Type Ia Supernovae meet Maximum Likelihood Estimators
|
|
|
- Eric Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Type Ia Supernovae meet Maximum Likelihood Estimators Alberto Guffanti Università degli Studi di Torino & INFN Torino J. Trøst Nielsen, AG and S. Sarkar, arxiv: J. Trøst Nielsen, arxiv: XXVIII th Rencontres de Blois - Particle Physics and Cosmology Blois, 29 May - 3 June, 2016
2 Type Ia Supernovae ~500 years Suzuki et al, SN 1572 (Tycho) NASA/CXC/Rutgers/Warren & Hughes
3 Type Ia Supernovae
4 Type Ia Supernovae Goobar & Leibundgut,
5 Type Ia Supernovae - Standard Candles? Hamuy, Phillips, 1993
6 Type Ia Supernovae - Standardizable Candles Corrected data M. Hamuy,
7 Type Ia Supernovae - Standardizable Candles We take as input to our analysis SN Ia standardises using the SALT2 LC fitting procedure [Guy et al, 2007, 2010] SALT 2 parameters Betoule et al., ? _??????
8 Distance moduli as probes of cosmology Astier et al., 2006
9 Supernova Cosmology: the conventional wisdom Brief overview of conventional wisdom SN data alone require cosmic acceleration at >99.999% confidence, including systematic effects Conley et al, 2011 Betoule et al, 2014 Astier et al, 2006
10 A critical appraisal of the standard constrained χ 2 µ B = m max B + α x 1 β c + δ P (m true <m threshold ) M B, (1 where M B is the absolute B-band magnitude of a SN Ia with x 1 =0, c =0and P (m true <m threshold )=0.Theparameters α, β, δ and M B are nuisance parameters that are fitted simultaneously with the cosmological parameters. The SN Ia photometry data and SALT2 light curve fits are shown in Fig Systematic errors In this paper, we follow the systematics analysis we presented in Amanullah et al. (2010). Systematic errors that directly affect supernova distance measurements (calibration, and galactic extinction, for example) are treated as nuisance parameters to be fit simultaneously with the cosmology. Minimizing over these nuisance parameters gives additional terms to add to the distance modulus covariance matrix U ij = ϵ dµ i (α, β) dϵ dµ j (α, β) σϵ 2 dϵ, (5) where the sum is over each of these distance systematic errors in the analysis. (Although the distance modulus depends on δ as well as α and β, thederivativeswithrespecttothezeropoints do not.) In this analysis, α and β have little interaction with cosmological parameters. When computing cosmologi Fitting the Cosmology Following Amanullah et al. (2010), the best-fit cosmology is determined by minimizing χ 2 stat = SNe [µ B (α, β, δ,m B ) µ(z; Ω m, Ω w,w)] 2 σlc 2 + σ2 ext + σsample 2. (4) Adetaileddiscussionofthetermsinthisequationcanbe found in Amanullah et al. (2010). We only comment on the final term in the denominator, σsample 2,whichiscomputedby setting the reduced χ 2 of each sample to unity. This term was referred to as σsystematic 2 inkowalskietal.(2008); Amanullah et al. (2010). We note that σsample 2 includes intrinsic dispersion as well as sample-dependent effects. This term effectively further deweights samples with poorer-qualitydata that has sources of error which have not been accounted for. As noted in Amanullah et al. (2010), this may occasionally deweight an otherwise well-measured supernova. Union2.1 - arxiv:
11 A critical appraisal of the standard constrained χ 2 µ B = m max B + α x 1 β c + δ P (m true <m threshold ) M B, (1 C. EMPIRICAL ADJUSTMENT OF UNCERTAINTIES The propagated uncertainties are underestimates, as they do not account for the pixel-pixel covariance introduced by warping, sub-sampling, stacking, and convolution of the images. In order to empirically determine by how much the uncertainties are underestimated, we measure the flux f r and its uncertainty r at random positions in a given di erence image in exactly the same way we measure the SN flux. We calculate the weighted mean f r of these flux measurements. In order to guard against reduction and image artifacts, we apply a 3 cut to the normalized flux distribution (f r fr )/ r, rather than cutting on the underestimated errors, r, for the following reason: let s assume that all uncertainties are underestimated by the same factor s r. If we nominally apply a N-sigma cut using these underestimated uncertainties, we e ectively apply an N/s r -cut, e.g. for a nominal 3-sigma cut and s r =1.5, the real cut-o is at 2-sigma. In order to avoid this, we determine the normalized flux distribution (f r fr )/ r, which has a standard deviation of s r. The true 3-sigma outliers can then be identified and removed by doing an 3-sigma cut on the normalized flux distribution. Note that the standard deviation s r is equivalent to the square-root of the chi-square distribution s r = p 2 r = 1 NX 2 fr fr r (C1) N 2 We multiply all uncertainties by the factor s r in order to empirically correct the uncertainties. We find that it is imperative to employ this robust way of determining s r for the method to work correctly. The fact that the reduced chi-square of the baseline flux of the SN light curves peaks at 1.0 validates our method (see 5.3.3). In addition, for a given di erence image, fr is an estimate of the bias in the flux measurements. The values of f r are in general very small, much smaller than the typical uncertainties. Nevertheless, we adjust all fluxes by this value. Pan-STARRS1 - arxiv:
12 Data - JLA catalogue Data Sky Coverage Redshift Coverage Our analysis is based on (and makes use of) the public information available through from the JLA website
13 Maximum Likelihood Estimator analysis It all starts with a likelihood L = probability density (data model) Disclaimer (for my statistics-savvy friends) I apologise for the abuse of language of defining the likelihood function as a probability density, since technically it is not normalised life (and talks) are often too short to discuss all the details
14 Maximum Likelihood Estimator analysis L= p[( ˆm B, ˆx 1, ĉ) ] (3) Z = p[( ˆm B, ˆx 1, ĉ) (M,x 1,c), ] p[(m,x 1,c) ]dmdx 1 dc, 150 p[(m,x 1,c) ] =p(m )p(x 1 )p(c ), where: n o p(m ) =(2 M 2 0 ) 1/2 exp [(M M 0 ) / M0 ] 2 /2, n (x1 p(x 1 ) =(2 x 2 1,0 ) 1/2 o 2 exp x 1,0 ) / x1,0 /2, n o p(c ) =(2 c 2 0 ) 1/2 exp [(c c 0 ) / c0 ] 2 /2. (4)
15 Maximum Likelihood Estimator analysis Likelihood intrinsic distributions cosmology SALT2
16 MLE fit result MLE, best fit Projected 10D confidence regions 2D confidence regions
17 MLE fit result - does it look like a good fit? Looks like a good fit when looking at the Hubble diagram but in all honesty any (half-decent) fit would
18 MLE fit result - Is it a good fit? Pulls distribution 90 Count Pull 0.1 PDF Do the best fit and its uncertainties satisfy Wilks theorem?
