Stable Discs aroundgalactic andlmcpost-agb Binaries
|
|
|
- Winifred Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHYGALAXIESCAREABOUTAGB STARSII: SHININGEXAMPLESANDCOMMONINHABITANTS ASP Conference Series,Vol.445 Kerschbaum, Lebzelter,and Wing,eds. c 2011 AstronomicalSociety ofthe Pacific Stable Discs aroundgalactic andlmcpost-agb Binaries C. Gielen, 1 H.Van Winckel, 1 M.Min, 2 R. Waters, 3 C. Dominik, 3,4 T.LloydEvans, 5 M.Matsuura, 6 P.Deroo, 7 J.Cami, 8 andthe SAGE-Spec team 9 1 Instituutvoor Sterrenkunde,Katholieke UniversiteitLeuven, Belgium 2 AstronomischInstituutUtrecht,UniversiteitUtrecht,TheNetherlands 3 SterrenkundigInstituut AntonPannekoek,UniversiteitAmsterdam, TheNetherlands 4 Departmentof Astrophysics,RadboudUniversityNijmegen,TheNetherlands 5 SUPA,SchoolofPhysicsandAstronomy,UniversityofStAndrews,North Haugh,St Andrews,Fife,UK 6 UCL-InstituteofOrigins,DepartmentofPhysicsand Astronomy,University CollegeLondon, UK 7 JetPropulsionLaboratory,PasadenaCA,USA 8 Departmentof Physics&Astronomy,UniversityofWesternOntario,London, Ontario,Canada 9 N2.php Abstract. The results of our study of a particular class of Galactic and extragalactic evolved stars, which are part of a binary system and surrounded by a stable dusty disc, are discussed. By combining spectroscopic, photometric and interferometric observations with detailed models describing dust properties and disc structure, we investigate theexact disccomposition and structure. 1. Binary Post-AGBStars Withthediscoveryofthefirstbinarypost-AGBstars,itbecameclearthattheseevolved stars have common observational characteristics such as a broad infrared (IR) excess. This observed broad IR excess points to the presence of both cool and hot (up to the sublimation temperature) dust around the star (De Ruyter et al. 2006). An outflow model is not adequate to explain the presence of such hot dust, since the near-infrared excess is expected to disappear within years after the cessation of the dusty mass loss. The dust must thus reside in a long-lived, stable reservoir close to the star. This led us tosuspectthattheseobjects aresurroundedbyastablekepleriandisc. Thespecificobservationalcharacteristicsallowedforasystematicsearchforthese objectsand,sofar,morethan70galacticobjectshavebeendiscovered(deruyteretal. 2006). Forthesestarsourgroupstartedanextensivemulti-wavelengthstudy,including high spectral resolution optical and infrared studies, submillimetre observations, and highspatialresolutioninterferometricstudies. 281
2 282 Gielen etal. Theformationofthediscisstillabadly-understoodprocess,probablytheresultof non-conservative Roche lobe overflow during evolution in a binary system (Verhoelst, van Aarle, & Acke 2007). To detect this binary motion, we started an extensive radial velocity monitoring programme, which confirmed the binary hypothesis and gave atypicalsemi-majoraxisfortheorbitofaround1au(vanwinckeletal.2009). Given the effective temperature of the central star and its high luminosity, all the discs must be circumbinary, since the orbits all lie well within the sublimation radius of the dust. The mass functions calculated from the orbit indicate that the companion is likely a main-sequence star. So far we have orbital parameters for about 30 sources, with orbital periods ranging from 100 to 2000 days and high eccentricities, up to 0.6. This is surprising, since theory predicts efficient circularisation by tidal forces on very short timescales (Polsetal.2003). Allorbitsdiscoveredsofararetoosmalltohaveaccommodatedafull-grownAGB star. This implies that the system must have been subject to severe binary interaction whilethe evolvedstarwas atgiantdimensions The CircumbinaryDisc The presence of the circumbinary disc has an impact on several observational characteristicsof thepost-agbstar: The strong infrared excess, L IR /L > 40% in most cases, shows that significant amounts of circumstellar material are present to reprocess the incoming stellar light. Surprisingly, a very low total reddening towards these stars is observed. This isclear evidence foranon-sphericalcircumstellarenvironment(ce). The binary disc sources are characterised by a depletion pattern in their photospheres(e.g.vanwinckeletal.1998;maasetal.2005). Generally,alackofcarbonor s-processenhancementisfound. Thesestarsapparentlydidnotundergoa thirddredge-upprocessontheagb,eventhoughtheyhaveinitialmasseswhich would theoretically make them evolve to carbon stars. The abundance pattern is the result of gas-dust separation in the CE, followed by a reaccretion of the gas component, which is now poor in refractory elements. Waters, Trams, & Waelkens (1992) had already proposedthat the mostlikely circumstance for this process tooccur iswhen thedustistrappedinadisc. Recent interferometric studies confirm the very compact nature of the circumstellar material (Deroo et al. 2007a,b). All disc sizes are similar, with N-band sizesbetween30and50au.someobjectsshowcrystallinedustspeciescloseto the inner rim,others showstrongprocessingthroughoutthedisc. Kinematical information on several objects detected in CO shows typical Keplerianrotationvelocities insteadof outflows(e.g.bujarrabal etal.2007). Submillimetre measurements (De Ruyter et al. 2005, Gielen et al., in prep.) indicate the presence of large grains (> cm-size) in the CE. A disc is an ideal environment for grain growth, since it is a long-lived stable reservoir, with relativelyhighdensities. Theselargegrainshavesmallerdust-settlingtimes,causing the disc to be inhomogeneous, consisting of small hot grains in the surface layer of thediscandacoolmidplaneof mainlylarge grains.
3 StableDiscs aroundgalacticand LMCPost-AGBBinaries 283 Figure 1. Left: The result from our full-spectrum fitting. The observed spectrum (black) is plotted together with the best model fit (red solid line) and the continuum (black solid line). Right: The result from our 2-D disc modelling. Observations are representedbycrosses;theunderlyingkuruczmodelisgivenbythedottedline. The full linerepresents the SED of the discmodel SimilarSources in thelmc Recently the SAGE (Surveying the Agents of Galaxy Evolution) Spitzer LMC survey (Meixner et al. 2006) observed the LMC, using all Spitzer IRAC/MIPS instruments. Thanks to this database, we found that the LMC post-agb objects have infrared excesses similar to the Galactic sources. A search for post-agb disc sources in this survey,basedontheirlocationincolour-colourdiagrams,resultedinalistofabout650 disccandidates(vanaarleetal.,inprep). Fromthefollow-upSAGE Specprogramme wealsohavespitzer IRS spectraforthe LMCobjects (Kemper etal.2010). Recentchemicalstudiesofafewextragalacticpost-AGBdiscsources(Reyniers& VanWinckel2007;Gielenetal.2009),showthat,asintheGalaxy,thedisccandidates displayadepletion patternintheir photospheres. 2. DiscComposition To study the mineralogy of the disc, we use Spitzer mid-infrared spectra. So far, we have spectra for 33 Galactic and 24 extragalactic LMC sources. Using a full-spectral fit routine (see Figure 1), we determined the parameters, such as composition and temperature,of thedustresponsiblefortheobservedspectra(gielenetal.2008). Allsamplestarsshowsignaturesofoxygen-richdustspeciesintheirinfraredspectra, more specifically amorphous and crystalline silicates. The magnesium-rich end members of crystalline silicates seem to prevail in the spectra, with strong emission due to forsterite, and to lesser extent enstatite. From our full spectral fitting we also find that the amorphous dust might be strongly Mg-rich. Detailed chemical studies of these stars (e.g. Maas et al. 2005; Gielen et al. 2009) have shown that the stellar photospheresaredevoidofiron,withtheironinsteadbeinglockedupinthedustofthe disc. If no iron is detected in the observed dust species, this could imply that iron is storedintheformofmetallicironorironoxide,whichhavenodistinctobservabledust signatures.
