FIRST VALIDATION OF MERIS AEROSOL PRODUCT OVER LAND
|
|
|
- Dwayne Barber
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ABSTRACT FIRST VALIDATION OF MERIS AEROSOL PRODUCT OVER LAND Didier Ramon (1), Richard Santer (2), Jerôme Vidot (2) 1. HYGEOS, 191 rue N. Appert, Villeneuve d Ascq, France, dr@hygeos.com 2. Université du Littoral Côte d Opale, MREN, Av. FOCH, Wimereux, France santer@mren2.univ-littoral.fr The detection of Dense Dark Vegetation (DDV) using the Atmospherically Resistant Vegetation Index (ARVI) and then the aerosol retrieval over DDV are the critical points of the land part of the processing of MERIS images implemented in the level 2 processor. We present here the first validation attempt of the MERIS aerosol product over land by checking its consistency and comparing it to AERONET data. We also applied an in-house version of the algorithm to L1B data in order to study the sensitivity of the algorithm to important parameters such as the ARVI thresholds and aerosol refractive index. SeaWiFS L1B images are also used to anticipate what will be the DDV cover throughout the year for Europe. This first validation exercise is promising and shows that the DDV approach is satisfactory in spring and summer. More extensive work is required for a full validation. Keywords: Aerosol Remote Sensing, ENVISAT/MERIS, SeaWIFS, Dense Dark Vegetation, Atmospheric corrections over land. 1 INTRODUCTION We were in charge of defining an algorithm for correcting MERIS images over land from atmospheric effects and providing the associated aerosol product. The image correction process itself consists of the correction from gaseous absorption and the correction from the molecular scattering. There is no correction for the aerosol scattering. However there is a further aerosol retrieval module and an accurate determination of the surface pressure from the reflectances in the oxygen absorption bands. All steps are based on simplified formulations of the signal in order to ease inversion of Top Of Atmosphere (TOA) reflectances [1]. Gaseous absorption is separated from the rest. This correction requires integrated values of gas content in the atmospheric column (mainly water vapour and Ozone) values generally available from the climatology. The Rayleigh correction is well defined and only requires knowledge of barometric pressure. This first estimation is performed via a Digital Elevation Model and the hypothesis of hydrostatic equilibrium for the lower atmosphere. Aerosol characterisation is primarily based on the inversion of the signal over dark targets for a set of standard aerosol models (here the 12 models used for POLarization and Directionality of the Earth Reflectance (POLDER). Reference to the aerosol climatology is mandatory to set the refractive index. Remaining aerosol optical thickness and slope of the Junge size distribution are determined from specific observations over DDV in the blue (412 and 443 nm) and in the red (665 nm). DDV pixels are detected using a spectral index: the Atmospheric Resistant Vegetation Index (ARVI)[2]. A pixel is flagged as DDV when its ARVI is greater than the ARVI threshold. This one is extracted from a LUT, as function of DDV model, geographical location, seasons and geometrical conditions. Standard values for DDV reflectances at 412 nm, 443 nm and 665 nm are proposed in order to retrieve the aerosol scattering functions and finally provide the aerosol product over land [3] which consists in the Aerosol Optical Thickness (AOT) at 865 nm and in the epsilon factor (ε) which is defined as the ratio of the aerosol path reflectance at 753 and 865 nm. The last output of the L2 land algorithm for MERIS is an accurate estimation of the barometric pressure from differential absorption of several close channels in the O 2 A absorption bands. The ratio of TOA reflectances in those close channels are directly linked to the barometric pressure with empirical relationships and correction factors for the absorption scattering coupling effects. First examples of this product are given in a companion paper [4] This paper is the first attempt to evaluate the quality of the aerosol product over land through: (i) consistency checks and (ii) preliminary validations. These two tasks are conducted directly on the level 2 as delivered by ESA. Then using an in-house prototype, we will conduct a sensitivity study going more deeply into the algorithm. Finally, a statistical study is proposed through the development of a level 3 product. Illustration of the DDV cover is done from SeaWiFS imagery.
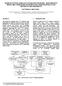
2 2. QUALITY CHECKS 2.1 Consistency Fig 1. Aerosol Optical Thickness at 865 nm in the Cheasapeake Bay on 23 October 2002 from L2 MERIS product. That day a coincidence with AERONET site in GSFC (39N ; 76W) occurs. Fig. 2. Zoom into the central part of the image of Fig. 1. Illustration of the land/water continuity of the AOT Fig. 3. Transect of the AOT as described in Fig. 2.
3 Fig. 4: Aerosol epsilon factor for the same scene as Fig. 1 We analysed an image acquired on over the US east coast near the AERONET GSFC site. The AOT at 865 nm (Fig. 1) gives a good impression at first glance. The order of magnitude is correct and the spatial distribution of the aerosol doesn t exhibit too large spatial variations. The consistency between the land and water algorithm is good except of course over highly turbid waters and for pixels just at the land-water interface. If we zoom into (Fig.2) a central region with two land/water borders, we see a good indication of the consistency of the retrieved AOT. Fig. 3 corresponds to AOT on the transect displays in Fig. 2. For the epsilon factor ε (Fig. 4), we find the same variability over land than over water. Over land, it shows some rapid changes and large zone with constant values. We have to remind that ε mainly describes the aerosol model and not the spectral dependence of the aerosol path radiance. The threshold effect on ε mainly results on the limited number of aerosol models (4 models only). This product will be greatly improves by adding more aerosol models. This recommendation will have a little impact on the algorithm. 2.2 First validation We compared the AOT at 865 nm for few coincidences with AERONET data for two zones (GSFC and North Italy) (Figure 5 and 6). This is a very first attempt since only four points are available. The error bars represents the spatial dispersion of MERIS data in a zone of 10 pixels around the AERONET site and an estimation of the temporal variability of the AERONET measurements. In case on cloud free cases (GSFC and Villefranche) the agreement is good. It becomes a bit noisy for the remaining two points since it was a day with high aerosol variability and frequent clouds overpass.
4 Fig. 5. ARVI map from a MERIS scene over Italy on 03 august 2002, 9H33 UT, and AERONET site location with coincident measurements ((1)Villefranche 43N, 7E; (2)Venise 45N, 12 E; (3)Ispra 45N, 8E) Fig. 6. Early validation of AOT at 865 nm combining results at GSFC (black), Villefranche (red), Venise (magenta) and Ispra (blue) AERONET site. 3. SENSITIVITY STUDY We took advantage of an in-house version of the L2 algorithm to process L1B images and study the influence of various parameters on the aerosol product. We focus here on two : (i) the ARVI of the DDV classified pixel and (ii) the choice of the aerosol refractive index which is at the moment set to 1.44 everywhere. The L1B image taken for this study is the one shown in Fig Sensitivity to the ARVI Fig. 7. summarises a general tendency observed for many other MERIS images and also for other sensors like SeaWiFS or MOS [5]. First as ARVI decreases below a certain value, the AOT increases. For the nominal ARVI threshold, the mean AOT is 0.15 while if we increase the ARVI threshold by 0.07, the mean AOT is Second, the retrieved aerosol model corresponds more and more to smaller particles: the epsilon coefficient increases from 1.14 to The ARVI threshold is then an important parameter which drives the aerosol model.