19 Comparison to JLA results Size of ellipses comparable to JLA Systematic shift towards larger values of Ωm
20 Recent developments - Unity & BAHAMAS More recently two extensive analyses based on Bayesian frameworks have appeared. [UNITY, Rubin et al., arxiv: ] [BAHAMAS, H. Shariff et al., arxiv: ] The frameworks they develop allow for the systematic study of effects that have been, up to now, disregarded (or poorly treated) in SN cosmology studies, i.e. a modelling of the redshift dependence of the color and stretch corrections BAHAMAS JLA SNIa only JLA SNIa + Planck 2015 z-linear z-jump z-linear z-jump Baseline color Corr color Corr Baseline color Corr color Corr Baseline Model parameters m ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± UNITY apple ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± n/a n/a ± n/a n/a Redshift evolution of color correction parameters 0 n/a ± ± n/a ± ± n/a ± n/a n/a ± n/a n/a n/a ± n/a n/a ± z t n/a n/a ± n/a n/a ± Intrinsic magnitude and residual dispersion parameters M ± ± ± ± ± ± res ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.005
21 Conclusions & Outlook Type Ia Supernovae are a crucial probe of cosmic acceleration The precision of present and upcoming (i.e. DES ) data needs to be matched by a comparably sound and accurate statistical analysis Maximum Likelihood Estimators methods provide such a framework, forcing one to make explicit the assumption made in the modelling of the data When MLE techniques are applied to the data from the data in the JLA catalogue marginal evidence (~3 sigma) for cosmic acceleration is supported by SN data alone A better modelling of SN standardisation corrections is crucial to improve the quality of the analysis
22 Backup Slides
23 Best fit correlations Results MLE, best fit
Embedding Supernova Cosmology into a Bayesian Hierarchical Model
 1 / 41 Embedding Supernova Cosmology into a Bayesian Hierarchical Model Xiyun Jiao Statistic Section Department of Mathematics Imperial College London Joint work with David van Dyk, Roberto Trotta & Hikmatali
1 / 41 Embedding Supernova Cosmology into a Bayesian Hierarchical Model Xiyun Jiao Statistic Section Department of Mathematics Imperial College London Joint work with David van Dyk, Roberto Trotta & Hikmatali
Observational cosmology and Type Ia Supernovae, Part II
 Observational cosmology and Type Ia Supernovae, Part II Rahman Amanullah, The Oskar Klein Centre, Stockholm University rahman@fysik.su.se Cosmology fits SN Ia cosmology tutorial Spectrum Search Subtraction
Observational cosmology and Type Ia Supernovae, Part II Rahman Amanullah, The Oskar Klein Centre, Stockholm University rahman@fysik.su.se Cosmology fits SN Ia cosmology tutorial Spectrum Search Subtraction
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Apr 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Apr 2016](/thumbs/85/92245306.jpg) BAHAMAS: new SNIa analysis reveals inconsistencies with standard cosmology Hikmatali Shariff Astrophysics Group, Physics Department, Imperial College London, Prince Consort Rd, London SW7 2AZ 1 arxiv:1510.05954v2
BAHAMAS: new SNIa analysis reveals inconsistencies with standard cosmology Hikmatali Shariff Astrophysics Group, Physics Department, Imperial College London, Prince Consort Rd, London SW7 2AZ 1 arxiv:1510.05954v2
Supernova Surveys. Julien GUY PPC2010, Torino, July LPNHE - IN2P3 - CNRS - Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7
 Supernova Surveys Julien GUY julien.guy@lpnhe.in2p3.fr LPNHE - IN2P3 - CNRS - Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7 PPC2010, Torino, July 2010 Outline 1 Cosmology wit Type Ia Supernovae 2 SN surveys SDSS Union2
Supernova Surveys Julien GUY julien.guy@lpnhe.in2p3.fr LPNHE - IN2P3 - CNRS - Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7 PPC2010, Torino, July 2010 Outline 1 Cosmology wit Type Ia Supernovae 2 SN surveys SDSS Union2
Dependence of low redshift Type Ia Supernovae luminosities on host galaxies
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2013 Vol. 13 No. 9, 1087 1096 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Dependence of low redshift Type Ia Supernovae
Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2013 Vol. 13 No. 9, 1087 1096 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Dependence of low redshift Type Ia Supernovae
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018](/thumbs/87/97336127.jpg) Open Astron. 2017; 26:111 119 Research Article David F. Crawford* A problem with the analysis of type Ia supernovae arxiv:1711.11237v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018 Abstract: Type Ia supernovae have light
Open Astron. 2017; 26:111 119 Research Article David F. Crawford* A problem with the analysis of type Ia supernovae arxiv:1711.11237v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018 Abstract: Type Ia supernovae have light
Testing the mutual consistency of different supernovae surveys
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv415 Testing the mutual consistency of different supernovae surveys N. V. Karpenka, 1 F. Feroz 2 and M. P. Hobson 2 1 The Oskar Klein Centre for Cosmoparticle Physics, Department of
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv415 Testing the mutual consistency of different supernovae surveys N. V. Karpenka, 1 F. Feroz 2 and M. P. Hobson 2 1 The Oskar Klein Centre for Cosmoparticle Physics, Department of
Cosmology of Photometrically- Classified Type Ia Supernovae
 Cosmology of Photometrically- Classified Type Ia Supernovae Campbell et al. 2013 arxiv:1211.4480 Heather Campbell Collaborators: Bob Nichol, Chris D'Andrea, Mat Smith, Masao Sako and all the SDSS-II SN
Cosmology of Photometrically- Classified Type Ia Supernovae Campbell et al. 2013 arxiv:1211.4480 Heather Campbell Collaborators: Bob Nichol, Chris D'Andrea, Mat Smith, Masao Sako and all the SDSS-II SN
Supernovae with Euclid
 Supernovae with Euclid Isobel Hook University of Oxford and INAF (Obs. Roma) Thanks to R. Nichol, M. Della Valle, F. Mannucci, A. Goobar, P. Astier, B. Leibundgut, A. Ealet Euclid Conference 17 18 Nov
Supernovae with Euclid Isobel Hook University of Oxford and INAF (Obs. Roma) Thanks to R. Nichol, M. Della Valle, F. Mannucci, A. Goobar, P. Astier, B. Leibundgut, A. Ealet Euclid Conference 17 18 Nov
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007](/thumbs/93/113115929.jpg) Survey Requirements for Accurate and Precise Photometric Redshifts for Type Ia Supernovae Yun Wang 1, Gautham Narayan 2, and Michael Wood-Vasey 2 arxiv:0708.0033v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007 ABSTRACT In this