4 284 Gielen etal. Wefindthatthediscsaretheidealenvironmentforstrongdustgrainprocessingto occur, both in grain growth and crystallinity. For our sample stars, the mass fraction in crystalline grains ranges from 10 to 70%, which is much higher than observed in outflowsources. Theobservedpeak-to-continuumratioshowsthat,onaverage,grainsizes above 0.1µm prevail. There thus seems to be a removal of the smallest grains in the discsurfacelayers. Several sourcesshowstrongcrystallineemissionfeatures at longer wavelengths, coming from rather cool crystalline dust grains in the disc. Crystalline dustistypicallyformedclosetotheinnerrim,wheretemperaturesarehighenoughfor crystallisation to occur. The presence of cool crystalline grains shows that either radial mixing must be very efficient or that the grains have a crystallinisation process which is alreadyefficient atlowtemperatures. A few sources show rather atypical spectral signatures, with emission features due to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), CO 2 gas lines, and/or fullerene C 60 emissionlines(gielenetal.,inprep). Thelow 12 C/ 13 Cratio,derivedfromthegaslines, againindicates thelackof thirddredge-upprocesses. So far, no clear difference is found in the disc composition of the Galactic and extragalacticsources. Also,nocorrelationisfoundbetweentheobserveddustparametersand other characteristics,suchas thecentralstaror binaryorbit. 3. DiscGeometry To determine the structure of the discs, we performed 2-D disc modelling on the observedphotometryandspectroscopyofthegalacticandlmcdiscsources(seefig.1), using the MCMax radiative transfer code (Min et al. 2009). We found that a good fit is obtained with a passively-irradiated, self-shadowed disc with a puffed-up inner rim. The inner radius of the disc is found slightly below the dust sublimation radius, but the outer radius is unfortunately less well constrained. Typical values for the inner and outer radius are 2 20AU and AU, respectively. Dust masses range from 10 6 to10 4 M,withasurfacedensitypowerlaw> 2,usingagas-to-dustratioof Conclusions Our studies show that, both in our Galaxy and beyond, circumbinary discs around evolvedstarsareclearlypresent,andareacommon by-productof binaryevolution. Both from our mineralogy study and from our disc modelling, we find that the chemicalandphysicalpropertiesofthesediscsaroundevolvedbinariesareverysimilar to those seen in protoplanetary discs around young stars a remarkable conclusion, since these discs have very different formation histories. All discs are oxygen rich, and thus formed when the star was oxygen rich. In both disc types, dust processing is very effective: large grain sizes prevail and the crystallinity is very high. The observed correlation between the evolutionary phase and the disc parameters found for young starsisnot yetobservedinour limitedsampleof evolvedbinarystars. Clearly, many open questions remain on the formation, structure and evolution of these circumbinary discs around evolved stars, and on the impact the disc has on the evolution of the central binary system. The interaction in the binary system is fundamental in trapping part of the dust in a stable circumbinary environment, and it determines thefurtherevolutionof thebinarystarand thedisc.
5 StableDiscs aroundgalacticand LMCPost-AGBBinaries 285 References Bujarrabal, V., Van Winckel, H., Neri,R., et al.2007, A&A, 468, L45 De Ruyter, S., Van Winckel, H., Dominik, C., Waters, L., & Dejonghe, H. 2005, A&A, 435, 161 DeRuyter, S., Van Winckel, H., Maas, T., et al.2006, A&A, 448, 641 Deroo, P., Acke, B.,Verhoelst, T.,et al. 2007a, A&A, 474, L45 Deroo, P., Van Winckel, H., Verhoelst, T., et al.2007b, A&A,467, 1093 Gielen,C.,VanWinckel,H.,Min,M.,Waters,L.B.F.M.,&LloydEvans,T.2008,A&A,490, 725 Gielen, C.,Van Winckel, H.,Reyniers, M., et al.2009, A&A, 508, 1391 Kemper, F., Woods, P. M.,Antoniou, V., et al. 2010, PASP, 122, 683 Maas, T., Van Winckel, H., & Lloyd Evans, T. 2005, A&A, 429, 297 Meixner, M.,Gordon, K. D., Indebetouw, R., et al.2006, AJ,132, 2268 Min,M.,Dullemond,C.P.,Dominik,C.,deKoter,A.,&Hovenier,J.W.2009,A&A,497,155 Pols, O. R., Karakas, A. I., Lattanzio, J. C., & Tout, C. A. 2003, in Symbiotic Stars Probing Stellar Evlution, edited by R. L. M. Corradi, J. Mikolajewska, & T. J. Mahoney, ASP Conf. Ser., 303, 290 Reyniers, M.,&Van Winckel, H. 2007, A&A, 463, L1 Van Winckel, H.,Lloyd Evans, T., Briquet, M., et al.2009, A&A, 505, 1221 Van Winckel, H.,Waelkens, C.,Waters, L. B. F. M.,et al. 1998, A&A, 336, L17 Verhoelst, T.,van Aarle, E.,&Acke, B. 2007, A&A, 470, L21 Waters, L. B. F. M.,Trams, N. R., &Waelkens, C. 1992, A&A, 262, L37 Discussion Meixner: Some past papers by Jura and others show very narrow and faint CO lines suggesting very low gas to dust ratios. Do you have measurements of gas masses in these sources (I see you will go after some with Herschel) and what gas-to-dust-mass ratiosdo youfind? Gielen: Several problems arise when trying to measure gas ratios in these post-agb disk systems. (i) the systems are located at great (unknown) distance (>>kpc) and the disks themselves are relatively small. This means they have very small angular scales on the sky (<<arcsecond, mas). This often gives a beam problem. (ii) the gas component of the disk is in mostcases probably optically thick, this means you cannot accurately measure the gas content, resulting only in lower limits (see Bujarrabal et al. 2007). (iii) the disk in these systems must be gas rich: to get the observed L IR /L ratios the disk must absorb a lot of stellar light, and thus needs a large surface. You cannot have such a large disk surface without sufficient gas pressure. A gas poor disk willcollapsedue togravityand willbecome toothin.
