Lecture notes for probability. Math 124
|
|
|
- Spencer Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture notes for probability Math 124
2 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result is not deterministic. An experiment is an activity whose results can be observed and recorded. Each of the possible results of an experiment is an outcome. A set of all possible outcomes for an experiment is a sample space. The outcomes in the sample space cannot overlap. Any subset of a sample space is an event. We typically find probabilities, or likelihood, of events.
3 Examples A possible experiment is tossing a coin. The outcomes for this experiment are: heads (H) and tails (T). The sample space for the experiment will consist of these two outcomes: S = {H, T }. Another possible experiment is tossing a die. The sample space for this experiment is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. A possible event would be tossing an even number, A = {2, 4, 6}. Another possible event is tossing a number bigger than 4, B = {5, 6}.
4 What is experimental probability?
5 What is experimental probability? The experimental probability of an event is the relative frequency with which it occurs in an experiment.
6 What is experimental probability? The experimental probability of an event is the relative frequency with which it occurs in an experiment. For example, if you toss a coin 50 times and heads comes up 22 times, the experimental probability of tossing heads is 22/50 or 44%.
7 What is theoretical probability?
8 What is theoretical probability? While experimental probability shows what actually happened, theoretical probability predicts what should happen.
9 What is theoretical probability? While experimental probability shows what actually happened, theoretical probability predicts what should happen. For an experiment with non-empty sample space S with equally likely outcomes, the probability of an event A is given by P(A) = Number of elements of A Number of elements of S = n(a) n(s). Note that this only works if the outcomes are equally likely.
10 What is theoretical probability? While experimental probability shows what actually happened, theoretical probability predicts what should happen. For an experiment with non-empty sample space S with equally likely outcomes, the probability of an event A is given by P(A) = Number of elements of A Number of elements of S = n(a) n(s). Note that this only works if the outcomes are equally likely. There are many situations in which it is impossible to find theoretical probability. For example, to find the likelihood that you will be hit by lightning, you would have to know how frequently people are hit by lightning. On the other hand, the probability of winning the lottery is purely theoretical.
11 What is the experimental probability of getting a sum of seven, based on your recorded data from the game?
12 What is the experimental probability of getting a sum of seven, based on your recorded data from the game? Answers will vary. I rolled some virtual dice, and I got the sum of seven, 7/30 of the time.
13 What is the theoretical probability of getting a sum of seven?
14 What is the theoretical probability of getting a sum of seven? It may appear that all sums are equally likely. This is not the case. There are six ways to get a sum of 7, so the theoretical probability is 6/36=1/6.
15 For some event, when both its experimental probability and theoretical probability are possible to determine, will the two probabilities be equal?
16 For some event, when both its experimental probability and theoretical probability are possible to determine, will the two probabilities be equal? Probabilities only suggest what will happen in the long run. This concept is called The Law of Large Numbers or sometimes Bernoulli s Theorem: If an experiment is repeated a large number of times, the experimental probability of a particular outcome approaches its theoretical probability as the number of repetitions increases.
17 For some event, when both its experimental probability and theoretical probability are possible to determine, will the two probabilities be equal? Probabilities only suggest what will happen in the long run. This concept is called The Law of Large Numbers or sometimes Bernoulli s Theorem: If an experiment is repeated a large number of times, the experimental probability of a particular outcome approaches its theoretical probability as the number of repetitions increases. That means that maybe you got a sum of 7 more often than any other sum in your game, but maybe you did not. But if we all played the game for three hours and put all our data together, we could be almost certain that the experimental probability of rolling a 7 would be close to 1/6.
18 Gambling The Law of Large Numbers works in favor of casinos. Though one or two patrons may have a running streak, in the long run the casino always wins, because all games have a higher probability of losing than winning.
19 Why is a probability limited to numbers between, and including, 0 and 1? When is it 0? When is it 1?
20 Why is a probability limited to numbers between, and including, 0 and 1? When is it 0? When is it 1? An event that has no outcomes is an impossible event and has probability 0. If event B is the empty set, then it has no elements and its probability is the ratio P(B) = 0 n(s). For example, the event of rolling a sum larger than 12 with two dice has probability 0.
21 Why is a probability limited to numbers between, and including, 0 and 1? When is it 0? When is it 1? An event that has no outcomes is an impossible event and has probability 0. If event B is the empty set, then it has no elements and its probability is the ratio P(B) = 0 n(s). For example, the event of rolling a sum larger than 12 with two dice has probability 0. An event that has probability 1 is a certain event. If A is a subset of the sample space S, the greatest number of elements that A can have is the number of elements in the sample space, S. So the probability of A in this case would be P(A) = n(a) n(s) = n(s) n(s) = 1.