5 Fig. 7. (Top) Histograms of the L2 aerosol product for the image corresponding to Fig. 5 for all DDV pixels, (Bottom) Same as for top but only for DDV pixels whose ARVI is greater than nominal thresholds Fig. 8. Aerosol path reflectance over DDV pixels of Fig. 5 as a function of the ARVI, (left) 670 nm, (right) 443 nm. This is explained by Fig. 8 where we plotted the retrieved aerosol path reflectance over DDV at two wavelengths where DDV is the darkest 670 and 443 nm. The chlorophyll absorption is higher in the blue compared to the red, the
6 reflectance in the blue remains quite constant when the ARVI decreases and thus there is no correlation between ARVI and aerosol path reflectance. Conversely, the vegetation reflectance increases in the red when the vegetation is less dense or less green (as ARVI decreases since ARVI is a good indicator of darkness). Therefore the increase of the aerosol path reflectance in the red is just a bias which should be corrected either in: (i) Increasing the ARVI thresholds stored in the level 2 processor Look Up Tables. Of course, when you increase the ARVI threshold, you reduce the number of DDV pixels and the spatial coverage of the aerosol product. (ii) Or applying a corrective method to be defined. Because the influence of the ARVI threshold on the aerosol product is understood, there is a possibility to do so. This alternative will allow proposing a reliable aerosol product with a better spatial coverage. 3.2 Sensitivity to the aerosol refractive index The aerosol algorithm allows retrieving one size parameter (the slope of the Junge size distribution) and the number of particles (or the AOT). A third key optical parameter is the aerosol refractive index. At the beginning of the project, it was foreseen to get this parameter as an auxiliary data from aerosol climatology. This climatology does not exist and by default, the aerosol refractive index is set to 1.44 everywhere. It corresponds to a continental aerosol model. We processed the same image with 1.55 and results are shown in Fig. 9. Once again the tendency shown by this figure is representative of many other scenes. The ε factor is insensitive to this choice: 1.14 for m=1.45 and 1.13 m=1.55. For a given refractive index, the aerosol scattering functions is almost spectrally neutral. Then ε simply corresponds to the spectral dependence of the measured aerosol path radiances irregardless of the aerosol refractive index. It is not the case for the OAT which varies from 0.15 if m=1.44 to 0.20 if m=1.55. The OAT retrieval depends upon the aerosol phase function which varies with the refractive index. Here for 1.55 (urban/industrial absorbing aerosol model) the phase function is generally lower than for 1.44 and thus the retrieved AOT is higher. The AOT distribution over that particular scene is broader for 1.55 than for 1.44 and this may indicate that this refractive index is not well adapted to this specific situation. The need to have aerosol climatology still exists. This task can be achieved to some extend by ground based data such as collected in the AERONET network. The validation of the AOT, as reported in Fig. 6, may correspond to different assumptions on the refractive index m in an in house software package. A more likely refractive index can be then proposed depending on time and location. Fig. 9. Same as top of Fig. 7 but for an aerosol refractive index set to 1.55
7 4. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF DDV COVER As we have not yet covered all seasons with MERIS, we examined what we can expect in term of DDV area cover from SeaWIFS. We applied a MERIS like algorithm to SeaWiFS data and we focus here on the DDV flagging aspect. 4.1 A level 3 product for SeaWiFS SeaWiFS (Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor) provides data since the beginning of 1998 and exhibits good radiometric quality and data services. It has been chosen at the laboratory for the building of a medium spatial resolution, visible and near infrared image database. The data acquired correspond to the High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) format that is direct SeaWiFS broadcast at full resolution (~ 1 km at nadir) over particular reception sites. Here Dundee University reception site was chosen as it runs without interruption since 1998 and covers most of Western Europe. Both widths and central wavelength of the bands are very similar and little adaptation of the atmospheric Look Up Tables (LUT's) was necessary. The spatial resolution at nadir is of the same order if one takes High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) data for SeaWIFS and reduced resolution L1B product for MERIS. The main difference is the geometry because SeaWiFS avoids sun glint (and therefore look in the hot spot direction above land) whereas MERIS does not. SeaWiFS input images are L1B images. They consist of 8 calibrated radiances, the sun zenith angle, the view zenith angle and the relative sun-view azimuth. The image is navigated and according to SeaWiFS team with an accuracy of ~1 pixel. Concerning the computational aspect, the algorithm is fully coded in IDL in order to be compliant with the SeaDAS software. It allows an easy comparison with the ocean product and makes visualising and saving results easy. Tab. 1. DDV occurrence on 4 SeaWiFS high resolution images acquired in 2000 for different seasons (from the HRPT station of the University of Dundee). Cloud and DDV covers are calculated by averaging the result of the high resolution pixel classification over 16x16 pixels boxes. Then the DDV is calculated by counting the number of super-pixel with DDV cover greater than a minimum value (here 2 %) and dividing by the number of land super-pixels. This calculation is done for cloud free, a maximum of 50% and 80 % of cloud cover for the super-pixels. For each image, DDV statistics are given for five ARVI thresholds starting from the nominal MERIS values and decreasing down to the nominal values minus 0.2. Image (1) S 2000 day : : 22 UT (2) S 2000 day : : 11UT (3) S 2000 day : : 33 UT (4) S 2000 day : : 44 UT Land super-pixel Number Cloud free <50% cloud cover <80% cloud cover ARVI Thresh. decrease >2% DDV cover (cloud free) >2% DDV cover (<50% cloud cover) >2% DDV cover (<80% cloud cover)
8 4.2 Results Among the 3 years of SeaWIFS data, we have chosen 4 images acquired during 2000 over Europe for different seasons. On Table 1 is summarised the analysis of the spatial and temporal variability of DDV cover. It is confirmed that, using nominal ARVI thresholds (ARVI threshold decrease =0) that have been computed for real dark vegetation and standard atmospheric condition, it is possible to detect significant DDV area in spring and summer. In the case of DDV observed in cloud free conditions, one can expect to get 4-5 % of DDV cover in average. If we accept also DDV zones which are embedded in a cloudy environment, then DDV cover reaches 10 %. This is quite acceptable and allows for example, to be confident on the potential aerosol scattering corrections that can be done to the Rayleigh corrected reflectance (the actual MERIS level 2 surface reflectance product). However, in autumn and winter there are very few DDV zones, at best 1% and in cloudy conditions. Things go better if the ARVI threshold is decreased a bit, but from what we know from Section 3, it is at the cost of an increase of the bias on the aerosol product. 5. CONCLUSION The first quality checks on MERIS aerosol products appear quite reasonable in terms of spatial continuity and values are in the expected range. Some threshold effects appear on the aerosol type characterization through the epsilon coefficient. These effects can be simply reduced by adding more aerosol models (here, a better discretisation of the slope of the Junge size distribution). Validation points are too few to really validate the products. An extensive validation exercise as to be conducted. An investigation on the refractive index should be included in this validation exercise because of the influence of m on the AOT. The concept of the DDV detection with ARVI works quite well. First, it seems that ARVI thresholds needs to be adjusted as DDV disappears late fall in some regions. Second, it appears that the aerosol optical thickness increases with ARVI and that the epsilon factor decreases with ARVI (leading to an aerosol model with larger particles) are significantly sensitive to ARVI. So, even if DDV appears to be suitable for aerosol remote sensing, more as to be done than simply consider DDV reflectances as constant above an ARVI threshold. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was essentially supported by the European Space Agency. Authors want to thank particularly NASA DAAC, the University of Dundee and Orbimage for providing the SeaWIFS data. We thank also Brockmann Consult for the efficient delivery of MERIS data as well as for the early access to the MERIS toolbox beta version. We thank PIs of AERONET instruments used in this report, B. Holben, G. Zibordi, and F. Cabot. REFERENCES 1. Santer R., Carrère V., Dubuisson P. and Roger J.C., Atmospheric corrections over land for MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sensing, vol. 20, no 9, , Kaufman Y.J. and Tanré D., Atmospherically resistant vegetation index (ARVI) for EOS-MODIS, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 30, , Ramon D. and Santer R., Operational Remote Sensing of Aerosols over Land to Account for Directional Effects, Applied Optics-LP, 40, , Ramon D., Santer R. and Dubuisson P., First validation of MERIS surface pressure, this issue. 5. Borde R., Ramon D., Schmechtig C. and Santer R., Extension of the DDV concept to retrieve aerosol properties over land from the Modular Optoelectronic Scanner sensor, accepted in Int. J. Remote Sensing, 2001.