1. The AGB dust budget in nearby galaxies
 **Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Identifying the chemistry of the dust around AGB stars in nearby galaxies
**Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Identifying the chemistry of the dust around AGB stars in nearby galaxies
E-ELT METIS * AND MATISSE: PROSPECTS FOR AGB-STARS
 E-ELT METIS * AND MATISSE: PROSPECTS FOR AGB-STARS J. Hron 1, J. Blommaert 2, L. Decin 2, T. Lebzelter 1, C. Paladini 3,1, H. Van Winckel 2 and the METIS and MATISSE teams (1) Universitätssternwarte Wien,
E-ELT METIS * AND MATISSE: PROSPECTS FOR AGB-STARS J. Hron 1, J. Blommaert 2, L. Decin 2, T. Lebzelter 1, C. Paladini 3,1, H. Van Winckel 2 and the METIS and MATISSE teams (1) Universitätssternwarte Wien,
The Interstellar Medium in Galaxies: SOFIA Science
 The Interstellar Medium in Galaxies: SOFIA Science Margaret Meixner (STScI) Xander Tielens (NASA/Ames/Leiden Univ.), Jesse Dotson (NASA/ARC), Bruce Draine (Princeton), Mark Wolfire (U. Maryland), Jackie
The Interstellar Medium in Galaxies: SOFIA Science Margaret Meixner (STScI) Xander Tielens (NASA/Ames/Leiden Univ.), Jesse Dotson (NASA/ARC), Bruce Draine (Princeton), Mark Wolfire (U. Maryland), Jackie
Dust. The four letter word in astrophysics. Interstellar Emission
 Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
Circumstellar disks The MIDI view. Sebastian Wolf Kiel University, Germany
 Circumstellar disks The MIDI view Sebastian Wolf Kiel University, Germany MPIA MIDI SG concluding meeting May 5, 2014 Overview Circumstellar disks: Potential of IR long-baseline interferometry MIDI: Exemplary
Circumstellar disks The MIDI view Sebastian Wolf Kiel University, Germany MPIA MIDI SG concluding meeting May 5, 2014 Overview Circumstellar disks: Potential of IR long-baseline interferometry MIDI: Exemplary
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Analysis of the infrared spectra of the peculiar post-agb stars EPLyrae and HD52961 Gielen, C.; van Winckel, H.; Matsuura, M.; Min, M.; Deroo, P.; Waters, L.B.F.M.;
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Analysis of the infrared spectra of the peculiar post-agb stars EPLyrae and HD52961 Gielen, C.; van Winckel, H.; Matsuura, M.; Min, M.; Deroo, P.; Waters, L.B.F.M.;
Symbiotic Stars: an ISO overview. R. Angeloni 1,2, M. Contini 2,1, S. Ciroi 1, P. Rafanelli 1 AJ, , 205. Rodolfo Angeloni May SNA
 Silicate Dust in D-type Symbiotic Stars: an ISO overview R. Angeloni 1,2, M. Contini 2,1, S. Ciroi 1, P. Rafanelli 1 AJ, 2007-134, 205 1 Dept. of Astronomy, University of Padova, Italy 2 School of Physics
Silicate Dust in D-type Symbiotic Stars: an ISO overview R. Angeloni 1,2, M. Contini 2,1, S. Ciroi 1, P. Rafanelli 1 AJ, 2007-134, 205 1 Dept. of Astronomy, University of Padova, Italy 2 School of Physics
The Ṁass- loss of Red Supergiants
 The Ṁass- loss of Red Supergiants Dr. Donald F. Figer Director, Center for Detectors Speaker: Yuanhao (Harry) Zhang RIT 9/12/13 1 9/12/13 2 Outline IntroducJon MoJvaJon Objects Method Need for SOFIA/FORCAST
The Ṁass- loss of Red Supergiants Dr. Donald F. Figer Director, Center for Detectors Speaker: Yuanhao (Harry) Zhang RIT 9/12/13 1 9/12/13 2 Outline IntroducJon MoJvaJon Objects Method Need for SOFIA/FORCAST
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Mar 2015](/thumbs/74/69828802.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa_acher_arxiv c ESO 2015 March 18, 2015 The evolved circumbinary disk of AC Her: a radiative transfer, interferometric and mineralogical study M. Hillen 1, B.L.
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa_acher_arxiv c ESO 2015 March 18, 2015 The evolved circumbinary disk of AC Her: a radiative transfer, interferometric and mineralogical study M. Hillen 1, B.L.
Devika kamath Institute of Astronomy, KU. Leuven, Belgium
 A NEWLY DISCOVERED STELLAR TYPE: DUSTY POST-RED GIANT BRANCH (POST-RGB) STARS IN THE MAGELLANIC CLOUDS Devika kamath Institute of Astronomy, KU. Leuven, Belgium Collaborators Peter Wood (1), Hans Van Winckel
A NEWLY DISCOVERED STELLAR TYPE: DUSTY POST-RED GIANT BRANCH (POST-RGB) STARS IN THE MAGELLANIC CLOUDS Devika kamath Institute of Astronomy, KU. Leuven, Belgium Collaborators Peter Wood (1), Hans Van Winckel
Interstellar Dust and Extinction
 University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
INDEX OF SUBJECTS 6, 14, 23, 50, 95, 191 4, 191, 234
 INDEX OF SUBJECTS Abundances, elemental Abundances, ionic AGB stars (see Stars, AGB) Age, nebulae Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) Be stars (see Stars, Be) Bipolar structure, nebulae Carbon stars Carbon stars,
INDEX OF SUBJECTS Abundances, elemental Abundances, ionic AGB stars (see Stars, AGB) Age, nebulae Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) Be stars (see Stars, Be) Bipolar structure, nebulae Carbon stars Carbon stars,
Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS. Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS
 Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS IRSIS meeting 05-12-2007 Overview Intestellar ice mantles Hydrocarbons in the galaxy and outside Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Interstellar
Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS IRSIS meeting 05-12-2007 Overview Intestellar ice mantles Hydrocarbons in the galaxy and outside Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Interstellar
Mid-IR and Far-IR Spectroscopic Measurements & Variability. Kate Su (University of Arizona)
 Mid-IR and Far-IR Spectroscopic Measurements & Variability Kate Su (University of Arizona) Five Zones of Debris Dust edge-on view of the Fomalhaut planetary system distance, r 1500 K very hot dust 500
Mid-IR and Far-IR Spectroscopic Measurements & Variability Kate Su (University of Arizona) Five Zones of Debris Dust edge-on view of the Fomalhaut planetary system distance, r 1500 K very hot dust 500
Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems
 Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems Meyer, Hillenbrand et al., Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems (FEPS): First Results from a Spitzer Legacy Science Program ApJ S 154: 422 427 (2004).
Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems Meyer, Hillenbrand et al., Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems (FEPS): First Results from a Spitzer Legacy Science Program ApJ S 154: 422 427 (2004).
