C. S. T. B. SOLAR DIAGRAMS
|
|
|
- Shon Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C. S. T. B. SOLAR DIAGRAMS by D.G, Stephenson December 1964 ARCH COUNCIL OTTAWA CANADA
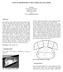
2 C. S. T. B. SOLAR DIAGRAMS by D. G. Stephenson Knowledge of the apparent position of the sun at different times and dates is essential for the design of shading systems and the determination of heat gain through windows. Tables of solar altitude and azimuth angles are available (1, 2), but they are less convenient for many purposes than a graphical presentation of the same data. Nearly all the solar charts or graphs that have been published are in polar form, i. e. a vector gives solar azimuth by its direction and altitude by its length. Some charts make the length directly proportional to the altitude angle and others make the length proportional to the cotangent of the altitude angle. The Diagrammes Solaires prepared by the Centre Scientifique et Technique du Bgtiment in France are of this latter type. Each chart presents the solar position data for all times and dates for one specific latitude. The C. S. T. B. charts can be thought of as the dial for a horizontal sun clock that has a gnomon of length d standing vertically at the principal point 0. Figure 1 is a half-scale reproduction of the chart for a latitude of 48 degrees. As a sun-clock dial the chart has to be oriented so that the XY line is exactly north and south, with the X arrow pointing toward the equator. The shadow of the point of the gnomon moves along a path like those labelled Courbe A to G. These are the shadow paths for different dates; at north latitudes A is for 21 June, B for 21 May and 21 July and so on to G, which is for 21 December. These curves are referred to as the date lines. The straight lines that intersect the date lines go through points on them where the shadow of the tip of the gnomon would be at a particular time of day. For example, the intersection of the line marked 10 with the curve A indicates the position of the shadow tip at 10 a. m. on 21 June. The slightly darker lines are for the hours indicated by the numbers adjacent to them and the lighter lives are for every 10 minutes between the hours. Whenever time is mentioned in this note, local apparent time (L. A. T. ) is meant. This is the time indicated by the shadow on a sun dial. It can differ from standard time by almost an hour for places near the boundaries between time zones. The correction of standard time to L.A. T. is described in BRN 47. The C.S. T. B. has published, in English as well as in French, a conci~l_ note on the main uses of their charts, but there are two applications nut :zlc~ tioned. Both derive from the cotangent type of plot used in the charts and represent part of the advantage of this type of chart over the direct altitude - angle type. This note is, therefore, intended to supplement the C. S. T. B.
3 brochure by giving additional uses. Positioning a Model The shadows cast by shading devices or by one part of a building - onto another can be determined quite easily by using a model. It is only necessary to position it in relation to a beam of light In the same way as the real building will sit with respect to the sun. One method of positioning a model is by using a heliodon QBRN 47), but the C. S. T. B. charts can also be used for this purpose. The model is attached to a drawing board and the C, S. T. B. chart for the appropriate latitude placed beside it on the board. The chart and model are so arranged that the building has the correct orientation relative to the North-South axis of the chart. A small cone of height equal to the distance d shown on the chart is located with its apex directly above the principal point 0 of the chart. If the model and the chart are set in direct sunshine (or illuminated by any other parallel beam of light), the point of the shadow cast by the cone indicates the time and date when that particular shadow pattern will occur. Alternatively, if the shadows are to be found for any specified time and date, it is only necessary to move the drawing board so as to make the point of the -shadow coincide with the intersection of the particular time and date lines. The shadows on and around the model are then as they would be for the real building at that particular time and date. Constructinp: Horizontal and Vertical Shadow Angles It is often necessary to determine the position of shadows when there is no model available. This can be done quite readily using plan and elevation drawings if the horizontal and vertical shadow angles are available. The H. S. A. is the angle on a plan drawing between a line perpendicular to the wall and the projection of the sun's rays on the horizontal plane. Similarly, the V. S. A. is the angle, on a vertical section drawing of the wall, between a line perpendicular to the wall and the projection of the sunvs rays on the plane of the drawing. The H. S. A. and V. S. A. can be obtained by a simple construction on a sheet of tracing paper laid over the C. S. T. B. chart for the particular latitude. Figure 2 shows an example. The first step is to draw, through point 0 a straight line with the same azimuth as the wall in question. This is the "wall liner1. For this application the arrow, X, points to the true North and the wall line will cut the angle scale around the perimeter of the chart at the wall azimuth angle. Then the point P is located at the intersection of the time and date lines on the underlying chart corresponding to the time and date for which the shadow angles are required. A line is drawn from P perpendicular to the wall line, cutting it at Q. A line is also drawn from P through 0 and the angle OPQ is the horizontal shadow angle. R is located on the wall line so that the distance from Q to R is equal to the length of the line labelled "Distance d" on the upper part of the chart. The angle QPR is the vertical shadow angle.
