Work. Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d
|
|
|
- Erik Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENERGY CHAPTER 11
2 Work Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d Units = Joules Work and energy transferred are equivalent in ideal systems.
3 Two Types of Energy Energy WRT position is called: Potential Energy or ( P.E. ). When an object is in motion, the mass has: Kinetic Energy or ( K.E. ).
4 Potential Energy and Base Levels A change in P.E. is always measured WRT some arbitrary position where the P.E. is defined as 0 J. An object in a high position can do work if it falls to a lower position.
5 The object has stored energy. Gravitational P.E. PE = W = Fd PE = PE F -PE I PE F -PE I = Fd Since the object is falling, it is changing heights. d = h PE F -PE I = F h
6 PE F -PE I = mg h = mg( h f -h i ) W = PE F -PE I = mg( h f -h i ) If PE I is assumed to be 0 J at h i, then: PE = mgh
7 (IC#1) A 10 kg block is lifted at a constant velocity from the floor to a shelf that is 3.0 meters off the ground by a forklift. A. What is the change in PE?
8 PE F 3 m PE 10 kg PE I PE F -PE I = mg( h f -h i ) PE = 10 kg ( 9.8 m ) 3 m PE = PE F = mgh f s 2 = 294 J
9 B. How much energy would be released if the block fell off the shelf? 10 kg PE I 3 m PE F PE = mg( h f -h i )
10 PE = mg( h f -h i ) PE = 10 kg ( 9.8 m ) - 3 m s 2 PE = -294 J Means energy was given off. 294 J of work could be done.
11 Kinetic Energy K.E. is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its motion.
12 F f F A ΣF X = F net = F A + F f If µ = 0, then F f = 0 N and F net = F A F net cause accelerations. F net = ma
13 If F net acts over a given distance: F net d = mad V f2 = V i2 + 2Ad Ad = V f2 -V2 i 2 F net d = m (V f2 -V i2 ) 2 W = F net d = 1mV 2-1mV f i 2 2 2
14 KE at any given time: KE = 1mV 2 2 KE depends on two things: Mass in kg Velocity in m/s W = F net d = KE f -KE i = KE
15 (IC#2) A 10 kg block is sliding at 50 m/s. A. What is the KE of the block? KE = 1mV 2 2 KE = 10 kg ( 50 m/s ) 2 2 KE = J
16 B. If the block slows to 30 m/s, what is the change in KE? KE = KE f -KE i KE = 1mV f 2-1mV i = 10 kg (30 m/s) 2-10 kg (50 m/s) Lost KE KE = J
17 C. If the block was slowed over a 35 meter distance, what was the force of friction? KE = F net d J = F net (35 m) F net = N Opposes motion
18 F f F A F X = F net = F A + F f F net = - F f N = - F f F f = N
19 D. How much work could be done by allowing the block to slow to a stop? W = KE = KE f -KE i = 10 kg (0 m/s) 2-10 kg (50 m/s) KE = J Energy lost translates to work that can be done.
20 (IC#2**) A 1400 kg car, starting from rest, has a net force of 4500 N applied to it. The car travels 100 meters. A. How much work was done on the car? W = F net d W = 4500 N ( 100 m) W = 4.5 X 10 5 J
21 B. What is the KE of the car at the 100 meter mark? W = KE = KE f -KE i W = KE 100m = 4.5 X 10 5 J
22 C. What is the velocity of the car at the 100 meter mark? KE = 1mV 2 2 V = 2 KE m V f = 2 (4.5 X 10 5 J ) 1400 kg V f = 25.4 m/s
23 Conservation of Energy Energy of an isolated system can t change unless work is done on it by an outside force... or the system does work on something outside the system. Energy can t be created or destroyed.
24 PE i + KE i = PE f + KE f mgh i + (1/2)mV i2 =mgh f + (1/2)mV f 2 As an object rises or falls, a tradeoff between PE and KE occurs. This energy tradeoff can be utilized to do work.
25 Energy Energy conserved. leaves system.
26
27 (IC#3) A 100 kg diver jumps off a 30 meter platform during the Olympic games. A. What is the PE and KE at this point?