Setting the Stage for Planet Formation: Grain Growth in Circumstellar Disks
 Setting the Stage for Planet Formation: Grain Growth in Circumstellar Disks Leonardo Testi (European Southern Observatory) Disk Evolution From Grains to Pebbles Do we understand what we observe? Wish List
Setting the Stage for Planet Formation: Grain Growth in Circumstellar Disks Leonardo Testi (European Southern Observatory) Disk Evolution From Grains to Pebbles Do we understand what we observe? Wish List
Star formation : circumstellar environment around Young Stellar Objects
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2005) 33, 327 331 Star formation : circumstellar environment around Young Stellar Objects Manoj Puravankara Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune - 411007,
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2005) 33, 327 331 Star formation : circumstellar environment around Young Stellar Objects Manoj Puravankara Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune - 411007,
Probing silicates in disks around T Tauri stars with Spitzer IRS
 Probing silicates in disks around T Tauri stars with Spitzer IRS Jacqueline Kessler-Silacci, Spitzer Fellow, Univ. of Texas the c2d IRS team: Jean-Charles Augereau, Vincent Geers, Adwin Boogert, Geoff
Probing silicates in disks around T Tauri stars with Spitzer IRS Jacqueline Kessler-Silacci, Spitzer Fellow, Univ. of Texas the c2d IRS team: Jean-Charles Augereau, Vincent Geers, Adwin Boogert, Geoff
Time-variable phenomena in Herbig Ae/Be stars
 Time-variable phenomena in Herbig Ae/Be stars! Péter Ábrahám Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, Hungary! Á. Kóspál, R. Szakáts! Santiago, 2014 April 7 Variability - and why it is interesting Herbig Ae/Be stars
Time-variable phenomena in Herbig Ae/Be stars! Péter Ábrahám Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, Hungary! Á. Kóspál, R. Szakáts! Santiago, 2014 April 7 Variability - and why it is interesting Herbig Ae/Be stars
Astrochemistry (2) Interstellar extinction. Measurement of the reddening
 Measurement of the reddening The reddening of stellar colours casts light on the properties of interstellar dust Astrochemistry (2) Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo The reddening is measured
Measurement of the reddening The reddening of stellar colours casts light on the properties of interstellar dust Astrochemistry (2) Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo The reddening is measured
The Infrared Universe as Seen by Spitzer and Beyond. February 20, 2007
 The Infrared Universe as Seen by Spitzer and Beyond The Holly Berry Cluster [NOT the Halle Berry cluster] in Serpens February 20, 2007 Presented to the Herschel Open Time Key Project Workshop Michael Werner,
The Infrared Universe as Seen by Spitzer and Beyond The Holly Berry Cluster [NOT the Halle Berry cluster] in Serpens February 20, 2007 Presented to the Herschel Open Time Key Project Workshop Michael Werner,
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars. Exoplanets Properties of the host stars. Characterization of the exoplanet host stars
 Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
University of Groningen. Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano
 University of Groningen Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth
 Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Location and sizes of forsterite grains in protoplanetary disks. Interpretation from the Herschel DIGIT programme
 A&A 574, A140 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201423770 c ESO 2015 Astronomy & Astrophysics Location and sizes of forsterite grains in protoplanetary disks Interpretation from the Herschel DIGIT programme
A&A 574, A140 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201423770 c ESO 2015 Astronomy & Astrophysics Location and sizes of forsterite grains in protoplanetary disks Interpretation from the Herschel DIGIT programme
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 22 Nov 2000
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** OAO1657 415 : A Missing Link in High Mass X-ray Binaries? arxiv:astro-ph/0011401v1 22 Nov 2000 D.H. Maxwell, A.J. Norton
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** OAO1657 415 : A Missing Link in High Mass X-ray Binaries? arxiv:astro-ph/0011401v1 22 Nov 2000 D.H. Maxwell, A.J. Norton
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018](/thumbs/94/118263605.jpg) AKARI color useful for classifying chemical types of Miras Noriyuki Matsunaga 1 1 Department of Astronomy, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan arxiv:1804.04940v1 [astro-ph.sr]
AKARI color useful for classifying chemical types of Miras Noriyuki Matsunaga 1 1 Department of Astronomy, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan arxiv:1804.04940v1 [astro-ph.sr]
Th. Henning, J. Bouwman, J. Rodmann MPI for Astronomy (MPIA), Heidelberg. Grain Growth in Protoplanetary Disks From Infrared to Millimetre Wavelengths
 Th. Henning, J. Bouwman, J. Rodmann MPI for Astronomy (MPIA), Heidelberg Grain Growth in Protoplanetary Disks From Infrared to Millimetre Wavelengths Cumber01.ppt 30.5.2001 Motivation From molecular cloud
Th. Henning, J. Bouwman, J. Rodmann MPI for Astronomy (MPIA), Heidelberg Grain Growth in Protoplanetary Disks From Infrared to Millimetre Wavelengths Cumber01.ppt 30.5.2001 Motivation From molecular cloud
Nearby Universe: Rapporteur
 Nearby Universe: Rapporteur Margaret Meixner (STScI) SAGE: Tracing the Lifecycle of Baryonic Matter: Intermediate mass stars High mass stars credit: http://hea-www.cfa.harvard.edu/champ/education/public/icons/
Nearby Universe: Rapporteur Margaret Meixner (STScI) SAGE: Tracing the Lifecycle of Baryonic Matter: Intermediate mass stars High mass stars credit: http://hea-www.cfa.harvard.edu/champ/education/public/icons/
HIGH-TEMPERATURE OPTICAL CONSTANTS OF DUST ANALOGUES FOR THE SOLAR NEBULA
 European Conference on Laboratory Astrophysics - ECLA C. Stehlé, C. Joblin and L. d Hendecourt (eds) EAS Publications Series, 58 (2012) 09 13 www.eas.org HIGH-TEMPERATURE OPTICAL CONSTANTS OF DUST ANALOGUES
European Conference on Laboratory Astrophysics - ECLA C. Stehlé, C. Joblin and L. d Hendecourt (eds) EAS Publications Series, 58 (2012) 09 13 www.eas.org HIGH-TEMPERATURE OPTICAL CONSTANTS OF DUST ANALOGUES
Lifecycle of Dust in Galaxies
 Lifecycle of Dust in Galaxies Karl Gordon Space Telescope Science Institute 3700 San Martin Drive Baltimore, MD 21218 Email: kgordon@stsci.edu Phone: 410-338-5031 co-authors: Margaret Meixner (Space Telescope
Lifecycle of Dust in Galaxies Karl Gordon Space Telescope Science Institute 3700 San Martin Drive Baltimore, MD 21218 Email: kgordon@stsci.edu Phone: 410-338-5031 co-authors: Margaret Meixner (Space Telescope
BUILDING GALAXIES. Question 1: When and where did the stars form?
