2. Allow students minutes to decide on their strategy to demonstrate the properties described.
|
|
|
- Sabina Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROLE PLAY Materials: Task card for each team Procedure: 1. Divide the class into 3 groups to role play as a team a model of the light indicated on their card. (Include more students in the Unpolarized Light group as they will need several students to represent different wavelengths in different planes.) 2. Allow students minutes to decide on their strategy to demonstrate the properties described. 3. Assess the students on applying information learned in previous activities regarding the card description. (Example: a wavelength has crests and troughs) 4. Have students demonstrate their model for the class. Task Observed Yes No Unpolarized Light Polarized Light Different wavelengths for different colors of light; light traveling in different directions to represent different planes Different wavelengths for different colors of light; Light traveling in one plane Laser Light The same wavelength for the same color of light; Light traveling in one plane
2 Task Cards UNPOLARIZED LIGHT The electromagnetic waves vibrate in a variety of directions and in different planes. Light is made of different colors, and thus, different wavelengths. POLARIZED LIGHT The electromagnetic waves vibrate in one plane. Light is made of different colors, and thus, different wavelengths. LASER LIGHT The electromagnet waves vibrate in one plane. Laser light is made of one wavelength.
3 Absorb, Reflect or Transmit? Imagine that electrons are connected to atoms by springs. The electrons of the atoms will vibrate at a natural frequency. The frequencies differ for elements. Light particles also vibrate at a natural frequency. As light waves strike matter (made of atoms), the light will be absorbed, transmitted or reflected. Light waves that have the same natural frequency as atoms making up an object will be absorbed, and they will set the electrons of the atoms into vibration at their natural frequency. The energy will then be changed to heat energy. Light waves that do not have the same natural frequency will be transmitted or reflected. Light is transmitted if the object is transparent and reflected if it is opaque. What determines the following: Light is absorbed? reflected? transmitted? The electrons that have the same frequency as the light are set into motion. This is an example of resonance--one object causes another object to vibrate because they have the same natural frequency.
4 Building a Spectroscope Materials: (per student) Toilet tissue tube Diffraction grating Index card Electrical tape Ruler Markers Scissors Pencil Packing tape Procedure: 1. Trace the end of the toilet tissue tube onto the index card and cut out the circle. 2. Cut a small square (~1.5 cm 2 ) or a small circle (~1.5 cm diameter) in the center of your circle made from the index card. 3. Place a piece of diffraction grating (slightly larger than the hole) over the hole. Tape the edges of the diffraction grating down with electrical tape. Do not tape over the center of the diffraction grating (you will look through this opening). 4. Place the cut-out circle on one end of the tube and secure it with electrical tape. 5. Cover the opposite end of the tube with electrical tape allowing for an opening in the center, measuring 1 mm and 1 cm long. This slit will allow the light into the tube. 6. Cover other holes or spaces with electrical tape to prevent light pollution. 7. Decorate your tube with a spectrum or other colorful images. 8. Cover the entire tube with packing tape for added protection. 9. Point the spectroscope at the lights and look through the end with diffraction grating. You should see a spectrum. 10. Look at different lights with your spectroscope to compare the patterns you observe. How does it work? Diffraction grating is a film with thousands of fine, parallel slits. As light travels to the film, it runs into obstacles and bends to pass through the grooves. The light spreads around the edges of the obstacle or defracts. As the light bends, it separates into its different wavelengths and a spectrum is visible. Activity adapted from Suzy Dunnum, Tahoka Hr. High School, 8 th grade
5 Building a KaLeidOscOPe Materials: 2 Dixie cups Polarizing film Transparent tape (glossy) Scissors Procedure: 1. Cut the bottom from two Dixie cups. 2. Tape a piece of polarizing film onto the end of each cup. 3. Tape over the polarizing film on each cup with numerous pieces of tape in random patterns (more tape and a more random placement makes for a better kaleidoscope!). 4. Slip one cup inside the other cup and look to the light through the open end as you twist the cups. Observe the spectacular display of color! How does it work? Activity adapted from Suzy Dunnum, Tahoka Hr. High School, 8 th grade
6
A Wave of Cooperation
 A Wave of Cooperation The students will peer teach in cooperative learning groups some basic topics regarding waves. Materials: Student sheets Note sheets Procedure: 1. Place students into home teams of
A Wave of Cooperation The students will peer teach in cooperative learning groups some basic topics regarding waves. Materials: Student sheets Note sheets Procedure: 1. Place students into home teams of
Build and Use a Simple Spectroscope
 Build and Use a Simple Spectroscope Subject Area: Physical Sciences Grade Level: 9 12 Overview In this activity students will build a spectroscope to analyze the composition of light. Our scope is inexpensive,
Build and Use a Simple Spectroscope Subject Area: Physical Sciences Grade Level: 9 12 Overview In this activity students will build a spectroscope to analyze the composition of light. Our scope is inexpensive,
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Spectrometers. Materials: Easy Spectrometer. Old CD Razor Index card Cardboard tube at least 10 inches long
 Spectrometers Overview: Spectrometers (spectroscopes) are used in chemistry and astronomy to measure light. In astronomy, we can find out about distant stars without ever traveling to them, because we
Spectrometers Overview: Spectrometers (spectroscopes) are used in chemistry and astronomy to measure light. In astronomy, we can find out about distant stars without ever traveling to them, because we
Name: Date: Room: No.
