Propulsion 1. Rockets transport astronauts and materials into space. 2. Animals such as
The Age of the Universe If the entire age of the Universe were 1 calendar year, then 1 month would be equivalent to roughly 1 billion years
 Astro.101 Sept. 9, 2008 Announcements A few slots are still open in the class; see prof. to sign up Web-page computer has been down; o.k. now Turn in your student contract Don t forget to do the OWL tutorial
Astro.101 Sept. 9, 2008 Announcements A few slots are still open in the class; see prof. to sign up Web-page computer has been down; o.k. now Turn in your student contract Don t forget to do the OWL tutorial
The Jamie Drake Equation
 The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
Name Date Period. 10. convection zone 11. radiation zone 12. core
 240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
Scale the Universe. Exploring your Universe from Inner to Outer Space. Linda L. Smith NASA Astrophysics Educator Ambassador
 Scale the Universe Exploring your Universe from Inner to Outer Space Linda L. Smith NASA Astrophysics Educator Ambassador lsmith@paulsboro.k12.nj.us 1 The Booklet This book is organized into 3-stand-alone
Scale the Universe Exploring your Universe from Inner to Outer Space Linda L. Smith NASA Astrophysics Educator Ambassador lsmith@paulsboro.k12.nj.us 1 The Booklet This book is organized into 3-stand-alone
4.8 Space Research and Exploration. Getting Into Space
 4.8 Space Research and Exploration Getting Into Space Astronauts are pioneers venturing into uncharted territory. The vehicles used to get them into space are complex and use powerful rockets. Space vehicles
4.8 Space Research and Exploration Getting Into Space Astronauts are pioneers venturing into uncharted territory. The vehicles used to get them into space are complex and use powerful rockets. Space vehicles
The Universe April 2, Lecture 2 1
 Beyond Our Comfort Zone Direct Experience: 10-5 to 10 5 meters Dust grain may have 0.01 mm = 10 micron diameter View from mountaintop may extend 100 km Experts may claim comfort with 10-7 to 10 7 m Optical
Beyond Our Comfort Zone Direct Experience: 10-5 to 10 5 meters Dust grain may have 0.01 mm = 10 micron diameter View from mountaintop may extend 100 km Experts may claim comfort with 10-7 to 10 7 m Optical
Measuring Distances to Galaxies. Galaxies in Motion. Hubble s Law. Galaxy Redshifts. Type Ia Supernovae. Supernovae are Good Standard Candles
 Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
CONTENT EXPECTATIONS
 THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
Universe. of Space Exploration. Future Space Missions
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Chapter Wrap-Up Observing the Universe Early History of Space Exploration Recent and Future Space Missions NASA/Ames Wendy Stenzel How do humans observe
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Chapter Wrap-Up Observing the Universe Early History of Space Exploration Recent and Future Space Missions NASA/Ames Wendy Stenzel How do humans observe
April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9,
 April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10,
April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10,
Nov 17, 2003 Astronomy 100 Fall _tips_ html
 Next week is Thanksgiving break Leonid meteor shower can be seen the night of the 18 th (really the early morning of the 19 th ). Should see dozens of meteors per hour at the peak 1:30 am CST. The shower
Next week is Thanksgiving break Leonid meteor shower can be seen the night of the 18 th (really the early morning of the 19 th ). Should see dozens of meteors per hour at the peak 1:30 am CST. The shower
Area 1: Space Exploration and Cosmology. 2. The weather information satellite NOAA-15 has a period of 99 minutes and an orbital height of 833 km.
 Multiple hoice Questions 1 10 rea 1: Space xploration and osmology 1. Identify the period of a geostationary satellite. 1 hour 1 day 1 week 1 month 1 year 2. The weather information satellite NO-15 has
Multiple hoice Questions 1 10 rea 1: Space xploration and osmology 1. Identify the period of a geostationary satellite. 1 hour 1 day 1 week 1 month 1 year 2. The weather information satellite NO-15 has
Astronomy. physics.wm.edu/~hancock/171/ A. Dayle Hancock. Small 239. Office hours: MTWR 10-11am
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
ASTRONOMY (ASTRON) ASTRON 113 HANDS ON THE UNIVERSE 1 credit.
 Astronomy (ASTRON) 1 ASTRONOMY (ASTRON) ASTRON 100 SURVEY OF ASTRONOMY 4 credits. Modern exploration of the solar system; our galaxy of stars, gas and dust; how stars are born, age and die; unusual objects
Astronomy (ASTRON) 1 ASTRONOMY (ASTRON) ASTRON 100 SURVEY OF ASTRONOMY 4 credits. Modern exploration of the solar system; our galaxy of stars, gas and dust; how stars are born, age and die; unusual objects
The Content of the Universe, and how we get heavy elements.
 The Content of the Universe, and how we get heavy elements http://www.lbl.gov/science-articles/archive/sabl/2006/jan/pie-chart.jpg 1 Outline The content of the universe How structure forms Elements heavier
The Content of the Universe, and how we get heavy elements http://www.lbl.gov/science-articles/archive/sabl/2006/jan/pie-chart.jpg 1 Outline The content of the universe How structure forms Elements heavier
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Protostars on the HR Diagram. Lifetimes of Stars. Lifetimes of Stars: Example. Pressure-Temperature Thermostat. Hydrostatic Equilibrium
 Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
The Death of Stars. Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages ) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars
 The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
2) On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find red giant stars? A) upper right B) lower right C) upper left D) lower left
 Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
New NASA Views of Storms in Space
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP New NASA Views of Storms in Space Presented by Dr. Eric Christian January 19, 2011 1 New NASA Views of Storms In Space The Sun as a Star Magnetism and the Sun Solar
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP New NASA Views of Storms in Space Presented by Dr. Eric Christian January 19, 2011 1 New NASA Views of Storms In Space The Sun as a Star Magnetism and the Sun Solar
and Universe Awareness
 Brought to you by s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Universe wareness Light Looking up at the night sky, you might think that space is dull, with lots of black, some white dots and just a hint of red if
Brought to you by s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Universe wareness Light Looking up at the night sky, you might think that space is dull, with lots of black, some white dots and just a hint of red if
LRO Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
 LRO Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Launch Date: June 18, 2009 Destination: Earth s moon Reached Moon: June 23, 2009 Type of craft: Orbiter Intended purpose: to map the moon like never before, add additional
LRO Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Launch Date: June 18, 2009 Destination: Earth s moon Reached Moon: June 23, 2009 Type of craft: Orbiter Intended purpose: to map the moon like never before, add additional
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016
 Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
Edwin Hubble Discovered galaxies other than the milky way. Galaxy:
 Edwin Hubble Discovered galaxies other than the milky way. Galaxy: A collection of stars, planets, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. Our sun and planets are in the Milky Way He noticed that
Edwin Hubble Discovered galaxies other than the milky way. Galaxy: A collection of stars, planets, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. Our sun and planets are in the Milky Way He noticed that
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM?
 4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
Assignment 9. Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment 9 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The astrophysicist who first calculated the highest mass that a dying star can
Assignment 9 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The astrophysicist who first calculated the highest mass that a dying star can
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 27 What s Next?
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