Survey Requirements for Accurate and Precise Photometric Redshifts for Type Ia Supernovae Yun Wang 1, Gautham Narayan 2, and Michael Wood-Vasey 2 arxiv:0708.0033v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007 ABSTRACT In this
Cosmological constraints from the 3rd year SNLS dataset
 IAS Workshop on Dark Energy November 2008 Cosmological constraints from the 3rd year SNLS dataset preliminary results with focus on systematics Julien Guy LPNHE IN2P3/CNRS Univ. Paris VI & VII Systematic
IAS Workshop on Dark Energy November 2008 Cosmological constraints from the 3rd year SNLS dataset preliminary results with focus on systematics Julien Guy LPNHE IN2P3/CNRS Univ. Paris VI & VII Systematic
Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey
 Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey J. Craig Wheeler Department of Astronomy University of Texas at Austin (adapted from presentation by Josh Frieman) Texas Cosmology
Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey J. Craig Wheeler Department of Astronomy University of Texas at Austin (adapted from presentation by Josh Frieman) Texas Cosmology
MEASURING TYPE IA SUPERNOVA POPULATIONS OF STRETCH AND COLOR AND PREDICTING DISTANCE BIASES
 May 11, 2016 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 MEASURING TYPE IA SUPERNOVA POPULATIONS OF STRETCH AND COLOR AND PREDICTING DISTANCE BIASES D. Scolnic 1 & R. Kessler 1 May 11, 2016
May 11, 2016 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 MEASURING TYPE IA SUPERNOVA POPULATIONS OF STRETCH AND COLOR AND PREDICTING DISTANCE BIASES D. Scolnic 1 & R. Kessler 1 May 11, 2016
Neutrinos in the era of precision Cosmology
 Neutrinos in the era of precision Cosmology Marta Spinelli Rencontres du Vietnam Quy Nhon - 21 July 2017 The vanilla model: -CDM (Late times) cosmological probes Supernovae Ia standard candles fundamental
Neutrinos in the era of precision Cosmology Marta Spinelli Rencontres du Vietnam Quy Nhon - 21 July 2017 The vanilla model: -CDM (Late times) cosmological probes Supernovae Ia standard candles fundamental
R. Pain CSP 07 June 17,
 http://www.cfht.hawaii.edu/snls R. Pain CSP 07 June 17, 2007 1 Outline SNLS : the SuperNova Legacy Survey Cosmological analysis & first results (+3yr update) Systematic uncertainties & expected precision
http://www.cfht.hawaii.edu/snls R. Pain CSP 07 June 17, 2007 1 Outline SNLS : the SuperNova Legacy Survey Cosmological analysis & first results (+3yr update) Systematic uncertainties & expected precision
The universe is static
 The universe is static David F. Crawford 1 44 Market St, Naremburn, 2065, NSW, Australia Abstract It is shown that the light curve widths of type Ia supernovae do not have time dilation and that their
The universe is static David F. Crawford 1 44 Market St, Naremburn, 2065, NSW, Australia Abstract It is shown that the light curve widths of type Ia supernovae do not have time dilation and that their
Photometric classification of SNe Ia in the SuperNova Legacy Survey with supervised learning
 Photometric classification of SNe Ia in the SuperNova Legacy Survey with supervised learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson CAASTRO Postdoc at the Australian National University (ANU) Photometric Classification
Photometric classification of SNe Ia in the SuperNova Legacy Survey with supervised learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson CAASTRO Postdoc at the Australian National University (ANU) Photometric Classification
SALT: a Spectral Adaptive Light curve Template for Type Ia Supernovae
 22nd Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics at Stanford University, Dec. 3, 2004 SALT: a Spectral Adaptive Light curve Template for Type Ia Supernovae J. Guy, P. Astier, S. Nobili, N. Regnault, and
22nd Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics at Stanford University, Dec. 3, 2004 SALT: a Spectral Adaptive Light curve Template for Type Ia Supernovae J. Guy, P. Astier, S. Nobili, N. Regnault, and
To Lambda or not to Lambda?
 To Lambda or not to Lambda? Supratik Pal Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata October 17, 2015 Conclusion We don t know :) Partly based on my works with Dhiraj Hazra, Subha Majumdar, Sudhakar Panda, Anjan
To Lambda or not to Lambda? Supratik Pal Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata October 17, 2015 Conclusion We don t know :) Partly based on my works with Dhiraj Hazra, Subha Majumdar, Sudhakar Panda, Anjan
SNLS supernovae photometric classification with machine learning
 SNLS supernovae photometric classification with machine learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson Anais Möller CAASTRO, Australian National University Statistical Challenges in Astronomy, Carnegie Mellon
SNLS supernovae photometric classification with machine learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson Anais Möller CAASTRO, Australian National University Statistical Challenges in Astronomy, Carnegie Mellon
Stages of a Big Project ***
 Stages of a Big Project *** The Five stages of SDSS: 1. Denial 2. Anger 3. Bargaining 4. Depression 5. Acceptance *** With apologies to Elizabeth Kubler Ross The Carnegie Supernovae Project Wendy Freedman
Stages of a Big Project *** The Five stages of SDSS: 1. Denial 2. Anger 3. Bargaining 4. Depression 5. Acceptance *** With apologies to Elizabeth Kubler Ross The Carnegie Supernovae Project Wendy Freedman
Type Ia SNe standardization accounting for the environment. Lluís Galbany CENTRA-IST, UTL, Lisbon
 Type Ia SNe standardization accounting for the environment Lluís Galbany CENTRA-IST, UTL, Lisbon Benasc, 17 August 2012 Type Ia SNe as standard candles Used as a cosmological probes because of their bright
Type Ia SNe standardization accounting for the environment Lluís Galbany CENTRA-IST, UTL, Lisbon Benasc, 17 August 2012 Type Ia SNe as standard candles Used as a cosmological probes because of their bright
Improved constraints on cosmological parameters from Type Ia supernova data
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 418, 308 39 011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-966.011.19584.x Improved constraints on cosmological parameters from Type Ia supernova data M. C. March, 1 R. Trotta, 1, P. Berkes, 3 G. D.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 418, 308 39 011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-966.011.19584.x Improved constraints on cosmological parameters from Type Ia supernova data M. C. March, 1 R. Trotta, 1, P. Berkes, 3 G. D.
