Lecture 28 Title: Diatomic Molecule : Vibrational and Rotational spectra
|
|
|
- Sabrina Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lctur 8 Titl: Diatomic Molcul : Vibrational and otational spctra Pag- In this lctur w will undrstand th molcular vibrational and rotational spctra of diatomic molcul W will start with th Hamiltonian for th diatomic molcul that dpnds on th nuclar and lctronic coordinat. Thn w will us th Born-Oppnhimr approximation, to sparat th nuclar and lctronic wavfunctions W will driv th ign nrgy valus to undrstand th rotational and vibrational spctra of th ground lctronic stat of diatomic molculs. At th nd w will discuss th rotational and vibrational spctra of som diatomic molculs.
2 Pag-1 For a diatomic molcul A - B with n lctrons as shown in figur-8.1, th Schrodringr quation can b writtn as n i + V Ψ = EΨ µ m i= 1.(8.1) Whr, Ψ is th total lctronic and nuclar wavfunction & E is th total nrgy. 1 st trm: K.E. of th rlativ motion of th nucli with rducd mass mam µ = B m A + m B nd trm: K.E. of all lctrons. r a r b - And th potntial, Z Z ZZ V = + r r r n n n A B A B i > j= 1 i j i= 1 ia i= 1 ib = V V + V n nn A Figur-8.1 B Th molcular wavfunction, Ψ dpnds on both lctron & nuclar coordinats, Ψ=Ψ ( x, y, z, x, y, z,... x, y, z, XYZ,, ) = Ψ ( r, ) n n n w.r.t. origin say nuclus A Sinc th wavfunction dpnds on both lctron and nuclus coordinats, it is difficult to solv this problm vn for a simpl molcul. W would lik to sparat lctronic and nuclar motion. Bcaus of th diffrnt masss of th lctrons and nucli, w can considr th nucli to b stationary to solv th lctronic problm (Born-Oppnhimr approximation).
3 Pag- Th ssnc of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation is to dcompos nuclar and lctronic motions basd on th larg disparity of th masss of nucli and mass of lctron. If w nd to solv th Schrodringr quation givn in quation-8.1 using Born- Oppnhimr approximation, w hav to follow fiv stps. Stp-1 Lt us assum that th nucli ar clampd in fixd positions. This approximation is almost clos to th rality bcaus th lctronic motion is so fast that it will s th nuclar motions almost stationary. This will liminat th nuclar kintic nrgy trm in th Hamiltonian in quation 8.1 Stp- Undr th assumption in stp-1, w can writ quation 8.1 as n i + V r r = E r m i= 1 (, ) φ(, ) φ(, )..(8.) Hr nuclar K.E. is zro, and appars only as a paramtr and φ ( r, ) wavfunction. W can follow th procdur to fix = 1 m Solv + V( r, ) φ( r, ) = E φ( r, ) i is th lctronic Thn, fix = m Solv + V( r, ) φ( r, ) = E φ( r, ) i and do it for th ntir rang of.
4 Pag-3 Stp-3 Having obtaind th lctronic wavfunction φ ( r, ), and molcular wavfunction, E w can writ th total ( r, ) φ( r, ) χ Ψ =..(8.3) whr, χ Nuclar wavfunction Stp-4 Now w can substitut quation 8.3 in quation 8.1 and w gt, i + V r r µ m i (, ) χ (, ) φ(, ) χ = φ χ + i + φ χ µ m i = Eφ r ( r, ) V( r, ) ( r, ) Stp-5 Sinc, oprats only on φ ( r, ) µ i. W can writ, φ χ χ φ χ = + = Now, ( r, ) E E ( r, ) is th diffrnc w.r.t., so can oprat on both ( r, ) φ and χ. As a concqunc, th lctronic wavfunction is rlativly insnsitiv to changs in th nuclar positions and momnta, and is thrfor capabl of adjusting itslf quasistatically to th nuclar motion. This is known as th adiabatic approximation. Assumption: Elctronic wavfunction varis slowly with th intr-nuclar distanc,
5 Pag-4 So w gt, ( r, ) ( r, ) φ χ φ χ µ So, + E χ = Eχ (8.4) This is th Schrödingr quation of nuclar motion of diatomic molcul. It is indpndnt of lctronic motion whos ffct appars only through E, which is lctronic nrgy as a function of and act as a potntial nrgy for th motion of th nucli. This is th cntral approximation of th Born-Oppnhimr approach. Its justification stms from th fact that nuclar vlocitis ar small compard to lctronic vlocitis. Now w ar rady to solv th quation-8.4. This is simpl as w hav solvd it for hydrogn atom. Lt us introduc sphrical polar coordinat (, θφ, ) of on nuclus with rspct to othr as origin in quation 8.4, and w gt 1 1 sin θ E χ(, θφ, ) Eχ(, θφ, ) µ = sinθ θ θ sin θ φ χ(,, ) (, ) Now, θφ = S θφ (8.5) Whr, ( θφ, ) ( θφ, ) S = S JM ar spcifid by th molcular total angular momntum quantum numbr J and Z - componnt M, analogous to H - atom quantum no. & m.
6 Pag-5 Th angular part, ( θφ, ) ( 1 ) ( θφ, ) JM ( + 1) 1 1 J J sin θ + SJM ( θφ, ) = S JM ( θφ, ) µ sinθ θ θ sin θ φ µ 1 1 sin θ + S, 1, JM θφ = J J + SJM θφ sinθ θ θ sin θ φ M S = J J + S JM This is nothing but th rotational motion as shown in figur-8. Putting it in th quation, (8.6) 1 1 sin θ E S, JM µ sinθ θ θ sin θ φ = + + µ = E υ, J J J E S JM S ( θφ, ) JM ( 1 ) ( θφ, ) ( θφ) θ,φ otation whr, υ Vibrational quantum numbr J otational quantum numbr Vibration ( + 1) J J E E + + = υ, µ µ.(8.7) This dpnds only on intr-nuclar distanc and is calld th radial quation for th nuclar motion. Vibrational Wavfunction SJM (, ) θφ otational Wavfunction Figur-8.