4 - 3- Finding the Position of Shadows on Vertical Walls The boundaries of the shadows on a wall, whether from a shading device OF an adjacent object, can be found by projecting the outline of the shading object on the wall, the lines of projection being parallel to the sun's rays. The shadow angle diagram obtained by the method described above can be used to find the solar projection of a point on the wall. The procedure is shown in Figure 3. Z is the shortest distance from the point A to the wall, i. e., AB is perpendicular to the plane of the wall. The solar projection of point A is at D, which is a distance X measured horizontally and Y measured vertically from B. The distances X and Y are related to the distance Z and the shadow angles by the expressions X = Z x tangent H. S.A. Y = Z x tangent V.S.A. The angle diagram in the lower part of Figure 3 shows how X and Y can be determined directly. The distance Z is laid off from P along PQ and X and Y measured as shown. Insolation on a Vertical Surface The insolation (i. e. incident solar energy), both direct and diffuse, on any wall can be found by using one of the overlay charts in conjunction with the appropriate solar diagram. The values indicated on the overlay sheets are in watts/sq metre; these can be converted to ~tu/ft~hr by multiplying them by The overlay sheets No. 4, 5 and.b are based on the French standard for insolation, which is slightly less for any given condition than the standard used in the United States. The insolation on walls facing North, East, South and West has been measured at Ottawa for about three years, and these records show that the insolation frequently exceeds the values indicated by both the American and French standards. On a very clear day it can exceed the values in the charts by about 25 per cent when there is no snow on the ground. (In winter, the radiation reflected from a snow surface can increase the radiation falling on a wall by a further 25 per cent. ) When more data are available, it will be possible to prepare alternative overlay charts appropriate for Canada. In the meantime, the French Diagrammes - de Puissance can be used to estimate the insolation that can be expected on a typical cloudless day.. Angle of Incidence The angle of incidence of the solar beam on any flat surface is defined as the angle between the solar beam and a line perpendicular to the surface. The angle of incidence at a vertical surface facing in any direction can be found by using overlay No. 3 in conjunction with the solar diagram for the appropriate latitude. (It cannot be used with the charts for latitudes greater than 52 degrees because the distance d is different for the high latitude charts. )
5 F Overlay No. 3 is laid on the solar diagram with its principal point directly over the principal point of the chart, and with the base line acting as the wall line. The incident angle, for any time and date represented by a point P on the solar diagram can be obtained by estimating the co-ordinate of P relative to the curved co-ordinate lines on the overlay. The angles marked on the chart are the complements of the incident angles; for example, if P is under the curved line marked 70 deg, the angle of incidence is 90-70, or 20 degrees. References: 1. Brown, G., and T. Tuominen. Solar Position at Various Hours, Dates and Latitudes - Tables. Rapport 75 Byggforskningen, Stockholm, U. S. Navy Hydrographic Office. Tables of Computed Altitude and Azimuth. Publication 2 14.
6
7 FIGURE 2 SHADOW ANGLE Dl AGRAM FROM C. S. T. B. CHART
8
Chapter 1 Solar Radiation
 Chapter 1 Solar Radiation THE SUN The sun is a sphere of intensely hot gaseous matter with a diameter of 1.39 10 9 m It is, on the average, 1.5 10 11 m away from the earth. The sun rotates on its axis
Chapter 1 Solar Radiation THE SUN The sun is a sphere of intensely hot gaseous matter with a diameter of 1.39 10 9 m It is, on the average, 1.5 10 11 m away from the earth. The sun rotates on its axis
Sundials With Punctiform Hour Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy)
 Sundials With Punctiform our Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy) Part 1 General Description Introduction Let us consider the line drawn in the sky by the points occupied by the Suns center at a given
Sundials With Punctiform our Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy) Part 1 General Description Introduction Let us consider the line drawn in the sky by the points occupied by the Suns center at a given
The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" Double Gnomon Polar Sundial
 1 Double Polar Sundial he purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of double gnomon polar sundials located at any latitude in either the
1 Double Polar Sundial he purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of double gnomon polar sundials located at any latitude in either the
Look at the date line of today and look at the shadow of the correct side of the cone. Read the mean time on the date line.
