ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-01
|
|
|
- Delilah Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-01 Probability Decision trees θ 1 u 1 α 1 θ 2 u 2 Decision α 2 θ 1 u 3 Actions Chance nodes States of nature θ 2 u 4 Consequences; utility Which action will be taken is a decision completely controlled by the user. Which state of nature will occur is beyond the user s control. Example 3.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ 1 = cold u 3 = brrr! α 2 don t wear coat u 4 = best of θ 2 = warm! all worlds!
2 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-02 The decision depends on the assessment of the probabilities of the states of nature and on the values of the utilities. Example 3.02 (platform for oil & gas development) Fixed platform Floating platform few Icebergs many Icebergs C O N S E Q U E N C E S This was one of the factors in the design decisions for the Hibernia and Terra Nova oil fields. Example 3.03 Investment High return u 1 Buy stocks Low return u 2 Buy bonds Safe known return u 3 The decision here depends not only on the average return but also on one s tolerance for risk. Risk aversion is a real life factor that we will not have the time to explore in this course.
3 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-03 Fair bet Example 3.04 A client gives a $100 reward iff (if and only if) the contractor s circuit board passes a reliability test. The contractor must pay a non-refundable deposit of $100p with the bid. What is a fair price for the deposit? Let E = (the event that the circuit board passes the test) and E ~ = ~E = not-e = (the event that the circuit board fails the test) then E ~ is known as the complementary event to E. Reward Let E = 1 represent E is true E 100 and E = 0 represent E is false then E + E = 1 Pay 100p E ~ 0 Decision tree: p = deposit reward Pay 0 0 The contractor has a free choice: to take the contract or not. If the contract is taken (= upper branches of decision tree): (Gain if E ~ ) = 100p (Gain if E) = 100p = 100(1 p) = 100 p Therefore Gain = 100p + 100E where E is random, (= 0 or 1; E is a Bernoulli random quantity). If the contract is not taken (= lowest branch of decision tree): Gain 0 A fair bet indifference between decisions 100p + 100E 0 Gain > 0 : too generous to contractor Gain < 0 : contract too expensive But gain is a random quantity
4 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-04 Balance of Judgement: [Simple mechanics can provide analogies for much of probability theory] Gain if E Loss if E ~ = 100 (1 p) = 100 p P[E] P[E ~ ] The bet is fair iff gain and loss balance: Taking moments: 100 (1 p) P[E] = 100 p P[ E ~ ] But E ~ = 1 E and P[ E ~ ] = 1 P[E] (1 p + p) P[E] = p Therefore the fair price for the bid deposit occurs when and the fair price is (deposit) = (contract reward) P[E]. p = P[E] Example 3.04 (continued) Suppose that past experience suggests that E occurs 24% of the time. Then we estimate that P[E] =.24 and the fair bid is = $24. Odds Let s be the reward at stake in the contract (= $100 in example 3.04). The odds on E occurring are the ratio r, where r = ~ loss if E gain if E = s s p = P[ E] ~ p ~ ( 1 p ) P[ E] p 1 p = = p P [ E] r = r + 1 In example 3.04, p.24 6 r = = = = 19 to 6 against (or 6 to 19 on, but usually larger # first) 1 p r and r = p = = = = = r
5 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-05 Even odds r = 1:1 p = ½ = 50% Odds on when p >.5, Odds against when p <.5. Incoherence: Suppose that no more than one of the events {E 1, E 2,..., E n } can occur. Then the events are incompatible (= mutually exclusive). If the events {E 1, E 2,..., E n } are such that they exhaust all possibilities, (so that at least one of them must occur), then the events are exhaustive. If the events {E 1, E 2,..., E n } are both incompatible and exhaustive, (so that exactly one of them must occur), then they form a partition, and Example 3.05 E 1 + E E n = 1 A bookmaker accepts bets on a partition { E i }. You place a non-refundable deposit (a bet) p i s i on E i occurring. The bookie pays a stake s i to you (but still retains your deposit) if E i occurs. If E i does not occur, then you lose your deposit p i s i. Assume that one bet is placed on each one of the events { E i }. The bookie s gain if E h is true is (gain) = (revenue) (payout) n gh = pisi sh (for h = 1, 2,..., n) i = 1 The bookie can arrange { p i } such that g h > 0 unfair bet! (= incoherence) Suppose s i = s i (for all values of i), then n gh = s p i = 1 i 1 A fair bet is then assured if the probabilities are then coherent. (for h = 1, 2,..., n) n p i = 1 (total probability theorem); i = 1