7 Pag-6 otational Spctra of Diatomic Molcul Simpl modl is rigid rotor i.. is fixd as at quilibrium. In classical mchanics, th magnitud of angular momntum J of such a molcul rotating about cntr of mass with angular vlocity ω. J = µ υ = I ω From 8.6, rotational nrgy: EJ E J = + µ J J 1 = J J + I ( 1) = putting, µ = I This is in nrgy unit joul. W will convrt it to cm -1. EJ 1 h F ( J ) = cm = J ( J + 1) = hc hci 8π cµ ( 1) = B J J + Enrgy Lvls as shown in figur 8.3 J = ; F = J = 1 ; F = B J = ; F = 6B J = 3 ; F = 1B..(8.8) ( cosθ ) M imφ SJM = PJ J = 3 F(J) = 1B J = J = 1 J = otational nrgy lvls Figur-8.3 F(J) = 6B F(J) = B F(J) =
8 Pag-6 Now w will driv th slction rul for th transitions. W know that w hav to calculat th lctric dipol transition momnt intgrals to driv th slction rul. W tak µ l as dipol momnt of th molcul. So th transition momnt intgral is = SJM µ SJ M dτ Th componnts of th dipol momnt µ l ( ) ( ) ( ) µ = µ sinθ cosφ x µ = µ sinθ sinφ dτ = sinθ dθ dφ y µ = µ cosθ z π M cos M π sin im φ im φ Z = J J µ P θ P θ dθ dφ Sphrical Harmonics M M J1 J M 1 = M M J + M M J M + 1 M cosθ PJ ( cosθ) = PJ 1 + PJ+ 1 J + 1 J + 1 J + M M M J M + 1 M M Z = πµ PJ 1 PJ sinθ dθ + PJ+ 1 PJ sinθ dθ J + 1 J + 1 P P sinθ dθ = if J J J 1= J J =± 1; M = J + 1= J =± 1.(8.9)
9 Pag-7 Using th slction rul drivd in quation 8.9, th transitions ar shown in th following figur-8.4. J = 3 F(J) = 1B J = J = 1 J = otational nrgy lvls Figur-8.4 F(J) = 6B F(J) = B F(J) = Th transition nrgis ar J = ± 1 ( + 1) = ( + 1)( + ) = B J( J + 1) ( J) = F( J + 1) F( J) = B ( J + 1)[ J + J] = B ( J + 1) F J B J J F J ν Whr J =, 1,,.. Intnsity B 4B 6B 8B B B B B Figur-8.5 υ cm 1 Th xpctd rotational spctrum is shown in figur-8.5 So w s that undr non-rigid approximation, th transition ar quidistant with valu B and dpnds on th valu of B.
10 Pag-8 Exampl: otational Spctrum of HCl molcul shown in figur-8.6 B = 1.18 cm B 1 1 = 1.59 cm = = Ihc 8π µ h = 8π µ c h hc Intnsity H = 1.79 amu Cl = amu 1 amu = gm B υ cm B B B Figur µ = gm sc.. = rg cm gm = cm o cm 1.7 A = = cm sc So th quilibrium bond lngth of th HCl molcul is 1.7Å. Thus from th rotational spctrum of a molcul, w can driv th bond lngth and structur. Not: For molculs without prmannt dipol momnts such as H, th lctric dipol pur rotation transition probability is zro. In that systm th momnt of inrtia & intrnuclr distanc can b found out from analysis of rotational structur of lctronic absorption bands or rotational aman Spctra. W will discuss ths two spctra in latr.
11 Pag-9 Vibrational Spctra of Diatomic Molcul adial quation 8.7, d d + + = µ d d Whr EOT E Eυ, J ( + 1) J( J + 1) J J µ µ = E OT Th total nrgy, Eυ, J = EOT + Evib = Enucl d d + + = + µ d d EOT E EOT Evib d d + = µ d d Putting = E Evib 1 ξ d + = µ E E E vib d ξ ξ ξ is th lctronic nrgy as shown in th following figur-8.7 which bhavs as th potntial nrgy of th nuclar motion. Enrgy Figur-8.7 E() Bonding ab
12 Pag-1 Expand this function in powr sris about =, E = E de 1 d E d d Choos zro of th nrgy at E( ) = minimum bcaus this point is minimum de d =. 3 1 de 1 de 3 = So, E ( ) ( ) 3 d 3! d Putting = ρ Enrgy E 1 = +... ( ρ) K ρ Harmonic potntial Whr K d E = d If nglct th highr powr d 1 ξ ρ + ρ ξ ρ = ξ ρ µ dρ vib K E Harmonic oscillator quation with potntial as shown in figur-8.8, so th nrgy valu 1 Evib = E υ = υ+ ω υ = vibrational quantum numbr =,1,,3,... ν Classical frquncy 1 K = π µ 1 E() Bonding Figur-8.8 ab
13 Pag-11 Wav Function ξ 1 β x υ = υ υ 4 β = π µν os ( β ) N H x h whr, H ( x) υ β Hrmit polynomial Th wavfunctions ar shown in th figur-8.9 with dashd curvs. Th solid curvs ar th Dipol momnt µ = µ + µ x 1 ξ υ υ = υ = 1 Intrnuclar distanc whr, µ Prmannt Slction rul : x µ 1 Inducd du to vibration = µ ξ ξ dx + µ xξ ξ dx * * υ υ 1 υ υ υ υ ; υ = υ E = ω 3 E ( 1) = ω E = ω ( 1) E υ = υ 1 So only on transition is prdictd undr harmonic oscillator approximation Figur- ω 8.9). Howvr, many transitions ar sn in Figur-8.9 th infra rd vibrational spctra of diatomic molcul. So harmonic approximation is not th good approximation. Not: Dipol momnt of molcul with qual nuclus is always zro. So for N,O,... no infrard spctrum. υ = 3 υ = υ = 1 υ = ω ω ω ω
14 Pag-1 Anharmonic Oscillator Introducing anharmonicity 3 E = f r r g r r +... Condition: g f Mors Potntial as shown in th figur-8.1 : ( ) ( 1 ) r r E = D β Enrgy lvls: Eυ = ω υ+ ωx υ+ + ωy υ Convrt in cm G( υ) = ω υ+ ωx υ+ + ωy υ+ Enrgy whr ω, ω x, ω y in trms of υ Vibrational quantum numbr ω > ω x > ω y Hr 1 cm. Mors potntial a Slction rul, υ =± 1, ±, ± 3 Zro point nrgy: G = ω ω x + ω y 4 8 If th nrgy rfrrd to th lowst lvl, ( υ) = ( υ) G G G = ω υ+ ωx υ+ + ωy υ ω ωx + ωy = ω ωx + ωy υ ωx ωy +... υ + ( ωy +...) υ 4 3 = ωυ ωxυ + ωyυ 3 ω = ω ωx + ωy 4 3 whr, ωx = ωx ωy +... ω y = ω y +... G() E() Bonding Figur-8.1