22 Why is a probability limited to numbers between, and including, 0 and 1? When is it 0? When is it 1? An event that has no outcomes is an impossible event and has probability 0. If event B is the empty set, then it has no elements and its probability is the ratio P(B) = 0 n(s). For example, the event of rolling a sum larger than 12 with two dice has probability 0. An event that has probability 1 is a certain event. If A is a subset of the sample space S, the greatest number of elements that A can have is the number of elements in the sample space, S. So the probability of A in this case would be P(A) = n(a) n(s) = n(s) n(s) = 1. For any set A that is a proper subset of S, n(a) is greater than or equal to 0 but less than n(s), so the probability of A is between 0 and 1.
23 Suppose you calculate the probability of each possible outcome of an experiment, and add these probabilities. What should the sum be?
24 Suppose you calculate the probability of each possible outcome of an experiment, and add these probabilities. What should the sum be? The probability of an event is equal to the sum of the probabilities of disjoint events whose union is the event.
25 Suppose you calculate the probability of each possible outcome of an experiment, and add these probabilities. What should the sum be? The probability of an event is equal to the sum of the probabilities of disjoint events whose union is the event. For example, the probabilities of rolling 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 with a die are all equal to 1/6. When you add them up, you get 1.
26 Suppose the probability of an event A is 2/3. What is the probability of event A not occurring?
27 Suppose the probability of an event A is 2/3. What is the probability of event A not occurring? Two events are mutually exclusive if they can t both happen at the same time. For example, you can roll an odd and even number at the same time.
28 Suppose the probability of an event A is 2/3. What is the probability of event A not occurring? Two events are mutually exclusive if they can t both happen at the same time. For example, you can roll an odd and even number at the same time. Two mutually exclusive events whose union is the sample space are complementary events. If A is an event, the complement of A, written A (or A C ), is also an event. If A is an event and A is its complement, then P( A) = 1 P(A).
29 Suppose the probability of an event A is 2/3. What is the probability of event A not occurring? Two events are mutually exclusive if they can t both happen at the same time. For example, you can roll an odd and even number at the same time. Two mutually exclusive events whose union is the sample space are complementary events. If A is an event, the complement of A, written A (or A C ), is also an event. If A is an event and A is its complement, then P( A) = 1 P(A). The probability of A not occurring in the example above is 1/3.
30 So what about the two-dice game? There is no one best strategy, especially since theoretical probability does not guarantee that what we predict to happen will actually happen. However, it is wisest to put more counters on the more likely numbers, for example, three counters on 7, two counters on 6 and 8, and 1 counter each on 4, 5, 9, and 10.
The enumeration of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space, denoted S. E.g.: S={head, tail}
 Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces
 Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces At the end of this recording, you should be able to define and use the basic terminology used in defining experiments. Terminology The next main topic in
Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces At the end of this recording, you should be able to define and use the basic terminology used in defining experiments. Terminology The next main topic in
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio
 4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
Probability Theory and Applications
 Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Lecture 3 Probability Basics
 Lecture 3 Probability Basics Thais Paiva STA 111 - Summer 2013 Term II July 3, 2013 Lecture Plan 1 Definitions of probability 2 Rules of probability 3 Conditional probability What is Probability? Probability
Lecture 3 Probability Basics Thais Paiva STA 111 - Summer 2013 Term II July 3, 2013 Lecture Plan 1 Definitions of probability 2 Rules of probability 3 Conditional probability What is Probability? Probability
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 19. Probabilities. CS 441 Discrete mathematics for CS. Probabilities
 CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 19 Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Experiment: a procedure that yields one of the possible outcomes Sample space: a set of possible outcomes
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 19 Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Experiment: a procedure that yields one of the possible outcomes Sample space: a set of possible outcomes
AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2
 AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2 Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Friday April 10, 2015 Probability: Introduction Probability:
AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2 Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Friday April 10, 2015 Probability: Introduction Probability:
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
Introduction to Probability
 Introduction to Probability Gambling at its core 16th century Cardano: Books on Games of Chance First systematic treatment of probability 17th century Chevalier de Mere posed a problem to his friend Pascal.