 Station 1 Projecting Visible Spectra (setting direction) Objective: To study the range of colors in the visible spectrum. Procedure: 1. Make a partition with a narrow slot in its center to block all but
Station 1 Projecting Visible Spectra (setting direction) Objective: To study the range of colors in the visible spectrum. Procedure: 1. Make a partition with a narrow slot in its center to block all but
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Chapter 35 Diffraction and Polarization
 Chapter 35 Diffraction and Polarization If light is a wave, it will diffract around a single slit or obstacle. The resulting pattern of light and dark stripes is called a diffraction pattern. This pattern
Chapter 35 Diffraction and Polarization If light is a wave, it will diffract around a single slit or obstacle. The resulting pattern of light and dark stripes is called a diffraction pattern. This pattern
Chapter 35 Diffraction and Polarization. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 35 Diffraction and Polarization 35-1 Diffraction by a Single Slit or Disk If light is a wave, it will diffract around a single slit or obstacle. 35-1 Diffraction by a Single Slit or Disk The resulting
Chapter 35 Diffraction and Polarization 35-1 Diffraction by a Single Slit or Disk If light is a wave, it will diffract around a single slit or obstacle. 35-1 Diffraction by a Single Slit or Disk The resulting
Electromagnetic spectra
 Properties of Light Waves, particles and EM spectrum Interaction with matter Absorption Reflection, refraction and scattering Polarization and diffraction Reading foci: pp 175-185, 191-199 not responsible
Properties of Light Waves, particles and EM spectrum Interaction with matter Absorption Reflection, refraction and scattering Polarization and diffraction Reading foci: pp 175-185, 191-199 not responsible
Guide for Reading. Vocabulary electron configurations aufbau principle Pauli exclusion principle Hund s rule. Reading Strategy
 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.2 Connecting to Your World Does this scene look natural to you? Surprisingly, it is. Arrangements like this are rare in nature because they are unstable. Unstable arrangements,
5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.2 Connecting to Your World Does this scene look natural to you? Surprisingly, it is. Arrangements like this are rare in nature because they are unstable. Unstable arrangements,
Introduction & Chapter 1: Matter
 Section 1 WHAT IS MATTER? Introduction & Chapter 1: Matter Use pages 3 5 of the student text to complete the worksheet. Choose the Answer. Circle the answer that correctly completes each sentence. 1. Matter
Section 1 WHAT IS MATTER? Introduction & Chapter 1: Matter Use pages 3 5 of the student text to complete the worksheet. Choose the Answer. Circle the answer that correctly completes each sentence. 1. Matter
Chapter 27: Light. What is light?