6 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-06 A More General Case of Example 3.05: An operator accepts deposits on a partition { E i }. k i people each place a non-refundable deposit p i s i on E i occurring. Note that p i is a measure of the likelihood of E i occurring. (The more likely E i is, the greater the deposit that the operator will require). If E i occurs, then the operator pays a stake s i to each of the k i contractors, (but still retains all of the deposits). If E i does not occur, then each of the k i contractors loses the deposit p i s i. The operator s gain if E h is true is (gain) = (revenue) (payout) n i i i h h (for h = 1, 2,..., n) i = 1 gh = k p s k s Now assume a more common situation, not of equal stakes, but of equal deposits: p 1 s 1 = p 2 s 2 =... = p n s n = b Then g h n b = b ki kh p i = 1 h (for h = 1, 2,..., n) The number p h is a measure of how likely the gain g h is to occur. Therefore use p h as a weighting factor, to arrive at an expected gain: n n n 1 E[ ] h h b p h k G = p g = i kh h = 1 h = 1 i = 1 p h n n n n n b k i p h k h b k i p = = i 1 i= 1 h= 1 h= 1 i= 1 i= 1 E[G] = 0 if and only if n p i i = 1 = 1 Notation: A B = events A and B both occur; A B = A B = A B A B = event A or B (or both) occurs; (but A B A + B unless A, B are incompatible)
7 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-07 Some definitions: Experiment = process leading to a single outcome Sample point (= simple event) = one possible outcome (which precludes all other outcomes) Event E = set of related sample points Possibility Space = universal set = Sample Space S = { all possible outcomes of an experiment } By the definition of S, any event E is a subset of S : E S Classical definition of probability (when sample points are equally likely): n( E) P[ E ] =, n( S) where n(e) = the number of [equally likely] sample points inside the event E. More generally, the probability of an event E can be calculated as the sum of the probabilities of all of the sample points included in that event: Empirical definition of probability: P[E] = Σ P[X] (summed over all sample points X in E.) P[E] = (limit as # exp ts of) { relative frequency of E } Example 3.06 (illustrating the evolution of relative frequency with an ever increasing number of trials): or import the following macro into a MINITAB session:
8 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-08 Example 3.07: rolling a standard fair die. The sample space is S = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 } n(s) = 6 (the sample points are equally likely) P[1] = 1/6 = P[2] = P[3] =... P[S] = 1 (S is absolutely certain) The empty set (= null set) = Ø = {} [Note: this is not { 0 }!] P[Ø] = 0 (Ø is absolutely impossible) The complement of a set A is A' (or A ~, A*, A c, NOT A, ~A, A ). n(~a ) = n(s) n(a) and P[~A ] = 1! P[A] The union A B = (A OR B) = A B
9 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-09 The intersection A B = (A AND B) = A B = A B = A B For any set or event E : Ø E = E E ~E = Ø E = E ~E = S S E = S ~(~E ) = E S E = E ~Ø = S The set B is a subset of the set P : B P. Read the symbol " " as "is contained entirely inside" If it is also true that P B, then P = B (the two sets are identical). If B P, B /= P and B /= Ø, then B P (B is a proper subset of the set P). B P = B For any set or event E : Ø E S B P = P Also: B ~P =
10 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-10 Example 3.08 Examples of Venn diagrams: 1. Events A and B both occur. 2. Event A occurs but event C does not. A B A C ' 3. At least two of events 4. Neither B nor C occur. A, B and C occur. (AB) (BC) (CA) ~B ~C = ~(B C)
11 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-11 Example above is an example of DeMorgan s Laws: ~(A B) = A B neither A nor B ~(A B) = A B not both A and B General Addition Law of Probability P[A B] = x + y + z P[A] = x + y P[B] = y + z P[A B] = y Extended to three events, this law becomes P[A B] = P[A] + P[B]! P[A B] P[A B C] = P[A] + P[B] + P[C] P[A B] P[B C] P[C A] + P[A B C]
12 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-12 If two events A and B are mutually exclusive (= incompatible = have no common sample points), then A B = Ø P[A B] = 0 and the addition law simplifies to P[A B] = P[A] + P[B]. Only when A and B are mutually exclusive may one say A B = A + B. Total Probability Law The total probability of an event A can be partitioned into two mutually exclusive subsets: the part of A that is inside another event B and the part that is outside B : P[A] = P[A B] + P[A ~B] Special case, when A = S and B = E: P[S] = P[S E] + P[S ~E] 1 = P[E] + P[ ~E] Example 3.09 Given the information that P[ABC] = 2%, P[AB] = 7%, P[AC] = 5% and P[A] = 26%, find the probability that, (of events A,B,C), only event A occurs. A only = AB'C' We know the intersection probabilities, therefore we start at the centre and work our way out. The sum of the probabilities in the three lens regions illustrated is =.10. The required probability is in the remaining one region of A and is =.16. On the next page is a more systematic way to solve this example.
