Earth Science Seasons Test Name Per Date
|
|
|
- Gavin Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Per Date Page 1 1. The diagram below represents four positions of the Earth as it revolves around the Sun. 5. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows the apparent paths of the Sun at the beginning of each season for an observer at a location in Connecticut. At which position is the Earth located on December 21? 1) A 2) B 3) C 4) D 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below. The diagram represents the Earth at a position in orbit around the Sun, the Sun's rays at solar noon, and the direction to Polaris. Letters A through D represent positions on the Earth's surface. What is the time interval from the Sun's apparent path A to the Sun's apparent path C? 1) 1 day 2) 1 month 3) 6 months 4) 12 months 6. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows a view of Earth as seen from space at a certain time of the year. Which date is represented by the diagram? 1) March 21 2) June 21 3) September 23 4) December During how many days of a calendar year is the Sun directly overhead at noon in New Jersey? 1) only 1 day 2) only 2 days 3) 365 days 4) 0 days 4. On June 21, where will the Sun appear to rise for an observer located in New Jersey? 1) due west 2) due east 3) north of due east 4) south of due east Compared to observers at 35 S latitude, observers at 35 N latitude are generally experiencing 1) fewer hours of daylight and warmer temperatures 2) fewer hours of daylight and cooler temperatures 3) more hours of daylight and warmer temperatures 4) more hours of daylight and cooler temperatures 7. Which two factors determine the number of hours of daylight at a particular location? 1) longitude and season 2) longitude and the Earth's average diameter 3) latitude and season 4) latitude and the Earth's average diameter
2 Page 2 8. The diagram below shows the apparent paths of the Sun in relation to a house in New York State on June 21 and December The maps below show the amount of sea ice surrounding the continent of Antarctica at two different times of the year. Map A represents late August when the area covered by sea ice approaches its greatest extent. Map B represents the minimum extent of sea ice. Which statement best explains the cause of this apparent change in the Sun's path? 1) The Sun's orbital velocity changes as it revolves around the Earth. 2) The Earth's orbital velocity changes as it revolves around the Sun. 3) The Earth's axis is tilted 23 4) The Sun's axis is tilted The cartoon characters below are watching the Sun set. Which month is most probably represented by map B? 1) February 2) May 3) June 4) October 11. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents an exaggerated view of Earth revolving around the Sun. Letters A, B, C, and D represent Earth's location in its orbit on the first day of each of the four seasons. Toward which general direction are the characters looking? 1) north 2) south 3) east 4) west Earth s rate of revolution around the Sun is approximately 1) 1 per day 2) 360 per day 3) 15 per hour 4) 23.5 per hour
3 Page Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows a model of the apparent path and position of the Sun in relation to an observer at four different locations, A, B, C, and D, on Earth s surface on the dates indicated. The zenith (z) and the actual position of the Sun in the model at the time of the observation are shown. [The zenith is the point directly over the observer.] From sunrise to sunset at location B, the length of the observer s shadow will 1) increase, only 2) decrease, only 3) increase, then decrease 4) decrease, then increase 13. The diagram below shows the noontime shadows cast by a student and a tree. 14. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below. The diagram represents a plastic hemisphere upon which lines have been drawn to show the apparent paths of the Sun on four days at a location in New York State. Two of the days are December 21 and June 21. The protractor is placed over the north-south line. If the time is solar noon and the student is located in New York State, in what direction is the student facing? 1) north 2) south 3) east 4) west Which graph best represents the relationship between the intensity of insolation and the time of the year for this location? 1) 2) 3) 4)
4 Page 4 Base your answers to questions 15 through 17 on the diagram below, which represents a model of the sky (celestial sphere) for an observer in New York State. The curved arrow represents the Sun s apparent path for part of one day. The altitude of Polaris is also indicated. 15. On which date could this observation of the Sun s apparent path have been made? 1) March 21 2) July 21 3) October 21 4) December Where is this observer most likely located? 1) Massena 2) Oswego 3) Slide Mountain 4) Mt. Marcy 17. According to this diagram, what is the Sun s altitude at solar noon? 1) ) 42 3) 48 4) 90
5 Page Base your answer to the following question on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on December 21, September 23, and June 21. Which graph best shows the altitude of the Sun, as measured by the observer located at 42 N, at various times on December 21? 1) 2) 3) 4)
