USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 2 Solutions Year 21 Academic Year
|
|
|
- Samuel Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1/2/21. Jeremy has a magic scale, each side of which holds a positive integer. He plays the following game: each turn, he chooses a positive integer n. He then adds n to the number on the left side of the scale, and multiplies by n the number on the right side of the scale. (For example, if the turn starts with 4 on the left and 6 on the right, and Jeremy chooses n = 3, then the turn ends with 7 on the left and 18 on the right.) Jeremy wins if he can make both sides of the scale equal. (a) Show that if the game starts with the left scale holding 17 and the right scale holding 5, then Jeremy can win the game in 4 or fewer turns. (b) Prove that if the game starts with the right scale holding b, where b 2, then Jeremy can win the game in b 1 or fewer turns. (a) Jeremy wins as follows: Turn n Left Right Start (b) Let a be the starting number on the left scale. First, notice that if on any turn Jeremy chooses n = 1, then the left side increases by 1 and the right side remains unchanged. Thus, our strategy is to have Jeremy choose 1 each turn until the left side is a multiple of b 1. This will take at most b 2 turns: if a is already a multiple of b 1, no turns are needed; otherwise, if a = d(b 1) + r, where 1 r b 2, the left side will be a multiple of b 1 after b 1 r b 2 turns in which Jeremy chooses 1. After this, the left side equals k(b 1), where k is some positive integer, and the right side is still b. If Jeremy now chooses k, the left side becomes k(b 1) + k = kb and the right side also becomes kb, so the game ends. This occurs in at most (b 2) + 1 = b 1 turns, as desired.
2 2/2/21. Alice has three daughters, each of whom has two daughters; each of Alice s six granddaughters has one daughter. How many sets of women from the family of 16 can be chosen such that no woman and her daughter are both in the set? (Include the empty set as a possible set.) We proceed by cases. If Alice is in the set, then we cannot choose any of her daughters, and for each of the 6 granddaughters, we can choose either that granddaughter, that granddaughter s daughter, or neither, for a total of 3 choices per granddaughter. Thus, there are 3 6 = 729 possible sets that include Alice. If Alice is not in the set, then we view Alice s three daughters as matriarchs of three disjoint identical family trees. For each of her three daughters, we can choose (a) 2 2 = 4 subsets that include the daughter and any number of that daughter s grandchildren, or (b) 3 2 = 9 subsets that do not include the daughter, but include her children and/or grandchildren (for each daughter, we can take her, her daughter, or neither). This gives = 13 subsets associated to each of Alice s three daughters, and thus there are (13) 3 = 2197 subsets that do not include Alice. This gives a total of = 2926 allowed subsets.
3 3/2/21. Prove that if a and b are positive integers such that a 2 + b 2 is a multiple of , then ab is a multiple of We first construct the following chart of squares modulo 7: k k The only pair of squares modulo 7 that can add to 0 (mod 7) is Thus, a 2 b 2 0 (mod 7). This means that a = 7a 1 and b = 7b 1 for some positive integers a 1 and b 1. But then (7a 1 ) 2 + (7a 2 ) 2 is a multiple of , so a a 2 2 is a multiple of By the same reasoning, a 1 = 7a 2 and b 1 = 7b 2 for some positive integers a 2 and b 2 ; hence a = 7 2 a 2 and b = 7 2 b 2. But then a b 2 2 is a multiple of , so we can repeat the process. Inductively, we get that a = a 1005 and b = b 1005 for some positive integers a 1005 and b 1005, so that ab = (a 1005 b 1005 ), as desired.
4 4/2/21. The Rational Unit Jumping Frog starts at (0, 0) on the Cartesian plane, and each minute jumps a distance of exactly 1 unit to a point with rational coordinates. (a) Show that it is possible for the frog to reach the point ( 1 5, 1 17) in a finite amount of time. (b) Show that the frog can never reach the point ( 0, 1 4). (a) We use the Pythagorean triples {3, 4, 5} and {8, 15, 17} to construct the path from (0, 0) to ( 1 17) shown below: ( 3 (0, 0) 5, 4 ) ( ) ( ) ( , 0 5, , 8 ) ( ) ( , , 1 ). 17, 1 5 (b) Suppose the frog jumps such that its position changes by (r, s), where r and s are rational. Let c be the least common denominator of r and s, so that r = a, s = b for some integers a c c and b with gcd(a, b) = 1. The length of each jump is 1, so we have ( ) a 2 ( c + b 2 c) = 1, which gives a 2 + b 2 = c 2. If a and b are both odd, then c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2 (mod 4). Since no square is congruent to 2 mod 4, we conclude that a and b cannot both be odd. We cannot have a and b both even because gcd(a, b) = 1. Therefore, one of a and b is even and the other is odd, so c 2 = a 2 + b 2 is odd, which means s odd. ( Letting the i th a jump change the frog s location by i, b i ), the frog s location after k jumps is ( k ) a i k b i,. i=1 Since all of the are odd, the denominator of each of these sums is odd. Therefore, the frog cannot reach a point with an even denominator. Specifically, the frog cannot reach ( 0, 1 4). i=1
5 5/2/21. Let ABC be a triangle with AB = 3, AC = 4, and BC = 5, let P be a point on BC, and let Q be the point (other than A) where the line through A and P intersects the circumcircle of ABC. Prove that P Q < Consider the triangle ABC. Points A, C, Q, and B are concyclic, so triangles AP C and BP Q are similar, which means AC/BQ = P C/P Q. Likewise, triangles ABP and CQP are similar, so AB/CQ = P B/P Q. Then P Q AC = BQ CP and P Q AB = BP CQ. Taking the product of these equations, we get B 3 A P 4 C P Q 2 AB AC = BP CP BQ CQ P Q = BP CP BQ CQ Q By the AM-GM Inequality, ( BP + CP BP CP 2 ) 2 = 25 4, which tells us P Q 2 25 BQ CQ. 48 B R C Now we must maximize BQ CQ. This value is the twice area of the triangle BCQ, since Q is also a right angle. Let R be the base of the altitude of BCQ from Q. Then Q BQ CQ = 2[BCQ] = BC RQ = 5RQ. Since Q lies on the unit circle and R lies on a diameter, the length of RQ is maximized when R is the center of the circle, making RQ the radius, so This tells us that BQ CQ = 5RQ = 25 2 P Q BQ CQ ,