13 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-13 [Example 3.09 continued] P[AB] =.07 = x +.02 x =.05 P[AC] =.05 = y +.02 y =.03 P[A] =.26 = z P[AB'C' ] = z = =.16 Alternatively, P[AB'C' ] = P[A] P[AB] P[AC] + P[ABC] = =.16 If the information had been provided in the form of unions instead of intersections, then we would have started at the outside of the Venn diagram and worked our way in, using demorgan s laws and the general addition law where necessary. [End of Section 3]
14 ENGI 3423 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 3-14 [Space for additional notes]
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page α 2 θ 1 u 3. wear coat. θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ 1 = cold u 3 = brrr!
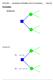 ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
Chapter 1 (Basic Probability)
 Chapter 1 (Basic Probability) What is probability? Consider the following experiments: 1. Count the number of arrival requests to a web server in a day. 2. Determine the execution time of a program. 3.
Chapter 1 (Basic Probability) What is probability? Consider the following experiments: 1. Count the number of arrival requests to a web server in a day. 2. Determine the execution time of a program. 3.
Review Basic Probability Concept
 Economic Risk and Decision Analysis for Oil and Gas Industry CE81.9008 School of Engineering and Technology Asian Institute of Technology January Semester Presented by Dr. Thitisak Boonpramote Department
Economic Risk and Decision Analysis for Oil and Gas Industry CE81.9008 School of Engineering and Technology Asian Institute of Technology January Semester Presented by Dr. Thitisak Boonpramote Department
18.600: Lecture 3 What is probability?
 18.600: Lecture 3 What is probability? Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws Axioms of probability Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws
18.600: Lecture 3 What is probability? Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws Axioms of probability Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws
Lecture notes for probability. Math 124
 Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes
 Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Lecture Lecture 5
 Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
CIVL 7012/8012. Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability
 CIVL 7012/8012 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
CIVL 7012/8012 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers Dr. Dewei Wang. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers Dr. Dewei Wang Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger 2 Probability CHAPTER OUTLINE 2-1 Sample Spaces and
STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers Dr. Dewei Wang Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger 2 Probability CHAPTER OUTLINE 2-1 Sample Spaces and
Introduction to Probability
 Introduction to Probability Content Experiments, Counting Rules, and Assigning Probabilities Events and Their Probability Some Basic Relationships of Probability Conditional Probability Bayes Theorem 2
Introduction to Probability Content Experiments, Counting Rules, and Assigning Probabilities Events and Their Probability Some Basic Relationships of Probability Conditional Probability Bayes Theorem 2
University of Technology, Building and Construction Engineering Department (Undergraduate study) PROBABILITY THEORY
 ENGIEERING STATISTICS (Lectures) University of Technology, Building and Construction Engineering Department (Undergraduate study) PROBABILITY THEORY Dr. Maan S. Hassan Lecturer: Azhar H. Mahdi Probability
ENGIEERING STATISTICS (Lectures) University of Technology, Building and Construction Engineering Department (Undergraduate study) PROBABILITY THEORY Dr. Maan S. Hassan Lecturer: Azhar H. Mahdi Probability
Origins of Probability Theory
 1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
CIVL Why are we studying probability and statistics? Learning Objectives. Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability
 CIVL 3103 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
CIVL 3103 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes. Set Operations and Relations. Venn Diagram 2.1. Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes
 Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Sixth Edition. Chapter 2 Probability. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Probability
 Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger Chapter 2 Probability 2 Probability CHAPTER OUTLINE 2-1 Sample Spaces and Events 2-1.1 Random Experiments
Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger Chapter 2 Probability 2 Probability CHAPTER OUTLINE 2-1 Sample Spaces and Events 2-1.1 Random Experiments
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability. Elements of Probability. Conditional probability. Sequential Calculation of Probability
 Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
The enumeration of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space, denoted S. E.g.: S={head, tail}
 Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Week 2. Section Texas A& M University. Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019
 Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
EnM Probability and Random Processes
 Historical Note: EnM 503 - Probability and Random Processes Probability has its roots in games of chance, which have been played since prehistoric time. Games and equipment have been found in Egyptian
Historical Note: EnM 503 - Probability and Random Processes Probability has its roots in games of chance, which have been played since prehistoric time. Games and equipment have been found in Egyptian
Probability Theory Review
 Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
4/17/2012. NE ( ) # of ways an event can happen NS ( ) # of events in the sample space
 I. Vocabulary: A. Outcomes: the things that can happen in a probability experiment B. Sample Space (S): all possible outcomes C. Event (E): one outcome D. Probability of an Event (P(E)): the likelihood
I. Vocabulary: A. Outcomes: the things that can happen in a probability experiment B. Sample Space (S): all possible outcomes C. Event (E): one outcome D. Probability of an Event (P(E)): the likelihood
Statistics for Business and Economics
 Statistics for Business and Economics Basic Probability Learning Objectives In this lecture(s), you learn: Basic probability concepts Conditional probability To use Bayes Theorem to revise probabilities
Statistics for Business and Economics Basic Probability Learning Objectives In this lecture(s), you learn: Basic probability concepts Conditional probability To use Bayes Theorem to revise probabilities
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
Announcements. Topics: To Do:
 Announcements Topics: In the Probability and Statistics module: - Sections 1 + 2: Introduction to Stochastic Models - Section 3: Basics of Probability Theory - Section 4: Conditional Probability; Law of
Announcements Topics: In the Probability and Statistics module: - Sections 1 + 2: Introduction to Stochastic Models - Section 3: Basics of Probability Theory - Section 4: Conditional Probability; Law of
Axioms of Probability
 Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Probability Theory and Applications
 Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Math Exam 1 Review. NOTE: For reviews of the other sections on Exam 1, refer to the first page of WIR #1 and #2.