28 PE = mgh PE i = 100 kg ( 9.8 m ) 30 m s 2 PE i = J KE i = 0 J Diver not moving.
29 B. The diver falls freely for 10 meters. What is the PE and KE at this point? PE i + KE i = PE f + KE f
30 PE f PE f = mgh f = 100 kg ( 9.8 m ) 20 m s 2 PE f = J J = J + KE f KE f = 9800 J
31 Note: How fast was the diver falling at this point? KE f = 9800 J KE = 1mV 2 2 V f = 14 m/s V f = 2 ( 9800 J ) 100 kg
32 C. The diver falls freely for another 5.0 m. What is the PE and KE at this point? PE i + KE i = PE f + KE f
33 PE f PE f = mgh f = 100 kg ( 9.8 m ) 15 m s 2 PE f = J J = J + KE f KE f = J
34 D. What is the PE and KE when the diver hits the water? PE i + KE i = PE f + KE f PE f = mgh f = 0 J
35 PE i = KE f J = KE f E. How fast is the diver moving as he hits the water? V f = 2 ( J ) 100 kg V f = 24.2 m/s
36
37 F PE i + KE i = PE f + KE f (IC#4) A 0.5 kg baseball is thrown straight up. A. If 500 J of work was done on the ball, how high will the ball go? KE i = PE f I
38 What provided the KE I? The 500 J of work that was done on the ball. 500 J = PE f 500 J = mgh f 500 J =.5 kg ( 9.8 m ) h f s 2 h f = 102 m
39 B. What was the velocity of the ball as it left the throwers hand? 500 J = KE KE = 1mV2 i J = (.5 kg )V i 2 2 V i = 44.7 m/s
40 Non Conservative and Conservative Forces If an object changes KE, it is changing velocity. Therefore, it is accelerating. The object had to have a F net exerted on it over a distance. F net d = KE
41 Looking closer at F net : F f F A F X = F net = F A + F f
42 In the case of an airplane, F net d can also cause a PE. F net d = KE + PE ( F A -F f ) d = KE + PE F A d - F f d = KE + PE W = F d W = W f + KE + PE
43 (IC#6) An airplane has a mass of kg and is moving at 60 m/s. The pilot revs the engine so that the forward thrust becomes N. If the force of air resistance on the plane is N, what is the speed of the plane after it has traveled 500 meters?
44 W = W f + KE + PE F A d = F f d +.5 m ( V f2 -V i2 ) + No change in elevation. mg( h f - h i ) 7.5 x 10 4 N ( 500 m ) = 4 x 10 4 N ( 500 m ) +.5 ( 1.5 x 10 4 kg ) [ V f2 -( 60 m/s ) 2 ] V f = 77 m/s
45 (IC#8) A N car is traveling at 100 m/s due east. Suddenly, the car slams into a N truck traveling at 50 m/s due west. A. What is the KE of the car before the collision? KE = 1mV 2 2
46 KE car = 1 ( N )( 100 m ) m s 2 s KE car = 1.02 x 10 7 J
47 B. What is the KE of the truck before the collision? KE truck = 1 ( N )( - 50 m ) m s 2 s Opposite direction KE truck = 2.55 x 10 7 J
48 C. What is the total KE before the collision? KE car = 1.02 x 10 7 J + KE truck = 2.55 x 10 7 J KE total = 3.57 x 10 7 J
49 D. If the collision is inelastic, what is the velocity of the car after the collision? P car + P truck = P car&truck 2041 kg (100 m/s) kg (-50m/s) = kg ( V car&truck ) V car&truck = m/s
50 E. What is the KE after the collision? KE total = 1 ( kg )( m ) 2 2 s KE total = x 10 7 J
51 F. What is the change in KE? Why is there a change? KE = x 10 7 J x 10 7 J KE = x 10 7 J Most energy is converted to heat and a small amount in the form of sound.
52 (IC#10) When a long barreled rifle is fired, the force of the expanding gases acts on the bullet through a longer distance. What effect does this have on the velocity of the emerging bullet? 1. More work is done on the bullet because the force acts over a longer distance.
53 2. Since more work is done on the bullet, there is a greater change in KE. 3. Since the mass of the bullet is constant, the change in KE is caused by an increased velocity.
54 The End
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Essentially, the amount of work accomplished can be determined two ways:
 1 Work and Energy Work is done on an object that can exert a resisting force and is only accomplished if that object will move. In particular, we can describe work done by a specific object (where a force
1 Work and Energy Work is done on an object that can exert a resisting force and is only accomplished if that object will move. In particular, we can describe work done by a specific object (where a force
Ch 11 ENERGY and its CONSERVATION. work causes a change in the energy of a system KE (an increase or decrease in KE) ket.