 BUILDING GALAXIES The unprecedented accuracy of recent observations of the power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background leaves little doubt that the universe formed in a hot big bang, later cooling
BUILDING GALAXIES The unprecedented accuracy of recent observations of the power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background leaves little doubt that the universe formed in a hot big bang, later cooling
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon from the Magellanic Clouds
 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon from the Magellanic Clouds Hony and Spitzer/SAGE-SPEC team Galliano, Seok, Neelamkodan, Kemper, Madden, Indebetouw, Gordon, Sandstrom 11 Aug 2017 S. Hony (Heidelberg University)
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon from the Magellanic Clouds Hony and Spitzer/SAGE-SPEC team Galliano, Seok, Neelamkodan, Kemper, Madden, Indebetouw, Gordon, Sandstrom 11 Aug 2017 S. Hony (Heidelberg University)
Mass-Loss Rates and Luminosities of Evolved Stars in the Magellanic Clouds
 Mass-Loss Rates and Luminosities of Evolved Stars in the Magellanic Clouds Martin Groenewegen Royal Observatory of Belgium/Koninklijke Sterrenwacht van België, Brussels (martin.groenewegen@oma.be) Monte
Mass-Loss Rates and Luminosities of Evolved Stars in the Magellanic Clouds Martin Groenewegen Royal Observatory of Belgium/Koninklijke Sterrenwacht van België, Brussels (martin.groenewegen@oma.be) Monte
Challenges for the Study of Hot Cores with ALMA: NGC 6334I
 Challenges for the Study of Hot Cores with ALMA: NGC 6334I Crystal Brogan (NRAO/North American ALMA Science Center) Collaborators: Todd Hunter (NRAO) Remy Indebetouw (UVa/NRAO), Ken (Taco) Young (CfA),
Challenges for the Study of Hot Cores with ALMA: NGC 6334I Crystal Brogan (NRAO/North American ALMA Science Center) Collaborators: Todd Hunter (NRAO) Remy Indebetouw (UVa/NRAO), Ken (Taco) Young (CfA),
IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies
 IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies Houck et al., ApJ, 2005 Weedman et al., ApJ, 2005 Lutz et al., ApJ, 2005 Astronomy 671 Jason Marshall Opening the IR Wavelength Regime for Discovery One of the primary
IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies Houck et al., ApJ, 2005 Weedman et al., ApJ, 2005 Lutz et al., ApJ, 2005 Astronomy 671 Jason Marshall Opening the IR Wavelength Regime for Discovery One of the primary
Dynamical Atmospheres & Winds of AGB Stars A Theorist's View
 Dynamical Atmospheres & Winds of AGB Stars A Theorist's View Susanne Höfner Department of Physics & Astronomy Uppsala University Dynamics of atmosphere & wind stellar pulsation & convection induce strong
Dynamical Atmospheres & Winds of AGB Stars A Theorist's View Susanne Höfner Department of Physics & Astronomy Uppsala University Dynamics of atmosphere & wind stellar pulsation & convection induce strong
Spectral Energy Distributions as probes of star formation in the distant Universe
 MODULO meeting 2-3 December 2010 Spectral Energy Distributions as probes of star formation in the distant Universe Simona Bovinelli ISSI International Space Science Institute IRAS (1983), ISO (1995) and
MODULO meeting 2-3 December 2010 Spectral Energy Distributions as probes of star formation in the distant Universe Simona Bovinelli ISSI International Space Science Institute IRAS (1983), ISO (1995) and
Lecture 5. Interstellar Dust: Optical Properties
 Lecture 5. Interstellar Dust: Optical Properties 1. Introduction 2. Extinction 3. Mie Scattering 4. Dust to Gas Ratio 5. Appendices References Spitzer Ch. 7, Osterbrock Ch. 7 DC Whittet, Dust in the Galactic
Lecture 5. Interstellar Dust: Optical Properties 1. Introduction 2. Extinction 3. Mie Scattering 4. Dust to Gas Ratio 5. Appendices References Spitzer Ch. 7, Osterbrock Ch. 7 DC Whittet, Dust in the Galactic
Infrared Observations of the Quintuplet Proper Members with SOFIA/FORCAST
 Infrared Observations of the Quintuplet Proper Members with SOFIA/FORCAST SOFIA/FORCAST 25, 31, & 37 µm Matt Hankins (Cornell University) Collaborators: R. M. Lau (JPL/Caltech), M. R. Morris (UCLA), J.
Infrared Observations of the Quintuplet Proper Members with SOFIA/FORCAST SOFIA/FORCAST 25, 31, & 37 µm Matt Hankins (Cornell University) Collaborators: R. M. Lau (JPL/Caltech), M. R. Morris (UCLA), J.
2018 TIARA Summer School Origins of the Solar System. Observations and Modelling of Debris Disks. J.P. Marshall (ASIAA) Wednesday 18 th July 2018
 2018 TIARA Summer School Origins of the Solar System Observations and Modelling of Debris Disks J.P. Marshall (ASIAA) Wednesday 18 th July 2018 [Hogerheijde 1998] Debris disks Tenuous belts of icy and
2018 TIARA Summer School Origins of the Solar System Observations and Modelling of Debris Disks J.P. Marshall (ASIAA) Wednesday 18 th July 2018 [Hogerheijde 1998] Debris disks Tenuous belts of icy and
Dust. Interstellar Emission. The four letter word in astrophysics Scattered in S&G mostly pgs , MBW
 Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Scattered in S&G mostly pgs 100-108, MBW 478-482 recent conference Proceedings of the International Astronomical Porous chondrite interplanetary dust particle.
Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Scattered in S&G mostly pgs 100-108, MBW 478-482 recent conference Proceedings of the International Astronomical Porous chondrite interplanetary dust particle.
Recent VLTI results on stellar winds and perspectives with second generation instruments. Xavier Haubois
 Recent VLTI results on stellar winds and perspectives with second generation instruments Xavier Haubois Outline - The VLTI and its instruments - Massive stars - HMXBs - AGBs - Planetary Nebulae - Perspectives
Recent VLTI results on stellar winds and perspectives with second generation instruments Xavier Haubois Outline - The VLTI and its instruments - Massive stars - HMXBs - AGBs - Planetary Nebulae - Perspectives
Basics, types Evolution. Novae. Spectra (days after eruption) Nova shells (months to years after eruption) Abundances
 Basics, types Evolution Novae Spectra (days after eruption) Nova shells (months to years after eruption) Abundances 1 Cataclysmic Variables (CVs) M.S. dwarf or subgiant overflows Roche lobe and transfers
Basics, types Evolution Novae Spectra (days after eruption) Nova shells (months to years after eruption) Abundances 1 Cataclysmic Variables (CVs) M.S. dwarf or subgiant overflows Roche lobe and transfers
Interstellar Medium. Alain Abergel. IAS, Université Paris-Sud, Orsay Cedex, France
 Interstellar Medium Alain Abergel IAS, Université Paris-Sud, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France ISO Legacy Colloquium, Dec 13, 2006 Main Topics Elemental abundances in the ionised gas of HII regions Interstellar
Interstellar Medium Alain Abergel IAS, Université Paris-Sud, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France ISO Legacy Colloquium, Dec 13, 2006 Main Topics Elemental abundances in the ionised gas of HII regions Interstellar
Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe
 Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe Prof. T. Jarrett (UCT) Infrared Window Telescopes ISM -- Galaxies Infrared Window Near-infrared: 1 to 5 µm Mid-infrared: 5 to 50 µm
Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe Prof. T. Jarrett (UCT) Infrared Window Telescopes ISM -- Galaxies Infrared Window Near-infrared: 1 to 5 µm Mid-infrared: 5 to 50 µm
Probing the embedded phase of star formation with JWST spectroscopy
 Probing the embedded phase of star formation with JWST spectroscopy NIRSPEC Spitzer NGC 1333 Low mass Herschel Cygnus X High mass Jorgensen et al. Gutermuth et al. 10 10 Motte, Henneman et al. E.F. van
Probing the embedded phase of star formation with JWST spectroscopy NIRSPEC Spitzer NGC 1333 Low mass Herschel Cygnus X High mass Jorgensen et al. Gutermuth et al. 10 10 Motte, Henneman et al. E.F. van
7. Dust Grains & Interstellar Extinction. James R. Graham University of California, Berkeley
 7. Dust Grains & Interstellar Extinction James R. Graham University of California, Berkeley Visual Extinction Presence of interstellar gas or nebulae has a long history Existence of absorbing interstellar
7. Dust Grains & Interstellar Extinction James R. Graham University of California, Berkeley Visual Extinction Presence of interstellar gas or nebulae has a long history Existence of absorbing interstellar
Determining the forsterite abundance of the dust around Asymptotic Giant Branch stars
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 1388 c ESO 21 March 17, 21 Determining the forsterite abundance of the dust around Asymptotic Giant Branch stars B.L. de Vries 1,2, M. Min 2, L.B.F.M. Waters 2,1,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 1388 c ESO 21 March 17, 21 Determining the forsterite abundance of the dust around Asymptotic Giant Branch stars B.L. de Vries 1,2, M. Min 2, L.B.F.M. Waters 2,1,
Age Dating A SSP. Quick quiz: please write down a 3 sentence explanation of why these plots look like they do.