 MEANTIME SUNDIAL WITH A CONE GNOMON Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 6 June 006 By Hendrik Hollander Basic principles of the mean time sundial with a cone gnomon On the sundial plane the hour lines and date
MEANTIME SUNDIAL WITH A CONE GNOMON Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 6 June 006 By Hendrik Hollander Basic principles of the mean time sundial with a cone gnomon On the sundial plane the hour lines and date
Earth & Space Science, Interpreting Data DURATION Preparation: 5 minutes Activity: 40 minutes (total over one day)
 Objectives In this activity students will: 1. Observe how the position of the sun in the sky changes during the course of the day 2. Discover the cardinal directions by tracking the motion of the sun Materials
Objectives In this activity students will: 1. Observe how the position of the sun in the sky changes during the course of the day 2. Discover the cardinal directions by tracking the motion of the sun Materials
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION
 ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
How to measure the wall declination by means of the Orologi Solari program
 How to measure the wall declination by means of the Orologi Solari program An important point in the design of a sundial is the measurement of the declination of the wall. Orologi Solari can help to perform
How to measure the wall declination by means of the Orologi Solari program An important point in the design of a sundial is the measurement of the declination of the wall. Orologi Solari can help to perform
Polar Sundial. Cut carefully on this line. Cut on this line.
 1 The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" The purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of polar sundials located at any latitude in either
1 The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" The purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of polar sundials located at any latitude in either
The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I.
 The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I. The new building erected by the Princely Government on the Quai de Plaisance of the Port of Monaco, and set apart for the use of the International
The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I. The new building erected by the Princely Government on the Quai de Plaisance of the Port of Monaco, and set apart for the use of the International
SOLAR GEOMETRY (AND RADIATION)
 SOLAR GEOMETRY (AND RADIATION) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 1 Grondzik 1 Solar Radiation Components glass will reflect some incoming radiation; absorb some; and transmit some SHGF (above)
SOLAR GEOMETRY (AND RADIATION) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 1 Grondzik 1 Solar Radiation Components glass will reflect some incoming radiation; absorb some; and transmit some SHGF (above)
Sec 1.1 CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name:
 Sec. CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name: The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
Sec. CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name: The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
ZW2000 and Your Sundial
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000. Initiate the program ZW2000. Figure 1
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000. Initiate the program ZW2000. Figure 1
SOLAR GEOMETRY (AND SOLAR RADIATION)
 SOLAR GEOMETRY (AND SOLAR RADIATION) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 1 Grondzik 1 Solar Radiation Components glass will reflect some incoming radiation; absorb some; and transmit some SHGF
SOLAR GEOMETRY (AND SOLAR RADIATION) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 1 Grondzik 1 Solar Radiation Components glass will reflect some incoming radiation; absorb some; and transmit some SHGF
ANALEMMAS. on the gnomon and on the dial plate. Declining Shadows (Declining-Shadows.pdf ) for declination curve insights and methods.