6 or P Q Finally notice that we used two inequalities in this argument. We maximized BP CP via the AM-GM Inequality, which is uniquely maximized at BP = CP, so when P is the center of the circle. We also maximized the area [BQC], which is uniquely maximized when AQ is the angle bisector of A. However the angle bisector can only pass through the center of the circle if AB = AC. Therefore we do not achieve both maxima simultaneously and the inequality is strict: P Q < Credits: Problem statements and solutions were written by USAMTS staff. Problem 1/2/21 was submitted by Gaku Liu. Problem 2/2/21 was submitted by Ben Dozier. Problem 3/2/21 is based on a problem that appeared in the March 1997 issue of Crux Mathematicorum with Mathematical Mayhem. Problem 4/2/21 is based on a problem from the 1994 Old Mutual Mathematics Olympiad and appeared in the January 1995 issue of Mathematical Digest. Problem 5/2/21 is a simplified version of a problem that appeared in issue 4/96 of Mathematics and Informatics Quarterly. c 2009 Art of Problem Solving Foundation
XX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad
 XX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad March, 008 Problem 1. Let ABC be a triangle with A < 60. Let X and Y be the points on the sides AB and AC, respectively, such that CA + AX = CB + BX and BA + AY =
XX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad March, 008 Problem 1. Let ABC be a triangle with A < 60. Let X and Y be the points on the sides AB and AC, respectively, such that CA + AX = CB + BX and BA + AY =
Baltic Way 2008 Gdańsk, November 8, 2008
 Baltic Way 008 Gdańsk, November 8, 008 Problems and solutions Problem 1. Determine all polynomials p(x) with real coefficients such that p((x + 1) ) = (p(x) + 1) and p(0) = 0. Answer: p(x) = x. Solution:
Baltic Way 008 Gdańsk, November 8, 008 Problems and solutions Problem 1. Determine all polynomials p(x) with real coefficients such that p((x + 1) ) = (p(x) + 1) and p(0) = 0. Answer: p(x) = x. Solution:
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 3 Solutions Year 20 Academic Year
 1/3/20. Let S be the set of all 10-digit numbers (which by definition may not begin with 0) in which each digit 0 through 9 appears exactly once. For example, the number 3,820,956,714 is in S. A number
1/3/20. Let S be the set of all 10-digit numbers (which by definition may not begin with 0) in which each digit 0 through 9 appears exactly once. For example, the number 3,820,956,714 is in S. A number
International Mathematical Olympiad. Preliminary Selection Contest 2017 Hong Kong. Outline of Solutions 5. 3*
 International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers: 06 0000 * 6 97 7 6 8 7007 9 6 0 6 8 77 66 7 7 0 6 7 7 6 8 9 8 0 0 8 *See the remar after the solution
International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers: 06 0000 * 6 97 7 6 8 7007 9 6 0 6 8 77 66 7 7 0 6 7 7 6 8 9 8 0 0 8 *See the remar after the solution
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 4 Solutions Year 20 Academic Year
 1/4/20. Consider a sequence {a n } with a 1 = 2 and a n = a2 n 1 a n 2 for all n 3. If we know that a 2 and a 5 are positive integers and a 5 2009, then what are the possible values of a 5? Since a 1 and
1/4/20. Consider a sequence {a n } with a 1 = 2 and a n = a2 n 1 a n 2 for all n 3. If we know that a 2 and a 5 are positive integers and a 5 2009, then what are the possible values of a 5? Since a 1 and
2011 Olympiad Solutions
 011 Olympiad Problem 1 Let A 0, A 1, A,..., A n be nonnegative numbers such that Prove that A 0 A 1 A A n. A i 1 n A n. Note: x means the greatest integer that is less than or equal to x.) Solution: We
011 Olympiad Problem 1 Let A 0, A 1, A,..., A n be nonnegative numbers such that Prove that A 0 A 1 A A n. A i 1 n A n. Note: x means the greatest integer that is less than or equal to x.) Solution: We
Mathematics 220 Homework 4 - Solutions. Solution: We must prove the two statements: (1) if A = B, then A B = A B, and (2) if A B = A B, then A = B.
 1. (4.46) Let A and B be sets. Prove that A B = A B if and only if A = B. Solution: We must prove the two statements: (1) if A = B, then A B = A B, and (2) if A B = A B, then A = B. Proof of (1): Suppose
1. (4.46) Let A and B be sets. Prove that A B = A B if and only if A = B. Solution: We must prove the two statements: (1) if A = B, then A B = A B, and (2) if A B = A B, then A = B. Proof of (1): Suppose
Baltic Way 2003 Riga, November 2, 2003
 altic Way 2003 Riga, November 2, 2003 Problems and solutions. Let Q + be the set of positive rational numbers. Find all functions f : Q + Q + which for all x Q + fulfil () f ( x ) = f (x) (2) ( + x ) f
altic Way 2003 Riga, November 2, 2003 Problems and solutions. Let Q + be the set of positive rational numbers. Find all functions f : Q + Q + which for all x Q + fulfil () f ( x ) = f (x) (2) ( + x ) f
36th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad
 36th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Let n be a positive integer. Define a sequence by setting a 1 = n and, for each k > 1, letting a k be the unique integer in the range 0 a k k 1 for
36th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Let n be a positive integer. Define a sequence by setting a 1 = n and, for each k > 1, letting a k be the unique integer in the range 0 a k k 1 for
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 Solutions
 IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 Solutions July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 Solutions July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training. Take Home Test Solutions. 15x 2 7y 2 = 9 y 2 0 (mod 3) x 0 (mod 3).
 Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training Take Home Test Solutions. Show that the equation 5x 2 7y 2 = 9 has no solution in integers. If the equation has a solution in integer,
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training Take Home Test Solutions. Show that the equation 5x 2 7y 2 = 9 has no solution in integers. If the equation has a solution in integer,
This class will demonstrate the use of bijections to solve certain combinatorial problems simply and effectively.
 . Induction This class will demonstrate the fundamental problem solving technique of mathematical induction. Example Problem: Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible
. Induction This class will demonstrate the fundamental problem solving technique of mathematical induction. Example Problem: Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible
HSMC 2017 Free Response
 HSMC 207 Free Response. What are the first three digits of the least common multiple of 234 and 360? Solution: 468. Note that 234 = 2 3 2 3, and 360 = 2 3 3 2 5. Thus, lcm =2 3 3 2 5 3 = 0 36 3 = 4680.
HSMC 207 Free Response. What are the first three digits of the least common multiple of 234 and 360? Solution: 468. Note that 234 = 2 3 2 3, and 360 = 2 3 3 2 5. Thus, lcm =2 3 3 2 5 3 = 0 36 3 = 4680.
March 5, Solution: D. The event happens precisely when the number 2 is one of the primes selected. This occurs with probability ( (
 March 5, 2007 1. We randomly select 4 prime numbers without replacement from the first 10 prime numbers. What is the probability that the sum of the four selected numbers is odd? (A) 0.21 (B) 0.30 (C)
March 5, 2007 1. We randomly select 4 prime numbers without replacement from the first 10 prime numbers. What is the probability that the sum of the four selected numbers is odd? (A) 0.21 (B) 0.30 (C)
Unofficial Solutions
 Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge 2016 Unofficial Solutions COMC exams from other years, with or without the solutions included, are free to download online. Please visit http://comc.math.ca/2016/practice.html
Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge 2016 Unofficial Solutions COMC exams from other years, with or without the solutions included, are free to download online. Please visit http://comc.math.ca/2016/practice.html
International Mathematical Olympiad. Preliminary Selection Contest 2011 Hong Kong. Outline of Solutions
 International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers:.. 76... 6. 7.. 6.. 6. 6.... 6. 7.. 76. 6. 7 Solutions:. Such fractions include. They can be grouped
International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers:.. 76... 6. 7.. 6.. 6. 6.... 6. 7.. 76. 6. 7 Solutions:. Such fractions include. They can be grouped
37th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad
 37th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Prove that for each positive integer n, there are pairwise relatively prime integers k 0, k 1,..., k n, all strictly greater than 1, such that k 0
37th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Prove that for each positive integer n, there are pairwise relatively prime integers k 0, k 1,..., k n, all strictly greater than 1, such that k 0
University of Melbourne Schools Mathematics Competition 2004 Senior Solutions
 University of Melbourne Schools Mathematics Competition 004 Senior Solutions 1. Jane and her friends are standing in a circle. It turns out that both neighbours of each child are the same gender. If there
University of Melbourne Schools Mathematics Competition 004 Senior Solutions 1. Jane and her friends are standing in a circle. It turns out that both neighbours of each child are the same gender. If there
41st International Mathematical Olympiad
 41st International Mathematical Olympiad Taejon, Korea, July 2000 1 Two circles Γ 1 and Γ 2 intersect at M and N Let l be the common tangent to Γ 1 and Γ 2 so that M is closer to l than N is Let l touch
41st International Mathematical Olympiad Taejon, Korea, July 2000 1 Two circles Γ 1 and Γ 2 intersect at M and N Let l be the common tangent to Γ 1 and Γ 2 so that M is closer to l than N is Let l touch
Problems and Solutions
 46 th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, April 2, 204 Problems and Solutions. Let a, a 2,..., a n be positive real numbers whose product is. Show that the sum a a 2 + + a ( + a )( + a 2 ) + a 3
46 th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, April 2, 204 Problems and Solutions. Let a, a 2,..., a n be positive real numbers whose product is. Show that the sum a a 2 + + a ( + a )( + a 2 ) + a 3
BMT 2018 Team Test Solutions March 18, 2018
 . A circle with radius is inscribed in a right triangle with hypotenuse 4 as shown below. What is the area of the triangle? Note that the diagram is not to scale. 4 Answer: 9 Solution : We wish to use
. A circle with radius is inscribed in a right triangle with hypotenuse 4 as shown below. What is the area of the triangle? Note that the diagram is not to scale. 4 Answer: 9 Solution : We wish to use
2017 Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament
 Team Round 1 Let P(x), Q(x) be nonconstant polynomials with real number coefficients. Prove that if P(y) = Q(y) for all real numbers y, then P(x) = Q(x) for all real numbers x. 2 Does there exist a two-variable
Team Round 1 Let P(x), Q(x) be nonconstant polynomials with real number coefficients. Prove that if P(y) = Q(y) for all real numbers y, then P(x) = Q(x) for all real numbers x. 2 Does there exist a two-variable
Solution: By direct calculation, or observe that = = ( ) 2222 = =
 1 Fillins 1. Find the last 4 digits of 3333 6666. Solution: 7778. By direct calculation, or observe that 3333 6666 = 9999 2222 = (10000 1) 2222 = 22220000 2222 = 22217778. 2. How many ways are there to
1 Fillins 1. Find the last 4 digits of 3333 6666. Solution: 7778. By direct calculation, or observe that 3333 6666 = 9999 2222 = (10000 1) 2222 = 22220000 2222 = 22217778. 2. How many ways are there to
Solutions of APMO 2017
 Solutions of APMO 2017 Problem 1. We call a 5-tuple of integers arrangeable if its elements can be labeled a, b, c, d, e in some order so that a b + c d + e = 29. Determine all 2017-tuples of integers
Solutions of APMO 2017 Problem 1. We call a 5-tuple of integers arrangeable if its elements can be labeled a, b, c, d, e in some order so that a b + c d + e = 29. Determine all 2017-tuples of integers
UNC Charlotte 2005 Comprehensive March 7, 2005
 March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
= 10 such triples. If it is 5, there is = 1 such triple. Therefore, there are a total of = 46 such triples.