Introduction to Probability Gambling at its core 16th century Cardano: Books on Games of Chance First systematic treatment of probability 17th century Chevalier de Mere posed a problem to his friend Pascal.
Week 2. Section Texas A& M University. Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019
 Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
Chapter 2: Probability Part 1
 Engineering Probability & Statistics (AGE 1150) Chapter 2: Probability Part 1 Dr. O. Phillips Agboola Sample Space (S) Experiment: is some procedure (or process) that we do and it results in an outcome.
Engineering Probability & Statistics (AGE 1150) Chapter 2: Probability Part 1 Dr. O. Phillips Agboola Sample Space (S) Experiment: is some procedure (or process) that we do and it results in an outcome.
Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes
 Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Topic 5 Basics of Probability
 Topic 5 Basics of Probability Equally Likely Outcomes and the Axioms of Probability 1 / 13 Outline Equally Likely Outcomes Axioms of Probability Consequences of the Axioms 2 / 13 Introduction A probability
Topic 5 Basics of Probability Equally Likely Outcomes and the Axioms of Probability 1 / 13 Outline Equally Likely Outcomes Axioms of Probability Consequences of the Axioms 2 / 13 Introduction A probability
Probability Rules. MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics
 Probability Rules MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Introduction Probability is a measure of the likelihood of the occurrence of a certain behavior
Probability Rules MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Introduction Probability is a measure of the likelihood of the occurrence of a certain behavior
Presentation on Theo e ry r y o f P r P o r bab a il i i l t i y
 Presentation on Theory of Probability Meaning of Probability: Chance of occurrence of any event In practical life we come across situation where the result are uncertain Theory of probability was originated
Presentation on Theory of Probability Meaning of Probability: Chance of occurrence of any event In practical life we come across situation where the result are uncertain Theory of probability was originated
Chapter 2. Probability. Math 371. University of Hawai i at Mānoa. Summer 2011
 Chapter 2 Probability Math 371 University of Hawai i at Mānoa Summer 2011 W. DeMeo (williamdemeo@gmail.com) Chapter 2: Probability math.hawaii.edu/ williamdemeo 1 / 8 Outline 1 Chapter 2 Examples Definition
Chapter 2 Probability Math 371 University of Hawai i at Mānoa Summer 2011 W. DeMeo (williamdemeo@gmail.com) Chapter 2: Probability math.hawaii.edu/ williamdemeo 1 / 8 Outline 1 Chapter 2 Examples Definition
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14 Introduction One of the key properties of coin flips is independence: if you flip a fair coin ten times and get ten
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14 Introduction One of the key properties of coin flips is independence: if you flip a fair coin ten times and get ten
I - Probability. What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring. 1classical probability. 2empirical probability. 3subjective probability
 What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness
 Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics
 Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Monty Hall Puzzle. Draw a tree diagram of possible choices (a possibility tree ) One for each strategy switch or no-switch
 Monty Hall Puzzle Example: You are asked to select one of the three doors to open. There is a large prize behind one of the doors and if you select that door, you win the prize. After you select a door,
Monty Hall Puzzle Example: You are asked to select one of the three doors to open. There is a large prize behind one of the doors and if you select that door, you win the prize. After you select a door,
Chapter 7 Wednesday, May 26th
 Chapter 7 Wednesday, May 26 th Random event A random event is an event that the outcome is unpredictable. Example: There are 45 students in this class. What is the probability that if I select one student,
Chapter 7 Wednesday, May 26 th Random event A random event is an event that the outcome is unpredictable. Example: There are 45 students in this class. What is the probability that if I select one student,
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Probability Pearson Education, Inc. Slide
 Probability The study of probability is concerned with random phenomena. Even though we cannot be certain whether a given result will occur, we often can obtain a good measure of its likelihood, or probability.
Probability The study of probability is concerned with random phenomena. Even though we cannot be certain whether a given result will occur, we often can obtain a good measure of its likelihood, or probability.
(6, 1), (5, 2), (4, 3), (3, 4), (2, 5), (1, 6)
 Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Mathematics. ( : Focus on free Education) (Chapter 16) (Probability) (Class XI) Exercise 16.2
 ( : Focus on free Education) Exercise 16.2 Question 1: A die is rolled. Let E be the event die shows 4 and F be the event die shows even number. Are E and F mutually exclusive? Answer 1: When a die is
( : Focus on free Education) Exercise 16.2 Question 1: A die is rolled. Let E be the event die shows 4 and F be the event die shows even number. Are E and F mutually exclusive? Answer 1: When a die is
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of
 Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Probability Year 10. Terminology
 Probability Year 10 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
Probability Year 10 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
2011 Pearson Education, Inc
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Recap. The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY INFERENTIAL STATISTICS
 Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
Recitation 2: Probability
 Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Probability Year 9. Terminology
 Probability Year 9 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
Probability Year 9 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
Lecture 1. Chapter 1. (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 ( ). 1. What is Statistics?
 Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
1 The Basic Counting Principles
 1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
HW2 Solutions, for MATH441, STAT461, STAT561, due September 9th
 HW2 Solutions, for MATH44, STAT46, STAT56, due September 9th. You flip a coin until you get tails. Describe the sample space. How many points are in the sample space? The sample space consists of sequences
HW2 Solutions, for MATH44, STAT46, STAT56, due September 9th. You flip a coin until you get tails. Describe the sample space. How many points are in the sample space? The sample space consists of sequences
Lecture Lecture 5
 Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
CSC Discrete Math I, Spring Discrete Probability
 CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Discrete Probability Probability of an Event Pierre-Simon Laplace s classical theory of probability: Definition of terms: An experiment is a procedure that yields
CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Discrete Probability Probability of an Event Pierre-Simon Laplace s classical theory of probability: Definition of terms: An experiment is a procedure that yields
1. When applied to an affected person, the test comes up positive in 90% of cases, and negative in 10% (these are called false negatives ).
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2006 Vazirani Lecture 8 Conditional Probability A pharmaceutical company is marketing a new test for a certain medical condition. According to clinical trials,
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2006 Vazirani Lecture 8 Conditional Probability A pharmaceutical company is marketing a new test for a certain medical condition. According to clinical trials,
LECTURE 1. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
 LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
Properties of Probability
 Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Compound Events. The event E = E c (the complement of E) is the event consisting of those outcomes which are not in E.
 Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Probabilities and Expectations
 Probabilities and Expectations Ashique Rupam Mahmood September 9, 2015 Probabilities tell us about the likelihood of an event in numbers. If an event is certain to occur, such as sunrise, probability of
Probabilities and Expectations Ashique Rupam Mahmood September 9, 2015 Probabilities tell us about the likelihood of an event in numbers. If an event is certain to occur, such as sunrise, probability of
The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that the event will occur.
 Chapter 5 This chapter introduces probability to quantify randomness. Section 5.1: How Can Probability Quantify Randomness? The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that
Chapter 5 This chapter introduces probability to quantify randomness. Section 5.1: How Can Probability Quantify Randomness? The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that
Lecture 8: Probability
 Lecture 8: Probability The idea of probability is well-known The flipping of a balanced coin can produce one of two outcomes: T (tail) and H (head) and the symmetry between the two outcomes means, of course,
Lecture 8: Probability The idea of probability is well-known The flipping of a balanced coin can produce one of two outcomes: T (tail) and H (head) and the symmetry between the two outcomes means, of course,
Chapter 1 (Basic Probability)
 Chapter 1 (Basic Probability) What is probability? Consider the following experiments: 1. Count the number of arrival requests to a web server in a day. 2. Determine the execution time of a program. 3.
Chapter 1 (Basic Probability) What is probability? Consider the following experiments: 1. Count the number of arrival requests to a web server in a day. 2. Determine the execution time of a program. 3.
Example 1. The sample space of an experiment where we flip a pair of coins is denoted by:
 Chapter 8 Probability 8. Preliminaries Definition (Sample Space). A Sample Space, Ω, is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment. Such a sample space is considered discrete if Ω has finite cardinality.
Chapter 8 Probability 8. Preliminaries Definition (Sample Space). A Sample Space, Ω, is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment. Such a sample space is considered discrete if Ω has finite cardinality.
Chapter 7: Section 7-1 Probability Theory and Counting Principles
 Chapter 7: Section 7-1 Probability Theory and Counting Principles D. S. Malik Creighton University, Omaha, NE D. S. Malik Creighton University, Omaha, NE Chapter () 7: Section 7-1 Probability Theory and
Chapter 7: Section 7-1 Probability Theory and Counting Principles D. S. Malik Creighton University, Omaha, NE D. S. Malik Creighton University, Omaha, NE Chapter () 7: Section 7-1 Probability Theory and
Axioms of Probability
 Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Probability deals with modeling of random phenomena (phenomena or experiments whose outcomes may vary)
 Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability How to measure a likelihood of an event? How likely is it to answer correctly one out of two true-false questions on a quiz? Is it more, less, or equally likely
Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability How to measure a likelihood of an event? How likely is it to answer correctly one out of two true-false questions on a quiz? Is it more, less, or equally likely
Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.)
 Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.) I. Statistical Independence A crucially important idea in probability and statistics is the concept of statistical independence. Suppose
Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.) I. Statistical Independence A crucially important idea in probability and statistics is the concept of statistical independence. Suppose
STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS
 STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS CHAPTER 5 Probability Theory - science of uncertainty 5.1 Probability Basics Equal-Likelihood Model Suppose an experiment has N possible outcomes, all equally likely. Then
STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS CHAPTER 5 Probability Theory - science of uncertainty 5.1 Probability Basics Equal-Likelihood Model Suppose an experiment has N possible outcomes, all equally likely. Then
Probability. VCE Maths Methods - Unit 2 - Probability
 Probability Probability Tree diagrams La ice diagrams Venn diagrams Karnough maps Probability tables Union & intersection rules Conditional probability Markov chains 1 Probability Probability is the mathematics
Probability Probability Tree diagrams La ice diagrams Venn diagrams Karnough maps Probability tables Union & intersection rules Conditional probability Markov chains 1 Probability Probability is the mathematics
Lecture 3. Probability and elements of combinatorics
 Introduction to theory of probability and statistics Lecture 3. Probability and elements of combinatorics prof. dr hab.inż. Katarzyna Zakrzewska Katedra Elektroniki, AGH e-mail: zak@agh.edu.pl http://home.agh.edu.pl/~zak
Introduction to theory of probability and statistics Lecture 3. Probability and elements of combinatorics prof. dr hab.inż. Katarzyna Zakrzewska Katedra Elektroniki, AGH e-mail: zak@agh.edu.pl http://home.agh.edu.pl/~zak
Lecture 15. DATA 8 Spring Sampling. Slides created by John DeNero and Ani Adhikari
 DATA 8 Spring 2018 Lecture 15 Sampling Slides created by John DeNero (denero@berkeley.edu) and Ani Adhikari (adhikari@berkeley.edu) Announcements Probability Basics Lowest value: 0 Chance of event that
DATA 8 Spring 2018 Lecture 15 Sampling Slides created by John DeNero (denero@berkeley.edu) and Ani Adhikari (adhikari@berkeley.edu) Announcements Probability Basics Lowest value: 0 Chance of event that
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
STAT Chapter 3: Probability
 Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
Section 13.3 Probability
 288 Section 13.3 Probability Probability is a measure of how likely an event will occur. When the weather forecaster says that there will be a 50% chance of rain this afternoon, the probability that it
288 Section 13.3 Probability Probability is a measure of how likely an event will occur. When the weather forecaster says that there will be a 50% chance of rain this afternoon, the probability that it
Math 493 Final Exam December 01
 Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
Stats Probability Theory
 Stats 241.3 Probability Theory Instructor: Office: W.H.Laverty 235 McLean Hall Phone: 966-6096 Lectures: Evaluation: M T W Th F 1:30pm - 2:50pm Thorv 105 Lab: T W Th 3:00-3:50 Thorv 105 Assignments, Labs,
Stats 241.3 Probability Theory Instructor: Office: W.H.Laverty 235 McLean Hall Phone: 966-6096 Lectures: Evaluation: M T W Th F 1:30pm - 2:50pm Thorv 105 Lab: T W Th 3:00-3:50 Thorv 105 Assignments, Labs,
Topic -2. Probability. Larson & Farber, Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World, 3e 1
 Topic -2 Probability Larson & Farber, Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World, 3e 1 Probability Experiments Experiment : An experiment is an act that can be repeated under given condition. Rolling a
Topic -2 Probability Larson & Farber, Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World, 3e 1 Probability Experiments Experiment : An experiment is an act that can be repeated under given condition. Rolling a
Lecture 1. ABC of Probability
 Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 1. ABC of Probability January 16, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 1 January 16, 2013 1 / 9 Agenda Sample Spaces Realizations, Events Axioms of Probability
Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 1. ABC of Probability January 16, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 1 January 16, 2013 1 / 9 Agenda Sample Spaces Realizations, Events Axioms of Probability
Ch 14 Randomness and Probability
 Ch 14 Randomness and Probability We ll begin a new part: randomness and probability. This part contain 4 chapters: 14-17. Why we need to learn this part? Probability is not a portion of statistics. Instead
Ch 14 Randomness and Probability We ll begin a new part: randomness and probability. This part contain 4 chapters: 14-17. Why we need to learn this part? Probability is not a portion of statistics. Instead
Basic Set Concepts (2.1)
 1 Basic Set Concepts (2.1) I. Set A collection of objects whose contents can be clearly determined. Capitol letters usually name a set. Elements are the contents in a set. Sets can be described using words,