15 Pag-13 Transitions btwn th vibrational lvls ν ( υ) ( υ ) abs = G G = G Thus th obsrvd absorption givs dirctly th positions of th nrgy lvls. Exampl: Obsrvd Vibration Frquncy of HCl -1 (cm ) Cal. Harmonic Approx. υ υabs G G G G G υ ωυ ω xυ = = ω ω x = = ω 4ω x = ω 4ω x = ω ω x = ( ) ( + ) ( ) ω x = 13.8 ω x = ( υ) ( υ 1) ( υ) G = G + G ( 1) x ( 1) x = ω υ+ ω υ+ ωυ+ ω υ = ωυ + ω ω x υ ωxυ ωx ωυ + ω x υ = ω ω x ω xυ ( υ) ( υ 1) ( υ) = + G G G = ω ω x ω x υ+ 1 ω + ω x + ω xυ = ω x which is dirctly th masurd anharmonicity.
16 Pag-14 cap In this lctur w hav larnt th origin of vibrational and rotational spctra. W startd with th Schrodingr quation for th diatomic molcul. Thn w usd th Born-Oppnhimr approximation, to sparat th nuclar and lctronic wavfunctions. W drivd th ign nrgy valus of th rotational and vibrational motions of th ground lctronic stat of diatomic molculs. At th nd w hav discussd th rotational and vibrational spctra of som diatomic molculs.
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Schrodinger Equation in 3-d
 Schrodingr Equation in 3-d ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) + + + Vxyz (,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) = Eψ( xyz,, ) m x y z p p p x y + + z m m m + V = E p m + V = E E + k V = E Infinit Wll in 3-d V = x > L, y > L,
Schrodingr Equation in 3-d ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) + + + Vxyz (,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) = Eψ( xyz,, ) m x y z p p p x y + + z m m m + V = E p m + V = E E + k V = E Infinit Wll in 3-d V = x > L, y > L,
Constants and Conversions:
 EXAM INFORMATION Radial Distribution Function: P 2 ( r) RDF( r) Br R( r ) 2, B is th normalization constant. Ordr of Orbital Enrgis: Homonuclar Diatomic Molculs * * * * g1s u1s g 2s u 2s u 2 p g 2 p g
EXAM INFORMATION Radial Distribution Function: P 2 ( r) RDF( r) Br R( r ) 2, B is th normalization constant. Ordr of Orbital Enrgis: Homonuclar Diatomic Molculs * * * * g1s u1s g 2s u 2s u 2 p g 2 p g
Phys 402: Nonlinear Spectroscopy: SHG and Raman Scattering
 Rquirmnts: Polariation of Elctromagntic Wavs Phys : Nonlinar Spctroscopy: SHG and Scattring Gnral considration of polariation How Polarirs work Rprsntation of Polariation: Jons Formalism Polariation of
Rquirmnts: Polariation of Elctromagntic Wavs Phys : Nonlinar Spctroscopy: SHG and Scattring Gnral considration of polariation How Polarirs work Rprsntation of Polariation: Jons Formalism Polariation of
Chapter 7b Electron Spin and Spin- Orbit Coupling
 Wintr 3 Chm 356: Introductory Quantum Mchanics Chaptr 7b Elctron Spin and Spin- Orbit Coupling... 96 H- atom in a Magntic Fild: Elctron Spin... 96 Total Angular Momntum... 3 Chaptr 7b Elctron Spin and
Wintr 3 Chm 356: Introductory Quantum Mchanics Chaptr 7b Elctron Spin and Spin- Orbit Coupling... 96 H- atom in a Magntic Fild: Elctron Spin... 96 Total Angular Momntum... 3 Chaptr 7b Elctron Spin and
Numerical Problem Set for Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy. Yr 2 HT SRM
 Numrical Problm St for Atomic and Molcular Spctroscopy Yr HT SRM Sction 1: Atomic Spctra 1. For ach of th atomic trm symbols 1 S, P, 3 P, 3 D, 4 D, writ down: a) Th associatd valus of th total spin and
Numrical Problm St for Atomic and Molcular Spctroscopy Yr HT SRM Sction 1: Atomic Spctra 1. For ach of th atomic trm symbols 1 S, P, 3 P, 3 D, 4 D, writ down: a) Th associatd valus of th total spin and
Determination of Vibrational and Electronic Parameters From an Electronic Spectrum of I 2 and a Birge-Sponer Plot
 5 J. Phys. Chm G Dtrmination of Vibrational and Elctronic Paramtrs From an Elctronic Spctrum of I 2 and a Birg-Sponr Plot 1 15 2 25 3 35 4 45 Dpartmnt of Chmistry, Gustavus Adolphus Collg. 8 Wst Collg
5 J. Phys. Chm G Dtrmination of Vibrational and Elctronic Paramtrs From an Elctronic Spctrum of I 2 and a Birg-Sponr Plot 1 15 2 25 3 35 4 45 Dpartmnt of Chmistry, Gustavus Adolphus Collg. 8 Wst Collg
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
Lecture 37 (Schrödinger Equation) Physics Spring 2018 Douglas Fields
 Lctur 37 (Schrödingr Equation) Physics 6-01 Spring 018 Douglas Filds Rducd Mass OK, so th Bohr modl of th atom givs nrgy lvls: E n 1 k m n 4 But, this has on problm it was dvlopd assuming th acclration