 . Two externally tangent unit circles are constructed inside square ABCD, one tangent to AB and AD, the other to BC and CD. Compute the length of AB. Answer: + Solution: Observe that the diagonal of the
. Two externally tangent unit circles are constructed inside square ABCD, one tangent to AB and AD, the other to BC and CD. Compute the length of AB. Answer: + Solution: Observe that the diagonal of the
1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why. (a b)(a c)(a d)(b c)(b d)(c d) a 2 + ab b = 2018.
 New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
WORKSHEET ON NUMBERS, MATH 215 FALL. We start our study of numbers with the integers: N = {1, 2, 3,...}
 WORKSHEET ON NUMBERS, MATH 215 FALL 18(WHYTE) We start our study of numbers with the integers: Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,... } and their subset of natural numbers: N = {1, 2, 3,...} For now we will not
WORKSHEET ON NUMBERS, MATH 215 FALL 18(WHYTE) We start our study of numbers with the integers: Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,... } and their subset of natural numbers: N = {1, 2, 3,...} For now we will not
SUMS PROBLEM COMPETITION, 2000
 SUMS ROBLEM COMETITION, 2000 SOLUTIONS 1 The result is well known, and called Morley s Theorem Many proofs are known See for example HSM Coxeter, Introduction to Geometry, page 23 2 If the number of vertices,
SUMS ROBLEM COMETITION, 2000 SOLUTIONS 1 The result is well known, and called Morley s Theorem Many proofs are known See for example HSM Coxeter, Introduction to Geometry, page 23 2 If the number of vertices,
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 2 Solutions Year 20 Academic Year
 //0. Sarah and Joe play a standard 3-by-3 game of tic-tac-toe. Sarah goes first and plays X, and Joe goes second and plays O. They alternate turns placing their letter in an empty space, and the first
//0. Sarah and Joe play a standard 3-by-3 game of tic-tac-toe. Sarah goes first and plays X, and Joe goes second and plays O. They alternate turns placing their letter in an empty space, and the first
1. Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible by 5 n all of whose digits are odd.
 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
Mathematical Olympiad for Girls
 UKMT UKMT UKMT Mathematical Olympiad for Girls Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust These are polished solutions and do not illustrate the process of failed ideas and rough work by which candidates
UKMT UKMT UKMT Mathematical Olympiad for Girls Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust These are polished solutions and do not illustrate the process of failed ideas and rough work by which candidates
3. A square has 4 sides, so S = 4. A pentagon has 5 vertices, so P = 5. Hence, S + P = 9. = = 5 3.
 JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 2003
 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
11 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament
 11 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 23 February 2008 Guts Round.. 1. [5] Determine all pairs (a, b) of real numbers such that 10, a, b, ab is an arithmetic progression. 2. [5] Given
11 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 23 February 2008 Guts Round.. 1. [5] Determine all pairs (a, b) of real numbers such that 10, a, b, ab is an arithmetic progression. 2. [5] Given
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 1 Solutions Year 22 Academic Year
 1/2/22. Show that there is a unique way to place positive integers in the grid to the right following these three rules: 1. Each entry in the top row is one digit. 2. Each entry in any row below the top
1/2/22. Show that there is a unique way to place positive integers in the grid to the right following these three rules: 1. Each entry in the top row is one digit. 2. Each entry in any row below the top
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 2007
 Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
27th Russian Mathematics Olympiad
 27th Russian Mathematics Olympiad 10 April 2001 (Communicated by Fedor Petrov) 9 FORM 1. The integers from 1 to 999999 are partioned into two groups: those integers for which the nearest perfect square
27th Russian Mathematics Olympiad 10 April 2001 (Communicated by Fedor Petrov) 9 FORM 1. The integers from 1 to 999999 are partioned into two groups: those integers for which the nearest perfect square
1 2n. i=1. 2m+1 i = m, while. 2m + 1 = 1. is the best possible for any odd n.