 Chapter 27: Light What is light? Scientists first theorized light was a wave as it behaved with a wave properties, i.e. diffraction and interference. In 1905, Einstein realized that light was behaving
Chapter 27: Light What is light? Scientists first theorized light was a wave as it behaved with a wave properties, i.e. diffraction and interference. In 1905, Einstein realized that light was behaving
Speed of Light Measurement with a Simple Way
 Speed of Light Measurement with a Simple Way Nikolaos F. Voudoukis Abstract A method for a measurement of the speed of light is described. It is used a combination of simple, low-cost experiments. We will
Speed of Light Measurement with a Simple Way Nikolaos F. Voudoukis Abstract A method for a measurement of the speed of light is described. It is used a combination of simple, low-cost experiments. We will
Experiment #4 Nature of Light: Telescope and Microscope and Spectroscope
 Experiment #4 Nature of Light: Telescope and Microscope and Spectroscope In this experiment, we are going to learn the basic principles of the telescope and the microscope that make it possible for us
Experiment #4 Nature of Light: Telescope and Microscope and Spectroscope In this experiment, we are going to learn the basic principles of the telescope and the microscope that make it possible for us
Building your own Pizza-Box Spectroscope. *You will need to bring in a medium- sized sturdy cardboard pizza box, shoe box, or similar from home.
 Building your own Pizza-Box Spectroscope Experimental Notes *You will need to bring in a medium- sized sturdy cardboard pizza box, shoe box, or similar from home. Color, Light, and Atomic Spectroscopy
Building your own Pizza-Box Spectroscope Experimental Notes *You will need to bring in a medium- sized sturdy cardboard pizza box, shoe box, or similar from home. Color, Light, and Atomic Spectroscopy
LAST NAME First Name(s) Student Number Practical Group as on student card as on student card Code
 LAST NAME First Name(s) Student Number Practical Group as on student card as on student card Code PHY132H1S Term Test version A Tuesday, January 27, 2015 Duration: 80 minutes Aids allowed: A pocket calculator
LAST NAME First Name(s) Student Number Practical Group as on student card as on student card Code PHY132H1S Term Test version A Tuesday, January 27, 2015 Duration: 80 minutes Aids allowed: A pocket calculator
LAST NAME First Name(s) Student Number Practical Group as on student card as on student card Code
 LAST NAME First Name(s) Student Number Practical Group as on student card as on student card Code PHY132H1S Term Test version B Tuesday, January 27, 2015 Duration: 80 minutes Aids allowed: A pocket calculator
LAST NAME First Name(s) Student Number Practical Group as on student card as on student card Code PHY132H1S Term Test version B Tuesday, January 27, 2015 Duration: 80 minutes Aids allowed: A pocket calculator
Producing and Harnessing Light
 Chemical Dominoes Activity 5 Producing and Harnessing Light GOALS In this activity you will: Describe the relationship between energy, frequency, and wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. Explain how
Chemical Dominoes Activity 5 Producing and Harnessing Light GOALS In this activity you will: Describe the relationship between energy, frequency, and wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. Explain how
 IGHT RADE ASSESSMENT PACKET Discover refraction, reflection, beam scattering, optical density, transmission, and absorption as you investigate the electromagnetic spectrum using lenses, mirrors and filters
IGHT RADE ASSESSMENT PACKET Discover refraction, reflection, beam scattering, optical density, transmission, and absorption as you investigate the electromagnetic spectrum using lenses, mirrors and filters
The Final Exam (Exam 4) will be on FRIDAY MAY 11 From 3 5 PM in LR1 VAN
 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29:006 SPRING 2012 PRACTICE EXAM 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29:006 SPRING 2012 PRACTICE EXAM 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths.
 Section7: The Bohr Atom Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths. Continuous Spectrum Everyone has seen the spectrum produced when white
Section7: The Bohr Atom Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths. Continuous Spectrum Everyone has seen the spectrum produced when white
A sound wave needs a medium through which it is transmitted. (MS-PS4-2)
 Title: Visible Light: Why is the Sky Blue? Time: 40 min Grade level: 4 th and 5 th Synopsis: In an effort to teach wavelength and frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum, students will look at the visible
Title: Visible Light: Why is the Sky Blue? Time: 40 min Grade level: 4 th and 5 th Synopsis: In an effort to teach wavelength and frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum, students will look at the visible
Build a Spectroscope 2005, 2004, 1994 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for classroom use provided original copyright is included.