6 Page Base your answer to the following question on diagram and data table below. The diagram represents the Sun's apparent paths as viewed by an observer located at 50 N latitude on June 21 and March 21. The data table shows the Sun's maximum altitude for the same two dates of the year. The Sun's maximum altitude for December 21 has been left blank. Which value should be placed in the data table for the Sun's maximum altitude on December 21? 1) ) ) 40 4) 90º
7 Page Base your answer to the following question on the world map below. Letters A through D represent locations on Earth's surface. At which location on December 21 is the Sun directly overhead at solar noon? 1) A 2) B 3) C 4) D
8 Questions 21 through 25 refer to the following: The diagram below shows observations made by a sailor who left his ship and landed on a small deserted island on June 21. The diagram represents the apparent path of the Sun and the position of Polaris, as observed by the sailor on this island. 21) On the diagram provided, label on the observer s horizon, the eight compass directions (north, northwest, west, southwest, south, southeast, east, and northeast). 22) On the diagram provided, draw an arrow on the June 21 path of the Sun to show the Sun's direction of apparent movement from sunrise to sunset. 23) The sailor was still on the island on September 23. On the diagram provided, draw the Sun's apparent path for September 23, as it would have appeared to the sailor. [Be sure your September 23 path indicates the correct altitude of the noon Sun and begins and ends at the correct points on the horizon.] 24) Based on the sailor's observations, what is the latitude of this island? [Include the units and the compass direction in your answer.] 25) In the situation described, the sailor observed a 1-hour difference between solar noon on the island and solar noon at his last measured longitude onboard his ship. How many degrees of longitude is the island from the sailor's last measured longitude onboard his ship? Page 8
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
Practice Questions: Seasons #2
 1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
C) wavelength C) eastern horizon B) the angle of insolation is high B) increases, only D) thermosphere D) receive low-angle insolation
 1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
Which table correctly shows the dates on which the apparent paths of the Sun were observed? A) B) C) D)
 1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern
 632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER)
 L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH
 L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
Midterm Review #2-2018
 1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date
 Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Which graph best shows the relationship between intensity of insolation and position on the Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
 1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
EARTHS SHAPE AND POLARIS PRACTICE 2017
 1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
Earth-Sun Relationships. The Reasons for the Seasons
 Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1
 MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Mid Term Prep-Latitude and Longitude
 1. What is the approximate altitude of Polaris at Syracuse, New York? A) 43 B) 47 C) 76 D) 90º 2. If an observer on Earth views Polaris on the horizon, the observer is located at the A) equator (0 ) B)
1. What is the approximate altitude of Polaris at Syracuse, New York? A) 43 B) 47 C) 76 D) 90º 2. If an observer on Earth views Polaris on the horizon, the observer is located at the A) equator (0 ) B)
March 21. Observer located at 42 N. Horizon
 March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface.
 1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2
 MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
Which phase of the Moon will be seen from the Earth at position 5? A) B) C) D)
 Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
1. Which graph best represents the altitude of Polaris observed at northern latitude positions on the Earth's surface?
 1. Which graph best represents the altitude of Polaris observed at northern latitude positions on the Earth's surface? A) 4. The diagram below shows an observer measuring the altitude of Polaris. B) C)
1. Which graph best represents the altitude of Polaris observed at northern latitude positions on the Earth's surface? A) 4. The diagram below shows an observer measuring the altitude of Polaris. B) C)
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
Energy and Seasons A B1. 9. Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature?
 Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator
![Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator](/thumbs/83/88077665.jpg) Earth Science Regents Interactive Path of the Sun University of Nebraska Resources Copyright 2011 by Z. Miller Name Period COMPANION WEBSITES: http://www.analemma.com/ http://www.stellarium.org/ INTRODUCTION:
Earth Science Regents Interactive Path of the Sun University of Nebraska Resources Copyright 2011 by Z. Miller Name Period COMPANION WEBSITES: http://www.analemma.com/ http://www.stellarium.org/ INTRODUCTION:
C) D) 2. The diagram below shows a large pendulum in motion over an 8-hour period.