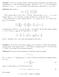 Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
4 a b 1 1 c 1 d 3 e 2 f g 6 h i j k 7 l m n o 3 p q 5 r 2 s 4 t 3 3 u v 2
 Round Solutions Year 25 Academic Year 201 201 1//25. In the hexagonal grid shown, fill in each space with a number. After the grid is completely filled in, the number in each space must be equal to the
Round Solutions Year 25 Academic Year 201 201 1//25. In the hexagonal grid shown, fill in each space with a number. After the grid is completely filled in, the number in each space must be equal to the
2009 Cayley Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2009 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Wednesday, February 18, 2009
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2009 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Wednesday, February 18, 2009
10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]
![10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152] 10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]](/thumbs/94/121826807.jpg) foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
27 th Annual ARML Scrimmage
 27 th Annual ARML Scrimmage Featuring: Howard County ARML Team (host) Baltimore County ARML Team ARML Team Alumni Citizens By Raymond Cheong May 23, 2012 Reservoir HS Individual Round (10 min. per pair
27 th Annual ARML Scrimmage Featuring: Howard County ARML Team (host) Baltimore County ARML Team ARML Team Alumni Citizens By Raymond Cheong May 23, 2012 Reservoir HS Individual Round (10 min. per pair
Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge
 The Canadian Mathematical Society in collaboration with The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING presents the Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge Wednesday, November, 006 Supported by: Solutions
The Canadian Mathematical Society in collaboration with The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING presents the Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge Wednesday, November, 006 Supported by: Solutions
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2
 IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the circumcircle
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the circumcircle
11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers, and Hints
 view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
15th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad. BAMO Exam. February 26, Solutions to BAMO-8 and BAMO-12 Problems
 15th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad BAMO Exam February 26, 2013 Solutions to BAMO-8 and BAMO-12 Problems 1 How many different sets of three points in this equilateral triangular grid are the vertices of
15th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad BAMO Exam February 26, 2013 Solutions to BAMO-8 and BAMO-12 Problems 1 How many different sets of three points in this equilateral triangular grid are the vertices of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Euclid Contest. Wednesday, April 15, 2015
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
The Geometric Mean and the AM-GM Inequality
 The Geometric Mean and the AM-GM Inequality John Treuer February 27, 2017 1 Introduction: The arithmetic mean of n numbers, better known as the average of n numbers is an example of a mathematical concept
The Geometric Mean and the AM-GM Inequality John Treuer February 27, 2017 1 Introduction: The arithmetic mean of n numbers, better known as the average of n numbers is an example of a mathematical concept
SOLUTIONS. x 2 and BV 2 = x
 SOLUTIONS /3 SOLUTIONS No problem is ever permanently closed The editor is always pleased to consider new solutions or new insights on past problems Statements of the problems in this section originally
SOLUTIONS /3 SOLUTIONS No problem is ever permanently closed The editor is always pleased to consider new solutions or new insights on past problems Statements of the problems in this section originally
40th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad
 40th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, March 26, 2008 Solutions - CMO 2008 1. ABCD is a convex quadrilateral in which AB is the longest side. Points M and N are located on sides AB and BC respectively,
40th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, March 26, 2008 Solutions - CMO 2008 1. ABCD is a convex quadrilateral in which AB is the longest side. Points M and N are located on sides AB and BC respectively,
Solutions I.N. Herstein- Second Edition
 Solutions I.N. Herstein- Second Edition Sadiah Zahoor 25, July 2016 Please email me if any corrections at sadiahzahoor@cantab.net. Problem 0.1. In the following determine whether the systems described
Solutions I.N. Herstein- Second Edition Sadiah Zahoor 25, July 2016 Please email me if any corrections at sadiahzahoor@cantab.net. Problem 0.1. In the following determine whether the systems described
EGYPTIAN FRACTIONS WITH EACH DENOMINATOR HAVING THREE DISTINCT PRIME DIVISORS
 #A5 INTEGERS 5 (205) EGYPTIAN FRACTIONS WITH EACH DENOMINATOR HAVING THREE DISTINCT PRIME DIVISORS Steve Butler Department of Mathematics, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa butler@iastate.edu Paul Erdős
#A5 INTEGERS 5 (205) EGYPTIAN FRACTIONS WITH EACH DENOMINATOR HAVING THREE DISTINCT PRIME DIVISORS Steve Butler Department of Mathematics, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa butler@iastate.edu Paul Erdős
3. Applying the definition, we have 2#0 = = 5 and 1#4 = = 0. Thus, (2#0)#(1#4) = 5#0 = ( 5) 0 ( 5) 3 = 2.
 JHMMC 01 Grade 7 Solutions October 1, 01 1. There are 16 words in the sentence, and exactly 5 of them have four letters, as shown: What is the probability that a randomly chosen word of this sentence has
JHMMC 01 Grade 7 Solutions October 1, 01 1. There are 16 words in the sentence, and exactly 5 of them have four letters, as shown: What is the probability that a randomly chosen word of this sentence has
NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY Thrusday, Oct 6th, 2011 ANSWERS FALL 2011 NU PUTNAM SELECTION TEST
 Problem A1. Let a 1, a 2,..., a n be n not necessarily distinct integers. exist a subset of these numbers whose sum is divisible by n. Prove that there - Answer: Consider the numbers s 1 = a 1, s 2 = a
Problem A1. Let a 1, a 2,..., a n be n not necessarily distinct integers. exist a subset of these numbers whose sum is divisible by n. Prove that there - Answer: Consider the numbers s 1 = a 1, s 2 = a
1. (A) Factor to get (2x+3)(2x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/2 and 5, which sum to 7/2.
 Solutions 00 53 rd AMC 1 A 1. (A) Factor to get (x+3)(x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/ and 5, which sum to 7/.. (A) Let x be the number she was given. Her calculations produce so x 9 3 = 43, x 9 = 19
Solutions 00 53 rd AMC 1 A 1. (A) Factor to get (x+3)(x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/ and 5, which sum to 7/.. (A) Let x be the number she was given. Her calculations produce so x 9 3 = 43, x 9 = 19
WORKSHEET MATH 215, FALL 15, WHYTE. We begin our course with the natural numbers:
 WORKSHEET MATH 215, FALL 15, WHYTE We begin our course with the natural numbers: N = {1, 2, 3,...} which are a subset of the integers: Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,... } We will assume familiarity with their
WORKSHEET MATH 215, FALL 15, WHYTE We begin our course with the natural numbers: N = {1, 2, 3,...} which are a subset of the integers: Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,... } We will assume familiarity with their
Organization Team Team ID#
 1. [4] A random number generator will always output 7. Sam uses this random number generator once. What is the expected value of the output? 2. [4] Let A, B, C, D, E, F be 6 points on a circle in that
1. [4] A random number generator will always output 7. Sam uses this random number generator once. What is the expected value of the output? 2. [4] Let A, B, C, D, E, F be 6 points on a circle in that
Lagrange s polynomial
 Lagrange s polynomial Nguyen Trung Tuan November 13, 2016 Abstract...In numerical analysis, Lagrange polynomials are used for polynomial interpolation. For a given set of distinct points x j and numbers
Lagrange s polynomial Nguyen Trung Tuan November 13, 2016 Abstract...In numerical analysis, Lagrange polynomials are used for polynomial interpolation. For a given set of distinct points x j and numbers
Chapter 8. P-adic numbers. 8.1 Absolute values
 Chapter 8 P-adic numbers Literature: N. Koblitz, p-adic Numbers, p-adic Analysis, and Zeta-Functions, 2nd edition, Graduate Texts in Mathematics 58, Springer Verlag 1984, corrected 2nd printing 1996, Chap.