 Build a Spectroscope 2005, 2004, 1994 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for classroom use provided original copyright is included. David A. Katz Chemist, Educator, Science Communicator,
Build a Spectroscope 2005, 2004, 1994 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for classroom use provided original copyright is included. David A. Katz Chemist, Educator, Science Communicator,
Recall: The Importance of Light
 Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Physics LESSON PLAN PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE(S): STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO:
 Physics LESSON PLAN Subject: Physics Grade: 7 12 Date: 6/21/2012 Concept: The wave nature of light, Estimated Time of Lesson: 100 Minutes PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE(S): STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO: (1) Understand
Physics LESSON PLAN Subject: Physics Grade: 7 12 Date: 6/21/2012 Concept: The wave nature of light, Estimated Time of Lesson: 100 Minutes PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE(S): STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO: (1) Understand
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Introduction to Properties of Waves
 Introduction to Properties of Waves Waves travel through materials as vibrations and transmit energy. Though nearly all waves travel through matter, they never transmit matter. Waves are created when a
Introduction to Properties of Waves Waves travel through materials as vibrations and transmit energy. Though nearly all waves travel through matter, they never transmit matter. Waves are created when a
Level 3 Physics, 2018
 91523 915230 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2018 91523 Demonstrate understanding of wave systems 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 20 November 2018 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
91523 915230 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2018 91523 Demonstrate understanding of wave systems 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 20 November 2018 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB. 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them.
 NAME: SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB 1) What is a spectrum? 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them. a. b. c. 3) Use Wien s law to calculate the surface temperature of the star Alnilam
NAME: SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB 1) What is a spectrum? 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them. a. b. c. 3) Use Wien s law to calculate the surface temperature of the star Alnilam
Sound Waves. Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium
 Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
RED LASER POINTER ITEM # LIGHT AND COLOR
 T E A C H E G U I R D S E RED LASER POINTER ITEM # 5135-00 LIGHT AND COLOR While it excels at its traditional purpose of drawing attention to a particular object from a distance, the humble laser pointer
T E A C H E G U I R D S E RED LASER POINTER ITEM # 5135-00 LIGHT AND COLOR While it excels at its traditional purpose of drawing attention to a particular object from a distance, the humble laser pointer
Astronomy. Optics and Telescopes
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Home Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings
 Home Lab Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Home Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Activity 15 1: Diffraction from a Transmission Grating Objective: To accurately measure the wavelength of light from a laser pointer
Home Lab Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Home Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Activity 15 1: Diffraction from a Transmission Grating Objective: To accurately measure the wavelength of light from a laser pointer
AS 101: Day Lab #2 Summer Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Last Name: First Name Network-ID
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Turn off your cell phone and put it out of sight. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators cannot be shared. This is a
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Turn off your cell phone and put it out of sight. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators cannot be shared. This is a
Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is energy? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: What is work? Q: Potential Energy
 Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Lesson 7: The Mean as a Balance Point
 Student Outcomes Students characterize the center of a distribution by its mean in the sense of a balance point. Students understand that the mean is a balance point by calculating the distances of the
Student Outcomes Students characterize the center of a distribution by its mean in the sense of a balance point. Students understand that the mean is a balance point by calculating the distances of the
Name Class Date. Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A
 Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A Predicting Spectra Background Information Some materials are transparent to nearly all frequencies of visible light. This means that
Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A Predicting Spectra Background Information Some materials are transparent to nearly all frequencies of visible light. This means that
UNIT 1 MODULE 2: OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES GENERAL OBJECTIVES EXPLANATORY NOTES SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES. On completion of this Module, students should:
 MODULE 2: OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand the different types of oscillatory motion; 2. appreciate the properties common to all 3.
MODULE 2: OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand the different types of oscillatory motion; 2. appreciate the properties common to all 3.