 Ch 11 ENERGY and its CONSERVATION 11.1 The Many Forms of Energy work causes a change in the energy of a system W = KE (an increase or decrease in KE) work energy theorem object + work object work increase
Ch 11 ENERGY and its CONSERVATION 11.1 The Many Forms of Energy work causes a change in the energy of a system W = KE (an increase or decrease in KE) work energy theorem object + work object work increase
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
This chapter covers all kinds of problems having to do with work in physics terms. Work
 Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
HNRS 227 Chapter 3. Energy presented by Prof. Geller Fall 2008
 HNRS 227 Chapter 3 Energy presented by Prof. Geller Fall 2008 Don t Forget the Following Units of length, mass and time Metric Prefixes The Scientific Method Speed, velocity, acceleration Force Falling
HNRS 227 Chapter 3 Energy presented by Prof. Geller Fall 2008 Don t Forget the Following Units of length, mass and time Metric Prefixes The Scientific Method Speed, velocity, acceleration Force Falling
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY. Chapter 6 (cont.)
 KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
Motion. Argument: (i) Forces are needed to keep things moving, because they stop when the forces are taken away (evidence horse pulling a carriage).
 1 Motion Aristotle s Study Aristotle s Law of Motion This law of motion was based on false assumptions. He believed that an object moved only if something was pushing it. His arguments were based on everyday
1 Motion Aristotle s Study Aristotle s Law of Motion This law of motion was based on false assumptions. He believed that an object moved only if something was pushing it. His arguments were based on everyday
Motion, Forces, and Energy
 Motion, Forces, and Energy What is motion? Motion - when an object changes position Types of Motion There are 2 ways of describing motion: Distance Displacement Distance Distance is the total path traveled.
Motion, Forces, and Energy What is motion? Motion - when an object changes position Types of Motion There are 2 ways of describing motion: Distance Displacement Distance Distance is the total path traveled.
WORK, POWER & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
Energy "is an abstract concept invented by scientists in the nineteenth century to describe quantitatively a wide variety of natural phenomena.
 Energy Energy "is an abstract concept invented by scientists in the nineteenth century to describe quantitatively a wide variety of natural phenomena." David Rose What is energy? Energy makes changes;
Energy Energy "is an abstract concept invented by scientists in the nineteenth century to describe quantitatively a wide variety of natural phenomena." David Rose What is energy? Energy makes changes;
Name. Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL KINETIC
 KINETIC Name Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL Name Period Work and Energy Intro questions Read chapter 9 pages 144 146 (Section 9.1) 1. Define work in terms of physics? 2. In order to do work on an object,
KINETIC Name Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL Name Period Work and Energy Intro questions Read chapter 9 pages 144 146 (Section 9.1) 1. Define work in terms of physics? 2. In order to do work on an object,
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B km C. 25 km D. 45 km E. 50 km
 Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
Momentum Practice Problems
 Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum Conceptual Questions. 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity?
 AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
Review. Kinetic Energy Work Hooke s s Law Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Power 1/91
 Review Kinetic Energy Work Hooke s s Law Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Power 1/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton B. Watt C. Joule D. Meter E. Second 2/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton
Review Kinetic Energy Work Hooke s s Law Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Power 1/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton B. Watt C. Joule D. Meter E. Second 2/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton
= 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ. T.E. initial. = T.E. Final. = P.E. final. + K.E. initial. + P.E. initial. K.E. initial =
 Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
velocity, force and momentum are vectors, therefore direction matters!!!!!!!
 1 Momentum, p is mass times velocity: p = m v vector! unit: (p) = kg m/s Newton s second law: Force = time rate of change of momentum Net force F will produce change in momentum Δp of the object on which
1 Momentum, p is mass times velocity: p = m v vector! unit: (p) = kg m/s Newton s second law: Force = time rate of change of momentum Net force F will produce change in momentum Δp of the object on which
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Work. The quantity of work done is equal to the amount of force the distance moved in the direction in which the force acts.
 Work The quantity of work done is equal to the amount of force the distance moved in the direction in which the force acts. Work falls into two categories: Work falls into two categories: work done against
Work The quantity of work done is equal to the amount of force the distance moved in the direction in which the force acts. Work falls into two categories: Work falls into two categories: work done against
Impulse/Momentum And Its Conservation
 Impulse/Momentum And Its Conservation Which is easier to stop? Truck, car, bowling ball, or baseball all moving at 30 mph. Baseball -it is the least massive. Baseball at 30 mph or a baseball at 90 mph.