Chapter 8 P-adic numbers Literature: N. Koblitz, p-adic Numbers, p-adic Analysis, and Zeta-Functions, 2nd edition, Graduate Texts in Mathematics 58, Springer Verlag 1984, corrected 2nd printing 1996, Chap.
11th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad
 11th ay rea Mathematical Olympiad ebruary 24, 2009 Problems (with Solutions) 1 square grid of 16 dots (see the figure) contains the corners of nine 1 1 squares, four 2 2 squares, and one 3 3 square, for
11th ay rea Mathematical Olympiad ebruary 24, 2009 Problems (with Solutions) 1 square grid of 16 dots (see the figure) contains the corners of nine 1 1 squares, four 2 2 squares, and one 3 3 square, for
SCTT The pqr-method august 2016
 SCTT The pqr-method august 2016 A. Doledenok, M. Fadin, À. Menshchikov, A. Semchankau Almost all inequalities considered in our project are symmetric. Hence if plugging (a 0, b 0, c 0 ) into our inequality
SCTT The pqr-method august 2016 A. Doledenok, M. Fadin, À. Menshchikov, A. Semchankau Almost all inequalities considered in our project are symmetric. Hence if plugging (a 0, b 0, c 0 ) into our inequality
2005 Hypatia Contest
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 005 Hypatia Contest Wednesday, April 0, 005 Solutions c
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 005 Hypatia Contest Wednesday, April 0, 005 Solutions c
= How many four-digit numbers between 6000 and 7000 are there for which the thousands digits equal the sum of the other three digits?
 March 5, 2007 1. Maya deposited 1000 dollars at 6% interest compounded annually. What is the number of dollars in the account after four years? (A) $1258.47 (B) $1260.18 (C) $1262.48 (D) $1263.76 (E) $1264.87
March 5, 2007 1. Maya deposited 1000 dollars at 6% interest compounded annually. What is the number of dollars in the account after four years? (A) $1258.47 (B) $1260.18 (C) $1262.48 (D) $1263.76 (E) $1264.87
INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS. Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0. Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints References
 INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS 1990 2002 Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0 Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints 15 3. References 16 1. Problems 021 Let n be a positive integer. Let T be the set of points
INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS 1990 2002 Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0 Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints 15 3. References 16 1. Problems 021 Let n be a positive integer. Let T be the set of points
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Cayley Contest. (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 27, 2018
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 018 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 7, 018 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, February 8, 018 (outside of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 018 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 7, 018 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, February 8, 018 (outside of
Solutions th AMC 12 A (E) Since $20 is 2000 cents, she pays (0.0145)(2000) = 29 cents per hour in local taxes.
 Solutions 2004 55 th AMC 12 A 2 1. (E) Since $20 is 2000 cents, she pays (0.0145)(2000) = 29 cents per hour in local taxes. 2. (C) The 8 unanswered problems are worth (2.5)(8) = 20 points, so Charlyn must
Solutions 2004 55 th AMC 12 A 2 1. (E) Since $20 is 2000 cents, she pays (0.0145)(2000) = 29 cents per hour in local taxes. 2. (C) The 8 unanswered problems are worth (2.5)(8) = 20 points, so Charlyn must
Solutions and Marking Schemes
 THIRTY FIRST IRISH MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIAD 1. Proposed by Bernd Kreussler. Saturday, 1 May 018 First Paper Solutions and Marking Schemes Mary and Pat play the following number game. Mary picks an initial
THIRTY FIRST IRISH MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIAD 1. Proposed by Bernd Kreussler. Saturday, 1 May 018 First Paper Solutions and Marking Schemes Mary and Pat play the following number game. Mary picks an initial
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad Training Problems
 Singapore International athematical Olympiad Training Problems 18 January 2003 1 Let be a point on the segment Squares D and EF are erected on the same side of with F lying on The circumcircles of D and
Singapore International athematical Olympiad Training Problems 18 January 2003 1 Let be a point on the segment Squares D and EF are erected on the same side of with F lying on The circumcircles of D and
Intermediate Math Circles February 22, 2012 Contest Preparation II
 Intermediate Math Circles February, 0 Contest Preparation II Answers: Problem Set 6:. C. A 3. B 4. [-6,6] 5. T 3, U and T 8, U 6 6. 69375 7. C 8. A 9. C 0. E Australian Mathematics Competition - Intermediate
Intermediate Math Circles February, 0 Contest Preparation II Answers: Problem Set 6:. C. A 3. B 4. [-6,6] 5. T 3, U and T 8, U 6 6. 69375 7. C 8. A 9. C 0. E Australian Mathematics Competition - Intermediate
RMT 2013 Geometry Test Solutions February 2, = 51.