 Math 166 Fall 2008 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 166 - Exam 1 Review NOTE: For reviews of the other sections on Exam 1, refer to the first page of WIR #1 and #2. Section 1.5 - Rules for Probability Elementary
Math 166 Fall 2008 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 166 - Exam 1 Review NOTE: For reviews of the other sections on Exam 1, refer to the first page of WIR #1 and #2. Section 1.5 - Rules for Probability Elementary
Probability the chance that an uncertain event will occur (always between 0 and 1)
 Quantitative Methods 2013 1 Probability as a Numerical Measure of the Likelihood of Occurrence Probability the chance that an uncertain event will occur (always between 0 and 1) Increasing Likelihood of
Quantitative Methods 2013 1 Probability as a Numerical Measure of the Likelihood of Occurrence Probability the chance that an uncertain event will occur (always between 0 and 1) Increasing Likelihood of
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Lecture 1. Chapter 1. (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 ( ). 1. What is Statistics?
 Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
Basic Set Concepts (2.1)
 1 Basic Set Concepts (2.1) I. Set A collection of objects whose contents can be clearly determined. Capitol letters usually name a set. Elements are the contents in a set. Sets can be described using words,
1 Basic Set Concepts (2.1) I. Set A collection of objects whose contents can be clearly determined. Capitol letters usually name a set. Elements are the contents in a set. Sets can be described using words,
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics
 Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Chapter 2 Class Notes
 Chapter 2 Class Notes Probability can be thought of in many ways, for example as a relative frequency of a long series of trials (e.g. flips of a coin or die) Another approach is to let an expert (such
Chapter 2 Class Notes Probability can be thought of in many ways, for example as a relative frequency of a long series of trials (e.g. flips of a coin or die) Another approach is to let an expert (such
Stat 225 Week 1, 8/20/12-8/24/12, Notes: Set Theory
 Stat 225 Week 1, 8/20/12-8/24/12, Notes: Set Theory The Fall 2012 Stat 225 T.A.s September 7, 2012 The material in this handout is intended to cover general set theory topics. Information includes (but
Stat 225 Week 1, 8/20/12-8/24/12, Notes: Set Theory The Fall 2012 Stat 225 T.A.s September 7, 2012 The material in this handout is intended to cover general set theory topics. Information includes (but
Topic 3: Introduction to Probability
 Topic 3: Introduction to Probability 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Simple Definitions 3. Types of Probability 4. Theorems of Probability 5. Probabilities under conditions of statistically independent events
Topic 3: Introduction to Probability 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Simple Definitions 3. Types of Probability 4. Theorems of Probability 5. Probabilities under conditions of statistically independent events
Basic Probabilistic Reasoning SEG
 Basic Probabilistic Reasoning SEG 7450 1 Introduction Reasoning under uncertainty using probability theory Dealing with uncertainty is one of the main advantages of an expert system over a simple decision
Basic Probabilistic Reasoning SEG 7450 1 Introduction Reasoning under uncertainty using probability theory Dealing with uncertainty is one of the main advantages of an expert system over a simple decision
STAT 430/510 Probability
 STAT 430/510 Probability Hui Nie Lecture 3 May 28th, 2009 Review We have discussed counting techniques in Chapter 1. Introduce the concept of the probability of an event. Compute probabilities in certain
STAT 430/510 Probability Hui Nie Lecture 3 May 28th, 2009 Review We have discussed counting techniques in Chapter 1. Introduce the concept of the probability of an event. Compute probabilities in certain
What is Probability? Probability. Sample Spaces and Events. Simple Event
 What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S
 Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events
 Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events Engineering Statistics Section 2.1 Josh Engwer TTU 01 February 2016 Josh Engwer (TTU) Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events 01 February 2016 1 / 29 The Need
Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events Engineering Statistics Section 2.1 Josh Engwer TTU 01 February 2016 Josh Engwer (TTU) Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events 01 February 2016 1 / 29 The Need
Mean, Median and Mode. Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability. Where do they come from? Graphically. We start with a set of 21 numbers, Sta102 / BME102
 Mean, Median and Mode Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability Sta102 / BME102 Colin Rundel September 1, 2014 We start with a set of 21 numbers, ## [1] -2.2-1.6-1.0-0.5-0.4-0.3-0.2 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.4 ## [12] 0.4
Mean, Median and Mode Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability Sta102 / BME102 Colin Rundel September 1, 2014 We start with a set of 21 numbers, ## [1] -2.2-1.6-1.0-0.5-0.4-0.3-0.2 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.4 ## [12] 0.4
I - Probability. What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring. 1classical probability. 2empirical probability. 3subjective probability
 What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
Introduction to Probability
 Introduction to Probability Gambling at its core 16th century Cardano: Books on Games of Chance First systematic treatment of probability 17th century Chevalier de Mere posed a problem to his friend Pascal.