Type Ia Supernovae: Standardizable Candles and Crayons
 Type Ia Supernovae: Standardizable Candles and Crayons Ryan Foley Clay Fellow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Collaborators: Stephane Blondin Dan Kasen Bob Kirshner Kaisey Mandel & Nathan Sanders
Type Ia Supernovae: Standardizable Candles and Crayons Ryan Foley Clay Fellow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Collaborators: Stephane Blondin Dan Kasen Bob Kirshner Kaisey Mandel & Nathan Sanders
Challenges of low and intermediate redshift supernova surveys
 Challenges of low and intermediate redshift supernova surveys Ribamar R. R. Reis Image credit: ESO / M. Kornmesser Introduction Type Ia supernovae (SNeIa) are thermonuclear explosions of CO white dwarfs
Challenges of low and intermediate redshift supernova surveys Ribamar R. R. Reis Image credit: ESO / M. Kornmesser Introduction Type Ia supernovae (SNeIa) are thermonuclear explosions of CO white dwarfs
Novel Bayesian approaches to supernova type Ia cosmology
 Novel Bayesian approaches to supernova type Ia cosmology - MCMSki 2014 07/01/14 - www.robertotrotta.com The cosmological concordance model The ΛCDM cosmological concordance model is built on three pillars:
Novel Bayesian approaches to supernova type Ia cosmology - MCMSki 2014 07/01/14 - www.robertotrotta.com The cosmological concordance model The ΛCDM cosmological concordance model is built on three pillars:
Énergie noire Formation des structures. N. Regnault C. Yèche
 Énergie noire Formation des structures N. Regnault C. Yèche Outline Overview of DE probes (and recent highlights) Hubble Diagram of supernovae Baryon accoustic oscillations Lensing Matter clustering (JLA)
Énergie noire Formation des structures N. Regnault C. Yèche Outline Overview of DE probes (and recent highlights) Hubble Diagram of supernovae Baryon accoustic oscillations Lensing Matter clustering (JLA)
Cosmology with Peculiar Velocity Surveys
 Cosmology with Peculiar Velocity Surveys Simulations Fest, Sydney 2011 Morag I Scrimgeour Supervisors: Lister Staveley-Smith, Tamara Davis, Peter Quinn Collaborators: Chris Blake, Brian Schmidt What are
Cosmology with Peculiar Velocity Surveys Simulations Fest, Sydney 2011 Morag I Scrimgeour Supervisors: Lister Staveley-Smith, Tamara Davis, Peter Quinn Collaborators: Chris Blake, Brian Schmidt What are
Introduction to CosmoMC
 Introduction to CosmoMC Part I: Motivation & Basic concepts Institut de Ciències del Cosmos - Universitat de Barcelona Dept. de Física Teórica y del Cosmos, Universidad de Granada, 1-3 Marzo 2016 What
Introduction to CosmoMC Part I: Motivation & Basic concepts Institut de Ciències del Cosmos - Universitat de Barcelona Dept. de Física Teórica y del Cosmos, Universidad de Granada, 1-3 Marzo 2016 What
Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe. Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007
 Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007 Overview How do we measure expansion? Use of supernovae 1a as a good measuring stick Techniques for observing supernovae
Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007 Overview How do we measure expansion? Use of supernovae 1a as a good measuring stick Techniques for observing supernovae
CosmoSIS Webinar Part 1
 CosmoSIS Webinar Part 1 An introduction to cosmological parameter estimation and sampling Presenting for the CosmoSIS team: Elise Jennings (Fermilab, KICP) Joe Zuntz (University of Manchester) Vinicius
CosmoSIS Webinar Part 1 An introduction to cosmological parameter estimation and sampling Presenting for the CosmoSIS team: Elise Jennings (Fermilab, KICP) Joe Zuntz (University of Manchester) Vinicius
ITP, Universität Heidelberg Jul Weak Lensing of SNe. Marra, Quartin & Amendola ( ) Quartin, Marra & Amendola ( ) Miguel Quartin
 ITP, Universität Heidelberg Jul 2013 Measuring σ8 with Weak Lensing of SNe Marra, Quartin & Amendola (1304.7689) Quartin, Marra & Amendola (1307.1155) Miguel Quartin Instituto de Física Univ. Federal do
ITP, Universität Heidelberg Jul 2013 Measuring σ8 with Weak Lensing of SNe Marra, Quartin & Amendola (1304.7689) Quartin, Marra & Amendola (1307.1155) Miguel Quartin Instituto de Física Univ. Federal do
Advanced Statistical Methods. Lecture 6
 Advanced Statistical Methods Lecture 6 Convergence distribution of M.-H. MCMC We denote the PDF estimated by the MCMC as. It has the property Convergence distribution After some time, the distribution
Advanced Statistical Methods Lecture 6 Convergence distribution of M.-H. MCMC We denote the PDF estimated by the MCMC as. It has the property Convergence distribution After some time, the distribution
Precision cosmology with Type Ia Supernovae?
 Precision cosmology with Type Ia Supernovae? Reynald Pain LPNHE, CNRS/IN2P3 & Universités Paris 6 and Paris 7 Outline I will used the SNLS 1st year data and analysis to try answer the following questions
Precision cosmology with Type Ia Supernovae? Reynald Pain LPNHE, CNRS/IN2P3 & Universités Paris 6 and Paris 7 Outline I will used the SNLS 1st year data and analysis to try answer the following questions
Constraints on Anisotropic Cosmic Expansion from Supernovae
 Constraints on Anisotropic Cosmic Expansion from Supernovae Based on BK, Schwarz, Seikel, Wiegand, arxiv:1212.3691 Benedict Kalus Bielefeld University 2 / 12 8. Kosmologietag 25 th April, 2013 IBZ, Bielefeld
Constraints on Anisotropic Cosmic Expansion from Supernovae Based on BK, Schwarz, Seikel, Wiegand, arxiv:1212.3691 Benedict Kalus Bielefeld University 2 / 12 8. Kosmologietag 25 th April, 2013 IBZ, Bielefeld
Set 5: Expansion of the Universe
 Set 5: Expansion of the Universe Cosmology Study of the origin, contents and evolution of the universe as a whole Expansion rate and history Space-time geometry Energy density composition Origin of structure
Set 5: Expansion of the Universe Cosmology Study of the origin, contents and evolution of the universe as a whole Expansion rate and history Space-time geometry Energy density composition Origin of structure
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 14 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 14 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 14 Apr 2018](/thumbs/89/97828241.jpg) Probing the isotropy of cosmic acceleration using different supernova samples Z. Q. Sun 1 and F. Y. Wang 1,2 * arxiv:1804.05191v1 [astro-ph.co] 14 Apr 2018 1 School of Astronomy and Space Science, Nanjing
Probing the isotropy of cosmic acceleration using different supernova samples Z. Q. Sun 1 and F. Y. Wang 1,2 * arxiv:1804.05191v1 [astro-ph.co] 14 Apr 2018 1 School of Astronomy and Space Science, Nanjing
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Apr 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Apr 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Apr 2019](/thumbs/95/124870951.jpg) Forecasting Cosmological Bias due to Local Gravitational Redshift Haoting Xu, Zhiqi Huang, Na Zhang, and Yundong Jiang School of Physics and Astronomy, Sun Yat-sen University, 2 Daxue Road, Tangjia, Zhuhai,
Forecasting Cosmological Bias due to Local Gravitational Redshift Haoting Xu, Zhiqi Huang, Na Zhang, and Yundong Jiang School of Physics and Astronomy, Sun Yat-sen University, 2 Daxue Road, Tangjia, Zhuhai,
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations Part I
 Baryon Acoustic Oscillations Part I Yun Wang (on behalf of the Euclid collaboration) ESTEC, November 17, 2009 Outline Introduction: BAO and galaxy clustering BAO as a standard ruler BAO as a robust dark
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations Part I Yun Wang (on behalf of the Euclid collaboration) ESTEC, November 17, 2009 Outline Introduction: BAO and galaxy clustering BAO as a standard ruler BAO as a robust dark
Set 1: Expansion of the Universe
 Set 1: Expansion of the Universe Syllabus Course text book: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology, 2nd edition Olber s paradox, expansion of the universe: Ch 2 Cosmic geometry, expansion rate, acceleration:
Set 1: Expansion of the Universe Syllabus Course text book: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology, 2nd edition Olber s paradox, expansion of the universe: Ch 2 Cosmic geometry, expansion rate, acceleration:
Cosmological Constraints on Dark Energy via Bulk Viscosity from Decaying Dark Matter
 Cosmological Constraints on Dark Energy via Bulk Viscosity from Decaying Dark Matter Nguyen Quynh Lan Hanoi National University of Education, Vietnam (University of Notre Dame, USA) Rencontres du Vietnam:
Cosmological Constraints on Dark Energy via Bulk Viscosity from Decaying Dark Matter Nguyen Quynh Lan Hanoi National University of Education, Vietnam (University of Notre Dame, USA) Rencontres du Vietnam:
Late time cosmology with GWs
 Late time cosmology with elisa Institut de Physique Théorique CEA-Saclay CNRS Université Paris-Saclay Outline Standard sirens: Concept and issues Forecast cosmological constraints for elisa: Approach:
Late time cosmology with elisa Institut de Physique Théorique CEA-Saclay CNRS Université Paris-Saclay Outline Standard sirens: Concept and issues Forecast cosmological constraints for elisa: Approach:
Approximate Bayesian computation: an application to weak-lensing peak counts
 STATISTICAL CHALLENGES IN MODERN ASTRONOMY VI Approximate Bayesian computation: an application to weak-lensing peak counts Chieh-An Lin & Martin Kilbinger SAp, CEA Saclay Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh
STATISTICAL CHALLENGES IN MODERN ASTRONOMY VI Approximate Bayesian computation: an application to weak-lensing peak counts Chieh-An Lin & Martin Kilbinger SAp, CEA Saclay Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh
Measuring BAO using photometric redshift surveys.