 RMT 0 Geometry Test Solutions February, 0. Answer: 5 Solution: Let m A = x and m B = y. Note that we have two pairs of isosceles triangles, so m A = m ACD and m B = m BCD. Since m ACD + m BCD = m ACB,
RMT 0 Geometry Test Solutions February, 0. Answer: 5 Solution: Let m A = x and m B = y. Note that we have two pairs of isosceles triangles, so m A = m ACD and m B = m BCD. Since m ACD + m BCD = m ACB,
8 th December th December 2018 Junior Category. a 2 + b + c = 1 a, b 2 + c + a = 1 b, c 2 + a + b = 1 c.
 7 th European Mathematical Cup 8 th December 018-16 th December 018 Junior Category MLADI NADARENI MATEMATIČARI Marin Getaldic Problems and Solutions Problem 1. Let a, b, c be non-zero real numbers such
7 th European Mathematical Cup 8 th December 018-16 th December 018 Junior Category MLADI NADARENI MATEMATIČARI Marin Getaldic Problems and Solutions Problem 1. Let a, b, c be non-zero real numbers such
vertices so that three such numbers sum to zero whenever the three vertices form a triangle with edges parallel to the sides of the big triangle.
 1 1 1 BALTIC WAY 015 Problems and Solutions 1 1 1 3 3 1 1 4 6 4 1 1 B AL TI C 1 1 W AY 0 15 6 1 Problem 1. For n, an equilateral triangle is divided into n congruent smaller equilateral triangles. Determine
1 1 1 BALTIC WAY 015 Problems and Solutions 1 1 1 3 3 1 1 4 6 4 1 1 B AL TI C 1 1 W AY 0 15 6 1 Problem 1. For n, an equilateral triangle is divided into n congruent smaller equilateral triangles. Determine
Introduction to Number Theory
 Introduction to Number Theory Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Spring 017 March 7, 017 Contents 10 Pythagorean and Heron triangles 57 10.1 Construction of Pythagorean triangles....................
Introduction to Number Theory Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Spring 017 March 7, 017 Contents 10 Pythagorean and Heron triangles 57 10.1 Construction of Pythagorean triangles....................
OLYMON. Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Issue 9:4.
 OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Please send your solution to Ms. Valeria Pandelieva 64 Kirkwood Avenue Ottawa, ON KZ
OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Please send your solution to Ms. Valeria Pandelieva 64 Kirkwood Avenue Ottawa, ON KZ
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY. Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice a prime.
 PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
45-th Moldova Mathematical Olympiad 2001
 45-th Moldova Mathematical Olympiad 200 Final Round Chişinǎu, March 2 Grade 7. Prove that y 3 2x+ x 3 2y x 2 + y 2 for any numbers x,y [, 2 3 ]. When does equality occur? 2. Let S(n) denote the sum of
45-th Moldova Mathematical Olympiad 200 Final Round Chişinǎu, March 2 Grade 7. Prove that y 3 2x+ x 3 2y x 2 + y 2 for any numbers x,y [, 2 3 ]. When does equality occur? 2. Let S(n) denote the sum of
COT 2104 Homework Assignment 1 (Answers)
 1) Classify true or false COT 2104 Homework Assignment 1 (Answers) a) 4 2 + 2 and 7 < 50. False because one of the two statements is false. b) 4 = 2 + 2 7 < 50. True because both statements are true. c)
1) Classify true or false COT 2104 Homework Assignment 1 (Answers) a) 4 2 + 2 and 7 < 50. False because one of the two statements is false. b) 4 = 2 + 2 7 < 50. True because both statements are true. c)
NOTES ON DIOPHANTINE APPROXIMATION
 NOTES ON DIOPHANTINE APPROXIMATION Jan-Hendrik Evertse January 29, 200 9 p-adic Numbers Literature: N. Koblitz, p-adic Numbers, p-adic Analysis, and Zeta-Functions, 2nd edition, Graduate Texts in Mathematics
NOTES ON DIOPHANTINE APPROXIMATION Jan-Hendrik Evertse January 29, 200 9 p-adic Numbers Literature: N. Koblitz, p-adic Numbers, p-adic Analysis, and Zeta-Functions, 2nd edition, Graduate Texts in Mathematics
Georgia Tech High School Math Competition
 Georgia Tech High School Math Competition Multiple Choice Test February 28, 2015 Each correct answer is worth one point; there is no deduction for incorrect answers. Make sure to enter your ID number on
Georgia Tech High School Math Competition Multiple Choice Test February 28, 2015 Each correct answer is worth one point; there is no deduction for incorrect answers. Make sure to enter your ID number on
UNM - PNM STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST XLVI - SOLUTIONS. February 1, 2014 Second Round Three Hours
 UNM - PNM STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST XLVI - SOLUTIONS February 1, 2014 Second Round Three Hours 1. Four siblings BRYAN, BARRY, SARAH and SHANA are having their names monogrammed on their towels. Different
UNM - PNM STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST XLVI - SOLUTIONS February 1, 2014 Second Round Three Hours 1. Four siblings BRYAN, BARRY, SARAH and SHANA are having their names monogrammed on their towels. Different
N E W S A N D L E T T E R S
 N E W S A N D L E T T E R S 74th Annual William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Editor s Note: Additional solutions will be printed in the Monthly later in the year. PROBLEMS A1. Recall that a regular
N E W S A N D L E T T E R S 74th Annual William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Editor s Note: Additional solutions will be printed in the Monthly later in the year. PROBLEMS A1. Recall that a regular
PRACTICE PROBLEMS: SET 1
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS: SET MATH 437/537: PROF. DRAGOS GHIOCA. Problems Problem. Let a, b N. Show that if gcd(a, b) = lcm[a, b], then a = b. Problem. Let n, k N with n. Prove that (n ) (n k ) if and only if
PRACTICE PROBLEMS: SET MATH 437/537: PROF. DRAGOS GHIOCA. Problems Problem. Let a, b N. Show that if gcd(a, b) = lcm[a, b], then a = b. Problem. Let n, k N with n. Prove that (n ) (n k ) if and only if
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars
 SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
SOLUTIONS EGMO AND UCD ENRICHMENT PROGRAMME IN MATHEMATICS SELECTION TEST 24 FEBRUARY 2018
 SOLUTIONS EGMO AND UCD ENRICHMENT PROGRAMME IN MATHEMATICS SELECTION TEST FEBRUARY 08. In triangle ABC, P is a point on AB, Q is a point on AC and X is the point of intersection of the line segments PC
SOLUTIONS EGMO AND UCD ENRICHMENT PROGRAMME IN MATHEMATICS SELECTION TEST FEBRUARY 08. In triangle ABC, P is a point on AB, Q is a point on AC and X is the point of intersection of the line segments PC
2005 Euclid Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2005 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 19, 2005 Solutions c
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2005 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 19, 2005 Solutions c
34 th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad
 34 th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Determine all composite positive integers n for which it is possible to arrange all divisors of n that are greater than 1 in a circle so that no
34 th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Determine all composite positive integers n for which it is possible to arrange all divisors of n that are greater than 1 in a circle so that no
 UNIT-8 SIMILAR TRIANGLES Geometry is the right foundation of all painting, I have decided to teach its rudiments and principles to all youngsters eager for art. 1. ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled
UNIT-8 SIMILAR TRIANGLES Geometry is the right foundation of all painting, I have decided to teach its rudiments and principles to all youngsters eager for art. 1. ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled
Circles & Interval & Set Notation.notebook. November 16, 2009 CIRCLES. OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form.
 OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form. Write the equation of a circle in standard form given a graph or two points (one being the center). Students will be able to write the domain
OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form. Write the equation of a circle in standard form given a graph or two points (one being the center). Students will be able to write the domain
2015 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 5, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 5, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November
The Advantage Testing Foundation Solutions
 The Advantage Testing Foundation 2016 Problem 1 Let T be a triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. If P is a point in or on T, what is the greatest possible sum of the distances from P to each of the three
The Advantage Testing Foundation 2016 Problem 1 Let T be a triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. If P is a point in or on T, what is the greatest possible sum of the distances from P to each of the three
Winter Mathematical Competition Varna, February, 9-11, 2007
 Winter Mathematical Competition Varna, February, 9-11, 007 Problem 91 (Peter Boyvalenkov) Find all values of the real parameter p such that the equation x + (p + 1)x + p = has two real distinct roots x
Winter Mathematical Competition Varna, February, 9-11, 007 Problem 91 (Peter Boyvalenkov) Find all values of the real parameter p such that the equation x + (p + 1)x + p = has two real distinct roots x
Proof 1: Using only ch. 6 results. Since gcd(a, b) = 1, we have
 Exercise 13. Consider positive integers a, b, and c. (a) Suppose gcd(a, b) = 1. (i) Show that if a divides the product bc, then a must divide c. I give two proofs here, to illustrate the different methods.
Exercise 13. Consider positive integers a, b, and c. (a) Suppose gcd(a, b) = 1. (i) Show that if a divides the product bc, then a must divide c. I give two proofs here, to illustrate the different methods.
Recreational Mathematics
 Recreational Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Summer 2003 Chapters 5 8 Version 030630 Chapter 5 Greatest common divisor 1 gcd(a, b) as an integer combination of
Recreational Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Summer 2003 Chapters 5 8 Version 030630 Chapter 5 Greatest common divisor 1 gcd(a, b) as an integer combination of
Gordon solutions. n=1 1. p n
 Gordon solutions 1. A positive integer is called a palindrome if its base-10 expansion is unchanged when it is reversed. For example, 121 and 7447 are palindromes. Show that if we denote by p n the nth
Gordon solutions 1. A positive integer is called a palindrome if its base-10 expansion is unchanged when it is reversed. For example, 121 and 7447 are palindromes. Show that if we denote by p n the nth
SOLUTIONS, what is the value of f(4)?
 005 Georgia Tech High School Mathematics Competition Junior-Varsity Multiple-Choice Examination Version A Problem : If f(x) = x4 x +x x SOLUTIONS, what is the value of f(4)? (A) 6 (B) 70 (C) 78 (D) 8 (E)
005 Georgia Tech High School Mathematics Competition Junior-Varsity Multiple-Choice Examination Version A Problem : If f(x) = x4 x +x x SOLUTIONS, what is the value of f(4)? (A) 6 (B) 70 (C) 78 (D) 8 (E)
a + b = b + a and a b = b a. (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) and (a b) c = a (b c). a (b + c) = a b + a c and (a + b) c = a c + b c.
 Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Lagrange s polynomial
 Lagrange s polynomial Nguyen Trung Tuan November 16, 2016 Abstract In this article, I will use Lagrange polynomial to solve some problems from Mathematical Olympiads. Contents 1 Lagrange s interpolation
Lagrange s polynomial Nguyen Trung Tuan November 16, 2016 Abstract In this article, I will use Lagrange polynomial to solve some problems from Mathematical Olympiads. Contents 1 Lagrange s interpolation
Properties of the Integers
 Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Pythagoras = $1 million problem. Ken Ono Emory University
 Pythagoras = $1 million problem Ken Ono Emory University Pythagoras The Pythagorean Theorem Theorem (Pythagoras) If (a, b, c) is a right triangle, then a 2 + b 2 = c 2. Pythagoras The Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagoras = $1 million problem Ken Ono Emory University Pythagoras The Pythagorean Theorem Theorem (Pythagoras) If (a, b, c) is a right triangle, then a 2 + b 2 = c 2. Pythagoras The Pythagorean Theorem