Introduction to Probability Gambling at its core 16th century Cardano: Books on Games of Chance First systematic treatment of probability 17th century Chevalier de Mere posed a problem to his friend Pascal.
P B A. conditional probabilities A B and unconditional probabilities are neither 0 nor 1, this note demonstrates two consequences when
 1 When P P A 1. Introduction Many students encountering probability theory for the first time have difficulty distinguishing conditional probabilities from joint or unconditional probabilities and they
1 When P P A 1. Introduction Many students encountering probability theory for the first time have difficulty distinguishing conditional probabilities from joint or unconditional probabilities and they
2011 Pearson Education, Inc
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Probability. Chapter 1 Probability. A Simple Example. Sample Space and Probability. Sample Space and Event. Sample Space (Two Dice) Probability
 Probability Chapter 1 Probability 1.1 asic Concepts researcher claims that 10% of a large population have disease H. random sample of 100 people is taken from this population and examined. If 20 people
Probability Chapter 1 Probability 1.1 asic Concepts researcher claims that 10% of a large population have disease H. random sample of 100 people is taken from this population and examined. If 20 people
STAT Chapter 3: Probability
 Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel/SPSS Chapter 4 Basic Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions
 Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel/SPSS Chapter 4 Basic Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions 1999 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap. 4-1 Chapter Topics Basic Probability Concepts: Sample
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel/SPSS Chapter 4 Basic Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions 1999 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap. 4-1 Chapter Topics Basic Probability Concepts: Sample
A survey of Probability concepts. Chapter 5
 A survey of Probability concepts Chapter 5 Learning Objectives Define probability. Explain the terms experiment, event, outcome. Define the terms conditional probability and joint probability. Calculate
A survey of Probability concepts Chapter 5 Learning Objectives Define probability. Explain the terms experiment, event, outcome. Define the terms conditional probability and joint probability. Calculate
CS4705. Probability Review and Naïve Bayes. Slides from Dragomir Radev
 CS4705 Probability Review and Naïve Bayes Slides from Dragomir Radev Classification using a Generative Approach Previously on NLP discriminative models P C D here is a line with all the social media posts
CS4705 Probability Review and Naïve Bayes Slides from Dragomir Radev Classification using a Generative Approach Previously on NLP discriminative models P C D here is a line with all the social media posts
Topic 2 Probability. Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability
 Topic 2 Probability Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability Random process: a process whose outcome can not be predicted with certainty Examples: rolling
Topic 2 Probability Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability Random process: a process whose outcome can not be predicted with certainty Examples: rolling
(6, 1), (5, 2), (4, 3), (3, 4), (2, 5), (1, 6)
 Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Section 13.3 Probability
 288 Section 13.3 Probability Probability is a measure of how likely an event will occur. When the weather forecaster says that there will be a 50% chance of rain this afternoon, the probability that it
288 Section 13.3 Probability Probability is a measure of how likely an event will occur. When the weather forecaster says that there will be a 50% chance of rain this afternoon, the probability that it
Exam III Review Math-132 (Sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3)
 1 Exam III Review Math-132 (Sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3) On this exam, questions may come from any of the following topic areas: - Union and intersection of sets - Complement of
1 Exam III Review Math-132 (Sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3) On this exam, questions may come from any of the following topic areas: - Union and intersection of sets - Complement of
Recap. The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY INFERENTIAL STATISTICS
 Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
3.1 Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability
 Chapter 3 Probability Probability is the tool that allows the statistician to use sample information to make inferences about or to describe the population from which the sample was drawn. 3.1 Events,
Chapter 3 Probability Probability is the tool that allows the statistician to use sample information to make inferences about or to describe the population from which the sample was drawn. 3.1 Events,
3 PROBABILITY TOPICS
 Chapter 3 Probability Topics 135 3 PROBABILITY TOPICS Figure 3.1 Meteor showers are rare, but the probability of them occurring can be calculated. (credit: Navicore/flickr) Introduction It is often necessary
Chapter 3 Probability Topics 135 3 PROBABILITY TOPICS Figure 3.1 Meteor showers are rare, but the probability of them occurring can be calculated. (credit: Navicore/flickr) Introduction It is often necessary
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness
 Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chapter. Probability
 Chapter 3 Probability Section 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability Section 3.1 Objectives Identify the sample space of a probability experiment Identify simple events Use the Fundamental Counting Principle
Chapter 3 Probability Section 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability Section 3.1 Objectives Identify the sample space of a probability experiment Identify simple events Use the Fundamental Counting Principle
Example. What is the sample space for flipping a fair coin? Rolling a 6-sided die? Find the event E where E = {x x has exactly one head}
 Chapter 7 Notes 1 (c) Epstein, 2013 CHAPTER 7: PROBABILITY 7.1: Experiments, Sample Spaces and Events Chapter 7 Notes 2 (c) Epstein, 2013 What is the sample space for flipping a fair coin three times?