 ANALEMMAS on the gnomon and on the dial plate armillary dials equatorial dials horizontal and vertical dials also and vertical decliners and polar and meridian please read: NOTE: using these: also see:
ANALEMMAS on the gnomon and on the dial plate armillary dials equatorial dials horizontal and vertical dials also and vertical decliners and polar and meridian please read: NOTE: using these: also see:
QUEEN S COLLEGE. Yearly Examination, Mathematics Paper II. Secondary 5 Date: 23 June, Time: 8:30-9:30 Full Marks: 80
 QUEEN S COLLEGE Yearly Examination, 00-0 Mathematics Paper II Secondary 5 Date: June, 0. Time: 8:0-9:0 Full Marks: 80. Write down the information required in the spaces provided on the Answer Sheet.. When
QUEEN S COLLEGE Yearly Examination, 00-0 Mathematics Paper II Secondary 5 Date: June, 0. Time: 8:0-9:0 Full Marks: 80. Write down the information required in the spaces provided on the Answer Sheet.. When
Map Projections. Chapter 4 MAP PROJECTION
 Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
CCMR Educational Programs
 CCMR Educational Programs Title: Date Created: August 10, 2006 Latest Revision: August 10, 2006 Author(s): Myriam Ibarra Appropriate Level: Grades 8-10 Abstract: Energy and the Angle of Insolation Sun
CCMR Educational Programs Title: Date Created: August 10, 2006 Latest Revision: August 10, 2006 Author(s): Myriam Ibarra Appropriate Level: Grades 8-10 Abstract: Energy and the Angle of Insolation Sun
Solar Energy Cooking with the Sun
 Student Handout: Experiment - Where is the sun? Name: Date: Measuring the current Solar Azimuth and Solar Angle 1. Use the level to find a section of concrete that is relatively level. Your instructor
Student Handout: Experiment - Where is the sun? Name: Date: Measuring the current Solar Azimuth and Solar Angle 1. Use the level to find a section of concrete that is relatively level. Your instructor
Angles and Applications
 CHAPTER 1 Angles and Applications 1.1 Introduction Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides, and angles of a triangle. Plane trigonometry, which is the
CHAPTER 1 Angles and Applications 1.1 Introduction Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides, and angles of a triangle. Plane trigonometry, which is the
ZW2000 and Your Vertical Sundial Carl Sabanski
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
Earth-Sun Relationships. The Reasons for the Seasons
 Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Latitude and Longitude. North. Latitude. South
 Latitude and Longitude North Latitude Longitude South 54 North America 55 Longitude Latitude United States 56 Latitude New York 72w 44n 42n 57 Site Location The site location is specified by a latitude
Latitude and Longitude North Latitude Longitude South 54 North America 55 Longitude Latitude United States 56 Latitude New York 72w 44n 42n 57 Site Location The site location is specified by a latitude
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2
 MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Definition (Polar Coordinates) Figure: The polar coordinates (r, )ofapointp
 Polar Coordinates Acoordinatesystemusesapairofnumberstorepresentapointontheplane. We are familiar with the Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system, (x, y). It is not always the most convenient system
Polar Coordinates Acoordinatesystemusesapairofnumberstorepresentapointontheplane. We are familiar with the Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system, (x, y). It is not always the most convenient system
Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial
 Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial Barbara Rovšek Citation: The Physics Teacher 48, 397 (2010); doi: 10.1119/1.3479720 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1119/1.3479720 View Table of Contents: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aapt/journal/tpt/48/6?ver=pdfcov
Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial Barbara Rovšek Citation: The Physics Teacher 48, 397 (2010); doi: 10.1119/1.3479720 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1119/1.3479720 View Table of Contents: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aapt/journal/tpt/48/6?ver=pdfcov
Chapter 6. Solar Geometry. Contents
 Chapter 6. Solar Geometry Contents 6.1 Introduction 6.2 The Sun 6.3 Elliptical Orbit 6.4 Tilt of the Earth s Axis 6.5 Consequences of the Altitude Angle 6.6 Winter 6.7 The Sun Revolves Around the Earth!
Chapter 6. Solar Geometry Contents 6.1 Introduction 6.2 The Sun 6.3 Elliptical Orbit 6.4 Tilt of the Earth s Axis 6.5 Consequences of the Altitude Angle 6.6 Winter 6.7 The Sun Revolves Around the Earth!
Calculating equation coefficients
 Solar Energy 1 Calculating equation coefficients Construction Conservation Equation Surface Conservation Equation Fluid Conservation Equation needs flow estimation needs radiation and convection estimation
Solar Energy 1 Calculating equation coefficients Construction Conservation Equation Surface Conservation Equation Fluid Conservation Equation needs flow estimation needs radiation and convection estimation
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
Trigonometric ratios:
 0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
Naples: A Disguised Analemmatic Dial
 aples: A Disguised Analemmatic Dial A Gnomonic xplanation by Frank H. King The ew Dial nearing completion In the autumn of 200 a novel analemmatic sundial was laid out in aples. The hour points are arranged
aples: A Disguised Analemmatic Dial A Gnomonic xplanation by Frank H. King The ew Dial nearing completion In the autumn of 200 a novel analemmatic sundial was laid out in aples. The hour points are arranged
CA1 2.11: Designing an Equatorial Sundial Activity
 Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Gnomon (a thin, round stick at least a foot long and capable of being put into the ground or stood up vertically)
 Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE COOKIT SOLAR COOKER
 OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE COOKIT SOLAR COOKER Ed Pejack University of the Pacific 3601 Pacific Avenue Stockton, CA 95211 USA (email: epejack@pacific.edu) ABSTRACT The CooKit is a solar cooker of the panel-cooker
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE COOKIT SOLAR COOKER Ed Pejack University of the Pacific 3601 Pacific Avenue Stockton, CA 95211 USA (email: epejack@pacific.edu) ABSTRACT The CooKit is a solar cooker of the panel-cooker
Vigyan Pratibha Learning Unit (Student version) Shadows
 Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
Foundation Pathway. End of Topic Assessment SPACE
 Name: Group: Year 7 Foundation Pathway End of Topic Assessment SPACE Analysis and Targets No. Score Below/On/Above Target for next Assessment. How will you achieve it? 1 /8 2 /4 3 /7 4 /5 5 /6 Now complete
Name: Group: Year 7 Foundation Pathway End of Topic Assessment SPACE Analysis and Targets No. Score Below/On/Above Target for next Assessment. How will you achieve it? 1 /8 2 /4 3 /7 4 /5 5 /6 Now complete
Important Instructions for the School Principal. (Not to be printed with the question paper) Note:
 Important Instructions for the School Principal (Not to be printed with the question paper) 1) This question paper is strictly meant for the use in School Based Summative Assessment- II, March-2012 only.