 1. An observer on Earth measured the apparent diameter of the Sun over a period of 2 years. Which graph best represents the Sun's apparent diameter during the 2 years? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below
1. An observer on Earth measured the apparent diameter of the Sun over a period of 2 years. Which graph best represents the Sun's apparent diameter during the 2 years? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below
Student Exploration: Seasons in 3D
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons in 3D Vocabulary: axis, equinox, latitude, Northern Hemisphere, revolve, rotate, solar energy, solar intensity, Southern Hemisphere, summer solstice, winter solstice
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons in 3D Vocabulary: axis, equinox, latitude, Northern Hemisphere, revolve, rotate, solar energy, solar intensity, Southern Hemisphere, summer solstice, winter solstice
3. Which color of the visible light has the shortest wavelength? A) violet B) green C) yellow D) red
 Name: Topic 6 Test 1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Base your
Name: Topic 6 Test 1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Base your
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
4. Which object best represents a true scale model of the shape of the Earth? A) a Ping-Pong ball B) a football C) an egg D) a pear
 Name Test on Friday 1. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional shape of the Earth? A) B) C) D) Date Review Sheet 4. Which object best represents a true scale model of the shape of the Earth?
Name Test on Friday 1. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional shape of the Earth? A) B) C) D) Date Review Sheet 4. Which object best represents a true scale model of the shape of the Earth?
Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice
 A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
Syosset High School Midterm Review
 Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
Motions of the Sun Model Exploration
 Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
Before you Sit. Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium
 Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season?
 Name: Date: LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season? The relationship between the Sun and Earth have been used since antiquity to measure time. The day is measured by the passage of the Sun
Name: Date: LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season? The relationship between the Sun and Earth have been used since antiquity to measure time. The day is measured by the passage of the Sun
Name: Exam 1, 9/30/05
 Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude
 Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude Overview This lesson is a modification of what Dave Hess and I, Stan Skotnicki, use in our Earth Science classes at Cheektowaga Central High School. It is an extension
Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude Overview This lesson is a modification of what Dave Hess and I, Stan Skotnicki, use in our Earth Science classes at Cheektowaga Central High School. It is an extension
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
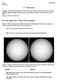 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
What causes the seasons? 2/11/09
 2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
November 20, NOTES ES Rotation, Rev, Tilt.notebook. vertically. night. night. counterclockwise. counterclockwise. East. Foucault.
 NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
A) M D) The Moon s distance from Earth varies in a cyclic manner.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)
 MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
NAME; LAB # SEASONAL PATH OF THE SUN AND LATITUDE Hemisphere Model #3 at the Arctic Circle
 NAME; PERIOD; DATE; LAB # SEASONAL PATH OF THE SUN AND LATITUDE Hemisphere Model #3 at the Arctic Circle 1 OBJECTIVE Explain how latitude affects the seasonal path of the Sun. I) Path of the Sun and Latitude.
NAME; PERIOD; DATE; LAB # SEASONAL PATH OF THE SUN AND LATITUDE Hemisphere Model #3 at the Arctic Circle 1 OBJECTIVE Explain how latitude affects the seasonal path of the Sun. I) Path of the Sun and Latitude.
2. The diagram below represents the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer at 65 N on March 21.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations
 LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
Earth is rotating on its own axis
 Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN
 Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN I. The Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun A star always rises and sets at the same place on the horizon and, hence, it is above the horizon for the same
Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN I. The Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun A star always rises and sets at the same place on the horizon and, hence, it is above the horizon for the same
b. So at 12:00 p.m., are the shadows pointing in the direction you predicted? If they are not, you must explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
A) greatest in diameter at the Equator B) 44 05' N 73 55' W B) Albany D) Polaris B) 8 h
 1. Measurements taken from space show the Earth to be A) greatest in diameter at the Equator B) greatest in diameter at the poles C) a perfect sphere D) pear shaped 2. New York State's highest peak, Mt.
1. Measurements taken from space show the Earth to be A) greatest in diameter at the Equator B) greatest in diameter at the poles C) a perfect sphere D) pear shaped 2. New York State's highest peak, Mt.