MERIS SURFACE PRESSURE AND CLOUD FLAG: PRESENT STATUS AND IMPROVEMENTS
 ABSTRACT MERIS SURFACE PRESSURE AND CLOUD FLAG: PRESENT STATUS AND IMPROVEMENTS D. Ramon (1), R. Santer (2), P. Dubuisson (2) (1) HYGEOS, 191 rue N. Appert, 59650 Villeneuve d Ascq, FRANCE, dr@hygeos.com
ABSTRACT MERIS SURFACE PRESSURE AND CLOUD FLAG: PRESENT STATUS AND IMPROVEMENTS D. Ramon (1), R. Santer (2), P. Dubuisson (2) (1) HYGEOS, 191 rue N. Appert, 59650 Villeneuve d Ascq, FRANCE, dr@hygeos.com
VALIDATION OF AEROSOL OPTICAL THICKNESS RETRIEVED BY BAER (BEMEN AEROSOL RETRIEVAL) IN THE MEDITERRANEAN AREA
 VALIDATION OF AEROSOL OPTICAL THICKNESS RETRIEVED BY BAER (BEMEN AEROSOL RETRIEVAL) IN THE MEDITERRANEAN AREA Wolfgang von Hoyningen-Huene (1), Alexander Kokhanovsky (1), John P. Burrows (1), Maria Sfakianaki
VALIDATION OF AEROSOL OPTICAL THICKNESS RETRIEVED BY BAER (BEMEN AEROSOL RETRIEVAL) IN THE MEDITERRANEAN AREA Wolfgang von Hoyningen-Huene (1), Alexander Kokhanovsky (1), John P. Burrows (1), Maria Sfakianaki
A Method for MERIS Aerosol Correction : Principles and validation. David Béal, Frédéric Baret, Cédric Bacour, Kathy Pavageau
 A Method for MERIS Aerosol Correction : Principles and validation David Béal, Frédéric Baret, Cédric Bacour, Kathy Pavageau Outlook Objectives Principles Training neural networks Validation Comparison
A Method for MERIS Aerosol Correction : Principles and validation David Béal, Frédéric Baret, Cédric Bacour, Kathy Pavageau Outlook Objectives Principles Training neural networks Validation Comparison
Estimation of ocean contribution at the MODIS near-infrared wavelengths along the east coast of the U.S.: Two case studies
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L13606, doi:10.1029/2005gl022917, 2005 Estimation of ocean contribution at the MODIS near-infrared wavelengths along the east coast of the U.S.: Two case studies
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L13606, doi:10.1029/2005gl022917, 2005 Estimation of ocean contribution at the MODIS near-infrared wavelengths along the east coast of the U.S.: Two case studies
Atmospheric correction in presence of sun glint: the POLYMER Algorithm
 Atmospheric correction in presence of sun glint: the POLYMER Algorithm Dominique Jolivet François Steinmetz Pierre-Yves Deschamps Jan 17, 2011 Atelier National Couleur de l'eau - GIS COOC c 2011 Atmospheric
Atmospheric correction in presence of sun glint: the POLYMER Algorithm Dominique Jolivet François Steinmetz Pierre-Yves Deschamps Jan 17, 2011 Atelier National Couleur de l'eau - GIS COOC c 2011 Atmospheric
In-flight Calibration Techniques Using Natural Targets. CNES Activities on Calibration of Space Sensors
 In-flight Calibration Techniques Using Natural Targets CNES Activities on Calibration of Space Sensors Bertrand Fougnie, Patrice Henry (DCT/SI, CNES, Toulouse, France) In-flight Calibration using Natural
In-flight Calibration Techniques Using Natural Targets CNES Activities on Calibration of Space Sensors Bertrand Fougnie, Patrice Henry (DCT/SI, CNES, Toulouse, France) In-flight Calibration using Natural
MERIS, A-MODIS, SeaWiFS, AATSR and PARASOL over the Salar de Uyuni March 2006 MAVT 2006 Marc Bouvet, ESA/ESTEC
 MERIS, A-MODIS, SeaWiFS, AATSR and PARASOL over the Salar de Uyuni Plan of the presentation 1. Introduction : from absolute vicarious calibration to radiometric intercomparison 2. Intercomparison at TOA
MERIS, A-MODIS, SeaWiFS, AATSR and PARASOL over the Salar de Uyuni Plan of the presentation 1. Introduction : from absolute vicarious calibration to radiometric intercomparison 2. Intercomparison at TOA
PROBA-V CLOUD MASK VALIDATION
 Version: 1 Page 1 PROBA-V CLOUD MASK VALIDATION Validation Report Version 1.0 Kerstin Stelzer, Michael Paperin, Grit Kirches, Carsten Brockmann 25.04.2016 Version: 1 Page 2 Table of content Abbreviations
Version: 1 Page 1 PROBA-V CLOUD MASK VALIDATION Validation Report Version 1.0 Kerstin Stelzer, Michael Paperin, Grit Kirches, Carsten Brockmann 25.04.2016 Version: 1 Page 2 Table of content Abbreviations
MERIS SMILE EFFECT CHARACTERISATION AND CORRECTION DOCUMENT. document title/ titre du document. prepared by/préparé par MERIS ESL
 DOCUMENT document title/ titre du document MERIS SMILE EFFECT CHARACTERISATION AND CORRECTION prepared by/préparé par MERIS ESL reference/réference issue/édition 2 revision/révision 0 date of issue/date
DOCUMENT document title/ titre du document MERIS SMILE EFFECT CHARACTERISATION AND CORRECTION prepared by/préparé par MERIS ESL reference/réference issue/édition 2 revision/révision 0 date of issue/date
VERIFICATION OF MERIS LEVEL 2 PRODUCTS: CLOUD TOP PRESSURE AND CLOUD OPTICAL THICKNESS
 VERIFICATION OF MERIS LEVEL 2 PRODUCTS: CLOUD TOP PRESSURE AND CLOUD OPTICAL THICKNESS Rene Preusker, Peter Albert and Juergen Fischer 17th December 2002 Freie Universitaet Berlin Institut fuer Weltraumwissenschaften
VERIFICATION OF MERIS LEVEL 2 PRODUCTS: CLOUD TOP PRESSURE AND CLOUD OPTICAL THICKNESS Rene Preusker, Peter Albert and Juergen Fischer 17th December 2002 Freie Universitaet Berlin Institut fuer Weltraumwissenschaften
EVALUATION OF MERIS AEROSOL PRODUCTS FOR NATIONAL AND REGIONAL AIR QUALITY IN AUSTRIA
 EVALUATION OF MERIS AEROSOL PRODUCTS FOR NATIONAL AND REGIONAL AIR QUALITY IN AUSTRIA Robert Höller (1),*, Christian Nagl (1), Herbert Haubold (1), Ludovic Bourg (2), Odile Fanton d Andon (2), and Philippe
EVALUATION OF MERIS AEROSOL PRODUCTS FOR NATIONAL AND REGIONAL AIR QUALITY IN AUSTRIA Robert Höller (1),*, Christian Nagl (1), Herbert Haubold (1), Ludovic Bourg (2), Odile Fanton d Andon (2), and Philippe
Invest in our future Issue: 1 Rev.: 0 Date: 21-Oct-13 Page: 1
 ISECA A2 Invest in our future Issue: 1 Rev.: 0 Date: 21-Oct-13 Page: 1 Title A regional climatology of the aerosols for MERIS atmospheric correction: Inherent Optical Properties (IOP) Version 0.1 Author(s)
ISECA A2 Invest in our future Issue: 1 Rev.: 0 Date: 21-Oct-13 Page: 1 Title A regional climatology of the aerosols for MERIS atmospheric correction: Inherent Optical Properties (IOP) Version 0.1 Author(s)
HICO Calibration and Atmospheric Correction
 HICO Calibration and Atmospheric Correction Curtiss O. Davis College of Earth Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA 97331 cdavis@coas.oregonstate.edu Oregon State Introduction
HICO Calibration and Atmospheric Correction Curtiss O. Davis College of Earth Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA 97331 cdavis@coas.oregonstate.edu Oregon State Introduction
Impacts of Atmospheric Corrections on Algal Bloom Detection Techniques
 1 Impacts of Atmospheric Corrections on Algal Bloom Detection Techniques Ruhul Amin, Alex Gilerson, Jing Zhou, Barry Gross, Fred Moshary and Sam Ahmed Optical Remote Sensing Laboratory, the City College
1 Impacts of Atmospheric Corrections on Algal Bloom Detection Techniques Ruhul Amin, Alex Gilerson, Jing Zhou, Barry Gross, Fred Moshary and Sam Ahmed Optical Remote Sensing Laboratory, the City College
MSI aerosol retrieval algorithm for the Multi- Spectral Imager (MSI) on EarthCare
 MSI aerosol retrieval algorithm for the Multi- Spectral Imager (MSI) on EarthCare Wolfgang von Hoyningen-Huene Huene,, Alexander Kokhanovsky, Vladimir Rozanov,, John P. Burrows,, Gerard Hesselmans 2),
MSI aerosol retrieval algorithm for the Multi- Spectral Imager (MSI) on EarthCare Wolfgang von Hoyningen-Huene Huene,, Alexander Kokhanovsky, Vladimir Rozanov,, John P. Burrows,, Gerard Hesselmans 2),
RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL OPTICAL DEPTH OVER URBAN AREAS USING TERRA/MODIS DATA
 RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL OPTICAL DEPTH OVER URBAN AREAS USING TERRA/MODIS DATA X. Q. Zhang a, *, L. P. Yang b, Y. Yamaguchi a a Dept. of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Graduate School of Environmental Studies,
RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL OPTICAL DEPTH OVER URBAN AREAS USING TERRA/MODIS DATA X. Q. Zhang a, *, L. P. Yang b, Y. Yamaguchi a a Dept. of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Graduate School of Environmental Studies,
THE LAND-SAF SURFACE ALBEDO AND DOWNWELLING SHORTWAVE RADIATION FLUX PRODUCTS