1 Basic Set Concepts (2.1) I. Set A collection of objects whose contents can be clearly determined. Capitol letters usually name a set. Elements are the contents in a set. Sets can be described using words,
EnM Probability and Random Processes
 Historical Note: EnM 503 - Probability and Random Processes Probability has its roots in games of chance, which have been played since prehistoric time. Games and equipment have been found in Egyptian
Historical Note: EnM 503 - Probability and Random Processes Probability has its roots in games of chance, which have been played since prehistoric time. Games and equipment have been found in Egyptian
14 - PROBABILITY Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions )
 - PROBABILITY Page ( ) Three houses are available in a locality. Three persons apply for the houses. Each applies for one house without consulting others. The probability that all the three apply for the
- PROBABILITY Page ( ) Three houses are available in a locality. Three persons apply for the houses. Each applies for one house without consulting others. The probability that all the three apply for the
Basic Concepts of Probability. Section 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability. Probability Experiments. Chapter 3 Probability
 Chapter 3 Probability 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability 3.2 Conditional Probability and the Multiplication Rule 3.3 The Addition Rule 3.4 Additional Topics in Probability and Counting Section 3.1 Basic
Chapter 3 Probability 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability 3.2 Conditional Probability and the Multiplication Rule 3.3 The Addition Rule 3.4 Additional Topics in Probability and Counting Section 3.1 Basic
UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1
 UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1 6.1: Simulation Simulation: The of chance behavior, based on a that accurately reflects the phenomenon under consideration. (ex 1) Suppose we are interested
UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1 6.1: Simulation Simulation: The of chance behavior, based on a that accurately reflects the phenomenon under consideration. (ex 1) Suppose we are interested
If S = {O 1, O 2,, O n }, where O i is the i th elementary outcome, and p i is the probability of the i th elementary outcome, then
 1.1 Probabilities Def n: A random experiment is a process that, when performed, results in one and only one of many observations (or outcomes). The sample space S is the set of all elementary outcomes
1.1 Probabilities Def n: A random experiment is a process that, when performed, results in one and only one of many observations (or outcomes). The sample space S is the set of all elementary outcomes
Probability Theory Review
 Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
Probability. Chapter 1 Probability. A Simple Example. Sample Space and Probability. Sample Space and Event. Sample Space (Two Dice) Probability
 Probability Chapter 1 Probability 1.1 asic Concepts researcher claims that 10% of a large population have disease H. random sample of 100 people is taken from this population and examined. If 20 people
Probability Chapter 1 Probability 1.1 asic Concepts researcher claims that 10% of a large population have disease H. random sample of 100 people is taken from this population and examined. If 20 people
Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com
 1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
Problems from Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) by Hogg, Tanis and Zimmerman.
 Math 224 Fall 2017 Homework 1 Drew Armstrong Problems from Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) by Hogg, Tanis and Zimmerman. Section 1.1, Exercises 4,5,6,7,9,12. Solutions to Book Problems.
Math 224 Fall 2017 Homework 1 Drew Armstrong Problems from Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) by Hogg, Tanis and Zimmerman. Section 1.1, Exercises 4,5,6,7,9,12. Solutions to Book Problems.
Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events
 Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events Engineering Statistics Section 2.1 Josh Engwer TTU 01 February 2016 Josh Engwer (TTU) Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events 01 February 2016 1 / 29 The Need
Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events Engineering Statistics Section 2.1 Josh Engwer TTU 01 February 2016 Josh Engwer (TTU) Probability: Sets, Sample Spaces, Events 01 February 2016 1 / 29 The Need
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS. Dr N A Heard. 1 Sample Spaces and Events Sample Spaces Events Combinations of Events...
 Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
Independence. P(A) = P(B) = 3 6 = 1 2, and P(C) = 4 6 = 2 3.
 Example: A fair die is tossed and we want to guess the outcome. The outcomes will be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 with equal probability 1 6 each. If we are interested in getting the following results: A = {1, 3,
Example: A fair die is tossed and we want to guess the outcome. The outcomes will be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 with equal probability 1 6 each. If we are interested in getting the following results: A = {1, 3,
STA111 - Lecture 1 Welcome to STA111! 1 What is the difference between Probability and Statistics?