Lctur 37 (Schrödingr Equation) Physics 6-01 Spring 018 Douglas Filds Rducd Mass OK, so th Bohr modl of th atom givs nrgy lvls: E n 1 k m n 4 But, this has on problm it was dvlopd assuming th acclration
Classical Magnetic Dipole
 Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
On the Hamiltonian of a Multi-Electron Atom
 On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
Contemporary, atomic, nuclear, and particle physics
 Contmporary, atomic, nuclar, and particl physics 1 Blackbody radiation as a thrmal quilibrium condition (in vacuum this is th only hat loss) Exampl-1 black plan surfac at a constant high tmpratur T h is
Contmporary, atomic, nuclar, and particl physics 1 Blackbody radiation as a thrmal quilibrium condition (in vacuum this is th only hat loss) Exampl-1 black plan surfac at a constant high tmpratur T h is
PH300 Modern Physics SP11 Final Essay. Up Next: Periodic Table Molecular Bonding
 PH Modrn Physics SP11 Final Essay Thr will b an ssay portion on th xam, but you don t nd to answr thos qustions if you submit a final ssay by th day of th final: Sat. 5/7 It dosnʼt mattr how smart you
PH Modrn Physics SP11 Final Essay Thr will b an ssay portion on th xam, but you don t nd to answr thos qustions if you submit a final ssay by th day of th final: Sat. 5/7 It dosnʼt mattr how smart you
Lecture 2: Rotational and Vibrational Spectra
 Lctur : Rotational and Vibrational Spctra 1. Light-mattr intraction. Rigid-rotor modl for diatomic molcul 3. Non-rigid rotation 4. Vibration-rotation for diatomics H O 1. Light-mattr intraction Possibilitis
Lctur : Rotational and Vibrational Spctra 1. Light-mattr intraction. Rigid-rotor modl for diatomic molcul 3. Non-rigid rotation 4. Vibration-rotation for diatomics H O 1. Light-mattr intraction Possibilitis
Collisions between electrons and ions
 DRAFT 1 Collisions btwn lctrons and ions Flix I. Parra Rudolf Pirls Cntr for Thortical Physics, Unirsity of Oxford, Oxford OX1 NP, UK This rsion is of 8 May 217 1. Introduction Th Fokkr-Planck collision
DRAFT 1 Collisions btwn lctrons and ions Flix I. Parra Rudolf Pirls Cntr for Thortical Physics, Unirsity of Oxford, Oxford OX1 NP, UK This rsion is of 8 May 217 1. Introduction Th Fokkr-Planck collision
Quasi-Classical States of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Coupled Pendulums. Two normal modes.
 Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Derivation of Electron-Electron Interaction Terms in the Multi-Electron Hamiltonian
 Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
Experiment 6, page 1 Version of March 17, 2015
 Exprimnt 6, pag 1 Vrsion of March 17, 015 Exprimnt 6 VIBRATION-ROTATION SPECTROSCOPY OF DIATOMIC MOLECULES IMPORTANT: Th cll should b stord in th dssicator whn not in us to prvnt moistur in th atmosphr
Exprimnt 6, pag 1 Vrsion of March 17, 015 Exprimnt 6 VIBRATION-ROTATION SPECTROSCOPY OF DIATOMIC MOLECULES IMPORTANT: Th cll should b stord in th dssicator whn not in us to prvnt moistur in th atmosphr
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Atomic and Laser Spectroscopy
 L-E B, OL, MOV 83 Atomic and Lasr Spctroscopy Th aim of this xrcis is to giv an ovrviw of th fild of lasr spctroscopy and to show modrn spctroscopic mthods usd in atomic, molcular and chmical physics.
L-E B, OL, MOV 83 Atomic and Lasr Spctroscopy Th aim of this xrcis is to giv an ovrviw of th fild of lasr spctroscopy and to show modrn spctroscopic mthods usd in atomic, molcular and chmical physics.
the electrons. Expanding the exponential and neglecting the constant term Ze 2 λ, we have
 LECTURE.8 Prof.R.Parthasarathy Atomic Structur - Elmntary Tratmnt Th ground stat of hydrogn atom has bn solvd xactly in th nonrlativistic tratmnt. Th ground stat of hlium atom has bn handld in variational
LECTURE.8 Prof.R.Parthasarathy Atomic Structur - Elmntary Tratmnt Th ground stat of hydrogn atom has bn solvd xactly in th nonrlativistic tratmnt. Th ground stat of hlium atom has bn handld in variational
I. The Connection between Spectroscopy and Quantum Mechanics
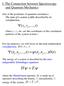 I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Chemical Physics II. More Stat. Thermo Kinetics Protein Folding...
 Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
High Energy Physics. Lecture 5 The Passage of Particles through Matter
 High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
Exam 2 Thursday (7:30-9pm) It will cover material through HW 7, but no material that was on the 1 st exam.