 Color is only a weak function of age after ~3Gyrs (for a given metallicity) (See MBW pg 473) But there is a strong change in M/L V and weak change in M/L K Age Dating A SSP Quick quiz: please write down
Color is only a weak function of age after ~3Gyrs (for a given metallicity) (See MBW pg 473) But there is a strong change in M/L V and weak change in M/L K Age Dating A SSP Quick quiz: please write down
Mass Transfer in Binaries
 Mass Transfer in Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) Understanding the physics of mass transfer is essential for understanding binary evolution Simplest assumption: stable, conservative mass transfer
Mass Transfer in Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) Understanding the physics of mass transfer is essential for understanding binary evolution Simplest assumption: stable, conservative mass transfer
A Unified Model for AGN. Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006
 A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
A PIONIER View on Mass-Transferring Red Giants
 A PIONIER View on Mass-Transferring Red Giants Henri M.J. Boffin 1, Nicolas Blind 2, Michel Hillen 3, Jean-Philippe Berger 1, Alain Jorissen 4, Jean-Baptiste Le Bouquin 5 1 ESO 2 Max Planck Institut für
A PIONIER View on Mass-Transferring Red Giants Henri M.J. Boffin 1, Nicolas Blind 2, Michel Hillen 3, Jean-Philippe Berger 1, Alain Jorissen 4, Jean-Baptiste Le Bouquin 5 1 ESO 2 Max Planck Institut für
THE LAST SURVEY OF THE OLD WSRT: TOOLS AND RESULTS FOR THE FUTURE HI ABSORPTION SURVEYS
 F. Maccagni; R. Morganti; T. Oosterloo; K. Geréb; N. Maddox, J. Allison THE LAST SURVEY OF THE OLD WSRT: TOOLS AND RESULTS FOR THE FUTURE HI ABSORPTION SURVEYS A SURVEY BEFORE THE BLIND SURVEYS During
F. Maccagni; R. Morganti; T. Oosterloo; K. Geréb; N. Maddox, J. Allison THE LAST SURVEY OF THE OLD WSRT: TOOLS AND RESULTS FOR THE FUTURE HI ABSORPTION SURVEYS A SURVEY BEFORE THE BLIND SURVEYS During
Detectability of extrasolar debris. Mark Wyatt Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge
 Detectability of extrasolar debris Mark Wyatt Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge Why image extrasolar debris? Emission spectrum shows dust thermal emission, used to infer radius of parent
Detectability of extrasolar debris Mark Wyatt Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge Why image extrasolar debris? Emission spectrum shows dust thermal emission, used to infer radius of parent
et al. 1996; Hansen 2005; Kalirai et al ML is a free parameter with a huge astrophysical impact
 Rood 1973; Fusi Pecci & Renzini 1975,1976; Renzini 1977; Castellani & Tornambe 1981; Peterson 1982; Castellani & Castellani 1993; Fusi Pecci et al. 1993; D Cruz et al. 1996; Hansen 2005; Kalirai et al.
Rood 1973; Fusi Pecci & Renzini 1975,1976; Renzini 1977; Castellani & Tornambe 1981; Peterson 1982; Castellani & Castellani 1993; Fusi Pecci et al. 1993; D Cruz et al. 1996; Hansen 2005; Kalirai et al.
Determining dust mass-loss rates
 Determining dust mass-loss rates Martin Groenewegen Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels (martin.groenewegen@oma.be) Nice, 5-5-15 p.1/36 Overview Talk Introduction Effect of size, type, shape AGB & RSG
Determining dust mass-loss rates Martin Groenewegen Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels (martin.groenewegen@oma.be) Nice, 5-5-15 p.1/36 Overview Talk Introduction Effect of size, type, shape AGB & RSG
Radial Velocities of T Dwarfs with FIRE
 Radial Velocities of T Dwarfs with FIRE Christine Nicholls, UCSD Adam Burgasser (USCD), John Bochanski (Penn State), Jackie Faherty (Chile), Rob Simcoe (MIT), Ben Burningham (Hertfordshire), Scott Sheppard
Radial Velocities of T Dwarfs with FIRE Christine Nicholls, UCSD Adam Burgasser (USCD), John Bochanski (Penn State), Jackie Faherty (Chile), Rob Simcoe (MIT), Ben Burningham (Hertfordshire), Scott Sheppard
Constraining the Evolution of Molecular Gas in Weak-Line T-Tauri Stars. 1. Motivation
 Constraining the Evolution of Molecular Gas in Weak-Line T-Tauri Stars 1. Motivation The formation of planets from protoplanetary disks is greatly influenced by the presence or absence of gas in these
Constraining the Evolution of Molecular Gas in Weak-Line T-Tauri Stars 1. Motivation The formation of planets from protoplanetary disks is greatly influenced by the presence or absence of gas in these
Star Formation. Spitzer Key Contributions to Date
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Interstellar Dust and Gas
 Interstellar Dust and Gas In 1783 William Herschel began a survey of the heavens using an 18 ¾ inch reflector of his own construction. His goal was to discover new star clusters, nebulae, and double stars.
Interstellar Dust and Gas In 1783 William Herschel began a survey of the heavens using an 18 ¾ inch reflector of his own construction. His goal was to discover new star clusters, nebulae, and double stars.
other Galactic science Jane Greaves St Andrews
 other Galactic science Jane Greaves St Andrews JCMT examples Sgr A*: massive black hole Evolved stars: dust and molecules Shell stars: violent mass-loss Shaping PNe: breaking spherical symmetry Pulsars:
other Galactic science Jane Greaves St Andrews JCMT examples Sgr A*: massive black hole Evolved stars: dust and molecules Shell stars: violent mass-loss Shaping PNe: breaking spherical symmetry Pulsars:
Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies.
 Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies. Thodoris Bitsakis Department of Physics, University of Crete Paper: Bitsakis T., Charmandaris V., da Cunha E., Diaz-Santos T., Le Floc h
Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies. Thodoris Bitsakis Department of Physics, University of Crete Paper: Bitsakis T., Charmandaris V., da Cunha E., Diaz-Santos T., Le Floc h
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
INTERFEROMETRIC OBSERVATIONS OF EVOLVED STARS
 INTERFEROMETRIC OBSERVATIONS OF EVOLVED STARS Iva KAROVICOVA MPIA Heidelberg, Germany M. WITTKOWSKI ESO Garching, Germany D. A. BOBOLTZ Naval Observatory, USA E. FOSSAT Observatoire de la Côte d'azur,
INTERFEROMETRIC OBSERVATIONS OF EVOLVED STARS Iva KAROVICOVA MPIA Heidelberg, Germany M. WITTKOWSKI ESO Garching, Germany D. A. BOBOLTZ Naval Observatory, USA E. FOSSAT Observatoire de la Côte d'azur,
Star Formation. Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Exoplanets: a dynamic field
 Exoplanets: a dynamic field Alexander James Mustill Amy Bonsor, Melvyn B. Davies, Boris Gänsicke, Anders Johansen, Dimitri Veras, Eva Villaver The (transiting) exoplanet population Solar System Hot Jupiters:
Exoplanets: a dynamic field Alexander James Mustill Amy Bonsor, Melvyn B. Davies, Boris Gänsicke, Anders Johansen, Dimitri Veras, Eva Villaver The (transiting) exoplanet population Solar System Hot Jupiters:
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Evolution, Mass Loss and Variability of Low and Intermediate-Mass Stars
 Evolution, Mass Loss and Variability of Low and Intermediate-Mass Stars Mass Loss from Low and Intermediate Mass Stars Significant mass loss occurs in two phases 1. In red giants before large amplitude
Evolution, Mass Loss and Variability of Low and Intermediate-Mass Stars Mass Loss from Low and Intermediate Mass Stars Significant mass loss occurs in two phases 1. In red giants before large amplitude
Stellar Populations with JWST: the Beginning and the End
 Stellar Populations with JWST: the Beginning and the End Margaret Meixner Phone : 410-338-5013 Space Telescope Science Institute meixner@stsci.edu and John Mather (NASA/GSFC, chair) Mark Clampin (NASA/GSFC)
Stellar Populations with JWST: the Beginning and the End Margaret Meixner Phone : 410-338-5013 Space Telescope Science Institute meixner@stsci.edu and John Mather (NASA/GSFC, chair) Mark Clampin (NASA/GSFC)
IRS SPECTRA OF SOLAR-TYPE STARS: A SEARCH FOR ASTEROID BELT ANALOGS
 IRS SPECTRA OF SOLAR-TYPE STARS: A SEARCH FOR ASTEROID BELT ANALOGS Debris disks Around Stars In our Solar System, dust is generated by collisions between larger bodies in the asteroid and Kuiper belts,
IRS SPECTRA OF SOLAR-TYPE STARS: A SEARCH FOR ASTEROID BELT ANALOGS Debris disks Around Stars In our Solar System, dust is generated by collisions between larger bodies in the asteroid and Kuiper belts,
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics
 Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Stefan Kraus 1,2 Gerd Weigelt 1 Karl-Heinz Hofmann 1 Fabien Malbet 3 Antonella Natta 4 Thomas Preibisch 5 Dieter Schertl 1 + AMBER consortium
 From circumstellar disks to planetary systems workshop 2009 November 5 ESO, Garching Image: ESO/Calçada Stefan Kraus 1,2 Gerd Weigelt 1 Karl-Heinz Hofmann 1 Fabien Malbet 3 Antonella Natta 4 Thomas Preibisch
From circumstellar disks to planetary systems workshop 2009 November 5 ESO, Garching Image: ESO/Calçada Stefan Kraus 1,2 Gerd Weigelt 1 Karl-Heinz Hofmann 1 Fabien Malbet 3 Antonella Natta 4 Thomas Preibisch
E-ELT/HIRES Disk-Star Interactions at the epoch of planet formation
 E-ELT/HIRES Disk-Star Interactions at the epoch of planet formation Leonardo Testi (ESO/INAF-Arcetri) B. Nisini (INAF-Monteporzio), J. Alcalaʼ (INAF-Capodimonte) From Cores to Planetary Systems Core (Hernandez
E-ELT/HIRES Disk-Star Interactions at the epoch of planet formation Leonardo Testi (ESO/INAF-Arcetri) B. Nisini (INAF-Monteporzio), J. Alcalaʼ (INAF-Capodimonte) From Cores to Planetary Systems Core (Hernandez
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5)
 Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1 4.2 4.3 Acquiring Spectroscopic or Photometric Redshifts Infrared SED Fitting for DSFGs Estimating L IR, T dust and M dust from an
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1 4.2 4.3 Acquiring Spectroscopic or Photometric Redshifts Infrared SED Fitting for DSFGs Estimating L IR, T dust and M dust from an
Dust formation in Asymptotic Giant Branch stars Ambra Nanni SISSA, Trieste (IT)
 Dust formation in Asymptotic Giant Branch stars Ambra Nanni SISSA, Trieste (IT) In collaboration with A. Bressan (SISSA), P. Marigo (UNIPD) & L. Danese (SISSA) 1 Introduction AGB Stars considered to account
Dust formation in Asymptotic Giant Branch stars Ambra Nanni SISSA, Trieste (IT) In collaboration with A. Bressan (SISSA), P. Marigo (UNIPD) & L. Danese (SISSA) 1 Introduction AGB Stars considered to account
Preliminary results from the e-merlin Legacy Cyg OB2 Radio Survey
 Preliminary results from the e-merlin Legacy Cyg OB2 Radio Survey Department of Physics & Astronomy, University College London, UK. E-mail: dmf@star.ucl.ac.uk Jack Morford Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Preliminary results from the e-merlin Legacy Cyg OB2 Radio Survey Department of Physics & Astronomy, University College London, UK. E-mail: dmf@star.ucl.ac.uk Jack Morford Department of Physics & Astronomy,
The Fomalhaut Debris Disk
 The Fomalhaut Debris Disk IRAS 12 micron http://ssc.spitzer.caltech.edu/documents/compendium/foma lhaut/ Fomalhaut is a bright A3 V star 7.7 pc away IRAS discovered an IR excess indicating a circumstellar
The Fomalhaut Debris Disk IRAS 12 micron http://ssc.spitzer.caltech.edu/documents/compendium/foma lhaut/ Fomalhaut is a bright A3 V star 7.7 pc away IRAS discovered an IR excess indicating a circumstellar
Guiding Questions. The Birth of Stars
 Guiding Questions The Birth of Stars 1 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve (bad use of term this is about the birth, life and death of stars and that is NOT evolution)? 2. What kind of matter
Guiding Questions The Birth of Stars 1 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve (bad use of term this is about the birth, life and death of stars and that is NOT evolution)? 2. What kind of matter
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
IR Instrumentation & AGN: Revealing Inner Secrets. Chris Packham University of Florida 7 th October, 2011
 IR Instrumentation & AGN: Revealing Inner Secrets Chris Packham University of Florida 7 th October, 2011 Presentation Outline T λ" i m e! Instrumentation past, present, and near future INGRID MMT-POL T-ReCS,
IR Instrumentation & AGN: Revealing Inner Secrets Chris Packham University of Florida 7 th October, 2011 Presentation Outline T λ" i m e! Instrumentation past, present, and near future INGRID MMT-POL T-ReCS,
X-ray data analysis. Andrea Marinucci. Università degli Studi Roma Tre