Chapter 7 Notes 1 (c) Epstein, 2013 CHAPTER 7: PROBABILITY 7.1: Experiments, Sample Spaces and Events Chapter 7 Notes 2 (c) Epstein, 2013 What is the sample space for flipping a fair coin three times?
F71SM STATISTICAL METHODS
 F71SM STATISTICAL METHODS RJG SUMMARY NOTES 2 PROBABILITY 2.1 Introduction A random experiment is an experiment which is repeatable under identical conditions, and for which, at each repetition, the outcome
F71SM STATISTICAL METHODS RJG SUMMARY NOTES 2 PROBABILITY 2.1 Introduction A random experiment is an experiment which is repeatable under identical conditions, and for which, at each repetition, the outcome
Chapter 4 - Introduction to Probability
 Chapter 4 - Introduction to Probability Probability is a numerical measure of the likelihood that an event will occur. Probability values are always assigned on a scale from 0 to 1. A probability near
Chapter 4 - Introduction to Probability Probability is a numerical measure of the likelihood that an event will occur. Probability values are always assigned on a scale from 0 to 1. A probability near
Example: Suppose we toss a quarter and observe whether it falls heads or tails, recording the result as 1 for heads and 0 for tails.
 Example: Suppose we toss a quarter and observe whether it falls heads or tails, recording the result as 1 for heads and 0 for tails. (In Mathematical language, the result of our toss is a random variable,
Example: Suppose we toss a quarter and observe whether it falls heads or tails, recording the result as 1 for heads and 0 for tails. (In Mathematical language, the result of our toss is a random variable,
Introduction to Probability. Experiments. Sample Space. Event. Basic Requirements for Assigning Probabilities. Experiments
 Introduction to Probability Experiments These are processes that generate welldefined outcomes Experiments Counting Rules Combinations Permutations Assigning Probabilities Experiment Experimental Outcomes
Introduction to Probability Experiments These are processes that generate welldefined outcomes Experiments Counting Rules Combinations Permutations Assigning Probabilities Experiment Experimental Outcomes
Probability and Applications
 Chapter 5 Probability and Applications 5.2 SOME USEFUL DEFINITIONS Random experiment: a process that has an unknown outcome or outcomes that are known only after the process is completed. Event: an outcome
Chapter 5 Probability and Applications 5.2 SOME USEFUL DEFINITIONS Random experiment: a process that has an unknown outcome or outcomes that are known only after the process is completed. Event: an outcome
3.2 Probability Rules
 3.2 Probability Rules The idea of probability rests on the fact that chance behavior is predictable in the long run. In the last section, we used simulation to imitate chance behavior. Do we always need
3.2 Probability Rules The idea of probability rests on the fact that chance behavior is predictable in the long run. In the last section, we used simulation to imitate chance behavior. Do we always need
Stats Probability Theory
 Stats 241.3 Probability Theory Instructor: Office: W.H.Laverty 235 McLean Hall Phone: 966-6096 Lectures: Evaluation: M T W Th F 1:30pm - 2:50pm Thorv 105 Lab: T W Th 3:00-3:50 Thorv 105 Assignments, Labs,
Stats 241.3 Probability Theory Instructor: Office: W.H.Laverty 235 McLean Hall Phone: 966-6096 Lectures: Evaluation: M T W Th F 1:30pm - 2:50pm Thorv 105 Lab: T W Th 3:00-3:50 Thorv 105 Assignments, Labs,
Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.)
 Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.) I. Statistical Independence A crucially important idea in probability and statistics is the concept of statistical independence. Suppose
Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.) I. Statistical Independence A crucially important idea in probability and statistics is the concept of statistical independence. Suppose
Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 2: Basic Set Theory March 19 th, 2006
 Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 2: Basic Set Theory March 19 th, 2006 Topics What is a set? Notations for sets Empty set Inclusion/containment and subsets Sample spaces and events Operations
Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 2: Basic Set Theory March 19 th, 2006 Topics What is a set? Notations for sets Empty set Inclusion/containment and subsets Sample spaces and events Operations
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel (3 rd Edition)
 Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel (3 rd Edition) Chapter 4 Basic Probability and Discrete Probability Distributions 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap 4-1 Chapter Topics Basic probability concepts
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel (3 rd Edition) Chapter 4 Basic Probability and Discrete Probability Distributions 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap 4-1 Chapter Topics Basic probability concepts
Probability Theory. Fourier Series and Fourier Transform are widely used techniques to model deterministic signals.
 Probability Theory Introduction Fourier Series Fourier Transform are widely used techniques to model deterministic signals. In a typical communication system, the output of an information source (e.g.
Probability Theory Introduction Fourier Series Fourier Transform are widely used techniques to model deterministic signals. In a typical communication system, the output of an information source (e.g.
A Probability Primer. A random walk down a probabilistic path leading to some stochastic thoughts on chance events and uncertain outcomes.
 A Probability Primer A random walk down a probabilistic path leading to some stochastic thoughts on chance events and uncertain outcomes. Are you holding all the cards?? Random Events A random event, E,
A Probability Primer A random walk down a probabilistic path leading to some stochastic thoughts on chance events and uncertain outcomes. Are you holding all the cards?? Random Events A random event, E,
Probability. 25 th September lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.)
 Probability 25 th September 2017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Properties of Probability Methods of Enumeration Conditional Probability Independent
Probability 25 th September 2017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Properties of Probability Methods of Enumeration Conditional Probability Independent
Probability - Lecture 4
 1 Introduction Probability - Lecture 4 Many methods of computation physics and the comparison of data to a mathematical representation, apply stochastic methods. These ideas were first introduced in the
1 Introduction Probability - Lecture 4 Many methods of computation physics and the comparison of data to a mathematical representation, apply stochastic methods. These ideas were first introduced in the
STA Module 4 Probability Concepts. Rev.F08 1
 STA 2023 Module 4 Probability Concepts Rev.F08 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Compute probabilities for experiments having equally likely outcomes. 2. Interpret
STA 2023 Module 4 Probability Concepts Rev.F08 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Compute probabilities for experiments having equally likely outcomes. 2. Interpret
STOR Lecture 4. Axioms of Probability - II
 STOR 435.001 Lecture 4 Axioms of Probability - II Jan Hannig UNC Chapel Hill 1 / 23 How can we introduce and think of probabilities of events? Natural to think: repeat the experiment n times under same
STOR 435.001 Lecture 4 Axioms of Probability - II Jan Hannig UNC Chapel Hill 1 / 23 How can we introduce and think of probabilities of events? Natural to think: repeat the experiment n times under same
Probability Pearson Education, Inc. Slide
 Probability The study of probability is concerned with random phenomena. Even though we cannot be certain whether a given result will occur, we often can obtain a good measure of its likelihood, or probability.
Probability The study of probability is concerned with random phenomena. Even though we cannot be certain whether a given result will occur, we often can obtain a good measure of its likelihood, or probability.
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS. Dr N A Heard. 1 Sample Spaces and Events Sample Spaces Events Combinations of Events...
 Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
1 Preliminaries Sample Space and Events Interpretation of Probability... 13
 Summer 2017 UAkron Dept. of Stats [3470 : 461/561] Applied Statistics Ch 2: Probability Contents 1 Preliminaries 3 1.1 Sample Space and Events...........................................................
Summer 2017 UAkron Dept. of Stats [3470 : 461/561] Applied Statistics Ch 2: Probability Contents 1 Preliminaries 3 1.1 Sample Space and Events...........................................................