 Exam 2 Thursday (7:30-9pm) It will covr matrial through HW 7, but no matrial that was on th 1 st xam. What happns if w bash atoms with lctrons? In atomic discharg lamps, lots of lctrons ar givn kintic
Exam 2 Thursday (7:30-9pm) It will covr matrial through HW 7, but no matrial that was on th 1 st xam. What happns if w bash atoms with lctrons? In atomic discharg lamps, lots of lctrons ar givn kintic
PHYS-333: Problem set #2 Solutions
 PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
The failure of the classical mechanics
 h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
Atomic energy levels. Announcements:
 Atomic nrgy lvls Announcmnts: Exam solutions ar postd. Problm solving sssions ar M3-5 and Tusday 1-3 in G-140. Will nd arly and hand back your Midtrm Exam at nd of class. http://www.colorado.du/physics/phys2170/
Atomic nrgy lvls Announcmnts: Exam solutions ar postd. Problm solving sssions ar M3-5 and Tusday 1-3 in G-140. Will nd arly and hand back your Midtrm Exam at nd of class. http://www.colorado.du/physics/phys2170/
Scattering States of l-wave Schrödinger Equation with Modified Rosen Morse Potential
 Commun. Thor. Phys. 66 06 96 00 Vol. 66, No., August, 06 Scattring Stats of l-wav Schrödingr Equation with Modifid Rosn Mors Potntial Wn-Li Chn í,, Yan-Wi Shi á, and Gao-Fng Wi Ôô, Gnral Education Cntr,
Commun. Thor. Phys. 66 06 96 00 Vol. 66, No., August, 06 Scattring Stats of l-wav Schrödingr Equation with Modifid Rosn Mors Potntial Wn-Li Chn í,, Yan-Wi Shi á, and Gao-Fng Wi Ôô, Gnral Education Cntr,
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 07 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat
Addition of angular momntum April, 07 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat
orbiting electron turns out to be wrong even though it Unfortunately, the classical visualization of the
 Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
Intro to Nuclear and Particle Physics (5110)
 Intro to Nuclar and Particl Physics (5110) March 09, 009 Frmi s Thory of Bta Dcay (continud) Parity Violation, Nutrino Mass 3/9/009 1 Final Stat Phas Spac (Rviw) Th Final Stat lctron and nutrino wav functions
Intro to Nuclar and Particl Physics (5110) March 09, 009 Frmi s Thory of Bta Dcay (continud) Parity Violation, Nutrino Mass 3/9/009 1 Final Stat Phas Spac (Rviw) Th Final Stat lctron and nutrino wav functions
Chapter 1 Late 1800 s Several failures of classical (Newtonian) physics discovered
 Chaptr 1 Lat 1800 s Svral failurs of classical (Nwtonian) physics discovrd 1905 195 Dvlopmnt of QM rsolvd discrpancis btwn xpt. and classical thory QM Essntial for undrstanding many phnomna in Chmistry,
Chaptr 1 Lat 1800 s Svral failurs of classical (Nwtonian) physics discovrd 1905 195 Dvlopmnt of QM rsolvd discrpancis btwn xpt. and classical thory QM Essntial for undrstanding many phnomna in Chmistry,
Problem Set 4 Solutions Distributed: February 26, 2016 Due: March 4, 2016
 Probl St 4 Solutions Distributd: Fbruary 6, 06 Du: March 4, 06 McQuarri Probls 5-9 Ovrlay th two plots using Excl or Mathatica. S additional conts blow. Th final rsult of Exapl 5-3 dfins th forc constant
Probl St 4 Solutions Distributd: Fbruary 6, 06 Du: March 4, 06 McQuarri Probls 5-9 Ovrlay th two plots using Excl or Mathatica. S additional conts blow. Th final rsult of Exapl 5-3 dfins th forc constant
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry
 Outlin olcular Orbitals in Inorganic Chmistry Dr. P. Hunt p.hunt@imprial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chmistry) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ octahdral complxs forming th O diagram for Oh colour, slction ruls Δoct, spctrochmical
Outlin olcular Orbitals in Inorganic Chmistry Dr. P. Hunt p.hunt@imprial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chmistry) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ octahdral complxs forming th O diagram for Oh colour, slction ruls Δoct, spctrochmical
As the matrix of operator B is Hermitian so its eigenvalues must be real. It only remains to diagonalize the minor M 11 of matrix B.
 7636S ADVANCED QUANTUM MECHANICS Solutions Spring. Considr a thr dimnsional kt spac. If a crtain st of orthonormal kts, say, and 3 ar usd as th bas kts, thn th oprators A and B ar rprsntd by a b A a and
7636S ADVANCED QUANTUM MECHANICS Solutions Spring. Considr a thr dimnsional kt spac. If a crtain st of orthonormal kts, say, and 3 ar usd as th bas kts, thn th oprators A and B ar rprsntd by a b A a and
de/dx Effectively all charged particles except electrons
 de/dx Lt s nxt turn our attntion to how chargd particls los nrgy in mattr To start with w ll considr only havy chargd particls lik muons, pions, protons, alphas, havy ions, Effctivly all chargd particls
de/dx Lt s nxt turn our attntion to how chargd particls los nrgy in mattr To start with w ll considr only havy chargd particls lik muons, pions, protons, alphas, havy ions, Effctivly all chargd particls
5.62 Physical Chemistry II Spring 2008
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.62 Physical Chmistry II Spring 2008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. 5.62 Lctur #7: Translational Part of
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.62 Physical Chmistry II Spring 2008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. 5.62 Lctur #7: Translational Part of
Division of Mechanics Lund University MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Examination Name (write in block letters):.
 Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Physics 2D Lecture Slides Lecture 14: Feb 1 st 2005
 Physics D Lctur Slids Lctur 14: Fb 1 st 005 Vivk Sharma UCSD Physics Compton Effct: what should Happn Classically? Plan wav [f,λ] incidnt on a surfac with loosly bound lctrons intraction of E fild of EM
Physics D Lctur Slids Lctur 14: Fb 1 st 005 Vivk Sharma UCSD Physics Compton Effct: what should Happn Classically? Plan wav [f,λ] incidnt on a surfac with loosly bound lctrons intraction of E fild of EM
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probability and Stochastic Procsss: A Frindly Introduction for Elctrical and Computr Enginrs Roy D. Yats and David J. Goodman Problm Solutions : Yats and Goodman,4.3. 4.3.4 4.3. 4.4. 4.4.4 4.4.6 4.. 4..7
Probability and Stochastic Procsss: A Frindly Introduction for Elctrical and Computr Enginrs Roy D. Yats and David J. Goodman Problm Solutions : Yats and Goodman,4.3. 4.3.4 4.3. 4.4. 4.4.4 4.4.6 4.. 4..7
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in Physics
 Atoic and olcular Physics JEST Q. Th binding nrgy of th hydrogn ato (lctron bound to proton) is.6 V. Th binding nrgy of positroniu (lctron bound to positron) is (a).6 / V (b).6 / 8 V (c).6 8 V (d).6 V.6
Atoic and olcular Physics JEST Q. Th binding nrgy of th hydrogn ato (lctron bound to proton) is.6 V. Th binding nrgy of positroniu (lctron bound to positron) is (a).6 / V (b).6 / 8 V (c).6 8 V (d).6 V.6
Physical Chemistry Spring 2018 TR 5:00-6:15 pm, 207 BrL Quiz #1
 Physical Chmistry 444-0 Spring 08 TR 5:00-6:5 pm, 07 BrL Quiz # Nam KEY Problm (3 points). Ammonia gas is vry hygroscopic (asily racts with watr), so it is packagd for shipping in a small dry gas cylindr
Physical Chmistry 444-0 Spring 08 TR 5:00-6:5 pm, 07 BrL Quiz # Nam KEY Problm (3 points). Ammonia gas is vry hygroscopic (asily racts with watr), so it is packagd for shipping in a small dry gas cylindr
Finite element discretization of Laplace and Poisson equations
 Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Chapter 8: Electron Configurations and Periodicity
 Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
Deepak Rajput
 Q Prov: (a than an infinit point lattic is only capabl of showing,, 4, or 6-fold typ rotational symmtry; (b th Wiss zon law, i.. if [uvw] is a zon axis and (hkl is a fac in th zon, thn hu + kv + lw ; (c
Q Prov: (a than an infinit point lattic is only capabl of showing,, 4, or 6-fold typ rotational symmtry; (b th Wiss zon law, i.. if [uvw] is a zon axis and (hkl is a fac in th zon, thn hu + kv + lw ; (c
1.2 Faraday s law A changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Their relation is given by:
 Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
2F1120 Spektrala transformer för Media Solutions to Steiglitz, Chapter 1
 F110 Spktrala transformr för Mdia Solutions to Stiglitz, Chaptr 1 Prfac This documnt contains solutions to slctd problms from Kn Stiglitz s book: A Digital Signal Procssing Primr publishd by Addison-Wsly.
F110 Spktrala transformr för Mdia Solutions to Stiglitz, Chaptr 1 Prfac This documnt contains solutions to slctd problms from Kn Stiglitz s book: A Digital Signal Procssing Primr publishd by Addison-Wsly.
2. Laser physics - basics
 . Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
. Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
ECE507 - Plasma Physics and Applications
 ECE507 - Plasma Physics and Applications Lctur 7 Prof. Jorg Rocca and Dr. Frnando Tomasl Dpartmnt of Elctrical and Computr Enginring Collisional and radiativ procsss All particls in a plasma intract with
ECE507 - Plasma Physics and Applications Lctur 7 Prof. Jorg Rocca and Dr. Frnando Tomasl Dpartmnt of Elctrical and Computr Enginring Collisional and radiativ procsss All particls in a plasma intract with
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in Physics NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF (JUNE-2011)
 NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF (JUNE-) 64 Q. Th radius of a 9Cu nuclus is masurd to b 4.8 - cm. (A). Th radius of a 7 Mg nuclus can b stimatd to b.86 - cm (b) 5. - cm (c).6 - cm (d) 8.6 - cm (c)
NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF (JUNE-) 64 Q. Th radius of a 9Cu nuclus is masurd to b 4.8 - cm. (A). Th radius of a 7 Mg nuclus can b stimatd to b.86 - cm (b) 5. - cm (c).6 - cm (d) 8.6 - cm (c)
ME 321 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines S. Lambert Winter 2002
 3.4 Forc Analysis of Linkas An undrstandin of forc analysis of linkas is rquird to: Dtrmin th raction forcs on pins, tc. as a consqunc of a spcifid motion (don t undrstimat th sinificanc of dynamic or
3.4 Forc Analysis of Linkas An undrstandin of forc analysis of linkas is rquird to: Dtrmin th raction forcs on pins, tc. as a consqunc of a spcifid motion (don t undrstimat th sinificanc of dynamic or
Statistical Thermodynamics: Sublimation of Solid Iodine
 c:374-7-ivap-statmch.docx mar7 Statistical Thrmodynamics: Sublimation of Solid Iodin Chm 374 For March 3, 7 Prof. Patrik Callis Purpos:. To rviw basic fundamntals idas of Statistical Mchanics as applid
c:374-7-ivap-statmch.docx mar7 Statistical Thrmodynamics: Sublimation of Solid Iodin Chm 374 For March 3, 7 Prof. Patrik Callis Purpos:. To rviw basic fundamntals idas of Statistical Mchanics as applid
Lecture 19: Free Energies in Modern Computational Statistical Thermodynamics: WHAM and Related Methods
 Statistical Thrmodynamics Lctur 19: Fr Enrgis in Modrn Computational Statistical Thrmodynamics: WHAM and Rlatd Mthods Dr. Ronald M. Lvy ronlvy@tmpl.du Dfinitions Canonical nsmbl: A N, V,T = k B T ln Q
Statistical Thrmodynamics Lctur 19: Fr Enrgis in Modrn Computational Statistical Thrmodynamics: WHAM and Rlatd Mthods Dr. Ronald M. Lvy ronlvy@tmpl.du Dfinitions Canonical nsmbl: A N, V,T = k B T ln Q
Pair (and Triplet) Production Effect:
 Pair (and riplt Production Effct: In both Pair and riplt production, a positron (anti-lctron and an lctron (or ngatron ar producd spontanously as a photon intracts with a strong lctric fild from ithr a
Pair (and riplt Production Effct: In both Pair and riplt production, a positron (anti-lctron and an lctron (or ngatron ar producd spontanously as a photon intracts with a strong lctric fild from ithr a
PRINCIPLES OF PLASMA PROCESSING Course Notes: Prof. J. P. Chang Part B3: ATOMIC COLLISIONS AND SPECTRA
 Atomic Collisions and Spctra 125 PRINCIPLES OF PLASMA PROCESSING Cours Nots: Prof. J. P. Chang Part B3: ATOMIC COLLISIONS AND SPECTRA I. ATOMIC ENERGY LEVELS Atoms and molculs mit lctromagntic radiation
Atomic Collisions and Spctra 125 PRINCIPLES OF PLASMA PROCESSING Cours Nots: Prof. J. P. Chang Part B3: ATOMIC COLLISIONS AND SPECTRA I. ATOMIC ENERGY LEVELS Atoms and molculs mit lctromagntic radiation
Why is a E&M nature of light not sufficient to explain experiments?