 THE LAND-SAF SURFACE ALBEDO AND DOWNWELLING SHORTWAVE RADIATION FLUX PRODUCTS Bernhard Geiger, Dulce Lajas, Laurent Franchistéguy, Dominique Carrer, Jean-Louis Roujean, Siham Lanjeri, and Catherine Meurey
THE LAND-SAF SURFACE ALBEDO AND DOWNWELLING SHORTWAVE RADIATION FLUX PRODUCTS Bernhard Geiger, Dulce Lajas, Laurent Franchistéguy, Dominique Carrer, Jean-Louis Roujean, Siham Lanjeri, and Catherine Meurey
Impact of Aerosol Model Selection on Water-Leaving Radiance Retrievals from Satellite Ocean Color Imagery
 Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3638-3665; doi:10.3390/rs4123638 Article OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensing ISSN 2072-4292 www.mdpi.com/journal/remotesensing Impact of Aerosol Model Selection on Water-Leaving Radiance Retrievals
Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3638-3665; doi:10.3390/rs4123638 Article OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensing ISSN 2072-4292 www.mdpi.com/journal/remotesensing Impact of Aerosol Model Selection on Water-Leaving Radiance Retrievals
GMES: calibration of remote sensing datasets
 GMES: calibration of remote sensing datasets Jeremy Morley Dept. Geomatic Engineering jmorley@ge.ucl.ac.uk December 2006 Outline Role of calibration & validation in remote sensing Types of calibration
GMES: calibration of remote sensing datasets Jeremy Morley Dept. Geomatic Engineering jmorley@ge.ucl.ac.uk December 2006 Outline Role of calibration & validation in remote sensing Types of calibration
In-flight Evaluation of the SPOT-6 Radiometric Calibration based on Acquisitions over Natural Targets and Automated in-situ Measurements
 In-flight Evaluation of the SPOT-6 Radiometric Calibration based on Acquisitions over Natural Targets and Automated in-situ Measurements Philippe GAMET, Bertrand FOUGNIE, Sophie LACHERADE (CNES), Mathieu
In-flight Evaluation of the SPOT-6 Radiometric Calibration based on Acquisitions over Natural Targets and Automated in-situ Measurements Philippe GAMET, Bertrand FOUGNIE, Sophie LACHERADE (CNES), Mathieu
Menzel/Matarrese/Puca/Cimini/De Pasquale/Antonelli Lab 2 Ocean Properties inferred from MODIS data June 2006
 Menzel/Matarrese/Puca/Cimini/De Pasquale/Antonelli Lab 2 Ocean Properties inferred from MODIS data June 2006 Table: MODIS Channel Number, Wavelength (µm), and Primary Application Reflective Bands Emissive
Menzel/Matarrese/Puca/Cimini/De Pasquale/Antonelli Lab 2 Ocean Properties inferred from MODIS data June 2006 Table: MODIS Channel Number, Wavelength (µm), and Primary Application Reflective Bands Emissive
Long-Term Time Series of Water Vapour Total Columns from GOME, SCIAMACHY and GOME-2
 Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Long-Term Time Series of Water Vapour Total Columns from GOME, SCIAMACHY and GOME-2 S. Noël, S. Mieruch, H. Bovensmann, J. P. Burrows Institute of Environmental
Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Long-Term Time Series of Water Vapour Total Columns from GOME, SCIAMACHY and GOME-2 S. Noël, S. Mieruch, H. Bovensmann, J. P. Burrows Institute of Environmental
AEROSOL RETRIEVAL AND ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION FOR MERIS DATA OVER LAKES
 AEROSOL RETRIEVAL AND ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION FOR MERIS DATA OVER LAKES Dana Floricioiu, Helmut Rott Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Innsbruck, Innrain, A-6 Innsbruck, Austria. Email:
AEROSOL RETRIEVAL AND ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION FOR MERIS DATA OVER LAKES Dana Floricioiu, Helmut Rott Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Innsbruck, Innrain, A-6 Innsbruck, Austria. Email:
ESA/MERIS vicarious adjustment
 ESA/MERIS vicarious adjustment Constant Mazeran (ACRI-ST Consultant) Christophe Lerebourg (ACRI-ST), Jean-Paul-Huot (ESA) David Antoine (CNRS-LOV, France & Curtin University, Perth, Australia) Ocean Colour
ESA/MERIS vicarious adjustment Constant Mazeran (ACRI-ST Consultant) Christophe Lerebourg (ACRI-ST), Jean-Paul-Huot (ESA) David Antoine (CNRS-LOV, France & Curtin University, Perth, Australia) Ocean Colour
Aerosol Retrieved from MODIS: Algorithm, Products, Validation and the Future
 Aerosol Retrieved from MODIS: Algorithm, Products, Validation and the Future Presented by: Rob Levy Re-presenting NASA-GSFC s MODIS aerosol team: Y. Kaufman, L. Remer, A. Chu,, C. Ichoku,, R. Kleidman,,
Aerosol Retrieved from MODIS: Algorithm, Products, Validation and the Future Presented by: Rob Levy Re-presenting NASA-GSFC s MODIS aerosol team: Y. Kaufman, L. Remer, A. Chu,, C. Ichoku,, R. Kleidman,,
Eight Years MOS-IRS Summary of Calibration Activities
 Eight Years MOS-IRS Summary of Calibration Activities Workshop on Inter-Comparison of Large Scale Optical and Infrared Sensors 12 14 October 2004, ESA / ESTEC Noordwijk, The Netherlands Horst Schwarzer,
Eight Years MOS-IRS Summary of Calibration Activities Workshop on Inter-Comparison of Large Scale Optical and Infrared Sensors 12 14 October 2004, ESA / ESTEC Noordwijk, The Netherlands Horst Schwarzer,
Aerosol Optical Depth Variation over European Region during the Last Fourteen Years
 Aerosol Optical Depth Variation over European Region during the Last Fourteen Years Shefali Singh M.Tech. Student in Computer Science and Engineering at Meerut Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Aerosol Optical Depth Variation over European Region during the Last Fourteen Years Shefali Singh M.Tech. Student in Computer Science and Engineering at Meerut Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Aerosol Characterization and Direct Radiative Forcing Assessment over the Ocean. Part I: Methodology and Sensitivity Analysis
 1799 Aerosol Characterization and Direct Radiative Forcing Assessment over the Ocean. Part I: Methodology and Sensitivity Analysis MARIA JOÃO COSTA Department of Physics, and Évora Geophysics Centre, University
1799 Aerosol Characterization and Direct Radiative Forcing Assessment over the Ocean. Part I: Methodology and Sensitivity Analysis MARIA JOÃO COSTA Department of Physics, and Évora Geophysics Centre, University
HICO OSU Website and Data Products
 HICO OSU Website and Data Products Curtiss O. Davis College of Earth Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA 97331 cdavis@coas.oregonstate.edu Oregon State Introduction
HICO OSU Website and Data Products Curtiss O. Davis College of Earth Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA 97331 cdavis@coas.oregonstate.edu Oregon State Introduction
Satellite remote sensing of aerosols & clouds: An introduction
 Satellite remote sensing of aerosols & clouds: An introduction Jun Wang & Kelly Chance April 27, 2006 junwang@fas.harvard.edu Outline Principals in retrieval of aerosols Principals in retrieval of water
Satellite remote sensing of aerosols & clouds: An introduction Jun Wang & Kelly Chance April 27, 2006 junwang@fas.harvard.edu Outline Principals in retrieval of aerosols Principals in retrieval of water
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
 Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
SAFNWC/MSG SEVIRI CLOUD PRODUCTS
 SAFNWC/MSG SEVIRI CLOUD PRODUCTS M. Derrien and H. Le Gléau Météo-France / DP / Centre de Météorologie Spatiale BP 147 22302 Lannion. France ABSTRACT Within the SAF in support to Nowcasting and Very Short
SAFNWC/MSG SEVIRI CLOUD PRODUCTS M. Derrien and H. Le Gléau Météo-France / DP / Centre de Météorologie Spatiale BP 147 22302 Lannion. France ABSTRACT Within the SAF in support to Nowcasting and Very Short
Calibration of Ocean Colour Sensors
 Dr. A. Neumann German Aerospace Centre DLR Remote Sensing Technology Institute Marine Remote Sensing What is Calibration, why do we need it? Sensor Components Definition of Terms Calibration Standards
Dr. A. Neumann German Aerospace Centre DLR Remote Sensing Technology Institute Marine Remote Sensing What is Calibration, why do we need it? Sensor Components Definition of Terms Calibration Standards
In-flight Spectral Calibration of MERIS/OLCI. Jürgen Fischer, Rene Preusker, Rasmus Lindstrot Institute for Space Science Free University Berlin
 In-flight Spectral Calibration of MERIS/OLCI Jürgen Fischer, Rene Preusker, Rasmus Lindstrot Institute for Space Science Free University Berlin 1 MERIS Instrument 2 MERIS Instrument Concept 3 MERIS Operation