 STA111 - Lecture 1 Welcome to STA111! Some basic information: Instructor: Víctor Peña (email: vp58@duke.edu) Course Website: http://stat.duke.edu/~vp58/sta111. 1 What is the difference between Probability
STA111 - Lecture 1 Welcome to STA111! Some basic information: Instructor: Víctor Peña (email: vp58@duke.edu) Course Website: http://stat.duke.edu/~vp58/sta111. 1 What is the difference between Probability
Statistical Inference
 Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
MATH 120. Test 1 Spring, 2012 DO ALL ASSIGNED PROBLEMS. Things to particularly study
 MATH 120 Test 1 Spring, 2012 DO ALL ASSIGNED PROBLEMS Things to particularly study 1) Critical Thinking Basic strategies Be able to solve using the basic strategies, such as finding patterns, questioning,
MATH 120 Test 1 Spring, 2012 DO ALL ASSIGNED PROBLEMS Things to particularly study 1) Critical Thinking Basic strategies Be able to solve using the basic strategies, such as finding patterns, questioning,
Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Lecture Outline October 18, 2018
 Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Lecture Outline October 18, 2018 The Total Probability Theorem. Consider events E and F. Consider a sample point ω E. Observe that ω belongs to either F or
Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Lecture Outline October 18, 2018 The Total Probability Theorem. Consider events E and F. Consider a sample point ω E. Observe that ω belongs to either F or
Statistical Theory 1
 Statistical Theory 1 Set Theory and Probability Paolo Bautista September 12, 2017 Set Theory We start by defining terms in Set Theory which will be used in the following sections. Definition 1 A set is
Statistical Theory 1 Set Theory and Probability Paolo Bautista September 12, 2017 Set Theory We start by defining terms in Set Theory which will be used in the following sections. Definition 1 A set is
Chapter 14. From Randomness to Probability. Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Dealing with Random Phenomena A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen,
Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Dealing with Random Phenomena A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen,
Probability Notes. Definitions: The probability of an event is the likelihood of choosing an outcome from that event.
 ability Notes Definitions: Sample Space: sample space is a set or collection of possible outcomes. Flipping a Coin: {Head, Tail} Rolling Two Die: {,,,, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0,, } Outcome: n outcome is an element
ability Notes Definitions: Sample Space: sample space is a set or collection of possible outcomes. Flipping a Coin: {Head, Tail} Rolling Two Die: {,,,, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0,, } Outcome: n outcome is an element
 CHAPTER - 16 PROBABILITY Random Experiment : If an experiment has more than one possible out come and it is not possible to predict the outcome in advance then experiment is called random experiment. Sample
CHAPTER - 16 PROBABILITY Random Experiment : If an experiment has more than one possible out come and it is not possible to predict the outcome in advance then experiment is called random experiment. Sample
Name: Exam 2 Solutions. March 13, 2017
 Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 00 Finite Math Spring 07 Name: Instructors: Conant/Galvin Exam Solutions March, 07 This exam is in two parts on pages and contains problems worth
Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 00 Finite Math Spring 07 Name: Instructors: Conant/Galvin Exam Solutions March, 07 This exam is in two parts on pages and contains problems worth
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page α 2 θ 1 u 3. wear coat. θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ 1 = cold u 3 = brrr!
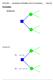 ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
P (A B) P ((B C) A) P (B A) = P (B A) + P (C A) P (A) = P (B A) + P (C A) = Q(A) + Q(B).
 Lectures 7-8 jacques@ucsdedu 41 Conditional Probability Let (Ω, F, P ) be a probability space Suppose that we have prior information which leads us to conclude that an event A F occurs Based on this information,
Lectures 7-8 jacques@ucsdedu 41 Conditional Probability Let (Ω, F, P ) be a probability space Suppose that we have prior information which leads us to conclude that an event A F occurs Based on this information,
Introduction to Probability. Ariel Yadin. Lecture 1. We begin with an example [this is known as Bertrand s paradox]. *** Nov.