 1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
Gradebook & Midterm & Office Hours
 Your commnts So what do w do whn on of th r's is 0 in th quation GmM(1/r-1/r)? Do w nd to driv all of ths potntial nrgy formulas? I don't undrstand springs This was th first lctur I actually larnd somthing
Your commnts So what do w do whn on of th r's is 0 in th quation GmM(1/r-1/r)? Do w nd to driv all of ths potntial nrgy formulas? I don't undrstand springs This was th first lctur I actually larnd somthing
From Classical to Quantum mechanics
 From Classical to Quantum mcanics Engl & Rid 99-300 vrij Univrsitit amstrdam Classical wav baviour Ligt is a wav Two-slit xprimnt wit potons (81-85) 1 On sourc Intrfrnc sourcs ttp://www.falstad.com/matpysics.tml
From Classical to Quantum mcanics Engl & Rid 99-300 vrij Univrsitit amstrdam Classical wav baviour Ligt is a wav Two-slit xprimnt wit potons (81-85) 1 On sourc Intrfrnc sourcs ttp://www.falstad.com/matpysics.tml
NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS
![NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS](/thumbs/79/79886930.jpg) . (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
. (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
Section 11.6: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Sction.6: Dirctional Drivativs and th Gradint Vctor Practic HW rom Stwart Ttbook not to hand in p. 778 # -4 p. 799 # 4-5 7 9 9 35 37 odd Th Dirctional Drivativ Rcall that a b Slop o th tangnt lin to th
Sction.6: Dirctional Drivativs and th Gradint Vctor Practic HW rom Stwart Ttbook not to hand in p. 778 # -4 p. 799 # 4-5 7 9 9 35 37 odd Th Dirctional Drivativ Rcall that a b Slop o th tangnt lin to th
6. The Interaction of Light and Matter
 6. Th Intraction of Light and Mattr - Th intraction of light and mattr is what maks lif intrsting. - Light causs mattr to vibrat. Mattr in turn mits light, which intrfrs with th original light. - Excitd
6. Th Intraction of Light and Mattr - Th intraction of light and mattr is what maks lif intrsting. - Light causs mattr to vibrat. Mattr in turn mits light, which intrfrs with th original light. - Excitd
Precise Masses of particles
 /1/15 Physics 1 April 1, 15 Ovrviw of topic Th constitunts and structur of nucli Radioactivity Half-lif and Radioactiv dating Nuclar Binding Enrgy Nuclar Fission Nuclar Fusion Practical Applications of
/1/15 Physics 1 April 1, 15 Ovrviw of topic Th constitunts and structur of nucli Radioactivity Half-lif and Radioactiv dating Nuclar Binding Enrgy Nuclar Fission Nuclar Fusion Practical Applications of
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING
 ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis
 AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
Pipe flow friction, small vs. big pipes
 Friction actor (t/0 t o pip) Friction small vs larg pips J. Chaurtt May 016 It is an intrsting act that riction is highr in small pips than largr pips or th sam vlocity o low and th sam lngth. Friction
Friction actor (t/0 t o pip) Friction small vs larg pips J. Chaurtt May 016 It is an intrsting act that riction is highr in small pips than largr pips or th sam vlocity o low and th sam lngth. Friction
September 23, Honors Chem Atomic structure.notebook. Atomic Structure
 Atomic Structur Topics covrd Atomic structur Subatomic particls Atomic numbr Mass numbr Charg Cations Anions Isotops Avrag atomic mass Practic qustions atomic structur Sp 27 8:16 PM 1 Powr Standards/ Larning
Atomic Structur Topics covrd Atomic structur Subatomic particls Atomic numbr Mass numbr Charg Cations Anions Isotops Avrag atomic mass Practic qustions atomic structur Sp 27 8:16 PM 1 Powr Standards/ Larning
4E : The Quantum Universe. Lecture 5, April 5 Vivek Sharma
 4E : Th Quantum Univrs Lctur 5, April 5 Vivk Sharma modphys@hpmail.ucsd.du An X-ray Tub from 0 th Cntury Xray Th High Enrgy Acclrator of 1900s: producd nrgtic light : X Ray, gav nw optic to subatomic world
4E : Th Quantum Univrs Lctur 5, April 5 Vivk Sharma modphys@hpmail.ucsd.du An X-ray Tub from 0 th Cntury Xray Th High Enrgy Acclrator of 1900s: producd nrgtic light : X Ray, gav nw optic to subatomic world
λ = 2L n Electronic structure of metals = 3 = 2a Free electron model Many metals have an unpaired s-electron that is largely free
 5.6 4 Lctur #4-6 pag Elctronic structur of mtals r lctron modl Many mtals av an unpaird s-lctron tat is largly fr Simplst modl: Particl in a box! or a cubic box of lngt L, ψ ( xyz) 8 xπ ny L L L n x π
5.6 4 Lctur #4-6 pag Elctronic structur of mtals r lctron modl Many mtals av an unpaird s-lctron tat is largly fr Simplst modl: Particl in a box! or a cubic box of lngt L, ψ ( xyz) 8 xπ ny L L L n x π
Principles of Humidity Dalton s law
 Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Basic Polyhedral theory
 Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Davisson Germer experiment
 Announcmnts: Davisson Grmr xprimnt Homwork st 5 is today. Homwork st 6 will b postd latr today. Mad a good guss about th Nobl Priz for 2013 Clinton Davisson and Lstr Grmr. Davisson won Nobl Priz in 1937.