Making Hard Decision. Probability Basics. ENCE 627 Decision Analysis for Engineering
 CHAPTER Duxbury Thomson Learning Making Hard Decision Probability asics Third Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 7b FALL 003 y Dr. Ibrahim. Assakkaf
CHAPTER Duxbury Thomson Learning Making Hard Decision Probability asics Third Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 7b FALL 003 y Dr. Ibrahim. Assakkaf
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Probability. Introduction to Biostatistics
 Introduction to Biostatistics Probability Second Semester 2014/2015 Text Book: Basic Concepts and Methodology for the Health Sciences By Wayne W. Daniel, 10 th edition Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi, BDS, MPH, DrPH
Introduction to Biostatistics Probability Second Semester 2014/2015 Text Book: Basic Concepts and Methodology for the Health Sciences By Wayne W. Daniel, 10 th edition Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi, BDS, MPH, DrPH
Basic Concepts of Probability. Section 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability. Probability Experiments. Chapter 3 Probability
 Chapter 3 Probability 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability 3.2 Conditional Probability and the Multiplication Rule 3.3 The Addition Rule 3.4 Additional Topics in Probability and Counting Section 3.1 Basic
Chapter 3 Probability 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability 3.2 Conditional Probability and the Multiplication Rule 3.3 The Addition Rule 3.4 Additional Topics in Probability and Counting Section 3.1 Basic
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA INTRODUCTION SUBSETS
 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA M. Ragheb 1/294/2018 INTRODUCTION Modern algebra is centered around the concept of an algebraic system: A, consisting of a set of elements: ai, i=1, 2,, which are combined by a set of operations
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA M. Ragheb 1/294/2018 INTRODUCTION Modern algebra is centered around the concept of an algebraic system: A, consisting of a set of elements: ai, i=1, 2,, which are combined by a set of operations
Probability Year 10. Terminology
 Probability Year 10 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
Probability Year 10 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability
 Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
Random Signals and Systems. Chapter 1. Jitendra K Tugnait. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering. James B Davis Professor.
 Random Signals and Systems Chapter 1 Jitendra K Tugnait James B Davis Professor Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University 2 3 Descriptions of Probability Relative frequency approach»
Random Signals and Systems Chapter 1 Jitendra K Tugnait James B Davis Professor Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University 2 3 Descriptions of Probability Relative frequency approach»
Compound Events. The event E = E c (the complement of E) is the event consisting of those outcomes which are not in E.
 Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
LECTURE 1. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
 LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio
 4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
Lecture 2: Probability
 Lecture 2: Probability MSU-STT-351-Sum-17B (P. Vellaisamy: MSU-STT-351-Sum-17B) Probability & Statistics for Engineers 1 / 39 Chance Experiment We discuss in this lecture 1 Random Experiments 2 Sample
Lecture 2: Probability MSU-STT-351-Sum-17B (P. Vellaisamy: MSU-STT-351-Sum-17B) Probability & Statistics for Engineers 1 / 39 Chance Experiment We discuss in this lecture 1 Random Experiments 2 Sample
UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1
 UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1 6.1: Simulation Simulation: The of chance behavior, based on a that accurately reflects the phenomenon under consideration. (ex 1) Suppose we are interested
UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1 6.1: Simulation Simulation: The of chance behavior, based on a that accurately reflects the phenomenon under consideration. (ex 1) Suppose we are interested
If S = {O 1, O 2,, O n }, where O i is the i th elementary outcome, and p i is the probability of the i th elementary outcome, then
 1.1 Probabilities Def n: A random experiment is a process that, when performed, results in one and only one of many observations (or outcomes). The sample space S is the set of all elementary outcomes
1.1 Probabilities Def n: A random experiment is a process that, when performed, results in one and only one of many observations (or outcomes). The sample space S is the set of all elementary outcomes
Some Practice Questions for Test 2
 ENGI 441 Probability and Statistics Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Some Practice Questions for Test 1. The probability mass function for X = the number of major defects in a randomly selected
ENGI 441 Probability and Statistics Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Some Practice Questions for Test 1. The probability mass function for X = the number of major defects in a randomly selected
Topic 4 Probability. Terminology. Sample Space and Event
 Topic 4 Probability The Sample Space is the collection of all possible outcomes Experimental outcome An outcome from a sample space with one characteristic Event May involve two or more outcomes simultaneously
Topic 4 Probability The Sample Space is the collection of all possible outcomes Experimental outcome An outcome from a sample space with one characteristic Event May involve two or more outcomes simultaneously
EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction. About EE178. About Probability. Course Goals. Course Topics. Lecture Notes EE 178
 EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction About EE178 About Probability Course Goals Course Topics Lecture Notes EE 178: Course Introduction Page 0 1 EE 178 EE 178 provides an introduction to probabilistic
EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction About EE178 About Probability Course Goals Course Topics Lecture Notes EE 178: Course Introduction Page 0 1 EE 178 EE 178 provides an introduction to probabilistic
MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Recommendations: 1. Take the Final Practice Exam and take note of questions 2. Use this study guide as you take the tests and cross off what you know well 3. Take the Practice
MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Recommendations: 1. Take the Final Practice Exam and take note of questions 2. Use this study guide as you take the tests and cross off what you know well 3. Take the Practice
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15. Lecture 2: Random Experiments. Prof. Vince Calhoun
 ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
Name: Exam 2 Solutions. March 13, 2017
 Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 00 Finite Math Spring 07 Name: Instructors: Conant/Galvin Exam Solutions March, 07 This exam is in two parts on pages and contains problems worth
Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 00 Finite Math Spring 07 Name: Instructors: Conant/Galvin Exam Solutions March, 07 This exam is in two parts on pages and contains problems worth