Impulse/Momentum And Its Conservation Which is easier to stop? Truck, car, bowling ball, or baseball all moving at 30 mph. Baseball -it is the least massive. Baseball at 30 mph or a baseball at 90 mph.
l Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an
 Motion and Machine Unit Notes DO NOT LOSE! Name: Energy Ability to do work To cause something to change move or directions Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but transferred from one form to another.
Motion and Machine Unit Notes DO NOT LOSE! Name: Energy Ability to do work To cause something to change move or directions Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but transferred from one form to another.
2. What would happen to his acceleration if his speed were half? Energy The ability to do work
 1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
Forces & Newton s Laws. Honors Physics
 Forces & Newton s Laws Honors Physics Newton s 1 st Law An object in motion stays in motion, and an object at rest stays at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts on it. An object will maintain a constant
Forces & Newton s Laws Honors Physics Newton s 1 st Law An object in motion stays in motion, and an object at rest stays at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts on it. An object will maintain a constant
Pre Comp Review Questions 7 th Grade
 Pre Comp Review Questions 7 th Grade Section 1 Units 1. Fill in the missing SI and English Units Measurement SI Unit SI Symbol English Unit English Symbol Time second s second s. Temperature Kelvin K Fahrenheit
Pre Comp Review Questions 7 th Grade Section 1 Units 1. Fill in the missing SI and English Units Measurement SI Unit SI Symbol English Unit English Symbol Time second s second s. Temperature Kelvin K Fahrenheit
What is Energy? Which has more energy? Who has more energy? 1/24/2017
 What is Energy? Energy is a measure of an object s ability to cause a change in itself and/or its surroundings Read pages 61-7 Which has more energy? Who has more energy? Mississippi River Cargo Barge
What is Energy? Energy is a measure of an object s ability to cause a change in itself and/or its surroundings Read pages 61-7 Which has more energy? Who has more energy? Mississippi River Cargo Barge
Chapter 4 Newton s Laws
 Chapter 4 Newton s Laws Isaac Newton 1642-1727 Some inventions and discoveries: 3 laws of motion Universal law of gravity Calculus Ideas on: Sound Light Thermodynamics Reflecting telescope In this chapter,
Chapter 4 Newton s Laws Isaac Newton 1642-1727 Some inventions and discoveries: 3 laws of motion Universal law of gravity Calculus Ideas on: Sound Light Thermodynamics Reflecting telescope In this chapter,
Efficiency = power out x 100% power in
 Work, Energy and Power Review Package 1) Work: change in energy. Measured in Joules, J. W = Fd W = ΔE Work is scalar, but can be negative. To remember this, ask yourself either: Is the object is losing
Work, Energy and Power Review Package 1) Work: change in energy. Measured in Joules, J. W = Fd W = ΔE Work is scalar, but can be negative. To remember this, ask yourself either: Is the object is losing
*************************************************************************
 Your Name: TEST #2 Print clearly. On the Scantron, fill out your student ID, leaving the first column empty and starting in the second column. Also write your name, class time (11:30 or 12:30), and Test
Your Name: TEST #2 Print clearly. On the Scantron, fill out your student ID, leaving the first column empty and starting in the second column. Also write your name, class time (11:30 or 12:30), and Test
Mechanics. Time (s) Distance (m) Velocity (m/s) Acceleration (m/s 2 ) = + displacement/time.
 Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Momentum. Impulse = F t. Impulse Changes Momentum
 Momentum and Energy Chapter 3 Momentum Momentum is inertia in motion Mass x velocity Has both magnitude and direction Large mass or high speed can give object great amount of momentum Momentum = m v Change
Momentum and Energy Chapter 3 Momentum Momentum is inertia in motion Mass x velocity Has both magnitude and direction Large mass or high speed can give object great amount of momentum Momentum = m v Change
Scaler Quantity (definition and examples) Average speed. (definition and examples)
 Newton s First Law Newton s Second Law Newton s Third Law Vector Quantity Scaler Quantity (definition and examples) Average speed (definition and examples) Instantaneous speed Acceleration An object at
Newton s First Law Newton s Second Law Newton s Third Law Vector Quantity Scaler Quantity (definition and examples) Average speed (definition and examples) Instantaneous speed Acceleration An object at
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy. No Recitation Quiz this week
 Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
AP Physics C. Momentum. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
Which iceboat crosses the finish line with more kinetic energy (KE)?