In-flight Spectral Calibration of MERIS/OLCI Jürgen Fischer, Rene Preusker, Rasmus Lindstrot Institute for Space Science Free University Berlin 1 MERIS Instrument 2 MERIS Instrument Concept 3 MERIS Operation
BAYESIAN METHODOLOGY FOR ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION OF PACE OCEAN-COLOR IMAGERY
 BAYESIAN METHODOLOGY FOR ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION OF PACE OCEAN-COLOR IMAGERY Robert Frouin, SIO/UCSD Topics 1. Estimating phytoplankton fluorescence and ocean Raman scattering from OCI super sampling in
BAYESIAN METHODOLOGY FOR ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION OF PACE OCEAN-COLOR IMAGERY Robert Frouin, SIO/UCSD Topics 1. Estimating phytoplankton fluorescence and ocean Raman scattering from OCI super sampling in
Comparison of Results Between the Miniature FASat-Bravo Ozone Mapping Detector (OMAD) and NASA s Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS)
 Comparison of Results Between the Miniature FASat-Bravo Ozone Mapping Detector (OMAD) and NASA s Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) Juan A. Fernandez-Saldivar, Craig I. Underwood Surrey Space Centre,
Comparison of Results Between the Miniature FASat-Bravo Ozone Mapping Detector (OMAD) and NASA s Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) Juan A. Fernandez-Saldivar, Craig I. Underwood Surrey Space Centre,
Verification of Sciamachy s Reflectance over the Sahara J.R. Acarreta and P. Stammes
 Verification of Sciamachy s Reflectance over the Sahara J.R. Acarreta and P. Stammes Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE de Bilt, The Netherlands Email Address: acarreta@knmi.nl,
Verification of Sciamachy s Reflectance over the Sahara J.R. Acarreta and P. Stammes Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE de Bilt, The Netherlands Email Address: acarreta@knmi.nl,
Aerosol Inherent Optical Properties
 Aerosol Inherent Optical Properties Aerosol Inherent Aerosol Inherent Optical Properties Optical Properties R. Santer, F. Zagolski and O. Aznay Université du Littoral 1 Outline Validation of the aerosol
Aerosol Inherent Optical Properties Aerosol Inherent Aerosol Inherent Optical Properties Optical Properties R. Santer, F. Zagolski and O. Aznay Université du Littoral 1 Outline Validation of the aerosol
DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL
 DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL Paulo M. Barbosa, Mário R. Caetano, and Teresa G. Santos Centro Nacional de Informação Geográfica (CNIG), Portugal barp@cnig.pt, mario@cnig.pt,
DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL Paulo M. Barbosa, Mário R. Caetano, and Teresa G. Santos Centro Nacional de Informação Geográfica (CNIG), Portugal barp@cnig.pt, mario@cnig.pt,
Spectral surface albedo derived from GOME-2/Metop measurements
 Spectral surface albedo derived from GOME-2/Metop measurements Bringfried Pflug* a, Diego Loyola b a DLR, Remote Sensing Technology Institute, Rutherfordstr. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany; b DLR, Remote Sensing
Spectral surface albedo derived from GOME-2/Metop measurements Bringfried Pflug* a, Diego Loyola b a DLR, Remote Sensing Technology Institute, Rutherfordstr. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany; b DLR, Remote Sensing
A HIGH RESOLUTION EUROPEAN CLOUD CLIMATOLOGY FROM 15 YEARS OF NOAA/AVHRR DATA
 A HIGH RESOLUTION EUROPEAN CLOUD CLIMATOLOGY FROM 15 YEARS OF NOAA/AVHRR DATA R. Meerkötter 1, G. Gesell 2, V. Grewe 1, C. König 1, S. Lohmann 1, H. Mannstein 1 Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt
A HIGH RESOLUTION EUROPEAN CLOUD CLIMATOLOGY FROM 15 YEARS OF NOAA/AVHRR DATA R. Meerkötter 1, G. Gesell 2, V. Grewe 1, C. König 1, S. Lohmann 1, H. Mannstein 1 Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt
Improvement of the retrieval of aerosol optical properties over oceans using SEVIRI
 Improvement of the retrieval of aerosol optical properties over oceans using SEVIRI A. Vermeulen 1, C. Moulin 2, F. Thieuleux 3, I. Chiapello 3, J. Descloitres 1, F. Ducos 3, J-M Nicolas 1, F.-M. Bréon
Improvement of the retrieval of aerosol optical properties over oceans using SEVIRI A. Vermeulen 1, C. Moulin 2, F. Thieuleux 3, I. Chiapello 3, J. Descloitres 1, F. Ducos 3, J-M Nicolas 1, F.-M. Bréon
A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa
 A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa Ian Chang and Sundar A. Christopher Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville, U.S.A.
A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa Ian Chang and Sundar A. Christopher Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville, U.S.A.
5.5. Coastal and inland waters
 5.5. Coastal and inland waters 5. Atmospheric Correction SeaWiFS and MODIS Experiences Show: High quality ocean color products for the global open oceans (Case-1 waters). Significant efforts are needed
5.5. Coastal and inland waters 5. Atmospheric Correction SeaWiFS and MODIS Experiences Show: High quality ocean color products for the global open oceans (Case-1 waters). Significant efforts are needed
Minutes of the First Meeting. of the IOCCG Working Group. L1 Requirements for Ocean-Colour Remote Sensing. April 20-21, 2010
 Minutes of the First Meeting of the IOCCG Working Group L1 Requirements for Ocean-Colour Remote Sensing April 20-21, 2010 Bethesda, Maryland (Washington, D.C.), USA Participants: - Charles R. McClain (chair,
Minutes of the First Meeting of the IOCCG Working Group L1 Requirements for Ocean-Colour Remote Sensing April 20-21, 2010 Bethesda, Maryland (Washington, D.C.), USA Participants: - Charles R. McClain (chair,
ASSESSMENT OF THE UNCERTAINTY OF ATMOSPHERIC SCATTERING FUNCTIONS USED IN MERIS ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION OVER WATER.
 ASSESSMENT OF THE UNCERTAINTY OF ATMOSPHERIC SCATTERING FUNCTIONS USED IN MERIS ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION OVER WATER Francis Zagolski Motivations Ø Contribute to the MERIS validation of L2 optical parameters
ASSESSMENT OF THE UNCERTAINTY OF ATMOSPHERIC SCATTERING FUNCTIONS USED IN MERIS ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION OVER WATER Francis Zagolski Motivations Ø Contribute to the MERIS validation of L2 optical parameters
TOTAL COLUMN OZONE AND SOLAR UV-B ERYTHEMAL IRRADIANCE OVER KISHINEV, MOLDOVA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 8, No 3, pp 204-209, 2006 Copyright 2006 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved TOTAL COLUMN OZONE AND SOLAR UV-B ERYTHEMAL IRRADIANCE OVER KISHINEV, MOLDOVA A.A. ACULININ
Global NEST Journal, Vol 8, No 3, pp 204-209, 2006 Copyright 2006 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved TOTAL COLUMN OZONE AND SOLAR UV-B ERYTHEMAL IRRADIANCE OVER KISHINEV, MOLDOVA A.A. ACULININ
Sentinel 2 Pre-processing Requirements for coastal and inland waters
 Sentinel 2 Pre-processing Requirements for coastal and inland waters K A I S Ø R E NSEN NIVA CARSTEN B R O CKMANN Ecological and chemical classification of water bodies in Norway Water quality - products
Sentinel 2 Pre-processing Requirements for coastal and inland waters K A I S Ø R E NSEN NIVA CARSTEN B R O CKMANN Ecological and chemical classification of water bodies in Norway Water quality - products
A unified, global aerosol dataset from MERIS, (A)ATSR and SEVIRI
 A unified, global aerosol dataset from MERIS, and SEVIRI Gareth Thomas gthomas@atm.ox.ac.uk Introduction GlobAEROSOL is part of the ESA Data User Element programme. It aims to provide a global aerosol
A unified, global aerosol dataset from MERIS, and SEVIRI Gareth Thomas gthomas@atm.ox.ac.uk Introduction GlobAEROSOL is part of the ESA Data User Element programme. It aims to provide a global aerosol
DETECTING AIR POLLUTION FROM SPACE USING IMAGE-BASED METHOD
 DETECTING AIR POLLUTION FROM SPACE USING IMAGE-BASED METHOD D.G. Hadjimitsis 1, 2, 3 and C.R.I Clayton 2 1 Frederick Institute of Technology, Department of Civil Engineering, 7, Y. Frederickou St., Palouriotisa,
DETECTING AIR POLLUTION FROM SPACE USING IMAGE-BASED METHOD D.G. Hadjimitsis 1, 2, 3 and C.R.I Clayton 2 1 Frederick Institute of Technology, Department of Civil Engineering, 7, Y. Frederickou St., Palouriotisa,