 X-ray data analysis Andrea Marinucci Università degli Studi Roma Tre marinucci@fis.uniroma3.it Goal of these lectures X-ray data analysis why? what? how? Why? Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Physics in a
X-ray data analysis Andrea Marinucci Università degli Studi Roma Tre marinucci@fis.uniroma3.it Goal of these lectures X-ray data analysis why? what? how? Why? Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Physics in a
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust
 8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
Revealing the evolution of disks at au from high-resolution IR spectroscopy
 Protoplanetary seen through the eyes of new-generation high-resolution instruments - Rome, June 6, 08 Revealing the evolution of at 0.0-0 au from high-resolution IR spectroscopy VLT IR interferometry (not
Protoplanetary seen through the eyes of new-generation high-resolution instruments - Rome, June 6, 08 Revealing the evolution of at 0.0-0 au from high-resolution IR spectroscopy VLT IR interferometry (not
OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS
 OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS Subhanjoy Mohanty (Spitzer Fellow, Harvard University) Gibor Basri, Ray Jayawardhana, Antonella Natta David Barrado y Navascués,
OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS Subhanjoy Mohanty (Spitzer Fellow, Harvard University) Gibor Basri, Ray Jayawardhana, Antonella Natta David Barrado y Navascués,
Spectroscopy of giants and supergiants! Maria Bergemann MPIA Heidelberg"
 Spectroscopy of giants and supergiants! Maria Bergemann MPIA Heidelberg" Spectroscopy of (cool) giants and supergiants! Maria Bergemann MPIA Heidelberg" Outline! Motivation why do spectroscopy of giant
Spectroscopy of giants and supergiants! Maria Bergemann MPIA Heidelberg" Spectroscopy of (cool) giants and supergiants! Maria Bergemann MPIA Heidelberg" Outline! Motivation why do spectroscopy of giant
Young Solar-like Systems
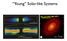 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Gas at the inner disk edge
 Star-Disk Interaction in Young Stars Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 243, 2007 J. Bouvier & I. Appenzeller, eds. c 2007 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Gas at the inner disk
Star-Disk Interaction in Young Stars Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 243, 2007 J. Bouvier & I. Appenzeller, eds. c 2007 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Gas at the inner disk
Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010
 Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010 Aim Review the characteristics of regions of ionized gas within young massive star forming regions. Will focus the discussion
Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010 Aim Review the characteristics of regions of ionized gas within young massive star forming regions. Will focus the discussion
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/75277
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/75277
Debris dust tell us much about planetesimals and planets and sheds light to formation and evolution of planetary systems. KALAS et al.
 Debris dust tell us much about planetesimals and planets and sheds light to formation and evolution of planetary systems KALAS et al. 2008 THE STAR Spectral type: F8 Distance : 17.4 pc Age : ~ 2 Gyr A
Debris dust tell us much about planetesimals and planets and sheds light to formation and evolution of planetary systems KALAS et al. 2008 THE STAR Spectral type: F8 Distance : 17.4 pc Age : ~ 2 Gyr A
Processing of silicate dust grains in Herbig Ae/Be systems
 A&A 375, 950 962 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010878 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Processing of silicate dust grains in Herbig Ae/Be systems J. Bouwman 1,G.Meeus 2,A.deKoter 1,S.Hony 1,C.Dominik
A&A 375, 950 962 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010878 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Processing of silicate dust grains in Herbig Ae/Be systems J. Bouwman 1,G.Meeus 2,A.deKoter 1,S.Hony 1,C.Dominik
Herschel Mission Overview and Key Programmes
 Herschel Mission Overview and Key Programmes SPIE Astronomical Instrumentation 2008 Space Telescopes and Instrumentation I: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave Marseille, 23-28 June 2008 Göran L. Pilbratt
Herschel Mission Overview and Key Programmes SPIE Astronomical Instrumentation 2008 Space Telescopes and Instrumentation I: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave Marseille, 23-28 June 2008 Göran L. Pilbratt
Redshifted Broad Absorption Troughs in Quasars
 Redshifted Broad Absorption Troughs in Quasars Pat Hall, York University with Niel Brandt and Nur Filiz Ak (PSU), Patrick Petitjean (IAP), and the SDSS-III/BOSS team If due to fallback or rotation, challenge
Redshifted Broad Absorption Troughs in Quasars Pat Hall, York University with Niel Brandt and Nur Filiz Ak (PSU), Patrick Petitjean (IAP), and the SDSS-III/BOSS team If due to fallback or rotation, challenge
Connection between phenomenon of active nucleus and disk dynamics in Sy galaxies
 Connection between phenomenon of active nucleus and disk dynamics in Sy galaxies Alexandrina Smirnova & Alexei Moiseev Special Astrophysical Observatory, Russian Academy of Sciences SAO RAS 6-m telescope
Connection between phenomenon of active nucleus and disk dynamics in Sy galaxies Alexandrina Smirnova & Alexei Moiseev Special Astrophysical Observatory, Russian Academy of Sciences SAO RAS 6-m telescope
Aromatic Features in M101 HII Regions and Starburst Galaxies
 **FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Aromatic Features in M101 HII Regions and Starburst Galaxies Karl D. Gordon, Charles Engelbracht, J.D.T.
**FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Aromatic Features in M101 HII Regions and Starburst Galaxies Karl D. Gordon, Charles Engelbracht, J.D.T.
Observations of exozodiacal disks. Jean-Charles Augereau LAOG, Grenoble, France. ISSI team: Exozodiacal dust diks and Darwin. Cambridge, August 2009
 + Olivier Absil Emmanuel Di Folco Hervé Beust Rémy Reche Alexander Krivov Philippe Thébault Torsten Loehne Vincent Coudé du Foresto Bertrand Menesson Pierre Kervella ISSI team: Exozodiacal dust diks and
+ Olivier Absil Emmanuel Di Folco Hervé Beust Rémy Reche Alexander Krivov Philippe Thébault Torsten Loehne Vincent Coudé du Foresto Bertrand Menesson Pierre Kervella ISSI team: Exozodiacal dust diks and
Olivier Absil. University of Liège
 Olivier Absil University of Liège Seminar at MPIfR Bonn July 15 th, 2011 We all live in a debris disk! 2 nd generation dust (asteroids, comets) Dust is luminous (much more than planets) Dust is expected
Olivier Absil University of Liège Seminar at MPIfR Bonn July 15 th, 2011 We all live in a debris disk! 2 nd generation dust (asteroids, comets) Dust is luminous (much more than planets) Dust is expected