 Two iceboats (one of mass m, one of mass 2m) hold a race on a frictionless, horizontal, frozen lake. Both iceboats start at rest, and the wind exerts the same constant force on both iceboats. Which iceboat
Two iceboats (one of mass m, one of mass 2m) hold a race on a frictionless, horizontal, frozen lake. Both iceboats start at rest, and the wind exerts the same constant force on both iceboats. Which iceboat
Mechanical Energy. Unit 4
 Mechanical Energy Unit 4 Expectations Cell phones put away, or upside down on your desk No talking during notes Raise your hand to ask a question Everyone will follow along and copy into their own notes
Mechanical Energy Unit 4 Expectations Cell phones put away, or upside down on your desk No talking during notes Raise your hand to ask a question Everyone will follow along and copy into their own notes
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation
 Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
Kinetic Energy. energy! l The kinetic energy of an object depends both on the mass of an object and its speed
 l 1 more day for LON-CAPA #4 l First exam: Feb 6 in Life Sciences A133 1:00 2:20 PM 40 questions, should not take full time review in 2 nd half of this lecture you may bring 1 8.5 X11 sheet of paper with
l 1 more day for LON-CAPA #4 l First exam: Feb 6 in Life Sciences A133 1:00 2:20 PM 40 questions, should not take full time review in 2 nd half of this lecture you may bring 1 8.5 X11 sheet of paper with
Momentum and Energy. Chapter 3
 Momentum and Energy Chapter 3 Momentum Momentum is inertia in motion Mass x velocity Has both magnitude and direction Large mass or high speed can give object great amount of momentum Momentum = m v Change
Momentum and Energy Chapter 3 Momentum Momentum is inertia in motion Mass x velocity Has both magnitude and direction Large mass or high speed can give object great amount of momentum Momentum = m v Change
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I
 PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
Unit 2- Energy and Momentum Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Unit 2- Energy and Momentum Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Unit 2- Energy and Momentum Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
Physical Science (SCI101) Final Exam
 Department of Mathematics and General Sciences Final Exam Second Semester, Term 132 Date: Wednesday 28/5/2014 Name: ID number: Section number or time: Instructor s name: Important instructions: 1. Examination
Department of Mathematics and General Sciences Final Exam Second Semester, Term 132 Date: Wednesday 28/5/2014 Name: ID number: Section number or time: Instructor s name: Important instructions: 1. Examination
Potential and Kinetic Energy
 Potential and Kinetic Energy 1 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is a system? 3 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 A system is an object or a group of objects.
Potential and Kinetic Energy 1 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is a system? 3 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 A system is an object or a group of objects.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PH105-007 Exam 2 VERSION A Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 1.0-kg block and a 2.0-kg block are pressed together on a horizontal
PH105-007 Exam 2 VERSION A Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 1.0-kg block and a 2.0-kg block are pressed together on a horizontal
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME:
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
PSI AP Physics B Dynamics
 PSI AP Physics B Dynamics Multiple-Choice questions 1. After firing a cannon ball, the cannon moves in the opposite direction from the ball. This an example of: A. Newton s First Law B. Newton s Second
PSI AP Physics B Dynamics Multiple-Choice questions 1. After firing a cannon ball, the cannon moves in the opposite direction from the ball. This an example of: A. Newton s First Law B. Newton s Second
PS 300 extra credit for exam 1 (5% max) due 2/13/18
 PS 300 extra credit for exam 1 (5% max) due 2/13/18 Name: 1. Name three physical properties that describes an object: mass, temperature, density, volume. 2. What is the mass of gasoline (ρ = 0.680 g/cm
PS 300 extra credit for exam 1 (5% max) due 2/13/18 Name: 1. Name three physical properties that describes an object: mass, temperature, density, volume. 2. What is the mass of gasoline (ρ = 0.680 g/cm
In this lecture we will discuss three topics: conservation of energy, friction, and uniform circular motion.