Remote Sensing Seminar 8 June 2007 Benevento, Italy. Lab 5 SEVIRI and MODIS Clouds and Fires
 Remote Sensing Seminar 8 June 2007 Benevento, Italy Lab 5 SEVIRI and MODIS Clouds and Fires Table: SEVIRI Channel Number, Wavelength (µm), and Primary Application Reflective Bands 1,2 0.635, 0.81 land/cld
Remote Sensing Seminar 8 June 2007 Benevento, Italy Lab 5 SEVIRI and MODIS Clouds and Fires Table: SEVIRI Channel Number, Wavelength (µm), and Primary Application Reflective Bands 1,2 0.635, 0.81 land/cld
Coastal Characterization Using EO-1 Hyperion Data
 Coastal Characterization Using EO-1 Hyperion Data Dr. Hsiao-hua K. Burke EO-1 SVT Meeting 18-21 November 2002 Sponsor: NOAA NESDIS GOES 2002-1 Channel Positions of Various Ocean- Color Sensors, 1978-2000*
Coastal Characterization Using EO-1 Hyperion Data Dr. Hsiao-hua K. Burke EO-1 SVT Meeting 18-21 November 2002 Sponsor: NOAA NESDIS GOES 2002-1 Channel Positions of Various Ocean- Color Sensors, 1978-2000*
Atmospheric Correction Using Hyperion
 Atmospheric Correction Using Hyperion Progress and Issues Investigation: Correlative Analysis of EO-1, Landsat, and Terra Data of the DOE ARM CART Sites: An Investigation of Instrument Performance and
Atmospheric Correction Using Hyperion Progress and Issues Investigation: Correlative Analysis of EO-1, Landsat, and Terra Data of the DOE ARM CART Sites: An Investigation of Instrument Performance and
SCIAMACHY REFLECTANCE AND POLARISATION VALIDATION: SCIAMACHY VERSUS POLDER
 SCIAMACHY REFLECTANCE AND POLARISATION VALIDATION: SCIAMACHY VERSUS POLDER L. G. Tilstra (1), P. Stammes (1) (1) Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI), P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE de Bilt, The Netherlands
SCIAMACHY REFLECTANCE AND POLARISATION VALIDATION: SCIAMACHY VERSUS POLDER L. G. Tilstra (1), P. Stammes (1) (1) Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI), P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE de Bilt, The Netherlands
Vicarious Calibration for MERIS 4 th Reprocessing
 Vicarious Calibration for MERIS 4 th Reprocessing Nicolas Lamquin on behalf of MERIS Quality Working Group FRM4SOC Options for future European satellite OCR vicarious adjustment infrastructure for the
Vicarious Calibration for MERIS 4 th Reprocessing Nicolas Lamquin on behalf of MERIS Quality Working Group FRM4SOC Options for future European satellite OCR vicarious adjustment infrastructure for the
VALIDATION RESULTS OF THE OPERATIONAL LSA-SAF SNOW COVER MAPPING
 VALIDATION RESULTS OF THE OPERATIONAL LSA-SAF SNOW COVER MAPPING Niilo Siljamo, Otto Hyvärinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Erik Palménin aukio 1, P.O.Box 503, FI-00101 HELSINKI Abstract Hydrological
VALIDATION RESULTS OF THE OPERATIONAL LSA-SAF SNOW COVER MAPPING Niilo Siljamo, Otto Hyvärinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Erik Palménin aukio 1, P.O.Box 503, FI-00101 HELSINKI Abstract Hydrological
Sentinel-3 Sea and Land Surface Temperature Radiometer (SLSTR) Mireya Etxaluze (STFC RAL Space)
 Sentinel-3 Sea and Land Surface Temperature Radiometer (SLSTR) Mireya Etxaluze (STFC RAL Space) RAL Space Radiometry Group Dave Smith Mireya Etxaluze, Ed Polehampton, Caroline Cox, Tim Nightingale, Dan
Sentinel-3 Sea and Land Surface Temperature Radiometer (SLSTR) Mireya Etxaluze (STFC RAL Space) RAL Space Radiometry Group Dave Smith Mireya Etxaluze, Ed Polehampton, Caroline Cox, Tim Nightingale, Dan
Recent Update on MODIS C6 and VIIRS Deep Blue Aerosol Products
 Recent Update on MODIS C6 and VIIRS Deep Blue Aerosol Products N. Christina Hsu, Photo taken from Space Shuttle: Fierce dust front over Libya Corey Bettenhausen, Andrew M. Sayer, and Rick Hansell Laboratory
Recent Update on MODIS C6 and VIIRS Deep Blue Aerosol Products N. Christina Hsu, Photo taken from Space Shuttle: Fierce dust front over Libya Corey Bettenhausen, Andrew M. Sayer, and Rick Hansell Laboratory
Calibration of MERIS on ENVISAT Status at End of 2002
 Calibration of MERIS on ENVISAT Status at End of 2002 Bourg L. a, Delwart S. b, Huot J-P. b a ACRI-ST, 260 route du Pin Montard, BP 234, 06904 Sophia-Antipolis Cedex, France b ESA/ESTEC, P.O. Box 299,
Calibration of MERIS on ENVISAT Status at End of 2002 Bourg L. a, Delwart S. b, Huot J-P. b a ACRI-ST, 260 route du Pin Montard, BP 234, 06904 Sophia-Antipolis Cedex, France b ESA/ESTEC, P.O. Box 299,
Current Application of Vicarious Calibration for Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) DATA
 Current Application of Vicarious Calibration for Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) DATA On behalf of Jae-Hyun Ahn & Young-je Park, Seongick CHO(Secondment at Astrium SAS, France) Korea Ocean Satellite
Current Application of Vicarious Calibration for Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) DATA On behalf of Jae-Hyun Ahn & Young-je Park, Seongick CHO(Secondment at Astrium SAS, France) Korea Ocean Satellite
TEMPO Aerosols. Need for TEMPO-ABI Synergy
 TEMPO Aerosols Need for TEMPO-ABI Synergy Omar Torres, Hiren Jethva, Changwoo Ahn CEOS - 2018 NOAA-College Park May 04, 2018 Use of near UV Satellite Observations for retrieving aerosol properties over
TEMPO Aerosols Need for TEMPO-ABI Synergy Omar Torres, Hiren Jethva, Changwoo Ahn CEOS - 2018 NOAA-College Park May 04, 2018 Use of near UV Satellite Observations for retrieving aerosol properties over
Simultaneous determination of aerosol- and surface characteristics from top-of-atmosphere reflectance using MERIS on board of ENVISAT
 Advances in Space Research 37 (2006) 2172 2177 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Simultaneous determination of aerosol- and surface characteristics from top-of-atmosphere reflectance using MERIS on board of
Advances in Space Research 37 (2006) 2172 2177 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Simultaneous determination of aerosol- and surface characteristics from top-of-atmosphere reflectance using MERIS on board of
Atmospheric Correction of Satellite Ocean-Color Imagery In the Presence of Semi-Transparent Clouds
 Atmospheric Correction of Satellite Ocean-Color Imagery In the Presence of Semi-Transparent Clouds Robert Frouin 1 *, Lucile Duforêt 2, François Steinmetz 3 1 Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla,
Atmospheric Correction of Satellite Ocean-Color Imagery In the Presence of Semi-Transparent Clouds Robert Frouin 1 *, Lucile Duforêt 2, François Steinmetz 3 1 Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla,
AATSR atmospheric correction
 AATSR atmospheric correction Objective: Retrieval of aerosol opacity and bidirectional reflectance over land surface Talk structure Science background and objectives Dual-angle method Validation and satellite
AATSR atmospheric correction Objective: Retrieval of aerosol opacity and bidirectional reflectance over land surface Talk structure Science background and objectives Dual-angle method Validation and satellite
A Comparative Study and Intercalibration Between OSMI and SeaWiFS
 A Comparative Study and Intercalibration Between OSMI and SeaWiFS KOMPSAT-1 Bryan A. Franz NASA SIMBIOS Project Yongseung Kim Korea Aerospace Research Institute ORBVIEW-2 Abstract Since 1996, following
A Comparative Study and Intercalibration Between OSMI and SeaWiFS KOMPSAT-1 Bryan A. Franz NASA SIMBIOS Project Yongseung Kim Korea Aerospace Research Institute ORBVIEW-2 Abstract Since 1996, following
Hyperspectral Atmospheric Correction
 Hyperspectral Atmospheric Correction Bo-Cai Gao June 2015 Remote Sensing Division Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC USA BACKGROUND The concept of imaging spectroscopy, or hyperspectral imaging,
Hyperspectral Atmospheric Correction Bo-Cai Gao June 2015 Remote Sensing Division Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC USA BACKGROUND The concept of imaging spectroscopy, or hyperspectral imaging,
Carsten Brockmann, Ana Ruescas, Simon Pinnock CoastColour Team: BC D, HZG D, PML UK, RBINS B, LISE F, FCUL P COASTCOLOUR SPOT 4 TAKE 5
 Carsten Brockmann, Ana Ruescas, Simon Pinnock CoastColour Team: BC D, HZG D, PML UK, RBINS B, LISE F, FCUL P COASTCOLOUR SPOT 4 TAKE 5 CoastColour CoastColour is providing ocean colour products for coastal