 Measuring BAO using photometric redshift surveys. Aurelio Carnero Rosell. E. Sanchez Alvaro, Juan Garcia-Bellido, E. Gaztanaga, F. de Simoni, M. Crocce, A. Cabre, P. Fosalba, D. Alonso. 10-08-10 Punchline
Measuring BAO using photometric redshift surveys. Aurelio Carnero Rosell. E. Sanchez Alvaro, Juan Garcia-Bellido, E. Gaztanaga, F. de Simoni, M. Crocce, A. Cabre, P. Fosalba, D. Alonso. 10-08-10 Punchline
Making Cosmologyʼs Best Standard Candles Even Better
 Making Cosmologyʼs Best Standard Candles Even Better The Nearby Supernova Factory and Spectrophotometric Observations of SNe Ia Stephen Bailey LPNHE, Paris for the Nearby Supernova Factory Deciphering
Making Cosmologyʼs Best Standard Candles Even Better The Nearby Supernova Factory and Spectrophotometric Observations of SNe Ia Stephen Bailey LPNHE, Paris for the Nearby Supernova Factory Deciphering
Hypothesis Testing, Bayes Theorem, & Parameter Estimation
 Data Mining In Modern Astronomy Sky Surveys: Hypothesis Testing, Bayes Theorem, & Parameter Estimation Ching-Wa Yip cwyip@pha.jhu.edu; Bloomberg 518 Erratum of Last Lecture The Central Limit Theorem was
Data Mining In Modern Astronomy Sky Surveys: Hypothesis Testing, Bayes Theorem, & Parameter Estimation Ching-Wa Yip cwyip@pha.jhu.edu; Bloomberg 518 Erratum of Last Lecture The Central Limit Theorem was
THE DARK ENERGY SURVEY: 3 YEARS OF SUPERNOVA
 THE DARK ENERGY SURVEY: 3 YEARS OF SUPERNOVA IN
THE DARK ENERGY SURVEY: 3 YEARS OF SUPERNOVA IN
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Apr 2018](/thumbs/89/98918289.jpg) Preprint 19 April 2018 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 Testing the Distance-Duality Relation in the R h = ct Universe J. Hu 1 & F. Y. Wang 1,2 1 School of Astronomy and Space Science, Nanjing
Preprint 19 April 2018 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 Testing the Distance-Duality Relation in the R h = ct Universe J. Hu 1 & F. Y. Wang 1,2 1 School of Astronomy and Space Science, Nanjing
Sample variance in the local measurements of H 0. Heidi Wu (Caltech OSU) with Dragan Huterer (U. Michigan) arxiv: , MNRAS accepted
 Sample variance in the al measurements of H 0 Heidi Wu (Caltech OSU) with Dragan Huterer (U. Michigan) arxiv:1706.09723, MNRAS accepted 1 Tension in H 0 measurements Beaton (2016); Freedman (2017) 2 H
Sample variance in the al measurements of H 0 Heidi Wu (Caltech OSU) with Dragan Huterer (U. Michigan) arxiv:1706.09723, MNRAS accepted 1 Tension in H 0 measurements Beaton (2016); Freedman (2017) 2 H
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey
 First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample
 Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample BOMEE LEE 1. Brief Introduction about BAO In our previous class we learned what is the Baryon Acoustic Oscillations(BAO).
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample BOMEE LEE 1. Brief Introduction about BAO In our previous class we learned what is the Baryon Acoustic Oscillations(BAO).
Supernovae and the Accelerating Universe
 Supernovae and the Accelerating Universe Nicholas B. Suntzeff Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas A&M University University of Texas/Austin Second Texas Cosmology
Supernovae and the Accelerating Universe Nicholas B. Suntzeff Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas A&M University University of Texas/Austin Second Texas Cosmology
SDSS-II: DETERMINATION OF SHAPE AND COLOR PARAMETER COEFFICIENTS FOR SALT-II FIT MODEL
 SDSS-II: DETERMINATION OF SHAPE AND COLOR PARAMETER COEFFICIENTS FOR SALT-II FIT MODEL L. Dojcsak, 1 J. Marriner 2 August 14, 2010 ABSTRACT In this study we look at the SALT-II model of Type IA supernova
SDSS-II: DETERMINATION OF SHAPE AND COLOR PARAMETER COEFFICIENTS FOR SALT-II FIT MODEL L. Dojcsak, 1 J. Marriner 2 August 14, 2010 ABSTRACT In this study we look at the SALT-II model of Type IA supernova
Cosmology with weak-lensing peak counts
 Durham-Edinburgh extragalactic Workshop XIV IfA Edinburgh Cosmology with weak-lensing peak counts Chieh-An Lin January 8 th, 2018 Durham University, UK Outline Motivation Why do we study WL peaks? Problems
Durham-Edinburgh extragalactic Workshop XIV IfA Edinburgh Cosmology with weak-lensing peak counts Chieh-An Lin January 8 th, 2018 Durham University, UK Outline Motivation Why do we study WL peaks? Problems
New techniques to measure the velocity field in Universe.