 1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 9 MECHANICS (8) In this lecture we will discuss three topics: conservation of energy, friction, and uniform circular motion. 9 1. Conservation of Energy. Energy is one of the most fundamental
1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 9 MECHANICS (8) In this lecture we will discuss three topics: conservation of energy, friction, and uniform circular motion. 9 1. Conservation of Energy. Energy is one of the most fundamental
WORK, POWER AND ENERGY
 WORK, POWER AND ENERGY Important Points:. Dot Product: a) Scalar product is defined as the product of the magnitudes of two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. The dot product of two vectors
WORK, POWER AND ENERGY Important Points:. Dot Product: a) Scalar product is defined as the product of the magnitudes of two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. The dot product of two vectors
NCERT solution for Work and energy
 1 NCERT solution for Work and energy Question 1 A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (See below figure). Let us take it that the force acts on the
1 NCERT solution for Work and energy Question 1 A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (See below figure). Let us take it that the force acts on the
Work Done by a Constant Force
 Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work scalar W = F S Cosθ Unit of work in SI system Work done by a constant force
 WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work Let a force be applied on a body so that the body gets displaced. Then work is said to be done. So work is said to be done if the point of application of force gets displaced.
WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work Let a force be applied on a body so that the body gets displaced. Then work is said to be done. So work is said to be done if the point of application of force gets displaced.
Physics Semester 1 Review
 Physics Semester 1 Review Name: 1. Define: Speed Velocity Acceleration Use the graph to the right to answer questions 2-4. 2. How far did the object travel in 3 seconds? 3. How long did it take for the
Physics Semester 1 Review Name: 1. Define: Speed Velocity Acceleration Use the graph to the right to answer questions 2-4. 2. How far did the object travel in 3 seconds? 3. How long did it take for the
Physics 101: Lecture 9 Work and Kinetic Energy
 Exam II Physics 101: Lecture 9 Work and Kinetic Energy Today s lecture will be on Textbook Sections 6.1-6.4 Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 1 Forms Energy Kinetic Energy Motion (Today) Potential Energy Stored
Exam II Physics 101: Lecture 9 Work and Kinetic Energy Today s lecture will be on Textbook Sections 6.1-6.4 Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 1 Forms Energy Kinetic Energy Motion (Today) Potential Energy Stored
Momentum. Momentum. Momentum Momentum = mass velocity or Momentum = mass speed (when direction is unimportant) Momentum = mv. Impulse.
 Momentum Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 4 MOMENTUM AND ENERGY Momentum is inertia in motion defined as the product of mass and velocity: momentum: p = mv Momentum Momentum
Momentum Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 4 MOMENTUM AND ENERGY Momentum is inertia in motion defined as the product of mass and velocity: momentum: p = mv Momentum Momentum
Physics 11 Review Questions
 Physics 11 Review Questions Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled by the
Physics 11 Review Questions Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled by the
Page 1. Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is A) 34 m B) 30.
 Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Lecture Notes (Work & Energy)
 Lecture Notes (Work & Energy) Intro: - one of the most central concepts in science is energy; the combination energy and matter makes up our universe - matter is the substance of the universe, while energy
Lecture Notes (Work & Energy) Intro: - one of the most central concepts in science is energy; the combination energy and matter makes up our universe - matter is the substance of the universe, while energy
Energy Conservation AP
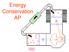 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Lectures Chapter 6 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition)
 PH 201-4A spring 2007 Work and Energy Lectures 16-17 Chapter 6 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 Work and Energy: Work done by a constant force Constant pushing force F pointing in the same direction
PH 201-4A spring 2007 Work and Energy Lectures 16-17 Chapter 6 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 Work and Energy: Work done by a constant force Constant pushing force F pointing in the same direction
PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam
 South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
4.) A baseball that weighs 1.6 N leaves a bat with a speed of 40.0 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball. 130 J
 AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
Slide 1 / A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? 10 km 22.5 km 25 km 45 km 50 km
 Slide 1 / 96 1 train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? 10 km 22.5 km 25 km 45 km 50 km Slide 2 / 96 2 bicyclist moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s. How long it will
Slide 1 / 96 1 train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? 10 km 22.5 km 25 km 45 km 50 km Slide 2 / 96 2 bicyclist moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s. How long it will
A. true. 6. An object is in motion when
 1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
An Introduction. Work
 Work and Energy An Introduction Work Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). W = F Dr
Work and Energy An Introduction Work Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). W = F Dr
An object moves back and forth, as shown in the position-time graph. At which points is the velocity positive?