Announcmnts: Davisson Grmr xprimnt Homwork st 5 is today. Homwork st 6 will b postd latr today. Mad a good guss about th Nobl Priz for 2013 Clinton Davisson and Lstr Grmr. Davisson won Nobl Priz in 1937.
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics Qualifying Examination
 Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
SECTION where P (cos θ, sin θ) and Q(cos θ, sin θ) are polynomials in cos θ and sin θ, provided Q is never equal to zero.
 SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
MCE503: Modeling and Simulation of Mechatronic Systems Discussion on Bond Graph Sign Conventions for Electrical Systems
 MCE503: Modling and Simulation o Mchatronic Systms Discussion on Bond Graph Sign Convntions or Elctrical Systms Hanz ichtr, PhD Clvland Stat Univrsity, Dpt o Mchanical Enginring 1 Basic Assumption In a
MCE503: Modling and Simulation o Mchatronic Systms Discussion on Bond Graph Sign Convntions or Elctrical Systms Hanz ichtr, PhD Clvland Stat Univrsity, Dpt o Mchanical Enginring 1 Basic Assumption In a
Lecture Outline. Skin Depth Power Flow 8/7/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics. Topic 3e
 8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
Optics and Non-Linear Optics I Non-linear Optics Tutorial Sheet November 2007
 Optics and Non-Linar Optics I - 007 Non-linar Optics Tutorial Sht Novmbr 007 1. An altrnativ xponntial notion somtims usd in NLO is to writ Acos (") # 1 ( Ai" + A * $i" ). By using this notation and substituting
Optics and Non-Linar Optics I - 007 Non-linar Optics Tutorial Sht Novmbr 007 1. An altrnativ xponntial notion somtims usd in NLO is to writ Acos (") # 1 ( Ai" + A * $i" ). By using this notation and substituting
Forces. Quantum ElectroDynamics. α = = We have now:
 W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
MCB137: Physical Biology of the Cell Spring 2017 Homework 6: Ligand binding and the MWC model of allostery (Due 3/23/17)
 MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
DIELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
10. The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Give the letter that represents an atom (6) (b) Atoms of A and D combine to form a compound containing covalent bonds.
 1 Th diagram shows th lctronic configurations of six diffrnt atoms. A B C D E F (a) You may us th Priodic Tabl on pag 2 to hlp you answr this qustion. Answr ach part by writing on of th lttrs A, B, C,
1 Th diagram shows th lctronic configurations of six diffrnt atoms. A B C D E F (a) You may us th Priodic Tabl on pag 2 to hlp you answr this qustion. Answr ach part by writing on of th lttrs A, B, C,
Davisson Germer experiment Announcements:
 Davisson Grmr xprimnt Announcmnts: Homwork st 7 is du Wdnsday. Problm solving sssions M3-5, T3-5. Th 2 nd midtrm will b April 7 in MUEN E0046 at 7:30pm. BFFs: Davisson and Grmr. Today w will go ovr th
Davisson Grmr xprimnt Announcmnts: Homwork st 7 is du Wdnsday. Problm solving sssions M3-5, T3-5. Th 2 nd midtrm will b April 7 in MUEN E0046 at 7:30pm. BFFs: Davisson and Grmr. Today w will go ovr th
Solution: APPM 1360 Final (150 pts) Spring (60 pts total) The following parts are not related, justify your answers:
 APPM 6 Final 5 pts) Spring 4. 6 pts total) Th following parts ar not rlatd, justify your answrs: a) Considr th curv rprsntd by th paramtric quations, t and y t + for t. i) 6 pts) Writ down th corrsponding
APPM 6 Final 5 pts) Spring 4. 6 pts total) Th following parts ar not rlatd, justify your answrs: a) Considr th curv rprsntd by th paramtric quations, t and y t + for t. i) 6 pts) Writ down th corrsponding
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Electrochemistry L E O
 Rmmbr from CHM151 A rdox raction in on in which lctrons ar transfrrd lctrochmistry L O Rduction os lctrons xidation G R ain lctrons duction W can dtrmin which lmnt is oxidizd or rducd by assigning oxidation
Rmmbr from CHM151 A rdox raction in on in which lctrons ar transfrrd lctrochmistry L O Rduction os lctrons xidation G R ain lctrons duction W can dtrmin which lmnt is oxidizd or rducd by assigning oxidation
In this lecture... Subsonic and supersonic nozzles Working of these nozzles Performance parameters for nozzles
 Lct-30 Lct-30 In this lctur... Subsonic and suprsonic nozzls Working of ths nozzls rformanc paramtrs for nozzls rof. Bhaskar Roy, rof. A M radp, Dpartmnt of Arospac, II Bombay Lct-30 Variation of fluid
Lct-30 Lct-30 In this lctur... Subsonic and suprsonic nozzls Working of ths nozzls rformanc paramtrs for nozzls rof. Bhaskar Roy, rof. A M radp, Dpartmnt of Arospac, II Bombay Lct-30 Variation of fluid
Lecture 13: Conformational Sampling: MC and MD
 Statistical Thrmodynamics Lctur 13: Conformational Sampling: MC and MD Dr. Ronald M. Lvy ronlvy@tmpl.du Contributions from Mik Andrc and Danil Winstock Importanc Sampling and Mont Carlo Mthods Enrgy functions
Statistical Thrmodynamics Lctur 13: Conformational Sampling: MC and MD Dr. Ronald M. Lvy ronlvy@tmpl.du Contributions from Mik Andrc and Danil Winstock Importanc Sampling and Mont Carlo Mthods Enrgy functions