 New techniques to measure the velocity field in Universe. Suman Bhattacharya. Los Alamos National Laboratory Collaborators: Arthur Kosowsky, Andrew Zentner, Jeff Newman (University of Pittsburgh) Constituents
New techniques to measure the velocity field in Universe. Suman Bhattacharya. Los Alamos National Laboratory Collaborators: Arthur Kosowsky, Andrew Zentner, Jeff Newman (University of Pittsburgh) Constituents
Fluctuations of cosmic parameters in the local universe
 Fluctuations of cosmic parameters in the local universe Alexander Wiegand Dominik Schwarz Fakultät für Physik Universität Bielefeld 6. Kosmologietag, Bielefeld 2011 A. Wiegand (Universität Bielefeld) Fluctuations
Fluctuations of cosmic parameters in the local universe Alexander Wiegand Dominik Schwarz Fakultät für Physik Universität Bielefeld 6. Kosmologietag, Bielefeld 2011 A. Wiegand (Universität Bielefeld) Fluctuations
Cosmological Constraints from Redshift Dependence of Galaxy Clustering Anisotropy
 Cosmological Constraints from Redshift Dependence of Galaxy Clustering Anisotropy Changbom Park (Korea Institute for Advanced Study) with Xiao-Dong Li, Juhan Kim (KIAS), Sungwook Hong, Cris Sabiu, Hyunbae
Cosmological Constraints from Redshift Dependence of Galaxy Clustering Anisotropy Changbom Park (Korea Institute for Advanced Study) with Xiao-Dong Li, Juhan Kim (KIAS), Sungwook Hong, Cris Sabiu, Hyunbae
BAO & RSD. Nikhil Padmanabhan Essential Cosmology for the Next Generation VII December 2017
 BAO & RSD Nikhil Padmanabhan Essential Cosmology for the Next Generation VII December 2017 Overview Introduction Standard rulers, a spherical collapse picture of BAO, the Kaiser formula, measuring distance
BAO & RSD Nikhil Padmanabhan Essential Cosmology for the Next Generation VII December 2017 Overview Introduction Standard rulers, a spherical collapse picture of BAO, the Kaiser formula, measuring distance
Precise measures of growth rate from RSD in the void-galaxy correlation
 Precise measures of growth rate from RSD in the void-galaxy correlation Seshadri Nadathur Moriond Cosmology, La Thuile Based on work with Paul Carter and Will Percival SN & Percival, arxiv:1712.07575 SN,
Precise measures of growth rate from RSD in the void-galaxy correlation Seshadri Nadathur Moriond Cosmology, La Thuile Based on work with Paul Carter and Will Percival SN & Percival, arxiv:1712.07575 SN,
Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties. Scott Oser Lecture #12
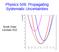 Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties Scott Oser Lecture #1 1 Additive offset model Suppose we take N measurements from a distribution, and wish to estimate the true mean of the underlying
Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties Scott Oser Lecture #1 1 Additive offset model Suppose we take N measurements from a distribution, and wish to estimate the true mean of the underlying
Science with large imaging surveys
 Science with large imaging surveys Hiranya V. Peiris University College London Science from LSS surveys: A case study of SDSS quasars Boris Leistedt (UCL) with Daniel Mortlock (Imperial) Aurelien Benoit-Levy
Science with large imaging surveys Hiranya V. Peiris University College London Science from LSS surveys: A case study of SDSS quasars Boris Leistedt (UCL) with Daniel Mortlock (Imperial) Aurelien Benoit-Levy
DECAM SEARCHES FOR OPTICAL SIGNATURES OF GW Soares-Santos et al arxiv:
 DECAM SEARCHES FOR OPTICAL SIGNATURES OF GW150914 Soares-Santos et al. 2016 arxiv:1602.04198 Marcelle Soares-Santos The DES Collaboration Fermilab Moriond Cosmology Conference March 20, 2016 INTRODUCTION
DECAM SEARCHES FOR OPTICAL SIGNATURES OF GW150914 Soares-Santos et al. 2016 arxiv:1602.04198 Marcelle Soares-Santos The DES Collaboration Fermilab Moriond Cosmology Conference March 20, 2016 INTRODUCTION
Testing gravity on cosmological scales with the observed abundance of massive clusters
 Testing gravity on cosmological scales with the observed abundance of massive clusters David Rapetti, KIPAC (Stanford/SLAC) In collaboration with Steve Allen (KIPAC), Adam Mantz (KIPAC), Harald Ebeling
Testing gravity on cosmological scales with the observed abundance of massive clusters David Rapetti, KIPAC (Stanford/SLAC) In collaboration with Steve Allen (KIPAC), Adam Mantz (KIPAC), Harald Ebeling
Optimal Supernova Search Strategies
 Optimal Supernova Search Strategies Dragan Huterer 1 and Michael S. Turner 1,2,3 1 Department of Physics, University of Chicago, Chicago IL 6637, USA 2 Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University
Optimal Supernova Search Strategies Dragan Huterer 1 and Michael S. Turner 1,2,3 1 Department of Physics, University of Chicago, Chicago IL 6637, USA 2 Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University
Cosmology with Wide Field Astronomy
 M. Moniez To cite this version: M. Moniez.. 35th International Conference on High Energy Physics (ICHEP2010), Jul 2010, Paris, France. Proceedings of Science, 441 (4 p.), 2010. HAL Id:
M. Moniez To cite this version: M. Moniez.. 35th International Conference on High Energy Physics (ICHEP2010), Jul 2010, Paris, France. Proceedings of Science, 441 (4 p.), 2010. HAL Id:
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 31 Mar 2006
 astro-ph/61453 Observational constraints on the acceleration of the Universe Yungui Gong College of Electronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 465, China and
astro-ph/61453 Observational constraints on the acceleration of the Universe Yungui Gong College of Electronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 465, China and
Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest
 Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest White dwarf Core of solar mass star No energy from fusion or gravitational contraction
Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest White dwarf Core of solar mass star No energy from fusion or gravitational contraction
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
Supernovae photometric classification of SNLS data with supervised learning
 Supernovae photometric classification of SNLS data with supervised learning Anais Möller CAASTRO & Australian National University A. Möller,V. Ruhlmann-Kleider, C. Leloup,J. Neveu, N. Palanque-Delabrouille,J.
Supernovae photometric classification of SNLS data with supervised learning Anais Möller CAASTRO & Australian National University A. Möller,V. Ruhlmann-Kleider, C. Leloup,J. Neveu, N. Palanque-Delabrouille,J.