C) D) 2. The model below shows the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer in New York State on the first day of one of the four seasons.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Mid Term Prep-Shape of the Earth
 1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The diagrams below represent
1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The diagrams below represent
3 - Celestial Sphere
 3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
Practice Questions: Shape of the Earth
 Practice Questions: Shape of the Earth 1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its
Practice Questions: Shape of the Earth 1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its
Earth s Time Zones. Time Zones In The United States
 Name: Mr. DeLeo Date: Period: Earth s Time Zones Goal: Students will understand why humans have developed time zones on Earth, and how to figure out time at different positions on Earth. Background: One
Name: Mr. DeLeo Date: Period: Earth s Time Zones Goal: Students will understand why humans have developed time zones on Earth, and how to figure out time at different positions on Earth. Background: One
Chapter 1 Image Slides. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 1 Image Slides Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH. 1: CYCLES OF THE SKY CO a 1.1 The Celestial Sphere CO b The nearest star to us is about
Chapter 1 Image Slides Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH. 1: CYCLES OF THE SKY CO a 1.1 The Celestial Sphere CO b The nearest star to us is about
The Celestial Sphere. From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2 dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere.
 1 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2 dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 2 The Celestial Sphere Although we know better, it is helpful to
1 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2 dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 2 The Celestial Sphere Although we know better, it is helpful to
Astron 104 Laboratory #2 The Celestial Sphere
 Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #2 The Celestial Sphere Basic Setup Once the celestial sphere is properly setup, it will serve as an exact model of the heavens relative to your location on Earth.
Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #2 The Celestial Sphere Basic Setup Once the celestial sphere is properly setup, it will serve as an exact model of the heavens relative to your location on Earth.
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
IV.B. VISUAL RESOURCES SHADE SHADOW
 IV.B. VISUAL RESOURCES SHADE SHADOW INTRODUCTION This section identifies and describes the visual characteristics of the Project site and surrounding area and evaluates the potential change in the existing
IV.B. VISUAL RESOURCES SHADE SHADOW INTRODUCTION This section identifies and describes the visual characteristics of the Project site and surrounding area and evaluates the potential change in the existing
Earth s Dimensions. Earth s shape. Evidence. Spheres of Earth: 1) Lithosphere- includes: 2) Hydrosphere includes: 3) Atmosphere - Earth Dimensions 23
 Earth s Dimensions Earth s shape Evidence Spheres of Earth: 1) Lithosphere- includes: 2) Hydrosphere includes: 3) Atmosphere - Earth Dimensions 23 Selected Properties of Earth s Atmosphere: Earth Science
Earth s Dimensions Earth s shape Evidence Spheres of Earth: 1) Lithosphere- includes: 2) Hydrosphere includes: 3) Atmosphere - Earth Dimensions 23 Selected Properties of Earth s Atmosphere: Earth Science
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
Period: Name: Astronomy Part 3A. Earth s Rotation: Video Notes Sheets. Earth Science with Mr. Sammartano Hommocks Middle School, Team 8-3
 Name: Period: Astronomy Part 3A Earth s Rotation: Video Notes Sheets Earth Science with Mr. Sammartano Hommocks Middle School, Team 8-3 PROOF #1 What is the Shape of the Earth? How do we know the Earth
Name: Period: Astronomy Part 3A Earth s Rotation: Video Notes Sheets Earth Science with Mr. Sammartano Hommocks Middle School, Team 8-3 PROOF #1 What is the Shape of the Earth? How do we know the Earth
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test
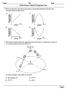 Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
Lab Activity: Climate Variables
 Name: Date: Period: Water and Climate The Physical Setting: Earth Science Lab Activity: Climate Variables INTRODUCTION:! The state of the atmosphere continually changes over time in response to the uneven
Name: Date: Period: Water and Climate The Physical Setting: Earth Science Lab Activity: Climate Variables INTRODUCTION:! The state of the atmosphere continually changes over time in response to the uneven
Ch. 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Ch. 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 1 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? 2 What does the universe look
Ch. 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 1 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? 2 What does the universe look
3. The Sun s Position
 3. The Sun s Position In order to understand how to collect energy from the sun, one must first be able to predict the location of the sun relative to the collection device. In this chapter we develop
3. The Sun s Position In order to understand how to collect energy from the sun, one must first be able to predict the location of the sun relative to the collection device. In this chapter we develop
Exercise 2: The UW planetarium
 Astronomy 100, Fall 2008 Name(s): Exercise 2: The UW planetarium The University of Washington Physics and Astronomy Building houses a wonderful planetarium, in addition to some other interesting displays.