learning outcomes end product a model showing a solar eclipse
 Solar eclipse Looking at the stars * 53 time 50 minutes learning outcomes To: know that during a solar eclipse the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth know that a solar eclipse does not take place
Solar eclipse Looking at the stars * 53 time 50 minutes learning outcomes To: know that during a solar eclipse the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth know that a solar eclipse does not take place
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER
 SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
FOR EXAMINER S USE There are four marks for the quality of written communication in Section Max. Mark
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE 2861 PHYSICS B (ADVANCING PHYSICS) Understanding Processes THURSDAY 22 MAY 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes *CUP/T43053* Candidates answer on the question paper Additional
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE 2861 PHYSICS B (ADVANCING PHYSICS) Understanding Processes THURSDAY 22 MAY 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes *CUP/T43053* Candidates answer on the question paper Additional
You Are the Spectrometer! A Look Inside Astronomy's Essential Instrument (Robert B. Friedman & Matthew K. Sharp)
 You Are the Spectrometer! A Look Inside Astronomy's Essential Instrument (Robert B. Friedman & Matthew K. Sharp) Introduction Astronomy is a unique science because unlike many of the other sciences, the
You Are the Spectrometer! A Look Inside Astronomy's Essential Instrument (Robert B. Friedman & Matthew K. Sharp) Introduction Astronomy is a unique science because unlike many of the other sciences, the
Dark Skies Outreach to Sub-Saharan Africa Program
 (This lesson was adapted from an activity by the International Dark-Sky Association: www.darksky.org.) Grades: 5 th 12 th grade Overview: Students each build a Magnitude Reader. They use the reader to
(This lesson was adapted from an activity by the International Dark-Sky Association: www.darksky.org.) Grades: 5 th 12 th grade Overview: Students each build a Magnitude Reader. They use the reader to
Problem. Hypothesis. Materials
 Problem If I put highlighters in water, will it make it glow with a black light? Hypothesis I think that the water will glow for all of the colors except for the yellow highlighter. Materials Some of the
Problem If I put highlighters in water, will it make it glow with a black light? Hypothesis I think that the water will glow for all of the colors except for the yellow highlighter. Materials Some of the
SPECTRAL WORKSHOP. Picture of the lamps, professional spectroscopes and 'DIY' spectroscopes. Larger view of the 'DIY' spectroscopes
 SPECTRAL WORKSHOP OVERVIEW I STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Equipment List Workshop guides II ADDITIONAL MATERIAL Picture of the lamps, professional spectroscopes and 'DIY' spectroscopes III Larger view of the 'DIY'
SPECTRAL WORKSHOP OVERVIEW I STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Equipment List Workshop guides II ADDITIONAL MATERIAL Picture of the lamps, professional spectroscopes and 'DIY' spectroscopes III Larger view of the 'DIY'
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see?
 Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Wave Properties of Light Karolina H. Czarnecka, PhD Department of Molecular Bases of Medicine
 Wave Properties of Light Karolina H. Czarnecka, PhD Department of Molecular Bases of Medicine karolina.czarnecka@umed.lodz.pl THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE One of the four fundamental forces, the electromagnetic
Wave Properties of Light Karolina H. Czarnecka, PhD Department of Molecular Bases of Medicine karolina.czarnecka@umed.lodz.pl THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE One of the four fundamental forces, the electromagnetic
Student Lab Investigation
 Student Lab Investigation Prediction: You have seen that white light has a definite spectrum. Would you predict that different colors of light have different spectra from each other? Will they be different
Student Lab Investigation Prediction: You have seen that white light has a definite spectrum. Would you predict that different colors of light have different spectra from each other? Will they be different
GRADE EIGHT CURRICULUM. Unit 1: The Makeup and Interactions of Matter
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GRADE EIGHT CURRICULUM Unit 1: The Makeup and Interactions of Matter OVERVIEW Summary The performance expectations for this unit help
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GRADE EIGHT CURRICULUM Unit 1: The Makeup and Interactions of Matter OVERVIEW Summary The performance expectations for this unit help
Color Science Light & Spectra
 COLOR Visible Light Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by it s wavelength Most light sources produce contributions over many wavelengths, contributions
COLOR Visible Light Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by it s wavelength Most light sources produce contributions over many wavelengths, contributions
C. Incorrect! The velocity of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is the same, 3.14 x 10 8 m/s.
 AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
Today: Finish Color (Ch. 27) Intro to Quantum Theory (Ch.31)
 Final exam: Dec 20, 11.30am -1.30pm, here, cumulative Chs: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31 Review Session Tue Dec 13 Today: Finish Color (Ch. 27) Intro to Quantum
Final exam: Dec 20, 11.30am -1.30pm, here, cumulative Chs: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31 Review Session Tue Dec 13 Today: Finish Color (Ch. 27) Intro to Quantum
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring 215 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring 215 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 38
 F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.1 Nature and Properties of Light Linda J. Vandergriff Director of Photonics System Engineering Science Applications International Corporation McLean, Virginia Light
F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.1 Nature and Properties of Light Linda J. Vandergriff Director of Photonics System Engineering Science Applications International Corporation McLean, Virginia Light
Energy and the Electron: Atomic View and Argumentation. b. Draw what you think an atom looks like. Label the different parts of the atom.