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles
 Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles Mario Hamuy 1 2 Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles Mario Hamuy 1 2 Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
Lies, damned lies, and statistics in Astronomy
 Lies, damned lies, and statistics in Astronomy Bayes Theorem For proposition A and evidence B,! P(A), the prior probability, is the initial degree of belief in A. P(A B), the conditional probability of
Lies, damned lies, and statistics in Astronomy Bayes Theorem For proposition A and evidence B,! P(A), the prior probability, is the initial degree of belief in A. P(A B), the conditional probability of
Constraints on dark energy and its models
 Constraints on dark energy and its models Dragan Huterer 1, Eric V. Linder 2 and Jochen Weller 3 1 Department of Physics, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637-1433 2 E. O. Lawrence Berkeley National
Constraints on dark energy and its models Dragan Huterer 1, Eric V. Linder 2 and Jochen Weller 3 1 Department of Physics, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637-1433 2 E. O. Lawrence Berkeley National
Physics 509: Error Propagation, and the Meaning of Error Bars. Scott Oser Lecture #10
 Physics 509: Error Propagation, and the Meaning of Error Bars Scott Oser Lecture #10 1 What is an error bar? Someone hands you a plot like this. What do the error bars indicate? Answer: you can never be
Physics 509: Error Propagation, and the Meaning of Error Bars Scott Oser Lecture #10 1 What is an error bar? Someone hands you a plot like this. What do the error bars indicate? Answer: you can never be
Ryo Tsutsui, JGRG 22(2012) Measuring distance with gamma-ray bursts RESCEU SYMPOSIUM ON GENERAL RELATIVITY AND GRAVITATION JGRG 22
 Ryo Tsutsui, JGRG 22(2012)111305 Measuring distance with gamma-ray bursts RESCEU SYMPOSIUM ON GENERAL RELATIVITY AND GRAVITATION JGRG 22 November 12-16 2012 Koshiba Hall, The University of Tokyo, Hongo,
Ryo Tsutsui, JGRG 22(2012)111305 Measuring distance with gamma-ray bursts RESCEU SYMPOSIUM ON GENERAL RELATIVITY AND GRAVITATION JGRG 22 November 12-16 2012 Koshiba Hall, The University of Tokyo, Hongo,
THE MGC. Simon Driver (RSAA) David Lemon, Jochen Liske (St Andrews) Nicholas Cross (JHU) [Rogier Windhorst, Steve Odewahn, Seth Cohen (ASU)]
![THE MGC. Simon Driver (RSAA) David Lemon, Jochen Liske (St Andrews) Nicholas Cross (JHU) [Rogier Windhorst, Steve Odewahn, Seth Cohen (ASU)] THE MGC. Simon Driver (RSAA) David Lemon, Jochen Liske (St Andrews) Nicholas Cross (JHU) [Rogier Windhorst, Steve Odewahn, Seth Cohen (ASU)]](/thumbs/95/123226887.jpg) THE MGC Simon Driver (RSAA) David Lemon, Jochen Liske (St Andrews) Nicholas Cross (JHU) [Rogier Windhorst, Steve Odewahn, Seth Cohen (ASU)] Overview The Millennium Galaxy Catalogue - The MGC A High Precision
THE MGC Simon Driver (RSAA) David Lemon, Jochen Liske (St Andrews) Nicholas Cross (JHU) [Rogier Windhorst, Steve Odewahn, Seth Cohen (ASU)] Overview The Millennium Galaxy Catalogue - The MGC A High Precision
A8824: Statistics Notes David Weinberg, Astronomy 8824: Statistics Notes 6 Estimating Errors From Data
 Where does the error bar go? Astronomy 8824: Statistics otes 6 Estimating Errors From Data Suppose you measure the average depression of flux in a quasar caused by absorption from the Lyman-alpha forest.
Where does the error bar go? Astronomy 8824: Statistics otes 6 Estimating Errors From Data Suppose you measure the average depression of flux in a quasar caused by absorption from the Lyman-alpha forest.
Using SN Ia Light Curve Shapes to Measure. The Hubble Constant. Adam G. Riess, William H. Press, Robert P. Kirshner. Abstract
 Using SN Ia Light Curve Shapes to Measure The Hubble Constant Adam G. Riess, William H. Press, Robert P. Kirshner Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge, MA 02138 Received:
Using SN Ia Light Curve Shapes to Measure The Hubble Constant Adam G. Riess, William H. Press, Robert P. Kirshner Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge, MA 02138 Received:
The Hubble Constant Tension: a Status Update
 The Hubble Constant Tension: a Status Update Stephen M. Feeney with Daniel J. Mortlock, Hiranya V. Peiris, Andrew R. Williamson, Samaya M. Nissanke, Justin Alsing, Dan Scolnic and Niccolò Dalmasso arxiv:1707.00007,
The Hubble Constant Tension: a Status Update Stephen M. Feeney with Daniel J. Mortlock, Hiranya V. Peiris, Andrew R. Williamson, Samaya M. Nissanke, Justin Alsing, Dan Scolnic and Niccolò Dalmasso arxiv:1707.00007,
Supernovae explosions and the Accelerating Universe. Bodo Ziegler
 Nobel Prize for Physics 2011 Supernovae explosions and the Accelerating Universe Institute for Astronomy University of Vienna Since 09/2010: ouniprof University of Vienna 12/2008-08/10: Staff member European
Nobel Prize for Physics 2011 Supernovae explosions and the Accelerating Universe Institute for Astronomy University of Vienna Since 09/2010: ouniprof University of Vienna 12/2008-08/10: Staff member European
Improvements to Type Ia Supernova Models. Clare M. Saunders. A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the. requirements for the degree of
 Improvements to Type Ia Supernova Models by Clare M. Saunders A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Physics in the Graduate Division
Improvements to Type Ia Supernova Models by Clare M. Saunders A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Physics in the Graduate Division
SN Ia analyses with the Nearby Supernova Factory spectrophotometric data
 SN Ia analyses with the Nearby Supernova Factory spectrophotometric data Nicolas Chotard THCA / IPNL 6th FCPPL Workshop March 28, 2013 LPNHE Laboratoire de physique nucléaire et des hautes énergies 1 CONTENTS
SN Ia analyses with the Nearby Supernova Factory spectrophotometric data Nicolas Chotard THCA / IPNL 6th FCPPL Workshop March 28, 2013 LPNHE Laboratoire de physique nucléaire et des hautes énergies 1 CONTENTS
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 10 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 10 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 10 Dec 2018](/thumbs/92/108822703.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa c ESO 2018 December 12, 2018 Generalised model-independent characterisation of strong gravitational lenses V: lensing distance ratio in a general Friedmann universe
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa c ESO 2018 December 12, 2018 Generalised model-independent characterisation of strong gravitational lenses V: lensing distance ratio in a general Friedmann universe
First combined studies on Lorentz Invariance Violation from observations of astrophysical sources
 First combined studies on Lorentz Invariance Violation from observations of astrophysical sources Leyre Nogués, Tony T.Y. Lin, Cedric Perennes, Alasdair E. Gent, Julien Bolmont, Markus Gaug, Agnieszka
First combined studies on Lorentz Invariance Violation from observations of astrophysical sources Leyre Nogués, Tony T.Y. Lin, Cedric Perennes, Alasdair E. Gent, Julien Bolmont, Markus Gaug, Agnieszka
Statistical Models with Uncertain Error Parameters (G. Cowan, arxiv: )
 Statistical Models with Uncertain Error Parameters (G. Cowan, arxiv:1809.05778) Workshop on Advanced Statistics for Physics Discovery aspd.stat.unipd.it Department of Statistical Sciences, University of