Astronomy 100, Fall 2008 Name(s): Exercise 2: The UW planetarium The University of Washington Physics and Astronomy Building houses a wonderful planetarium, in addition to some other interesting displays.
1. Which continents are experiencing daytime? 2. Which continents are experiencing nighttime?
 Name: Section: Astronomy 101: Seasons Lab Objective: When you have completed this lab, you will be able to describe the seasons of the year and explain the reasons for those seasons. Answer the questions
Name: Section: Astronomy 101: Seasons Lab Objective: When you have completed this lab, you will be able to describe the seasons of the year and explain the reasons for those seasons. Answer the questions
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
3. a. In the figure below, indicate the direction of the Sun with an arrow.
 Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Name Homeroom. Science Quiz Day/Night, Sun s Energy, Seasons September 24, 2012
 Name Homeroom Science Quiz Day/Night, Sun s Energy, Seasons September 24, 2012 1. The winter solstice occurs on either December 21 or 22, depending on the year. Which of the following statements best explains
Name Homeroom Science Quiz Day/Night, Sun s Energy, Seasons September 24, 2012 1. The winter solstice occurs on either December 21 or 22, depending on the year. Which of the following statements best explains
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why?
 (1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
Chapter 2 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Discovering the Universe for Yourself Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Seasons. What causes the seasons?
 Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Patterns of Change on Earth
 TEKS collect and analyze data to identify sequences and predict patterns of change in shadows, tides, seasons, and the observable appearance of the Moon over time Patterns of Change on Earth Patterns and
TEKS collect and analyze data to identify sequences and predict patterns of change in shadows, tides, seasons, and the observable appearance of the Moon over time Patterns of Change on Earth Patterns and
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
b. Assuming that the sundial is set up correctly, explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Midterm Review #4 -FR
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which represents a north polar view of Earth on a specific day of the year. Solar times at selected longitude lines are shown. Letter A
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which represents a north polar view of Earth on a specific day of the year. Solar times at selected longitude lines are shown. Letter A
CA1 2.11: Designing an Equatorial Sundial Activity
 Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Name: Date: 5. The bright stars Vega, Deneb, and Altair form A) the summer triangle. B) the winter triangle. C) the Big Dipper. D) Orion, the Hunter.
 Name: Date: 1. If there are about 6000 stars in the entire sky that can be seen by the unaided human eye, about how many stars would be seen at a particular instant on a given dark night from a single
Name: Date: 1. If there are about 6000 stars in the entire sky that can be seen by the unaided human eye, about how many stars would be seen at a particular instant on a given dark night from a single
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements
 ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
Mid Term Prep-Moon Review 2
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 1. Which statement best explains why
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 1. Which statement best explains why
Astronomy 115 Section 4 Week 2. Adam Fries SF State
 Astronomy 115 Section 4 Week 2 Adam Fries SF State afries@sfsu.edu Important Notes: Homework #1 is Due at the beginning of class next time. Attendance Sheet is going around one last time! Homework Questions?
Astronomy 115 Section 4 Week 2 Adam Fries SF State afries@sfsu.edu Important Notes: Homework #1 is Due at the beginning of class next time. Attendance Sheet is going around one last time! Homework Questions?
Astronomy Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
Earth s Rotation. How often does the day-and-night cycle occur on Earth?
 How often does the day-and-night cycle occur on Earth? Earth moves through space in several important ways. One type of motion is called rotation. A rotation is a spin around a center. For example, imagine
How often does the day-and-night cycle occur on Earth? Earth moves through space in several important ways. One type of motion is called rotation. A rotation is a spin around a center. For example, imagine