 Name Energy and the Electron: Atomic View and Argumentation Part I: Warm Up 1. Consider the following questions individually: a. What do you know about the structure of the atom? b. Draw what you think
Name Energy and the Electron: Atomic View and Argumentation Part I: Warm Up 1. Consider the following questions individually: a. What do you know about the structure of the atom? b. Draw what you think
Nature of Light. Objectives. What is light What are the different forms
 Nature of Light Objectives What is light What are the different forms Light s Importance Light contributes 99% of all observations in Astronomy Light is a form of energy Light is electromagnetic radiation
Nature of Light Objectives What is light What are the different forms Light s Importance Light contributes 99% of all observations in Astronomy Light is a form of energy Light is electromagnetic radiation
Science Lab I Properties of Light
 Art & Science of Light Fall 2007 Science Lab I Properties of Light Prepared by: Dr. Dharshi Bopegedera 1 Using the Filtergraph (15 minutes) 1. Turn on the filtergraph, place a card on it and look at the
Art & Science of Light Fall 2007 Science Lab I Properties of Light Prepared by: Dr. Dharshi Bopegedera 1 Using the Filtergraph (15 minutes) 1. Turn on the filtergraph, place a card on it and look at the
Focusing on Light What is light? Is it a particle or a wave? An age-old debate that has persisted among scientists is related to the question, "Is
 Focusing on Light What is light? Is it a particle or a wave? An age-old debate that has persisted among scientists is related to the question, "Is light a wave or a stream of particles?" Very noteworthy
Focusing on Light What is light? Is it a particle or a wave? An age-old debate that has persisted among scientists is related to the question, "Is light a wave or a stream of particles?" Very noteworthy
Answer Key Grade 5. Practice Test. What is Light? How Light Behaves
 Answer Key Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves 1. Part A Based on the text and diagram, how many major bands of radiant energy are there? A Incorrect. Look at the Kinds of Radiant Energy diagram.
Answer Key Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves 1. Part A Based on the text and diagram, how many major bands of radiant energy are there? A Incorrect. Look at the Kinds of Radiant Energy diagram.
where c m s (1)
 General Physics Experiment 6 Spectrum of Hydrogen s Emission Lines Objectives: < To determine wave lengths of the bright emission lines of hydrogen. < To test the relationship between wavelength and energy
General Physics Experiment 6 Spectrum of Hydrogen s Emission Lines Objectives: < To determine wave lengths of the bright emission lines of hydrogen. < To test the relationship between wavelength and energy
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light
 Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
3. The very long ones are called waves, and the very short ones are called waves.
 NASA Mission: Science Introduction to the Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest Directions: Load the following website which will discuss the electromagnetic spectrum in detail. http://missionscience.nasa.gov/ems/01_intro.html
NASA Mission: Science Introduction to the Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest Directions: Load the following website which will discuss the electromagnetic spectrum in detail. http://missionscience.nasa.gov/ems/01_intro.html
Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the number of lines per metre suggested by this marking.
 Q1.A student has a diffraction grating that is marked 3.5 10 3 lines per m. (a) Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the number of lines per metre suggested by this marking. percentage uncertainty =...
Q1.A student has a diffraction grating that is marked 3.5 10 3 lines per m. (a) Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the number of lines per metre suggested by this marking. percentage uncertainty =...
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER
 Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
UNIT 2 THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
 UNIT 2 THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Introduction Contrary to popular belief, outer space is not empty space. It is filled with electromagnetic radiation that crisscrosses the universe. This radiation comprises
UNIT 2 THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Introduction Contrary to popular belief, outer space is not empty space. It is filled with electromagnetic radiation that crisscrosses the universe. This radiation comprises
The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra
 PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
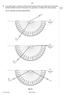 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
PHSY133 Lab 5 Atomic Spectra
 Instructional Goals: PHSY133 Lab 5 Goal: Investigate the wavelengths of light produced b atoms. Background Reading: Background reading for this lab can be found in our class notes and Chapter 5 of our
Instructional Goals: PHSY133 Lab 5 Goal: Investigate the wavelengths of light produced b atoms. Background Reading: Background reading for this lab can be found in our class notes and Chapter 5 of our
Overview: In this activity, students will learn how the moon affects ocean tides and also will create and interpret graphs of regional tide data.