Statistical Models with Uncertain Error Parameters (G. Cowan, arxiv:1809.05778) Workshop on Advanced Statistics for Physics Discovery aspd.stat.unipd.it Department of Statistical Sciences, University of
Constraining Dark Energy and Modified Gravity with the Kinetic SZ effect
 Constraining Dark Energy and Modified Gravity with the Kinetic SZ effect Eva-Maria Mueller Work in collaboration with Rachel Bean, Francesco De Bernardis, Michael Niemack (arxiv 1408.XXXX, coming out tonight)
Constraining Dark Energy and Modified Gravity with the Kinetic SZ effect Eva-Maria Mueller Work in collaboration with Rachel Bean, Francesco De Bernardis, Michael Niemack (arxiv 1408.XXXX, coming out tonight)
Leïla Haegel University of Geneva
 Picture found at: http://www.ps.uci.edu/~tomba/sk/tscan/pictures.html Leïla Haegel University of Geneva Seminar at the University of Sheffield April 27th, 2017 1 Neutrinos are: the only particle known
Picture found at: http://www.ps.uci.edu/~tomba/sk/tscan/pictures.html Leïla Haegel University of Geneva Seminar at the University of Sheffield April 27th, 2017 1 Neutrinos are: the only particle known
Cosmology with Planck clusters. Nabila Aghanim IAS, Orsay (France)
 Cosmology with Planck clusters Nabila Aghanim IAS, Orsay (France) Starting point Planck results March 2013 ~3σ sigma tension between Planck CMB and cluster counts Planck results February 2015 extensions:
Cosmology with Planck clusters Nabila Aghanim IAS, Orsay (France) Starting point Planck results March 2013 ~3σ sigma tension between Planck CMB and cluster counts Planck results February 2015 extensions:
Supernova Legacy Survey 3-years data sample Delphine HARDIN, on behalf of the Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS)
 Supernova Legacy Survey 3-years data sample Delphine HARDIN, on behalf of the Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS) LPNHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France E-mail: hardin@in2p3.fr We present the
Supernova Legacy Survey 3-years data sample Delphine HARDIN, on behalf of the Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS) LPNHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France E-mail: hardin@in2p3.fr We present the
Statistical Tools and Techniques for Solar Astronomers
 Statistical Tools and Techniques for Solar Astronomers Alexander W Blocker Nathan Stein SolarStat 2012 Outline Outline 1 Introduction & Objectives 2 Statistical issues with astronomical data 3 Example:
Statistical Tools and Techniques for Solar Astronomers Alexander W Blocker Nathan Stein SolarStat 2012 Outline Outline 1 Introduction & Objectives 2 Statistical issues with astronomical data 3 Example:
Dark Matter and Dark Energy components chapter 7
 Dark Matter and Dark Energy components chapter 7 Lecture 4 See also Dark Matter awareness week December 2010 http://www.sissa.it/ap/dmg/index.html The early universe chapters 5 to 8 Particle Astrophysics,
Dark Matter and Dark Energy components chapter 7 Lecture 4 See also Dark Matter awareness week December 2010 http://www.sissa.it/ap/dmg/index.html The early universe chapters 5 to 8 Particle Astrophysics,
Planck constraints on neutrinos. Massimiliano Lattanzi Università di Ferrara on behalf of the Planck Collaboration
 Planck constraints on neutrinos Massimiliano Lattanzi Università di Ferrara on behalf of the Planck Collaboration The Cosmic Neutrino Background (CnB) The presence of a background of relic neutrinos is
Planck constraints on neutrinos Massimiliano Lattanzi Università di Ferrara on behalf of the Planck Collaboration The Cosmic Neutrino Background (CnB) The presence of a background of relic neutrinos is
CORE-COLLAPSE SUPERNOVAE
 CORE-COLLAPSE SUPERNOVAE Ryan Chornock (Ohio University) J. Hester & A. Loll/NASA/ESA WHY CC SUPERNOVAE ARE IMPORTANT Final deaths of massive (M > 8 M ) stars Formation of compact objects (i.e., NS/BH)
CORE-COLLAPSE SUPERNOVAE Ryan Chornock (Ohio University) J. Hester & A. Loll/NASA/ESA WHY CC SUPERNOVAE ARE IMPORTANT Final deaths of massive (M > 8 M ) stars Formation of compact objects (i.e., NS/BH)
A COSMOLOGY-INDEPENDENT CALIBRATION OF GAMMA-RAY BURST LUMINOSITY RELATIONS AND THE HUBBLE DIAGRAM
 The Astrophysical Journal, 685:354Y360, 2008 September 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A A COSMOLOGY-INDEPENDENT CALIBRATION OF GAMMA-RAY BURST LUMINOSITY
The Astrophysical Journal, 685:354Y360, 2008 September 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A A COSMOLOGY-INDEPENDENT CALIBRATION OF GAMMA-RAY BURST LUMINOSITY
Weighing the Giants:
 Weighing the Giants: Accurate Weak Lensing Mass Measurements for Cosmological Cluster Surveys Anja von der Linden Tycho Brahe Fellow DARK Copenhagen + KIPAC, Stanford IACHEC, May 14, 2014 1 Hello! Copenhagen
Weighing the Giants: Accurate Weak Lensing Mass Measurements for Cosmological Cluster Surveys Anja von der Linden Tycho Brahe Fellow DARK Copenhagen + KIPAC, Stanford IACHEC, May 14, 2014 1 Hello! Copenhagen
HST RAISINS: Doing WFIRST Science TODAY!
 HST RAISINS: Doing WFIRST Science TODAY! Robert Kirshner Harvard University & Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation Better knowledge of dark energy through infrared observations RAISIN1: 24 Targets from Pan-STARRS
HST RAISINS: Doing WFIRST Science TODAY! Robert Kirshner Harvard University & Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation Better knowledge of dark energy through infrared observations RAISIN1: 24 Targets from Pan-STARRS
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 31 Jan 2007
 Type Ia supernova diversity: Standardizing the candles Tamara M. Davis, J. Berian James, Brian P. Schmidt and Alex G. Kim arxiv:astro-ph/0701904v1 31 Jan 2007 Dark Cosmology Centre, Niels Bohr Institute,
Type Ia supernova diversity: Standardizing the candles Tamara M. Davis, J. Berian James, Brian P. Schmidt and Alex G. Kim arxiv:astro-ph/0701904v1 31 Jan 2007 Dark Cosmology Centre, Niels Bohr Institute,
Cosmology using Long Gamma Ray Bursts: Statistical Analysis of Errors in the calibrated Data
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2018 Vol. X No. XX, 000 000 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Cosmology using Long Gamma Ray Bursts: Statistical
Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2018 Vol. X No. XX, 000 000 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Cosmology using Long Gamma Ray Bursts: Statistical
PoS(ICRC2017)765. Towards a 3D analysis in Cherenkov γ-ray astronomy
 Towards a 3D analysis in Cherenkov γ-ray astronomy Jouvin L. 1, Deil C. 2, Donath A. 2, Kerszberg D. 3, Khelifi B. 1, Lemière A. 1, Terrier R. 1,. E-mail: lea.jouvin@apc.in2p3.fr 1 APC (UMR 7164, CNRS,
Towards a 3D analysis in Cherenkov γ-ray astronomy Jouvin L. 1, Deil C. 2, Donath A. 2, Kerszberg D. 3, Khelifi B. 1, Lemière A. 1, Terrier R. 1,. E-mail: lea.jouvin@apc.in2p3.fr 1 APC (UMR 7164, CNRS,
Treatment and analysis of data Applied statistics Lecture 4: Estimation
 Treatment and analysis of data Applied statistics Lecture 4: Estimation Topics covered: Hierarchy of estimation methods Modelling of data The likelihood function The Maximum Likelihood Estimate (MLE) Confidence
Treatment and analysis of data Applied statistics Lecture 4: Estimation Topics covered: Hierarchy of estimation methods Modelling of data The likelihood function The Maximum Likelihood Estimate (MLE) Confidence