Important Instructions for the School Principal (Not to be printed with the question paper) 1) This question paper is strictly meant for the use in School Based Summative Assessment- II, March-2012 only.
Exercise 6. Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Introduction to the importance of solar panel orientation DISCUSSION
 Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1
 MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
EE Properties of Sunlight. Y. Baghzouz Professor of Electrical Engineering
 EE 495-695 2.2 Properties of Sunlight Y. Baghzouz Professor of Electrical Engineering Azimuth angle The azimuth angle is the compass direction from which the sunlight is coming. At the equinoxes, the sun
EE 495-695 2.2 Properties of Sunlight Y. Baghzouz Professor of Electrical Engineering Azimuth angle The azimuth angle is the compass direction from which the sunlight is coming. At the equinoxes, the sun
LIGHT. A beam is made up of several rays. It maybe parallel, diverging (spreading out) or converging (getting narrower). Parallel Diverging Converging
 LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
AN ELABORATION ON THE DESIGN PRINCIPLES OF A UNIVERSAL- SOLAR-CHART SHADOW-PLOTTER
 , Volume 4, Number 4, p.168-184, 2003 AN ELABORATION ON THE DESIGN PRINCIPLES OF A UNIVERSAL- SOLAR-CHART SHADOW-PLOTTER K.P. Cheung Department of Architecture, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road,
, Volume 4, Number 4, p.168-184, 2003 AN ELABORATION ON THE DESIGN PRINCIPLES OF A UNIVERSAL- SOLAR-CHART SHADOW-PLOTTER K.P. Cheung Department of Architecture, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road,
If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph.
 Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator
 Solar Schoolhouse Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator Overview Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts
Solar Schoolhouse Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator Overview Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts
b. Assuming that the sundial is set up correctly, explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
ELECTRIC FIELD. 2. If you have an equipotential surface that means that the potential difference is zero, along that surface. a. true b.
 ELECTRIC FIELD Pre-Lab Questions Page Name: Class: Roster Number: Instructor: Multiply Choice: Circle the correct answer 1. Electric field lines are drawn from a. positive charges to negative charges b.
ELECTRIC FIELD Pre-Lab Questions Page Name: Class: Roster Number: Instructor: Multiply Choice: Circle the correct answer 1. Electric field lines are drawn from a. positive charges to negative charges b.
ME 430 Fundamentals of Solar Energy Conversion for heating and Cooling Applications
 ME 430 Fundamentals of Solar Energy Conversion for heating and Cooling Applications Lecture (1 of 2) Solar Energy Resource and Availability C. Cruickshank and S. Harrison 2008 The Solar Constant 1 Variation
ME 430 Fundamentals of Solar Energy Conversion for heating and Cooling Applications Lecture (1 of 2) Solar Energy Resource and Availability C. Cruickshank and S. Harrison 2008 The Solar Constant 1 Variation
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
Mathematics Extension 1
 Name: St George Girls High School Trial Higher School Certificate Examination 2014 Mathematics Extension 1 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 2 hours Write using blue or black pen.
Name: St George Girls High School Trial Higher School Certificate Examination 2014 Mathematics Extension 1 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 2 hours Write using blue or black pen.
PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING
 PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING By Susan Grinstead Level: Junior Intermediate Gr. 7-12 Subject: Geography, Environment Sciences or Renewable Energies Objective: to understand the concept of
PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING By Susan Grinstead Level: Junior Intermediate Gr. 7-12 Subject: Geography, Environment Sciences or Renewable Energies Objective: to understand the concept of
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern
 632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Study Materials
 5. Measurement and Measuring Instrument 1. What was the writing of Claudius Ptolemy? He wrote that the moon, the sun and all the planets around the Earth in an almost circular path. 2. Who was the first
5. Measurement and Measuring Instrument 1. What was the writing of Claudius Ptolemy? He wrote that the moon, the sun and all the planets around the Earth in an almost circular path. 2. Who was the first
Practice Questions: Seasons #2
 1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools
 Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Solar Time, Angles, and Irradiance Calculator: User Manual
 Solar Time, Angles, and Irradiance Calculator: User Manual Circular 674 Thomas Jenkins and Gabriel Bolivar-Mendoza 1 Cooperative Extension Service Engineering New Mexico Resource Network College of Agricultural,
Solar Time, Angles, and Irradiance Calculator: User Manual Circular 674 Thomas Jenkins and Gabriel Bolivar-Mendoza 1 Cooperative Extension Service Engineering New Mexico Resource Network College of Agricultural,
APPENDIX F ACTIVITY #1 - CALCULATION OF THE TILT OF THE EARTH S AXIS AND THE OBSERVER S LATITUDE
 APPENDIX F ACTIVITY #1 - CALCULATION OF THE TILT OF THE EARTH S AXIS AND THE OBSERVER S LATITUDE The calculation of the Tilt of the Earth s Axis and the Observer s Latitude is essentially a reversal of
APPENDIX F ACTIVITY #1 - CALCULATION OF THE TILT OF THE EARTH S AXIS AND THE OBSERVER S LATITUDE The calculation of the Tilt of the Earth s Axis and the Observer s Latitude is essentially a reversal of
Designing with the Pilkington Sun Angle Calculator
 Designing with the Pilkington Sun Angle Calculator In 1951, Libbey-Owens-Ford introduced the first Sun Angle Calculator, to provide a relatively simple method of determining solar geometry variables for
Designing with the Pilkington Sun Angle Calculator In 1951, Libbey-Owens-Ford introduced the first Sun Angle Calculator, to provide a relatively simple method of determining solar geometry variables for
C) D) 2. The diagram below shows a large pendulum in motion over an 8-hour period.
 1. An observer on Earth measured the apparent diameter of the Sun over a period of 2 years. Which graph best represents the Sun's apparent diameter during the 2 years? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below
1. An observer on Earth measured the apparent diameter of the Sun over a period of 2 years. Which graph best represents the Sun's apparent diameter during the 2 years? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below
Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes
 First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes 2.1 THE TANGENT RATIO 2 Ch. 2.1 HW: p. 75 #3 16, 19 4 2.2 USING THE TANGENT RATIO TO CALCULATE LENGTHS 5 Ch. 2.2 HW: p. 82 # 3 5 (a, c), #6 14 6 2.4
First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes 2.1 THE TANGENT RATIO 2 Ch. 2.1 HW: p. 75 #3 16, 19 4 2.2 USING THE TANGENT RATIO TO CALCULATE LENGTHS 5 Ch. 2.2 HW: p. 82 # 3 5 (a, c), #6 14 6 2.4
3. a. In the figure below, indicate the direction of the Sun with an arrow.
 Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. accurately drawn. x + 2. x + 4. x + 2
 1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
The time they chose was the Vernal Equinox of March 20, 2000, at 7:30 AM Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Right Ascension Offset
 Star Coordinates and the Celestial Dome Astronomers have mapped out the sky in the shape of a spherical dome the Celestial Sphere, where earth is just a tiny spec at the center of the dome. The celestial
Star Coordinates and the Celestial Dome Astronomers have mapped out the sky in the shape of a spherical dome the Celestial Sphere, where earth is just a tiny spec at the center of the dome. The celestial
Name: Partner(s): 1101 or 3310: Desk # Date: Eclipses. Purpose
 Name: Partner(s): 1101 or 3310: Desk # Date: Purpose Eclipses Describe the orbit of the Moon Explain the differences between the types of solar eclipses Explain the differences between the types of lunar
Name: Partner(s): 1101 or 3310: Desk # Date: Purpose Eclipses Describe the orbit of the Moon Explain the differences between the types of solar eclipses Explain the differences between the types of lunar
Orientation of Building
 Orientation of Building Prof. S.K.Gupta 1 1 Dean &DirectorAmity University HaryanaPanchgaon, Manesar, Gurgaon I. INTRODUCTION The need to conserve essential building materials has drawn attention again
Orientation of Building Prof. S.K.Gupta 1 1 Dean &DirectorAmity University HaryanaPanchgaon, Manesar, Gurgaon I. INTRODUCTION The need to conserve essential building materials has drawn attention again
Earth Science Seasons Test Name Per Date
 Name Per Date Page 1 1. The diagram below represents four positions of the Earth as it revolves around the Sun. 5. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows the apparent
Name Per Date Page 1 1. The diagram below represents four positions of the Earth as it revolves around the Sun. 5. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows the apparent
Horizontal/Vertical/Inclining Sundial
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up SONNE on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with SONNE
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up SONNE on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with SONNE
COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR THE ANGLES DESCRIBING THE SUN S APPARENT MOVEMENT IN THE SKY
 COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR THE ANGLES DESCRIBING THE SUN S APPARENT MOVEMENT IN THE SKY B. BUTUC 1 Gh. MOLDOVEAN 1 Abstract: The paper presents software developed for the determination of the Sun-Earth geometry.
COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR THE ANGLES DESCRIBING THE SUN S APPARENT MOVEMENT IN THE SKY B. BUTUC 1 Gh. MOLDOVEAN 1 Abstract: The paper presents software developed for the determination of the Sun-Earth geometry.
Vigyan Pratibha Learning Unit (Teacher version) Shadows
 Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6
 NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
Sunlight and its Properties II. EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz
 Sunlight and its Properties II EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz Solar Time (ST) and Civil (clock) Time (CT) There are two adjustments that need to be made in order to convert ST to CT: The first is the Longitude
Sunlight and its Properties II EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz Solar Time (ST) and Civil (clock) Time (CT) There are two adjustments that need to be made in order to convert ST to CT: The first is the Longitude
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
rises in the east High Noon sets in the west, 9:00 a.m. 12:00 p.m. 3:30 p.m. flagpole meter stick
 . Sec 3.5 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving with Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded
. Sec 3.5 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving with Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded
SECONDARY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT UNIT- EDUCATION DIVISION. FORM 3 PHYSICS Time: 1h 30min
 SECONDARY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT UNIT- EDUCATION DIVISION FORM 3 PHYSICS Time: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator
SECONDARY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT UNIT- EDUCATION DIVISION FORM 3 PHYSICS Time: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator
THE PATH OF THE SUN. Page 1 of 6
 THE PATH OF THE SUN Goal(s): To observe the path of the sun across the sky and how this varies according to the time of day or the season. Ultimately, this will help the pupils to learn about solar energy.
THE PATH OF THE SUN Goal(s): To observe the path of the sun across the sky and how this varies according to the time of day or the season. Ultimately, this will help the pupils to learn about solar energy.