 Tides & Lunar Cycles Overview: In this activity, students will learn how the moon affects ocean tides and also will create and interpret graphs of regional tide data. Episode Connection: Tides At the conclusion
Tides & Lunar Cycles Overview: In this activity, students will learn how the moon affects ocean tides and also will create and interpret graphs of regional tide data. Episode Connection: Tides At the conclusion
Activity #5 How Do Atmospheres Change Over Time? The Greenhouse Effect [Cadette]
![Activity #5 How Do Atmospheres Change Over Time? The Greenhouse Effect [Cadette] Activity #5 How Do Atmospheres Change Over Time? The Greenhouse Effect [Cadette]](/thumbs/83/88151439.jpg) Activity #5 How Do Atmospheres Change Over Time? The Greenhouse Effect [Cadette] Adapted from: Global Warming & The Greenhouse Effect, Great Explorations in Math and Science (GEMS) Lawrence Hall of Science,
Activity #5 How Do Atmospheres Change Over Time? The Greenhouse Effect [Cadette] Adapted from: Global Warming & The Greenhouse Effect, Great Explorations in Math and Science (GEMS) Lawrence Hall of Science,
Atomic Spectra & Electron Energy Levels
 CHM151LL: ATOMIC SPECTRA & ELECTRON ENERGY LEVELS 1 Atomic Spectra & Electron Energy Levels OBJECTIVES: To measure the wavelength of visible light emitted by excited atoms to calculate the energy of that
CHM151LL: ATOMIC SPECTRA & ELECTRON ENERGY LEVELS 1 Atomic Spectra & Electron Energy Levels OBJECTIVES: To measure the wavelength of visible light emitted by excited atoms to calculate the energy of that
Standing waves [49 marks]
![Standing waves [49 marks] Standing waves [49 marks]](/thumbs/92/110837906.jpg) Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
EXPERIMENT 09 OBSERVATION OF SPECTRA
 EXPERIMENT 09 OBSERVATION OF SPECTRA INTRODUCTION: In physics, as in very other area of study, one of the most valuable questions a student can learn to ask is, How do they know that? Thus, when you read
EXPERIMENT 09 OBSERVATION OF SPECTRA INTRODUCTION: In physics, as in very other area of study, one of the most valuable questions a student can learn to ask is, How do they know that? Thus, when you read
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016
 Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY
 AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light
 Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 30/ May 2/3/4, 2018 Background All
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 30/ May 2/3/4, 2018 Background All
PHYS General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source. c = speed of light = 3 x 10 8 m/s
 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
Decomposing white light into its components:
 Decomposing white light into its components: a. Look through a spectroscope at a white light from within the lab (if possible a fluorescent bulb output as well as a regular incandescent bulb) and the natural
Decomposing white light into its components: a. Look through a spectroscope at a white light from within the lab (if possible a fluorescent bulb output as well as a regular incandescent bulb) and the natural
A Teacher Resource Guide for
 A Teacher Resource Guide for For Grades 2 6 (primarily designed for Grade 5) Children s Museum of Virginia Lesson Overview The education resource was developed using the 5E model of learning and involves
A Teacher Resource Guide for For Grades 2 6 (primarily designed for Grade 5) Children s Museum of Virginia Lesson Overview The education resource was developed using the 5E model of learning and involves
Here Comes the Sun: Engineering Insulated Homes. Name:
 Engineering Notebook Here Comes the Sun: Engineering Insulated Homes Name: Prep Activity 1 Criteria and Constraints Woolly Mammoth Melt Your goal is to design an insulated transportation tank that will
Engineering Notebook Here Comes the Sun: Engineering Insulated Homes Name: Prep Activity 1 Criteria and Constraints Woolly Mammoth Melt Your goal is to design an insulated transportation tank that will
Physics Spring 2008 Midterm #1 Solution
 Physics 102-1 Spring 2008 Midterm #1 Solution Grading note: There are seven problems on nine pages. Point values are given with each problem. They add up to 110 points. In multi-part problems, points are
Physics 102-1 Spring 2008 Midterm #1 Solution Grading note: There are seven problems on nine pages. Point values are given with each problem. They add up to 110 points. In multi-part problems, points are
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Introduction to Spectroscopy
 Introduction to Spectroscopy Assistant s Manual Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst DAAD German Academic Exchange Service by Katja Streidel Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg Fakultät für Chemie