Carsten Brockmann, Ana Ruescas, Simon Pinnock CoastColour Team: BC D, HZG D, PML UK, RBINS B, LISE F, FCUL P COASTCOLOUR SPOT 4 TAKE 5 CoastColour CoastColour is providing ocean colour products for coastal
EXTRACTION OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF YELLOW SAND DUST AND ITS OPTICAL PROPERTIES FROM ADEOS/POLDER DATA
 EXTRACTION OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF YELLOW SAND DUST AND ITS OPTICAL PROPERTIES FROM ADEOS/POLDER DATA Takashi KUSAKA, Michihiro KODAMA and Hideki SHIBATA Kanazawa Institute of Technology Nonoichi-machi
EXTRACTION OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF YELLOW SAND DUST AND ITS OPTICAL PROPERTIES FROM ADEOS/POLDER DATA Takashi KUSAKA, Michihiro KODAMA and Hideki SHIBATA Kanazawa Institute of Technology Nonoichi-machi
Sub-pixel regional land cover mapping. with MERIS imagery
 Sub-pixel regional land cover mapping with MERIS imagery R. Zurita Milla, J.G.P.W. Clevers and M. E. Schaepman Centre for Geo-information Wageningen University 29th September 2005 Overview Land Cover MERIS
Sub-pixel regional land cover mapping with MERIS imagery R. Zurita Milla, J.G.P.W. Clevers and M. E. Schaepman Centre for Geo-information Wageningen University 29th September 2005 Overview Land Cover MERIS
GSICS UV Sub-Group Activities
 GSICS UV Sub-Group Activities Rosemary Munro with contributions from NOAA, NASA and GRWG UV Subgroup Participants, in particular L. Flynn 1 CEOS Atmospheric Composition Virtual Constellation Meeting (AC-VC)
GSICS UV Sub-Group Activities Rosemary Munro with contributions from NOAA, NASA and GRWG UV Subgroup Participants, in particular L. Flynn 1 CEOS Atmospheric Composition Virtual Constellation Meeting (AC-VC)
MAPPING NATURAL SURFACE UV RADIATION WITH MSG: MAPS SERIES IN SPRING 2004, COMPARISON WITH METEOSAT DERIVED RESULTS AND REFERENCE MEASUREMENTS
 MAPPING NATURAL SURFACE UV RADIATION WITH MSG: MAPS SERIES IN SPRING 2004, COMPARISON WITH METEOSAT DERIVED RESULTS AND REFERENCE MEASUREMENTS Jean Verdebout & Julian Gröbner European Commission - Joint
MAPPING NATURAL SURFACE UV RADIATION WITH MSG: MAPS SERIES IN SPRING 2004, COMPARISON WITH METEOSAT DERIVED RESULTS AND REFERENCE MEASUREMENTS Jean Verdebout & Julian Gröbner European Commission - Joint
«Action Thématique Incitative sur Programme» CNRS/INSU
 Development and validation of a regional model of desert dust for the study of seasonal and interannual variations over Sahara and Sahel coupling with satellite observations «Action Thématique Incitative
Development and validation of a regional model of desert dust for the study of seasonal and interannual variations over Sahara and Sahel coupling with satellite observations «Action Thématique Incitative
Chapter 4 Nadir looking UV measurement. Part-I: Theory and algorithm
 Chapter 4 Nadir looking UV measurement. Part-I: Theory and algorithm -Aerosol and tropospheric ozone retrieval method using continuous UV spectra- Atmospheric composition measurements from satellites are
Chapter 4 Nadir looking UV measurement. Part-I: Theory and algorithm -Aerosol and tropospheric ozone retrieval method using continuous UV spectra- Atmospheric composition measurements from satellites are
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS AS POLLUTION MODEL VALIDATION AND EMISSION ASSESSMENT TOOLS. Athens, Athens, Greece
 REMOTE SENSING AND GIS AS POLLUTION MODEL VALIDATION AND EMISSION ASSESSMENT TOOLS Michael Petrakis 1, Theodora Kopania 1, David Briggs 2, Asbjorn Aaheim 3, Gerard Hoek 4, Gavin Shaddick 5, Adrianos Retalis
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS AS POLLUTION MODEL VALIDATION AND EMISSION ASSESSMENT TOOLS Michael Petrakis 1, Theodora Kopania 1, David Briggs 2, Asbjorn Aaheim 3, Gerard Hoek 4, Gavin Shaddick 5, Adrianos Retalis
RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL PROPERTIES OVER LAND AND WATER USING (A)ATSR DATA
 RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL PROPERTIES OVER LAND AND WATER USING (A)ATSR DATA ABSTRACT/RESUME Gerrit de Leeuw and Robin Schoemaker TNO, P.O. Box 96864, 2509 JG The Hague, The Netherlands The retrieval of aerosol
RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL PROPERTIES OVER LAND AND WATER USING (A)ATSR DATA ABSTRACT/RESUME Gerrit de Leeuw and Robin Schoemaker TNO, P.O. Box 96864, 2509 JG The Hague, The Netherlands The retrieval of aerosol
Making Accurate Field Spectral Reflectance Measurements By Dr. Alexander F. H. Goetz, Co-founder ASD Inc., Boulder, Colorado, 80301, USA October 2012
 Making Accurate Field Spectral Reflectance Measurements By Dr. Alexander F. H. Goetz, Co-founder ASD Inc., Boulder, Colorado, 80301, USA October 2012 Introduction Accurate field spectral reflectance measurements
Making Accurate Field Spectral Reflectance Measurements By Dr. Alexander F. H. Goetz, Co-founder ASD Inc., Boulder, Colorado, 80301, USA October 2012 Introduction Accurate field spectral reflectance measurements
Polar Multi-Sensor Aerosol Product: User Requirements
 Polar Multi-Sensor Aerosol Product: User Requirements Doc.No. Issue : : EUM/TSS/REQ/13/688040 v2 EUMETSAT EUMETSAT Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Fax: +49 6151 807 555 Telex: 419
Polar Multi-Sensor Aerosol Product: User Requirements Doc.No. Issue : : EUM/TSS/REQ/13/688040 v2 EUMETSAT EUMETSAT Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Fax: +49 6151 807 555 Telex: 419
A Time Series of Photo-synthetically Available Radiation at the Ocean Surface from SeaWiFS and MODIS Data
 A Time Series of Photo-synthetically Available Radiation at the Ocean Surface from SeaWiFS and MODIS Data Robert Frouin* a, John McPherson a, Kyozo Ueyoshi a, Bryan A. Franz b a Scripps Institution of
A Time Series of Photo-synthetically Available Radiation at the Ocean Surface from SeaWiFS and MODIS Data Robert Frouin* a, John McPherson a, Kyozo Ueyoshi a, Bryan A. Franz b a Scripps Institution of
Preparation and dissemination of the averaged maps and fields of selected satellite parameters for the Black Sea within the SeaDataNet project
 Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology 11, No 4, 1568 1578 (2010) Environmental informatics Preparation and dissemination of the averaged maps and fields of selected satellite parameters for the
Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology 11, No 4, 1568 1578 (2010) Environmental informatics Preparation and dissemination of the averaged maps and fields of selected satellite parameters for the
Status of Libya-4 Activities - RAL
 Status of Libya-4 Activities - RAL Dr David L Smith Preparation for reprocessing AATSR Long term drift correction LUT version 2.09 implemented in reprocessing V3.00 available based on revised BRF modelling
Status of Libya-4 Activities - RAL Dr David L Smith Preparation for reprocessing AATSR Long term drift correction LUT version 2.09 implemented in reprocessing V3.00 available based on revised BRF modelling
Mission Performance Centre SEN2COR ACIX-2 CMIX JOINT MEETING WASHINGTON DC UNITED STATES 17 OCTOBER 2018 SENTINEL-2 MISSION PERFORMANCE CENTRE / 1
 Mission Performance Centre SEN2COR ACIX-2 CMIX JOINT MEETING WASHINGTON DC UNITED STATES 17 OCTOBER 2018 SENTINEL-2 MISSION PERFORMANCE CENTRE / 1 OUTLINE âsen2cor overview âcloud Screening and scene Classification
Mission Performance Centre SEN2COR ACIX-2 CMIX JOINT MEETING WASHINGTON DC UNITED STATES 17 OCTOBER 2018 SENTINEL-2 MISSION PERFORMANCE CENTRE / 1 OUTLINE âsen2cor overview âcloud Screening and scene Classification
9/12/2011. Training Course Remote Sensing - Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods September 2011
 Training Course Remote Sensing - Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Introduction to Remote Sensing Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Electro Magnetic (EM)
Training Course Remote Sensing - Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Introduction to Remote Sensing Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Electro Magnetic (EM)
THE GLI 380-NM CHANNEL APPLICATION FOR SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING OF TROPOSPHERIC AEROSOL
 THE GLI 380-NM CHANNEL APPLICATION FOR SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING OF TROPOSPHERIC AEROSOL Robert Höller, 1 Akiko Higurashi 2 and Teruyuki Nakajima 3 1 JAXA, Earth Observation Research and Application Center