 1 The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the instantaneous velocity 2 The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: displacement from the original position to its position
1 The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the instantaneous velocity 2 The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: displacement from the original position to its position
Motion and Forces study Guide
 Motion and Forces study Guide Completion Complete each statement. 1. The motion of an object looks different to observers in different. 2. The SI unit for measuring is the meter. 3. The direction and length
Motion and Forces study Guide Completion Complete each statement. 1. The motion of an object looks different to observers in different. 2. The SI unit for measuring is the meter. 3. The direction and length
AQA Physics P2 Topic 1. Motion
 AQA Physics P2 Topic 1 Motion Distance / Time graphs Horizontal lines mean the object is stationary. Straight sloping lines mean the object is travelling at a constant speed. The steeper the slope, the
AQA Physics P2 Topic 1 Motion Distance / Time graphs Horizontal lines mean the object is stationary. Straight sloping lines mean the object is travelling at a constant speed. The steeper the slope, the
Chapter 10: Energy and Work. Slide 10-2
 Chapter 10: Energy and Work Slide 10-2 Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy K U g U s Thermal Energy Other forms include E th E chem E nuclear The Basic Energy Model An exchange of energy between the system
Chapter 10: Energy and Work Slide 10-2 Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy K U g U s Thermal Energy Other forms include E th E chem E nuclear The Basic Energy Model An exchange of energy between the system
MOTION & FORCES. Observing Motion. Speed and Velocity. Distance vs. Displacement CHAPTERS 11 & 12
 Observing Motion CHAPTERS 11 & 12 MOTION & FORCES Everything surrounding us is in motion, but it is relative to other object that remain in place. Motion is observed using a frame of reference. Motion
Observing Motion CHAPTERS 11 & 12 MOTION & FORCES Everything surrounding us is in motion, but it is relative to other object that remain in place. Motion is observed using a frame of reference. Motion
Foundations of Physical Science. Unit 2: Work and Energy
 Foundations of Physical Science Unit 2: Work and Energy Chapter 5: Work, Energy, and Power 5.1 Work 5.2 Energy Conservation 5.3 Energy Transformations Learning Goals Calculate the amount of work done by
Foundations of Physical Science Unit 2: Work and Energy Chapter 5: Work, Energy, and Power 5.1 Work 5.2 Energy Conservation 5.3 Energy Transformations Learning Goals Calculate the amount of work done by
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
W = Fd cos θ. W = (75.0 N)(25.0 m) cos (35.0º) = 1536 J = J. W 2400 kcal =
 8 CHAPTER 7 WORK, ENERGY, AND ENERGY RESOURCES generator does negative work on the briefcase, thus removing energy from it. The drawing shows the latter, with the force from the generator upward on the
8 CHAPTER 7 WORK, ENERGY, AND ENERGY RESOURCES generator does negative work on the briefcase, thus removing energy from it. The drawing shows the latter, with the force from the generator upward on the
A scalar quantity has just magnitude A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction
 Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Exam 2--PHYS 101--F17
 Name: Exam 2--PHYS 0--F7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A ball is thrown in the air at an angle of 30 to the ground, with an initial speed
Name: Exam 2--PHYS 0--F7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A ball is thrown in the air at an angle of 30 to the ground, with an initial speed
Physics-MC Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1.
 Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Friction and losses. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment 6/5/14. Define friction and provide examples. Solve problems involving friction.
 Friction and losses Objectives Define friction and provide examples. Solve problems involving friction. Calculate the efficiency of a system. 1. Which of these events does NOT involve the force of friction?
Friction and losses Objectives Define friction and provide examples. Solve problems involving friction. Calculate the efficiency of a system. 1. Which of these events does NOT involve the force of friction?