![Introduction to Probability. Ariel Yadin. Lecture 1. We begin with an example [this is known as Bertrand s paradox]. *** Nov. Introduction to Probability. Ariel Yadin. Lecture 1. We begin with an example [this is known as Bertrand s paradox]. *** Nov.](/thumbs/87/97208194.jpg) Introduction to Probability Ariel Yadin Lecture 1 1. Example: Bertrand s Paradox We begin with an example [this is known as Bertrand s paradox]. *** Nov. 1 *** Question 1.1. Consider a circle of radius
Introduction to Probability Ariel Yadin Lecture 1 1. Example: Bertrand s Paradox We begin with an example [this is known as Bertrand s paradox]. *** Nov. 1 *** Question 1.1. Consider a circle of radius
Chapter 5 : Probability. Exercise Sheet. SHilal. 1 P a g e
 1 P a g e experiment ( observing / measuring ) outcomes = results sample space = set of all outcomes events = subset of outcomes If we collect all outcomes we are forming a sample space If we collect some
1 P a g e experiment ( observing / measuring ) outcomes = results sample space = set of all outcomes events = subset of outcomes If we collect all outcomes we are forming a sample space If we collect some
Probability: Part 2 *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m39373 1 Probability: Part 2 * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 Relative
OpenStax-CNX module: m39373 1 Probability: Part 2 * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 Relative
Randomized Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker
 Randomized Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Randomized Algorithms A randomized algorithm is an algorithm that makes random choices during its execution. A randomized algorithm uses values generated by a
Randomized Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Randomized Algorithms A randomized algorithm is an algorithm that makes random choices during its execution. A randomized algorithm uses values generated by a
Lecture 1 Introduction to Probability and Set Theory Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss
 Lecture 1 to and Set Theory Text: A Course in by Weiss 1.2 2.3 STAT 225 to Models January 13, 2014 to and Whitney Huang Purdue University 1.1 Agenda to and 1 2 3 1.2 Motivation Uncertainty/Randomness in
Lecture 1 to and Set Theory Text: A Course in by Weiss 1.2 2.3 STAT 225 to Models January 13, 2014 to and Whitney Huang Purdue University 1.1 Agenda to and 1 2 3 1.2 Motivation Uncertainty/Randomness in
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S
 Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
324 Stat Lecture Notes (1) Probability
 324 Stat Lecture Notes 1 robability Chapter 2 of the book pg 35-71 1 Definitions: Sample Space: Is the set of all possible outcomes of a statistical experiment, which is denoted by the symbol S Notes:
324 Stat Lecture Notes 1 robability Chapter 2 of the book pg 35-71 1 Definitions: Sample Space: Is the set of all possible outcomes of a statistical experiment, which is denoted by the symbol S Notes:
Homework (due Wed, Oct 27) Chapter 7: #17, 27, 28 Announcements: Midterm exams keys on web. (For a few hours the answer to MC#1 was incorrect on
 Homework (due Wed, Oct 27) Chapter 7: #17, 27, 28 Announcements: Midterm exams keys on web. (For a few hours the answer to MC#1 was incorrect on Version A.) No grade disputes now. Will have a chance to
Homework (due Wed, Oct 27) Chapter 7: #17, 27, 28 Announcements: Midterm exams keys on web. (For a few hours the answer to MC#1 was incorrect on Version A.) No grade disputes now. Will have a chance to
ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model
 ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model Fall 2018 Prof Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 35 1. Probability Model 2 / 35 What is Probability? It is a number.
ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model Fall 2018 Prof Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 35 1. Probability Model 2 / 35 What is Probability? It is a number.
Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes. Set Operations and Relations. Venn Diagram 2.1. Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes
 Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture 2: Probability. Readings: Sections Statistical Inference: drawing conclusions about the population based on a sample
 Lecture 2: Probability Readings: Sections 5.1-5.3 1 Introduction Statistical Inference: drawing conclusions about the population based on a sample Parameter: a number that describes the population a fixed
Lecture 2: Probability Readings: Sections 5.1-5.3 1 Introduction Statistical Inference: drawing conclusions about the population based on a sample Parameter: a number that describes the population a fixed
Unit 7 Probability M2 13.1,2,4, 5,6
 + Unit 7 Probability M2 13.1,2,4, 5,6 7.1 Probability n Obj.: I will be able to determine the experimental and theoretical probabilities of an event, or its complement, occurring. n Vocabulary o Outcome
+ Unit 7 Probability M2 13.1,2,4, 5,6 7.1 Probability n Obj.: I will be able to determine the experimental and theoretical probabilities of an event, or its complement, occurring. n Vocabulary o Outcome
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15. Lecture 2: Random Experiments. Prof. Vince Calhoun
 ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