THE GLI 380-NM CHANNEL APPLICATION FOR SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING OF TROPOSPHERIC AEROSOL Robert Höller, 1 Akiko Higurashi 2 and Teruyuki Nakajima 3 1 JAXA, Earth Observation Research and Application Center
Status of CNES Cal/Val Activities
 GSICS Executive Panel Meeting 16-17th May 2014, Guangzhou, China Status of CNES Cal/Val Activities Patrice Henry CNES 1 Summary Overview of CNES Cal/Val Activities Summary Re-Calibration Activities POLDER(s)/PARASOL
GSICS Executive Panel Meeting 16-17th May 2014, Guangzhou, China Status of CNES Cal/Val Activities Patrice Henry CNES 1 Summary Overview of CNES Cal/Val Activities Summary Re-Calibration Activities POLDER(s)/PARASOL
SATELLITE RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL PROPERTIES OVER BRIGHT REFLECTING DESERT REGIONS
 SATELLITE RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL PROPERTIES OVER BRIGHT REFLECTING DESERT REGIONS Tilman Dinter 1, W. von Hoyningen-Huene 1, A. Kokhanovsky 1, J.P. Burrows 1, and Mohammed Diouri 2 1 Institute of Environmental
SATELLITE RETRIEVAL OF AEROSOL PROPERTIES OVER BRIGHT REFLECTING DESERT REGIONS Tilman Dinter 1, W. von Hoyningen-Huene 1, A. Kokhanovsky 1, J.P. Burrows 1, and Mohammed Diouri 2 1 Institute of Environmental
A AVHRR NDVI dataset for Svalbard. Stian Solbø, Inge Lauknes, Cecilie Sneberg Grøtteland, Stine Skrunes, Hannah Vickers, Kjell Arild Høgda
 A 1986-2014 AVHRR NDVI dataset for Svalbard Stian Solbø, Inge Lauknes, Cecilie Sneberg Grøtteland, Stine Skrunes, Hannah Vickers, Kjell Arild Høgda AVHRR series of satellites/instruments Satellite name
A 1986-2014 AVHRR NDVI dataset for Svalbard Stian Solbø, Inge Lauknes, Cecilie Sneberg Grøtteland, Stine Skrunes, Hannah Vickers, Kjell Arild Høgda AVHRR series of satellites/instruments Satellite name
Measuring Carbon Dioxide from the A-Train: The OCO-2 Mission
 Measuring Carbon Dioxide from the A-Train: The OCO-2 Mission David Crisp, OCO-2 Science Team Leader for the OCO-2 Science Team Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology March 2013 Copyright
Measuring Carbon Dioxide from the A-Train: The OCO-2 Mission David Crisp, OCO-2 Science Team Leader for the OCO-2 Science Team Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology March 2013 Copyright
CNES WGCV-36 Report Cal/Val Activities
 CEOS WGCV Meeting 13-17th May 2013, Shangai, China CNES WGCV-36 Report Cal/Val Activities Bertrand Fougnie, Sophie Lachérade, Denis Jouglet, Eric Péquignot, Aimé Meygret, Patrice Henry CNES 1 Summary Pleiades
CEOS WGCV Meeting 13-17th May 2013, Shangai, China CNES WGCV-36 Report Cal/Val Activities Bertrand Fougnie, Sophie Lachérade, Denis Jouglet, Eric Péquignot, Aimé Meygret, Patrice Henry CNES 1 Summary Pleiades
Simulated Radiances for OMI
 Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Sentinel-3: Lessons from AATSR/MERIS Synergy. Peter North Swansea University
 Sentinel-3: Lessons from AATSR/MERIS Synergy Peter North Swansea University Introduction ESA projects relevant to Sentinel-3: Aerosol CCI MERIS/AATSR Synergy GlobAlbedo SEN4LST S3 Algorithm development
Sentinel-3: Lessons from AATSR/MERIS Synergy Peter North Swansea University Introduction ESA projects relevant to Sentinel-3: Aerosol CCI MERIS/AATSR Synergy GlobAlbedo SEN4LST S3 Algorithm development
Mapping water constituents in Lake Constance using CHRIS/Proba
 S. Miksa, T. Heege, V. Kisselev and P. Gege Mapping water constituents in Lake Constance using CHRIS/Proba 3rd ESA CHRIS/Proba Workshop Frascati,, 21-23 23 March 2005 Overview - Test site and in-situ data
S. Miksa, T. Heege, V. Kisselev and P. Gege Mapping water constituents in Lake Constance using CHRIS/Proba 3rd ESA CHRIS/Proba Workshop Frascati,, 21-23 23 March 2005 Overview - Test site and in-situ data
Simulation of UV-VIS observations
 Simulation of UV-VIS observations Hitoshi Irie (JAMSTEC) Here we perform radiative transfer calculations for the UV-VIS region. In addition to radiance spectra at a geostationary (GEO) orbit, air mass
Simulation of UV-VIS observations Hitoshi Irie (JAMSTEC) Here we perform radiative transfer calculations for the UV-VIS region. In addition to radiance spectra at a geostationary (GEO) orbit, air mass
Climatology of Oceanic Zones Suitable for In-flight Calibration of Space Sensors
 1 Climatology of Oceanic Zones Suitable for In-flight Calibration of Space Sensors Bertrand Fougnie* a, Jérome Llido b, Lydwine Gross-Colzy b, Patrice Henry a, Denis Blumstein a a Centre National d Etudes
1 Climatology of Oceanic Zones Suitable for In-flight Calibration of Space Sensors Bertrand Fougnie* a, Jérome Llido b, Lydwine Gross-Colzy b, Patrice Henry a, Denis Blumstein a a Centre National d Etudes
Detection of ship NO 2 emissions over Europe from satellite observations
 Detection of ship NO 2 emissions over Europe from satellite observations Huan Yu DOAS seminar 24 April 2015 Ship Emissions to Atmosphere Reporting Service (SEARS project) Outline Introduction Shipping
Detection of ship NO 2 emissions over Europe from satellite observations Huan Yu DOAS seminar 24 April 2015 Ship Emissions to Atmosphere Reporting Service (SEARS project) Outline Introduction Shipping
Undergraduate Research Final Report: Estimation of suspended sediments using MODIS 250 m bands in Mayagüez Bay, Puerto Rico
 Undergraduate Research Final Report: Estimation of suspended sediments using MODIS 250 m bands in Mayagüez Bay, Puerto Rico Abstract: José F. Martínez Colón Undergraduate Research 2007 802-03-4097 Advisor:
Undergraduate Research Final Report: Estimation of suspended sediments using MODIS 250 m bands in Mayagüez Bay, Puerto Rico Abstract: José F. Martínez Colón Undergraduate Research 2007 802-03-4097 Advisor:
Coastal Water Quality Monitoring in Cyprus using Satellite Remote Sensing
 Coastal Water Quality Monitoring in Cyprus using Satellite Remote Sensing D. G. Hadjimitsis 1*, M.G. Hadjimitsis 1, 2, A. Agapiou 1, G. Papadavid 1 and K. Themistocleous 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering
Coastal Water Quality Monitoring in Cyprus using Satellite Remote Sensing D. G. Hadjimitsis 1*, M.G. Hadjimitsis 1, 2, A. Agapiou 1, G. Papadavid 1 and K. Themistocleous 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering
MSG system over view
 MSG system over view 1 Introduction METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION Overview 2 MSG Missions and Services 3 The SEVIRI Instrument 4 The MSG Ground Segment 5 SAF Network 6 Conclusions METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION
MSG system over view 1 Introduction METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION Overview 2 MSG Missions and Services 3 The SEVIRI Instrument 4 The MSG Ground Segment 5 SAF Network 6 Conclusions METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION
RadCalNet Quick Start Guide. RadCalNet Quick Start Guide
 RadCalNet Quick Start Guide RadCalNet Quick Start Guide 1. Scope of the document... 2 2. How to access the RadCalNet data?... 2 3. RadCalNet: which data for which purpose?... 2 4. How to use the data?...
RadCalNet Quick Start Guide RadCalNet Quick Start Guide 1. Scope of the document... 2 2. How to access the RadCalNet data?... 2 3. RadCalNet: which data for which purpose?... 2 4. How to use the data?...
SCIAMACHY Level 1b-2 Data Processing Status & Changes
 SCIAMACHY Level 1b-2 Data Processing Status & Changes Albrecht von Bargen ACVE-2 Workshop, Frascati, Italy May 3 rd, 2004 SCIAMACHY Level 1b-2: Data Processing Status & Changes Contents Data Processor
SCIAMACHY Level 1b-2 Data Processing Status & Changes Albrecht von Bargen ACVE-2 Workshop, Frascati, Italy May 3 rd, 2004 SCIAMACHY Level 1b-2: Data Processing Status & Changes Contents Data Processor
Inversion of Satellite Ocean-Color Data
 Inversion of Satellite Ocean-Color Data Robert Frouin Scripps Institution of Oceanography La Jolla, California, USA ADEOS-2 AMSR/GLI Workshop,Tsukuba, Japan, 30 January 2007 Collaborators Pierre-Yves Deschamps,
Inversion of Satellite Ocean-Color Data Robert Frouin Scripps Institution of Oceanography La Jolla, California, USA ADEOS-2 AMSR/GLI Workshop,Tsukuba, Japan, 30 January 2007 Collaborators Pierre-Yves Deschamps,