Maximum Power Point (Teacher Notes) (The Principles of Optimizing Photovoltaic Cell Power Output)
 Maximum Power Point (Teacher Notes) (The Principles of Optimizing Photovoltaic Cell Power Output) Notes on Part 1: Basic Electricity Review 1 To understand photovoltaics, it is necessary to know something
Maximum Power Point (Teacher Notes) (The Principles of Optimizing Photovoltaic Cell Power Output) Notes on Part 1: Basic Electricity Review 1 To understand photovoltaics, it is necessary to know something
Photovoltaic Systems Solar Radiation
 PowerPoint Presentation Photovoltaic Systems Solar Radiation The Sun Solar Radiation Sun- Earth Relationships Array Orientation Solar Radiation Data Sets Estimating Array Performance Arizona Solar Power
PowerPoint Presentation Photovoltaic Systems Solar Radiation The Sun Solar Radiation Sun- Earth Relationships Array Orientation Solar Radiation Data Sets Estimating Array Performance Arizona Solar Power
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH
 L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
announcements 5/1/08 L10 Analysis and Design Tools 5/1/08 Analysis and Design Tools
 Analysis and Design Tools ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 10 announcements 5/1/08 Information Meeting: INDIA program winter 2009 Friday May 2, 12:30, Gould 208P Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available
Analysis and Design Tools ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 10 announcements 5/1/08 Information Meeting: INDIA program winter 2009 Friday May 2, 12:30, Gould 208P Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available
CHAPTER 3. The sun and the seasons. Locating the position of the sun
 zenith 90 observer summer solstice 75 altitude angles equinox 52 winter solstice 29 Figure 3.1: Solar noon altitude angles for Melbourne SOUTH winter midday shadow WEST summer midday shadow summer EAST
zenith 90 observer summer solstice 75 altitude angles equinox 52 winter solstice 29 Figure 3.1: Solar noon altitude angles for Melbourne SOUTH winter midday shadow WEST summer midday shadow summer EAST
Unit 2 Math II - History of Trigonometry
 TSK # Unit Math II - History of Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
TSK # Unit Math II - History of Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
announcements 4/29/08
 Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006
 Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
L9 Solar Geometry 4/29/08
 Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Making a Sundial. Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory. iau.org/astroedu
 Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
THE SUN. LENGTH: Course of the semester
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 139 The Sun THE SUN SYNOPSIS: This exercise involves making measurements of the Sun every week throughout the semester, and then analyzing your results at semester s end. You ll
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 139 The Sun THE SUN SYNOPSIS: This exercise involves making measurements of the Sun every week throughout the semester, and then analyzing your results at semester s end. You ll
Spacetime Diagrams Lab Exercise
 Spacetime Diagrams Lab Exercise The spacetime diagram (also known as a Minkowski diagram) is a tool that can used to graphically describe complex problems in special relativity. In many cases, with a properly
Spacetime Diagrams Lab Exercise The spacetime diagram (also known as a Minkowski diagram) is a tool that can used to graphically describe complex problems in special relativity. In many cases, with a properly
Period 22: Uses of Solar Energy
 Name Section Period 22: Uses of Solar Energy 22.1 Using Solar Energy 1) Energy from the Sun a) What is solar insolation? b) What is the average solar insolation in Columbus, OH, in the summer? What is
Name Section Period 22: Uses of Solar Energy 22.1 Using Solar Energy 1) Energy from the Sun a) What is solar insolation? b) What is the average solar insolation in Columbus, OH, in the summer? What is
LESSON PLAN - Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data
 LESSON PLAN - Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Title of Lesson: Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Description of class: High School physics, astronomy, or environmental
LESSON PLAN - Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Title of Lesson: Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Description of class: High School physics, astronomy, or environmental
Triangles and Vectors
 Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Design of Heliostat Field for Small Scale Central Receiver System
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Sapana
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Sapana
SHADOW STUDY REPORT REGARDING
 SHADOW STUDY REPORT REGARDING an APPLICATION TO REDEVELOP Three 6 Storey Condominiums Regional Road 25 (Ontario Street) and Britannia Road Milton, Ontario KNYMH FILE # 17030 Prepared by: Krista Lilley
SHADOW STUDY REPORT REGARDING an APPLICATION TO REDEVELOP Three 6 Storey Condominiums Regional Road 25 (Ontario Street) and Britannia Road Milton, Ontario KNYMH FILE # 17030 Prepared by: Krista Lilley
Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander
 Volume 3 Number ISSN 074-397 (printed) ISSN 074-8059 (digital) June 006 The Journal of the North American Sundial Society Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander Time and reflection change
Volume 3 Number ISSN 074-397 (printed) ISSN 074-8059 (digital) June 006 The Journal of the North American Sundial Society Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander Time and reflection change
Earth s Orbit. Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology
 1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
MATHEMATICS ( CANDIDATES WITH PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) ( CANDIDATES WITHOUT PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT )
 Total No. of Printed Pages 6 X/3/M 0 3 MATHEMATICS ( CANDIDATES WITH PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 80 Pass Marks : 4 ( CANDIDATES WITHOUT PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 00
Total No. of Printed Pages 6 X/3/M 0 3 MATHEMATICS ( CANDIDATES WITH PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 80 Pass Marks : 4 ( CANDIDATES WITHOUT PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 00
March 21. Observer located at 42 N. Horizon
 March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS
 A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS usable all over the world by fer j. de vries, netherlands example of sundials on a dodecahedron date: january 1997, revised october 2002 Last Modified 02/05/2004
A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS usable all over the world by fer j. de vries, netherlands example of sundials on a dodecahedron date: january 1997, revised october 2002 Last Modified 02/05/2004