Broughton High School of Wake County
 Name: Section: 1 Section 1: Which picture describes Newton s Laws of Motion? 5. Newton s Law 1. Newton s Law 2. Newton s Law 6. Newton s Law 3. Newton s Law 7. Newton s Law 4. Newton s Law 8. Newton s
Name: Section: 1 Section 1: Which picture describes Newton s Laws of Motion? 5. Newton s Law 1. Newton s Law 2. Newton s Law 6. Newton s Law 3. Newton s Law 7. Newton s Law 4. Newton s Law 8. Newton s
Work and Energy Energy Conservation
 Work and Energy Energy Conservation MidterM 1 statistics Mean = 16.48 Average = 2.74 2 Clicker Question #5 Rocket Science!!! The major principle of rocket propulsion is: a) Conservation of energy b) Conservation
Work and Energy Energy Conservation MidterM 1 statistics Mean = 16.48 Average = 2.74 2 Clicker Question #5 Rocket Science!!! The major principle of rocket propulsion is: a) Conservation of energy b) Conservation
Physics 23 Exam 2 March 3, 2009
 Use the following to answer question 1: A stationary 4-kg shell explodes into three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third
Use the following to answer question 1: A stationary 4-kg shell explodes into three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Clicker Question 4.3 A mass at rest on a ramp. How does the friction between the mass and the table know how much force will EXACTLY balance the gravity
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Clicker Question 4.3 A mass at rest on a ramp. How does the friction between the mass and the table know how much force will EXACTLY balance the gravity
1 kg. 10,000 kg. 1 Page. Momentum is a vector so it has a magnitude and a velocity. Its magnitude is the product of its mass and velocity, p = mv.
 Momentum The momentum of a single object is simply equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. The symbol for momentum is p. Since mass is a scalar and velocity is a vector, momentum is also a vector.
Momentum The momentum of a single object is simply equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. The symbol for momentum is p. Since mass is a scalar and velocity is a vector, momentum is also a vector.
UNIT 4 MOMENTUM & IMPULSE
 UNIT 4 UNIT 4 MOMENTUM & IMPULSE IMPULSE-MOMENTUM THEOREM Remember, means final initial p = p f p i v = v f v i J = F( t) = p = m v = (mv f mv i ) The impulse, J, that acts on an object is equal to the
UNIT 4 UNIT 4 MOMENTUM & IMPULSE IMPULSE-MOMENTUM THEOREM Remember, means final initial p = p f p i v = v f v i J = F( t) = p = m v = (mv f mv i ) The impulse, J, that acts on an object is equal to the
Unit Assessment: Relationship Between Force, Motion, and Energy
 Assessment Unit Assessment: Relationship Between Force, Motion, and Energy Instructions Check your understanding with this assessment. 1) Lifting a 20,000 N anvil one meter requires 20,000 joules (newtons/meter).
Assessment Unit Assessment: Relationship Between Force, Motion, and Energy Instructions Check your understanding with this assessment. 1) Lifting a 20,000 N anvil one meter requires 20,000 joules (newtons/meter).
Review Energy and Momentum a. a. b. b. c a. b. 4. c a. a. b. 6. b.
 Review 6 Energy and Momentum 1. A player pushes a 250 g hockey puck over frictionless ice with a constant force, causing it to accelerate at 24 m/s 2 over a distance of 50 cm. a. Find the work done by
Review 6 Energy and Momentum 1. A player pushes a 250 g hockey puck over frictionless ice with a constant force, causing it to accelerate at 24 m/s 2 over a distance of 50 cm. a. Find the work done by
RELEASED. Go to next page. 2. The graph shows the acceleration of a car over time.
 1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
s_3x03 Page 1 Physics Samples
 Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Clicker Question: Momentum. If the earth collided with a meteor that slowed it down in its orbit, what would happen: continued from last time
 Momentum continued from last time If the earth collided with a meteor that slowed it down in its orbit, what would happen: A: It would maintain the same distance from the sun. B: It would fall closer in
Momentum continued from last time If the earth collided with a meteor that slowed it down in its orbit, what would happen: A: It would maintain the same distance from the sun. B: It would fall closer in
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts
 Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
2009 A-level Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved
 2 This book is under copyright to A-level Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents Newton s Laws 3 connected particles 9 work & energy 18 power &
2 This book is under copyright to A-level Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents Newton s Laws 3 connected particles 9 work & energy 18 power &
Lecture 7 Chapter 7 Work Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 7 Chapter 7 Work Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy -- The money of physics Demo: Elastic Collisions Objects of equal mass exchange momentum in elastic collisions. 1 Demo: Blaster Balls
Lecture 7 Chapter 7 Work Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy -- The money of physics Demo: Elastic Collisions Objects of equal mass exchange momentum in elastic collisions. 1 Demo: Blaster Balls
Chapter 4 Conservation Laws
 Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 4 Conservation Laws Section Review 4.1 1. List three action and reaction pairs in the picture at right, on page 82 in text. a. Force of paddle on water, and
Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 4 Conservation Laws Section Review 4.1 1. List three action and reaction pairs in the picture at right, on page 82 in text. a. Force of paddle on water, and
This Week. 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall
 This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