Introduction to Spectroscopy Assistant s Manual Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst DAAD German Academic Exchange Service by Katja Streidel Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg Fakultät für Chemie
Laboratory Exercise. Atomic Spectra A Kirchoff Potpourri
 1 Name: Laboratory Exercise Atomic Spectra A Kirchoff Potpourri Purpose: To examine the atomic spectra from several gas filled tubes and understand the importance of spectroscopy to astronomy. Introduction
1 Name: Laboratory Exercise Atomic Spectra A Kirchoff Potpourri Purpose: To examine the atomic spectra from several gas filled tubes and understand the importance of spectroscopy to astronomy. Introduction
Thursday 9 June 2016 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Thursday 9 June 2016 Afternoon AS GCE PHYSICS B (ADVANCING PHYSICS) G492/01 Understanding Processes / Experimentation and Data Handling * 1 1 6 5 2 2 0 7 4 0 * Candidates answer
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Thursday 9 June 2016 Afternoon AS GCE PHYSICS B (ADVANCING PHYSICS) G492/01 Understanding Processes / Experimentation and Data Handling * 1 1 6 5 2 2 0 7 4 0 * Candidates answer
Visible spectrum 1. Spectroscope. Name:
 Name: Visible spectrum 1 You know by now that different atoms have different configurations of electrons. You also know that electrons generate electromagnetic waves when they oscillate (remember that
Name: Visible spectrum 1 You know by now that different atoms have different configurations of electrons. You also know that electrons generate electromagnetic waves when they oscillate (remember that
POP ROCKET TRASH TO TREASURE
 POP ROCKET TRASH TO TREASURE Connie Stammen, 2nd-grade teacher North Star Elementary North Star, OH Lesson Summary for Grades 2 5 Students design a paper rocket propelled by an effervescent antacid tablet
POP ROCKET TRASH TO TREASURE Connie Stammen, 2nd-grade teacher North Star Elementary North Star, OH Lesson Summary for Grades 2 5 Students design a paper rocket propelled by an effervescent antacid tablet
Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018
 www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
Physics Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING
 Physics Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Physics Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light
 1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light 1. Double-Slit Eperiment reading: Chapter 22 2. Single-Slit Diffraction reading: Chapter 22 3. Diffraction Grating reading: Chapter
1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light 1. Double-Slit Eperiment reading: Chapter 22 2. Single-Slit Diffraction reading: Chapter 22 3. Diffraction Grating reading: Chapter
Name Class Date. What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How can electromagnetic waves be used?
 CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
SCIENCE 600 CA SUPPLY LIST
 2014-2015 Supply List SCIENCE 600 CA SUPPLY LIST 2014 GLYNLYON, INC. Table of Contents UNIT 1: PLANT SYSTEMS... 1 UNIT 2: WEATHER... 2 UNIT 3: PLANT AND ANIMAL BEHAVIOR... 2 UNIT 4: EARTH IN SPACE... 3
2014-2015 Supply List SCIENCE 600 CA SUPPLY LIST 2014 GLYNLYON, INC. Table of Contents UNIT 1: PLANT SYSTEMS... 1 UNIT 2: WEATHER... 2 UNIT 3: PLANT AND ANIMAL BEHAVIOR... 2 UNIT 4: EARTH IN SPACE... 3
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves. What is a wave?
 Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Colorado State Standards Mathematics Standards 3.4 Science Standard 1, 2, 4, 5. Teaching Time: One 60-minute period
 Lesson Summary In this activity, students use the spectrograph and homework from the activity Building a Fancy Spectrograph. Students look at various light sources and make conjectures about composition.
Lesson Summary In this activity, students use the spectrograph and homework from the activity Building a Fancy Spectrograph. Students look at various light sources and make conjectures about composition.
Southern Nevada Regional Professional Development Program. What happens when water changes to a solid?
 3-5 Physical Science What happens when water changes to a solid? Two large soft vials with caps One plastic 50 ml syringe Plastic ice tray Water Freezer compartment 1. Completely fill the ice tray and
3-5 Physical Science What happens when water changes to a solid? Two large soft vials with caps One plastic 50 ml syringe Plastic ice tray Water Freezer compartment 1. Completely fill the ice tray and
Review: Properties of a wave
 Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION
 Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
